SABE-YOLO: Structure-Aware and Boundary-Enhanced YOLO for Weld Seam Instance Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To address the challenges of elongated geometry, complex shapes, and difficult feature extraction in weld seams, a Structure-Aware Fusion Module (SAFM) is proposed. By integrating local directional information with global structural semantics, the module effectively enhances the capacity to capture weld seam geometry.
- (2)
- To mitigate the issue of blurred weld boundaries, a C2f-based Boundary-Enhanced Aggregation Module (C2f-BEAM) is introduced. This module strengthens boundary representation by extracting multi-scale boundary details, thereby improving the perception and recognition of complex boundary structures.
- (3)
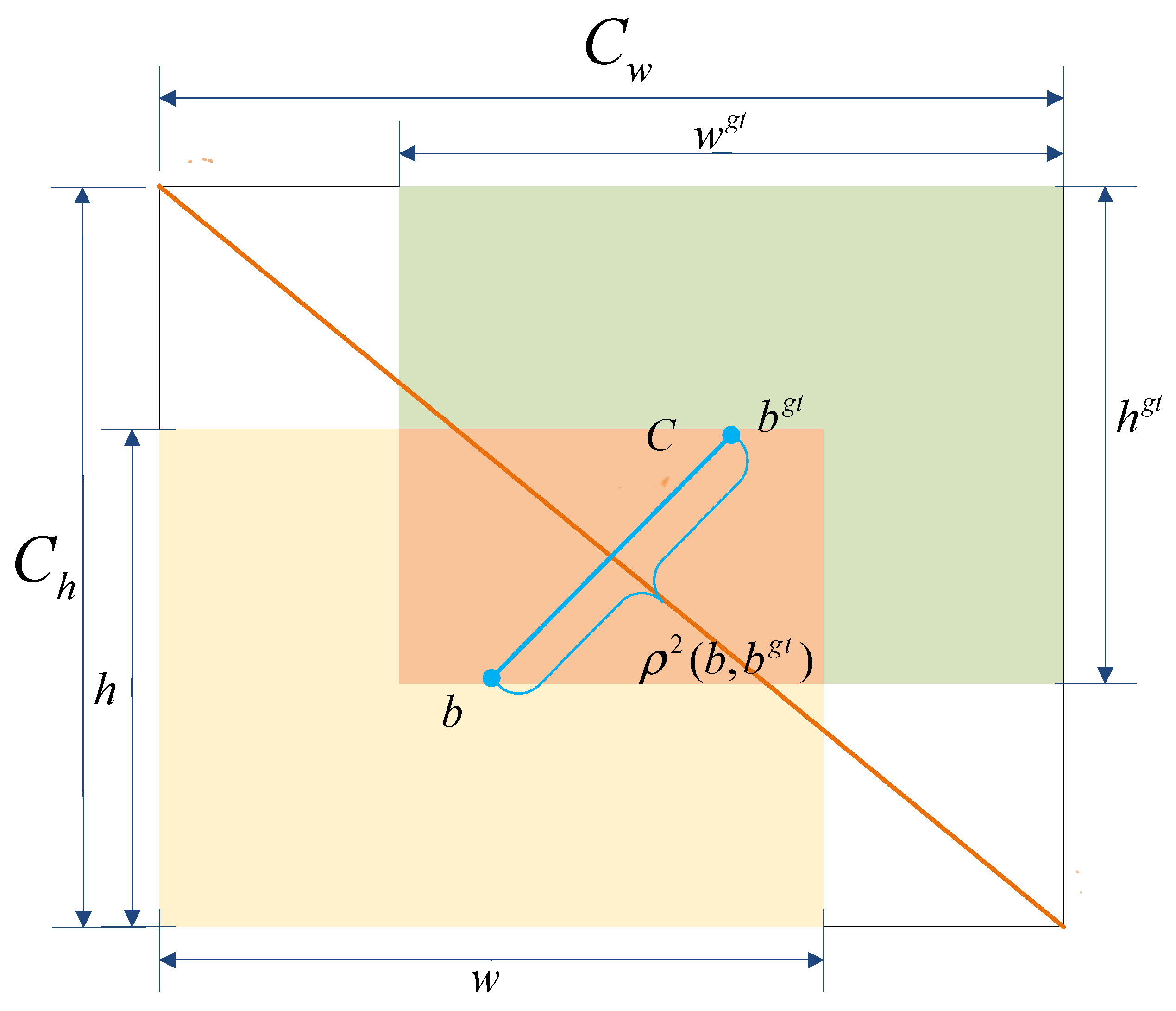
- To improve localization accuracy under irregular weld seam shapes, the Inner-MPDIoU loss function is adopted. By constraining the internal overlap between predicted and ground truth boxes based on the minimum point distance, this loss enhances segmentation performance in geometrically complex regions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Progress of Instance Segmentation in Weld Seam Inspection
2.2. Application of Attention Mechanisms in Instance Segmentation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
3.1.1. Data Acquisition and Analysis
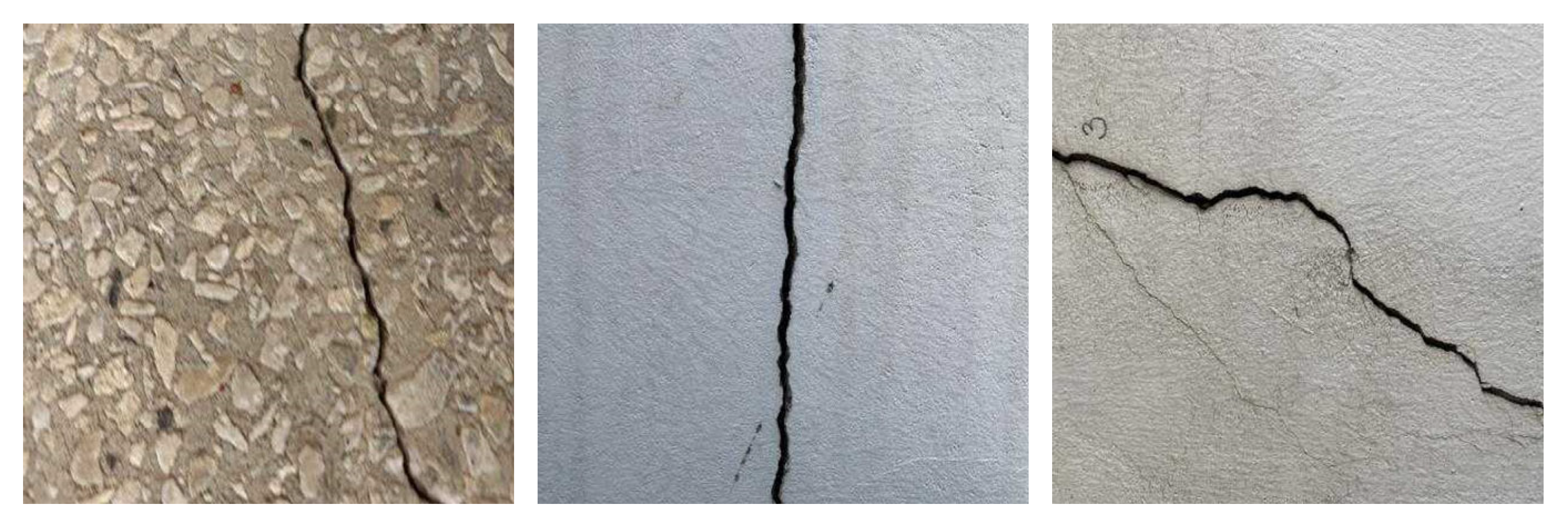
3.1.2. Generalization Validation Dataset: Crack Segmentation Dataset
3.2. Methods
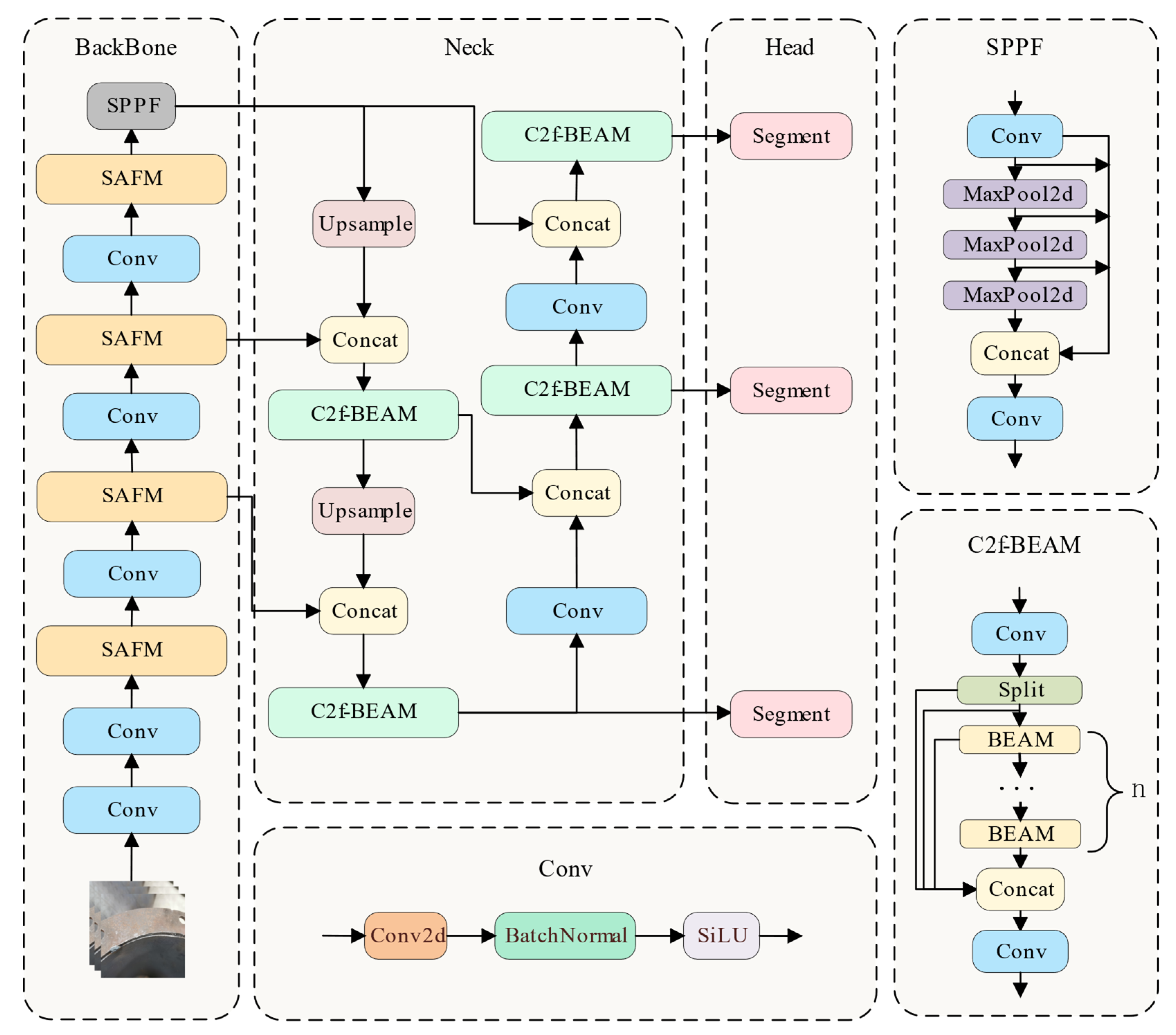
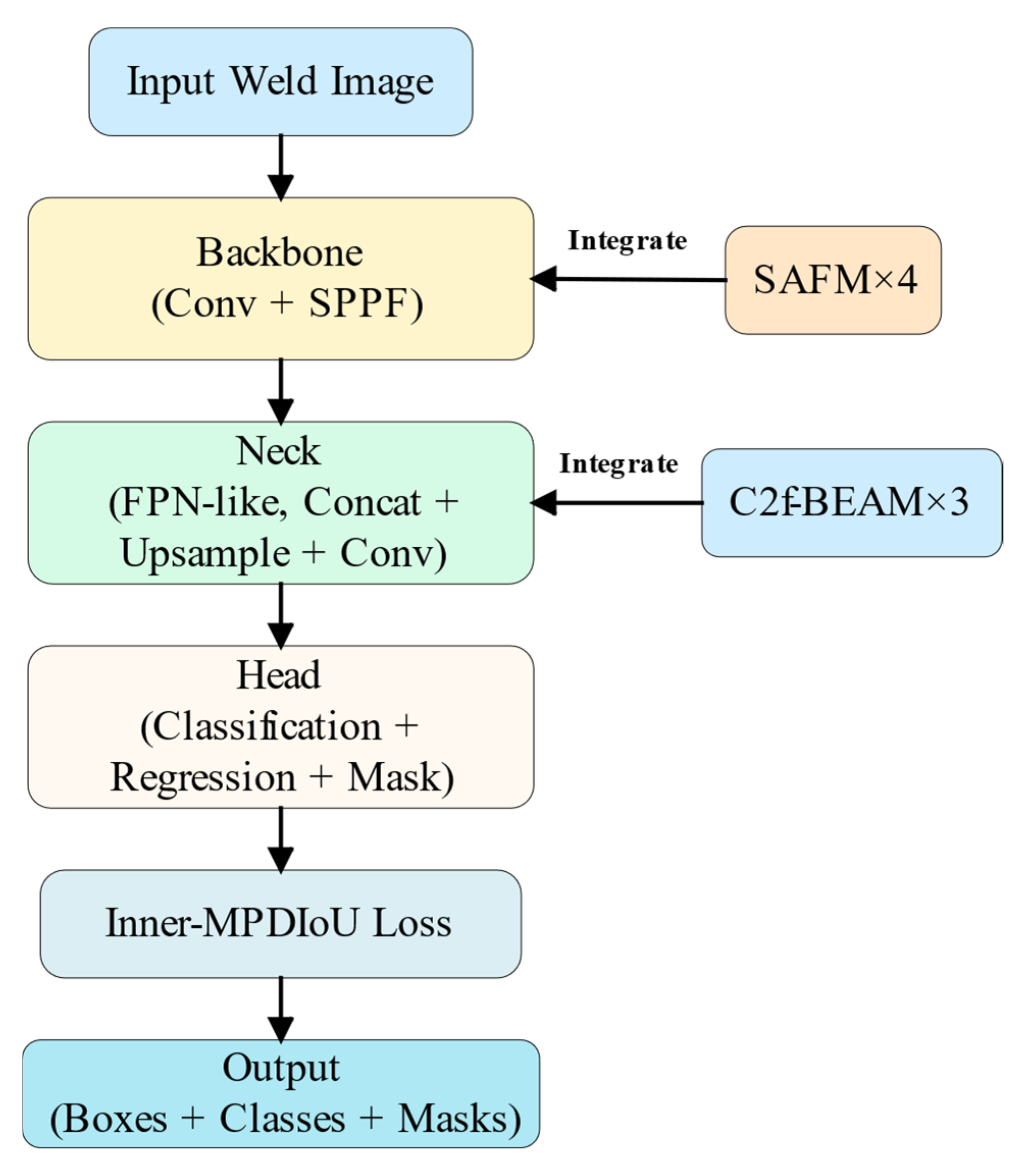
3.2.1. SABE-YOLO Network Architecture
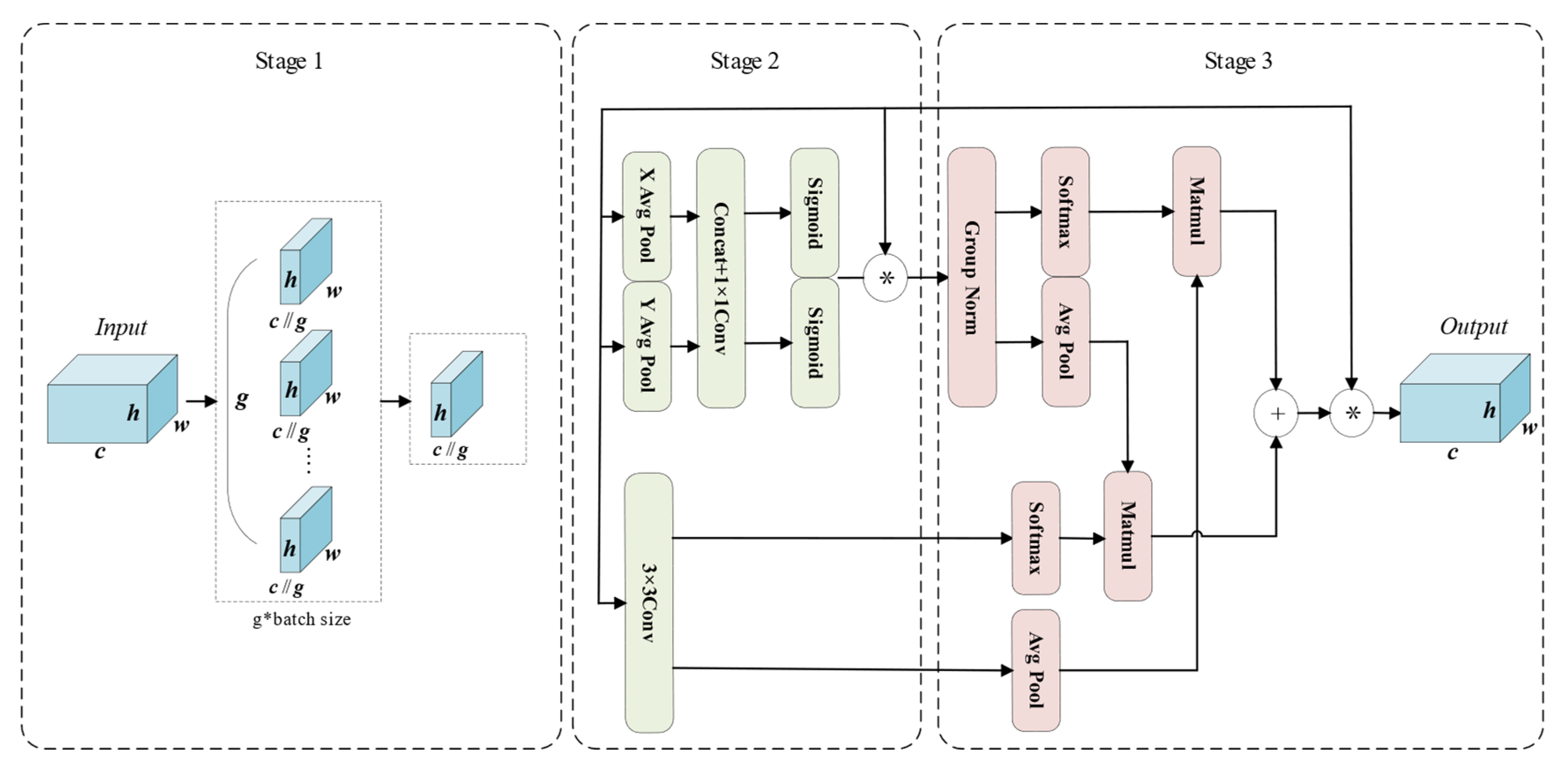
3.2.2. Structure-Aware Fusion Module (SAFM)
3.2.3. C2f-Based Boundary-Enhanced Aggregation Module (C2f-BEAM)
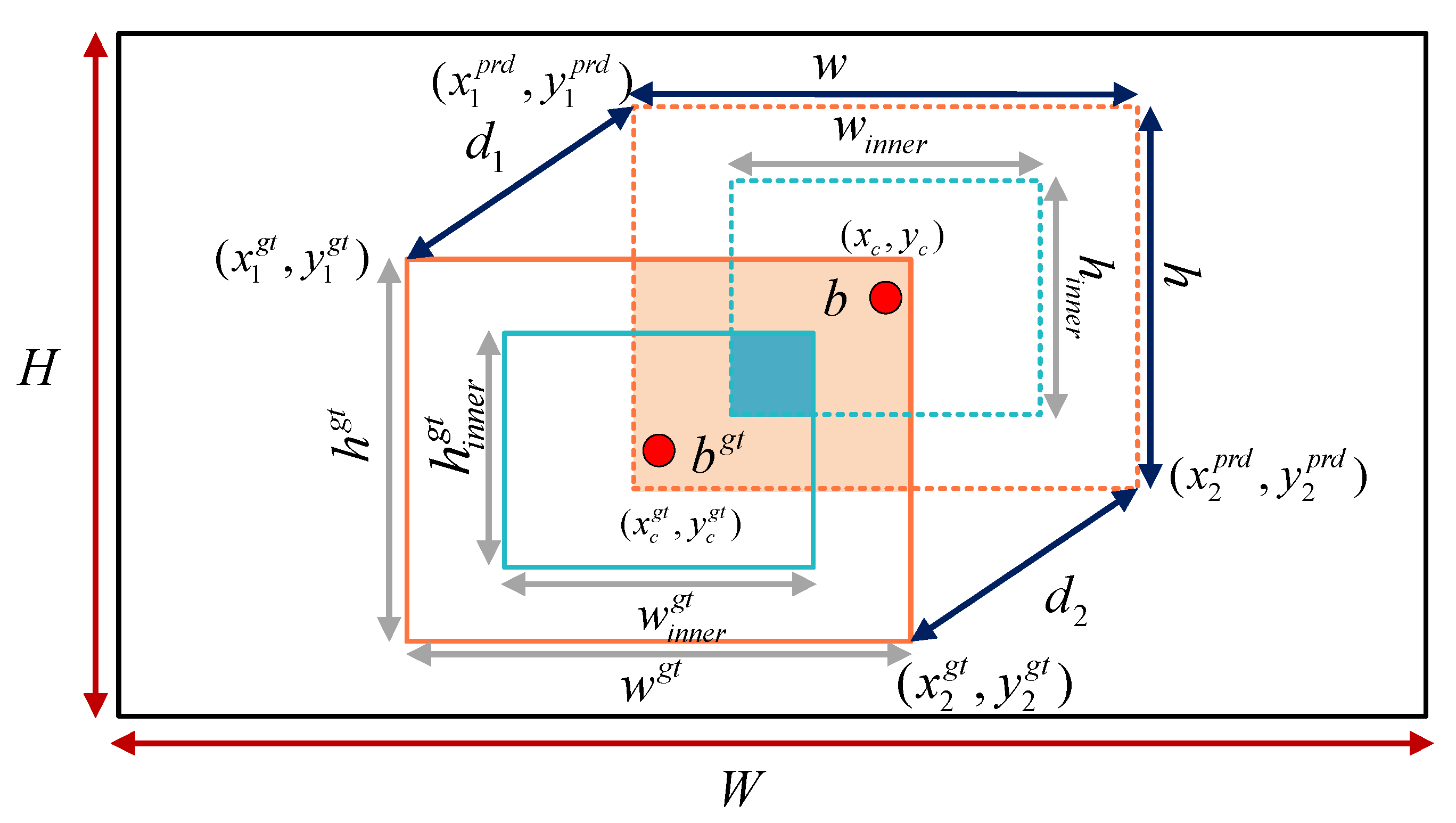
3.2.4. Inner Minimum Point Distance Based Intersection over Union (Inner-MPDIoU)
3.2.5. Weld Seam Instance Segmentation Method Based on SABE-YOLO
| Algorithm 1: Inference Algorithm of Weld Seam Segmentation Based on SABE-YOLO |
| Input: An input weld seam image I with shape H × W × 3. Output: Predicted class labels, bounding boxes, and instance masks 1: multi_scale_features = extract_SAFM_backbone(I) 2: pyramid_features = PANet_BEAM-fusion(multi_scale_features) 3: for each scale_feature in pyramid_features do: 4: grid_centers = generate_grid_centers(scale_feature) 5: cls_feat, reg_feat = depthwise_sep_conv(scale_feature) 6: pred_scores = class_conv(cls_feat) 7: bbox_preds = bbox_conv(reg_feat) 8: mask_coeff = mask_conv(reg_feat) 9: End for 10: all_preds = concat([pred_scores, bbox_preds, mask_coeff]) 11: decoded_boxes = decode_bbox(grid_centers, bbox_preds) 12: topk_indices = select_topk(all_preds) 13: nms_results = NMS(decoded_boxes, topk_indices) 14: final_masks = assemble_masks(mask_proto, mask_coeff) 15: return nms_results.classes, nms_results.boxes, final_masks |
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Environment and Parameters
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
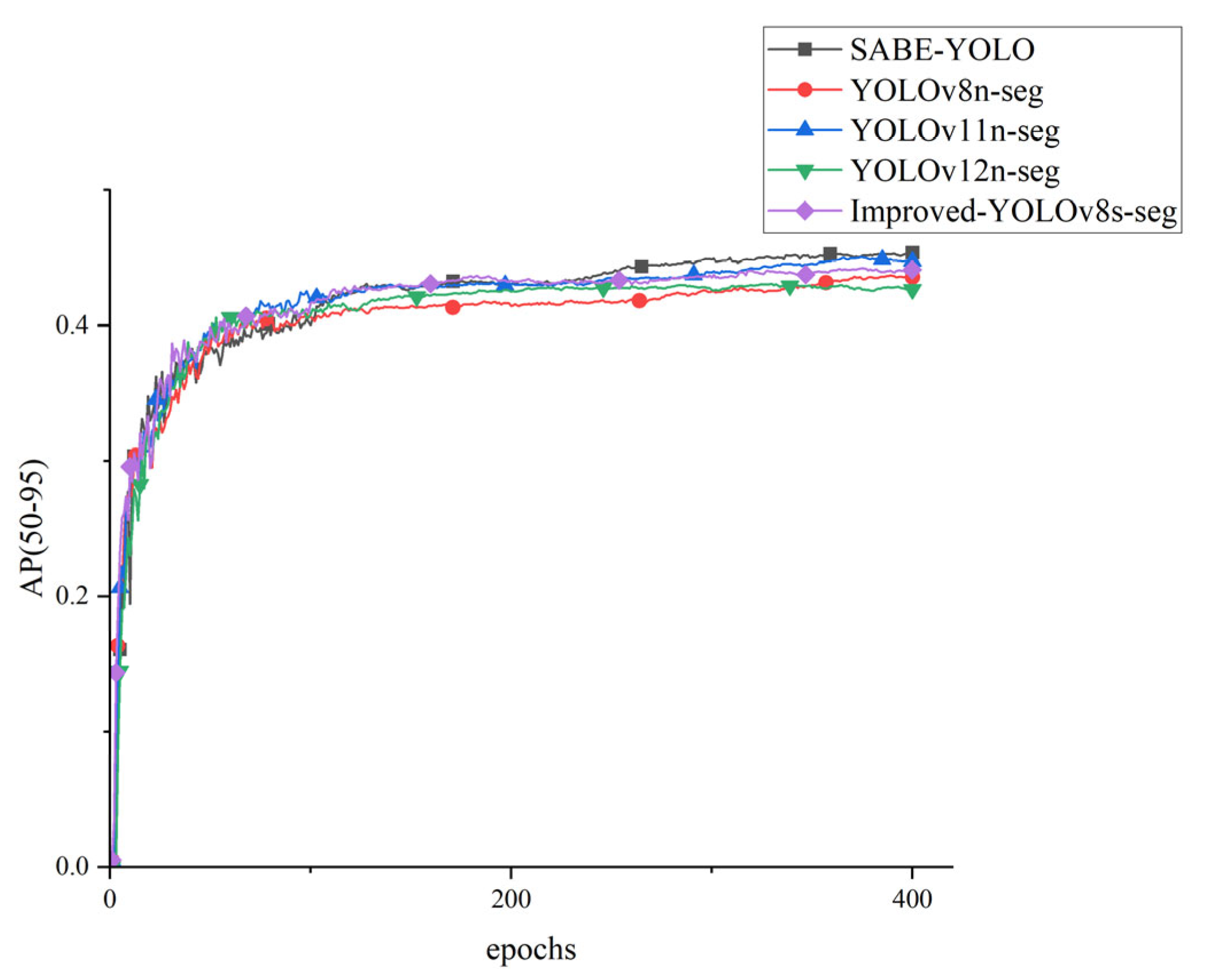
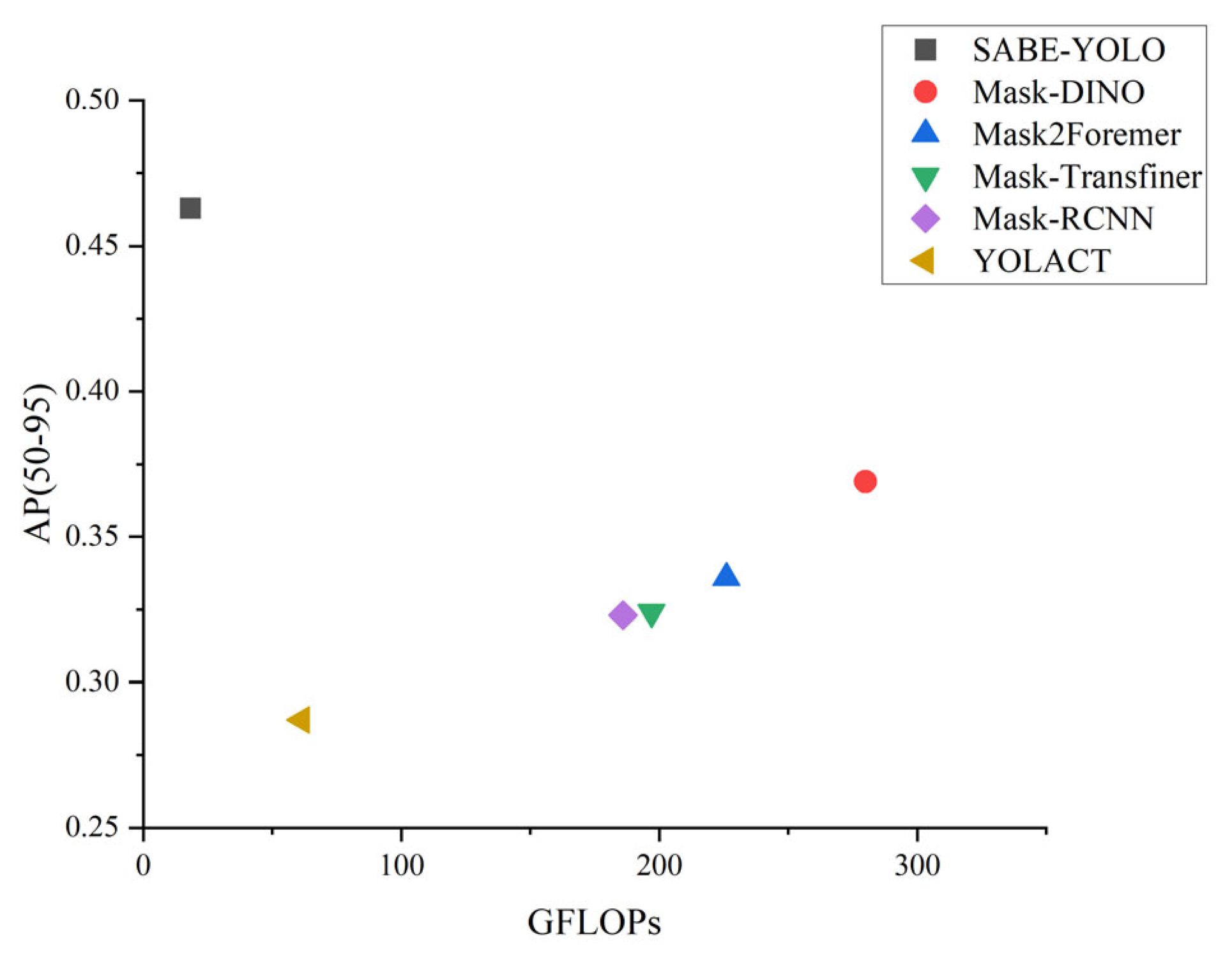
4.3. Performance Comparison Between SABE-YOLO and Mainstream Instance Segmentation Models
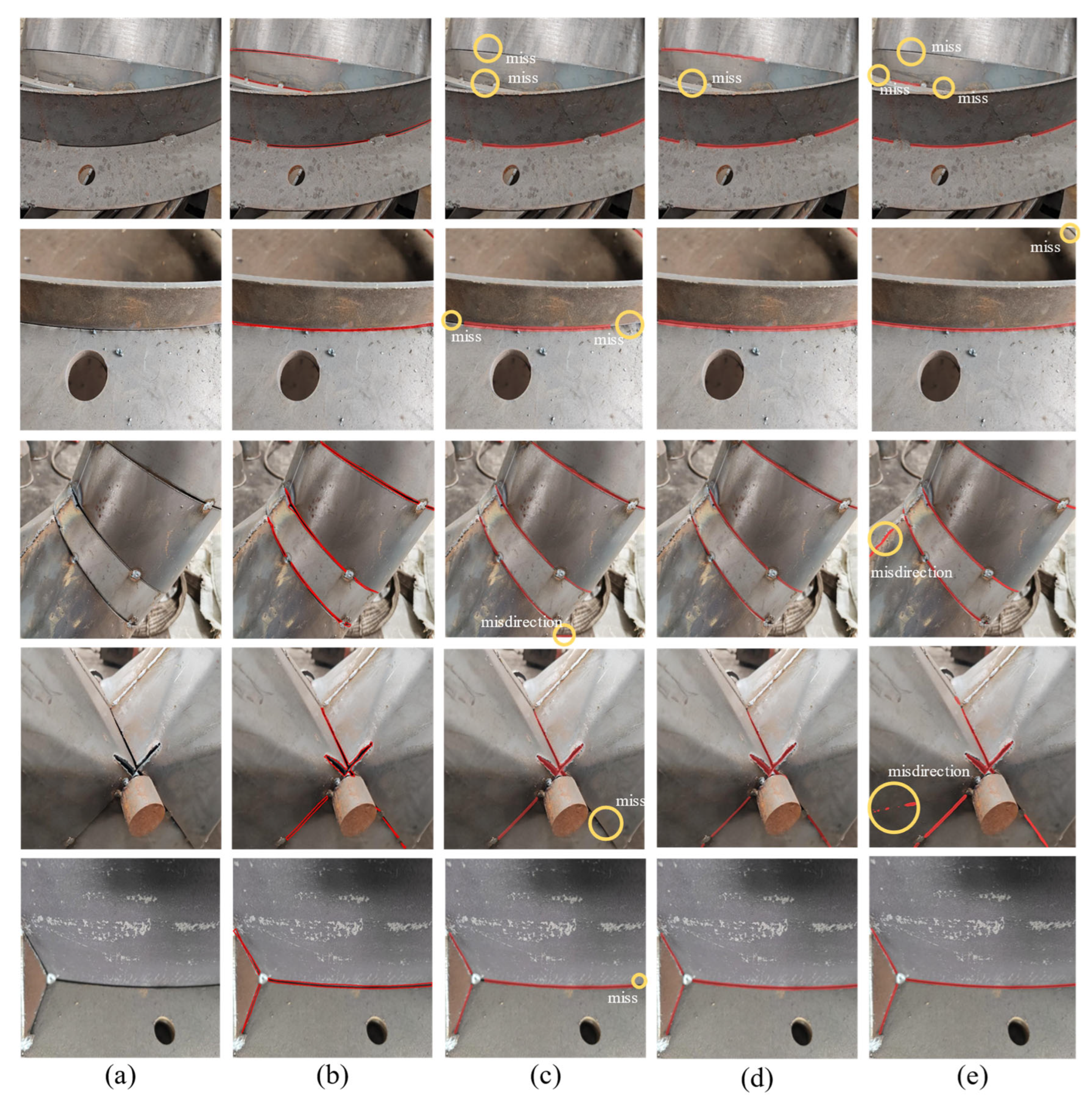
4.4. Qualitative Results
4.5. Ablation Study
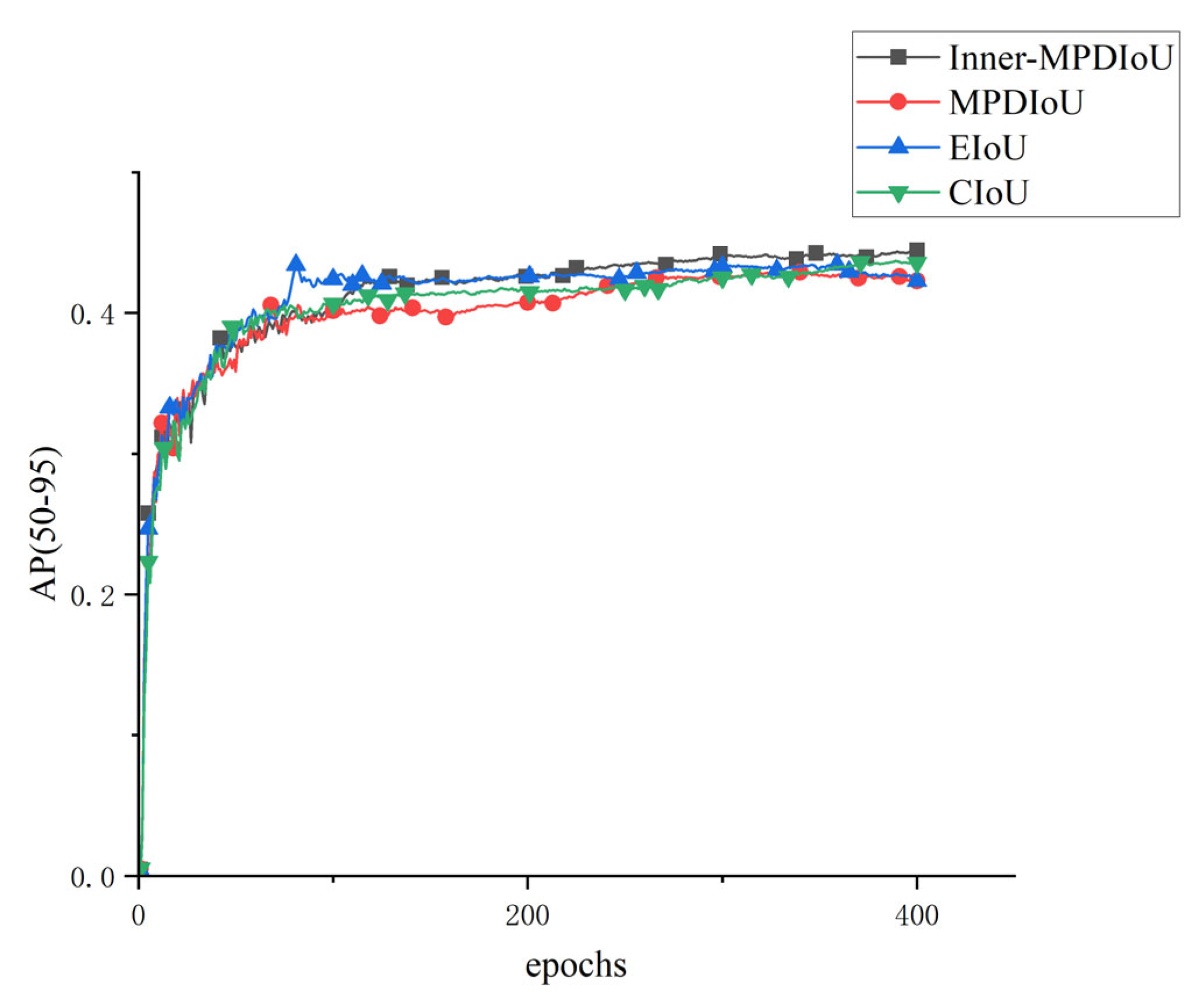
4.6. Performance Comparison of Different Loss Functions on YOLOv8n-Seg
4.7. Evaluation of Different Scaling Factors in Inner-MPDIoU
4.8. Selection of Dual-Branch Fusion Strategy in SAFM
4.9. Effect of the Number of Boundary Enhancement Paths in BEAM on Performance
4.10. Zero-Shot Generalization Experiment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, T.; Rong, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, M. A review of vision-aided robotic welding. Comput. Ind. 2020, 123, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. The active visual sensing methods for robotic welding: Review, tutorial and prospect. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hu, S. Research on trajectory recognition and control technology of real-time tracking welding. Sensors 2022, 22, 8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Chang, B.; Peng, G.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Z.; Du, D.; Wang, G. A vision based detection method for narrow butt joints and a robotic seam tracking system. Sensors 2019, 19, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Kong, T.; Shen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L. Solo: Segmenting objects by locations. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 649–665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Kong, T.; Li, L.; Shen, C. Solov2: Dynamic and fast instance segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17721–17732. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Ni, L.M.; Shum, H.-Y. Mask dino: Towards a unified transformer-based framework for object detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 3041–3050. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, R.; Sambath, M. Yolov8: A novel object detection algorithm with enhanced performance and robustness. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 18–19 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.-M.; Feng, J. Strip pooling: Rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4003–4012. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Dai, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y. Rewrite the stars. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5694–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023—2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, S. Inner-iou: More effective intersection over union loss with auxiliary bounding box. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.02877. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Xu, Y. Mpdiou: A loss for efficient and accurate bounding box regression. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.07662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 6, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, J.; Kittler, J. A survey of the Hough transform. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1988, 44, 87–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G. YOLOv5 Release, v6.1. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/tag/v6.1 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A. Ultralytics YOLO, Version 8.3.0 [Computer software]. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Yolov12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, A.; Fan, Z.; Li, A.; Le, Q.; Wu, D.; Du, F. YOLO-weld: A modified YOLOv5-based weld feature detection network for extreme weld noise. Sensors 2023, 23, 5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zeng, G. Light-weight segmentation network based on SOLOv2 for weld seam feature extraction. Measurement 2023, 208, 112492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Q.; Wang, P.; Su, Y. Welding seam tracking and inspection robot based on improved YOLOv8s-Seg model. Sensors 2024, 24, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, X. An overview of overfitting and its solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1168, 022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University. Crack Dataset. Roboflow Universe. Roboflow: 2022. Available online: https://universe.roboflow.com/university-bswxt/crack-bphdr (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Bai, Y. RELU-function and derived function review. In Proceedings of the SHS Web of Conferences, Changsha, China, 23–25 September 2022; p. 02006. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, P.; Yan, T.; Lu, H. Multi-scale and detail-enhanced segment anything model for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 9894–9903. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Ren, D.; Liu, W.; Ye, R.; Hu, Q.; Zuo, W. Enhancing geometric factors in model learning and inference for object detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 8574–8586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12993–13000. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.; Danelljan, M.; Li, X.; Tai, Y.-W.; Tang, C.-K.; Yu, F. Mask transfiner for high-quality instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4412–4421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, E.; Yigit, C.B.; Boyraz, P. A hybrid image dataset toward bridging the gap between real and simulation environments for robotics. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2019, 30, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, E.; Yigit, C.B.; Boyraz, P. Object manipulation with a variable-stiffness robotic mechanism using deep neural networks for visual semantics and load estimation. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 2724–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, E.; Yigit, C.B. Conditional-Pooling for Improved Data Transmission. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Model | P% | R% | AP(50–95)% | Params/M | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved YOLOv8s-seg [28] | 89.3 | 83.2 | 43.7 | 6.36 | 21.2 | 159 |
| YOLOv8n-seg [12] | 88.6 | 83.8 | 43.3 | 3.3 | 12 | 217 |
| YOLOv11n-seg [23] | 89.9 | 82.9 | 43.5 | 2.8 | 10.2 | 231 |
| YOLOv12n-seg [24] | 90.2 | 83.7 | 43.5 | 2.8 | 10.2 | 224 |
| YOLACT [6] | - | - | 28.7 | 34.7 | 61.4 | 86 |
| Mask-RCNN [5] | - | - | 32.3 | 44 | 186 | 48 |
| Mask DINO [10] | - | - | 36.9 | 52 | 280 | 15 |
| Mask Transfiner [39] | - | - | 32.4 | 44 | 197 | 18 |
| Mask2Former [11] | - | - | 33.6 | 44 | 226 | 6 |
| SABE-YOLO (ours) | 89 | 83.6 | 46.3 | 6.6 | 18.3 | 127 |
| YOLOv8n-seg | C2f-BEAM | SAFM | Inner-MPDIoU | AP(50–95)% | Params/M | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 43.3 | 3.2 | 12.1 | |||
| √ | √ | 43.7 | 3.3 | 12.3 | ||
| √ | √ | 44.2 | 6.5 | 18.3 | ||
| √ | √ | 43.9 | 3.2 | 12.1 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 45.5 | 6.6 | 18.4 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 44.6 | 3.3 | 12.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 45.0 | 6.5 | 18.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 46.3 | 6.6 | 18.4 |
| Loss Function | P% | R% | AP(50–95)% | F1-Score% | Params/M | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIoU [40] | 87.3 | 82.7 | 41.2 | 84.94 | 3 | 12 |
| CIoU [37] | 88.6 | 83.8 | 43.3 | 86.13 | 3 | 12 |
| MPDIoU [18] | 85.9 | 83.8 | 41 | 84.84 | 3 | 12 |
| Inner-MPDIoU | 88.9 | 84.4 | 43.9 | 86.59 | 3 | 12 |
| Ratio | P% | R% | AP(50–95)% | F1-Score% | Params/M | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75 | 86.9 | 85 | 41.9 | 85.94 | 3.258 | 12 |
| 0.9 | 88.9 | 84.4 | 43.9 | 86.59 | 3.258 | 12 |
| 1 | 85.9 | 83.8 | 41 | 84.84 | 3.258 | 12 |
| 1.1 | 87.8 | 83.6 | 42.6 | 85.65 | 3.258 | 12 |
| 1.25 | 86.8 | 84.3 | 42.6 | 85.53 | 3.258 | 12 |
| Fusion Strategy | AP(50–95)% | Params/M | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element-wise Add | 42.1 | 6.45 | 18.2 | 129 |
| Concat + Conv | 42.8 | 6.88 | 19.1 | 127 |
| Weighted Multiply | 44.2 | 6.5 | 18.3 | 127 |
| Number of Enhancement Paths (d) | AP(50–95)% | Params/M | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 42.6 | 3.33 | 12.1 | 213 |
| 3 | 43.7 | 3.34 | 12.1 | 207 |
| 4 | 42 | 3.35 | 12.2 | 200 |
| Model | AP(50–95)% | Params/M | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n-seg | 14 | 3.3 | 12 | 97 |
| YOLOv12n-seg | 21.1 | 2.8 | 10.2 | 99 |
| Mask DINO | 19.2 | 52 | 280 | 11 |
| SABE-YOLO (ours) | 34.3 | 6.6 | 18.3 | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, R.; Xie, W.; Fan, Y.; Shen, L. SABE-YOLO: Structure-Aware and Boundary-Enhanced YOLO for Weld Seam Instance Segmentation. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11080262
Wen R, Xie W, Fan Y, Shen L. SABE-YOLO: Structure-Aware and Boundary-Enhanced YOLO for Weld Seam Instance Segmentation. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(8):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11080262
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Rui, Wu Xie, Yong Fan, and Lanlan Shen. 2025. "SABE-YOLO: Structure-Aware and Boundary-Enhanced YOLO for Weld Seam Instance Segmentation" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 8: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11080262
APA StyleWen, R., Xie, W., Fan, Y., & Shen, L. (2025). SABE-YOLO: Structure-Aware and Boundary-Enhanced YOLO for Weld Seam Instance Segmentation. Journal of Imaging, 11(8), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11080262






