Abstract
Unintentional fatal drowning among older people is an issue as lifespans lengthen and older people embrace active retirement. While pre-existing medical conditions are a known risk factor for drowning among this age group, less is known about the role of alcohol and drugs. This 15-year (1 July 2002 to 30 June 2017) Australian study used coronial data to investigate the impact on older people (aged 65 years and older) of the obtundent effects of prescribed drugs which had been ingested by those with a positive blood alcohol concentration (BAC). Of the closed coronial cases with toxicological information (N = 471), one quarter (24.6%; N = 116) had consumed alcohol prior to drowning (one in seven BAC ≥ 0.05%), of which a third also had obtundent drugs present (33.6%; N = 39). Rivers/creeks/streams and swimming pools were the locations with the highest number of drowning deaths. Bathtubs (36.8%) and rivers/creeks/streams (17.9%) recorded the highest proportion of cases with victims having a BAC ≥ 0.05%. Bathtubs (13.2%), lakes (7.0%), and rivers/creeks/streams (6.8%) recorded the highest proportion of drowning cases with obtundent drug involvement. Obtundent drug involvement was significantly more likely for activities where the person who drowned was alone (i.e., unknown activity) (X2 = 6.8; p = 0.009). Common obtundent drugs included Diazepam, Tempazepam, and Codeine. Advocacy to prevent drowning in older people is a complex challenge, due to the myriad of locations where drowning occurs, the consumption of alcohol, and polypharmacy required for treating illness and maintaining good health.
1. Introduction
Drowning has been defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a threat to global public health, estimated to claim the lives of 372,000 people annually [1]. In developed nations, overall drowning rates have fallen [2], with reductions seen since the 1990s [3]. In Australia, an average of 279 people die from unintentional drowning each year [4], a reduction on the annual average of 290 between July 2002 and June 2006 [5].
Such reductions in drowning rates in Australia have largely been seen among children under the age of five [6] due to improved pool fencing requirements [6,7,8] and increased awareness of the need for active adult supervision of children [9,10].
In contrast with the reduction of childhood drowning, drowning rates in the elderly have remained consistent [11]. Drowning among seniors (defined in this study as those aged 65 years and older) has become an issue worthy of further attention, as lifespans lengthen and older people are encouraged to become more active in retirement [12,13,14]. Globally, the population is aging, with 8.5% of people worldwide aged 65 years and over. This is projected to increase to nearly 17% by 2050 [15]. In Australia, 15% of the total population was aged 65 years and older in 2017. By 2057, this is estimated to increase to 22% of the population and 25% by 2097 [16].
An average of 57 people aged 65 years and over drown in Australia each year [4], most commonly in rivers, creeks, and streams [17], followed by ocean and harbor locations [11]. Drowning risk factors among older people include being male, rurality, increasing age, and alcohol [11,12,17,18,19].
Drowning research has emphasized the importance of identifying specific drowning syndromes, with targeted preventive programs directed to defined at-risk groups [7]. This paper aims to describe the association between alcohol, drugs, and fatal unintentional drowning in Australian seniors over a 15-year (2002–2017) period.
2. Materials and Methods
All unintentional drowning deaths in Australia of people aged 65 years and older were extracted from the Royal Life Saving National (Australian) Fatal Drowning Database, which draws data from the National (Australian) Coronial Information System (NCIS) [20]. This study is a retrospective, unselected, total population study with every case of unintentional drowning included. Data analysed covers a 15 financial year period (2002/03 to 2016/17). In Australia, financial years run from 1 July to 30 June.
In Australia, all sudden and unexpected deaths (such as drowning) must be reported to and investigated by a coroner. While under investigation, a coroner will consider police, autopsy, and toxicology reports to determine the circumstances and cause of death. Once determined, a coroner’s report is completed and the case is closed on the NCIS. Cases may go to coronial inquest where recommendations are made to prevent future loss of life in similar circumstances [21]. Cases which remain open at time of analysis, do not have autopsy, toxicology, and police reports available, therefore limiting available data on alcohol and drug involvement and presence of pre-existing medical conditions.
Forensic data were extracted and analyzed, including blood alcohol concentrations (BAC) and drug ingestion profiles. A positive BAC was defined as any detection of blood alcohol (i.e., a BAC ≥ 0.001%); and a contributory blood alcohol level was defined as a BAC ≥ 0.050% [22]. One author (J.H.P., a specialist physician and toxicologist) recorded obtundent (meaning to dull or blunt, in this instance referring to respiratory depression) effects of prescribed drugs, which had been ingested by those who also had recorded a positive BAC. Such combinations, the authors believe, are contributory to the risk of drowning, as has been identified in other previously published studies [5,23,24].
Univariate and chi square analyses were undertaken, with statistical significance deemed p < 0.05. A modified Bonferonni (as suggested by Keppel [25]) has been applied, where multiple chi-square tests were undertaken within a variable. Non-parametric analysis was conducted using the proportional basis of the population as the assumed outcome numbers. Population data on people aged 65 years and older in Australia were sourced from the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) [26]. We have examined drowning deaths by age group (65–74 years and 75+ years), as we are aware that the over-65 year population (generally “retirees”) is not a homogenous one with respect to drowning risks. Those of more senior years (75 years and over) tend to be frailer [27], and suffer from more complex co-morbidities [28].
The aquatic location categories of bathtub/spa bath, lake/dam/lagoon, ocean/harbor and river/creek/stream are henceforth referred to as bathtubs, lakes, oceans, and rivers, respectively. The activity of “diving” refers to SCUBA diving and free diving.
Ethics approval for this study was given by the Victorian Department of Justice and Regulation Human Research Ethics Committee (CF/07/13729, CF/10/25057, CF/13/19798).
3. Results
In Australia, 803 unintentional drowning deaths of older people occurred in the study period. Of these, 651 (81.1%) were closed coronial cases (Figure 1). Drowning deaths among people aged 65 years and over have been as low as 38 in 2006/07 and as high as 70 in 2016/17. Fatal drowning rates among older people in Australia have varied from a high of 1.99 per 100,000 population to a low of 1.38. The 15-year average drowning rate is 1.76 per 100,000 population (Figure 1).
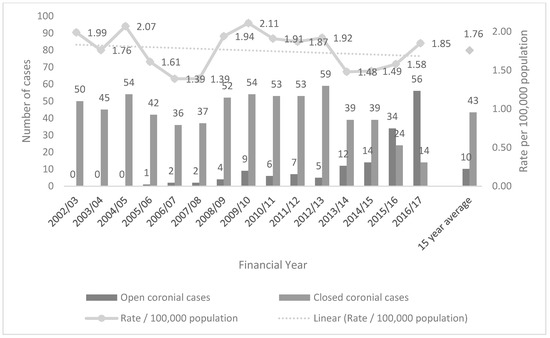
Figure 1.
Unintentional fatal drowning incidence and rate among people aged 65 years and over in Australia by status within National Coronial Information System (NCIS), 15-year average, Australia (N = 803).
When examined by sex, males accounted for 74.0% of drowning deaths overall, with a significantly higher proportion of males recorded in the 65–74 years age group (56.4% of all male drowning deaths) than among those aged 75+ years (43.6%) (X2 = 12.7; p < 0.001). When compared to females, males were significantly more likely to drown in the ocean (X2 = 26.5; p < 0.001) and in boating-related incidents (X2 = 31.4; p < 0.001). By comparison, females, when compared to males, were significantly more likely to drown while bathing (X2 = 55.2; p < 0.001), in baths (X2 = 54.7; p < 0.001), in swimming pools (X2 = 9.0; p = 0.003), and due to a fall into water (X2 = 9.4; p = 0.002).
Just over half of all drowning deaths occurred in the 65–74 years age group (52.7%). The largest proportion of drowning deaths among older people occurred at rivers (26.8%), accounting for 24.6% of deaths in the 65–74 years age group and 29.2% of deaths in the 75+ years age group. Swimming pools (17.2%) were the second most common drowning location among older people overall, followed by beaches (15.3%). Drowning deaths at ocean locations (X2 = 19.7; p < 0.001) were significantly more likely among 65–74 year olds than people aged 75 years and older. Drowning locations coded as “other” include irrigation channels, tanks, fish ponds, and drains. In three locations (bathtubs, rivers, and swimming pools) the number of drowning deaths increased with age, with more drowning deaths in 75+ year olds, than among 65–74 year olds (Table 1).

Table 1.
Demographics and circumstances of unintentional fatal drowning among people aged 65 years and over, by age group, Australia, 2002/03 to 2016/17 (N = 803).
The largest proportion of drowning deaths among older people occurred as a result of a fall into water (22.5%), followed by swimming and recreating (19.3%). In 101 cases (12.6%), the activity being undertaken immediately prior to drowning was unknown, indicating the person was alone when the drowning incident occurred and therefore the activity was unwitnessed (Table 1).
People aged 65 years and over were significantly more likely to drown as a result of a boating-related incident (X2 = 14.9; p < 0.001) and diving (X2 = 6.0; p = 0.014), whereas people aged 75 years and older were more likely to drown as a result of falls into water (X2 = 31.8; p < 0.001) (Table 1).
A slightly higher proportion of people aged 75 years and older were known to have a pre-existing medical condition (68.7%) than those aged 65–74 years (59.3%). Ten percent (10.0%) of all people aged 65 years and over who drowned in Australia during the study period recorded a BAC ≥ 0.05% at autopsy. People aged 65–74 years were significantly more likely to record a BAC ≥ 0.05% (X2 = 12.2; p < 0.001) (Table 1).
Of the 651 closed coronial cases, 471 (72.4%) had toxicological information available. One quarter (24.6%) had a positive BAC and one in seven (15.9%) had a BAC over the upper legal limit for driving (≥0.05%) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Closed coronial cases by involvement of alcohol and presence of obtundent drugs among drowning fatalities in Australia, by location of drowning incident, 2002/03 to 2016/17 with toxicological information available, in victims aged 65 years and over (N = 471).
People who drowned in bathtubs or rivers were more likely to record a positive BAC (X2 = 17.6; p = 0.014). People who drowned in rivers were also significantly more likely to record a BAC between 0.001% and 0.049% (X2 = 6.1; p = 0.013) than elderly people who drowned in other categories of aquatic location. Drowning deaths as a result of diving (X2 = 3.9; p = 0.049) and other activities (X2 = 3.9; p = 0.049) were significantly more likely to record low levels of alcohol (a BAC between 0.001% and 0.049%) than drowning deaths among the elderly as a result of other activities.
Common obtundent drugs implicated in drowning deaths of older people were Diazepam (N = 12), Temazepam (N = 9), Codeine (N = 8), Tramadol (N = 5), and Benzodiazepines (N = 2). Rivers (N = 11) were the location with the highest number of drowning cases with obtundent drug involvement, followed by swimming pools (N = 8). Obtundent drug involvement was significantly more likely for activities where the person who drowned was alone (i.e., unknown activity) (X2 = 6.8; p = 0.009) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Closed coronial cases by involvement of alcohol and presence of obtundent drugs among drowning fatalities in Australia, by activity being undertaken immediately prior to drowning, 2002/03 to 2016/17 with toxicological information available, in victims aged 65 years and over (N = 471).
4. Discussion
Older people, who are rarely the targets of prevention initiatives, are a group at increased risk of drowning [11,12]. This study reports an annual incidence of 53 drowning deaths among people aged 65 years and older in Australia, with virtually no decline in the crude drowning rate over the course of the study. Rivers (27%) and swimming pools (17%) were identified as common drowning locations for older people.
When examining drowning by location of incident, rivers were found to be the leading location for drowning risk among older people aged 65–74 and 75+ years. This mirrors findings that show, even when exposure is taken into account, people aged 75+ years record the highest crude drowning rate [29]. Further research will be required to determine if drowning prevention strategies targeted at younger people in rivers [30,31] will be suitable for the older age group.
Drowning locations in and around the home, such as bathtubs and swimming pools, pose a risk to the elderly, as they do for young children [6,32]. Australia may consider looking to other countries with an aging population and similar drowning burden among the elderly (such as Japan, Finland, and Greece) [33] to explore drowning prevention strategies for older people that may have proved to be successful. In particular, drowning prevention practitioners from Japan may be able to provide insight into bathtub drowning prevention among the elderly, given the prevalence of the issue in that country [34].
This study highlights drowning risk among older people, likely compounded by the concomitants of senior years—frailty, comorbid chronic medical conditions, and polypharmacy (especially anxiolytics and narcotics causing obtundation) [28,30]. Also shown in this paper is the further exacerbation of risk by consumption of alcohol [23,35]. A BAC, albeit below the legal limit for driving (<0.05%), also impairs cognition and coordination.
Alcohol consumption is present in approximately a quarter of all deaths, although this proportion is higher among those who drown in rivers and bathtubs. To the issue of alcohol consumption alone, we add the increased risk of drowning created by the synergy of alcohol and prescribed medications. We posit that this increased risk is causal, and not simply associative, similar to the proven causal risks of alcohol-impaired driving. Medical practitioners and drowning prevention advocates should encourage reduction or elimination of alcohol consumption when undertaking aquatic activity, or when older people are near the water.
Alcohol has been found to significantly increase the risk of drowning in other age groups [18,19,22,24,36,37], however little is known about the risk, particularly when combined with prescription medication. This paper shows significant levels of alcohol consumption (10% of those aged 65 years and older had a BAC ≥ 0.05%) however we note that in the Australian population, people aged over 65 years are likely to be regular drinkers [38]. Further work is required in understanding consumption of alcohol around water by older people to inform prevention.
While alcohol consumption is a clear contributor to increased drowning risk, less is understood about the impact of frailty [39], water safety knowledge levels, activities around aquatic locations, swimming ability, and exposure [29,40]. More research around effective stratagems for this age group, especially those focusing on the concomitants of alcohol and prescription medication, is required. Aquatic activity has been found to be beneficial for those requiring activities which are less impactful on the body [41], however further research is needed in validating the efficacy of such programs on drowning risk.
Polypharmacy in Australia is increasing, with 33% of those aged 65–74 years on four or more medications [11,35]. Drug combinations ingested by older people contribute to unsteadiness and falls [11]. We posit that the synergistic effects of such drug cocktails with alcohol increases the risk of drowning. These risks become manifest in falls into home swimming pools, boating incidents, and while bathing [11].
As noted in this study, 64% of those aged over 65 years who drowned had a pre-existing medical condition. In a previous study [11], pre-existing medical conditions were found to contribute to 36% of drowning deaths of older people. Little is known about the impact of pre-existing medical conditions, medication, alcohol, and age. In the current study, common pre-existing medical conditions linked to increased drowning risk were cardiac conditions, dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease. Carers of the elderly and health professionals should be made aware of the risks and involved in the development of appropriate care strategies to support aquatic activity and prevent drowning.
Three aquatic locations showed an increase in the number of drowning deaths as the age of the victim increased, being bathtubs, rivers, and swimming pools. Bathtubs and swimming pools are likely to have an increased drowning risk due to their proximity to where people live. Rivers are a leading location for drowning in Australia [17], however little is known about the risk factors for drowning among older people in such locations.
Common activities being undertaken prior to drowning among older people were falls into water (23%) and swimming and recreating (19%), however in 13% of cases, the activity undertaken prior to drowning was unknown, suggesting that the person was alone when they drowned. A common mantra in drowning prevention is to “always swim with a buddy” [42,43], which may have helped prevent some of these deaths. We do, however, note the risk of the “rescuer who drowns” while attempting a rescue [44,45].
Strengths and Limitations
The strengths of this study are that it is a total population survey based on detailed medico-legal investigations. It is longitudinal in nature, spanning a 15-year study period. This study includes all unintentional fatal drowning, not only the narrow definition of drowning using International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes (W65-74 only) [46]. Limitations are that we have assumed that where activity was unknown, that this equates to the person who drowned being alone. Nineteen percent (18.9%) of cases remain open (i.e., under investigation) and the outcome of such investigations may change. Cases which were open at the time of analysis may not have information available on alcohol and drug involvement and presence of pre-existing medical conditions, and may therefore be underreported. Alcohol and drug(s) involvement may also be underreported if no body was recovered or autopsy or toxicological testing was not performed or was opposed by the victim’s family. Alcohol is naturally produced as a result of decomposition, which may artificially inflate BACs among those who drowned [47].
5. Conclusions
This research shows that advocacy to prevent drowning in older people is a complex challenge due to the myriad of locations where drowning occurs, the consumption of alcohol, pre-existing medical conditions, and polypharmacy required for treating illness and maintaining good health. These factors highlight the need for health carers to discuss implications of medication regimens with all older patients who undertake aquatic activities. Drowning prevention interventions, particularly targeting elderly males, will be required. In spite of 30 years of advocacy, proportionately more seniors drown today than previously. This neglected group needs our attention.
Author Contributions
J.H.P., A.E.P., and R.C.F. conceptualized the study. A.E.P. and R.C.F. cleaned and coded the cases and ran the analysis. J.H.P. identified drugs with obtundent properties. J.H.P. and A.E.P. prepared the original draft manuscript. A.E.P. provided the data visualization. R.C.F. provided critical revision of the manuscript. All authors approve the submitted manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by Royal Life Saving Society—Australia to aid in the reduction of drowning. Research at Royal Life Saving Society—Australia is supported by the Australian Government.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Drowning: Preventing A Leading Killer; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Preventing drowning: An Implementation Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haagsma, J.A.; Graetz, N.; Bolliger, I.; Naghavi, M.; Higashi, H.; Mullany, E.C.; Abera, S.F.; Abraham, J.P.; Adofo, K.; Alsharif, U.; et al. The global burden of injury: Incidence, mortality, disability-adjusted life years and time trends from the Global Burden of Disease study 2013. Inj. Prev. 2016, 22, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Life Saving Society—Australia. Royal Life Saving National Drowning Report 2018; Royal Life Saving Society—Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, R.C.; Scarr, J.P.; Pearn, J.H. Reducing drowning deaths: The continued challenge of immersion fatalities in Australia. Med J. Aust. 2010, 192, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.C.; Peden, A.E. Improving Pool Fencing Legislation in Queensland, Australia: Attitudes and Impact on Child Drowning Fatalities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearn, J.H.; Nixon, J.W.; Franklin, R.C.; Wallis, B. Safety legislation, public health policy and drowning prevention. Int. J. Inj. Control Saf. Promot. 2008, 15, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, M.R.; Rimajova, M.; Edgecombe, D.; Vickery, K. Childhood Drowning: Barriers Surrounding Private Swimming Pools. Pediatrics 2003, 111, e115–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugeja, L.; Franklin, R.C. An analysis of stratagems to reduce drowning deaths of young children in private swimming pools and spas in Victoria, Australia. Int. J. Inj. Control. Saf. Promot. 2012, 20, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugeja, L.; Franklin, R.C. Drowning deaths of zero- to five-year-old children in Victorian dams, 1989–2001. Aust. J. Rural Health 2005, 13, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahony, A.J.; Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Pearn, J.H.; Scarr, J. Fatal, unintentional drowning in older people: Pre-existing medical conditions. Healthy Aging Res. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Queiroga, A.C. Epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for the prevention of global unintentional fatal drowning in people aged 50 years and older: A systematic review. Inj. Prev. 2018, 24, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.; Brechat, P.; Leprêtre, P.; Kaltenbach, G.; Berthel, M.; Lonsdorfer, J. Health benefits of physical activity in older patients: A review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergance, J.M.; Calmbach, W.L.; Dhanda, R.; Miles, T.P.; Hazuda, H.P.; Mouton, C.P. Barriers to and Benefits of Leisure Time Physical Activity in the Elderly: Differences Across Cultures. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003, 51, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Goodkind, D.; Kowal, P.U.S. Census Bureau, International Population Reports, P95/16-1, An Aging World: 2015, U.S.; Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Older Australia at a Glance, Cat. No: AGE 87; Australian Government, Australian Institute of Health and Welfare: Canberra, Australia, 2018. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/older-people/older-australia-at-a-glance/contents/australia-s-changing-age-and-gender-profile (accessed on 4 January 2019).
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Leggat, P.A. The Hidden Tragedy of Rivers: A decade of unintentional fatal drowning in Australia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, K.; Keech, J.J.; Peden, A.E.; Hagger, M.S. Alcohol use, aquatic injury, and unintentional drowning: A systematic literature review. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, T.; Harrison, J.E.; Steenkamp, M. Review of the role of alcohol in drowning associated with recreational aquatic activity. Inj. Prev. 2004, 10, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine. National Coronial Information System. 2018. Available online: www.ncis.org.au (accessed on 28 October 2018).
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Leggat, P.A. Preventing river drowning deaths: Lessons from coronial recommendations. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2018, 29, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Leggat, P.A. Alcohol and its contributory role in fatal drowning in Australian rivers, 2002–2012. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2017, 98, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlm, K.; Saveman, B.-I.; Björnstig, U. Drowning deaths in Sweden with emphasis on the presence of alcohol and drugs—A retrospective study, 1992–2009. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunetta, P.; Smith, G.S.; Pentilã, A.; Sajantila, A. Unintentional drowning in Finland 1970–2000: A population-based study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppel, G. Design and Analysis: A Researcher’s Handbook, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3101.0. Australian Demographic Statistics, March 2018. Table 59. Estimated Resident Population by Single Year of Age; Australian Government: Canberra, Australia, 2018. Available online: http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/3101.0Mar%202018?OpenDocument (accessed on 30 November 2018).
- Rogers, N.T.; Marshall, A.; Roberts, C.H.; Demakakos, P.; Steptoe, A.; Scholes, S. Physical activity and trajectories of frailty among older adults: Evidence from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt-Ferrier, N. Older patients, multiple comorbidities, polymedication should we treat everything? Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2011, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Leggat, P.A. Exploring Visitation at Rivers to Understand Drowning Risk. Inj. Prev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Life Saving Society—Australia. Respect the River; Royal Life Saving Society—Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2019; Available online: https://www.royallifesaving.com.au/programs/respect-the-river (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- Royal Life Saving Society—Australia. Don’t Let Your Mates Drink and Drown. Royal Life Saving Society—Australia, 2019. Available online: https://www.royallifesaving.com.au/programs/dont-let-your-mates-drink-and-drown (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Pearn, J.H. Unintentional fatal child drowning in the bath: A 12-year Australian review (2002–2014). J. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 54, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Lu, T.H.; Kawach, I. Unintentional drowning mortality, by age and body of water: An analysis of 60 countries. Inj. Prev. 2015, 21, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, F.; Osawa, M.; Hasegawa, I.; Seto, Y.; Tsuboi, A. Dead in Hot Bathtub Phenomenon: Accidental Drowning or Natural Disease? Am. J. Forensic. Med. Pathol. 2013, 34, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmer, S.N.; Gnjidic, D. The effects of polypharmacy in older adults. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 85, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, T.R.; Harrison, J.E.; Steenkamp, M. Alcohol and drowning in Australia. Inj. Control Saf Promot. 2004, 11, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.S.; Keyl, P.M.; Hadley, J.A.; Bartley, C.L.; Foss, R.D.; Tolbert, W.G.; McKnight, J. Drinking and Recreational Boating Fatalities: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 286, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Risk Factors to Health—Excessive Alcohol Consumption. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2017. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/biomedical-risk-factors/risk-factors-to-health/contents/excessive-alcohol-consumption (accessed on 30 December 2018).
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Williamson, A.M.; Olivier, J. Estimates of drowning morbidity and mortality adjusted for exposure to risk. Inj. Prev. 2010, 16, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamin, M.; Zanuso, S.; Alvar, B.A.; Ermolao, A.; Zaccaria, M. Is water-based exercise training sufficient to improve physical fitness in the elderly? Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, K.; Quan, L.; Franklin, R.; Bennett, E. Where the Evidence and Expert Opinion Meet: A review of Open-Water Recreational Safety Messages. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2011, 5, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.; Bennett, E.; Moran, K.; Bierens, J.J. Use of a consensus-based process to develop international guidelines to decrease recreational open water drowning deaths. Int. J. Health Promot. Educ. 2012, 50, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.C.; Pearn, J.H. Drowning for love: The aquatic victim-instead-of-rescuer syndrome: Drowning fatalities involving those attempting to rescue a child. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2011, 47, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgut, A.; Turgut, T. A study on rescuer drowning and multiple drowning incidents. J. Saf. Res. 2012, 43, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, A.E.; Franklin, R.C.; Mahony, A.; Barnsley, P.; Scarr, J. Using a retrospective cross-sectional study to analyse unintentional fatal drowning in Australia: ICD-10 coding-based methodologies verses actual deaths. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e019407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, J.A.; Smith, G.S. Evidence for an early onset of endogenous alcohol production in bodies recovered from the water: Implications for studying alcohol and drowning. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2003, 35, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).