Recent Trends in Compressive Raman Spectroscopy Using DMD-Based Binary Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Compressive Detection (CD) Strategies
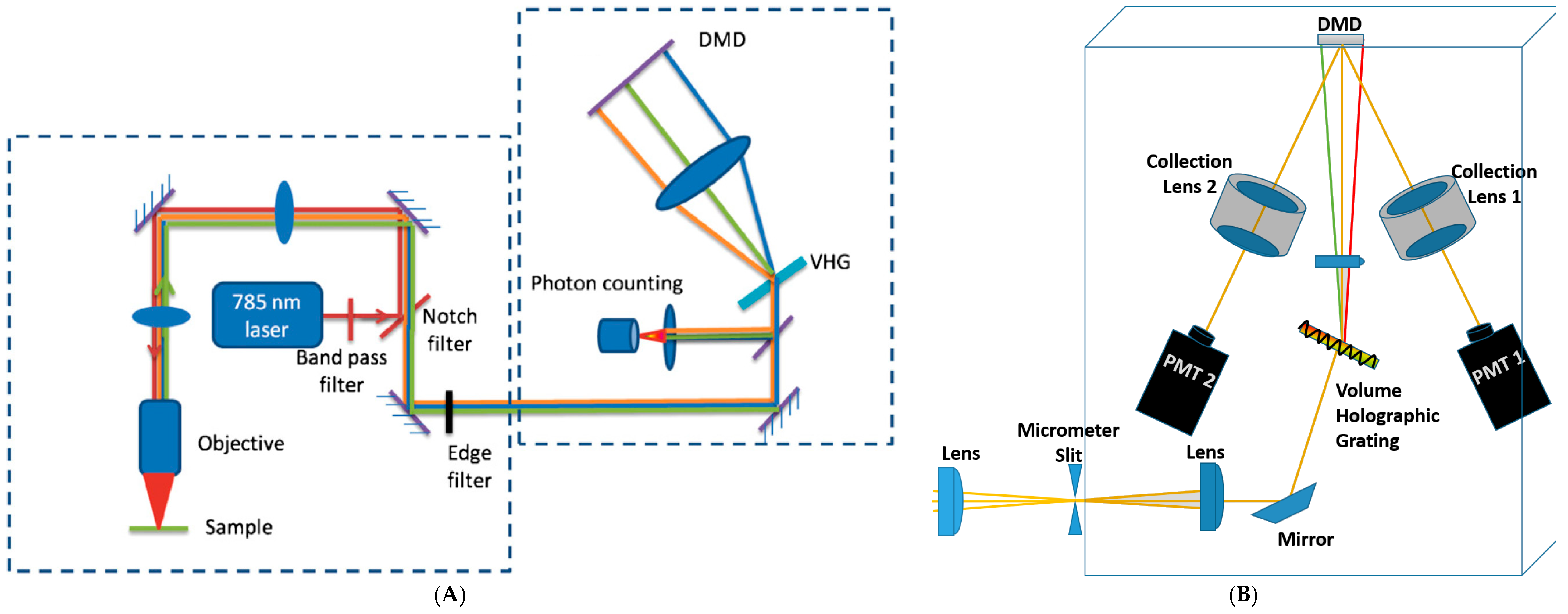
Digital Micromirror Device (DMD)-Based Compressive Raman Detection
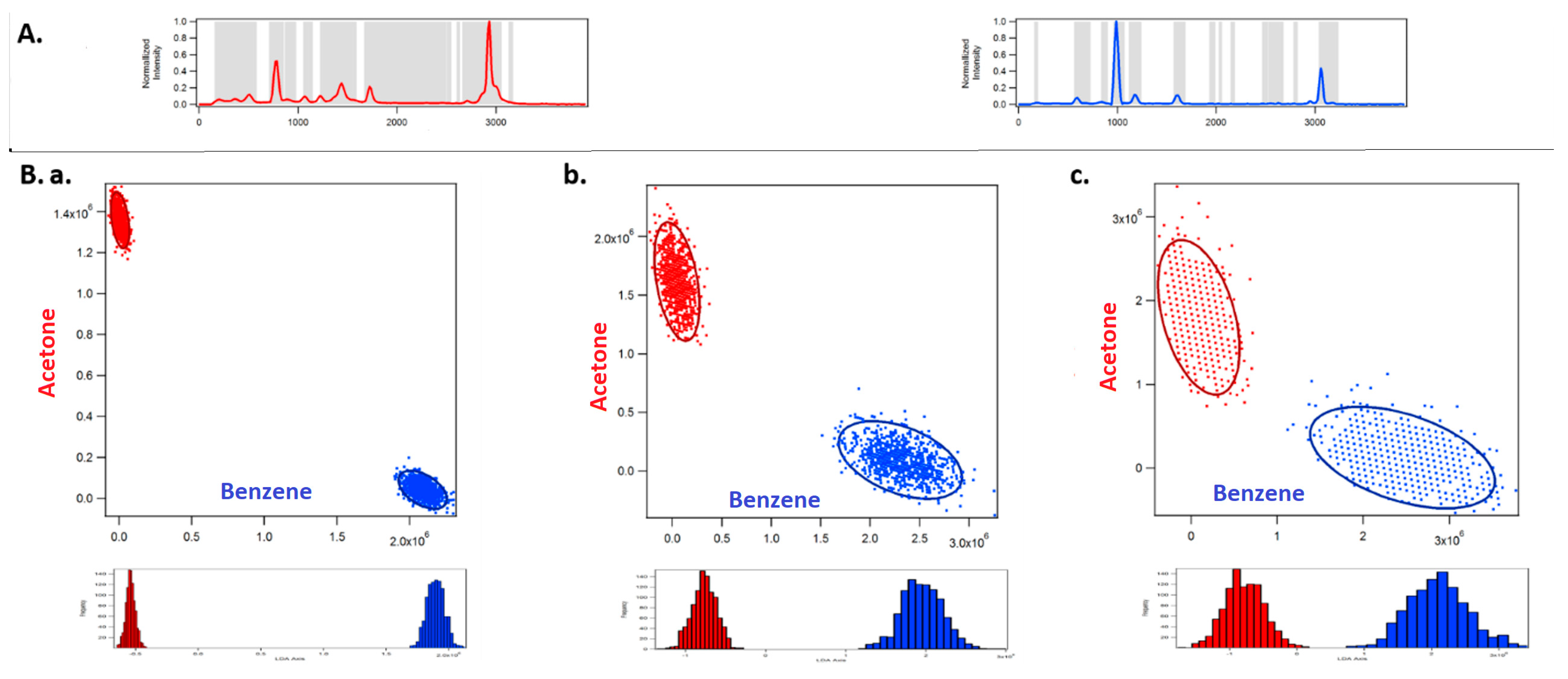
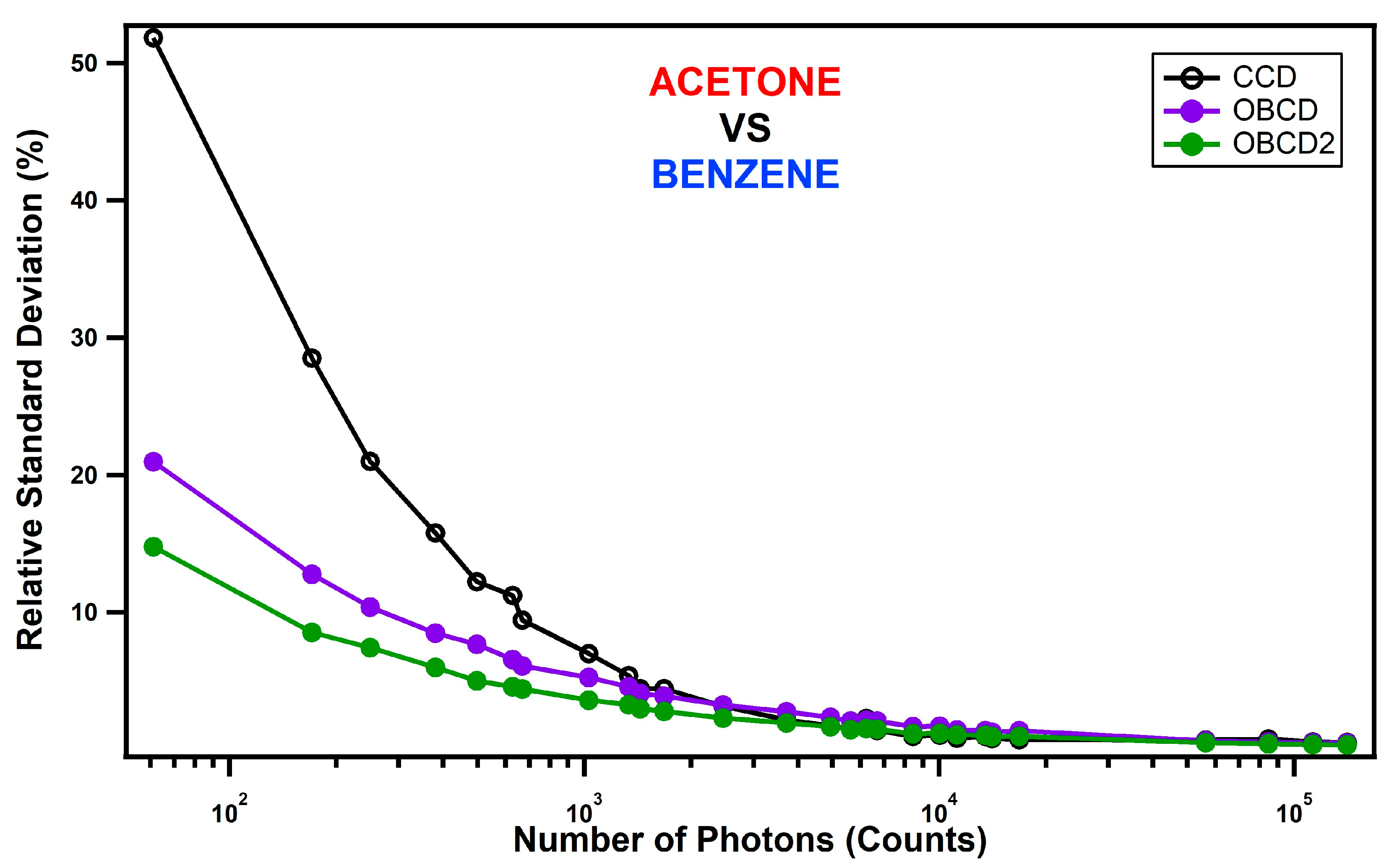
3. Assessment of DMD-Based Raman vs. CCD-Based Raman Detection
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilcox, D.S.; Buzzard, G.T.; Lucier, B.J.; Wang, P.; Ben-Amotz, D. Photon level chemical classification using digital compressive detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 755, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.M.; Hemphill, A.J.; Cebeci Maltas, D.; Zipper, M.A.; Wang, P.; Ben-Amotz, D. Multivariate Hyperspectral Raman Imaging Using Compressive Detection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5086–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quyen, N.T.; Da Silva, E.; Dao, N.Q.; Jouan, M.D. New Raman Spectrometer Using a Digital Micromirror Device and a Photomultiplier Tube Detector for Rapid On-Line Industrial Analysis. Part I: Description of the Prototype and Preliminary Results. Appl. Spectrosc. 2008, 62, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Z.J.; Strombom, S.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S. Multivariate optical computing using a digital micromirror device for fluorescence and Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 16950–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.P.; Aust, J.F.; Dobrowolski, J.A.; Verly, P.G.; Myrick, M.L. Multivariate Optical Computation for Predictive Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzunbajakava, N.; de Peinder, P.; Hooft, G.; van Gogh, A. Low-cost spectroscopy with a variable multivariate optical element. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 7302–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehrauer, O.G.; Dinh, V.C.; Mankani, B.R.; Buzzard, G.T.; Lucier, B.J.; Ben-Amotz, D. Binary Complementary Filters for Compressive Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehrauer, O.G.; Mankani, B.R.; Buzzard, G.T.; Lucier, B.J.; Ben-Amotz, D. Fluorescence modeling for optimized-binary compressive detection Raman spectroscopy. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 23935–23951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corden, C.J.; Shipp, D.W.; Matousek, P.; Notingher, I. Fast Raman spectral mapping of highly fluorescing samples by time-gated spectral multiplexed detection. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 5733–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, B.; Soldevila, F.; Tajahuerce, E.; Gigan, S.; Rigneault, H.; De Aguiar, H.B. High-sensitivity high-speed compressive spectrometer for Raman imaging. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1811.06954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Henson, M.J.; Sekulic, S.S. Multivariate data analysis for Raman imaging of a model pharmaceutical tablet. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 545, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalahti, T.; Kvalheim, O.M. Multivariate data analysis in pharmaceutics: A tutorial review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 417, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasic, S.; Clark, D.A.; Mitchell, J.C.; Snowden, M.J. A comparison of Raman chemical images produced by univariate and multivariate data processing-a simulation with an example from pharmaceutical practice. Analyst 2004, 129, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.F.; Davenport, M.A.; Takhar, D.; Laska, J.N.; Sun, T.; Kelly, K.F.; Baraniuk, R.G. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scotté, C.; de Aguiar, H.B.; Marguet, D.; Green, E.M.; Bouzy, P.; Vergnole, S.; Winlove, C.P.; Stone, N.; Rigneault, H. Assessment of Compressive Raman versus Hyperspectral Raman for Microcalcification Chemical Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankani, B.R. Advances in Raman Hyperspectral Compressive Detection Instrumentation for Fast Label Free Classificiation, Quantification and Imaging; Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vornehm, J.E.; Dong, A.J.; Boyd, R.W.; Shi, Z. Multiple-output multivariate optical computing for spectrum recognition. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 25005–25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, D.; Thackara, J.I.; Clark, N.A.; Handschy, M.A. Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal Spatial Light Modulator. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 1987, 144, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriman, J.; Serati, S.; Stockley, J. Comparison of transmissive and reflective spatial light modulators for optical manipulation applications. In Proceedings of the Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 26 August 2005; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beek, M.C.; Schuurmans, F.J.P.; Bakker, L.P. Optical Analysis System Using Multivariate Optical Elements; Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, T.; Ahmed, B. The diversity in the applications of partial least squares: An overview. J. Chemom. 2016, 30, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geladi, P.; Kowalski, B.R. Partial least-squares regression: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci-Maltaş, D.; McCann, R.; Wang, P.; Pinal, R.; Romañach, R.; Ben-Amotz, D. Pharmaceutical Application of Fast Raman Hyperspectral Imaging with Compressive Detection Strategy. J. Pharm. Innov. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci Maltaş, D.; Kwok, K.; Wang, P.; Taylor, L.S.; Ben-Amotz, D. Rapid classification of pharmaceutical ingredients with Raman spectroscopy using compressive detection strategy with PLS-DA multivariate filters. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 80, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G. Applied Chemometrics for Scientists; John Wiley and Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ruckebusch, C.; Blanchet, L. Multivariate curve resolution: A review of advanced and tailored applications and challenges. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treado, P.J.; Morris, M.D. A thousand points of light: The Hadamard transform in chemical analysis and instrumentation. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 723A–734A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, T.C. Compressive Detection of Highly Overlapped Spectra Using Walsh–Hadamard-Based Filter Functions. Appl. Spectrosc. 2018, 72, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ApplicationNote. DMD 101: Introduction to Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) Technology; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P. Texas Instruments DLP® Technology for Spectroscopy; Texas Instruments: Dallas, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, D.; Duncan, W.M.; Slaughter, J. Emerging digital micromirror device (DMD) applications. In Proceedings of the Micromachining and Microfabrication, San Jose, CA, USA, 20 January 2003; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hornbeck, L.J. Digital Light Processing for high-brightness high-resolution applications. In Proceedings of the Electronic Imaging, San Jose, CA, USA, 8 May 1997; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, E.P.; Smith, B.W.; Madden, S.; Winefordner, J.D.; Mignardi, M. Construction and Evaluation of a Visible Spectrometer Using Digital Micromirror Spatial Light Modulation. Appl. Spectrosc. 1995, 49, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzard, G.T.; Lucier, B.J. Optimal filters for high-speed compressive detection in spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the IS&T/SPIE Electronic Imaging, Burlingame, CA, USA, 14 February 2013; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Réfrégier, P.; Scotté, C.; de Aguiar, H.B.; Rigneault, H.; Galland, F. Precision of proportion estimation with binary compressed Raman spectrum. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2018, 35, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Amotz, D.; Lucier, B.J.; Buzzard, G.T.; Wilcox, D.S.; Wang, P.; Mankani, B.R. Optical Chemical Classification. U.S. Patent 9476824 B2, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, D.S.; Buzzard, G.T.; Lucier, B.J.; Rehrauer, O.G.; Wang, P.; Ben-Amotz, D. Digital compressive chemical quantitation and hyperspectral imaging. Analyst 2013, 138, 4982–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turtaev, S.; Leite, I.T.; Mitchell, K.J.; Padgett, M.J.; Phillips, D.B.; Čižmár, T. Comparison of nematic liquid-crystal and DMD based spatial light modulation in complex photonics. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 29874–29884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USFDA. PAT-A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development, Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance; USFDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2004.


| Classification Strategy | 30 mW, 1 ms | 3 mW, 1 ms | 1 mW, 1 ms |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCD | 26 | 3 | 1 |
| OBCD | 22 | 7 | 4 |
| OBCD2 | 32 | 13 | 6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cebeci, D.; Mankani, B.R.; Ben-Amotz, D. Recent Trends in Compressive Raman Spectroscopy Using DMD-Based Binary Detection. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010001
Cebeci D, Mankani BR, Ben-Amotz D. Recent Trends in Compressive Raman Spectroscopy Using DMD-Based Binary Detection. Journal of Imaging. 2019; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleCebeci, Derya, Bharat R. Mankani, and Dor Ben-Amotz. 2019. "Recent Trends in Compressive Raman Spectroscopy Using DMD-Based Binary Detection" Journal of Imaging 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010001
APA StyleCebeci, D., Mankani, B. R., & Ben-Amotz, D. (2019). Recent Trends in Compressive Raman Spectroscopy Using DMD-Based Binary Detection. Journal of Imaging, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5010001





