Influence Variables in Occupational Injuries among Men Teachers
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Specialization of the teacher (physical education, musicians, or special education)
- Part of the body affected (neck, back, upper extremities, etc.)
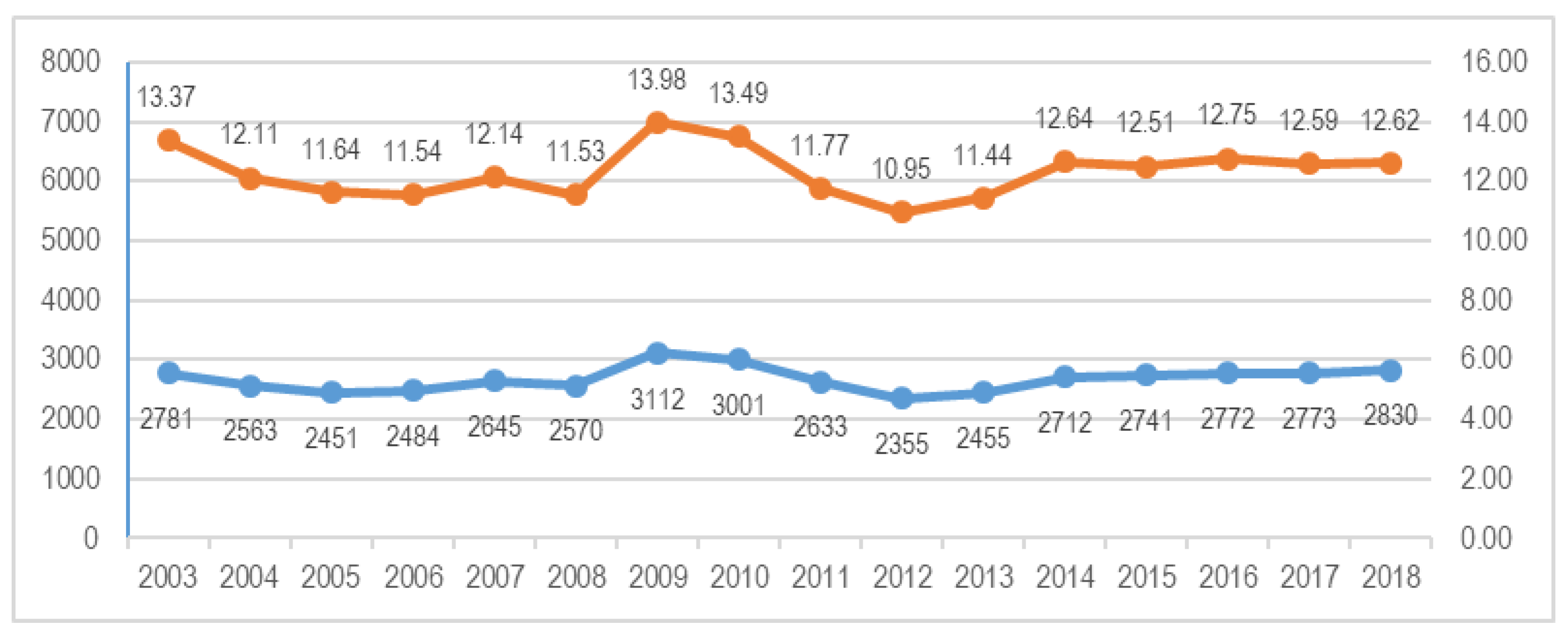
2. Methodology
- Age: Provides the of the worker injured.
- Nationality: Supplies the nationality of the worker injured.
- Length: Lenght of service in the organization.
- Temporal: Type of contract.
- Public. Category of the workplace as Public or Private.
- Traffic: If the accident was associated with a crash or not.
- Monday: Describes if the accident was occurred on Monday or not.
- Severity: Describes the consequence of the accident in the worker in two groups: Ligth, or rest ( serious, very serious and Fatal).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Neck
3.2. Back
3.3. Trunk
3.4. Upper and Lower Extremities
3.5. Multiple Injuries
4. Conclusions
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| OR | Odd Ratio |
| Prot | Protective factor |
| Sig | Bilateral Significance at 95% |
References
- Van den Broek, K.; De Greef, M.; Van der Heyden, S.; Schmitz-Felten, E.; Kunl, K. Socio-Economic Costs of Accidents at Work and Work-Related Ill Health; EU Publications: Bologna, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Erick, P.N.; Smith, D.R. Musculoskeletal disorders in the teaching profession: An emerging workplace hazard with significant repercussions for developing countries. Ind. Health 2015, 53, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünlü, H.; Filiz, B. Work ability of the Turkish physical education teachers. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2019, 90, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, A.J.; Pappas, E.; Stamatakis, E.; Hiller, C.E. Injury fear, stigma, and reporting in professional dancers. Saf. Health Work 2019, 10, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erick, P.N.; Smith, D.R. A systematic review of musculoskeletal disorders among school teachers. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, A.N.; Karuppiah, K.; How, V.; Perumal, V. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDS) among primary school female teachers in Terengganu, Malaysia. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2020, 77, 102957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanandi, V.H. Association between Work Experience and Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders among the Clinical and Teaching Physiotherapists of Gujarat, India—An Observational Study. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Health 2021, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, L.M.; T Malabarbas, G. Prevalence and risk-factors of musculoskeletal disorders among provincial high school teachers in the philippines. J. UOEH 2020, 42, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.A.; Björkqvist, K. Occupational stress and mental and musculoskeletal health among university teachers. Eurasia J. Med. Investig. 2018, 2, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nyawose, Z.Z.; Naidoo, R. Prevalence of shoulder musculoskeletal disorders among school teachers: A systematic review. S. Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Recreat. 2019, 41, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, Y.M.; Voo, P.; Maakip, I. Psychosocial factors, depression, and musculoskeletal disorders among teachers. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovač, M.; Leskošek, B.; Hadžić, V.; Jurak, G. Occupational health problems among slovenian physical education teachers. Kinesiology 2013, 45, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lemoyne, J.; Laurencelle, L.; Lirette, M.; Trudeau, F. Occupational health problems and injuries among Quebec’s physical educators. Appl. Ergon. 2007, 38, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, L.; Vercruysse, S.; Cardon, G.; Haerens, L.; Witvrouw, E.; De Clercq, D. Musculoskeletal injuries in physical education versus non-physical education teachers: A prospective study. J. Sport. Sci. 2016, 34, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beijsterveldt, A.M.; Richardson, A.; Clarsen, B.; Stubbe, J. Sports injuries and illnesses in first-year physical education teacher education students. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, e000189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramsay, J.; Denny, F.; Szirotnyak, K.; Thomas, J.; Corneliuson, E.; Paxton, K.L. Identifying nursing hazards in the emergency department: A new approach to nursing job hazard analysis. J. Saf. Res. 2006, 37, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.; Roriz, A.; Leite, A.; Colim, A.; Carneiro, P. Exposure to Musculoskeletal Risk of Piano Teachers. Stud. Syst. Decis. Control 2020, 277, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Piñeiro, P.; Díaz-Pereira, M.P.; Martínez, A. Musicians, postural quality and musculoskeletal health: A literature’s review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2017, 21, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajidahun, A.T.; Myezwa, H.; Mudzi, W.; Wood, W.A. Barriers and facilitators in implementing an exercise-based injury prevention program for string players. Work 2019, 64, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebaw, T.A.; Weldegebriel, M.K.; Gebremichael, B.; Abaerei, A.A. Prevalence and associated factors of low back pain among teachers working at governmental primary schools in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A cross sectional study. Biomed. J. 2018, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Conti, J.; Carbonell, G.; Cantallops, J.; Borràs, P.A. Knowledge of low back pain among primary school teachers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-González, P.; Šutvajová, M.; Lesňáková, A.; Bartík, P.; Bul’áková, K.; Friediger, T. Back pain prevalence, intensity, and associated risk factors among female teachers in Slovakia during the COVID-19 pandemic: A cross-sectional study. Healthcare 2021, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, R.; Parthiban, B.; Parghavi, M. Evaluation of work related musculoskeletal disorders in shoulder and neck with ergonomic intervention among school teachers. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirupa, K.; Mary, S.D.; Nithyanisha, R.; Vaishnavi, G.; Pavithralochini, V.; Jaiganesh, G. A comparative study of posture alteration and stretching program to reduce neck pain in teachers. Biomedicine 2020, 40, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bliekendaal, S.; Stubbe, J.; Verhagen, E. Dynamic balance and ankle injury odds: A prospective study in 196 Dutch physical education teacher education students. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e032155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen-Rey Merchán, M.D.; López-Arquillos, A. Gender differences in teachers’ occupational accidents. In Health Care for Women International; Talylor Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Merchán, M.D.C.R.; López-Arquillos, A. Injury analysis of teachers’ occupational accidents. Work 2022, 71, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino López, M.A.; Gonzalez Alcantara, O.J.; Fontaneda, I. Gender differences in commuting injuries in Spain and their impact on injury prevention. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3834827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaghela, N.; Parekh, S. Prevalence of the musculoskeletal disorder among school teachers. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 8, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, D.H.; Jeong, B.Y. Work-related injuries of educational support staff in schools. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2019, 25, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.; Roan, A. Exploring teachers’ early-retirement decisions: A qualitative study. Work Aging Retire. 2016, 2, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. The World Needs Almost 69 Million New Teachers to Reach the 2030 Education Goals; UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Pasarín, M.; Regidor, E.; Borrell, C.; Fernández, E. ¿Odds ratio o razón de proporciones? Su utilización en estudios transversales. Gac. Sanit. 2003, 17, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Liu, F.; Li, L. Neck/shoulder pain and low back pain among school teachers in China, prevalence and risk factors. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Y.M.; Voo, P.; Maakip, I. The relationships between risk factors and musculoskeletal disorders among teachers: An exploratory investigation in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the Kuala Lumpur International Communication, Education, Language and Social Sciences, Bandar Baru Bangi, Malaysia, 23–24 November 2019; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, J.M.; Pinto, R.Z.; Tebar, W.R.; Gil, F.C.; Delfino, L.D.; Morelhão, P.K.; Da Silva, C.C.; Oliveira, C.B.; Christofaro, D.G. Association of musculoskeletal pain with poor sleep quality in public school teachers. Work 2020, 65, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alias, A.N.; Karuppiah, K.; How, V.; Perumal, V. Does Prolonged Standing at Work Among Teachers Associated With Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2020, 16, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Erick, P.N.; Smith, D.R. Low back pain among school teachers in Botswana, prevalence and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2014, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.Y.K.; Wong, M.T.; Yu, Y.C.; Ju, Y.Y. Work-related musculoskeletal disorders and ergonomic risk factors in special education teachers and teacher’s aides. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, S.; Nakahara, H.; Aoki, T.; Kinoshita, H. Prevalence and causal factors of playing-related musculoskeletal disorders of the upper extremity and trunk among Japanese pianists and piano students. Med. Probl. Perform. Artist. 2006, 21, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiklieng, S.; Suggaravetsiri, P. Risk factors for repetitive strain injuries among school teachers in Thailand. Work 2012, 41, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Merchán, M.D.C.; López-Arquillos, A. Organizational and personal factors in occupational traffic injuries at work in Spain. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2021, 22, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Values | Neck | Back | Trunk | Upper Ex | Lower Ex | Multiple | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | ||
| Age | <45 | 1.94 | 1.8–2.1 | 0.84 | 0.8–0.9 | 0.522 | 0.4–0.5 | 0.918 | 0.8–0.9 | 1.004 | 1.0–1.0 | 1.011 | 0.9–1.1 |
| >45 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Nationality | National | 1.76 | 1.4–2.0 | 0.91 | 0.8–1.0 | 1.017 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.815 | 0.7–0.8 | 1.067 | 0.9–1.1 | 1.136 | 0.9–1.3 |
| Foreign | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Length | <1 year | 1.09 | 1.1–1.2 | 0.86 | 0.8–0.9 | 0.84 | 0.7–0.9 | 1.204 | 1.1–1.2 | 0.863 | 0.8–0.9 | 0.924 | 0.8–1.0 |
| >1 year | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Temporal | No | 0.98 | 0.9–1.0 | 1.19 | 1.1–1.2 | 1.224 | 1.1–1.3 | 0.773 | 0.7–0.8 | 1.197 | 1.1–1.2 | 1.051 | 0.9–1.1 |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Public | Yes | 1.18 | 1.1–1.2 | 0.99 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.872 | 0.7–0.9 | 0.824 | 0.7–0.8 | 1.207 | 1.1–1.2 | 0.915 | 0.8–1.0 |
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Traffic | No | 0.04 | 0.1–0.1 | 1.52 | 1.4–1.6 | 1.094 | 0.9–1.2 | 2.983 | 2.7–3.2 | 4.306 | 4.0–4.6 | 0.117 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Monday | Yes | 0.94 | 0.8–1.0 | 1.3 | 1.2–1.3 | 0.978 | 0.8–1.1 | 0.937 | 0.9–0.9 | 0.994 | 0.9–1.0 | 0.883 | 0.7–0.9 |
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Severity | Light | 6.5 | 3.6–11.5 | 4.94 | 3.2–7.5 | 0.188 | 0.1–0.2 | 1.831 | 1.5–2.2 | 1.399 | 1.1–1.6 | 0.241 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Rest | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Variable | Values | Neck | Back | Trunk | Upper Ex | Lower Ex | Multiple |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <45 | Risk | Prot | Prot | Prot | N.S | N.S |
| >45 | Prot | Risk | Risk | Risk | N.S | N.S | |
| Nationality | National | Risk | N.S | N.S | Prot | N.S | N.S |
| Foreign | Prot | N.S | N.S | Risk | N.S | N.S | |
| Length | <1 year | Risk | Prot | Prot | Risk | Prot | N.S |
| >1 year | Prot | Risk | Risk | Prot | Risk | N.S | |
| Temporal | No | N.S | Risk | Risk | Prot | Risk | N.S |
| Yes | N.S | Prot | Prot | Risk | Prot | N.S | |
| Public | Yes | Risk | N.S | Prot | Prot | Risk | N.S |
| No | Prot | N.S | Risk | Risk | Prot | N.S | |
| Traffic | No | Prot | Risk | N.S | Risk | Risk | Prot |
| Yes | Risk | Prot | N.S | Prot | Prot | Risk | |
| Monday | Yes | N.S | Risk | N.S | Prot | N.S | Prot |
| No | N.S | Prot | N.S | Risk | N.S | Risk | |
| Severity | Light | Risk | Risk | Prot | Risk | Risk | Prot |
| Rest | Prot | Prot | Risk | Prot | Prot | Risk |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rey-Merchán, M.d.C.; López-Arquillos, A. Influence Variables in Occupational Injuries among Men Teachers. Safety 2022, 8, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8030051
Rey-Merchán MdC, López-Arquillos A. Influence Variables in Occupational Injuries among Men Teachers. Safety. 2022; 8(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleRey-Merchán, María del Carmen, and Antonio López-Arquillos. 2022. "Influence Variables in Occupational Injuries among Men Teachers" Safety 8, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8030051
APA StyleRey-Merchán, M. d. C., & López-Arquillos, A. (2022). Influence Variables in Occupational Injuries among Men Teachers. Safety, 8(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/safety8030051







