A Brief Survey on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Methods for Magnetic Resonance Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
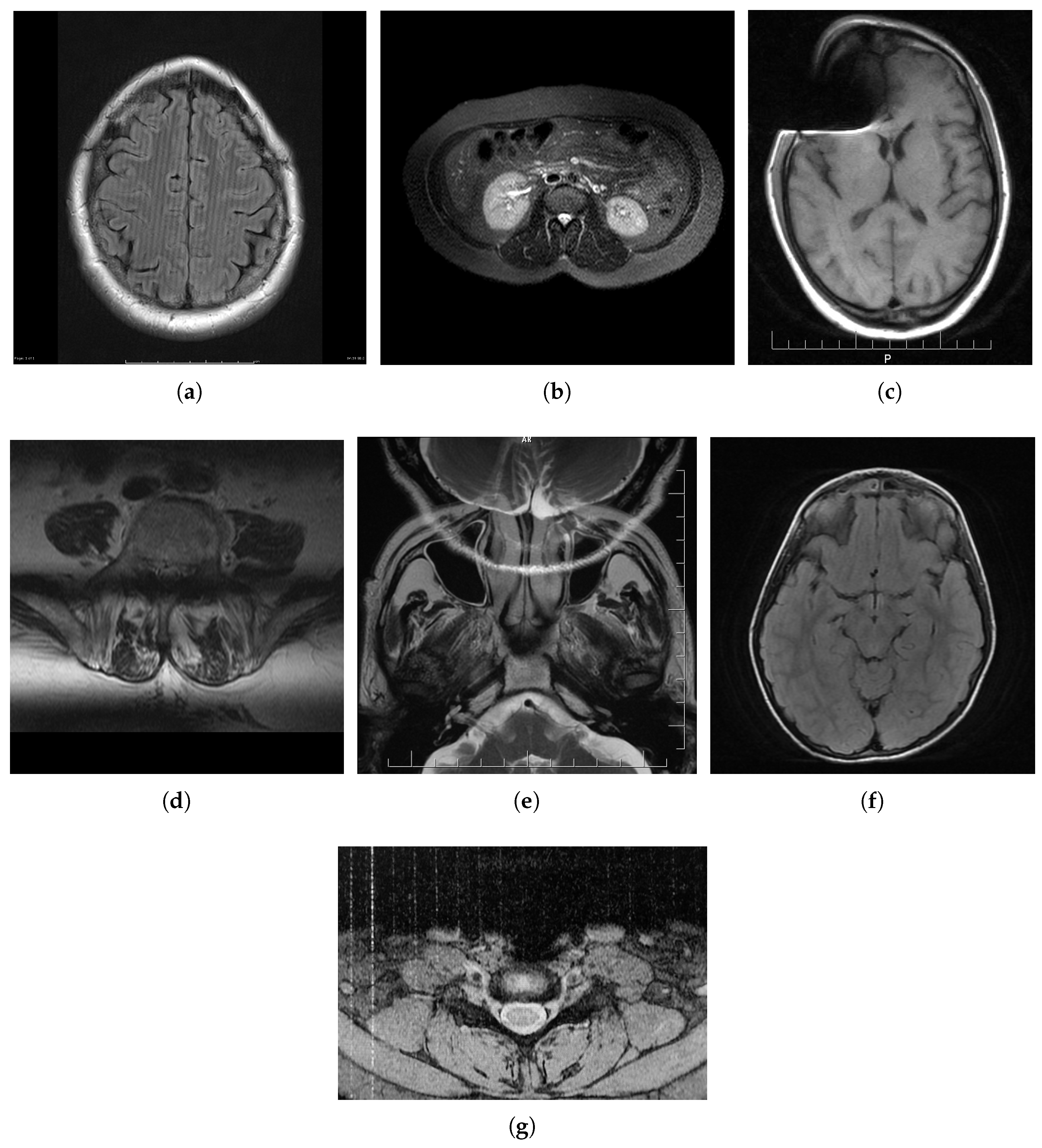
2. MRI Distortions
2.1. Spike (Herringbone) Artifact
2.2. Zipper Artifact
2.3. Ghosting
2.4. Blurring
2.5. Aliasing Artifacts
2.6. Gibbs Effect
2.7. Slice-Overlap Artifact
2.8. Gradient-Related Distortion
2.9. Parallel Imaging Artifact
2.10. Susceptibility Effect
3. NR-IQA Approaches
3.1. A Two-Step Automated Quality Assessment for Liver MR Images Based on Convolutional Neural Network
3.2. Semi-Supervised Learning for Fetal Brain MRI Quality Assessment with ROI Consistency
3.3. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment of T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images in Prostate Cancer Patients
3.4. Two-Stage Multi-Modal MR Images Fusion Method Based on Parametric Logarithmic Image Processing Model
3.5. Hierarchical Non-Local Residual Networks for Image Quality Assessment of Pediatric Diffusion MRI with Limited and Noisy Annotations
3.6. HyS-Net
3.7. QEMDIM
3.8. AQASB
3.9. Multi-Class Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Image Quality Assessment Using Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
3.10. MRIQC
3.11. Brain and Cardiac MRI Images in Multi-Center Clinical Trials
3.12. Modified Blind/Referenceless Image Spatial Quality Evaluator (BRISQUE)
3.13. R50GR18
3.14. Entropy-Based Magnetic Resonance Image Quality Assessment Measure (ENMIQA)
3.15. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment of Magnetic Resonance Images with High-Boost Filtering and Local Features (NOMRIQA)
3.15.1. PSNR/SNR
3.15.2. Maximum Difference
3.15.3. Normalized Cross-Correlation
4. Evaluation of IQA Models
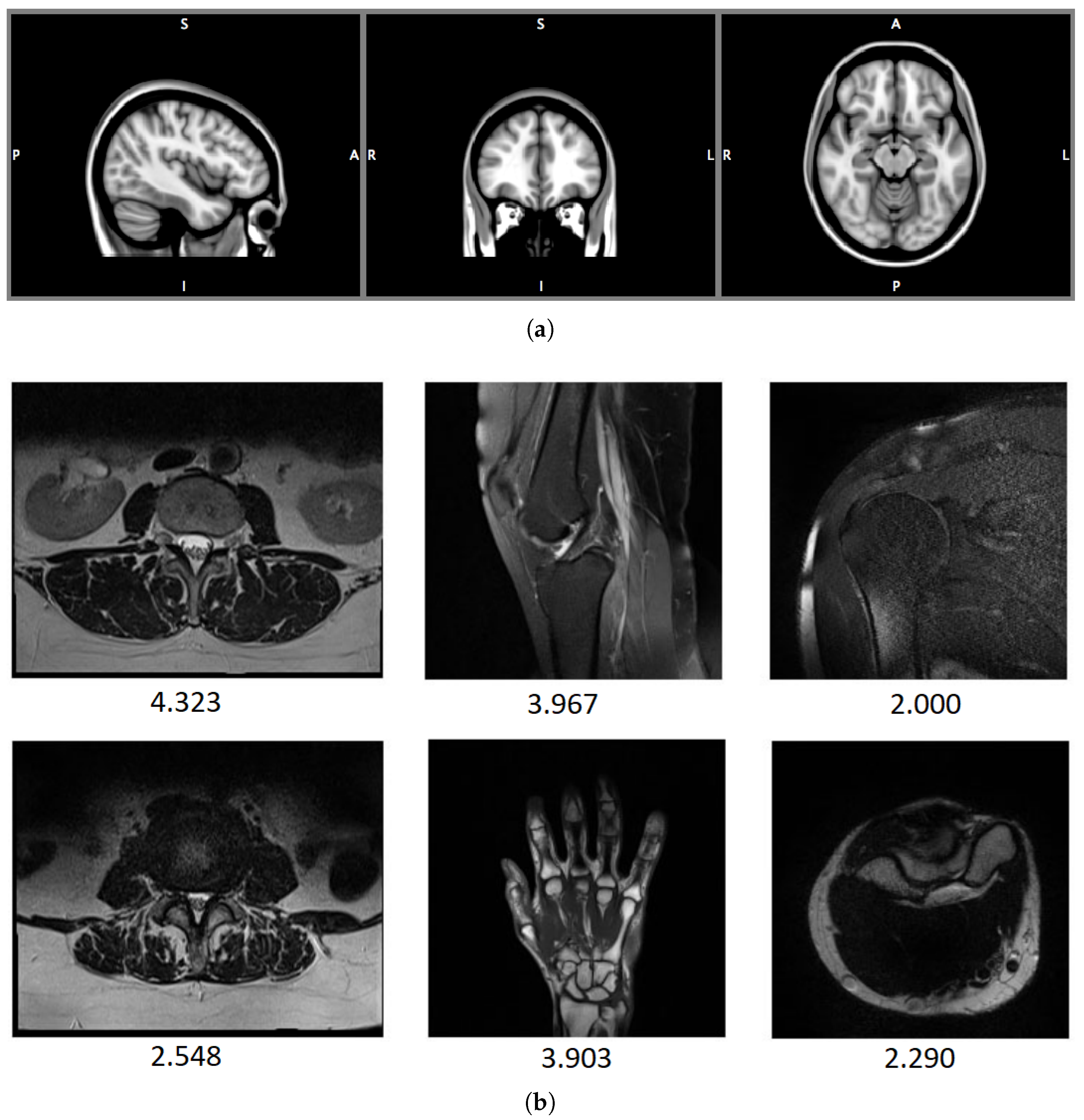
4.1. Databases
4.1.1. OpenfMRI
4.1.2. ADNI
4.1.3. National Resource for Quantitative Functional MRI
4.1.4. Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE)
4.1.5. 1.5 T T2-Weighted MR Image Databases: DB1, DB2
4.2. Evaluation Protocol
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krupinski, E.A.; Jiang, Y. Anniversary paper: Evaluation of medical imaging systems. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolind, S.H.; MacKay, A.L.; Munk, P.L.; Xiang, Q.S. Quantitative evaluation of metal artifact reduction techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging: Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 20, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Whitehead, T.D.; Quirk, J.D.; Salter, A.; Ademuyiwa, F.O.; Li, S.; An, H.; Shoghi, K.I. Optimal co-clinical radiomics: Sensitivity of radiomic features to tumour volume, image noise and resolution in co-clinical T1-weighted and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westbrook, C.; Talbot, J. MRI in Practice; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 56, 125, 141, 260–280, 331–332. [Google Scholar]
- Soher, B.J.; Dale, B.M.; Merkle, E.M. A Review of MR Physics: 3 T versus 1.5 T. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2007, 15, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largent, A.; Kapse, K.; Barnett, S.D.; De Asis-Cruz, J.; Whitehead, M.; Murnick, J.; Zhao, L.; Andersen, N.; Quistorff, J.; Lopez, C.; et al. Image quality assessment of fetal brain MRI using multi-instance deep learning methods. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lala, S.; Gagoski, B.; Abaci Turk, E.; Grant, P.E.; Golland, P.; Adalsteinsson, E. Semi-supervised learning for fetal brain MRI quality assessment with ROI consistency. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Virtual Conference, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Okarma, K. Current Trends and Advances in Image Quality Assessment. Elektron. Ir Elektrotechnika 2019, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Modern Image Quality Assessment. Synth. Lect. Image Video, Multimed. Process. 2006, 2, 1–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. Reduced- and No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2011, 28, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.; Min, X. Perceptual image quality assessment: A survey. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2020, 63, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.S.; Paramesran, R. Review of medical image quality assessment. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 27, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, D.; Ma, C.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X.; Ma, K. Continual Learning for Blind Image Quality Assessment. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, D. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment with Convolutional Neural Networks and Decision Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Freitas, P.; Da Eira, L.P.; Santos, S.S.; Farias, M.C.Q.d. On the Application LBP Texture Descriptors and Its Variants for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment. J. Imaging 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, D. Analysis of Benford’s Law for No-Reference Quality Assessment of Natural, Screen-Content, and Synthetic Images. Electronics 2021, 10, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, M.; Napoletano, P.; Schettini, R.; Rozza, A. No Reference, Opinion Unaware Image Quality Assessment by Anomaly Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsougos, I. Image Principles, Neck, and the Brain; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 93–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, J.A.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Craig, J.K.; Wolfe, O.H.; Price, R.; Partain, C.L.; James, A.E., Jr. Techniques, pitfalls and artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging. Radiographics 1987, 7, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezrich, R. A perspective on K-space. Radiology 1995, 195, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, M.J.; Mitchell, D.G. Body MRI artifacts in clinical practice: A physicist’s and radiologist’s perspective. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuo, J.; Gullapalli, R.P. MR Artifacts, Safety, and Quality Control. RadioGraphics 2006, 26, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashemi, R.H.; Bradley, W.G.; Lisanti, C.J. MRI: The Basics: The Basics; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Allisy-Roberts, P.J.; Williams, J. Farr’s Physics for Medical Imaging; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmane, A.; Gulani, V.; Griswold, M.A.; Seiberlich, N. Parallel MR imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, J.; Franson, D.; Seiberlich, N. Recent advances in parallel imaging for MRI. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2017, 101, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehman, R.L.; Felmlee, J.P. Flow artifact reduction in MRI: A review of the roles of gradient moment nulling and spatial presaturation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 14, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.L.; Henkelman, R.M. The magnetic field dependence of the breathing artifact. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1986, 4, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, M.; Maclaren, J.; Herbst, M. Motion artifacts in MRI: A complex problem with many partial solutions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadebey, M.E.; Pedersen, M.; Arnold, D.L.; Wendel-Mitoraj, K.E. Blind blur assessment of MRI images using parallel multiscale difference of Gaussian filters. BioMedical Eng. OnLine 2018, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Lin, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. Subjective Quality Assessment of Stereoscopic Omnidirectional Image. In Proceedings of the Advances in Multimedia Information Processing—PCM 2018, Hefei, China, 21–22 September 2018; Hong, R., Cheng, W.H., Yamasaki, T., Wang, M., Ngo, C.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Morelli, J.N.; Runge, V.M.; Ai, F.; Attenberger, U.; Vu, L.; Schmeets, S.H.; Nitz, W.R.; Kirsch, J.E. An image-based approach to understanding the physics of MR artifacts. Radiographics 2011, 31, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusey, E.; Lufkin, R.B.; Brown, R.; Solomon, M.A.; Stark, D.D.; Tarr, R.; Hanafee, W. Magnetic resonance imaging artifacts: Mechanism and clinical significance. Radiographics 1986, 6, 891–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Block, K.T.; Uecker, M.; Frahm, J. Suppression of MRI truncation artifacts using total variation constrained data extrapolation. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2008, 2008, 184123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharczyk, W.; Crawley, A.P.; Kelly, W.; Henkelman, R.M. Effect of multislice interference on image contrast in T2-and T1-weighted MR images. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1988, 9, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, S.J.; Charles-Edwards, L.; Reinsberg, S.A.; Leach, M.O. A complete distortion correction for MR images: I. Gradient warp correction. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramanos, Z.; Fonov, V.S.; Francis, S.J.; Narayanan, S.; Pike, G.B.; Collins, D.L.; Arnold, D.L. Gradient distortions in MRI: Characterizing and correcting for their effects on SIENA-generated measures of brain volume change. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, P.; Bammer, R.; Reinhold, C.; Haider, M.A. Parallel imaging artifacts in body magnetic resonance imaging. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2009, 60, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, P.; Kumaran, S.S.; Tripathi, R.; Khushu, S.; Kaushik, S. Protocol error artifacts in MRI: Sources and remedies revisited. Radiography 2007, 13, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lu, W.; Tao, D.; Li, X. Image quality assessment and human visual system. SPIE Proc. 2010, 7744, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthaharan, S. No-reference visually significant blocking artifact metric for natural scene images. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhateja, V.; Nigam, M.; Bhadauria, A.S.; Arya, A. Two-stage multi-modal MR images fusion method based on parametric logarithmic image processing (PLIP) model. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 136, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Thung, K.H.; Lin, W.; Shen, D.; Yap, P.T. Hierarchical nonlocal residual networks for image quality assessment of pediatric diffusion MRI With Limited and Noisy Annotations. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Ali, H. Generative Adversarial Network for Medical Images (MI-GAN). J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, K.; Li, H.; Rong, C.; Gong, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S. Blind Image Quality Assessment for MRI with A Deep Three-dimensional content-adaptive Hyper-Network. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.06888. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, L.S.; Rajagopal, H. Modified-BRISQUE as no reference image quality assessment for structural MR images. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 43, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. Blind/Referenceless Image Spatial Quality Evaluator. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2011; pp. 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.; Bang, K.; Jang, H.; Hwang, D.; Initiative, A.D.N. Quality evaluation of no-reference MR images using multidirectional filters and image statistics. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.; Simchi, H.; Moghaddam, M.E.; Frangi, A.F.; Abin, A.A. Automatic Multi-Class Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Image Quality Assessment using Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Spatial and Frequency Domains. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.06806. [Google Scholar]
- Stępień, I.; Obuchowicz, R.; Piórkowski, A.; Oszust, M. Fusion of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for No-Reference Magnetic Resonance Image Quality Assessment. Sensors 2021, 21, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Oszust, M.; Bielecka, M.; Bielecki, A.; Piórkowski, A. Magnetic resonance image quality assessment by using non-maximum suppression and entropy analysis. Entropy 2020, 22, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oszust, M.; Piórkowski, A.; Obuchowicz, R. No-reference image quality assessment of magnetic resonance images with high-boost filtering and local features. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 1648–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Gao, X.; Han, Z.; Shi, L.; Shao, G.; Fan, M.; Yang, G. A two-step automated quality assessment for liver MR images based on convolutional neural network. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 124, 108822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi, S.; Harmon, S.; Mehralivand, S.; Lay, N.; Bagci, U.; Wood, B.J.; Pinto, P.A.; Choyke, P.; Turkbey, B. No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Of T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Images In Prostate Cancer Patients. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Virtual Conference, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1201–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Joshi, N.; Kapoor, A. Learning a blind measure of perceptual image quality. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickie, D.A.; Shenkin, S.D.; Anblagan, D.; Lee, J.; Blesa Cabez, M.; Rodriguez, D.; Boardman, J.P.; Waldman, A.; Job, D.E.; Wardlaw, J.M. Whole brain magnetic resonance image atlases: A systematic review of existing atlases and caveats for use in population imaging. Front. Neuroinformatics 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esteban, O.; Blair, R.W.; Nielson, D.M.; Varada, J.C.; Marrett, S.; Thomas, A.G.; Poldrack, R.A.; Gorgolewski, K.J. Crowdsourced MRI quality metrics and expert quality annotations for training of humans and machines. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, Q.; Ma, C.; Lam, F.; Liang, Z.P. Spectral quantification for high-resolution MR spectroscopic imaging with spatiospectral constraints. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 64, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Martino, A.; O’connor, D.; Chen, B.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Balsters, J.H.; Baxter, L.; Beggiato, A.; Bernaerts, S.; et al. Enhancing studies of the connectome in autism using the autism brain imaging data exchange II. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortamet, B.; Bernstein, M.A.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Gunter, J.L.; Ward, C.; Britson, P.J.; Meuli, R.; Thiran, J.P.; Krueger, G. Automatic quality assessment in structural brain magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, W.; Sinclair, M.; Tarroni, G.; Oktay, O.; Rajchl, M.; Vaillant, G.; Lee, A.M.; Aung, N.; Lukaschuk, E.; Sanghvi, M.M.; et al. Automated cardiovascular magnetic resonance image analysis with fully convolutional networks. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2018, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreopoulos, A.; Tsotsos, J.K. Efficient and generalizable statistical models of shape and appearance for analysis of cardiac MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, O.; Birman, D.; Schaer, M.; Koyejo, O.O.; Poldrack, R.A.; Gorgolewski, K.J. MRIQC: Advancing the automatic prediction of image quality in MRI from unseen sites. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Gorgolewski, K.J. OpenfMRI: Open sharing of task fMRI data. Neuroimage 2017, 144, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osadebey, M.; Pedersen, M.; Arnold, D.; Wendel-Mitoraj, K. Image quality evaluation in clinical research: A case study on brain and cardiac mri images in multi-center clinical trials. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, R.S.; Evans, A.C.; Pike, G.B. MRI simulation-based evaluation of image-processing and classification methods. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Khanna, R. Support vector regression. In Efficient Learning Machines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, L.; Kramer, D.M.; Crooks, L.E.; Ortendahl, D.A. Measuring signal-to-noise ratios in MR imaging. Radiology 1989, 173, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkelman, R.M. Measurement of signal intensities in the presence of noise in MR images. Med. Phys. 1985, 12, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, O.; Raya, J.G.; Reeder, S.B.; Reiser, M.F.; Schoenberg, S.O. Measurement of signal-to-noise ratios in MR images: Influence of multichannel coils, parallel imaging, and reconstruction filters. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 26, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogmus, D.; Larsson, E.G.; Yan, R.; Principe, J.C.; Fitzsimmons, J.R. Measuring the Signal-to-Noise Ratio in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Caveat. Signal Process. 2004, 84, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Malathi, G. A comparative analysis on image quality assessment for real time satellite images. Indian J. Sci. Technol 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Gao, W. Image matching by normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006; Volume 2, p. II. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.P.; Cunningham, C.H.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Xu, D.; Hurd, R.E.; Pauly, J.M.; Carvajal, L.; Karpodinis, K.; Vigneron, D.B. High-resolution 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the prostate at 3 T with the MLEV-PRESS sequence. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Dong, K.; Cui, D.; Jiao, Q.; Qiu, J. Quality assurance of human functional magnetic resonance imaging: A literature review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinck, P. Magnetic resonance: A critical peer-reviewed introduction. In Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. The Basic Textbook of the European Magnetic Resonance Forum; BoD: Norderstedt, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Di Martino, A.; Yan, C.G.; Li, Q.; Denio, E.; Castellanos, F.X.; Alaerts, K.; Anderson, J.S.; Assaf, M.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Dapretto, M.; et al. The autism brain imaging data exchange: Towards a large-scale evaluation of the intrinsic brain architecture in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griswold, M.A.; Heidemann, R.M.; Jakob, P.M. Direct parallel imaging reconstruction of radially sampled data using GRAPPA with relative shifts. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting of the ISMRM, Toronto, ON, Canada, 10–16 July 2003; Volume 2349. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Bansal, D.; Singh, C. Image Quality Assessment Using Non-Linear MultiMetric Fusion Approach. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 822–826. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C.; De Veciana, G. An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, P.; Jakhetiya, V.; Abrol, P.; Lehana, P.K.; Subudhi, B.N.; Guntuku, S.C. Perceptual quality evaluation of hazy natural images. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 8046–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esses, S.J.; Lu, X.; Zhao, T.; Shanbhogue, K.; Dane, B.; Bruno, M.; Chandarana, H. Automated image quality evaluation of T2-weighted liver MRI utilizing deep learning architecture. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.J.; Nakarmi, U.; Kin, C.Y.S.; Sandino, C.M.; Cheng, J.Y.; Syed, A.B.; Wei, P.; Pauly, J.M.; Vasanawala, S.S. Diagnostic image quality assessment and classification in medical imaging: Opportunities and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 337–340. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Li, J.; Fu, X. No-reference quality assessment of contrast-distorted images using contrast enhancement. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08879. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, M.; Couprie, C.; LeCun, Y. Deep multi-scale video prediction beyond mean square error. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.05440. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | Approach and Features | Number of Features | Datasets |
|---|---|---|---|
| A two-step automated quality assessment for liver MR images based on convolutional neural network [53] |
| - | Not defined in the paper |
| Semi-supervised learning for fetal brain MRI quality assessment with ROI consistency [7] |
| - | Scans acquired at Boston Children’s Hospital |
| No-reference image quality assessment of T2-weighted magnetic resonance images in prostate cancer patients [54] |
| - |
|
| Two-stage multi-modal MR images fusion method based on parametric logarithmic image processing (PLIP) model [55] |
| - |
|
| Hierarchical non-local residual networks for image quality assessment of pediatric diffusion MRI with limited and noisy annotations [43] |
| - |
|
| HyS-net [45] |
| - |
|
| QEMDIM [48] |
| 20 | |
| AQASB [60] |
| - |
|
| Multi-class cardiovascular magnetic resonance image quality assessment using unsupervised domain adaptation [49,61] |
| 512 |
|
| MRIQC [63] |
| 64 | |
| Brain and cardiac MRI images in multi-center clinical trials [65] |
| The number of features depends on the image |
|
| Modified-BRISQUE [46] |
| 36 |
|
| R50GR18 [50] |
| 3584 | |
| ENMIQA [51] |
| 1 |
|
| NOMRIQA [52] |
| 3840 |
| Name | Year | No. of Images | Link (Accessed on 27 April 2022) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenfMRI | 2010 | Not specified/repository of datasets | openfmri.org |
| ADNI-1 | 2004–2010 | 200 elderly controls, 400 MCI, 200 AD | adni.loni.usc.edu |
| ADNI-GO | 2009–2011 | Existing ADNI-1 + 200 early MCI | adni.loni.usc.edu |
| ADNI-2 | 2011–2017 | Existing ADNI-1 and ADNI-GO + additional images | adni.loni.usc.edu |
| ADNI-3 | 2017–2022 | Existing ADNI-1, ADNI-GO, ADNI-2 + additional images | adni.loni.usc.edu |
| ABIDE I | 2012 | 1112 datasets | fcon1000.projects.nitrc.org |
| ABIDE II | 2016 | Existing ABIDE I and 1000 datasets | fcon1000.projects.nitrc.org |
| DB1 | 2020 | 70 | marosz.kia.prz.edu.pl/ENMIQA.html |
| DB2 | 2020 | 240 | marosz.kia.prz.edu.pl/NOMRIQA.html |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępień, I.; Oszust, M. A Brief Survey on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Methods for Magnetic Resonance Images. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8060160
Stępień I, Oszust M. A Brief Survey on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Methods for Magnetic Resonance Images. Journal of Imaging. 2022; 8(6):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8060160
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępień, Igor, and Mariusz Oszust. 2022. "A Brief Survey on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Methods for Magnetic Resonance Images" Journal of Imaging 8, no. 6: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8060160
APA StyleStępień, I., & Oszust, M. (2022). A Brief Survey on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Methods for Magnetic Resonance Images. Journal of Imaging, 8(6), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging8060160







