Surgical Treatment for the Refractory Allergic Rhinitis: State of the Art
Abstract
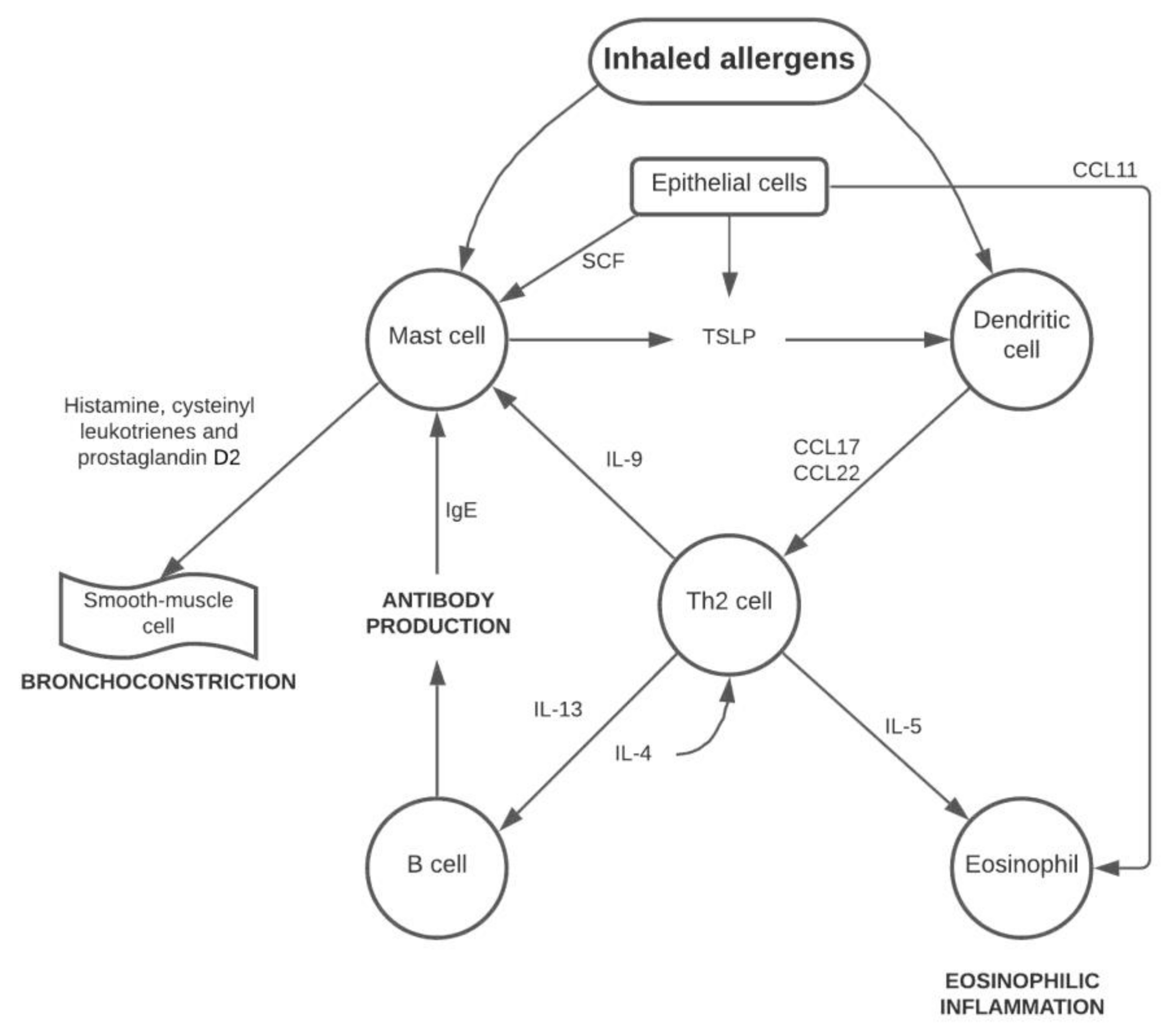
1. Introduction
- -
- Quality of life (QoL) and nasal breathing improvement [17];
- -
- Symptomatic gain achieved through various mechanisms: exuberant mucous tissue reduction determines a reduction of the contact points for the allergens present in the inhaled air [9];
- -
- Reduction in the use of drugs with better patient compliance;
- -
- Preservation of the nasal mucosa using techniques that maintain mucociliary activity unchanged;
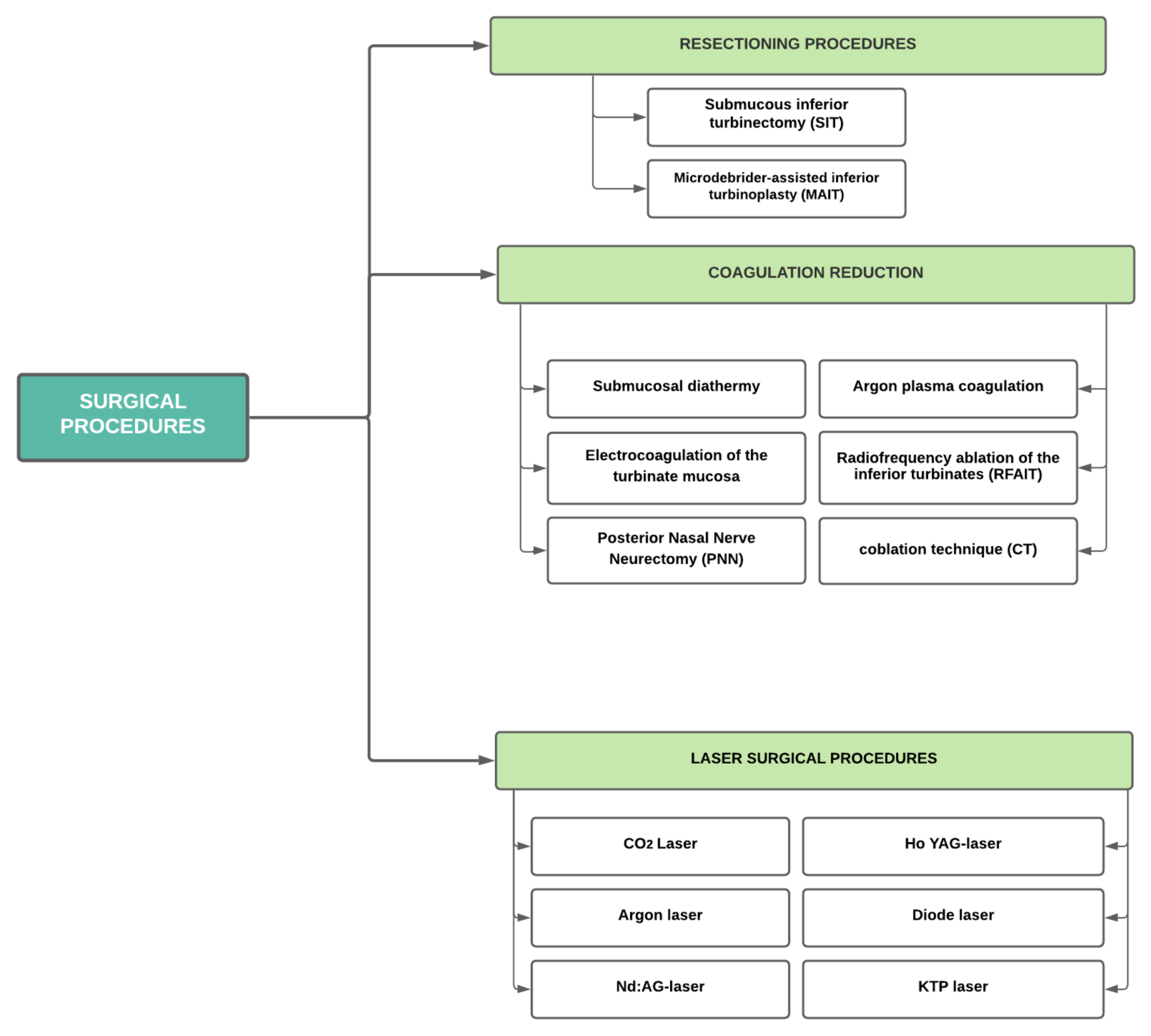
2. Surgical Therapy of the Inferior Turbinate in AR
- how effective the method was in decreasing hypersecretion from respiratory obstruction, headaches, and sneezing episodes;
- side outcomes occurring in the short and long term.
3. Resectioning Procedures
3.1. Submucous Inferior Turbinectomy (SIT)
3.2. Microdebrider-Assisted Inferior Turbinoplasty (MAIT)
4. Coagulating Reduction
4.1. Submucosal Diathermy (SMD)
4.2. Electrocoagulation of the Turbinate Mucosa
4.3. Posterior Nasal Nerve Neurectomy (PNN)
4.4. Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC)
4.5. Radiofrequency Ablation of the Inferior Turbinates (RFAIT) and Coblation Technique
5. Laser Surgical Procedures
5.1. CO2 Laser
5.2. Argon Laser
5.3. Neodymium: Yttrium Aluminium Garnet Laser (Nd: YAG-Laser)
5.4. Holmium: Yttrium-Aluminium-Granat-Laser (Ho: YAG-laser)
5.5. Diode Laser
5.6. Potassium Titanyl Phosphate Laser (KTP)
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juniper, E.F. Impact of upper respiratory allergic diseases on quality of life. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 101, S386–S391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B.M.; Werner, J.A. Nd: YAG-laserlichtinduzierte Nasenmuschelreduktion. Laryngorhinootologie 1996, 75, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, F.; Capaccio, P.; Cesana, B.M.; Manzo, R.; Peri, A. Argon plasma coagulation in the treatment of non-allergic hy-pertrophic inferior nasal turbinates. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2003, 24, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocuzza, S.; Maniaci, A.; Di Luca, M.; La Mantia, I.; Grillo, C.; Spinato, G.; Motta, G.; Testa, D.; Ferlito, S. Long-term results of nasal surgery: Comparison of mini-invasive turbinoplasty. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, P.; Hwang, P. Surgery of the septum and turbinates. In Rhinology: Diseases of the Nose, Sinuses, and Skull Base; Kennedy, D.P.H., Ed.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, I.; Klimek, L.; Mösges, R.; Hörmann, K. Mediators of inflammation in the early and the late phase of allergic rhinitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 4, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dullaers, M.; De Bruyne, R.; Ramadani, F.; Gould, H.J.; Gevaert, P.; Lambrecht, B.N. The who, where, and when of IgE in allergic airway disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurieva, R.I.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. Yin-Yang of costimulation: Crucial controls of immune tolerance and function. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Fujieda, S.; Igarashi, M.; Fan, G.K.; Saito, H. Submucous turbinectomy decreases not only nasal stiffness but also sneezing and rhinorrhea in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passàli, D.; Anselmi, M.; Lauriello, M.; Bellussi, L. Treatment of Hypertrophy of the Inferior Turbinate: Long-Term Results in 382 Patients Randomly Assigned to Therapy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1999, 108, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, E.; Percodani, J.; Yardeni, E.; Lombard, L.; Laffitte, F.; Pessey, J.J. The holmium:YAG laser for treatment of inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Rhinol. J. 1998, 36, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Elwany, S.; Abel Salaam, S. Laser surgery for allergic rhinitis: The effect on seromucinous glands. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999, 120, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidman, M.D.; Gurgel, R.K.; Lin, S.Y.; Schwartz, S.R.; Baroody, F.M.; Bonner, J.R.; Dawson, D.E.; Dykewicz, M.S.; Hackell, J.M.; Han, J.K.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, S1–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; Lin, P.-W.; Friedman, M.; Chang, H.-W.; Su, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Pulver, T.M. Long-term Results of Radiofrequency Turbinoplasty for Allergic Rhinitis Refractory to Medical Therapy. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladina, R.; Risavi, R.; Subaric, M. CO2 laser anterior turbinectomy in the treatment of non-allergic vasomotor rhinopathia. A prospective study upon 78 patients. Rhinol. J. 1991, 29, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Cassano, M.; Del Giudice, A.M.; Russo, G.; Russo, L.; Ciprandi, G. The Role of Nasal Cytology in the Management of Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passàli, D.; Passàli, F.M.; Passàli, G.C.; Damiani, V.; Bellussi, L. Treatment of Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2003, 112, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.K.; Lin, S.Y.; Toskala, E.; Orlandi, R.R.; Akdis, C.A.; Alt, J.A.; Azar, A.; Baroody, F.M.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, G.W.; et al. International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Allergic Rhinitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 108–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, M.K.; Huizing, E.H. Treatment of inferior turbinate pathology: A review and critical evaluation of the different techniques. Rhinology 2000, 38, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Joniau, S.; Wong, I.; Rajapaksa, S.; Carney, S.A.; Wormald, P.-J. Long-Term Comparison Between Submucosal Cauterization and Powered Reduction of the Inferior Turbinates. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.F.; Freeman, T.J.; Ogren, F.P.; Yonkers, A.J. Extended Follow-Up of Total Inferior Turbinate Resection for Relief of Chronic Nasal Obstruction. Laryngoscope 1985, 95, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talmon, Y.; Samet, A.; Gilbey, P. Total Inferior Turbinectomy: Operative Results and Technique. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizing, E.H.; de Groot, J.A.M. Surgical of the nasal cavity. In Functional Reconstructive Nasal Surgery; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S.; Fujieda, S.; Yamada, T.; Kimura, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Saito, H. Long-Term Effect of Submucous Turbinectomy in Patients With Perennial Allergic Rhinitis. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Tan, C.D.; Lee, F.P.; Lin, K.N.; Huang, H.M. Microdebrider-assisted versus radiofrequency-assisted inferior tur-binoplasty. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-W.; Cheng, P.-W. Changes in Nasal Resistance and Quality of Life After Endoscopic Microdebrider-Assisted Inferior Turbinoplasty in Patients with Perennial Allergic Rhinitis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y. Efficacy of intra- and extraturbinal microdebrider turbinoplasty in perennial allergic rhinitis. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2945–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Tan, C.-T.; Huang, H.-M. Long-Term Efficacy of Microdebrider-Assisted Inferior Turbinoplasty With Lateralization for Hypertrophic Inferior Turbinates in Patients With Perennial Allergic Rhinitis. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwany, S.; Gaimaee, R.; Fattah, H.A. Radiofrequency bipolar submucosal diathermy of the inferior turbinates. Am. J. Rhinol. 1999, 13, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradis, M.; Danino, J.; Gaitini, L.; Gershinski, M.; Malatskey, S.; Golz, A.; Goldsher, M.; Armush, W. Inferior Turbinectomy versus Submucosal Diathermy for Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, B.M.; Werner, J.A. Comparison of carbon dioxide and neodymium: Yttrium-aluminium-garnet lasers in surgery of the inferior turbinate. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1997, 106, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, G.M. Surgical reduction of hypertrophied inferior turbinates: A comparison of electrofulguration and partial re-section. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1988, 81, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmila, D. Comparative Study of Response Through Reduction in the Size of Hypertrophied Inferior Turbinate Causing Nasal Obstruction by Different Surgical Modalities: A Prospective Study. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 67, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Golding-Wood, P.H. Observations on Petrosal and Vidian Neurectomy in Chronic Vasomotor Rhinitis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1961, 75, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Hyodo, M.; Nakamura, K.; Komobuchi, H.; Honda, N. Resection of peripheral branches of the posterior nasal nerve compared to conventional posterior neurectomy in severe allergic rhinitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2012, 39, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, S.; Asako, M.; Momotani, A.; Ikeda, H.; Kubo, N.; Yamashita, T. Submucosal turbinectomy with posterior-superior nasal nerurectomy for patients with allergic rhinitis. Pract. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2000, 93, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikawada, T. Endoscopic posterior nasal neurectomy: Analternative to vidian neurectomy. Oper. Tech. Otolaryngol. 2007, 18, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalingeswaran, A.; Kumar, R.D. Newer Surgical Options for Nasal Allergy. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 72, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergler, W.F. Argon plasma coagulation (APC) surgery in otorhinolaryngology. Surg. Technol. Int. 2003, 11, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bergler, W.F.; Sadick, H.; Hammerschmitt, N.; Oulmi, J.; Hörmann, K. Long-Term Results of Inferior Turbinate Reduction With Argon Plasma Coagulation. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierek, T.; Jura-Szołtys, E. Long-term results after argon plasma coagulation (APC) inferior turbinates reduction. Otolaryngol. Pol. 2007, 61, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura-Szołtys, E.; Ficek, R.; Ficek, J.; Markowski, J.; Chudek, J. Bronchial asthma control after argon plasma coagulation turbinectomy in patients with chronic rhinitis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bhandarkar, N.D.; Smith, T.L. Outcomes of surgery for inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 18, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhiran, W.; Tantilipikorn, P.; Metheetrairut, C.; Assanasen, P.; Bun-nag, C. Quality of life in patients with chronic rhinitis after radiofrequency inferior turbinate reduction. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2010, 93, 950–960. [Google Scholar]
- Cukurova, I.; Demirhan, E.; Cetinkaya, E.; Yigitbasi, O.G. Long-term clinical results of radiofrequency tissue volume reduction for inferior turbinate hypertrophy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, B.; Korkut, A.Y.; Kaya, K.S.; Salepçi, E.; Coşkun, B.U.; Turgut, S. Results of radiofrequency ablation of inferior turbinate hypertrophy in allergic and non-allergic rhinitis patients. Med Bull. Sisli Hosp. 2018, 52, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corso, E.; Bastanza, G.; Di Donfrancesco, V.; Guidi, M.; Sbarra, G.M.; Passali, G.; Poscia, A.; De Waure, C.; Paludetti, G.; Galli, J. Radiofrequency volumetric inferior turbinate reduction: Long-term clinical results. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2016, 36, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hytönen, M.L.; Bäck, L.J.J.; Malmivaara, A.V.; Roine, R.P. Radiofrequency thermal ablation for patients with nasal symptoms: A systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 266, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siméon, R.; Soufflet, B.; Delacour, I.S. Coblation turbinate reduction in childhood allergic rhinitis. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2010, 127, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ye, T.; Zhou, B. Update on surgical management of adult inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 23, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukutake, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tomoda, K.; Kumazawa, T. Laser Surgery for Allergic Rhinitis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1986, 112, 1280–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, P.; Sroka, R.; Baumgartner, R.; Grevers, G.; Leunig, A. Laser treatment of hyperplastic inferior nasal turbinates: A review. Lasers Surg. Med. 2001, 28, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.D.; Ries, W.R. Surgical treatment of the inferior turbinate: New techniques. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 12, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapçi, T.; Sahin, B.; Karavus, A.; Akbulut, U.G. Comparison of the Effects of Radiofrequency Tissue Ablation, CO2 Laser Ablation, and Partial Turbinectomy Applications on Nasal Mucociliary Functions. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, D.; Motta, G.; Galli, V.; Iovine, R.; Guerra, G.; Marenzi, G.; Testa, B. Outcome assessment in patients with chronic obstructive rhinitis CO2 laser treated. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2006, 26, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeno, S.; Ishino, T.; Osada, R.; Yajin, K. Laser surgery of the inferior turbinate for allergic rhinitis with seasonal exacerbation: An acoustic rhinometry study. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2003, 112, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, J.L.; Dixon, J.A. Laser Photocoagulation in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1981, 89, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, J.A.; Rudert, H. Der Einsatz des Nd: YAG-Lasers in der Hals- Nasen-Ohrenheilkunde. HNO 1992, 40, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lippert, B.M.; Werner, J.A. Die Behandlung der hypertrophen unteren Nasenmuschel. Teil 1. HNO 2000, 48, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthoff, A.; Martin, A.; Liebmann, F. Nd: YAG-laser treatment of the lower turbinates with contact in hyperreflexic and allergic rhinopathy. Laryngorhinootology 1999, 78, 740–743. [Google Scholar]
- Vagnetti, A.; Gobbi, E.; Algieri, G.M.; D’Ambrosio, L. Wedge Turbinectomy: A New Combined Photocoagulative Nd:YAG Laser Technique. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 1034–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, P.; Sroka, R.; Betz, C.S.; Baumgartner, R.; Leunig, A. Comparison of laser induced effects on hyperplastic inferior nasal turbinates by means of scanning electron microscopy. Lasers Surg. Med. 2002, 30, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, R.; Janda, P.; Killian, T.; Vaz, F.; Betz, C.S.; Leunig, A. Comparison of long term results after Ho:YAG and diode laser treatment of hyperplastic inferior nasal turbinates. Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejali, S.; Upile, T.; McLellan, D.; Bingham, B. Inferior turbinate reduction in children using Holmium YAG laser?a clinical and histological study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2004, 34, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffier, P.P.; Frieler, K.; Scherer, H.; Sedlmaier, B.; Göktas, Ö. Rhinitis Medicamentosa: Therapeutic Effect of Diode Laser Inferior Turbinate Reduction on Nasal Obstruction and Decongestant Abuse. Am. J. Rhinol. 2008, 22, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffier, P.P.; Scherer, H.; Neumann, K.; Lück, S.; Enzmann, H.; Haisch, A. Diode laser treatment in therapy-resistant allergic rhinitis: Impact on nasal obstruction and associated symptoms. Lasers Med. Sci. 2010, 26, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Kc, T.; Regmi, D. Diode Laser Turbinate Reduction in Allergic Rhinitis: A Cross-sectional Study. J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2018, 56, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supiyaphun, P.; Aramwatanapong, P.; Kerekhanjanarong, V.; Sastarasadhit, V. KTP laser inferior turbinoplasty: An alternative procedure to treat the nasal obstruction. Auris Nasus Larynx 2003, 30, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.K.; Tsai, Y.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Wang, P.C. Endoscopic potassium titanyl phosphate laser treatment for hypertrophic inferior turbinate. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2004, 22, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunachak, S.; Kulapaditharom, B.; Prakunhungsit, S. Minimally invasive KTP laser treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis: A preliminary report. J. Otolaryngol. 2000, 29, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Divakaran, S.; Parida, P.K.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Potassium Titanyl Phosphate Laser Turbinate Reduction in the Management of Allergic Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy: Our Experience. Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 7, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.K.; Ravichandran, S.P.; Ramasamy, K.; Parida, P.K.; Alexander, A.; Ganesan, S. Comparison of efficacy of potassium titanyl phosphate laser & diode laser in the management of inferior turbinate hypertrophy: A randomized controlled trial. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Year | Study Design | Features (Allergic Patients vs. Control Group) | Follow-Up Time | Objective Evaluation (p-Value) | Subjective Evaluation (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Türk | 2018 | Prospective non-randomized | RFA (23 allergic vs. 36 non allergic) | 3, 6 months | Nasal obstruction (<0.001); Acoustic rhinometry (<0.001) | VAS (<0.001) |
| De Corso | 2016 | Prospective | RFA (114 allergic vs. 191 non-allergic) | 1 month, yearly for 5 years | NOSE (<0.05) | |
| Di Rienzo Businco | 2014 | Randomized controlled trial | QMR (145 treated vs. 145 control) | 3 months | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.05); Rhinoendoscopy clinic score (<0.05); STT (No statistically different from pretreatment) | SNOT-22 (<0.05); VAS (<0.05) |
| Gunhan | 2011 | Prospective randomized | RFT (28) vs. INS (27) | 12 months | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.003) | VAS (<0.05); RQLQ (<0.05) |
| Ravichandran | 2020 | Randomized controlled trial | KTP (105) vs. Diode (104) [allergy not specified] | 1, 2 days, 1, 3 months | STT (Severely prolonged, statistically insignificant. ‘Need more time to follow-up’) | NOSE (<0.001) |
| Gupta | 2018 | Descriptive cross-sectional | Diode (60) | 3 months | VAS (significant) | |
| Vijayakumar | 2016 | Descriptive | KTP (30) | 1 week, 1, 3 months | STT (Return to preoperative value by the end of 3 months) | SNOT (<0.0001) |
| Parida | 2013 | Prospective | Diode (45) [allergy not specified] | 1 week, 1, 3, 6 months | STT (Return to preoperative value by the end of 6 months) | VAS (<0.001) |
| Sroka | 2007 | Retrospective non-randomized comparative | Ho:Yag or Diode (44 allergic vs. 46 non allergic) | 6 months, 3 years | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.001) | Subjective questionnaires (85% improvement) |
| Lee | 2013 | Prospective | MAIT (60) | 3, 6, 12 months | Acustic rhinometry (<0.05) | VAS (<0.05) |
| Chen | 2008 | Prospective | MAITL (80) vs. SR (80) | 1, 2, 3 years | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.05); STT (<0.05) | VAS (<0.05) |
| Liu | 2009 | Prospective | MAIT (60) vs. RAIT (60) | 6 months, 1, 2, 3 years | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.05); STT (<0.05) | VAS (<0.05) |
| Huang | 2006 | Prospective | MAIT (50) | 1 year | Active anterior rhinomanometry (<0.001) | RQLQ (<0.005) |
| Nagalingeswaran | 2020 | Retrospective | PNN Selective Resection (212) | 2 weeks, 1, 2, 6, 12 months | ND | SNOT-22 (<0.001) |
| Krespi | 2018 | Prospective | Diode Laser PNN (32) | 1, 3 months | ND | TNSS (<0.001) |
| Lai | 2017 | Retrospective | Diode laser-assisted VN (43) vs. Cold instrument (75) | 6 months | ND | VAS (<0.001) |
| Tan | 2012 | Prospective | Bilateral VN (93) vs. Partial inferior turbinectomy and/or septoplasty (51) vs. Control group (92) | 6 months, 1, 3 years | ND | VAS (<0.05); RQLQ (<0.05) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniaci, A.; Di Luca, M.; La Mantia, I.; Grillo, C.; Grillo, C.M.; Privitera, E.; Vicini, C.; Iannella, G.; Renna, C.; Bannò, V.; et al. Surgical Treatment for the Refractory Allergic Rhinitis: State of the Art. Allergies 2021, 1, 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010005
Maniaci A, Di Luca M, La Mantia I, Grillo C, Grillo CM, Privitera E, Vicini C, Iannella G, Renna C, Bannò V, et al. Surgical Treatment for the Refractory Allergic Rhinitis: State of the Art. Allergies. 2021; 1(1):48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiaci, Antonino, Milena Di Luca, Ignazio La Mantia, Calogero Grillo, Caterina Maria Grillo, Elio Privitera, Claudio Vicini, Giannicola Iannella, Claudia Renna, Vittoria Bannò, and et al. 2021. "Surgical Treatment for the Refractory Allergic Rhinitis: State of the Art" Allergies 1, no. 1: 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010005
APA StyleManiaci, A., Di Luca, M., La Mantia, I., Grillo, C., Grillo, C. M., Privitera, E., Vicini, C., Iannella, G., Renna, C., Bannò, V., Migliore, F., & Cocuzza, S. (2021). Surgical Treatment for the Refractory Allergic Rhinitis: State of the Art. Allergies, 1(1), 48-62. https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies1010005








