A Survey on Anti-Spoofing Methods for Facial Recognition with RGB Cameras of Generic Consumer Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
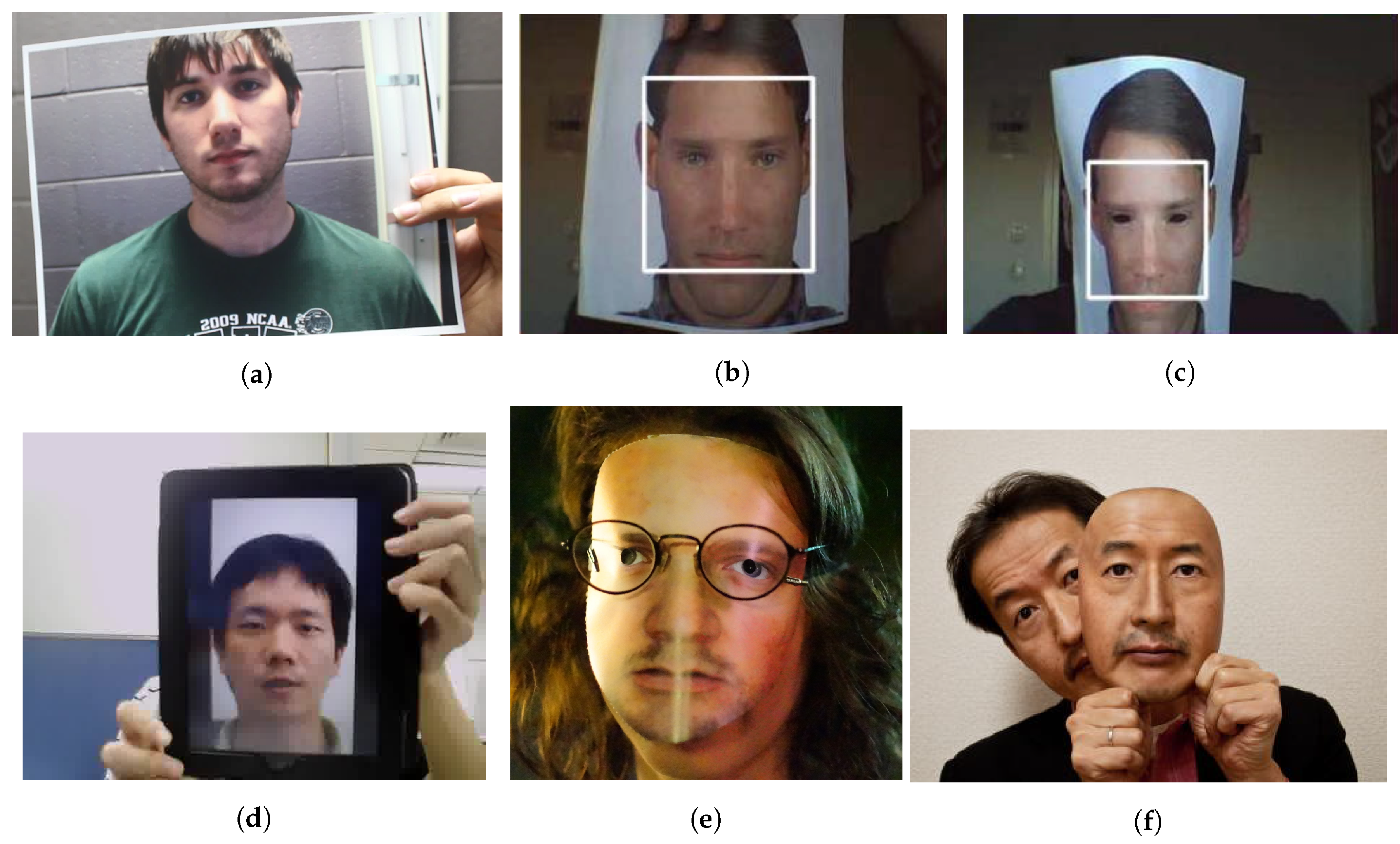
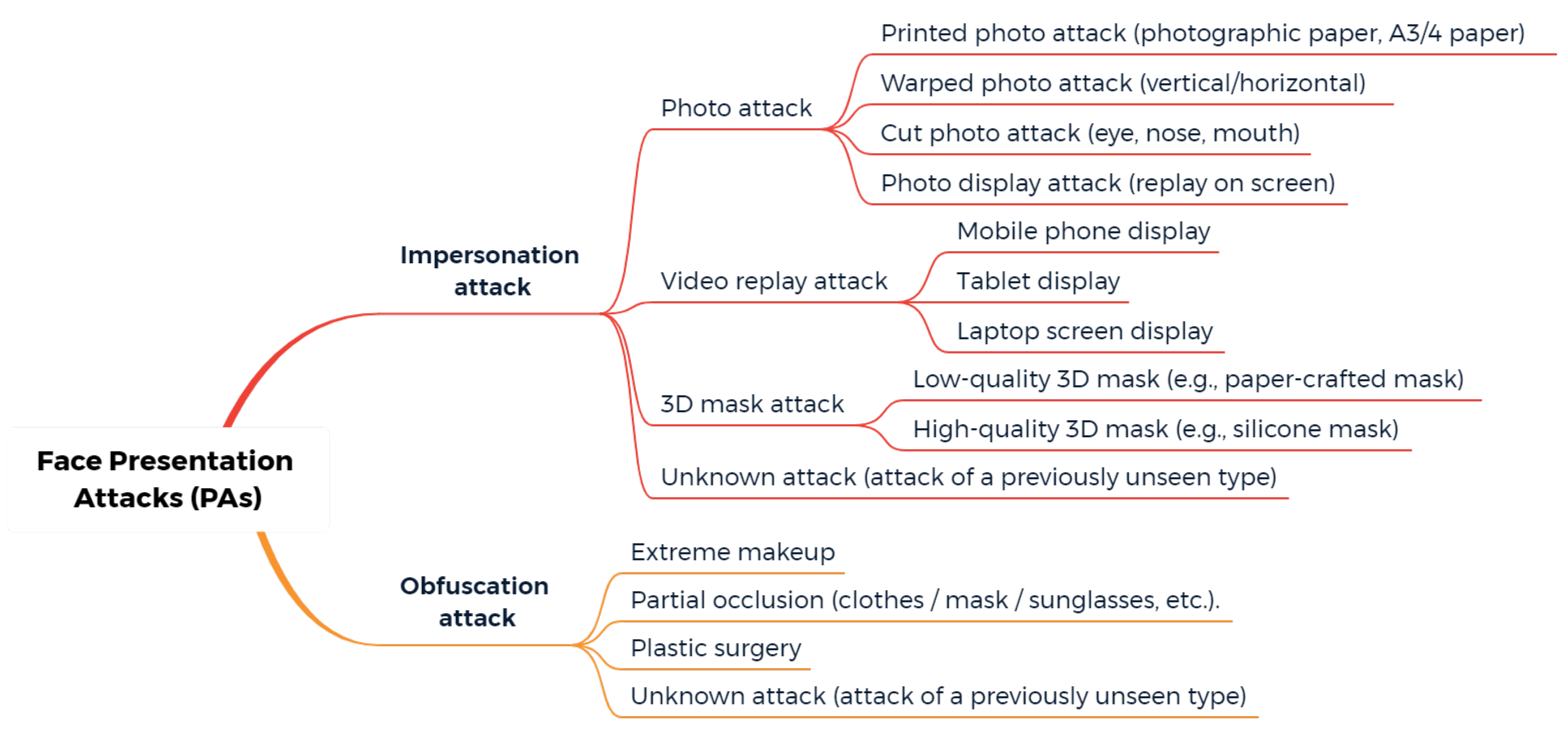
1.2. Categories of Facial Presentation Attacks
1.3. Facial PAD Methods with Generic Consumer Devices (GCD)
1.4. Main Contributions of This Paper
- We propose a typology of existing facial PAD methods based on the type of PAs they aim to detect and some specificities of the applicative scenario.
- We provide a comprehensive review of over 50 recent facial PAD methods that only require (as input) images captured by RGB cameras embedded in most GCDs.
- We provide a summarized overview of the available public databases for both 2D attacks and 3D mask attacks, which are of vital importance for both model training and testing.
- We report extensively the results detailed in the reviewed works and quantitatively compare the different PAD methods under uniform benchmarks, metrics and protocols.
- We discuss some less-studied topics in the field of facial PAD, such as unknown PAs and obfuscation attacks, and we provide some insights for future work.
1.5. Structure of This Paper
2. Overview of Facial PAD Methods Using Only RGB Cameras from GCDs
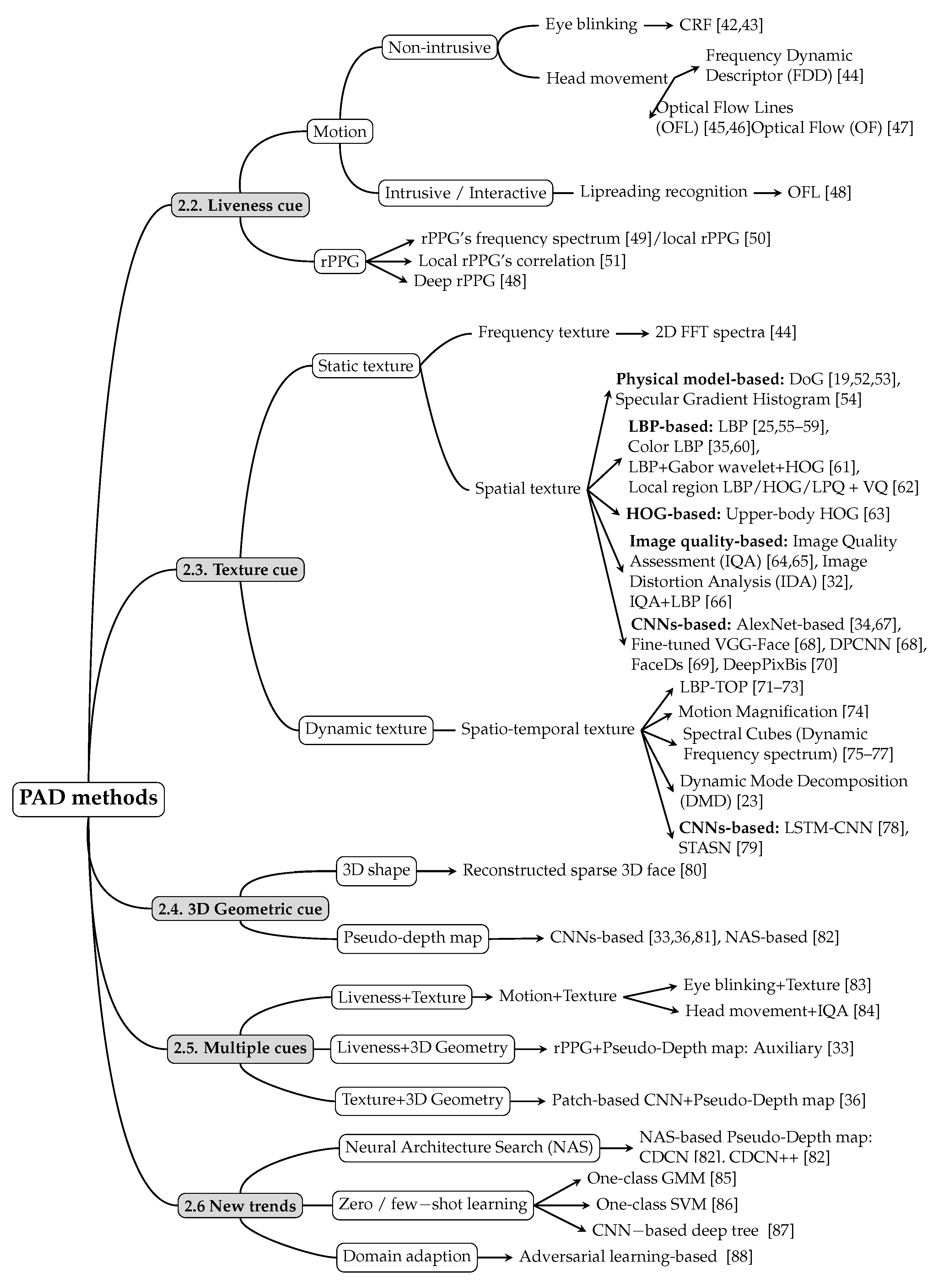
2.1. Typology of Facial PAD Methods
- liveness cue-based methods;
- texture cue-based methods;
- 3D geometric cue-based methods;
- multiple cues-based methods; and
- methods using new trends.
- Liveness cue-based methods aim to detect liveness cues in facial presentation or PAI. The most widely used liveness cues so far are motion (head movements, facial expressions, etc.) and micro-intensity changes corresponding to blood pulse. Thus, liveness cue-based methods can be classified into the following two subcategories:
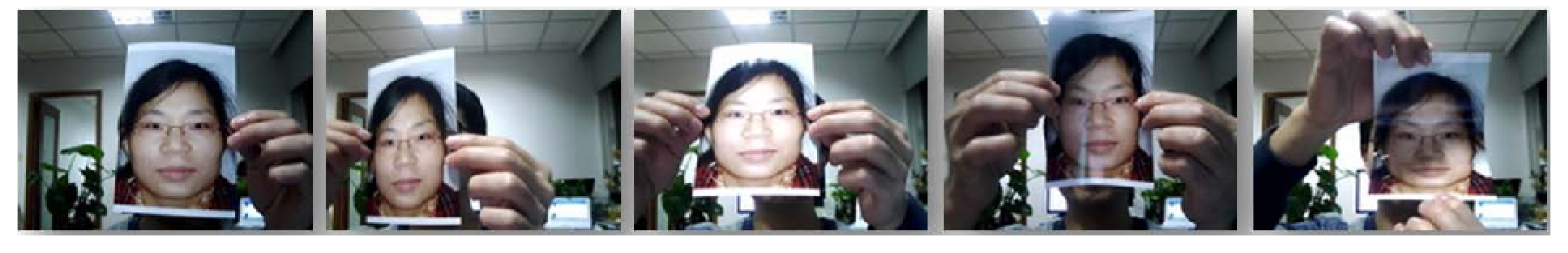
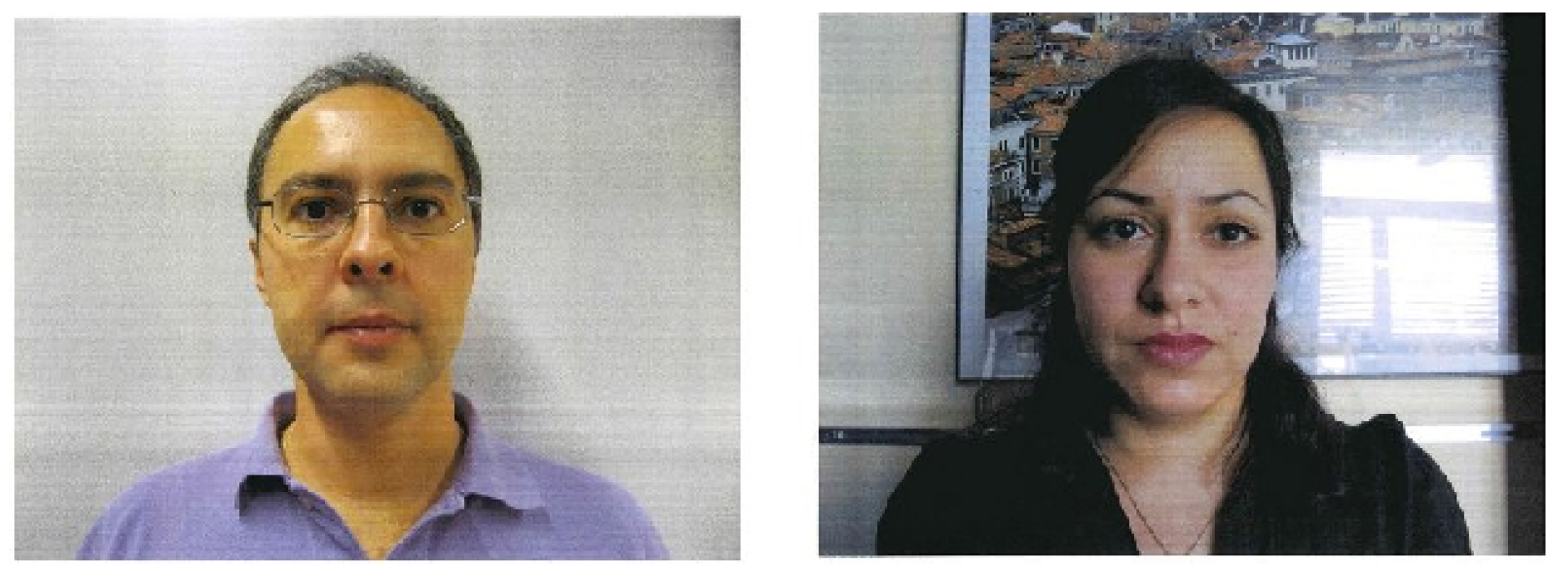
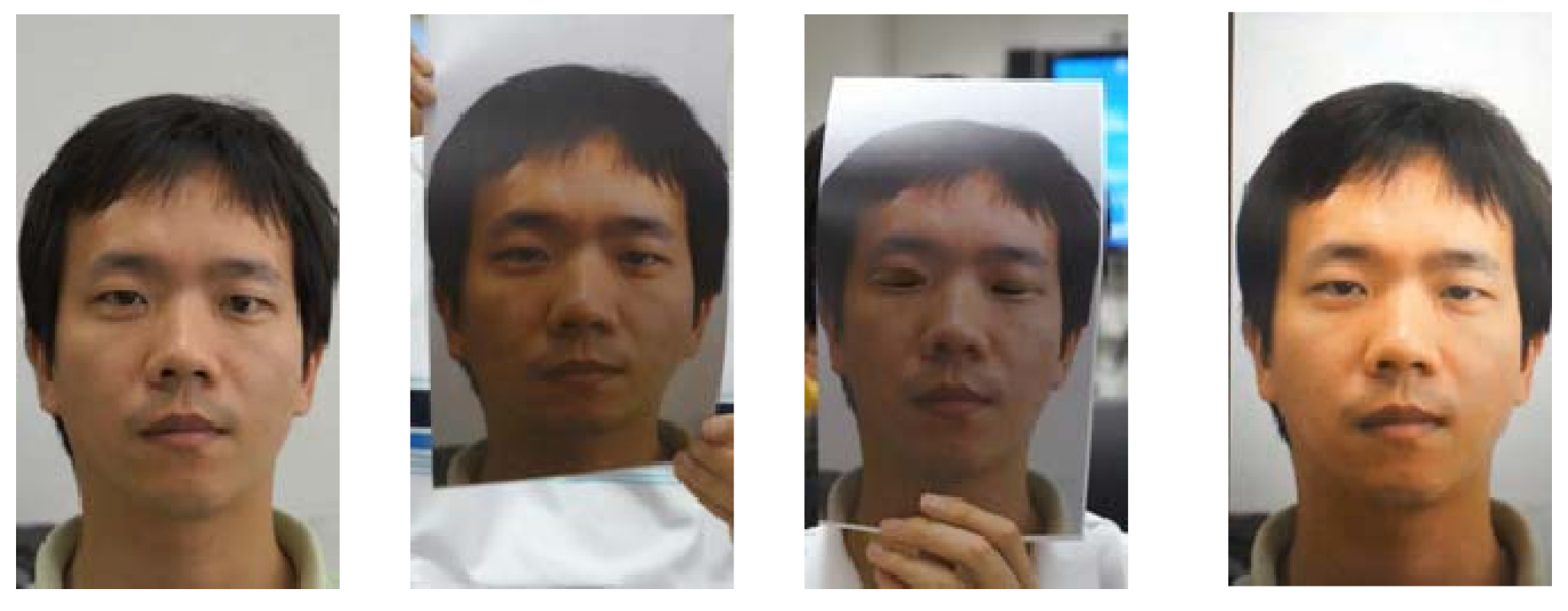
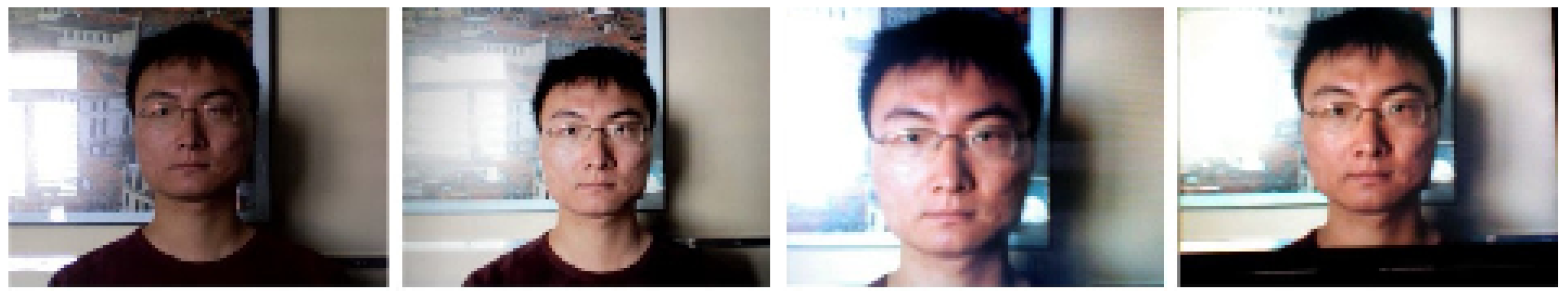
- Motion cue-based methods employ motion cues in video clips to discriminate between genuine (alive) faces and static photo attacks. Such methods can effectively in detecting static photo attacks but not video replay with motion/liveness cues and 3D mask attacks;
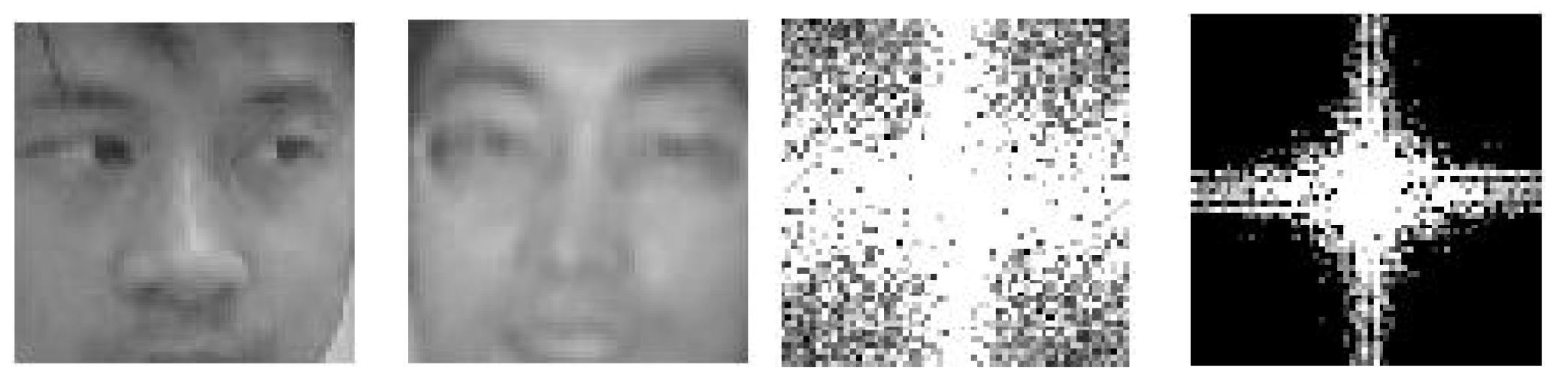
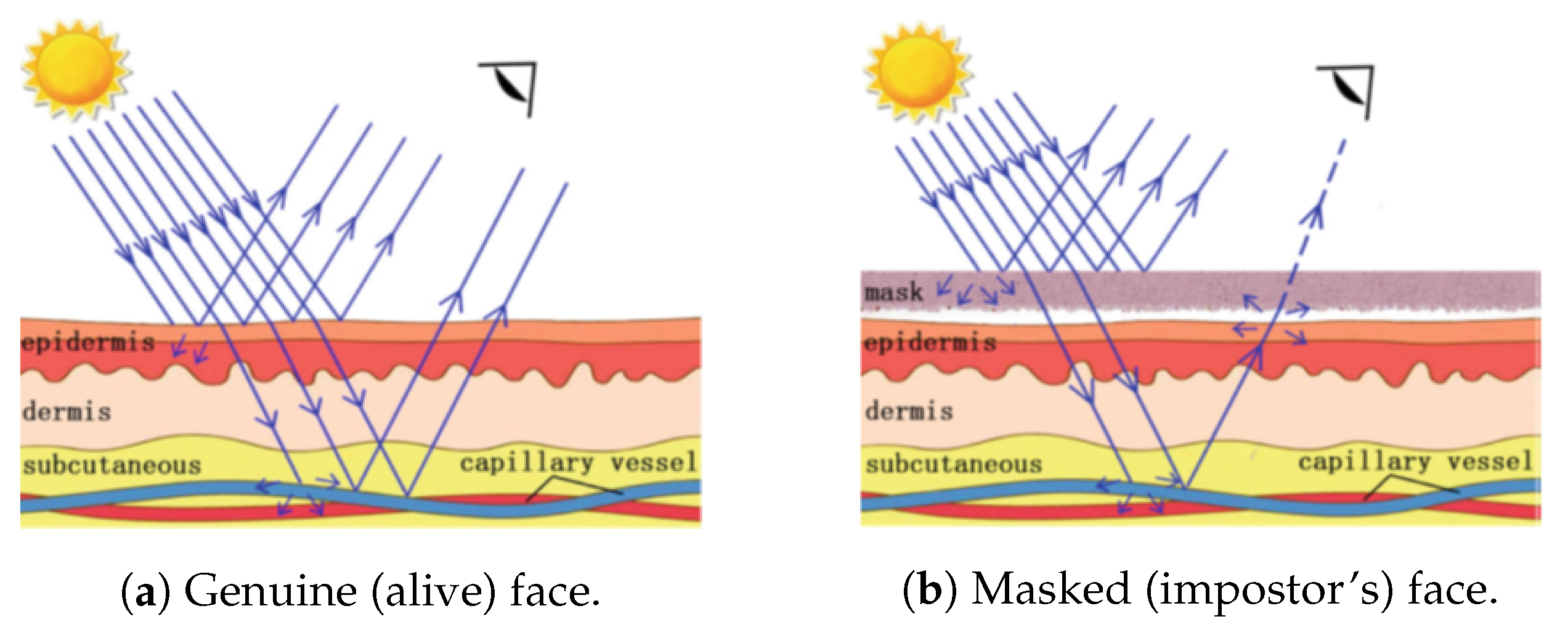
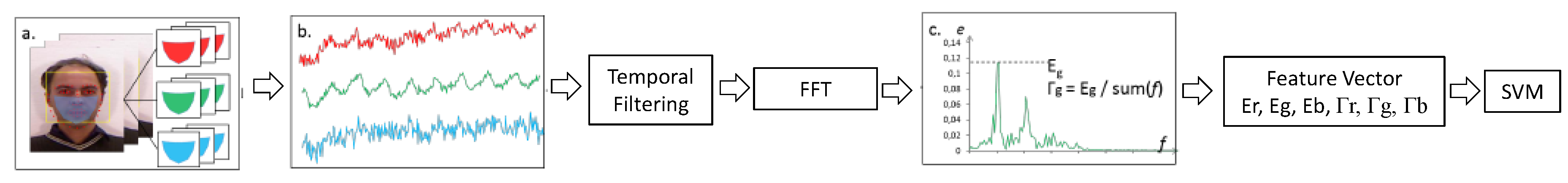
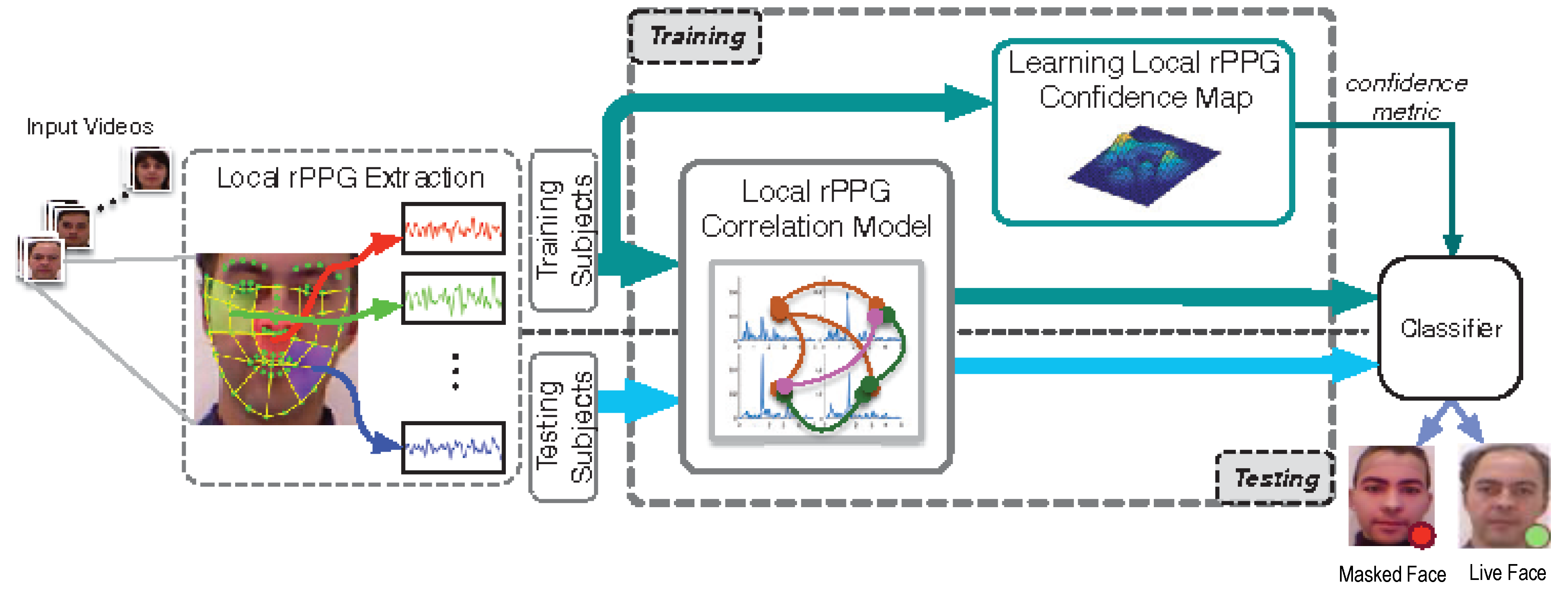
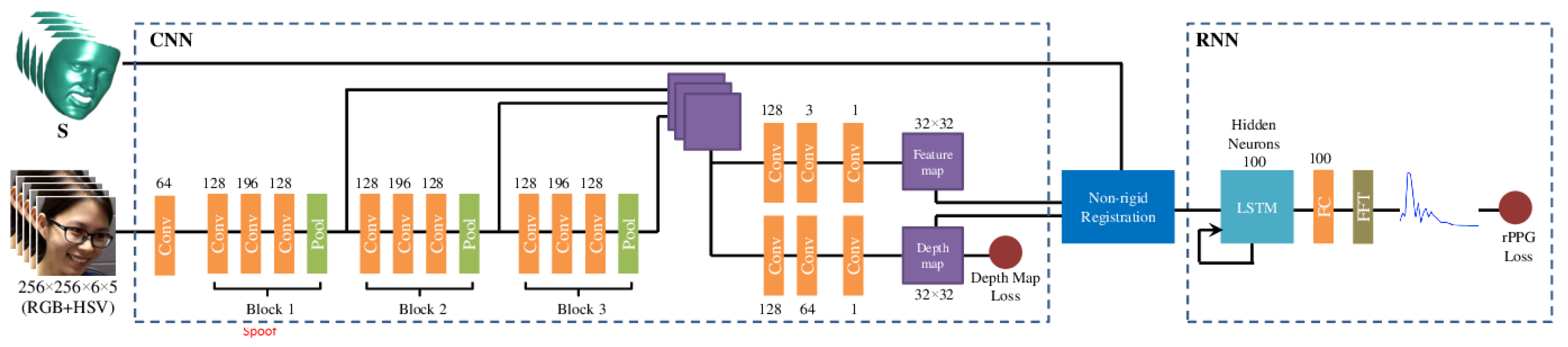
- Remote PhotoPlethysmoGraphy (rPPG) is the most widely used technique for measuring facial micro-intensity changes corresponding to blood pulse. rPPG cue-based methods can detect photo and 3D mask attacks, as these PAIs do not show the periodic intensity changes that are characteristic of facial skin. They can also detect “low-quality” video replay attacks that are not able to display those subtle changes (due to the capture conditions and/or PAI characteristics). However, “high-quality” video replay attacks (displaying the dynamic changes of the genuine face’s skin) cannot be detected by rPPG cue-based methods.
- Texture cue-based methods use static or dynamic texture cues to detect facial PAs by analyzing the micro-texture of the surface presented to the camera. Static texture cues are generally spatial texture features that can be extracted from a single image. In contrast, dynamic texture cues usually consist of spatiotemporal texture features, extracted from an image sequence. Texture cue-based facial PAD methods can detect all types of PAs. However, they might be fooled by “high-quality” 3D masks (masks with a surface texture that mimics good facial texture);
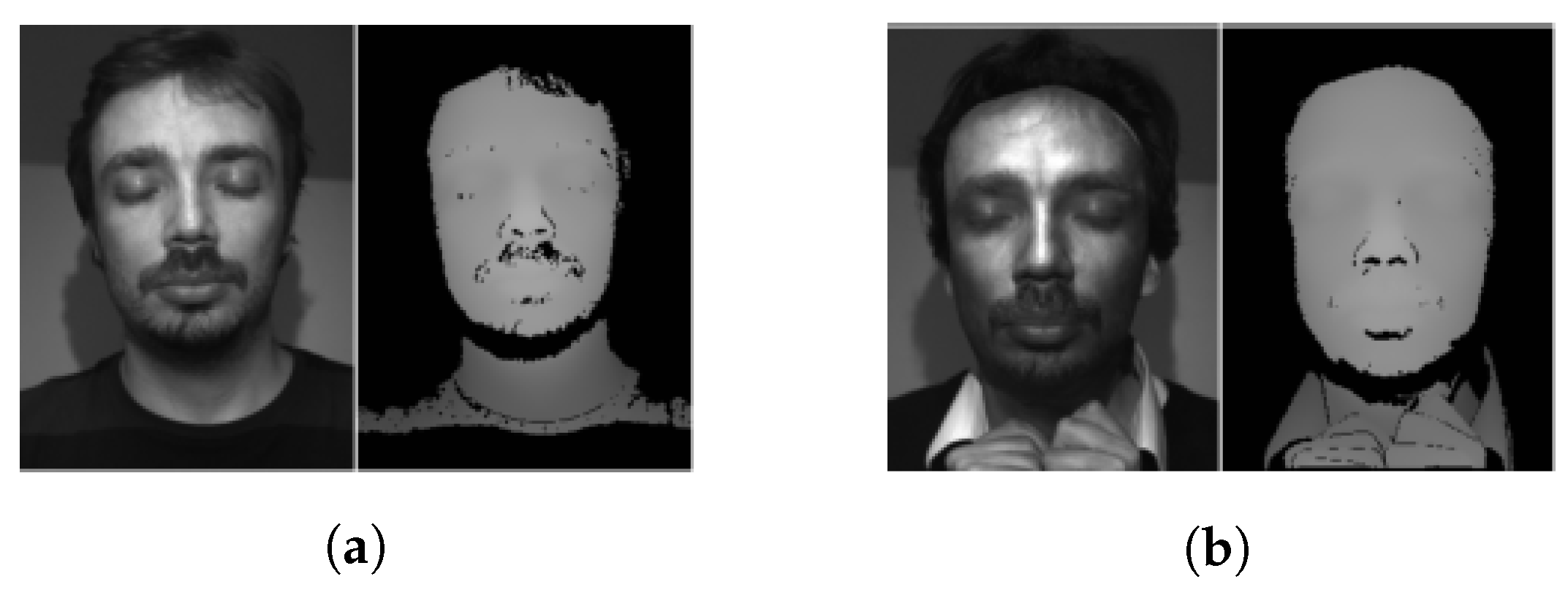
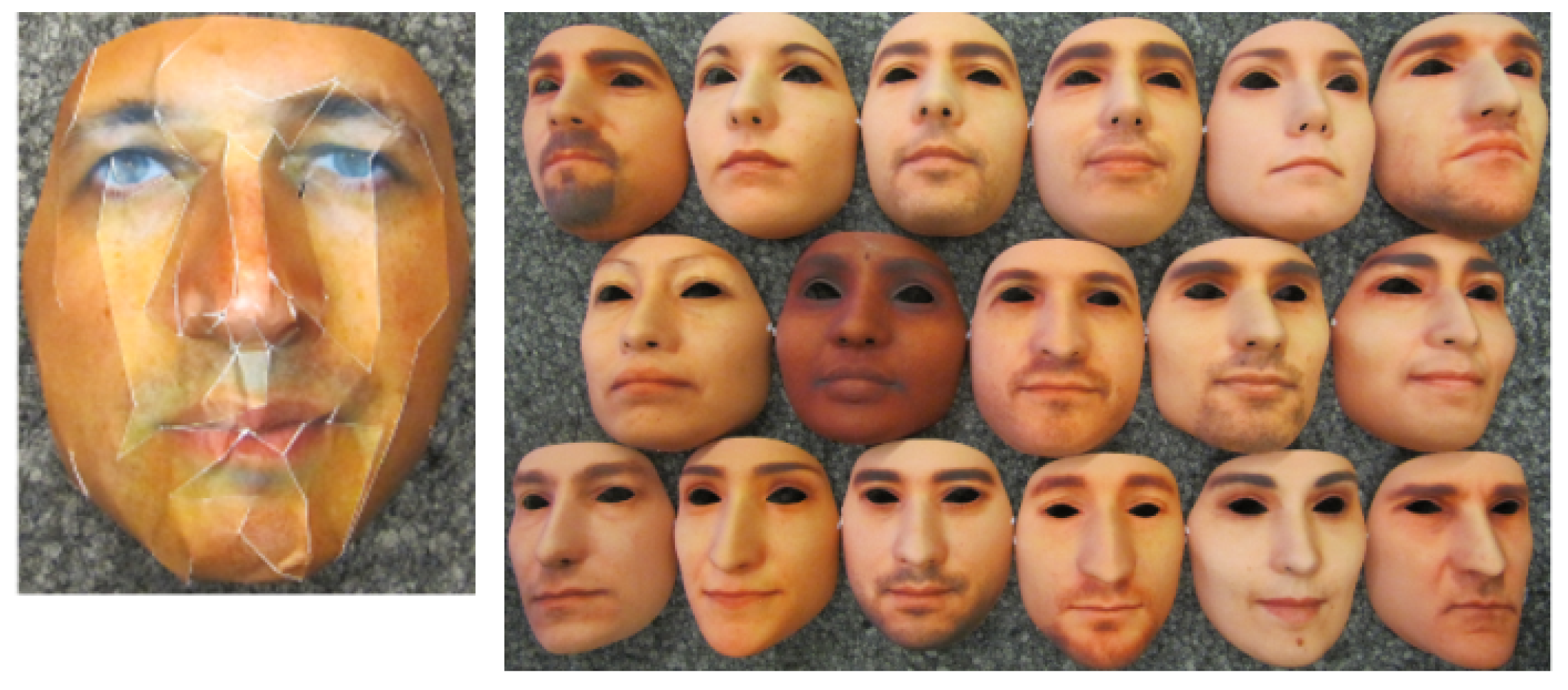
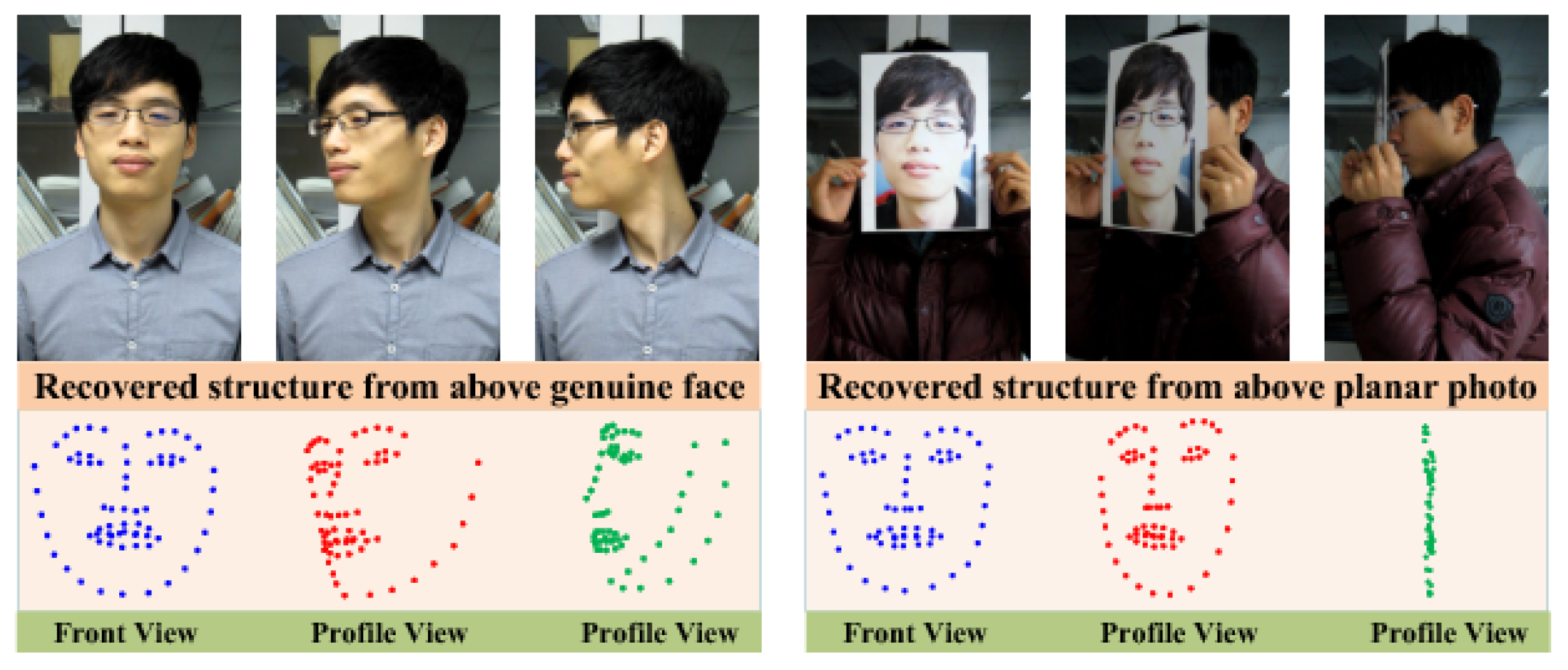
- Three-dimensional geometric cue-based methods use 3D geometrical features, generally based on the 3D structure or depth information/map of the user’s face or PAIs. Three-dimensional geometric cue-based PAD methods can detect planar photo and video replay attacks but not (in general) 3D mask attacks;
- Multiple cues-based methods consider different cues (e.g., motion features with texture features) to detect a wider variety of face PAs;
- Methods using new trends do not necessarily aim to detect specific types of PAs, but their common trait is that they rely on cutting-edge machine learning technology, such as Neural Architecture Search (NAS), zero-shot learning, domain adaption, etc.
2.2. Liveness Cue-Based Methods
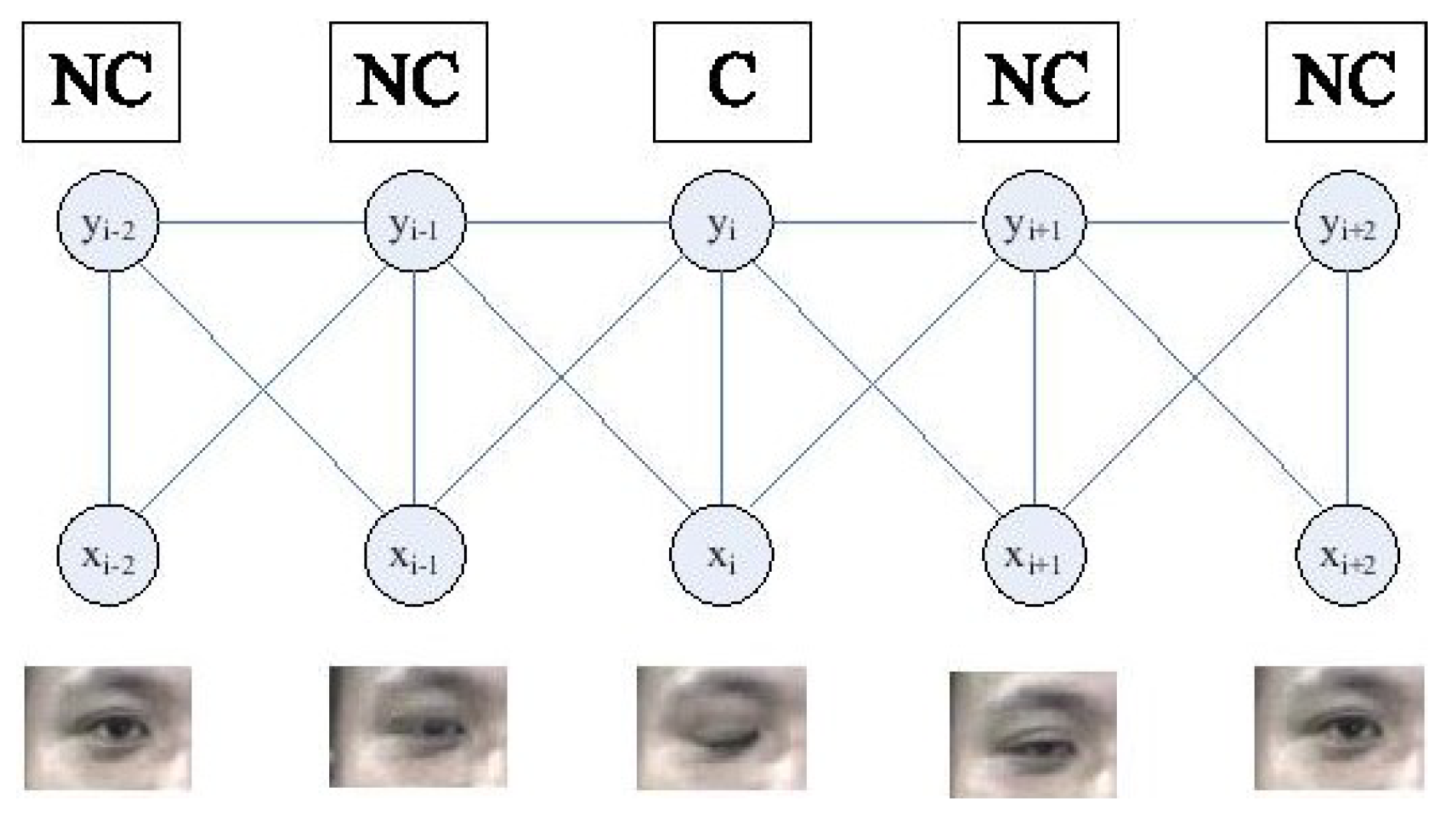
2.2.1. Motion-Based Methods
(a) Nonintrusive motion-based methods
(b) Intrusive motion-based methods
2.2.2. Liveness Detection Based on Remote PhotoPlethysmoGraphy (rPPG)
2.3. Texture Cue-Based Methods
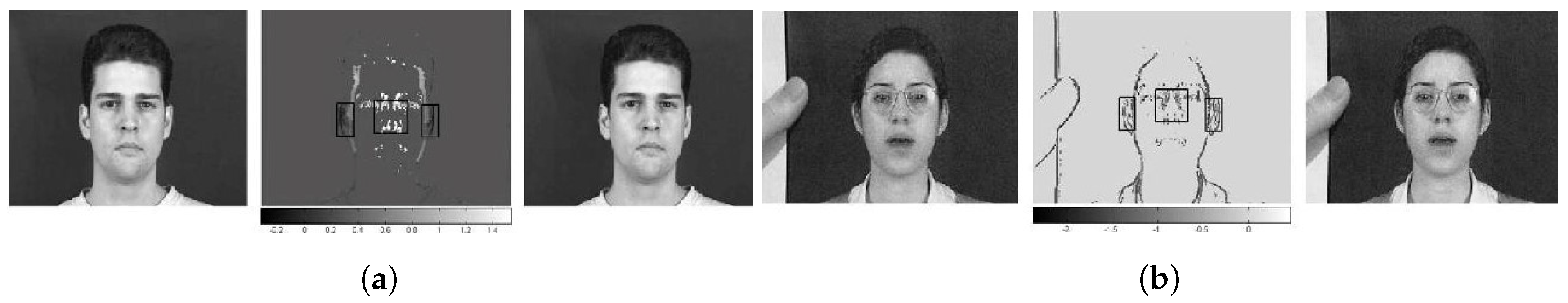
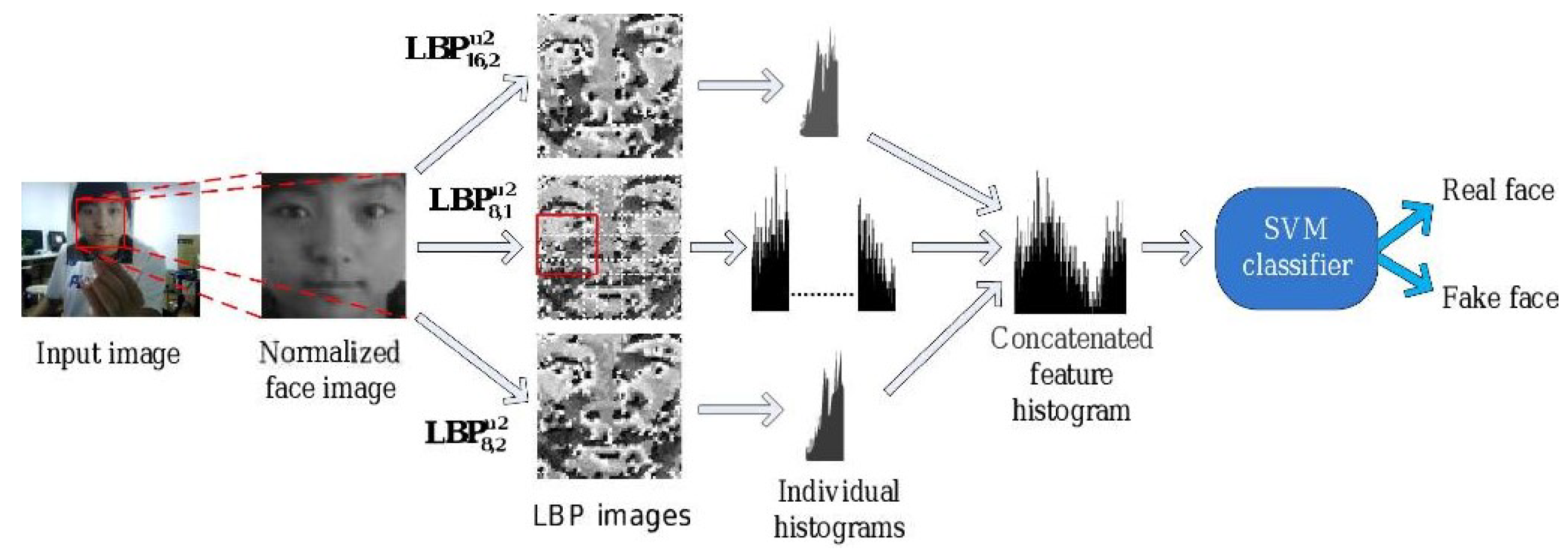
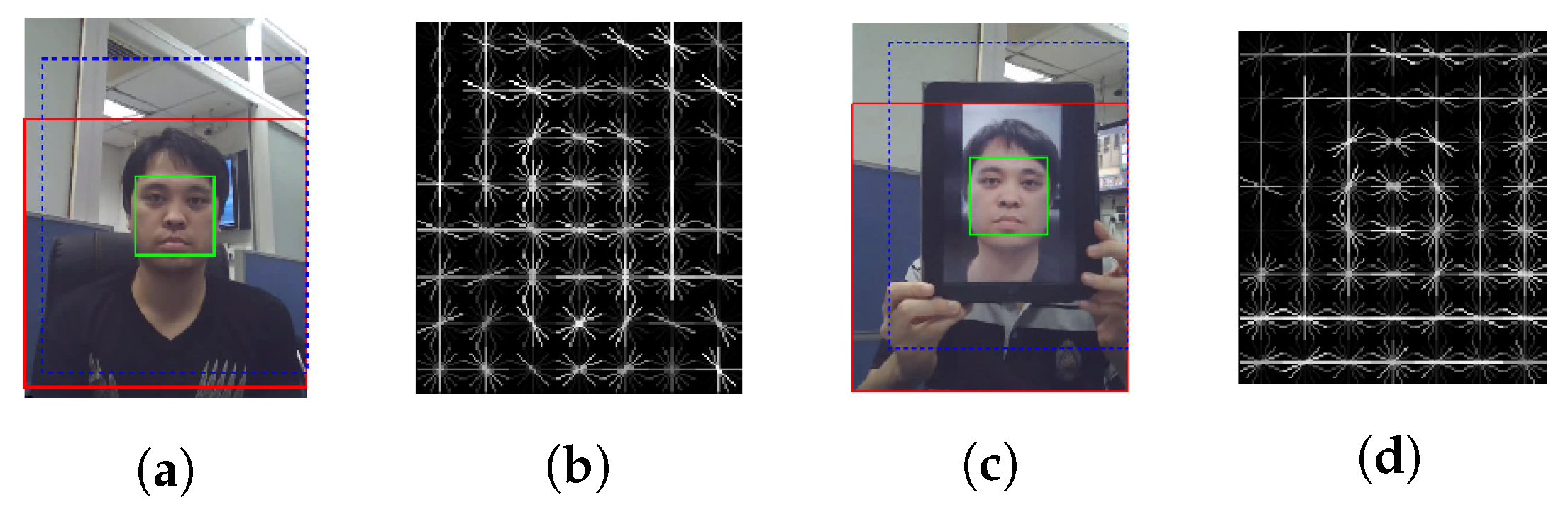
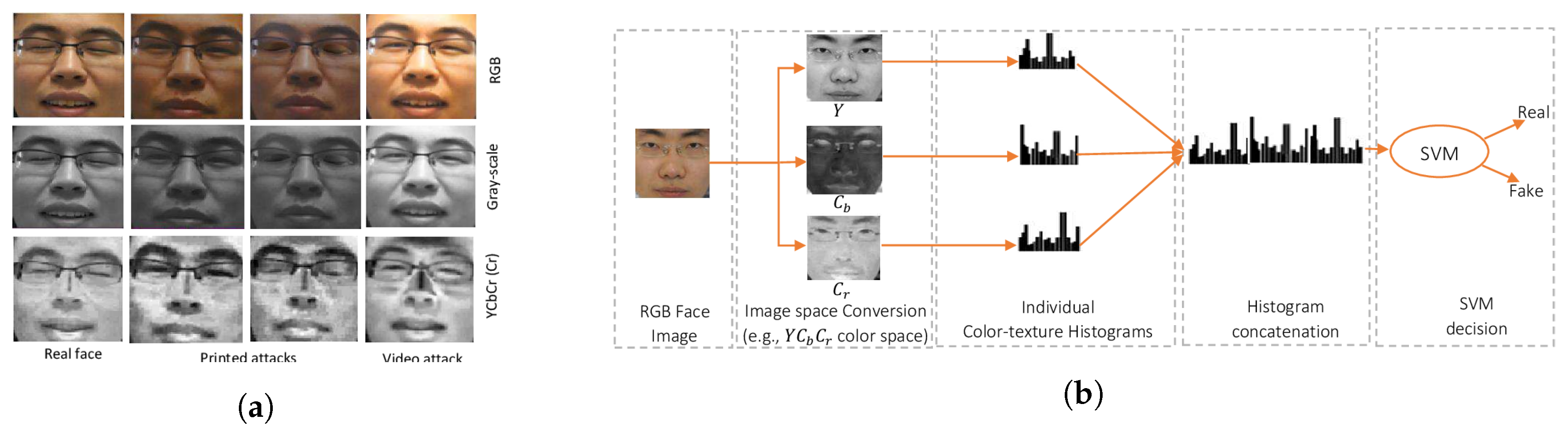
2.3.1. Static Texture-Based Methods
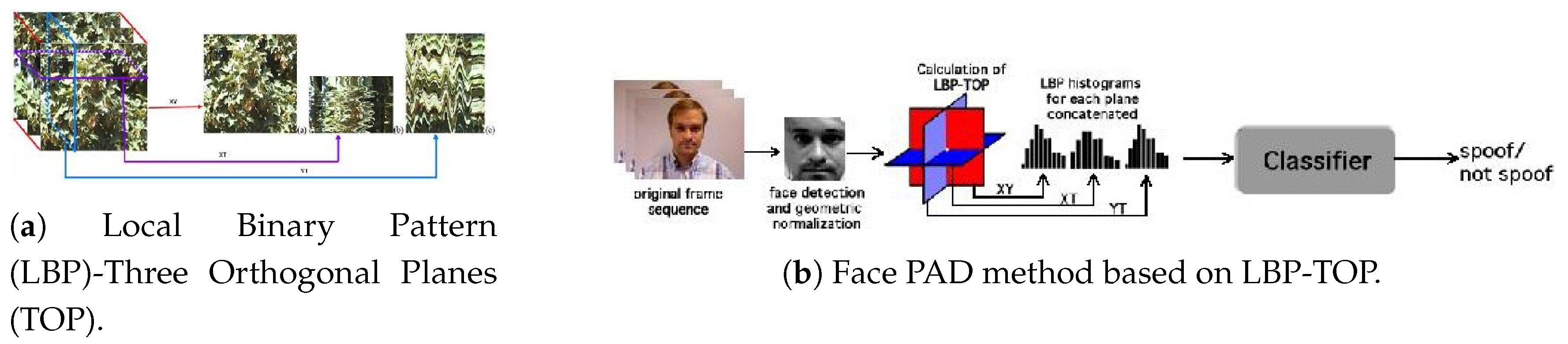
2.3.2. Dynamic Texture-Based Methods
2.4. 3D Geometric Cue-Based Methods
2.4.1. 3D Shape-Based Methods
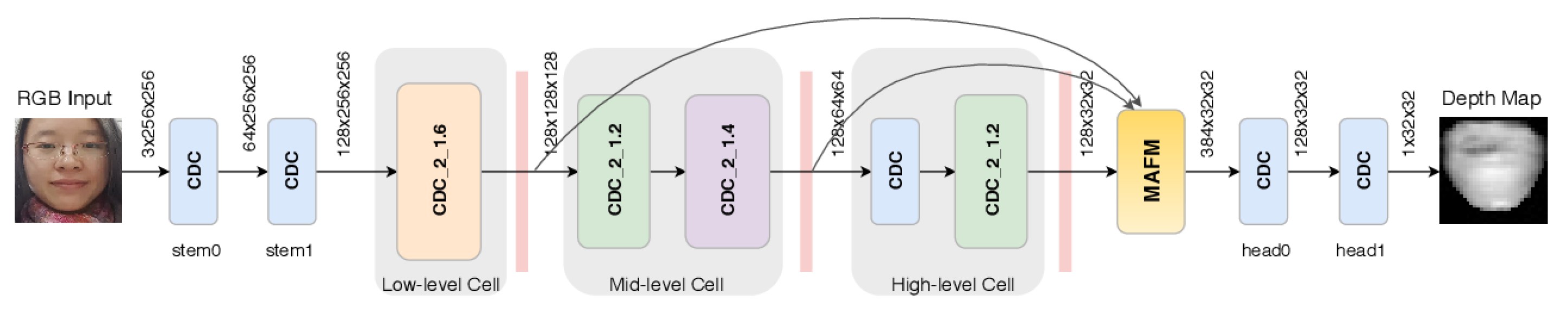
2.4.2. Pseudo-Depth Map-Based Methods
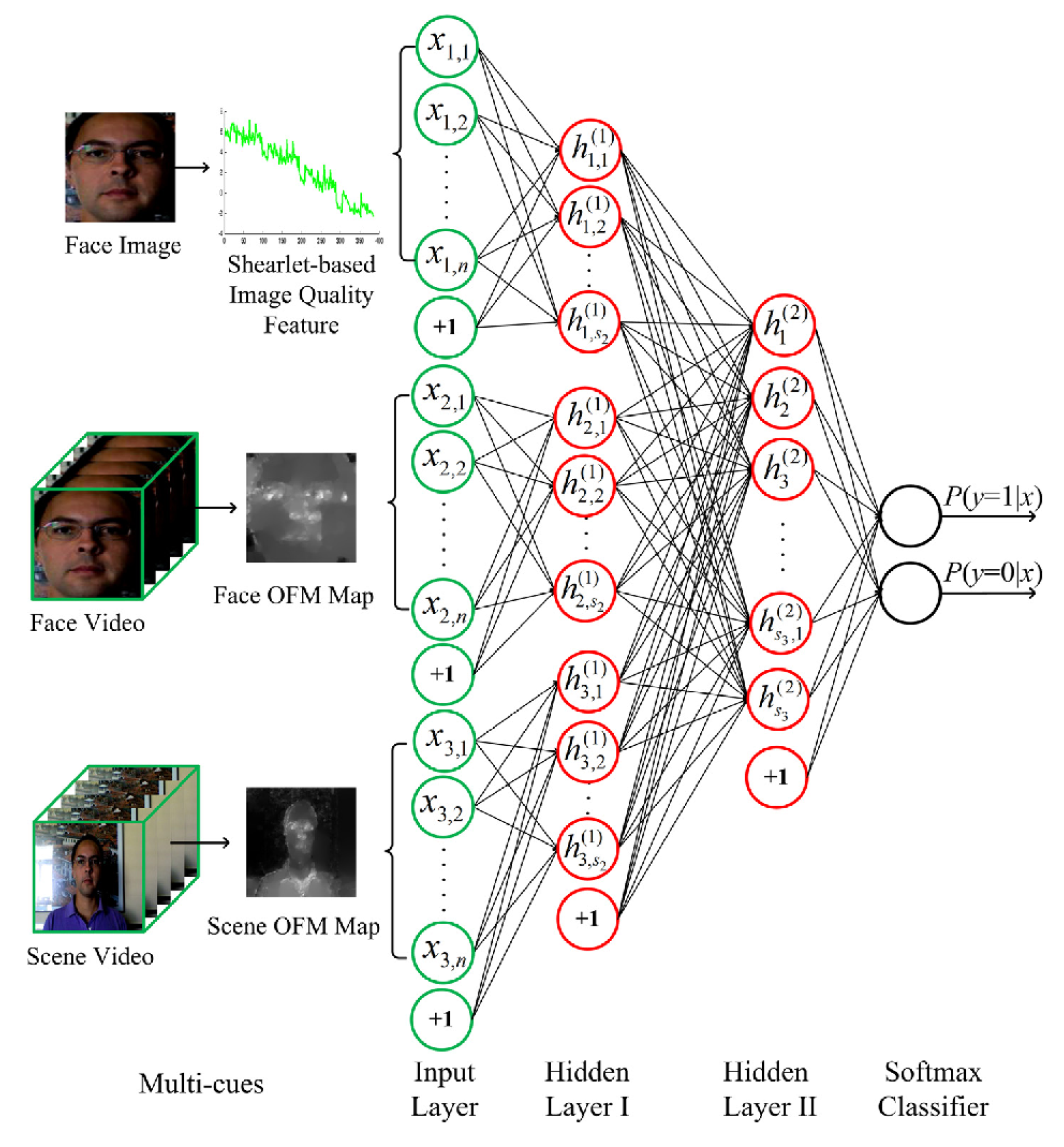
2.5. Multiple Cue-Based Methods
2.5.1. Fusion of Liveness Cue and Texture Cues
2.5.2. Fusion of Liveness and 3D Geometric Cues
2.5.3. Fusion of Texture and 3D Geometric Cues
2.6. New Trends in PAD Methods
- the proposal of new cues to detect the face artifact (e.g., the pseudo-depth maps described in Section 2.4.2);
- learning the most appropriate neural networks architectures for facial PAD (e.g., using Neural Architecture Search (NAS) (see hereafter Section 2.6.1)); and
- address of the generalization issues, especially towards types of attacks that are not (or insufficiently) represented in the learning dataset. Generalization issues can be (at least partially) addressed using zero/few shot learning (see Section 2.6.2) and/or domain adaptation and adversarial learning (see Section 2.6.3).
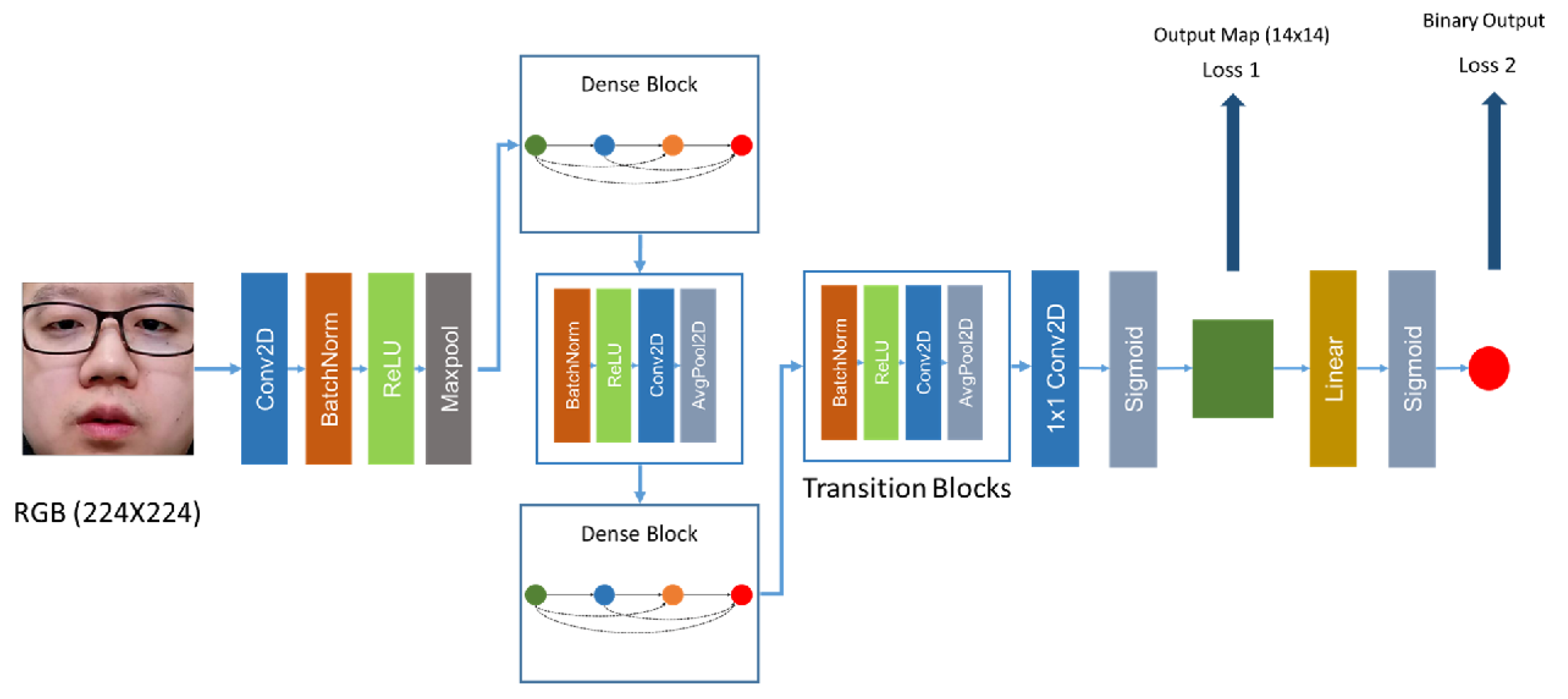
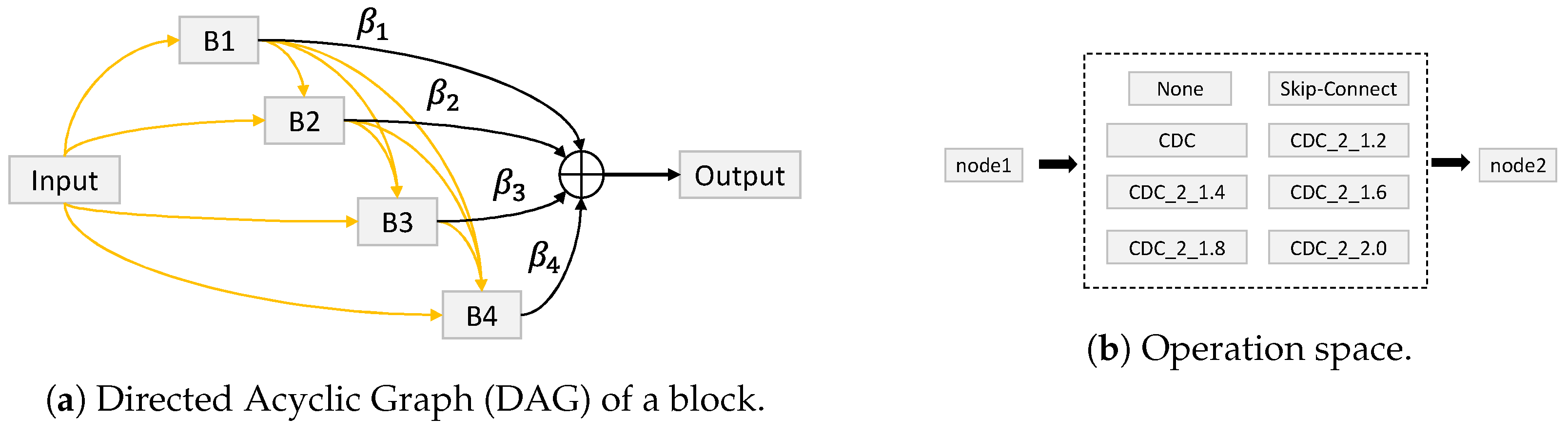
2.6.1. Neural Architecture Search (NAS)-Based PAD Methods
2.6.2. Zero/Few-Shot Learning Based PAD Methods
2.6.3. Domain Adaption-Based PAD Methods
3. Existing Face Anti-Spoofing Datasets and Their Major Limitations
3.1. Some Useful Definitions
- the set of “genuine faces”, that contains photos or videos of the genuine users’ faces (authentic faces of the alive genuine users), and
- the set of “PA documents”, containing photos or videos of the PAI (printed photo, video replay, 3D mask, etc.)
3.2. Brief Overview of the Existing Datasets
3.3. Major Limitations of the Existing Datasets
3.4. Detailed Description of the Existing Datasets
- 4 kinds of translations: vertical, horizontal, toward the sensor and toward the background
- 2 kinds of rotations: along the horizontal axis and along the vertical axis (in-depth rotation)
- 2 kinds of bending: along the horizontal and vertical axis (inward and outward)
4. Evaluation
4.1. Evaluation Protocol
(a) Dataset division
(b) Intra-database vs. inter-database evaluation
4.2. Evaluation Metric
4.3. Comparison and Evaluation of the Results
4.3.1. Intra-Database Evaluation on Public Benchmarks
- Protocol 1 aims to test the PAD methods under different environmental conditions (illumination and background);
- Protocol 2’s objective is to test the generalization abilities of the methods learnt using different PAIs;
- Protocol 3 aims to test the generalization across the different acquisition devices (i.e., using Leave One Camera Out (LOCO) protocol to test the method over six smartphones); and
- Protocol 4 is the most challenging scenario, as it combines the three previous protocols to simulate real-world operational conditions.
- Protocol 1 deals with variations in facial pose and expression;
- Protocol 2 tests the model over different spoof mediums (PAIs) for video replay; and
- Protocol 3 tests the methods over different PAs, e.g., learning from photo attacks and testing on video attacks and vice versa.
4.3.2. Cross-Database Evaluation on Public Benchmarks
5. Discussion
- all hand-crafted features show a limited generalization ability, as they are not powerful enough to capture all the possible variations in the acquisition conditions; and
- the features learned by deep/wide neural networks are of very high dimensions, compared to the limited size of the training data.
5.1. Current Trends and Perspectives
5.2. Obfuscation Face PAD
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turk, M.; Pentland, A. Eigenfaces for recognition. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1991, 3, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Taigman, Y.; Yang, M.; Ranzato, M.; Wolf, L. Deepface: Closing the gap to human-level performance in face verification. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1701–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deeply learned face representations are sparse, selective, and robust. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 2892–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Face Recognition. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Swansea, UK, 7–10 September 2015; Volume 1, p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Schroff, F.; Kalenichenko, D.; Philbin, J. Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 8–10 June 2015; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, M.; Raj, B.; Song, L. Sphereface: Deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition. In Proceedings of the the CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017; Volume 1, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Guo, J.; Xue, N.; Zafeiriou, S. Arcface: Additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4690–4699. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Columbus, OH, USA, 24–27 June 2014; pp. 1891–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Ramesh, M.; Berg, T.; Learned-Miller, E. Labeled Faces in the Wild: A Database for Studying Face Recognition in Unconstrained Environments; Technical Report, Technical Report 07-49; University of Massachusetts: Amherst, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, L.; Hassner, T.; Maoz, I. Face recognition in unconstrained videos with matched background similarity. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 529–534. [Google Scholar]
- de Luis-García, R.; Alberola-López, C.; Aghzout, O.; Ruiz-Alzola, J. Biometric identification systems. Signal Process. 2003, 83, 2539–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.; Oliveira, L.; Pamplona, M.; Papa, J. How far did we get in face spoofing detection? Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 72, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 Biometrics. Information Technology—Biometric Presentation Attack Detection—Part 1: Frame-Work; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Yuen, P.C.; Zhao, G. A 3D mask face anti-spoofing database with real world variations. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, LasVegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Bigun, J. Verifying liveness by multiple experts in face biometrics. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J. A face antispoofing database with diverse attacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, New Delhi, India, 30 March–1 April 2012; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.urmesurveillance.com (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Marcel, S.; Nixon, M.S.; Li, S.Z. Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Face liveness detection by learning multispectral reflectance distributions. In Proceedings of the Face and Gesture 2011, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–24 March 2011; pp. 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Tirunagari, S.; Poh, N.; Windridge, D.; Iorliam, A.; Suki, N.; Ho, A.T. Detection of face spoofing using visual dynamics. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbally, J.; Satta, R. Three-dimensional and two-and-a-half-dimensional face recognition spoofing using three-dimensional printed models. IET Biom. 2016, 5, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogmus, N.; Marcel, S. Spoofing face recognition with 3D masks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagorio, A.; Tistarelli, M.; Cadoni, M.; Fookes, C.; Sridharan, S. Liveness detection based on 3D face shape analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF), Lisbon, Portugal, 4–5 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S. The casia nir-vis 2.0 face database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Portland, OR, USA, 25–27 June 2013; pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Marcel, S. What you can’t see can help you-extended-range imaging for 3d-mask presentation attack detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Ortega, J.; Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Tome, P. Time analysis of pulse-based face anti-spoofing in visible and NIR. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 544–552. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.Z. Face anti-spoofing: Multi-spectral approach. In Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 83–102. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Wu, M. TIR/VIS correlation for liveness detection in face recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Seville, Spain, 29–31 August 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, D.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K. Face spoof detection with image distortion analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jourabloo, A.; Liu, X. Learning Deep Models for Face Anti-Spoofing: Binary or Auxiliary Supervision. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Learn convolutional neural network for face anti-spoofing. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1408.5601. [Google Scholar]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Hadid, A. Face anti-spoofing based on color texture analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 2636–2640. [Google Scholar]
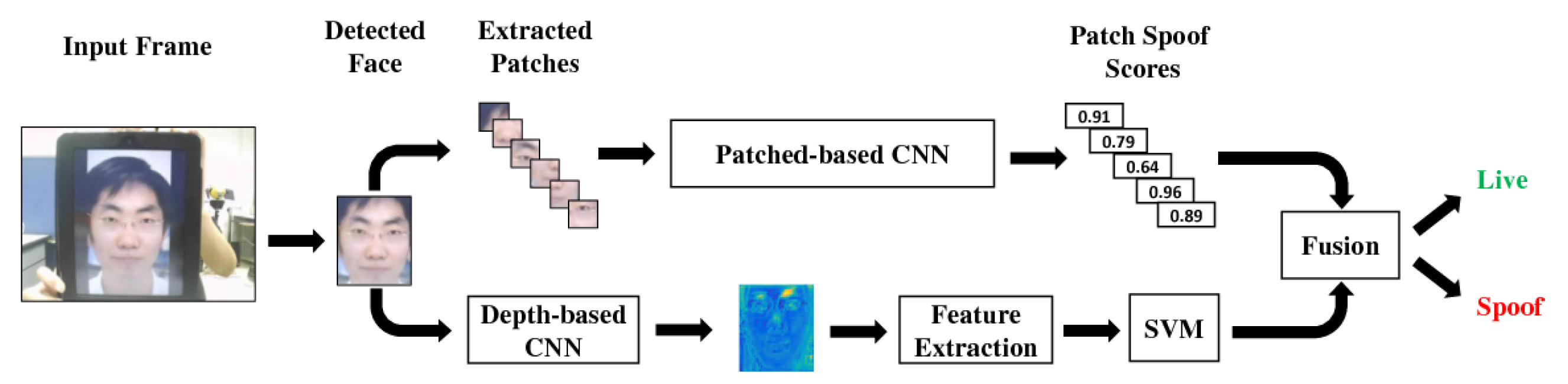
- Atoum, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jourabloo, A.; Liu, X. Face anti-spoofing using patch and depth-based CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, CO, USA, 1–4 October 2017; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Chingovska, I.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. On the effectiveness of local binary patterns in face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 6–7 September 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Pazo, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Vazquez-Fernandez, E.; Marcel, S. The replay-mobile face presentation-attack database. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 21–23 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandra, R.; Busch, C. Presentation attack detection methods for face recognition systems: A comprehensive survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2017, 50, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ortega, J.; Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Galbally, J. Introduction to face presentation attack detection. In Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 187–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Mohammadi, A.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. Recent advances in face presentation attack detection. In Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Lao, S. Eyeblink-based anti-spoofing in face recognition from a generic webcamera. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–20 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Pan, G.; Wu, Z.; Lao, S. Blinking-based live face detection using conditional random fields. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Seoul, Korea, 27–29 August 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 252–260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Tan, T.; Jain, A.K. Live face detection based on the analysis of fourier spectra. Biometric technology for human identification. Int. Soc. Opt. Photonics 2004, 5404, 296–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Bigun, J. Evaluating liveness by face images and the structure tensor. In Proceedings of the Fourth IEEE Workshop on Automatic Identification Advanced Technologies (AutoID’05), Buffalo, NY, USA, USA, 17–18 October 2005; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Bigun, J. Non-intrusive liveness detection by face images. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Jiang, W. A liveness detection method for face recognition based on optical flow field. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 18–19 November 2009; pp. 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kollreider, K.; Fronthaler, H.; Faraj, M.I.; Bigun, J. Real-time face detection and motion analysis with application in “liveness” assessment. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2007, 2, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Komulainen, J.; Zhao, G.; Yuen, P.C.; Pietikäinen, M. Generalized face anti-spoofing by detecting pulse from face videos. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 4244–4249. [Google Scholar]
- Nowara, E.M.; Sabharwal, A.; Veeraraghavan, A. Ppgsecure: Biometric presentation attack detection using photopletysmograms. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yuen, P.C.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, G. 3D mask face anti-spoofing with remote photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–16 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. Face liveness detection from a single image with sparse low rank bilinear discriminative model. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2010, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 504–517. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, B.; Michelassi, C.; Rocha, A. Face liveness detection under bad illumination conditions. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belguim, 11–14 September 2011; pp. 3557–3560. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Ng, T.T.; Gao, X.; Shi, Y.Q. Is physics-based liveness detection truly possible with a single image? In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, France, 30 May–2 June 2010; pp. 3425–3428. [Google Scholar]
- Määttä, J.; Hadid, A.; Pietikäinen, M. Face spoofing detection from single images using micro-texture analysis. In Proceedings of the Biometrics (IJCB), 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics, Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 October 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, N.; Dugelay, J.L. Countermeasure for the protection of face recognition systems against mask attacks. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Shanghai, China, 22–26 April 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kose, N.; Dugelay, J.L. Shape and texture based countermeasure to protect face recognition systems against mask attacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogmus, N.; Marcel, S. Spoofing 2D face recognition systems with 3D masks. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference of the BIOSIG Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 4–6 September 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, K.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K.; Ott, G. Live face video vs. spoof face video: Use of moiré patterns to detect replay video attacks. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Phuket, Thailand, 19–22 May 2015; pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Hadid, A. Face spoofing detection using colour texture analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Määttä, J.; Hadid, A.; Pietikäinen, M. Face spoofing detection from single images using texture and local shape analysis. IET Biom. 2012, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Face liveness detection with component dependent descriptor. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Komulainen, J.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Context based face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Arlington, VA, USA, 29 September–2 October 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
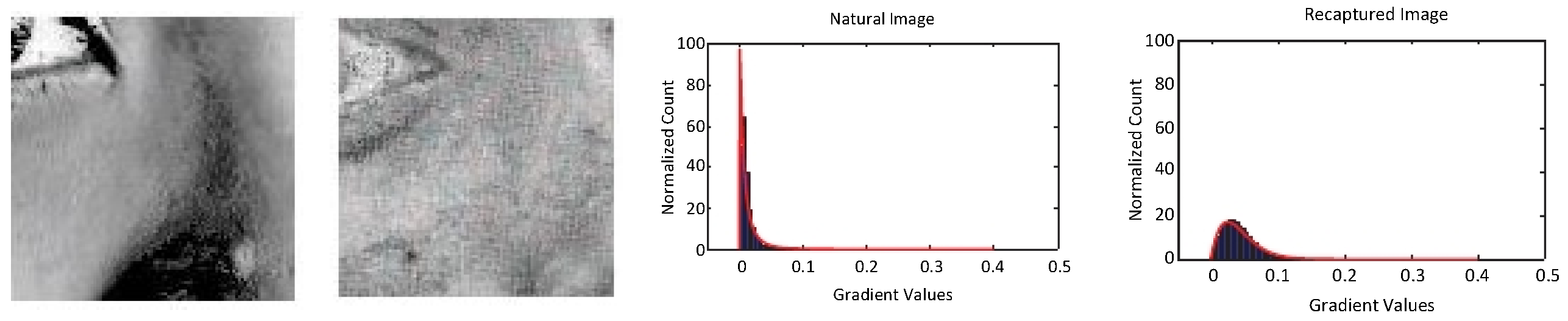
- Galbally, J.; Marcel, S. Face Anti-spoofing Based on General Image Quality Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR ’14), Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 1173–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Galbally, J.; Marcel, S.; Fierrez, J. Image quality assessment for fake biometric detection: Application to iris, fingerprint, and face recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 710–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K. Secure face unlock: Spoof detection on smartphones. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 2268–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K. Cross-database face antispoofing with robust feature representation. In Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition, Shenyang, China, 7–9 November 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Feng, X.; Boulkenafet, Z.; Xia, Z.; Li, M.; Hadid, A. An original face anti-spoofing approach using partial convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 Sixth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Oulu, Finland, 12–15 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jourabloo, A.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Face de-spoofing: Anti-spoofing via noise modeling. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 290–306. [Google Scholar]
- George, A.; Marcel, S. Deep pixel-wise binary supervision for face presentation attack detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas Pereira, T.; Anjos, A.; De Martino, J.M.; Marcel, S. LBP-TOP based countermeasure against face spoofing attacks. In Proceedings of the ACCV, Daejeon, Korea, 5–9 November 2012; pp. 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas Pereira, T.; Komulainen, J.; Anjos, A.; De Martino, J.M.; Hadid, A.; Pietikäinen, M.; Marcel, S. Face liveness detection using dynamic texture. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2014, 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Pereira, T.; Anjos, A.; De Martino, J.M.; Marcel, S. Can face anti-spoofing countermeasures work in a real world scenario? In Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
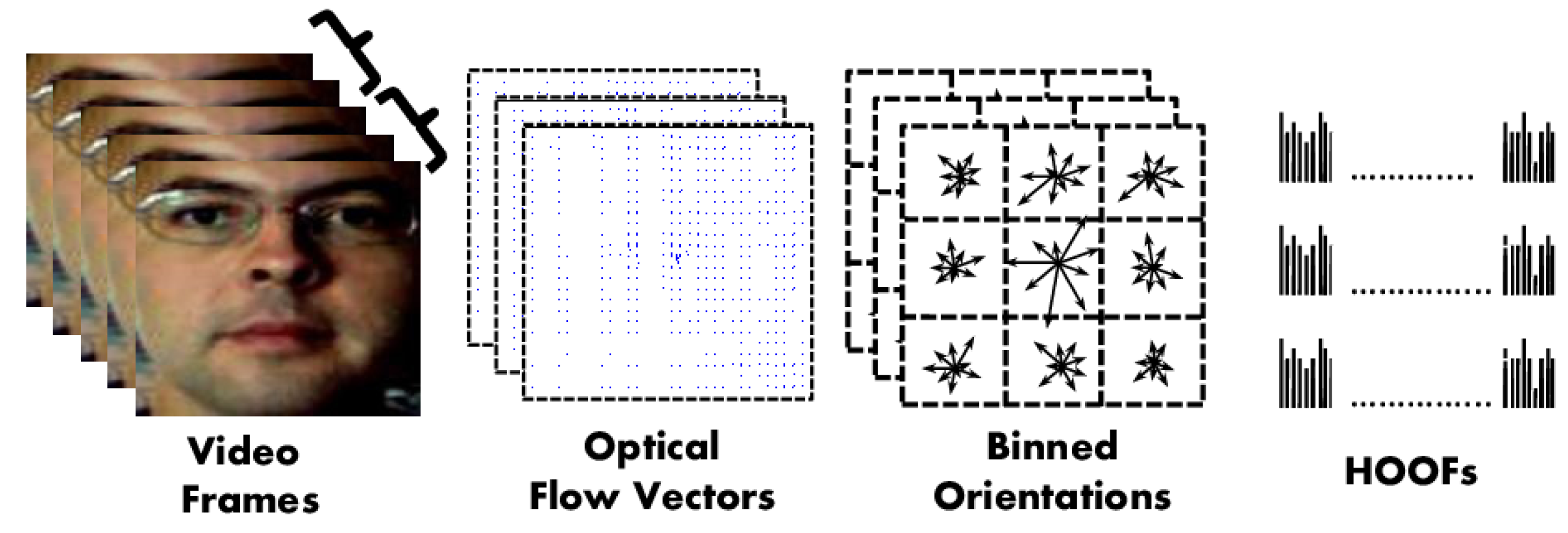
- Bharadwaj, S.; Dhamecha, T.I.; Vatsa, M.; Singh, R. Computationally efficient face spoofing detection with motion magnification. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, Portland, OR, USA, 23–24 June 2013; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
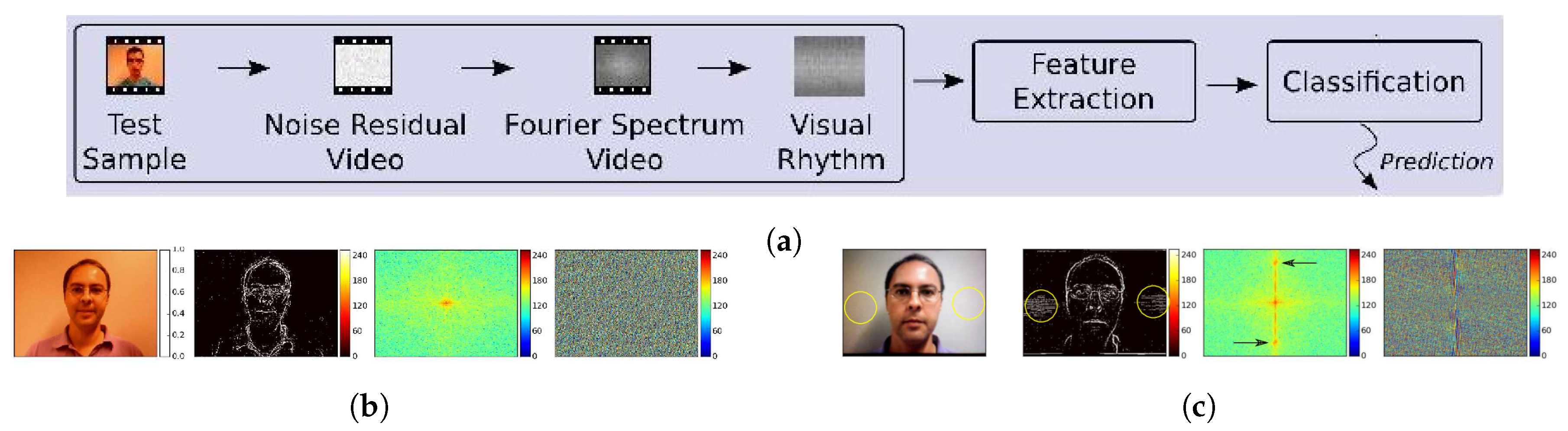
- da Silva Pinto, A.; Pedrini, H.; Schwartz, W.; Rocha, A. Video-based face spoofing detection through visual rhythm analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 25th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, Ouro Preto, Brazil, 22–25 August 2012; pp. 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, A.; Schwartz, W.R.; Pedrini, H.; de Rezende Rocha, A. Using visual rhythms for detecting video-based facial spoof attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.; Pedrini, H.; Schwartz, W.R.; Rocha, A. Face spoofing detection through visual codebooks of spectral temporal cubes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 4726–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
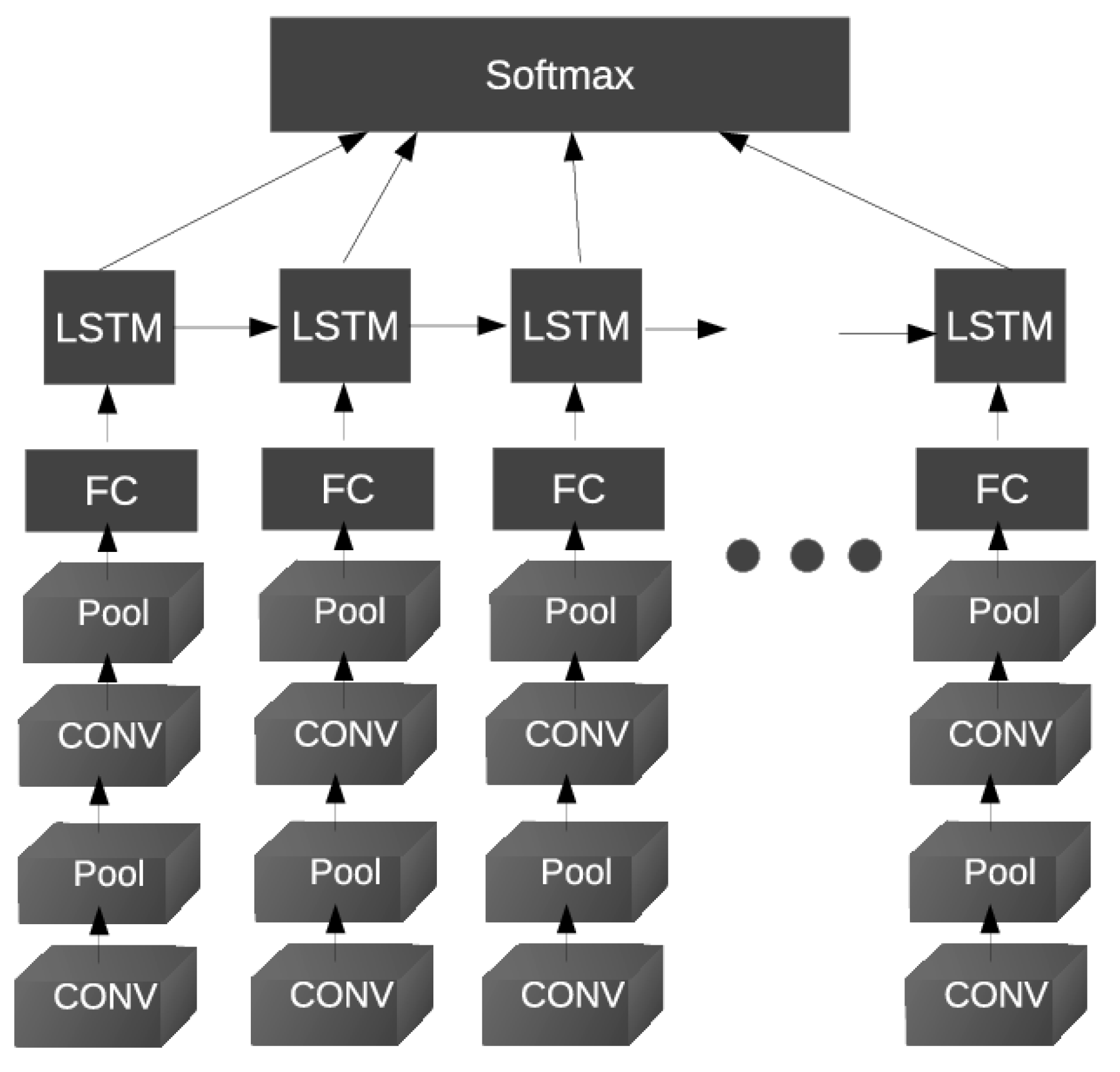
- Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, W. Learning temporal features using LSTM-CNN architecture for face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–6 November 2015; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Luo, W.; Bao, L.; Gao, Y.; Gong, D.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Face anti-spoofing: Model matters, so does data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3507–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Face liveness detection using 3D structure recovered from a single camera. In Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on biometrics (ICB), Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, G.; Wan, J.; Lei, Z. Exploiting temporal and depth information for multi-frame face anti-spoofing. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.05118. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, G. Searching central difference convolutional networks for face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5295–5305. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Sun, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y. Monocular camera-based face liveness detection by combining eyeblink and scene context. Telecommun. Syst. 2011, 47, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Po, L.M.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Yuan, F.; Cheung, T.C.H.; Cheung, K.W. Integration of image quality and motion cues for face anti-spoofing: A neural network approach. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 38, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikisins, O.; Mohammadi, A.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. On effectiveness of anomaly detection approaches against unseen presentation attacks in face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Crete, Greece, 4–7 June 2018; pp. 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Arashloo, S.R.; Kittler, J.; Christmas, W. An anomaly detection approach to face spoofing detection: A new formulation and evaluation protocol. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 13868–13882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
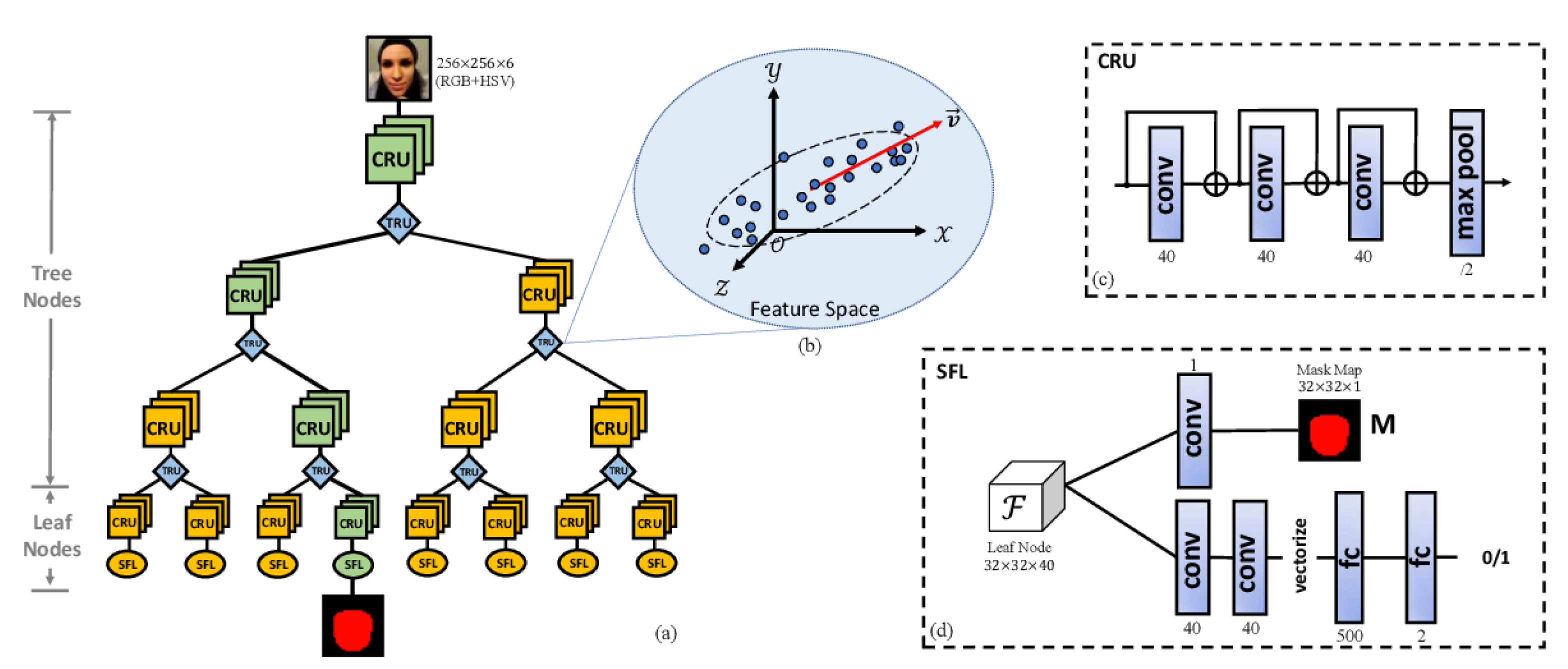
- Liu, Y.; Stehouwer, J.; Jourabloo, A.; Liu, X. Deep tree learning for zero-shot face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4680–4689. [Google Scholar]
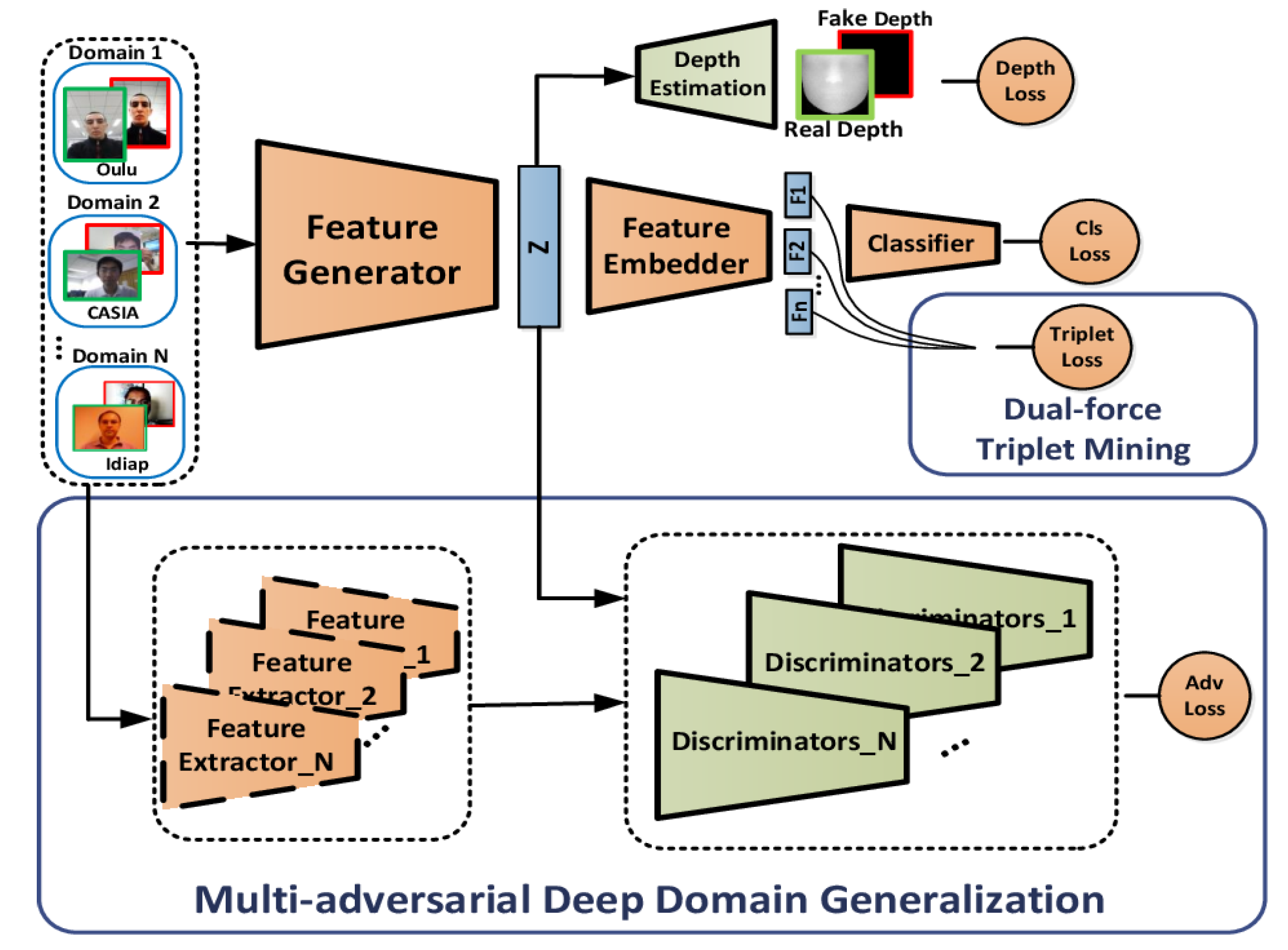
- Shao, R.; Lan, X.; Li, J.; Yuen, P. Multi-Adversarial Discriminative Deep Domain Generalization for Face Presentation Attack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10015–10023. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, J.; Nandhakumar, N. On the computation of motion from sequences of images—A review. Proc. IEEE 1988, 76, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarbayejani, A.; Starner, T.; Horowitz, B.; Pentland, A. Visually controlled graphics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1993, 15, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bigün, J.; Granlund, G.H.; Wiklund, J. Multidimensional orientation estimation with applications to texture analysis and optical flow. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karson, C.N. Spontaneous eye-blink rates and dopaminergic systems. Brain 1983, 106, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; Volume 1, p. I. [Google Scholar]
- Vapnik, V. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Howcroft, E. How Faking Videos Became Easy and Why That’s So Scary; Bloomberg: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chesney, R.; Citron, D. Deepfakes and the new disinformation war: The coming age of post-truth geopolitics. Foreign Aff. 2019, 98, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, C.M.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nahavandi, S. Deep learning for deepfakes creation and detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11573. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, S.; Luettin, J. Audio-visual speech modeling for continuous speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2000, 2, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepfakes Web. Available online: https://deepfakesweb.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Metaxas, D.N. Stackgan++: Realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1947–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FaceApp. Available online: https://www.faceapp.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- FakeApp. Available online: https://www.fakeapp.org/ (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Fernandes, S.; Raj, S.; Ortiz, E.; Vintila, I.; Salter, M.; Urosevic, G.; Jha, S. Predicting Heart Rate Variations of Deepfake Videos using Neural ODE. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ciftci, U.A.; Demir, I.; Yin, L. Fakecatcher: Detection of synthetic portrait videos using biological signals. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Bao, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wen, F.; Guo, B. Face x-ray for more general face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5001–5010. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.T.; Rubanova, Y.; Bettencourt, J.; Duvenaud, D.K. Neural ordinary differential equations. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 6571–6583. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, M.; Nayar, S.K. Generalization of the Lambertian model and implications for machine vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1995, 14, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Triggs, B. Enhanced local texture feature sets for face recognition under difficult lighting conditions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1635–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Zuiderveld, K. Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization. In Graphics Gems; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 474–485. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.T.; Ikeuchi, K. Separating reflection components of textured surfaces using a single image. In Digitally Archiving Cultural Objects; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 353–384. [Google Scholar]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, R.; Xiang, S.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Face detection based on multi-block lbp representation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Gold Coast, Australia, 20–23 February 2007; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Pietikainen, M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, B.S.; Ma, W.Y. Texture features for browsing and retrieval of image data. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1996, 18, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Efficient additive kernels via explicit feature maps. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, V.; Marin-Jimenez, M.; Zisserman, A. Progressive search space reduction for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ojansivu, V.; Heikkilä, J. Blur insensitive texture classification using local phase quantization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image and Signal Processing, Cherbourg-Octeville, France, 1–3 July 2008; pp. 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik, S.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Ng, T.T.; Qiu, B.; Chang, S.F. Single-view recaptured image detection based on physics-based features. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Singapore, 19–23 July 2010; pp. 1469–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Crete, F.; Dolmiere, T.; Ladret, P.; Nicolas, M. The blur effect: Perception and estimation with a new no-reference perceptual blur metric. In Proceedings of the Human Vision and Electronic Imaging XII. International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 January–1 February 2007; Volume 6492, p. 64920I. [Google Scholar]
- Marziliano, P.; Dufaux, F.; Winkler, S.; Ebrahimi, T. A no-reference perceptual blur metric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, New York, NY, USA, 22–25 September 2002; Volume 3, p. III. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Ma, W.Y. Automatic classification of photographs and graphics. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–12 July 2006; pp. 973–976. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.; Nandakumar, K.; Ross, A. Score normalization in multimodal biometric systems. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 2270–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, D.; Lei, Z.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Learning face representation from scratch. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.7923. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Y.; Rubinstein, M.; Shih, E.; Guttag, J.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W. Eulerian video magnification for revealing subtle changes in the world. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2012, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.; Ravichandran, A.; Hager, G.; Vidal, R. Histograms of oriented optical flow and binet-cauchy kernels on nonlinear dynamical systems for the recognition of human actions. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1932–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, S.S.; Kim, H.; Jung-Rim, K.; Oh, S.; Sull, S. Fast text caption localization on video using visual rhythm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Visual Information Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Guimar, S.J.F.; Couprie, M.; Leite, N.J.; Araujo, D.A. A method for cut detection based on visual rhythm. In Proceedings of the XIV Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image, Florianopolis, Brazil, 15–18 October 2001; pp. 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.S.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivic, J.; Zisserman, A. Video Google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 14–17 October 2003; p. 1470. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, P.J.; Li, L.; Juniper, M.P.; Pust, O. Applications of the dynamic mode decomposition. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 2011, 25, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragih, J.M.; Lucey, S.; Cohn, J.F. Deformable model fitting by regularized landmark mean-shift. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2011, 91, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.I.; Sturm, P. Triangulation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1997, 68, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourabloo, A.; Liu, X. Large-pose face alignment via CNN-based dense 3D model fitting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4188–4196. [Google Scholar]
- Jourabloo, A.; Liu, X. Pose-invariant face alignment via CNN-based dense 3D model fitting. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 124, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, F.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Joint 3d face reconstruction and dense alignment with position map regression network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 534–551. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Blanz, V.; Vetter, T. Face recognition based on fitting a 3d morphable model. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T. Graphics System Shadow Generation Using a Depth Buffer. U.S. Patent 5043922, 27 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. Counter-measures to photo attacks in face recognition: A public database and a baseline. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 October 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Socolinsky, D.A.; Selinger, A.; Neuheisel, J.D. Face recognition with visible and thermal infrared imagery. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2003, 91, 72–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komulainen, J.; Boulkenafet, Z.; Akhtar, Z. Review of face presentation attack detection competitions. In Handbook of Biometric Anti-Spoofing; Springer: Berlin/Heisenberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 291–317. [Google Scholar]
- Chakka, M.M.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S.; Tronci, R.; Muntoni, D.; Fadda, G.; Pili, M.; Sirena, N.; Murgia, G.; Ristori, M.; et al. Competition on counter measures to 2-d facial spoofing attacks. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 October 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chingovska, I.; Yang, J.; Lei, Z.; Yi, D.; Li, S.Z.; Kahm, O.; Glaser, C.; Damer, N.; Kuijper, A.; Nouak, A.; et al. The 2nd competition on counter measures to 2D face spoofing attacks. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yi, D.; Li, S.Z. Face liveness detection by exploring multiple scenic clues. In Proceedings of the 2012 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Guangzhou, China, 5–7 December 2012; pp. 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Altun, Y.; Tsochantaridis, I.; Hofmann, T. Hidden Markov support vector machines. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-03), Washington, DC, USA, 21–24 August 2003; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Benlamoudi, A.; Samai, D.; Bekhouche, S.E.; Ouafi, A.; Dornaika, F.; Taleb-Ahmed, A.; Qin, L. A competition on generalized software-based face presentation attack detection in mobile scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, CO, USA, 1–4 October 2017; pp. 688–696. [Google Scholar]
- Easley, G.; Labate, D.; Lim, W.Q. Sparse directional image representations using the discrete shearlet transform. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2008, 25, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Po, L.M.; Xu, X.; Feng, L. No-reference image quality assessment using statistical characterization in the shearlet domain. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Beyond Pixels: Exploring New Representations and Applications for Motion Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Martens, J.; Dahl, G.; Hinton, G. On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 1139–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07261. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, A.; Lim, T.; Ritchie, J.M.; Weston, N. Smash: One-shot model architecture search through hypernetworks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.05344. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Le, Q.V. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01578. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8697–8710. [Google Scholar]
- Real, E.; Moore, S.; Selle, A.; Saxena, S.; Suematsu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Le, Q.; Kurakin, A. Large-scale evolution of image classifiers. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01041. [Google Scholar]
- Real, E.; Aggarwal, A.; Huang, Y.; Le, Q.V. Regularized evolution for image classifier architecture search. In Proceedings of the aaai Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 4780–4789. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Simonyan, K.; Yang, Y. Darts: Differentiable architecture search. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.09055. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, G.J.; Tian, Q.; Xiong, H. Pc-darts: Partial channel connections for memory-efficient differentiable architecture search. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.05737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N. Neural architecture search for deep face recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09523. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.; Hong, X.; Zhao, G. Video action recognition via neural architecture searching. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, R.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Auto-reid: Searching for a part-aware convnet for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3750–3759. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. Nas-fpn: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7036–7045. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yao, T.; Liu, D.; Mei, T. Customizable architecture search for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11641–11650. [Google Scholar]
- Tax, D.M.J. One-Class Classification: Concept Learning in the Absence of Counter-examples. Ph.D. thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delf, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Saenko, K.; Kulis, B.; Fritz, M.; Darrell, T. Adapting visual category models to new domains. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Torralba, A.; Efros, A.A. Unbiased look at dataset bias. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1521–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.Z.; Hospedales, T.M. Deeper, broader and artier domain generalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5542–5550. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Jialin Pan, S.; Wang, S.; Kot, A.C. Domain generalization with adversarial feature learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5400–5409. [Google Scholar]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Hadid, A. OULU-NPU: A mobile face presentation attack database with real-world variations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 612–618. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Zhao, C.; Wan, J.; Escalera, S.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.Z. A dataset and benchmark for large-scale multi-modal face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 919–928. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Hoi, S.C.; He, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mei, T.; Luo, J. Retrieval-based face annotation by weak label regularized local coordinate coding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I.; Seitz, S.M.; Miller, D.; Brossard, E. The megaface benchmark: 1 million faces for recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4873–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Song, F.; Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, S. Enhanced pictorial structures for precise eye localization under incontrolled conditions. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1621–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Anjos, A.; Chakka, M.M.; Marcel, S. Motion-based counter-measures to photo attacks in face recognition. IET Biom. 2013, 3, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dantcheva, A.; Ross, A. Automatic facial makeup detection with application in face recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, F.; Finkelstein, A. Pairedcyclegan: Asymmetric style transfer for applying and removing makeup. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 40–48. [Google Scholar]

















| PAD Methods | Subtypes | PAs |
|---|---|---|
| Liveness cue-based | Nonintrusive motion-based | Photo attack (except cut photo attack) |
| Intrusive motion-based | Photo attack (except cut photo attack) | |
| Video replay attacks (except sophisticated DeepFakes) | ||
| rPPG-based | Photo attack | |
| “Low quality” video replay attacks | ||
| 3D mask attack (low/high quality) | ||
| Texture cue-based | Static texture-based
Dynamic texture-based | Photo attack |
| Video replay attack | ||
| 3D mask attack (low quality) | ||
| 3D Geometry cue-based | 3D shape-based Pseudo-depth map-based | Photo attack Video replay attack |
| Multiple cues-based | Liveness (Motion) + Texture | Photo attack |
| Video replay attack | ||
| Liveness + 3D Geometry (rPPG + Pseudo-depth map) | Photo attack | |
| Video replay attack | ||
| 3D mask attack (low/high quality) | ||
| Texture + 3D Geometry (Patched-base texture + Pseudo-depth map) | Photo attack Video replay attack |
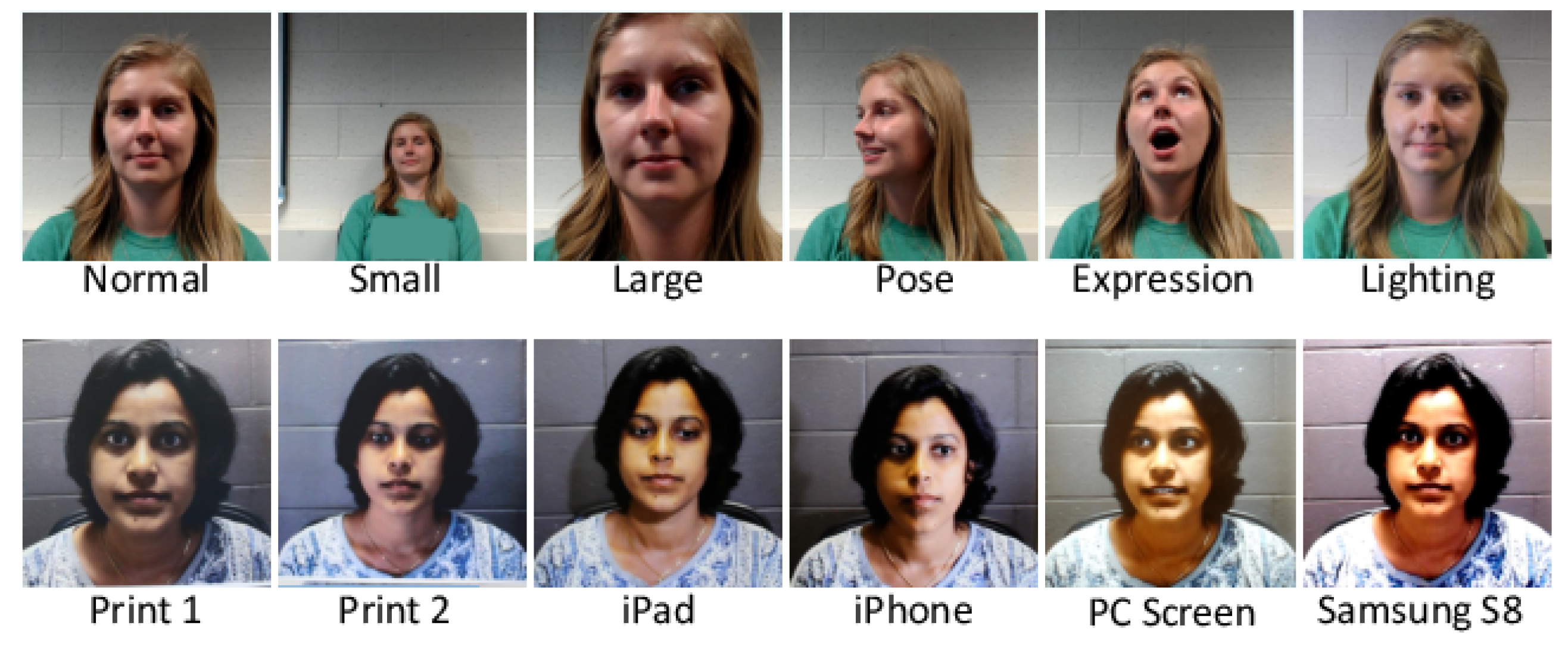
| Database | Year | ♯ Subj. | Ethnicity | PA Type(s) | Document ♯ & Type(s) Images (I)/Videos (V) | PAI | Pose | Expression | Biometric System Acquisition Device | PA Acquisition Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUAA [52] | 2010 | 15 | Asian | Printed photos Warped photos | 5105/7509 (I) | A4 paper | Frontal | No | Webcam (640 × 480) | Webcam (640 × 480) |
| PRINT-ATTACK [147] | 2011 | 50 | Caucasian | Printed photos | 200/200 (V) | A4 paper | Frontal | No | Macbook Webcam (320 × 340) | Cannon PowerShot SX150 (12.1 MP) |
| CASIA-FASD [19] | 2012 | 50 | Asian | Printed photos Warped photos Cut photos Video replay | 200/450 (V) | Copper paper iPad 1 (1024 × 768) | Frontal | No | Sony NEX-5 (1280 × 720) USB Camera (640 × 480) | Sony NEX-5 (1280 × 720) Webcam (640 × 480) |
| REPLAY-ATTACK [37] | 2012 | 50 | Caucasian 76% Asian 22% African 2% | Printed photos Photo display 2× video replays a | 200/1000 (V) | A4 paper iPad 1 (1024 × 768) iPhone 3GS (480 × 320) | Frontal | No | Macbook Webcam (320 × 340) | Canon PowerShot SX 150 (12.1MP) iPhone 3GS |
| 3DMAD [25,58] | 2013 | 17 | Caucasian | 2× 3D masks b | 170/85 (V) | Paper-crafted mask Hard resin mask (ThatsMyFace.com) | Frontal | No | Kinect (RGB camera) (Depth sensor) | — |
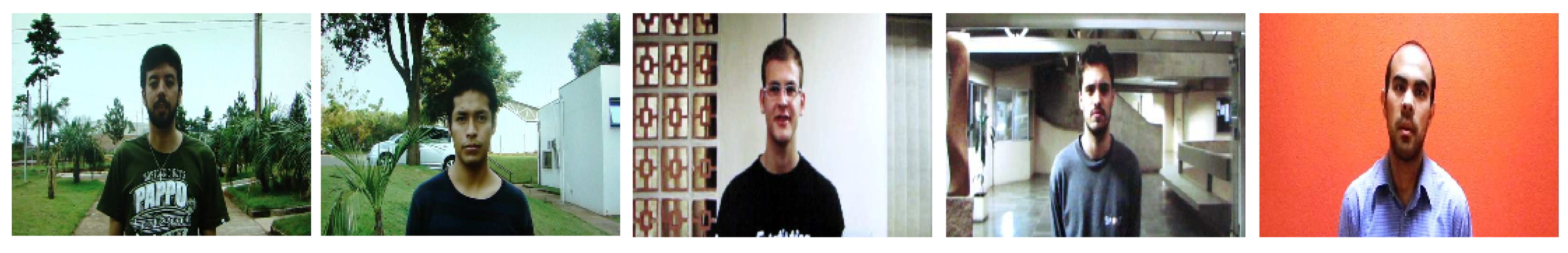
| MSU-MFSD [32] | 2015 | 35 | Caucasian 70% Asian 28% African 2% | Printed photos 2× video replays | 110/330 (V) | A3 paper iPad Air (2048 × 1536) iPhone 5s (1136 × 640) | Frontal | No | Nexus 5 (built-in camera software 720 × 480) Macbook Air (640 × 480) | Cannon 550D (1920 × 1088) iPhone 5s (1920 × 1080) |
| MSU-RAFS [59] | 2015 | 55 | Caucasian 44% Asian 53% African 3% | Video replays | 55/110 (V) | Macbook (1280 × 800) | Frontal | No | Nexus 5 (rear: 3264 × 2448) iPhone 6 (rear: 1920 × 1080) | The biometric system acquistion devices used in MSU-MFSD, CASIA-FASD, REPLAY-ATTACK. |
| UAD [76] | 2015 | 404 | Caucasian 44% Asian 53% African 3% | 7× video replays | 808/16,268 (V) | 7 display devices | Frontal | No | 6 different cameras (no moible phone) (1366 × 768) | 6 different cameras (no moible phone) (1366 × 768) |
| MSU-USSA [66] | 2016 | 1140 | Diverse set (from web faces database from the [183]) | Printed photos Photo display 3× video replays | 1140/9120 (V) | White paper (11 × 8.5 paper) Macbook (2080 × 1800) Nexus 5 (1920 × 1080) Tablet (1920 × 1200) | Frontal | Yes | Nexus 5 front: 1280 × 960) (rear: 3264 × 2448) iPhone 6 (rear: 1920 × 1080) | Same as MSU-RAFS Cameras used to capture celebrities’ photos are unknown. |
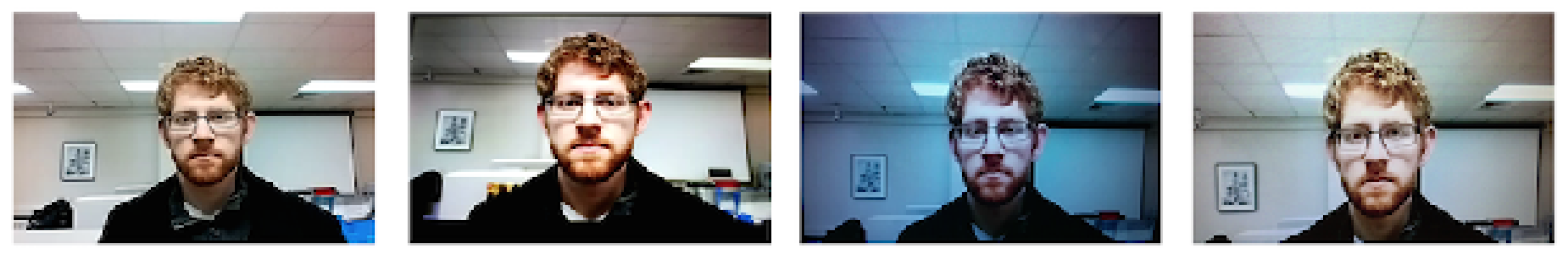
| OULU-NPU [181] | 2017 | 55 | Caucasian 5% Asian 95% | Printed photos 2× video replays | 1980/3960 (V) | A3 glossy paper Dell display (1280 × 1024) Macbook (2560 × 1600) | Frontal | No | Samsung Galaxy S6 (rear: 16 MP) | Samsung Galaxy S6 (front: 5 MP) HTC Desire EYE (front: 13 MP) MEIZU X5 (front: 5 MP) ASUS Zenfone Selfi (front: 13 MP) Sony XPERIA C5 (front: 13 MP) OPPO N3 (front: 16 MP) |
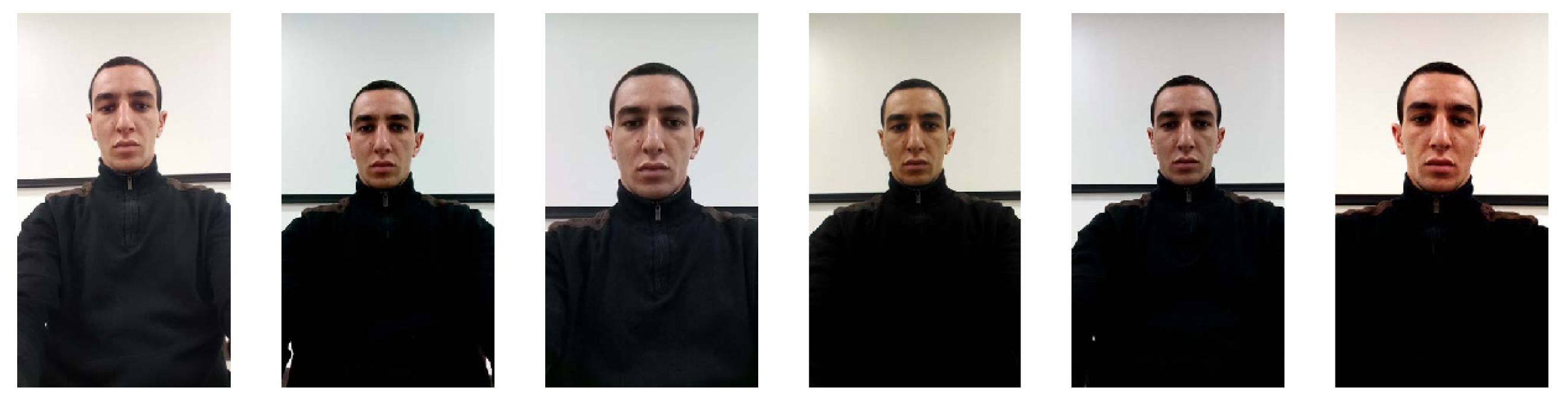
| SiW [33] | 2018 | 165 | Caucasian 35% Asian 35% African American 7% Indian 23% | Printed photos (high/low-quality photos) 4× video replays | 1320/3300 (V) | Printed paper (High/low-quality) Samsung Galaxy S8 iPhone 7 iPad Pro PC screen(Asus MB168B) | [] | Yes | Camera (1920 × 1080) | Camera (1920 × 1080) Camera (5184 × 3456) |
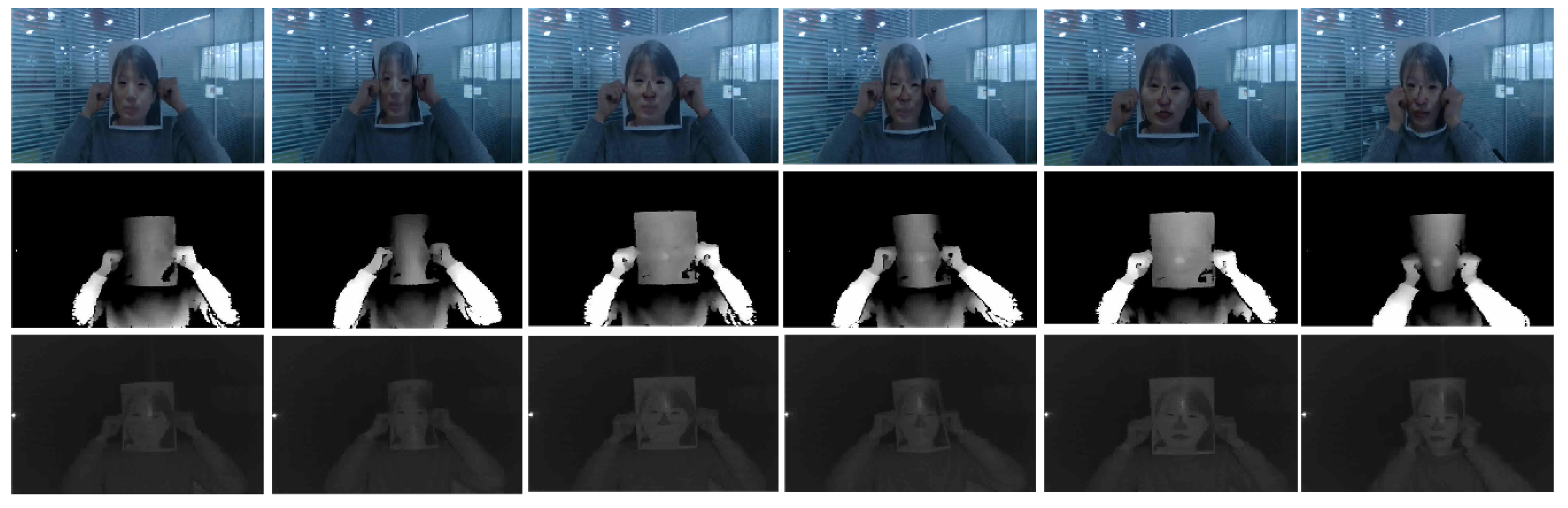
| CASIA-SURF [182] | 2019 | 1000 | Asian | Flat-cut/Warped-cut photos (eyes, nose, mouth) | 3000/18,000 (V) | A4 paper | [] | No | RealSense (RGB camera) (1280 × 720) (Depth sensor) (640 × 480) (IR sensor) (640 × 480) | RealSense (RGB camera) (1280 × 720) (Depth sensor) (640 × 480) (IR sensor) (640 × 480) |
| Method | Year | Feature | Cues | EER (%) | HTER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DoG [19] | 2012 | DoG | Texture (static) | 17.00 | - |
| LBP [37] | 2012 | LBP | Texture (static) | - | 18.21 |
| LBP-TOP [72] | 2014 | LBP | Texture (dynamic) | 10.00 | - |
| Yang et al. [34] | 2014 | CNN | Texture (static) | 4.92 | 4.95 |
| Spectrual Cubes [77] | 2015 | FourrierSpectrum +codebook | Texture (dynamic) | 14.00 | - |
| DMD [23] | 2015 | LBP | Texture (dynamic) | 21.80 | - |
| Color texture [35] | 2015 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 6.20 | - |
| LSTM-CNN [78] | 2015 | CNN | Texture (dynamic) | 5.17 | 5.93 |
| Color LBP [60] | 2016 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 3.20 | - |
| Fine-tuned VGG-Face [68] | 2016 | CNN | Texture (static) | 5.20 | - |
| DPCNN [68] | 2016 | CNN | Texture (static) | 4.50 | - |
| Patch-based CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Texture (static) | 4.44 | 3.78 |
| Depth-based CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Depth | 2.85 | 2.52 |
| Patch-Depth CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Texture+Depth | 2.67 | 2.27 |
| Method | Year | Feature | Cues | EER (%) | HTER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBP [37] | 2012 | LBP | Texture (static) | 13.90 | 13.87 |
| Motion Mag [74] | 2013 | HOOF | Texture (dynamic) | - | 1.25 |
| LBP-TOP [72] | 2014 | LBP | Texture (dynamic) | 7.88 | 7.60 |
| Yang et al. [34] | 2014 | CNN | Texture (static) | 2.54 | 2.14 |
| Spectral Cubes [77] | 2015 | Fourier Spectrum +codebook | Texture (dynamic) | - | 2.80 |
| DMD [23] | 2015 | LBP | Texture (dynamic) | 5.30 | 3.80 |
| Color texture [35] | 2015 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 0.40 | 2.90 |
| Moire pattern [59] | 2015 | LBP+SIFT | Texture (static) | - | 3.30 |
| Color LBP [60] | 2016 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 0.10 | 2.20 |
| Fine-tuned VGG-Face [68] | 2016 | CNN | Texture (static) | 8.40 | 4.30 |
| DPCNN [68] | 2016 | CNN | Texture (static) | 2.90 | 6.10 |
| Patch-based CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Texture (static) | 2.50 | 1.25 |
| Depth-based CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Depth | 0.86 | 0.75 |
| Patch-Depth CNN [36] | 2017 | CNN | Texture+Depth | 0.79 | 0.72 |
| Protocol | Method | Year | Feature | Cues | APCER (%) | BPCER (%) | ACER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CPqD [155] | 2017 | Inception-v3 [188] | Texture (static) | 2.9 | 10.8 | 6.9 |
| 1 | GRADIANT [155] | 2017 | LBP | Texture (HSV/dynamic) | 1.3 | 12.5 | 6.9 |
| 1 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| 1 | FaceDs [69] | 2018 | CNN | Texture (Quality/static) | 1.2 | 1.7 | 1.5 |
| 1 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | 1.2 | 2.5 | 1.9 |
| 1 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | 2.5 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| 1 | DeepPixBis [70] | 2019 | DenseNet [131] | Texture | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| 1 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | 0.4 | 1.7 | 1.0 |
| 1 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| 2 | MixedFASNet [155] | 2017 | DNN | Texture (HSV/static) | 9.7 | 2.5 | 6.1 |
| 2 | GRADIANT [155] | 2017 | LBP | Texture (HSV/dynamic) | 3.1 | 1.9 | 2.5 |
| 2 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| 2 | FaceDs [69] | 2018 | CNN | Texture (Quality/static) | 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.3 |
| 2 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | 4.2 | 0.3 | 2.2 |
| 2 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | 1.7 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
| 2 | DeepPixBis [70] | 2019 | DenseNet [131] | Texture (static) | 11.4 | 0.6 | 6.0 |
| 2 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | 1.5 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| 2 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | 1.8 | 0.8 | 1.3 |
| 3 | MixedFASNet [155] | 2017 | DNN | Texture (HSV/static) | |||
| 3 | GRADIANT [155] | 2017 | LBP | Texture (HSV/dynamic) | |||
| 3 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | |||
| 3 | FaceDs [69] | 2018 | CNN | Texture (Quality/static) | |||
| 3 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | |||
| 3 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | |||
| 3 | DeepPixBis [70] | 2019 | DenseNet [131] | Texture | |||
| 3 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | |||
| 3 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | |||
| 4 | Massy_HNU [155] | 2017 | LBP | Texture (HSV+YCbCr) | |||
| 4 | GRADIANT [155] | 2017 | LBP | Texture (HSV/dynamic) | |||
| 4 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | |||
| 4 | FaceDs [69] | 2018 | CNN | Texture (Quality/static) | |||
| 4 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | |||
| 4 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | |||
| 4 | DeepPixBis [70] | 2019 | DenseNet [131] | Texture (static) | |||
| 4 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | |||
| 4 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth |
| Protocol | Method | Year | Feature | Cues | APCER (%) | BPCER (%) | ACER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | 3.58 | 3.58 | 3.58 |
| 1 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | - | - | 1.0 |
| 1 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | 0.96 | 0.50 | 0.73 |
| 1 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| 1 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| 2 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | |||
| 2 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | - | - | |
| 2 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | |||
| 2 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | |||
| 2 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | |||
| 3 | Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | |||
| 3 | STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | - | - | |
| 3 | FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | |||
| 3 | CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | |||
| 3 | CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth |
| Method | Year | Feature | Cues | Train | Test | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASIA- FASD | REPLAY- ATTACK | REPLAY- ATTACK | CASIA- FASD | ||||
| LBP [37] a | 2012 | LBP | Texture (static) | 55.9 | 57.6 | ||
| Correlation 19 [189] | 2013 | MLP | Motion | 50.2 | 47.9 | ||
| LBP-TOP [73] | 2013 | LBP | Texture (dynamic) | 49.7 | 60.6 | ||
| Motion Mag [74] | 2013 | HOOF | Texture+Motion | 50.1 | 47.0 | ||
| Yang et al. [34] | 2014 | CNN | Texture (static) | 48.5 | 45.5 | ||
| Spectral cubes [77] | 2015 | Fourier Spectrum +codebook | Texture (dynamic ) | 34.4 | 50.0 | ||
| Color texture [35] | 2015 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 47.0 | 39.6 | ||
| Color LBP [60] | 2016 | LBP | Texture (HSV/static) | 30.3 | 37.7 | ||
| Auxiliary [33] | 2018 | CNN+LSTM | Depth+rPPG | 27.6 | 28.4 | ||
| FaceDs [69] | 2018 | CNN | Texture (Quality/static) | 28.5 | 41.1 | ||
| STASN [79] | 2019 | CNN+Attention | Texture (dynamic) | 31.5 | 30.9 | ||
| FAS_TD [81] | 2019 | CNN+LSTM | Depth | 17.5 | 24.0 | ||
| CDCN [82] | 2020 | CNN | Depth | 15.5 | 32.6 | ||
| CDCN++ [82] | 2020 | NAS+Attention | Depth | 6.5 | 29.8 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ming, Z.; Visani, M.; Luqman, M.M.; Burie, J.-C. A Survey on Anti-Spoofing Methods for Facial Recognition with RGB Cameras of Generic Consumer Devices. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120139
Ming Z, Visani M, Luqman MM, Burie J-C. A Survey on Anti-Spoofing Methods for Facial Recognition with RGB Cameras of Generic Consumer Devices. Journal of Imaging. 2020; 6(12):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120139
Chicago/Turabian StyleMing, Zuheng, Muriel Visani, Muhammad Muzzamil Luqman, and Jean-Christophe Burie. 2020. "A Survey on Anti-Spoofing Methods for Facial Recognition with RGB Cameras of Generic Consumer Devices" Journal of Imaging 6, no. 12: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120139
APA StyleMing, Z., Visani, M., Luqman, M. M., & Burie, J.-C. (2020). A Survey on Anti-Spoofing Methods for Facial Recognition with RGB Cameras of Generic Consumer Devices. Journal of Imaging, 6(12), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging6120139








