Abstract
With high health requirements for FIFO work at industry, workers may experience adverse changes in psychological well-being and health status. This makes it relevant when developing the job performance model to rely on considering not only the effectiveness by employees but also their psychophysiological “cost of activity”, which is not reflected in modern scientific research. This article theoretically substantiates and empirically develops a job performance typology of fly-in-fly-out workers at industrial enterprises by correlating three components: effectiveness, psychophysiological resources, and the way of accomplishing tasks. The study involved 359 fly-in-fly-out workers in oil and gas, diamond mining and construction industries with different duration of the fly-in period, operating in the South and the North of the Russian Federation. The research methods included questioning, psychophysiological instrumental testing, and psychological testing. Statistical processing was carried out using the methods of descriptive statistics, two-stage cluster analysis, and multivariate analysis of variance. As a result of the study, six types of job performance of fly-in-fly-out personnel of industrial enterprises were identified. The employees at industrial enterprises of all six types of job performance correspond to their position and perform the assigned tasks, the difference in them lies in the desire to show an average or the highest possible result, as well as how much internal resources the employee spends to achieve this result and how quickly he restores them, which is expressed in terms of his state and well-being. Based on the results of these connections, measures for personnel management for industrial enterprises were proposed.
1. Introduction
Fly-in-fly-out (FIFO) employment continues to expand at the present time. This method is used to service all remote production areas, including both offshore oil and gas fields and onshore production projects. It is important to note that FIFO work is “the only viable option for the offshore oil and gas industry, since, unlike onshore mining sites, daily commuting to work is not possible under these conditions, and permanent places of residence are not available” [1]. Companies see FIFO work as an efficient way to meet the growing demand for minerals and an opportunity that also offers several benefits [2].
The FIFO method of organizing work is denoted by the terms “fly-in-fly-out”, “long distance labor commuting”, or “shift work” and is understood as “any job in which work is so isolated from the places of permanent residence of workers that food and housing are provided at the workplace, and lists are created according to which workers spend a fixed number of days at the site (shift camp), followed by a fixed number of days of rest at home” [1], (p. 2).
The FIFO work organization method is used in many countries of the world: Australia, Norway, USA, England, Canada, Russia, and others, both on land and at sea during oil and gas production on offshore platforms. In particular, the FIFO workforce attracts a wide range of workers in the mining sector in Western Australia: it directly employs 52,000 people and indirectly 156,000 people; overall, this industry employs approximately 21% of the Western Australian workforce [3].
The researchers from different countries have similar opinions regarding the advantages of using a rotational work organization method, which are:
- (a)
- Lower capital costs are required to organize a FIFO work method, compared with the construction of a new settlement suitable for housing workers and their families, and also significantly reduce the initial cost of developing a new field [2].
- (b)
- In fact, large costs of creating urban infrastructure are replaced by transport costs, which are evenly distributed throughout the project (this is especially important for companies, since in some fields the duration of production is very short) [2].
- (c)
- Employment in the FIFO labor organization plays an important role in meeting the economic, social, and labor needs of the modern resource extraction industry. The practice of employing offshore personnel on production platforms differs from the practice of working in onshore fields [3,4].
The study by Parkes [5] that looked at employee satisfaction with 2/2 and 3/3 equal work schedules found that there was the following difference: workers with 2/2 work schedules generally report higher satisfaction rates than employees with a 3/3 schedule.
The results of the study by Gardner B. et al. revealed difficulties adapting to responsibilities and different perceptions of life during the fly-in (shift) period than in the fly-out period, as well as in managing the potential psychological distance that arises when workers are on shift [6].
The partners noted that one of the most negative aspects of FIFO work is the concern that the employee will not be able to return home in case of personal need. However, this may not apply to workers in all occupational groups, as only 46% of production and maintenance workers were satisfied that they could return home in an emergency, compared with 75% of executives [7].
The onshore and offshore FIFO workers requiring multiple changes in circadian rhythm (day and night shifts) reported lower work control levels than workers with regular work schedules. The job requirements are a risk factor for mental disorders on offshore platforms, while job control, clarity of roles, and fair and empowering leadership protect against mental disorders [8].
The potential stressors experienced by offshore personnel include limited living and working conditions, lack of privacy, constant noise, and complex production tasks with heavy workloads ranging from periods of boredom to periods of concentrated activity [5].
The fly-in-fly-out method is used in other industries: construction, oil and gas production, diamond mining, logging, energy, metallurgy, etc. [9]. Most of these industries are harmful and potentially life-threatening in accordance. There are certain jobs at the enterprises of the extractive industry and construction in which people are exposed to various stress factors (such as intellectual, sensory, emotional, monotonous loads, and intensive work) and labor severity (dynamic physical, stereotypical, and monotonous loads). This leads to the development of various psychological risks in fly-in-fly-out personnel.
The following psychological risks of fly-in-fly-out workers are mentioned in the recent literature: symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress among workers in the Australian industry [10]; occupational stress, health status, and overcoming difficulties in German wind energy employees [11]; employee involvement and emotional exhaustion of fly-in-fly-out workers [12]; depression, suicide risk, and workplace bullying: a comparative study of fly-in-fly-out workers in resource extraction in Australia [13], the impact of isolation in the workplace on remote health workers [14].
Fly-in-fly-out work at offshore facilities is stressful and potentially hazardous [5,15,16,17,18,19]. A number of studies show a fairly high level of positive health effects for workers [20,21,22], which is due to the high health standards of this personnel. At the same time, the researchers note health complaints among these workers: sleep problems [5,22,23,24], complaints about the musculoskeletal system [25], and body weight issues [22,23,24,25], and others. There is also conflicting evidence regarding mental health: some studies have established good mental health of oil and gas workers [5,8,17], other studies have noted higher levels of nervousness [5], mental fatigue [5,22], and anxiety [5] in offshore oil and gas workers compared to onshore workers.
In particular, fly-in-fly-out workers are generally healthier (as measured by self-reported current health status) and reported more exercise and sleep during the work period than workers on expeditionary activities [7]. In addition, fly-in-fly-out workers with long shifts reported significantly more sleep and exercise than those with shorter shifts. Previous research has also shown that fly-in-fly-out workers have better overall health and more physical activity than field workers [26].
Based on the objective sleep monitoring of shift workers in the mining industry [27] and qualitative data, it was concluded that FIFO workers constantly experience excessive fatigue [28]. The 12-h shift work, typical of FIFO work, leads to fatigue, which negatively affects productivity [29]. Fatigue can impair performance to levels equivalent to alcohol intoxication [30] and exposes workers to a higher risk of accidents and injury [31,32]. Reducing fatigue and associated health and safety risks will require input from both FIFO organizations and workers themselves.
For many participants, the geographical distance and the regular and prolonged absence of FIFO workers led to psychological effects from the separation of workers from their families. The similar problems are typical for other categories of workers, such as truckers and fishermen [33]. This can have many adverse effects on well-being. Many FIFO workers felt isolated and lonely, which is a common experience for FIFO workers [34].
The development of these unfavorable phenomena among fly-in-fly-out workers is associated both with the action of unfavorable, harmful, and hazardous production factors and with the influence of extreme climatic and geographical conditions and group isolation of employees.
The central methodological problem for solving applied problems of psychological support of intense work staff is a job performance assessment of specialists, reflecting the compliance of the result with the set goals and objectives. It also allows us to highlight the key professional requirements to employees’ personalities, as well as to identify the risk factors for the psychological safety of work and preserve the professional health of employees.
In the current literature, job performance is often understood as a complex characteristic expressed in quantitative and qualitative indicators, ensuring the achievement of a sufficiently high socially significant result, obtaining labor products (material, spiritual) that meet the requirements of society, and taking into account material, time, and psychophysiological costs [35].
It should be noted that the problem of studying job performance in labor psychology is not new. In their works, Zinchenko, Munipov, and Rubakhin define the quality of labor as “an integral characteristic of this type of activity, in which indicators of the quality and quantity of products are recorded, taken in relation to raw materials and time costs for its production, to the psychological and physiological ‘cost’ of labor efforts, as well as in relation to indicators of health and personality development of workers” [36]. This concept reflects the ratio of objective effectiveness and the psychophysiological “cost” of activities [37].
The working capacity is one of the indicators of the psychophysiological (physiological) “cost of activity” and the result of work [38]. Consequently, the assessment of professional performance should be based on the correlation of these two components.
At the same time, depending on the studied professional sphere, a specific profession and organization, as well as the author’s approach, different researchers selected different criteria for job performance components. We analyzed studies and classified various job performance criteria found in these works. The results of this analysis are presented in Appendix A in Table A1.
As can be seen from our analysis (Appendix A, Table A1), in the studies, an approach has gained a great popularity, within which job performance is determined by three components: task performance, contextual performance, and counterproductive behavior [39,40,41,42]. Completing a task is an activity that directly or indirectly affects the assessment of an organization. Contextual effectiveness is said to be effective for an organization in terms of its social and psychological context. Counterproductive behavior, such as stealing, sabotaging, and insulting other people, is treated as dangerous.
Within the framework of our methodology, the characteristics of counterproductive behavior correlate with psychological risk in professional activity, which is understood as “the likelihood of the occurrence of professional personality deformations and the formation of unfavorable functional states of workers during the performance of labor functions due to prolonged exposure to negative social, domestic, and production factors with insufficient personal and environmental resource” [43,44]. In our previous studies, it was established that unfavorable functional states and well-being and professional personality deformations are the main criteria for psychological risks for FIFO workers in the Arctic [43].
The authors most often consider external objective and subjective parameters of performance. With regard to the method of activity, an assessment of the adaptability and initiative of employees is used; certain qualities, which are important for the effective implementation of any type of activity are identified.
When determining the job performance, it is important to evaluate three key components: the effectiveness of the activity, the psychophysiological “cost” of the activity, and the way of performing the tasks [36,37]. Thus, with high health requirements for workers to fly-in-fly-out work in industry, with an increase in the length of fly-in-fly-out experience, workers may experience unfavorable changes in psychological well-being and health. Depending on the psychological and medical support at the enterprises, the risks can be reduced. In this connection, when working on a job performance model, we relied on considering not only the effective performance of tasks by employees (an external objective criterion–task orientation) but also their state and psychological well-being as markers of their health status, or in other words, the psychophysiological “cost of activity”. One of the reasons for the increase in the psychophysiological “cost of activity” of the employee is the choice of a non-optimal way of solving problems, which will require large expenses from the employee.
In our research, we will empirically determine the variability of each component of job performance: efficiency, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the method of solving problems among fly-in-fly-out workers at industrial enterprises. Further, we will develop the job performance typology of fly-in-fly-out personnel of industrial enterprises, including all the resulting diversity among each of its components.
The research purpose is to identify and describe the job performance types of fly-in-fly-out employees in oil, gas, diamond mining, and construction industrial enterprises and compare three factors: effectiveness, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the way of solving problems.
Hypothesis: In view of the above, we assumed that when correlating various effectiveness types, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the way of performing tasks, several kinds of job performance of fly-in-fly-out workers at industrial enterprises can be developed, which will allow developing targeted measures for psychological support for each category of employees.
It is interesting to identify not only the polar types of job performance, such as high performance (a combination of high effectiveness, optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the way of performing tasks) but also the intermediate ones when an employee achieves high results due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity” or has a high psychophysiological “cost of activity” due to a non-optimal way of performing tasks, etc. This typology will allow us to determine possible combinations and features and ensure the implementation of the “golden rule” of labor psychology about the correspondence between the subject of labor and the job, which implies not only the need to perform professional activities with excellent results but also the safety for employees, preserving their physical and mental health. When assessing professional efficiency, objective and subjective criteria are considered. When correlating them, various job performance types can be determined, which make it possible to determine a unique complexity of professionally important qualities, skills, and abilities of a professional, ensuring the performance of professional activities at a certain level and to develop targeted directions of psychological support of personnel to achieve the optimal level of labor productivity while maintaining employees’ health and well-being.
The private hypotheses:
1. On the basis of the whole variety of different inductors, the FIFO workers’ efficiency at industrial enterprises can be divided into the following groups: with high and medium efficiency.
2. On the basis of the totality of objective, projective, and subjective characteristics of the functional states, FIFO workers at industrial enterprises can be divided into the following groups: with optimal and high psychophysiological “cost of activity”.
3. Based on the totality of characteristics of subjective assessments of danger and adaptive strategies, it is possible to divide FIFO workers at industrial enterprises into the following groups: emergency confident and mixed cautious.
4. With long-term FIFO work, there is a cumulative effect of adverse environmental factors, which enhances their impact [9]. What is expressed in the fact that with an increase in FIFO work experience and age, FIFO workers at industrial enterprises are characterized by job performance types with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”.
2. Materials and Methods
Research type is empirical, analytical, and transverse. All research methods were considered at the ethics committee of the Higher School of Psychology, Pedagogy and Physical Culture of the Northern (Arctic) Federal University and recommended for use (protocol No. 5, 2017).
2.1. Sample
To achieve this goal, a study was carried out at the following industrial facilities with a fly-in-fly-out work organization:
1. The construction of gas pipelines, Republic of Komi, North, where 82 employees took part (average age 34.91 ± 0.926, average fly-in-fly-out work experience 4.57 ± 0.343, fly-in period–52 days)
2. Oil production, NAO, North, where 67 employees took part (average age 38.46 ± 1.410, average fly-in-fly-out work experience 9.85 ± 1.072, fly-in period–28 days);
3. Diamond mining production, Arkhangelsk region, North, where 77 employees took part (average age 38.56 ± 1.151, average fly-in-fly-out work experience 8.16 ± 0.701, fly-in period–14 days);
4. The construction of the Crimean Bridge, Krasnodar Territory, South, where 83 employees took part (average age 41.31 ± 1.242, average fly-in-fly-out work experience 8.02 ± 0.721, fly-in period–28 days); and
5. The offshore ice-resistant oil production platform, the Caspian Sea, South, where 50 employees took part (average age 36.17 ± 1.064, average fly-in-fly-out work experience 7.97 ± 0.839, fly-in period–14 days).
The total sample size was 359 fly-in-fly-out employees of industrial enterprises. The participation in the study was voluntary (a written voluntary informed consent of each participant was obtained).
It should be noted that, in this study, attention was paid to fly-in-fly-out workers who had to return home frequently, i.e., their fly-in and fly-out periods did not exceed two months. As previous studies have shown, these frequent journeys, and, consequently, frequent cycles of adaptation-readaptation, serve as additional negative factors requiring large internal resources from employees [45].
Longer rotational periods (sailors, polar explorers, etc.) are characterized by their specificity in the peculiarities of adaptation and environmental factors affecting personnel. Groups of participants in polar expeditions are few in number and, as a rule, are isolated for a very long period. The specificity of their group isolation, according to some studies, is similar to space expeditions, which is widely used in modeling team interaction during space flights [46].
The variability of the enterprises selected for the study was due to the possibility of their division at each of the levels of differential analysis.
Note: The Figure 1 shows how the survey sample is distributed in relation to each of the levels; in parentheses is the % of the sample corresponding to each group.
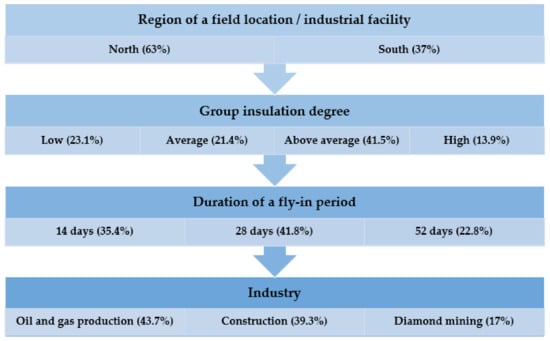
Figure 1.
Distribution of research samples by levels of differential analysis of FIFO work (% of the total research sample).
Figure 1 shows the distribution of the research samples by the levels of differential analysis of FIFO work. These data confirm the diversity presented and the consideration of the main factors in the formation of research samples and also allows us to determine the sufficiency of empirical data for comparative studies at each level of differential analysis.
2.2. Procedure
In our research, we relied on Leonova and Kuznetsova’s approach of determining “job performance through a system of three mandatory components: (1) effectiveness–the facts of achieving certain results; objective data on their quantitative and qualitative characteristics; (2) psychophysiological “cost of activity”–the amount of effort applied by a person to accomplish tasks; (3) the way of solving a problem–the way to achieve a result, the choice of which was carried out by taking into account the orientation toward compliance/non-compliance with organizational requirements and professional standards” [37].
Table 1 presents the criteria of professional efficiency assessed in this study and methods of their assessment.

Table 1.
Criteria for the job performance of FIFO workers.
Based on the studies, the necessary list of criteria was determined, sufficient for assessing each of the three components of the job performance model. Based on the results of the previous studies [45,47,48,49,50], the criteria had been supplemented with the following ones:
- (a)
- fly-in-fly-out work experience [45];
- (b)
- satisfaction with the work schedule; personal qualities required for fly-in-fly-out work [48];
- (c)
- adaptation strategy type [45,47];
- (d)
- psychological safety parameters [49,50].
The effectiveness according to our model (Table 1) included both external and internal parameters of work result, as well as fly-in-fly-out work experience. In previous studies, it was found that adaptation to fly-in-fly-out work method lasts at least 3 years [45], and also that the incidence of maladaptive disorders in fly-in-fly-out personnel significantly increased during the 1st, the 5th–6th, the 8th, the 12th–13th, the 15th–16th, and the 18th years of the experience of working in the gas industry in the North [51]. In the studies on other samples, the relationship between work experience and performance was discussed by Quinones et al. [52] and Kornilova et al. [53].
We chose the adaptation strategy type and psychological safety as criteria for the way of performing professional tasks. Activities in extreme conditions impose special requirements on workers’ professional adaptation, which is due to the combination of many unfavorable environmental factors and the unpredictability of the occurrence of stressful or emergency situations [6,11,54,55]. In such conditions, adaptation is always unfinished and adaptation strategies will be formed as a result of the adaptation process.
In our previous studies, the adaptation strategies classification has been developed, and the prevailing adaptation strategy types for fly-in-fly-out workers in the Far North and the Arctic have been identified [47]. In this work, we understand adaptation strategies as a holistic management by an employee of his ergatic system, aimed at maintaining the required level of performance and functional state in the process of performing professional duties in various conditions while maintaining the physical and mental health of the employee, which is also considered for a long, completed period of time [45,47].
We distinguish two types of adaptation strategies for fly-in-fly-out personnel–economical and emergency. The economical adaptation strategy presupposes that the employee, without increasing his level of activation more than necessary, is able to readjust in the middle of the fly-in period, when the psychological load becomes excessive, his body starts the mechanism of bilateral regulation for the correct distribution of forces. An economical adaptation strategy is more characteristic of trainees (employees with more than three years of fly-in-fly-out work) and consists in a more consistent and deliberate use of self-regulation psychological mechanisms, in the ability to consciously subordinate one’s state and mood to professional tasks and perform most tasks at the level of skills and automatisms.
The emergency adaptation strategy is characteristic of employees who are just adapting to new working conditions and has the following features: it is physiologically oriented and uneven, while it looks effective, since it allows maintaining a relatively high level of the functional state until the end of the fly-in period but ultimately leads to a general decline in health, which will become obvious after a couple of years of fly-in-fly-out work [56].
When working on a fly-in-fly-out basis, the personnel at industrial enterprises are exposed to a number of dangerous factors associated with the group isolation conditions and extreme climatic conditions. This causes difficulties, such as transport accessibility, and makes it difficult to leave the shift facilities to return home, limited availabilities of medical care, etc. ([10,12,13,44,57,58] fourteen). FIFO workers evaluate these factors and conditions differently. With a low danger assessment of such situations by employees, it can be argued that they are adapted to them and know specific actions to resolve them. A high assessment of the danger of these factors suggests the opposite: a lack of understanding in how to act and the presence of great difficulties for employees in resolving the danger. The factors with a high subjective assessment of danger for employees require great attention and additional measures from the management of these organizations. This led to the inclusion in the method of solving professional problems’ parameters, the employees’ self-assessment of knowledge, and the use of safety in the workplace, as well as a subjective assessment of the danger of key professional situations that may arise during a shift period.
The psychophysiological “cost of activity” was analyzed by us from the point of view of assessing functional states. As shown in our previous studies, the analysis of the available literature sources demonstrates the active use of various objective, subjective, and projective methods in a variable combination to assess functional states. Obviously, the measurement of the same objects by different methods can give different results, and in the case of functional states, reflect their different levels [59]. In this connection, when assessing functional states to characterize the psychophysiological “cost of activity”, we used objective psychophysiological assessment methods (using the “Psychophysiologist” devices) and identified the following parameters: operator performance and the level of functional state and the level of functional capabilities, both projective (by calculating Aminev’s interpretation coefficients of Luscher’s color test), which reveal work capacity, stress, unproductive neuropsychic stress, and subjective (test method “Well-being. Activity. Mood.”), revealing the characteristics of the state on the basis of self-reports. Thus, we have implemented an integrated an approach to assessing the psychophysiological “cost of activity” parameters.
2.3. Methods
The research was carried out using questionnaires, psychophysiological testing, and psychological testing. The psychophysiological “cost” of activity component was estimated using the following methods:
1. The original questionnaire developed by Korneeva, Simonova, and Tyulyubaeva included questions related to effectiveness and the way of performing tasks, which are presented in Figure 2 and included the following sections: general information about education and work experience; marital status; subjective assessment of the discomfort of climatic–geographical, industrial, and social factors that affect workers during the shift arrival; features of the organization of free time during the fly-in period; subjective assessment of professional efficiency; subjective assessment of the danger of various situations that may arise during the fly-in period; subjective assessment of the hazard in the workplace and the factors contributing to its emergence. The hazard situations were identified based on the results of previous field studies and analysis of labor protection documentation for oil and gas companies [60]. All assessments of the studied parameters were made on point and rank scales. The workers were asked to assess these situations according to the degree of danger on a 7-point scale, where 1 indicated the situation was not dangerous, and 7 indicated the situation was maximally dangerous. It is assumed that a high assessment of the danger of the above situations by employees indicates their low adaptation and a lack of full understanding of how to act in such situations, i.e., poses the greatest risks. A low assessment of the danger of situations indicates the opposite–adaptability and confidence about how to act in such situations [9]. Individual question weights were considered equal, and no alpha coefficients were calculated. This is also due to the fact that the sample is a priori inhomogeneous in terms of the weight contributions to the factors taken into account [9].
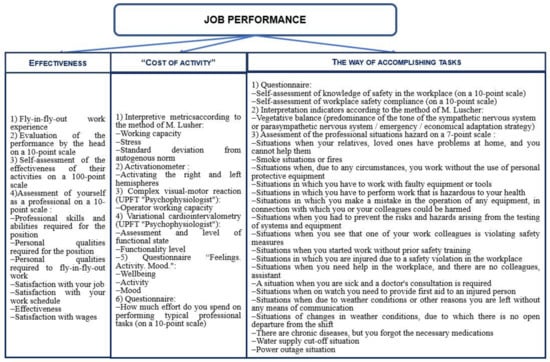
Figure 2.
Distribution of research methods with job performance components of FIFO workers.
Figure 2 shows which indicators were evaluated for each of the three components of job performance. Using static procedures, the entire sample was divided into groups according to the severity of indicators (two-stage cluster analysis); then, using MANOVA, an experiment was carried out identifying which indicator made a greater contribution to the differences in the groups. Therefore, it is enough to evaluate them in order to determine the group for each of the components in the future. Initially, they tried to evaluate the largest number of different indicators of each of the components of job performance.
2. The objective methods using the device for psychophysiological testing UPFT-1/30 “Psychophysiologist” (MTD Medikom, Taganrog, Russia) and the hardware and software complex “Activationometer” AC-9K (NPO “APK” LLC, Kazan, Russia) were used.
-Complex visual–motor reaction (CVMR) determines the speed and accuracy of responses to incoming light signals. By correlating these two characteristics, the operator’s performance is determined.
The essence of the CVMR technique is to determine the time and stability of the visual–motor reaction to light stimuli (green and red squares in the center of the monitor screen). The statistical indicators analysis of the time a complex visual–motor reaction makes it possible to evaluate, in addition to the absolute time of the reaction, stability, the probability of errors, and disruptions. The characteristics of the reaction time distribution make it possible to assess the stress degree, personal readiness to work, the fatigue degree, and in some cases, the presence of pathological functional disorders or organic disorders of the central nervous system.
It allows the operator to assess the operator working capacity level on two alternative parameters of a complex visual–motor reaction (75 stimuli). The accuracy of the reaction (the number of correct responses to the stimulus) and the speed of response are evaluated, and the level of operator performance is determined by their correlation.
-Variational cardiointervalometry (VCM) based on the adaptive capabilities of the cardiovascular system makes it possible to determine the level of a person’s functional state (negative, critical, maximum allowable, acceptable, close to optimal, or optimal) and the level of functional capabilities (low, medium, or high). The duration is 128 cardiocycles and 5 min. It allows us to identify workers’ conditions, characterized by overstrain and depletion of regulatory mechanisms. During the examination, an ECG signal is recorded. The time between adjacent RR intervals is measured. The minimum cycle for examination by the method is equal to the time required to register 128 cardiointervals.
3. The subjective method uses the questionnaire “Well-being. Activity. Mood” (WAM), developed by Doskin, Lavrentieva, Sharai, and Miroshnikov [61]. It consists of 30 pairs of words reflecting the studied features of the psychoemotional state (health, mood, activity), expressed in polar assessments. WAM constructive validity was established on the basis of comparison with the results of psychophysiological methods, considering indicators of the critical frequency of flickering, temperature dynamics of the body, and chronoreflexometry. The current validity was established by comparing the data of contrasting groups, as well as by comparing the results of the subjects at different times of the working day [59,61]. Cronbach’s alpha for questionnaire scales is well-being (0,76), activity (0,65), mood (0,69).
4. The projective method uses the test of color preferences Luscher [62] adapted by Sobchik [63] with the calculation of interpretation coefficients by Aminev [64]. On the basis of factor analysis, he identified the following coefficients: heteronomy, concentricity, balance of personality traits, balance of the autonomic (autonomic) nervous system, working capacity, and the presence of a stress state. M. Luscher singled out a working group of colors (red, green, and yellow). He argued that high working capacity corresponds to the preference of these colors by subjects. Indicators of stress, according to M. Luscher’s theory, are finding the main active colors in the last positions of the choice and finding brown, black, and gray cards in the first places of the row [43]. All these coefficients are calculated according to the appropriate formulas reflecting a particular combination of colors (see Korneeva, Simonova, 2020 [59]).
The rationale for this comprehensive approach to assessing functional states with a detailed description of diagnostic methods is presented in our work [59].
2.4. Data Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using descriptive statistics, two-stage cluster analysis, and multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). The MANOVA method was used because the study of the relationship of many factors was carried out.
For all parameters presented in this research, the criterion of equality of the variances of Levene’s errors is greater than 0.05. Before the analysis, the data were checked for normality of distribution for the possibility of using MANOVA. The statistical normality test of Kolmogorov–Smirnov is used.
Processing was carried out using the SPSS 23.00 software package (license agreement No. Z125-3301-14).
The stages of developing the job performance typology of fly-in-fly-out workers at industrial enterprises is as follows:
1. The employees’ distribution into groups depending on effectiveness as a job performance component by means of two-stage cluster analysis; the description of their characteristics in the representatives of each group by means of MANOVA.
2. The employees’ distribution into groups depending on the parameters of the psychophysiological “cost of activity” as a job performance component by means of two-stage cluster analysis; the description of their characteristics in the representatives of each group by means of MANOVA and descriptive statistics.
3. The employees’ distribution into groups depending on the parameters of the way of performing tasks as a job performance component by means of two-stage cluster analysis; the description of their characteristics in the representatives of each group by means of MANOVA and descriptive statistics.
4. Development of the job performance typology of fly-in-fly-out workers when correlating effectiveness, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the method of solving problems.
5. Description of the relationship between job performance types with the fly-in-fly-out work experience and age characteristics of employees in industrial enterprises by means of MANOVA and descriptive statistics.
3. Results
3.1. Classification of Employees into Groups Depending on Effectiveness as a Job Performance Component
In order to classify FIFO employees by groups, depending on the effectiveness parameters as a component of the job performance, a two-stage cluster analysis was carried out. The variables are subjected to clustering; the effectiveness criteria are presented in Figure 2. Based on the results of the two-stage cluster analysis, all the subjects were divided into two clusters.
To identify significant differences in effectiveness parameters among representatives of the two previously identified clusters, a multivariate analysis of variance was used, where the fixed factor was the assignment to one of the two clusters, and the dependent variables were the criteria for the performance of employees on a FIFO basis. Data correspond to normal distribution. M Box 85.2 at p = 0.432. For all parameters presented in Table 2, the criterion of equality of the variances of Levene’s errors is greater than 0.05. According to the data of multivariate criteria (Pillai Trace 0.704, F = 10.04 at p < 0.001), there are statistically significant differences between the two clusters representatives in assessing performance.

Table 2.
Effectiveness indicators of the employees from two clusters.
According to the data of the univariate criteria, the differences between the clusters are observed for all the effectiveness criteria.
As can be seen from Table 2, the representatives of the first cluster are distinguished by higher assessments of the effectiveness (both from the standpoint of self-assessment and assessment by the manager) and believe that they have the necessary skills and personal qualities to occupy this position and fly-in-fly-out work.
At the same time, their satisfaction with their work, work schedule, wages, and labor results are also higher than among the representatives of the second cluster. Representatives of the second cluster are distinguished by average values of effectiveness, job satisfaction, and wages, and they tend to assess their skills and abilities, as well as the personal qualities necessary for the position and fly-in-fly-out work, slightly above average. Consequently, the first cluster includes the employees with high effectiveness, and the second one includes those with average effectiveness, which confirms the first particular hypothesis of the study.
3.2. Classification of Employees into Groups Depending on the Parameters of the Psychophysiological “Cost of Activity” as a Job Performance Component
The next stage of this study is the distribution of the employees into groups depending on the psychophysiological “cost of activity” parameters and the description of their characteristics in the representatives of each group. For this purpose, a two-stage cluster analysis was also used. The clustering variables are the psychophysiological “cost of activity” criteria presented in Figure 2. Based on the results of the two-stage cluster analysis, all the subjects were divided into two clusters.
To identify significant differences in psychophysiological “cost of activity” parameters among representatives of the two previously identified clusters, a multivariate analysis of variance was used, where the fixed factor was the assignment to one of the two clusters, and the dependent variables were the criteria for the psychophysiological “cost of activity” of FIFO employees. According to the multivariate criteria data (Pillai Trace 0.182, F = 2.25 at p = 0.010), there are statistically significant differences between the representatives of the two clusters in the assessment of their psychophysiological “cost of activity” parameters. Data correspond to normal distribution. M Box 92.1 at p = 0.115. For all parameters presented in Table 3, the criterion of equality of the variances of Levene’s errors is greater than 0.05.

Table 3.
Indicators of the psychophysiological “cost of activity” of employees from two clusters.
For a qualitative description of the differences between the clusters in terms of nominative variables, contingency tables (Pearson χ2) were used.
According to the data of univariate criteria and Pearson’s χ2, the differences between the clusters are observed according to the following psychophysiological “cost of activity” criteria: working capacity, the standard deviation from the autogenous norm, well-being, activation of the left cerebral hemisphere, operator performance, levels of functional state, and functional capabilities.
According to Table 3, the representatives of the first cluster are characterized by high working capacity (according to the projective assessment indicator), unexpressed unproductive neuropsychic stress, well-being, optimal functional state, and a high level of functional capabilities. The average (optimal) psychophysiological “cost of activity” is typical for the first cluster.
At the same time, representatives of the second cluster are characterized by reduced working capacity, increased unproductive neuropsychic stress, reduced well-being, and reduced activation of the left hemisphere of the brain. Their functional state of the body is most often characterized as the maximum permissible, and they are characterized by a low level of psychophysiological reserves; therefore, they can be included in the cluster with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”. This confirms the second particular hypothesis.
3.3. Classification of Employees into Groups Depending on the Parameters of the Way of Performing Tasks as a Job Performance Component
The next stage of this study is the distribution of employees into groups depending on the way of performing tasks parameters, a description of their characteristics in representatives of each group. For this purpose, a two-stage cluster analysis was also used. Clustering variables are the criteria of performing tasks, presented in Figure 2. Based on the results of a two-stage cluster analysis, all the subjects were divided into two clusters.
To identify significant differences in the tasks parameters among representatives of the two previously identified clusters, a multivariate analysis of variance was used, where the fixed factor was the assignment to one of the two clusters and the dependent variables were the criteria for the way FIFO employees perform tasks. According to the data of multivariate criteria (Pillai Trace 0.75, F = 28.46 at p < 0.001), there are statistically significant differences between the representatives of the two clusters in assessing problem solving. Data correspond to normal distribution. M Box 78.3 at p = 0.351. For all parameters presented in Table 4, the criterion of equality of the variances of Levene’s errors is greater than 0.05.

Table 4.
Indicators of the way the employees from two clusters perform tasks.
For the qualitative description of the differences between the clusters in terms of nominative variables, contingency tables (Pearson χ2) were used.
According to the univariate criteria and Pearson’s χ2, the differences between the clusters are observed in all the ways task parameters are performed, except for “knowledge of safety at the workplace” and “compliance with safety at the workplace”.
According to Table 4, the first cluster representatives are characterized by the predominant use of the emergency adaptation strategy, which is expressed in the extensive use of internal resources, starting from the first day of the fly-in period, and the absence of their systematic expenditure during the entire work period. Additionally, these cluster representatives give low assessments of the danger of all professional situations, which may indicate their confidence in the possibility of resolution and adaptation; at the same time, this may also be a sign of self-confident behavior. Thus, it can be said that the first cluster representatives have an emergency and confident way of solving problems.
The second cluster representatives are distinguished by the use of both economical and emergency strategies. An economical adaptation strategy consists of a more consistent and deliberate use of psychological mechanisms of self-regulation, in the ability to consciously subordinate one’s state and mood to professional tasks, and in the ability to perform most tasks at the level of skills and automatisms [56]. It is typical for them to give high differentiated assessments of the danger of professional situations during the fly-in period, which may indicate either their caution or a desire to provide for various options for solutions, and it may also mean insufficient adaptation and uncertainty. In this connection, the representatives of the second cluster may be said to possess a mixed, cautious way of solving problems. This confirms the third particular hypothesis of the study.
3.4. Development of the Job Performance Typology of Fly-In-Fly-Out Workers
The next stage of this study is the development of a job performance typology of FIFO workers with the correlation of effectiveness, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the problem-solving way (Figure 3).
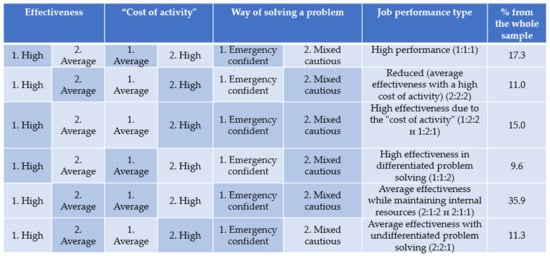
Figure 3.
Job performance typology of fly-in-fly-out workers.
Thus, as a result, the six types of FIFO workers’ job performance have been developed with the correlation of effectiveness, psychophysiological “the cost of activity”, and the problem-solving way (Figure 3).
The first type of high job performance includes employees who demonstrate high labor effectiveness and invest an average psychophysiological “cost” in activities, i.e., make the best use of internal resources to complete tasks. At the same time, an urgent and confident type of problem solving is used, which is expressed in the predominant use of similar solution strategies and the orientation toward activity and actions, rather than prolonged pondering over situations.
The second type of reduced professional efficiency includes employees who demonstrate average labor effectiveness and use the maximum number of internal resources; as a result, their depletion and unfavorable functional states are observed. In other words, it is the workers who invest a high psychophysiological “cost” in the results of their labor. These employees do not have a clearly expressed way of solving problems and use various options. Not being fully prepared for dangerous situations, they respond to them with caution.
The third job performance type is employees with high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity” who are distinguished by the fact that they strive to ensure high effectiveness of their work through excessive use of internal resources. In doing so, they use both problem-solving ways. In this case, there is no differentiation in the method since this does not affect the efficient use of internal reserves. It can be assumed that these types of employees do not have the necessary set and expression level of professionally important qualities or have high psychological and professional risks, as a result of which such results are observed.
The fourth type of employees are those with high effectiveness with differentiated problem solving and are distinguished by the fact that the result of their activity is influenced by the problem-solving way, namely, mixed and cautious. We assume that these employees are distinguished by a special combination of professionally important qualities and a sufficiently high level of internal reserves, which allow them to approach solving problems in different ways.
The fifth type of employees are those with average effectiveness while maintaining internal resources that dominate in the surveyed sample (35.9%) and are characterized by average performance indicators and a reduced psychophysiological “cost of activity”. This may be due to motivational characteristics (a decrease in motivation to FIFO work), or it may be an understanding that performing work at a high level will require many more costs and resources and will contribute to the development of psychological risks and worsen the state of health. Perhaps, this is an employee type with a long record of FIFO work or the one working in more extreme, difficult, and/or stressful conditions.
The sixth type of professional efficiency includes employees with average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving. It can be assumed that this problem-solving way is ineffective for these specialists, because the psychophysiological “cost” of their activities is high, and the effectiveness is average. In other words, by investing all resources in their work, employees cannot achieve high results.
The obtained results confirm the main hypothesis of the study.
3.5. Relationship between Job Performance Types with the Fly-In-Fly-Out Work Experience and Age Characteristics of Employees in Industrial Enterprises
The next study stage was to identify the relationship between the job performance types with FIFO work experience and age characteristics of employees in industrial enterprises. We assumed that the division of employees into different job performance types may be due to age and the characteristics FIFO work experience. This assumption can be explained by the fact that during long-term FIFO work, there is a cumulative effect of the action of adverse environmental factors (climatic, industrial, and social), which enhances their impact.
In addition, with age, the amount of internal resources of employees may decrease (with insufficient psychological support and recreational activities) and lead to an increase in the psychophysiological “cost of activity”.
In order to test our assumption, we conducted two univariate analyses of variance, where the fixed factor was attributed to one of the six types of job performance, and the dependent variables were age and FIFO work experience.
According to the data of intergroup effects, there is a statistically significant relationship between the job performance type of employees in industrial enterprises and their FIFO work experience (F = 2.643 at p = 0.024), as well as age (F = 2.852 at p = 0.016). This confirms the fourth particular hypothesis.
According to Figure 4, the employees with a longer FIFO work experience and age belong to the types with average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving and with high performance due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity”. These two types are characterized by a high psychophysiological “cost of activity” and confirmed our hypothesis that, over time, there is a cumulative effect of the negative impact of environmental factors, which leads to the expenditure of employees’ internal resources. As a result, additional recreational (recovery) activities are required for employees who have been working on a rotational basis for more than eight years.
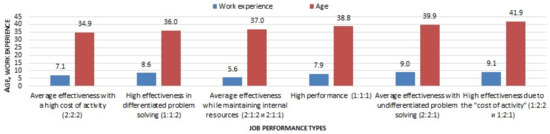
Figure 4.
The relationship between employees’ job performance types in industrial enterprises with fly-in-fly-out work experience and age.
The differences in the effectiveness of these two employees’ categories may be due, first of all, to motivational characteristics, since some of them strive to show high performance despite their limited resources while the others meet the minimum necessary requirements and fulfill their responsibilities at an acceptable level.
The employees with average effectiveness at a high psychophysiological “cost of activity” may be insufficiently adapted to FIFO work due to the use of the problem-solving method, which is not optimal for their job performance type–a mixed cautious one. With relatively low internal reserves, this method requires additional costs for the choice of various alternatives, re-checking their assumptions, and a differentiated approach to information analysis, which can ultimately lead to the psychophysiological “cost of activity” increase. Such employees can be distinguished by insecure behavior and anxiety.
The specialists with an average effectiveness while maintaining internal resources may be distinguished by reduced motivation for FIFO work; they may not be suitable for this method of work, or they experience significant difficulties in adaptation because their average FIFO work experience is 5.6 years.
The two remaining groups are employees with high effectiveness are optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity” and differing in the problem-solving ways, which are due to the peculiarities of the professionally important qualities and their combination.
Thus, the main hypothesis of the study was confirmed: when correlating various job performance types, psychophysiological “cost of activity” and the way of performing tasks, several kinds of job performance of fly-in-fly-out workers at industrial enterprises can be developed, which will allow developing targeted measures for psychological support for each category of employees. As a result of the study, six job performance types of FIFO workers of industrial enterprises were highlighted: (1) high performance, (2) average effectiveness with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”, (3) high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity”, (4) high effectiveness with a differentiated solution of problems, (5) average effectiveness while preserving internal resources, and (6) average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving.
The private hypotheses also received confirmation. As a result of two-stage cluster analyses, all the employees were divided into the following groups: high and medium effectiveness; high and optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity”; emergency confident problem-solving way and a mixed, cautious one.
The statistically significant relationships were established between age and FIFO work experience with job performance types. The employees with a longer FIFO work experience and age belong to the types with average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving and with high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity”.
4. Discussion
Having carried out the distribution of FIFO workers with different job performance types in relation to industries and professional groups, the following should be noted. Among the industries, the oil and gas industry have a more extreme impact on employees, which is reflected in a higher percentage of employees with average effectiveness while maintaining internal resources (24.2%) and high effectiveness due to the “cost of activity” (21.2%).
Comparison of professional groups found that a greater number of employees with high effectiveness (33.3%) refer to labor optimization. Their professional activities are as diverse as possible and involve elements of creativity, which explains the high interest and motivation of staff and the desire to achieve maximum results.
Among the management personnel, there is also a fairly large number of employees with high effectiveness (21.6%), which can be explained by their responsibility for the overall result and the need to motivate other employees to work.
The maintenance specialists and management of universal equipment have a high psychophysiological “cost of action” to a greater extent because they are dominated by high effectiveness due to the “cost of activity” (18.8%) and average effectiveness while maintaining internal resources (21.7%), which requires consideration when developing psychological support for personnel.
Our results regarding the relationship between job performance types and FIFO work experience are consistent with those of Roozbehani et al. [65], who showed that long-term employment on offshore platforms is accompanied by personality changes. Workers with a FIFO work experience of over four years on an offshore platform compared to employees with less than one year of work experience had higher rates of neuroticism and lower rates of extraversion, compliance, and consciousness [65].
Bowers et al. [66] studied the prevalence and correlation of psychological disorders in FIFO workers in the mining and construction industries in Australia. A total of 28% of workers was found to have high levels of psychological stress (compared to 10.8% of the general Australian population). The employees identified the following as key stressors: lack of interesting events, problems in relationships with partners, financial problems, work schedules, and conditions of group isolation. The risk group with high psychological stress is employees aged 25–34 years old and working a schedule of “two weeks of work, one week of rest” [66].
Confirming the cumulative negative effect of environmental factors in FIFO work, especially in the North and in the Arctic, Sobakin determined the features of changes in physical and mental performance during the working day and shift period among newcomers who come to work on a FIFO basis in the Far North and the Arctic. He determined a periodic decrease in physical and mental performance and the recovery processes speed in FIFO workers in the northern gas fields, depending on the increase in northern experience and growing during powerful geomagnetic disturbances. Sobakin also found a rhythmological pattern of changes in the incidence of maladaptive disorders in watch personnel with a significant increase in their number by 1, 5–6, 8, 12–13, 15–16 and 18 years of work experience in the gas industry in the North [51].
The importance of the psychophysiological “cost of activity” can be proved by the studies devoted to the negative impact of production factors associated with the labor organization and social and household factors caused by group isolation. FIFO work, especially if it includes night shifts, negatively affects physical health, psychological well-being, and increases the risk of accidents and injuries at work [4].
The employees with shorter fly-in periods (i.e., with the shortest fly-in period during all hours of work) are much more dissatisfied with their work schedules than those with longer fly-in periods (i.e., with the longest vacation period during all hours of work), which is consistent with previous studies. More research is needed to investigate the optimal fly-in period to minimize employees’ dissatisfaction [7].
The negative consequences of long work hours and fatigue are common to both operational risk and the risk of human error. Offshore platform personnel are required to remain at the facility outside of business hours, so leisure and sleep conditions are limited by onboard facilities [23,24].
The working hours and shifts as risk factors for health deterioration have been studied mainly in relation to sleep complaints and psychosomatic problems [23,24].
The results showed that FIFO work directly caused stomach problems and sleep disturbances. Parkes [4] concluded that these effects may be related to circadian adjustments caused by the transitions from day to night work and vice versa. This problem is especially relevant for offshore production platforms since employees usually work 12-h shifts, and the change from day to night work occurs in the middle of a two-week work schedule.
When job types in relation to health complaints were assessed, the results showed that construction workers were most likely to report work-related injuries, while drillers were most likely to report musculoskeletal problems [4]. Headaches were a common health complaint among both construction workers and drilling workers. It has been suggested that this may be due to harsh environmental conditions and the physical nature of these works.
Objective monitoring of sleep of FIFO workers in the mining industry [27] and qualitative data indicate that FIFO workers are constantly experiencing excessive fatigue [28]. Twelve-hour shift work, which is typical for FIFO work, leads to fatigue, which negatively affects productivity [29]. Fatigue can impair performance to levels equivalent to alcohol intoxication [30] and exposes workers to a higher risk of accidents and injury [31,32].
Potential stressors for offshore personnel include poor living and working conditions, lack of privacy, constant noise, and demanding work tasks with high workloads ranging from periods of boredom to periods of concentrated activity [5].
Restrictions on alcohol consumption by employees during the fly-in period due to limited leisure time, restrictions on alcohol availability in the quarters of FIFO personnel, and random alcohol tests upon arrival on shift combined with relatively high salaries and long vacation periods can lead to drinking problems among some workers on vacation [67] requiring further training or behavior change strategies.
Thus, when one of the job performance types is identified among employees, which implies a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”, i.e., characterized by an unfavorable state, depletion of internal reserves, a decrease in working capacity, and well-being and mood (these include the types “average effectiveness with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”, “high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological ‘cost of activity’”, and “average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving “), it is necessary to develop measures for their recovery and rehabilitation.
The Practical Applications for Job Performance Management of Fly-In-Fly-Out Workers at Industrial Enterprises
Table 5 provides the correlation of results regarding job performance types with possible measures for personnel management.

Table 5.
Proposed activities for personnel management of various job performance types.
Due to the fact that the study was carried out at various industrial facilities in different years, as well as by means of a scientific expedition, which involved repeated measurements of the state of workers, this article concludes the relative stability of the types. At the same time, it is shown how the types of job performance are interconnected with the length of FIFO work experience (Figure 4). The obtained connections indicate the possibility of changes in the types of job performance after certain periods of time. We propose to evaluate the job performance of employees periodically (once a year) in order to apply the advisory management decisions presented in Table 5.
The key theoretical significance of the study is the expansion of the concept of job performance through a comprehensive study of its parameters and the definition of job performance types when comparing the effectiveness, the psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the method of solving problems.
This study’s limitations are related to the possibility of their distribution to FIFO workers in the oil and gas, diamond, and construction industries, while the FIFO method can be applied in other areas with different specifics. The expansion of the data obtained by applying this design to industrial sites in other countries, considering national specificities. The research limitation is also the set of indicators for each job performance components and methods for their assessment, which can be refined in future studies.
To explain the reasons and mechanisms underlying the obtained classification, it is necessary to analyze the factors and conditions of the professional environment, as well as the characteristics, qualities, and properties of all components of the professional suitability of FIFO workers. When developing this typology, all the required materials were collected both in relation to environmental factors and in a relatively complex comprehensive study of the personality of all types of employees. These results will be described in our next article.
The study of the factors and conditions of the professional environment will be built at all levels of the differential analysis of professional activity using FIFO forms of work.
5. Conclusions
As a result of this study, the job performance typology of FIFO workers at industrial enterprises was developed by correlating three components: effectiveness, psychophysiological “cost of activity”, and the way of accomplishing tasks. As a result of two-stage cluster analyses, all the employees were divided into the following groups: high and medium effectiveness; high and optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity”; and emergency problem-solving way and a mixed, cautious one. Various combinations of these components made it possible to develop six job performance types of FIFO personnel at industrial enterprises: (1) high performance, (2) average effectiveness with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”, 3) high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity”, (4) high effectiveness with a differentiated solution of problems, (5) average effectiveness while preserving internal resources, and (6) average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving.
The statistically significant relationships were established between age and FIFO work experience with job performance types. The employees with a longer FIFO work experience and age belong to the types with average effectiveness with undifferentiated problem solving and with high effectiveness due to the psychophysiological “cost of activity”. The employees with average effectiveness at a high psychophysiological “cost of activity” have relatively little FIFO work experience. The specialists with an average effectiveness and with high effectiveness with an optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity” have average work experience. Based on the results of these connections, some possible reasons for the manifestation of each job performance type were identified, and a few measures for personnel management at industrial enterprises were proposed.
Among the studied industries, most of the employees with a high psychophysiological “cost of activity” are observed in the oil and gas industry, high efficiency and an optimal psychophysiological “cost of activity” in the diamond mining sector, and an average efficiency while preserving internal resources in construction.
Among the various professional groups’ representatives, most of the employees with high efficiency relate to work on optimization and managerial work, and the maintenance specialists and management of universal equipment to a greater extent have a high psychophysiological “cost of activity”.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, Project number FSRU-2020-006 as part of the Russian state task for fundamental research “Assessment of psychological risks in the professional activities of extreme specialists”, 2020–2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Higher School of Psychology, Pedagogy and Physical Education, Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after M.V. Lomonosov (protocol code 2/04 and 12 February 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Certificate of registration of the database 2021621448, 7 May 2021. Application No. 2021621308 dated 24 June 2021. Psychological safety and adaptability of oil and gas production workers in the shift organization of labor in the conditions of the Far North; Certificate of registration of the database 2021621433, 7 January 2021. Application No. 2021621309 dated 24 June 2021. Psychological safety and adaptability of the builders of the “Crimean Bridge” object in the rotational organization of labor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Job performance criteria as seen by the scientists.
Table A1.
Job performance criteria as seen by the scientists.
| Job Performance Component | Job Performance Subcomponent | Job Performance Criteria as Seen by Foreign Scientists | Job Performance Criteria as Seen by Soviet/Russian Scientists |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | External (objective) effectiveness parameters | Quality of work Tabak et al., 2009 [68], Hashim et al., 2012 [69], Judge et al., 2014 [70], Mehmood et al., 2016 [71] Quality of Service, Mount et al., 1998 [72]; Compliance with the goals of the organization Campbell, 1990 [73] Task execution and peripheral performance Borman, Motowidlo, 1993 [74] A job well done, on track Beverly, 2019 [75] Task Execution Penney et al., 2011 [42]; Pradhan, Jena, 2017 [39]; Koopmans et al., 2014 [40]; Motowidlo, Schmit, 1999 [41] | Performance, quality, and reliability Lomov, 1966 [76]; Shadrikov, 1982 [77], as well as the job satisfaction indicator Bodrov [38]. The degree of fulfilment of planned tasks, the quality of work, the levels of mutual acceptability, accidents, status stability, the time to reach production standards from the beginning of joint work Argentova, 1984 [78], The degree of goals achievement. Ponomarenko, 1992 [79], Stable efficiency of the team and the level of complexity of the operational situation in the region, Kossov, 1983 [80]; Indicators of the quality and quantity of products taken in relation to raw materials and time costs for its production Zinchenko et al., 1984 [35] The number of successful actions and indicators of the amount of active behavior (the total number of actions on the field) of athletes Ageev et al., 1987 [81] The number of “incentives” (gratitude), “punishments” (reprimands, remarks, dismissals) Gutsykova, 2012 [82] The quality and quantity of the produced product. Obozov, 1982 [83] The degree of success in achieving the goals of activities. Ponomarenko, 1992 [79] |
| Internal effectiveness parameters (self-assessment of the result and one’s own qualities) | Job satisfaction Christiansen et al., 2014 [84]; Tokar, Subich, 1997 [85]; Self-efficacy by Bandura, 1997 [86]; Stajkovic, Luthans 1998 [87]; Mitchell et al., 1994 [88] | Satisfaction of the subject of activity Tolochyok, 2000 [89] Importance of the opinion of colleagues, management, labor consumers and the subject of labor Kornilova et al., 1993 [53]; Self-assessment of performance, mobility, multifunctionality, emotional and behavioral stability, predictability Karapetyan, 2019 [90] | |
| Internal parameters of effectiveness (management’s attitude and attitude to management) | Strengths and weaknesses of individual employees and groups. Cascio, 1996 [91] | Importance of the opinion of colleagues, management, labor consumers, and the subject of labor Kornilova et al., 1993 [53]; | |
| Internal effectiveness parameters (attitude towards colleagues and citizens) | Mutual assistance to other employees, mutual respect of employees Hashim et al., 2012 [69] Work behavior. Borman, Motowidlo, 1993 [74] Contextual Performance Penney et al., 2011 [42] Collaboration between colleagues Mehmood et al., 2016 [71] Contextual performance Pradhan, Jena, 2017 [39]; Borman, Motowidlo, 1993 [74]; Koopmans et al., 2014 [40]; Motowidlo, Schmit, 1999 [41] | Importance of the opinion of colleagues, management, labor consumers, and the subject of labor Kornilova et al., 1993 [53]; | |
| Work experience | Professional Experience Quinones et al., 1995 [52] | Successful brokers working on the exchange for at least one year [53] | |
| The way of accomplishing tasks | Adaptation style | Adaptive performance Pradhan, Jena, 2017 [39] | |
| Personality traits that determine performance | Discipline and Attention Christiansen et al., 2014 [85] Responsibility for the result–“I am ready to bear the risk of faulty work, while completing the task.” Salgado, 2003 [92], Tabak et al., 2009 [68], Hashim et al., 2012 [69], Christiansen et al., 2014 [85] Responsibility for risk–“Initiatives are taken due to creativity in order to improve productivity by coming up with new ideas” Barrick, Mount 1991, Salgado 2003 [93], Tabak et al. 2009 [68], Hashim et al. 2012 [69], Judge et al. 2014 [70] Proactive personality Thompson, 2005 [94] Discipline and attention, responsibility for results and initiative Mehmood et al., 2016 [71] | Compliance of the subject of labor with the requirements to their personality Rodina, 1996 [93] Evaluation by experts of the following professionally important qualities: (1) professional knowledge, abilities, skills; (2) emotional stability; (3) ability to predict the course of events; (4) endurance, ability to maintain performance; (5) professional motivation; (6) self-control, self-possession; (7) ability of emergency mobilization; (8) observation, vigilance; (9) independence, initiative; (10) the ability to work in a team, Gutsykova, 2012 [82] Assessment of 16 generalized management skills by experts (the ability to prepare qualified information, make reasonable proposals to the management; a high level of ability to personally organize work with personnel–selection, placement, preparation of a reserve for promotion, etc.) Kossov, 1983 [80] | |
| Psychophysiological “cost of activity” | Functional states and internal reserves | Contribution of efforts, psychophysiological cost of activity, psychological and physiological “cost” of labor efforts, as well as in relation to indicators of health and personality development of workers Zinchenko et al., 1984 [35]; Rodina, 1996 [93]; Tolochyok, 2000 [84]; Gutsykova, 2012 [82] The value of energy consumption of participants in joint activities. Obozov, 1982 [83] | |
| Destructive changes | Counterproductive Behavior, Penney et al., 2011 [42], Koopmans et al., 2014 [40] | Contribution of efforts, the psychophysiological cost of activity in relation to indicators of health and personality development of workers. Zinchenko et al., 1984 [35] |
References
- Storey, K.; Shrimpton, M. Long Distance Labour Commuting in the Canadian Mining Industry; Queen’s University, Centre for Resource Studies: Kingston, ON, Canada, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, D. Long distance commuting: A new approach to mining in Australia. Geogr. J. 1993, 159, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamber of Minerals and Energy of Western Australia. People at Work; CMEWA: Perth, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, K. Shiftwork and Health. In Cambridge Handbook of Psychology, Health and Medicine, 2nd ed.; Ayers, S., Baum, A., McManus, C., Newman, S., Wallston, K., Weinman, J., West, R., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, K. Psychosocial aspects of stress, health and safety on North Sea installations. Scand. J. Work. Environ. Health 1998, 24, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B.; Alfrey, K.L.; Vandelanotte, C.; Rebar, A.L. Mental health and well-being concerns of fly-in fly-out workers and their partners in Australia: A qualitative study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, S. The Effects of Fly-In/Fly-Out Commute Arrangements and Extended Working Hours on the Stress, Lifestyle, Relationship and Health Characteristics of Western Australian Mining Employees and their Partners: Report of Research Findings. Master’s Thesis, The University of Western Australia, Crawley, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen, M.; Pallesen, S.; Bjorvatn, B.; Knardahl, S. Shift schedules, work factors, and mental health among onshore and offshore workers in the Norwegian petroleum industry. Ind. Health 2015, 53, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korneeva, Y. The Adverse Environmental Impact Factors Analysis on Fly-In-Fly-Out Personnel at Industrial Enterprises. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojnovic, P.; Bahn, S. Depression, anxiety and stress symptoms among Fly-In Fly-Out Australian industry workers. J. Health Saf. Environ. 2015, 31, 207–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mette, J.; Velasco Garrido, M.; Harth, V.; Preisser, A.M.; Mache, S. Healthy offshore workforce? A qualitative study on offshore wind employees’ occupational strain, health, and coping. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.L.; Anglim, J. Employee engagement and emotional exhaustion of fly-in-fly-out workers: A diary study. Aust. J. Psychol. 2018, 70, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.; Brook, L.; Stomski, N.J.; Ditchburn, G.; Morrison, P. Depression, suicide risk, and workplace bullying: A comparative study of fly-in, fly-out and residential resource workers in Australia. Aust. Health Rev. A Publ. Aust. Hosp. Assoc. 2019, 44, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.E.; Lazarsfeld-Jensen, A.; Francis, K. The implications of isolation for remote industrial health workers. Rural. Remote Health 2019, 19, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco Garrido, M.; Mette, J.; Mache, S.; Harth, V.; Preisser, A.M. Demands and hazards of working in the offshore wind power industry (Belastungen und Gefährdungen der Beschäftigten in der Offshore-Windindustrie [German]). Arb. Soz. Umw. 2017, 52, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Q.; Wong, T.W.; Yu, T.S. Mental health issues in Chinese offshore oil workers. Occup Med. 2009, 59, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nielsen, M.B.; Tvedt, S.D.; Matthiesen, S.B. Prevalence and occupational predictors of psychological distress in the offshore petroleum industry: A prospective study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2013, 86, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mette, J.; Velasco Garrido, M.; Preisser, A.M.; Harth, V.; Mache, S. Mental strain among workers in the German offshore wind industry (Psychische Belastung von Beschäftigten in der deutschen Offshore-Windindustrie [German]). Zbl Arb. 2016, 66, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, T. Conflict and contestation in Kyrgyz mining infrastructure. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2020, 7, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkan, A.M. Work and health: A comparison between Norwegian onshore and offshore employees. Work 2011, 40, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroleum Safety Authority Norway. Trends in Risk Level in the Norwegian Petroleum Activity; Summary Report 2015; Norwegian Continental Shelf Petroleum Safety Authority Norway: Stavanger, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Riethmeister, V.; Brouwer, S.; van der Klink, J.; Bültmann, U. Work, eat and sleep: Towards a healthy ageing at work program offshore. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, K.R. Psychosocial Aspects of Work and Health in the North Sea Oil and Gas Industry; Research Report 002; University of Oxford for the Health and Safety Executive: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Parkes, K. Age, smoking, and negative affectivity as predictors of sleep patterns among shift workers in two environments. J. Occup. Health Psychol. 2002, 7, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mearns, K.; Hope, L. Health and Well-Being in the Offshore Environment: The Management of Personal Health; Research Report 305; University of Aberdeen for the Health and Safety Executive: Aberdeen, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Keown, N. Digging Deep for Better Health: A Study of the Health Status of Men in the Goldfields Mining Industry in Western Australia, Executive Summary; Goldfields Men’s Health Inc.: Kalgoorlie, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Paech, G.M.; Jay, S.M.; Lamond, N.; Roach, G.D.; Ferguson, S.A. The effects of different roster schedules on sleep in miners. Appl. Ergon. 2010, 41, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkington, A.M.; Larkins, S.; Gupta, T.S. The psychosocial impacts of fly-in fly-out and drive-in drive-out mining on mining employees: A qualitative study. Aust. J. Rural Health 2011, 19, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.A.; Paech, G.; Dorrian, J.; Roach, G.; Jay, S.M. Performance on a simple response time task: Is sleep or work more important for miners? Appl. Ergon. 2011, 42, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamond, N.; Dawson, D. Quantifying the performance impairment associated with fatigue. J. Sleep Res. 1999, 8, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinges, D.F. An overview of sleepiness and accidents. J. Sleep Res. 1995, 4, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkard, S.; Lombardi, D.A. Modeling the impact of the components of long work hours on injuries and “accidents”. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2006, 49, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, H.; Schmidt, G. The women who remain behind: Challenges in the LDC lifestyle. Rural Soc. 2016, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.; Kaczmarek, E. An Exploration of Generation Y’s Experiences of Offshore Fly-in/Fly-out Employment. Aust. Psychol. 2009, 21, 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, V.V. Psychological Determinants of the Effectiveness of Professional Activities: The Example of Salespeople. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University, M.V. Lomonosov, Moscow, Russia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zinchenko, V.P.; Munipov, V.M.; Rubakhin, V.F. Psychological problems of efficiency and quality of labor. Psychol. J. 1984, 2, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Leonova, A.B.; Kuznetsova, A.S. Structural-integrative approach to the analysis of functional states: History of creation and development prospects. Mosc. Univ. Psychol. Bull. 2019, 2019, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodrov, V.A. Working capacity of a human operator and ways to improve it. Psychol. J. 1987, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, R.K.; Jena, L.K. Employee Performance at Workplace: Conceptual Model and Empirical Validation. Bus. Perspect. Res. 2017, 5, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, L.; Berhnaards, C.M.; Hildebrandt, V.H.; Vet, H.C.W.; Berk, A.J. Construct validity of the individual work performance questionnaire. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motowidlo, S.J.; Schmit, M.J. Performance Assessment in Unique Jobs. In The Changing Nature of Performance; Ilgen, D.R., Pulakos, E.D., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 56–86. [Google Scholar]
- Penney, L.M.; David, E.; Witt, L.A. A review of personality and performance: Identifying boundaries, contingencies, and future research directions. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2011, 21, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, Y.; Simonova, N.; Shadrina, N. The Psychosocial Risk Factors Evaluation and Management of Shift Personnel at Forest Harvesting. Forests 2022, 13, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, Y.A.; Simonova, N.N. Analysis of Psychological Risks in the Professional Activities of Oil and Gas Workers in the Far North of the Russian Federation. Behav. Sci. 2018, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonova, N.N. Psychological Analysis of the Professional Activity of Specialists in the Oil-Producing Complex: On the Example of Shift Work in the Far North. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov, Moscow, Russia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McPhee, J.C.; Charles, J.B. Human Health and Performance Risks of Space Exploration Missions: Evidence reviewed by the NASA Human Research Program; NASA SP-2009-3405; Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center: Houston, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Korneeva, Y.A. Adaptation Strategies in the Professional Activity of Those Working on a Rotational Basis in the Far North. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov, Moscow, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Korneeva, Y.; Tyulyubaeva, T.; Simonova, N. The Components of Psychological Safety of Oil and Gas Shift Workers in the Arctic. In Interconnected Arctic—Uarctic Congress 2016; Springer Polar Sciences: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, Y.; Simonova, N.; Tyulyubaeva, T. Analysis of the dangers of professional situations for oil and gas workers of various professional groups in the Arctic. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 787, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, Y.A.; Simonova, N.N. Psychological safety of oil and gas workers in the South and North of the Russian Federation. In Proceedings of the SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference, RPTC 2020, Virtual, 26–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobakin, A.K. Efficiency of Shift Personnel in Gas Fields in Extreme Environmental Conditions of the North. Ph.D. Thesis, Novosibirsk State Agrarian University, Novosibirsk, Russia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Quinones, M.A.; Ford, J.K.; Teachout, M.S. The relationship between work experience and job performance: A conceptual and meta-analytic review. Pers. Psychol. 1995, 48, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornilova, T.V.; Bulygina, V.G.; Kornilov, A.P. Personal prerequisites for a successful broker. Psychol. J. 1993, 1, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rebar, A.L.; Alfrey, K.L.; Gardner, B.; Vandelanotte, C. Health behaviours of Australian fly-in, fly-out workers and partners during on-shift and off-shift days: An ecological momentary assessment study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e023631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbel, A.M.; Kaczmarek, E.; Drake, D. Fly-In/Fly-Out Accommodation: Workers’ Perspectives. In Labour Force Mobility in the Australian Resources Industry; Haslam McKenzie, F., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneeva, Y.; Simonova, N. Differential analysis of adaptation strategies of fly-in-fly-out personnel. Eur. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2020, 91, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonova, N.N. Group isolation of oil workers during rotational work in the North. News Samara Sci. Cent. Russ. Acad. Sci. 2009, 11, 964–969. [Google Scholar]
- Mette, J.; Robelski, S.; Kirchhöfer, M.; Harth, V.; Mache, S. Living the 14/14 Schedule: Qualitative Analysis of the Challenges and Coping Strategies among Families of Offshore Wind Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korneeva, Y.; Simonova, N. Job Stress and Working Capacity among Fly-In-Fly-Out Workers in the Oil and Gas Extraction Industries in the Arctic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korneeva, Y.A.; Simonova, N.N.; Tyulyubaeva, T.O. An employee’s subjective assessment of the danger of various situations arising in professional activity during the shift work organization in the Arctic. Labor Saf. Ind. 2016, 7, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Doskin, V.A.; Lavrentyeva, N.A.; Miroshnikov, M.P.; Sharay, V.B. Test of differentiated self-assessment of the functional state. Quest. Psychol. 1973, 6, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Luscher, M.; Scott, I. The Luscher Color Test; Random House: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Sobchik, L.N. Color Selection Method. Modification of the Eight-Color Luscher Test. A Practical Guide; Speech: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aminev, G.A. Mathematical Methods in Engineering Psychology; BSU: Ufa, Russia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Roozbehani, A.; Tarkhan, M.; Alipour, A.; Saffarina, M. Comparing personality change of the newly employed and old employees working at the offshore oil industry: A cross-sectional study. J. Psychol. Clin. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, J.; Lo, J.; Miller, P.; Mawren, D.; Jones, B. Psychological distress in remote mining and construction workers in Australia. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 208, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B. Boom towns, drug towns? Mining, alcohol and other drugs. Subst. Natl. Mag. Alcohol Tob. Other Drugs 2009, 7, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tabak, F.; Nguyen, N.; Basuray, T.; Darrow, W. Exploring the impact of personality on performance: How time-on-task moderates the mediation by self-efficacy. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2009, 4, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.; Rashid, W.; Othman, A.; Hamzah, M.; Sunai, F. The Effect of Personality Traits on the Relationship between organization conflict and job performance in telecommunication company. J. Manag. 2012, 56, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, T.A.; Simon, L.S.; Hurst, C.; Kelley, K. What I experienced yesterday is who I am today: Relationship of work motivations and behaviors to within-individual variation in the five-factor model of personality. J. Appl. Psychol. 2014, 99, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.; Mehmood, A.; Siddique, M. Personality Traits Nexus Employee’s Performance: An Application of Big Five Personality Dimensions Model. Abasyn J. Soc. Sci. 2016, 101–119. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317290952 (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Mount, M.K.; Barrick, M.R.; Stewart, G.L. Five-factor model of personality and performance in jobs involving interpersonal interactions. Hum. Perform. 1998, 11, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P. Modeling the performance prediction problem in industrial and organizational psychology. In Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, 2nd ed.; Dunnette, M.D., Hough, L.M., Eds.; Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 1, pp. 687–732. [Google Scholar]
- Borman, W.C.; Motowidlo, S.J. Expanding the criterion domain to include elements of contextual performance. In Personnel Selection in Organizations; Schmitt, N., Borman, W.C., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 71–98. [Google Scholar]
- Beverly, E.R. Personality and employee performance. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2019, 11, 4830–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomov, B.F. Man and Technology: Essays in Engineering Psychology; Sov. Radio: Moscow, Russia, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Shadrikov, V.D. Problems of the System Genesis of Professional Activity; Science: Moscow, Russia, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Argentova, T.E. Communication style as a factor in the effectiveness of joint activities. Psychol. J. 1984, 6, 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Ponomarenko, V.A. Engineering Psychology and Increasing the Efficiency of Operator Activity. System Approach in Engineering Psychology and Labor Psychology; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kossov, B.B. Typological features of the style of activity of leaders of different efficiency. Quest. Psychol. 1983, 5, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ageev, B.C.; Dubova, T.F.; Ryzhonkin, Y.Y. The type of explanation of the reasons for failure and the effectiveness of sports activity. Bull. Mosc. State Univ. 1987, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gutsykova, S.V. The Relationship of Integrative Professionally Important Qualities and Personal Characteristics of Specialists with Different Efficiency of Activity. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Psychology RAS, Moscow, Russia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Obozov, N.N. Psychological compatibility and workability as factors of labor efficiency. In Industrial Social Psychology; Publishing House LSU: Leningrad, Russia, 1982; pp. 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, N.; Sliter, M.; Frost, C. What employees dislike about their jobs: Relationship between personality-based fit and work satisfaction. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2014, 71, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokar, D.M.; Subich, L.M. Relative contribution of congruence and personality dimensions to job satisfaction. J. Vocat. Behav. 1997, 50, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajkovic, A.D.; Luthans, F. Self-efficacy and work-related performance: A metaanalysis. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.R.; Hopper, H.; Daniels, D.; George-Falvy, J. Predicting self-efficacy and performance during skill acquisition. J. Appl. Psychol. 1994, 79, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolochek, V.A. Styles of Professional Activity; Smysl: Moscow, Russia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Karapetyan, L.V. Psychological determinants of professional success of EMERCOM of Russia rescuers. Med.-Biol. Socio-Psychol. Probl. Saf. Emerg. Situat. 2019, 3, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, W.F. Managing for maximum performance. HR Mon. 1996, 84, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, J.F. Predicting job performance using FFM and non-FFM personality measures. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2003, 76, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodina, O.N. On the concept of “successful work”. Mosc. Univ. Bull. 1996, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J. Proactive Personality and Job Performance: A Social Capital Perspective. J. Appl. Psychol. 2005, 90, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).