Noise-Robust Pulse Wave Estimation from Near-Infrared Face Video Images Using the Wiener Estimation Method †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
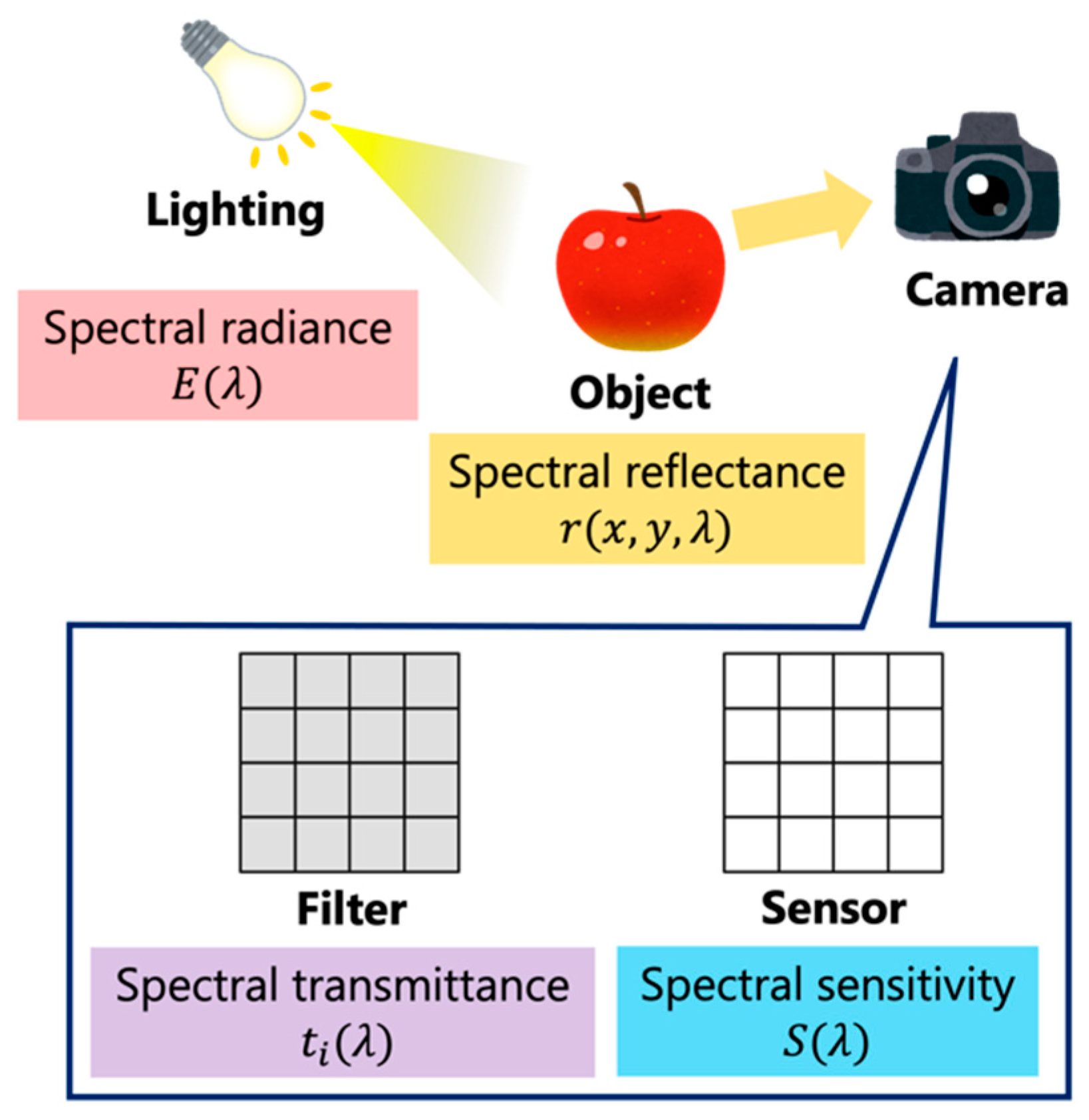
2. Skin Model in the Near-Infrared Environment
3. Hemoglobin and Shade Component Separation
3.1. Conventional Method
3.2. Proposed Method
4. Experimental Setup and Methods
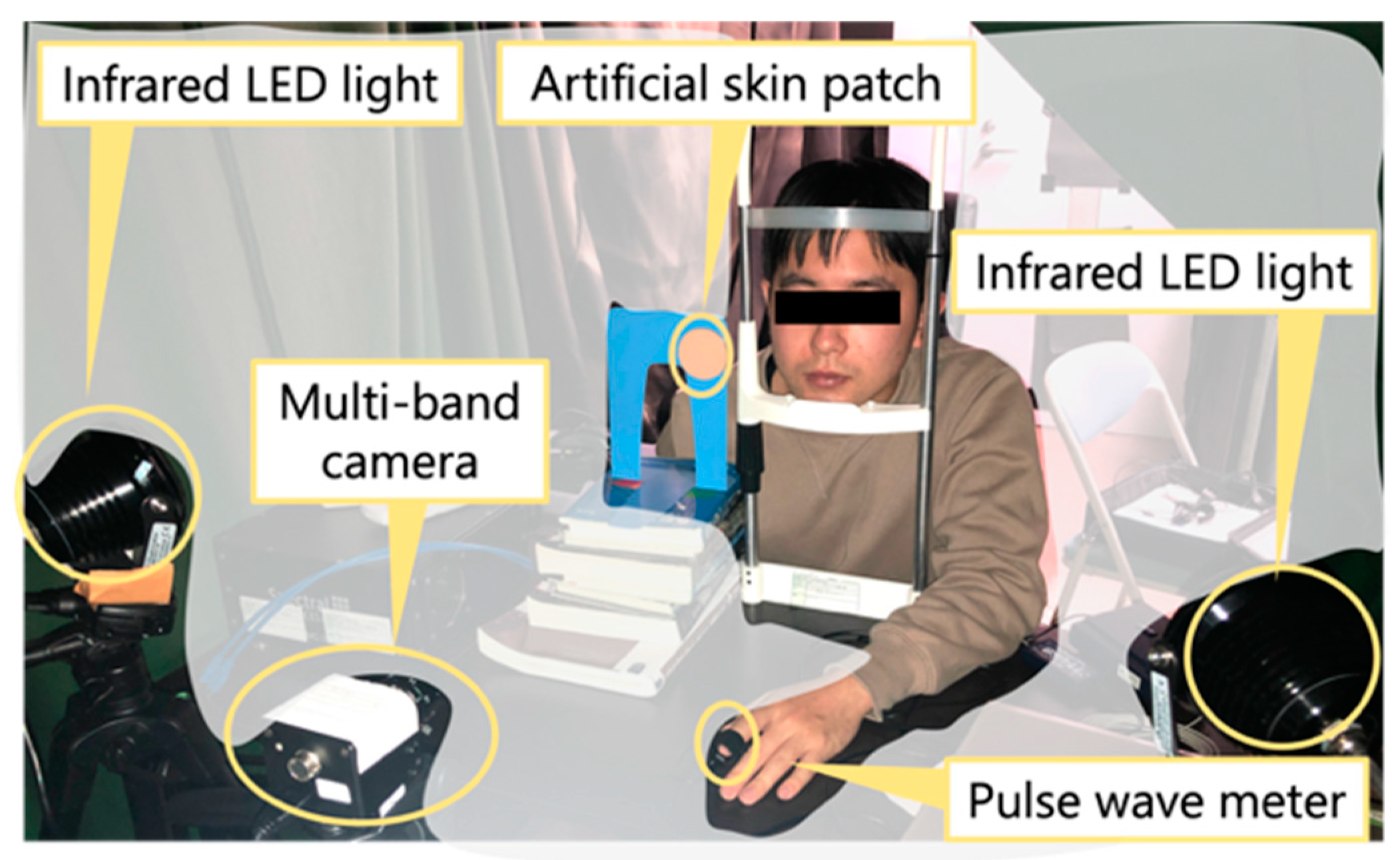
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Calculation Autocorrelation Matrixes
4.3. Acquisition of the Original Pulse Wave Signal and Signal Processing
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
5. Results
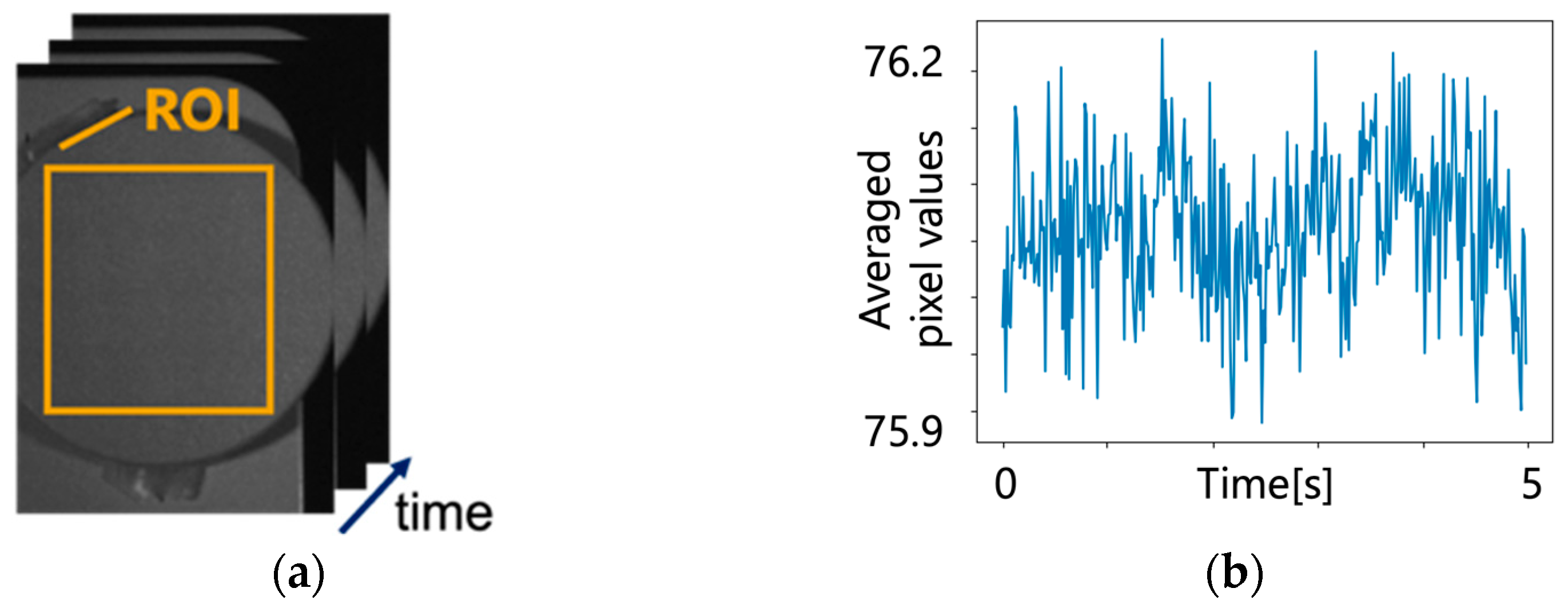
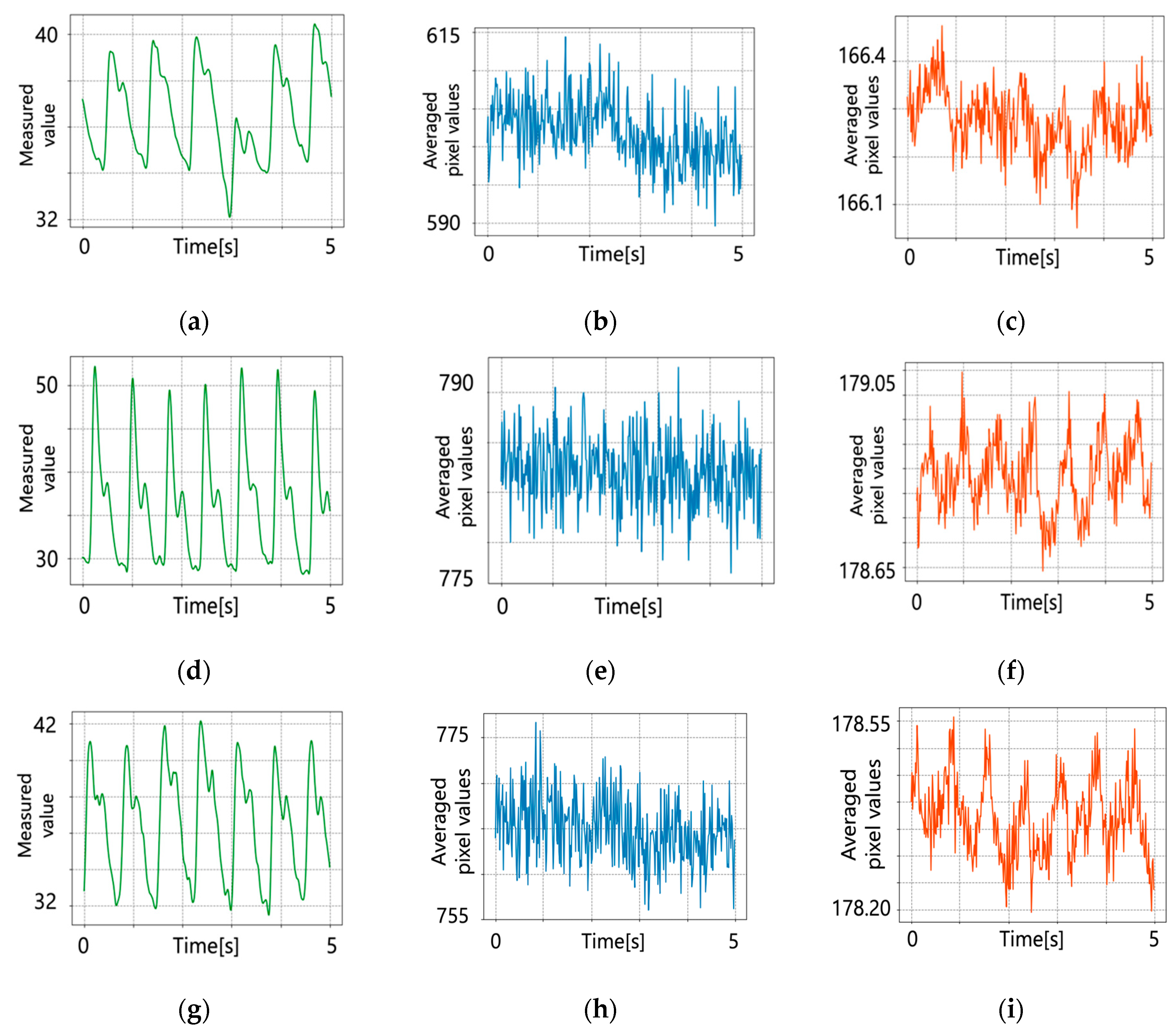
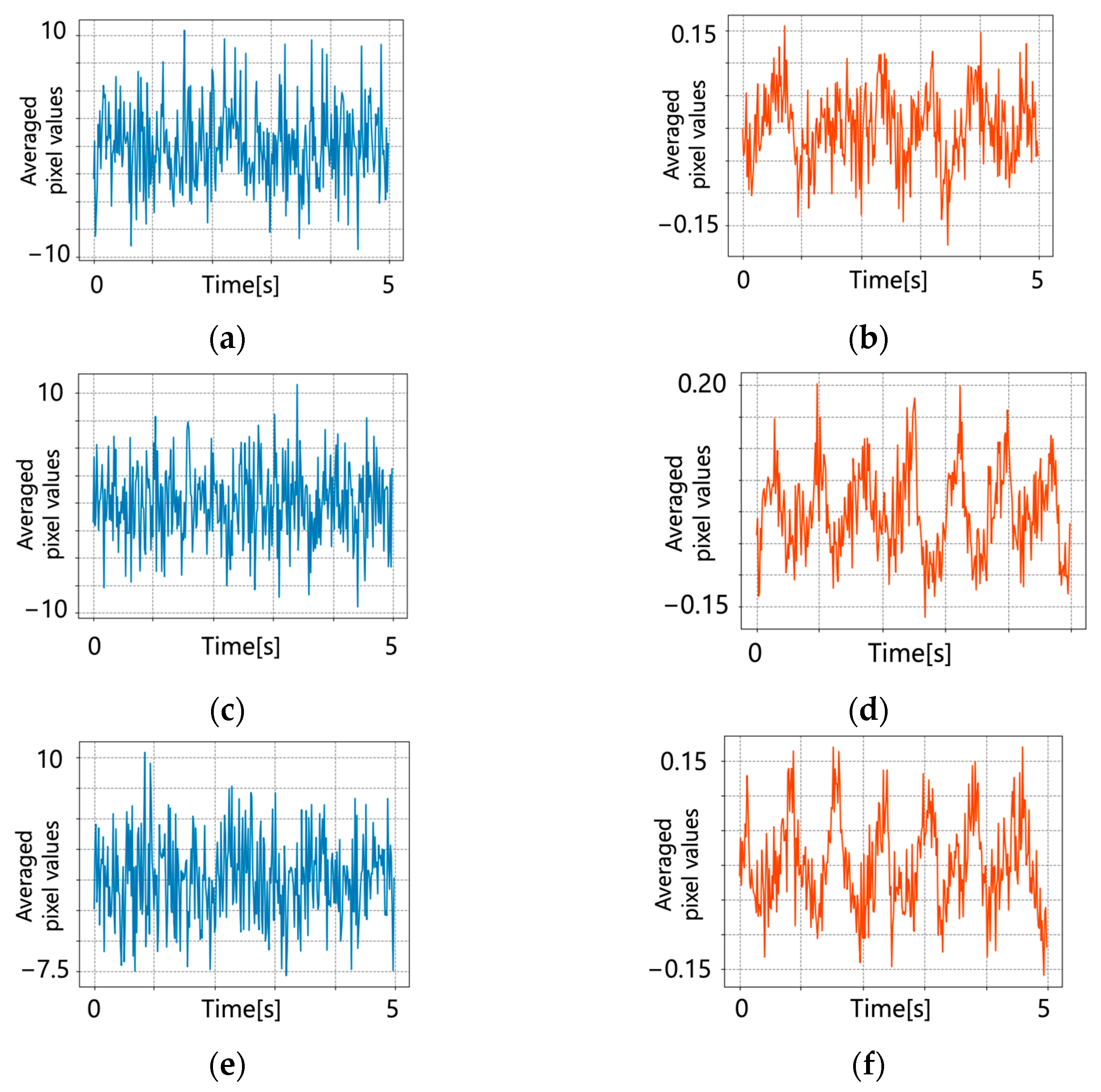
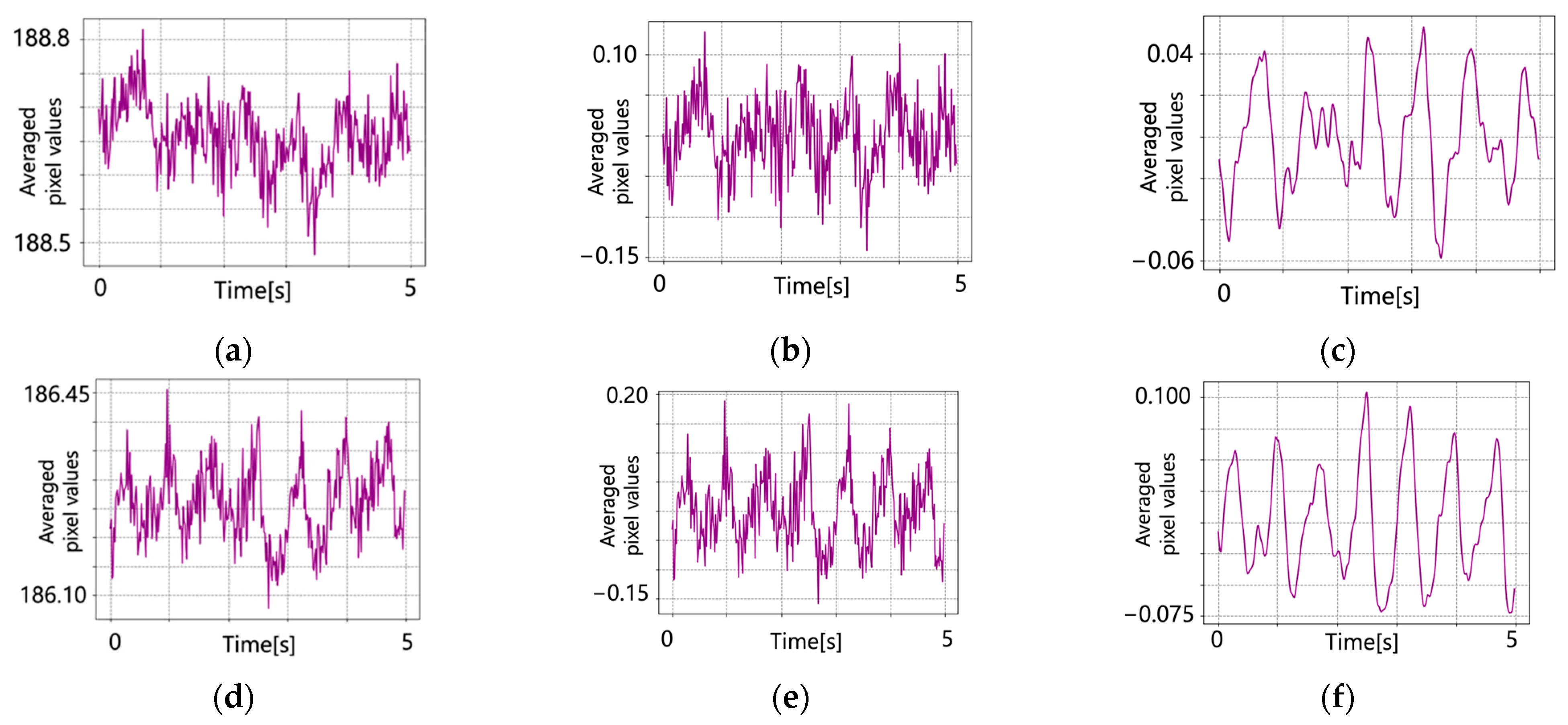
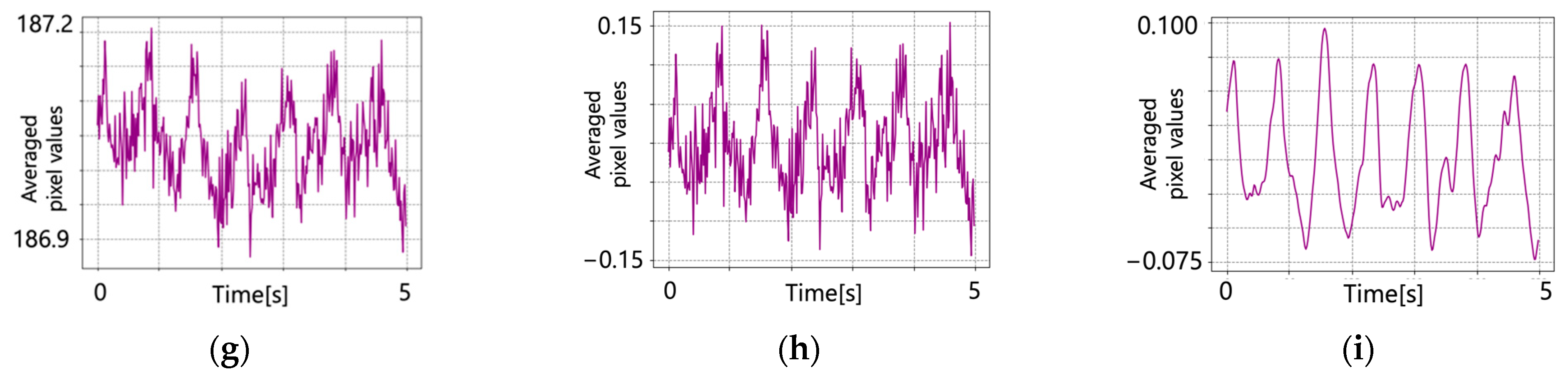
5.1. Original Pulse Wave Signals
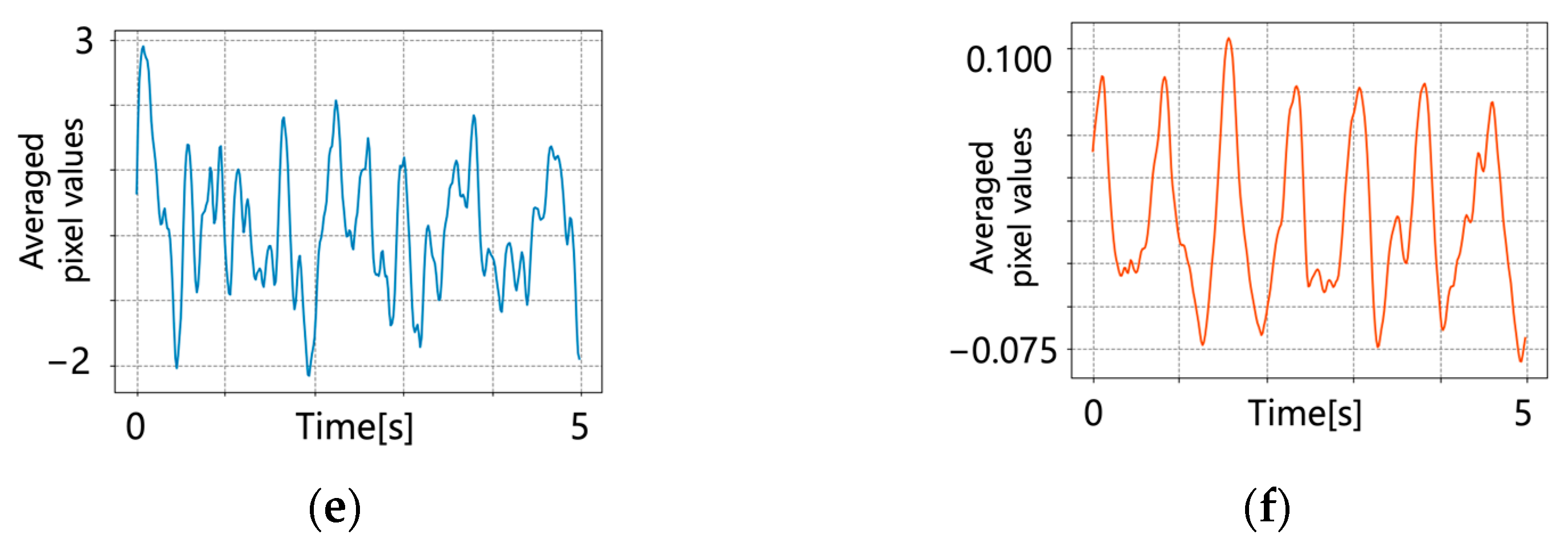
5.2. After Signal Processing
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hino, Y.; Ashida, K.; Tsumura, N. A noise-robust pulse wave estimation from NIR video using Wiener estimation method. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Scottsdale, AR, USA, 13–17 November 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastel, M.V.; Stuijk, S.; Overeem, S.; Dijk, J.P.V.; Gilst, M.M.V.; Haan, G.D. Camera-based vital signs monitoring during sleep-A proof of concept study. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, L.A.M.; Jeanne, V.; Cleary, J.P.; Nelson, J.S.; Oetomo, S.B.; Verkruysse, W. Non-contact heart rate monitoring utilizing camera photoplethysmography in the neonatal intensive care unit—A pilot study. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iozzia, L.; Cerina, L.; Mainardi, L.T. Assessment of beat-to-beat heart rate detection method using a camera as contactless sensor. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Thakor, N. Photoplethysmography Revisited: From Contact to Noncontact, From Point to Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkruysse, W.; Svaasand, L.O.; Nelson, J.S. Remote plethysmographic imaging using ambient light. Opt Express. 2008, 16, 21434–21445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Kuroshima, M.; Tsumura, N. Non-contact Video Based Estimation for Heart Rate Variability Spectrogram using Ambient Light by Extracting Hemoglobin Information. In Proceedings of the Color and Imaging Conference, Darmstadt, Germany, 19–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garbey, M.; Sun, N.; Merla, A.; Pavlidis, I. Contact-Free Measurement of Cardiac Pulse Based on the Analysis of Thermal Imagery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, G.; Liang, G. Infrared Video based Non-invasive Heart Rate Measurement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Zhuhai, China, 6–9 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi, R.; Okada, G.; Kurita, K.; Kawahito, S.; Koopipat, C.; Tsumura, N. Noncontact pulse wave detection by two-band infrared video-based measurement on face without visible lighting. Artif. Life Robot. 2018, 23, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, D.M.; Bolinger, L.; Li, H.; Kendrick, K.; Chance, B.; Wilson, J.R. Validation of near-infrared spectroscopy in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDuff, D. Camera Measurement of Physiological Vital Signs. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokendra, B.; Puneet, G. AND-rPPG: A novel denoising-rPPG network for improving remote heart rate estimation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 141, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Hwang, G.; Ryu, M.; Lee, S.J. LSTC-rPPG: Long Short-Term Convolutional Network for Remote Photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ash, C.; Dubec, M.; Donne, K.; Bashford, T. Effect of wavelength and beam width on penetration in light-tissue interaction using computational methods. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.R.; Parrish, J.A. The optics of human skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1981, 77, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yan, B.P.; Dai, W.X.; Ding, X.R.; Zhang, Y.T.; Zhao, N. Multi-wavelength photoplethysmography method for skin arterial pulse extraction. Biomed. Opt. Express. 2016, 7, 4313–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumura, N.; Haneishi, H.; Miyake, Y. Estimation of Spectral Reflectances from Multi-Band Images by Multiple Regression Analysis. Jpn. J. Opt. 1998, 27, 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Sabharwal, A. DistancePPG: Robust non-contact vital signs monitoring using a camera. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1565–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, K. ROI analysis for remote photoplethysmography on facial video. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Ranta-Aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. An advanced detrending method with application to HRV analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.Z.; McDuff, D.J.; Picard, R.W. Non-contact, automated cardiac pulse measurements using video imaging and blind source separation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10762–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Brinker, A.C.D.; Haan, G.D. Discriminative signatures for Remote-PPG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakoshi, T.; Lee, J.; Matsumura, K.; Yamakoshi, Y.; Rolfe, P.; Kiyohara, D.; Yamakoshi, K. Integrating Sphere Finger-Photoplethysmography: Preliminary Investigation towards Practical Non-Invasive Measurement of Blood Constituents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moco, A.V.; Stuijk, S.; Haan, G.D. New insights into the origin of remote PPG signals in visible light and infrared. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Subjects | Methods | Correlation Coefficient | SNR [dB] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | Conventional | −0.004 | −8.1 |
| Proposed | −0.027 | −4.8 | |
| Subject 2 | Conventional | −0.020 | −8.4 |
| Proposed | −0.078 | −4.6 | |
| Subject 3 | Conventional | −0.004 | −8.2 |
| Proposed | 0.059 | −3.0 |
| Subjects | Methods | Signal Processing | Correlation Coefficient | SNR [dB] | AER [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | Conventional | Detrend | 0.027 | −8.8 | - |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.109 | −5.5 | 20.6 | ||
| Proposed | Detrend | 0.342 | 0.3 | - | |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.506 | 3.3 | 0.90 | ||
| Subject 2 | Conventional | Detrend | 0.096 | −8.8 | - |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.187 | 2.1 | 7.68 | ||
| Proposed | Detrend | 0.353 | −4.8 | - | |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.411 | 5.6 | 0.06 | ||
| Subject 3 | Conventional | Detrend | 0.090 | −2.9 | - |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.246 | 2.1 | 9.31 | ||
| Proposed | Detrend | 0.332 | −5.1 | - | |
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.517 | 4.7 | 1.50 |
| Subjects | Methods | Signal Processing | Correlation Coefficient | SNR [dB] | AER [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | Proposed | Original pulse | −0.027 | −4.8 | - |
| Detrend | 0.342 | 0.3 | - | ||
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.506 | 3.3 | 0.90 | ||
| Subject 2 | Proposed | Original pulse | −0.078 | −4.6 | - |
| Detrend | 0.353 | −4.8 | - | ||
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.411 | 5.6 | 0.06 | ||
| Subject 3 | Proposed | Original pulse | 0.059 | −3.0 | - |
| Detrend | 0.332 | −5.1 | - | ||
| Detrend and bandpass filter | 0.517 | 4.7 | 1.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hino, Y.; Ashida, K.; Ogawa-Ochiai, K.; Tsumura, N. Noise-Robust Pulse Wave Estimation from Near-Infrared Face Video Images Using the Wiener Estimation Method. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100202
Hino Y, Ashida K, Ogawa-Ochiai K, Tsumura N. Noise-Robust Pulse Wave Estimation from Near-Infrared Face Video Images Using the Wiener Estimation Method. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(10):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100202
Chicago/Turabian StyleHino, Yuta, Koichi Ashida, Keiko Ogawa-Ochiai, and Norimichi Tsumura. 2023. "Noise-Robust Pulse Wave Estimation from Near-Infrared Face Video Images Using the Wiener Estimation Method" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 10: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100202
APA StyleHino, Y., Ashida, K., Ogawa-Ochiai, K., & Tsumura, N. (2023). Noise-Robust Pulse Wave Estimation from Near-Infrared Face Video Images Using the Wiener Estimation Method. Journal of Imaging, 9(10), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9100202








