Scoring-Based Genetic Algorithm for Wavefront Shaping to Optimize Multiple Objectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
2.1. Multi-Point Focusing
2.2. Controlled Intensity Distribution
2.3. Intensity Minimization in Neighboring Region
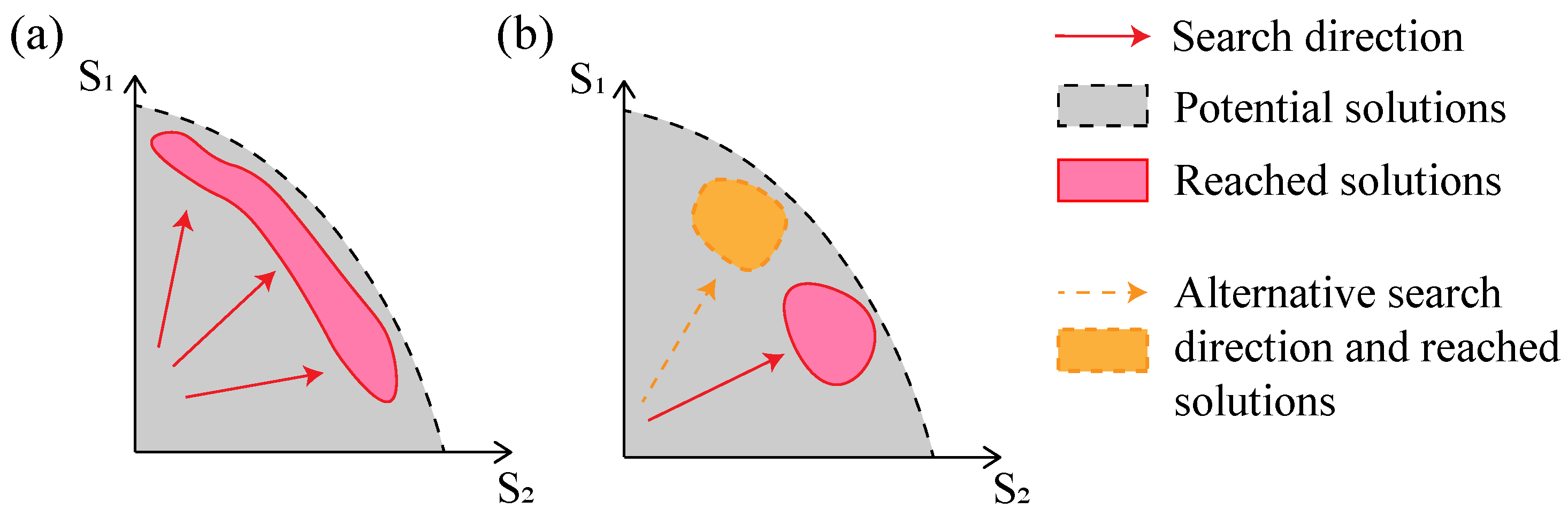
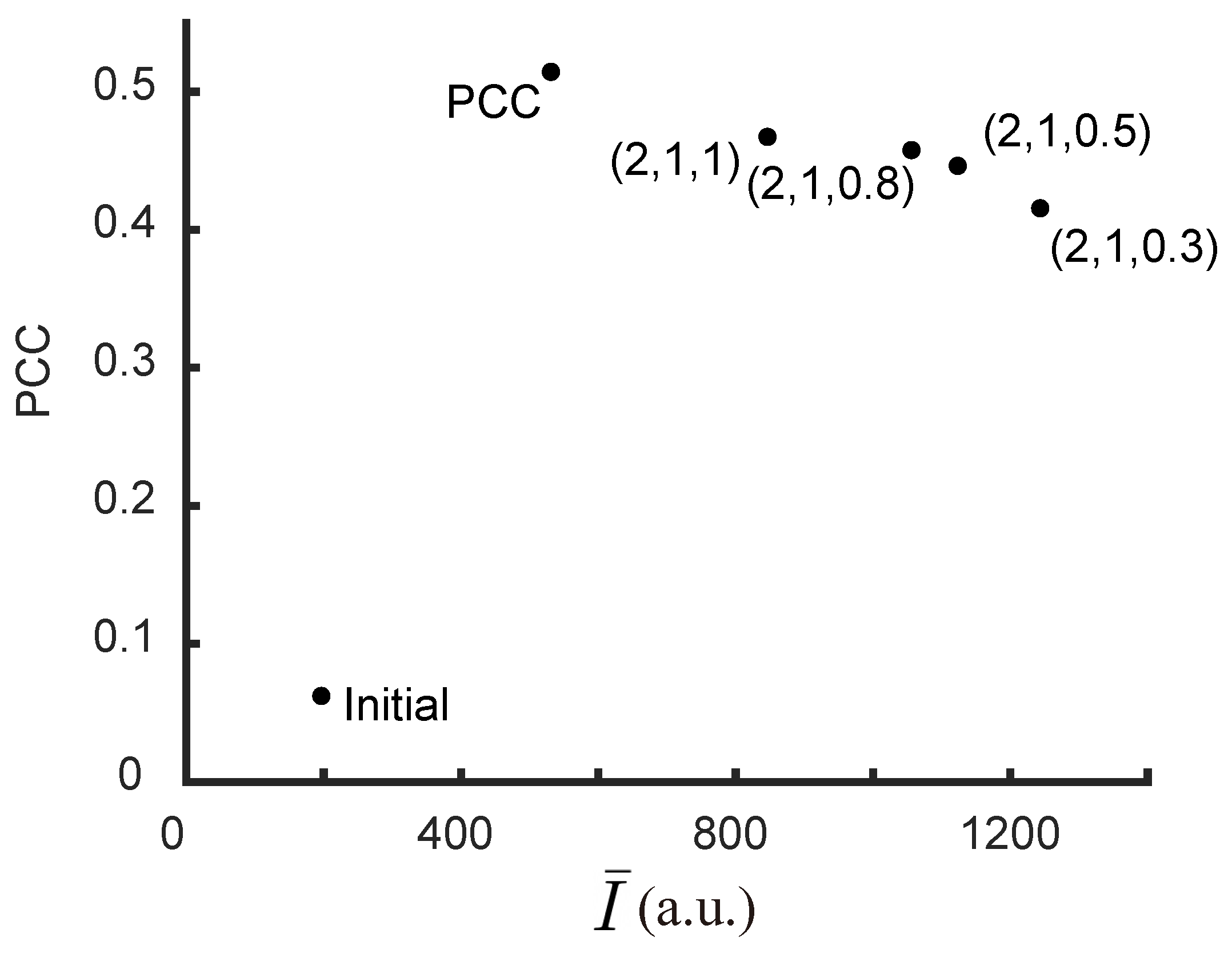
2.4. Comparison with NSGA2
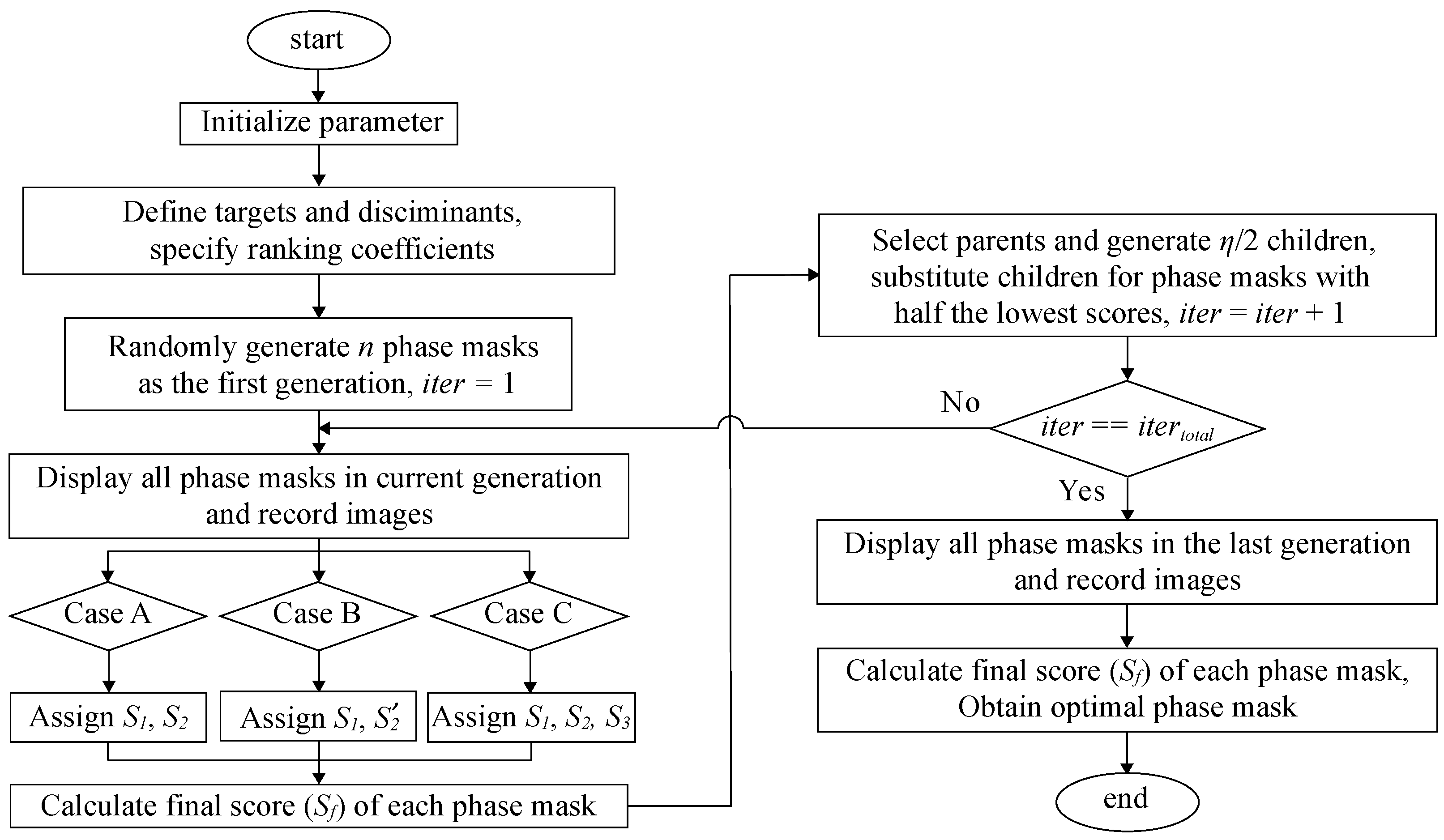
2.5. Detailed Steps
- Step 1.
- Set up the parameters for the experiment: the population size or the number of phase masks in each generation (n), dimension (number of superpixels) of a single phase mask (), number of phase steps for every superpixel (), total number of iterations or generations (), current iteration count (), rate of mutation ().
- Step 2.
- Choose targets and discriminants according to the desired objectives. For the cases described in Section 2.2 and Section 2.3, desired intensity and the region of neighboring pixels need to be defined, respectively. Specify ranking coefficients (a, b, and c).
- Step 3.
- Generate n random phase masks that contain superpixels in the first iteration. The phase of each superpixel is randomly selected from .
- Step 4.
- Display all phase masks in the current generation, and record the intensity of the area of interest.
- Step 5.
- Determine individual phase masks’ scores based on each objective function and calculate final score .
- Step 6.
- Select parents based on scores and generate children (half of the population size, , Appendix A). The children will replace half of the phase masks with the lowest scores from the previous generation. (current iteration count, )
- Step 7.
- Continue to step 8 if . Otherwise, go back to step 4.
- Step 8.
- The mask with the best score from the last generation is chosen as the optimal solution.
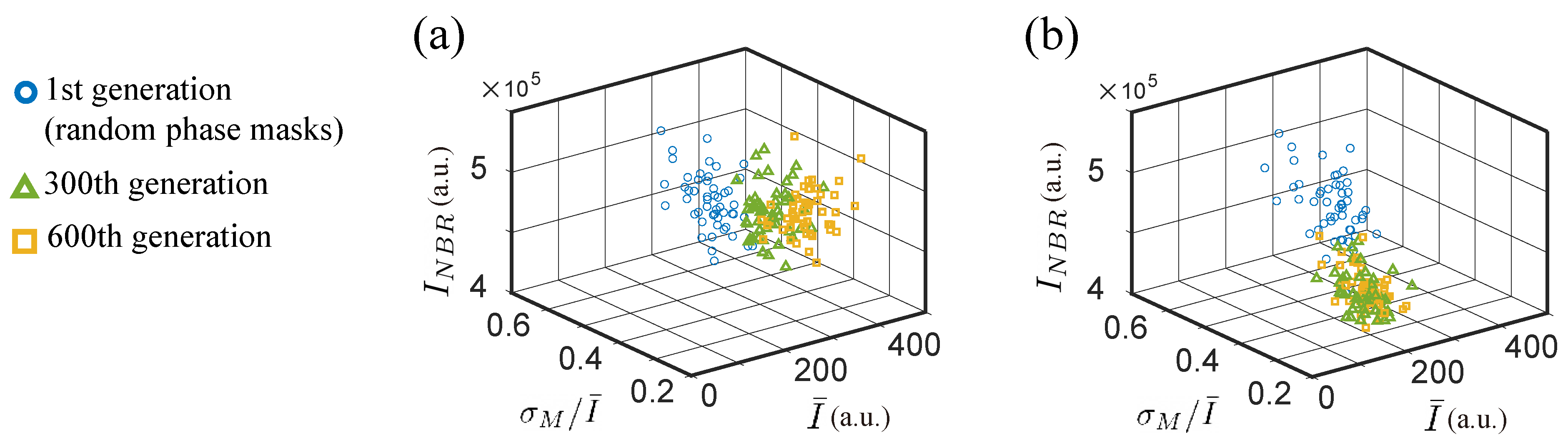
3. Simulation Results
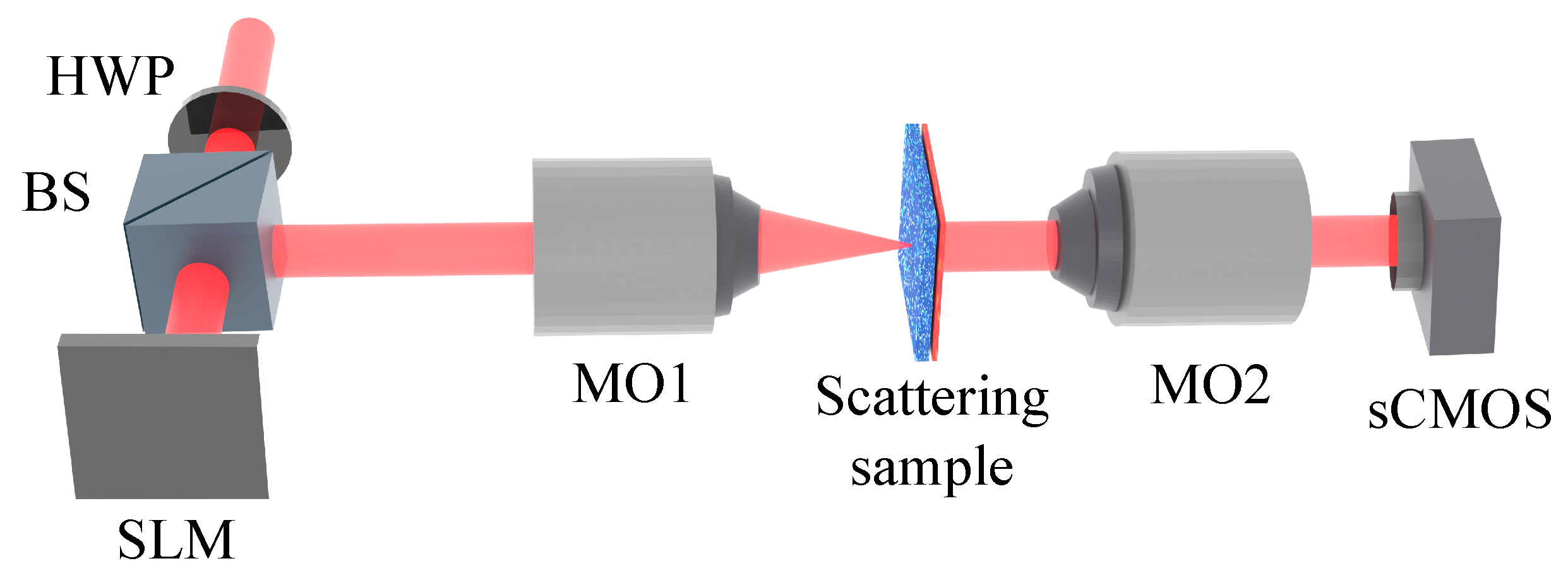
4. Experimental Setup
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
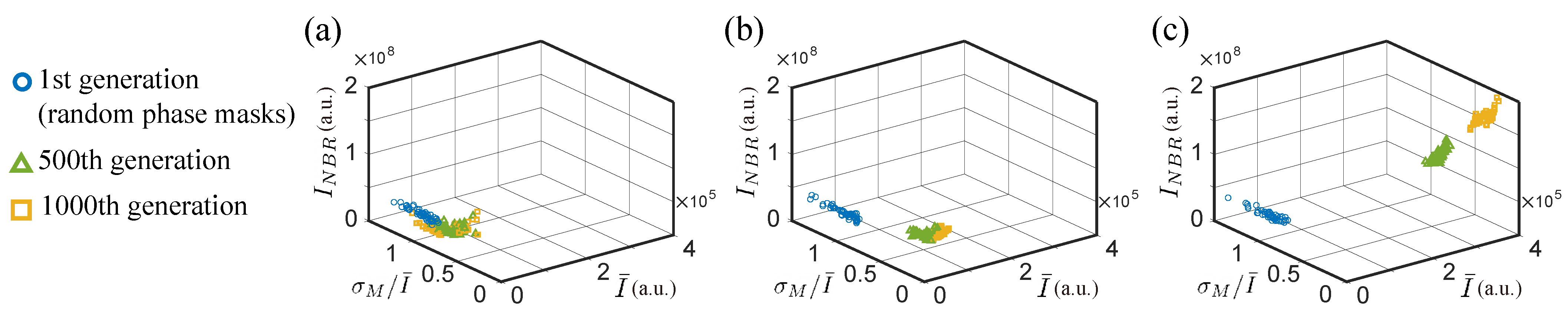
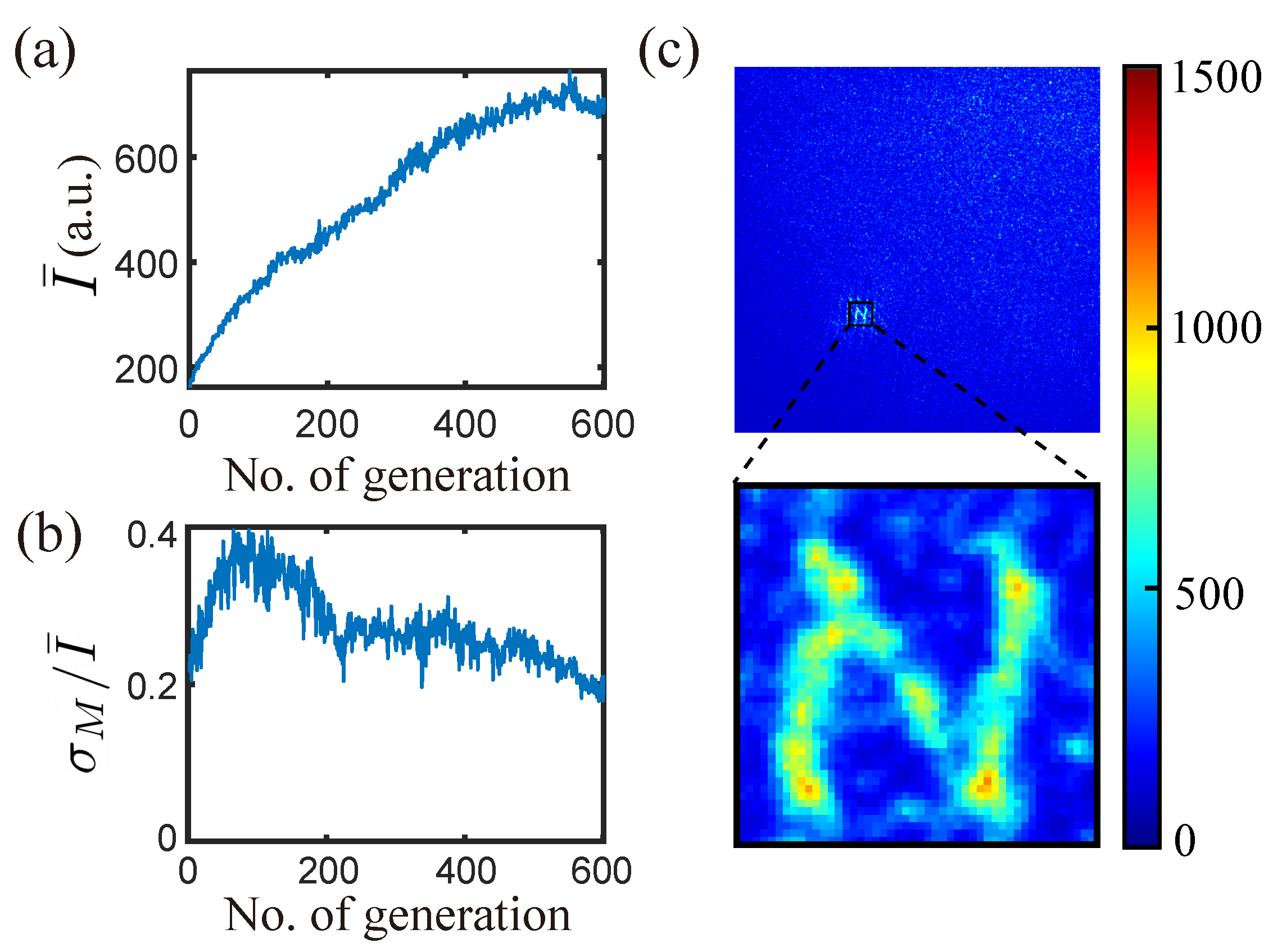
5.1. Multi-Point Focusing
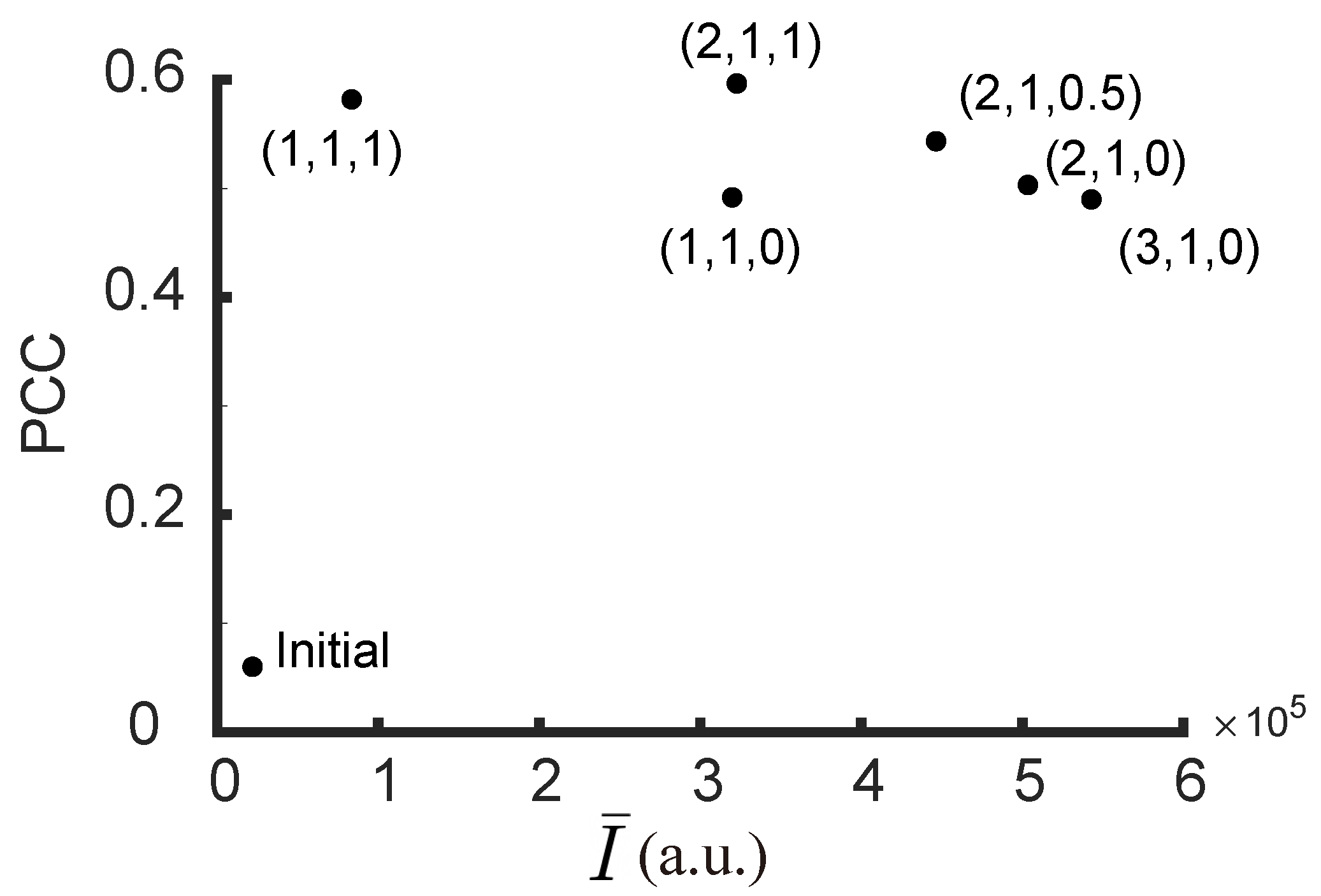
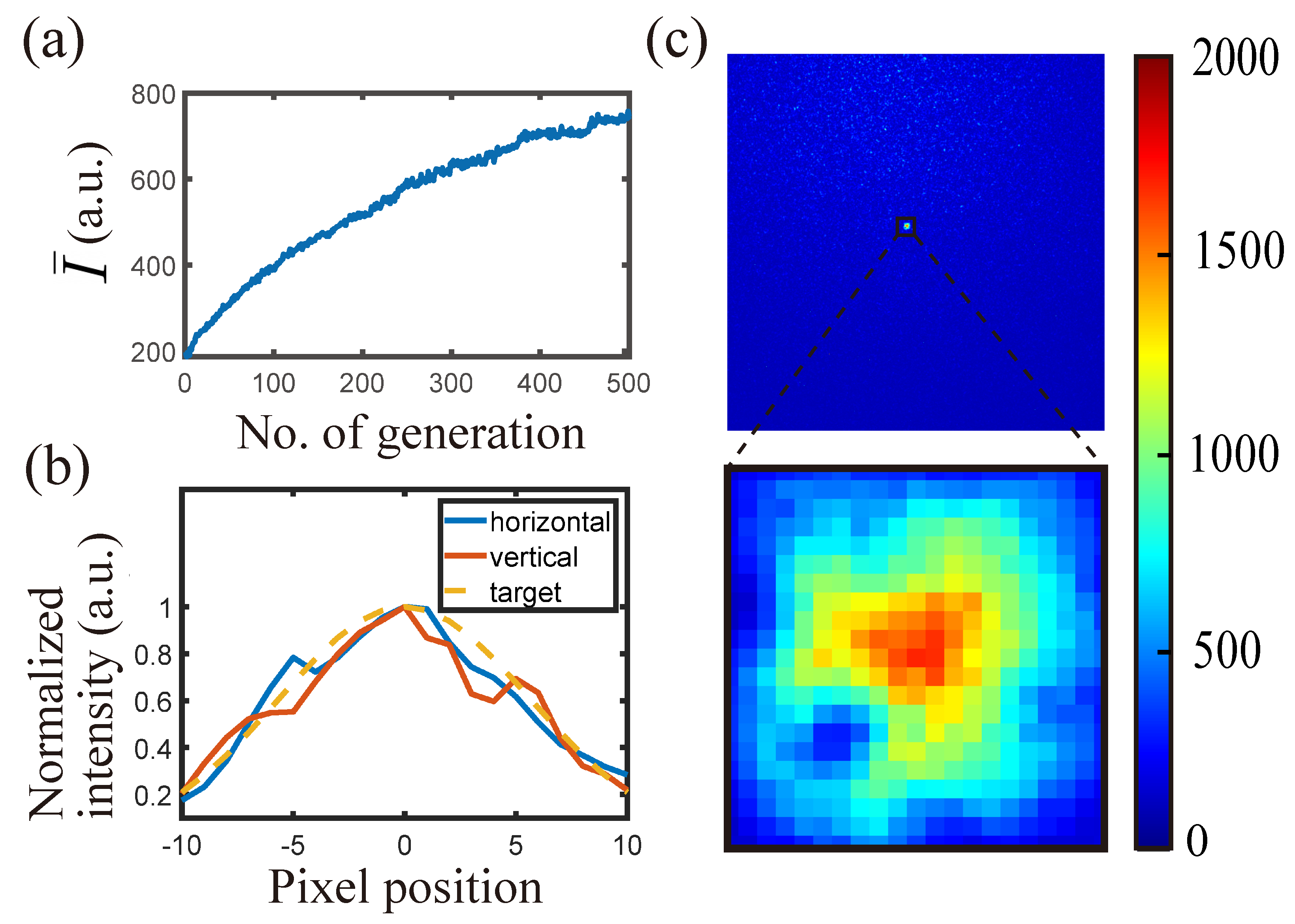
5.2. Controlled Intensity Distribution
5.3. Intensity Minimization in Neighboring Region
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| NSGA2 | Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm |
| SBGA | Scoring-based genetic algorithm |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| SLM | Spatial light modulator |
| HWP | Half-wave plate |
| BS | Beam splitter |
| MO | Microscope objective |
| sCMOS camera | scientific complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor camera |
Appendix A. Parents Selection and Children Generation
Appendix B. List of Variables
References
- Vellekoop, I.M.; Mosk, A.P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2309–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqoob, Z.; Psaltis, D.; Feld, M.; Yang, C. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppresion in biological samples. Nat. Photonics 2008, 116, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Shen, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.V. Focusing light inside dynamic scattering media with millisecond digital optical phase conjugation. Optica 2017, 4, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoff, S.M.; Lerosey, G.; Carminati, R.; Fink, M.; Boccara, A.C.; Gigan, S. Measuring the Transmission Matrix in Optics: An Approach to the Study and Control of Light Propagation in Disordered Media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 100601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Gom, M.; Norris, T.B.; Michielssen, E.; Nadakuditi, R.R. Mode control in a multimode fiber through acquiring its transmission matrix from a reference-less optical system. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Gom, M.; Lien, M.B.; Estakhri, N.M.; Norris, T.B.; Michielssen, E.; Nadakuditi, R.R. Controlling Light Transmission Through Highly Scattering Media Using Semi-Definite Programming as a Phase Retrieval Computation Method. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2045–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockbridge, C.; Lu, Y.; Moore, J.; Hoffman, S.; Paxman, R.; Toussaint, K.; Bifano, T. Focusing through dynamic scattering media. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 15086–15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellekoop, I.M. Feedback-based wavefront shaping. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 12189–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellekoop, I.; Mosk, A. Phase control algorithms for focusing light through turbid media. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 3071–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, G.; Katz, O. Noninvasive focusing through scattering layers using speckle correlations. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.; Oron, D.; Silberberg, Y. Light focusing through scattering media via linear fluorescence variance maximization, and its application for fluorescence imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 21778–21786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, H.; Pang, L. Focusing light through random scattering media by four-element division algorithm. Opt. Commun. 2018, 407, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.F.; de Almeida, D.R.Q.; Terra, L.F.; Baptista, M.S.; Labriola, L. Photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment—An update review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2019, 5, 2454–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenno, L.; Yizhar, O.; Deisserothz, K. The development and application of optogenetics. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerdemann, M.; Alpmann, C.; Esseling, M.; Denz, C. Advanced optical trapping by complex beam shaping. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, F.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Q. Multi-objective optimization genetic algorithm for multi-point light focusing in wavefront shaping. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 36459–36473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolpakar, N.A.; Lodhi, S.S.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, M.A. Application of Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm (MOGA) Optimization in Machining Processes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conkey, D.B.; Brown, A.N.; Caravaca-Aguirre, A.M.; Piestun, R. Genetic algorithm optimization for focusing through turbid media in noisy environments. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 4840–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y. A thorough study on genetic algorithms in feedback-based wavefront shaping. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2019, 12, 1942004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kner, P. Binary wavefront optimization using a genetic algorithm. J. Opt. 2014, 16, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.R.; Eilers, H. Genetic algorithms for focusing inside opaque media. J. Opt. 2020, 22, 085601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Xiang, C.; Ding, Y. Superpixel-based multi-point intensity customizable light focusing for reflective iterative optimization wavefront shaping. Optik 2021, 242, 167319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konak, A.; Coit, D.W.; Smith, A.E. Multi-objective optimization using genetic algorithms: A tutorial. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 992–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Masuyama, N.; Nojima, Y. Effects of Dominance Resistant Solutions on the Performance of Evolutionary Multi-Objective and Many-Objective Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference, Cancun, Mexico, 8–12 July 2020; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; He, J.; Ding, Y. Controllable multi-point light focusing of feedback wavefront shaping based on phase superposition Hadamard encoding algorithm. Optik 2022, 253, 168549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, A. NSGA-II: A Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm. MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2022. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/10429-nsga-ii-a-multi-objective-optimization-algorithm (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Marcoleonetti1. Laser Speckle/Point Spread Function Generator. MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2022. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/94310-laser-speckle-point-spread-function-generator (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Wan, L.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; Pu, J. Focusing light into desired patterns through turbid media by feedback-based wavefront shaping. Appl. Phys. 2016, 122, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conkey, D.B.; Piestun, R. Color image projection through a strongly scattering wall. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 27312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Rumman, N.; Bassène, P.; N'Gom, M. Scoring-Based Genetic Algorithm for Wavefront Shaping to Optimize Multiple Objectives. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9020049
Wang T, Rumman N, Bassène P, N'Gom M. Scoring-Based Genetic Algorithm for Wavefront Shaping to Optimize Multiple Objectives. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(2):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9020049
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianhong, Nazifa Rumman, Pascal Bassène, and Moussa N'Gom. 2023. "Scoring-Based Genetic Algorithm for Wavefront Shaping to Optimize Multiple Objectives" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 2: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9020049
APA StyleWang, T., Rumman, N., Bassène, P., & N'Gom, M. (2023). Scoring-Based Genetic Algorithm for Wavefront Shaping to Optimize Multiple Objectives. Journal of Imaging, 9(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9020049





