Depth-Dependent Variability in Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging for Hepatic Steatosis: A Pilot Study of ATI and HRI in Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
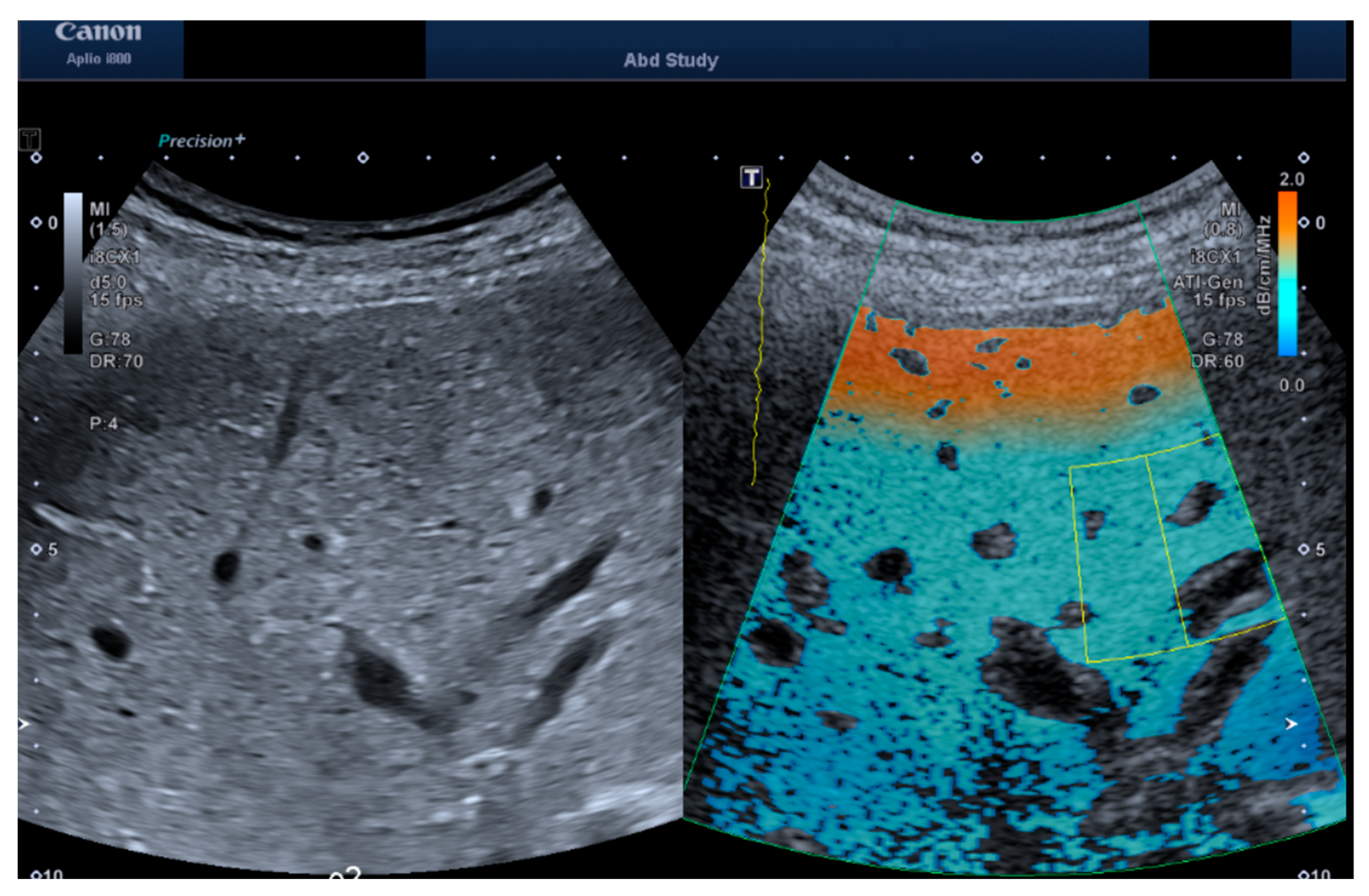
2.1. Measurement Protocol
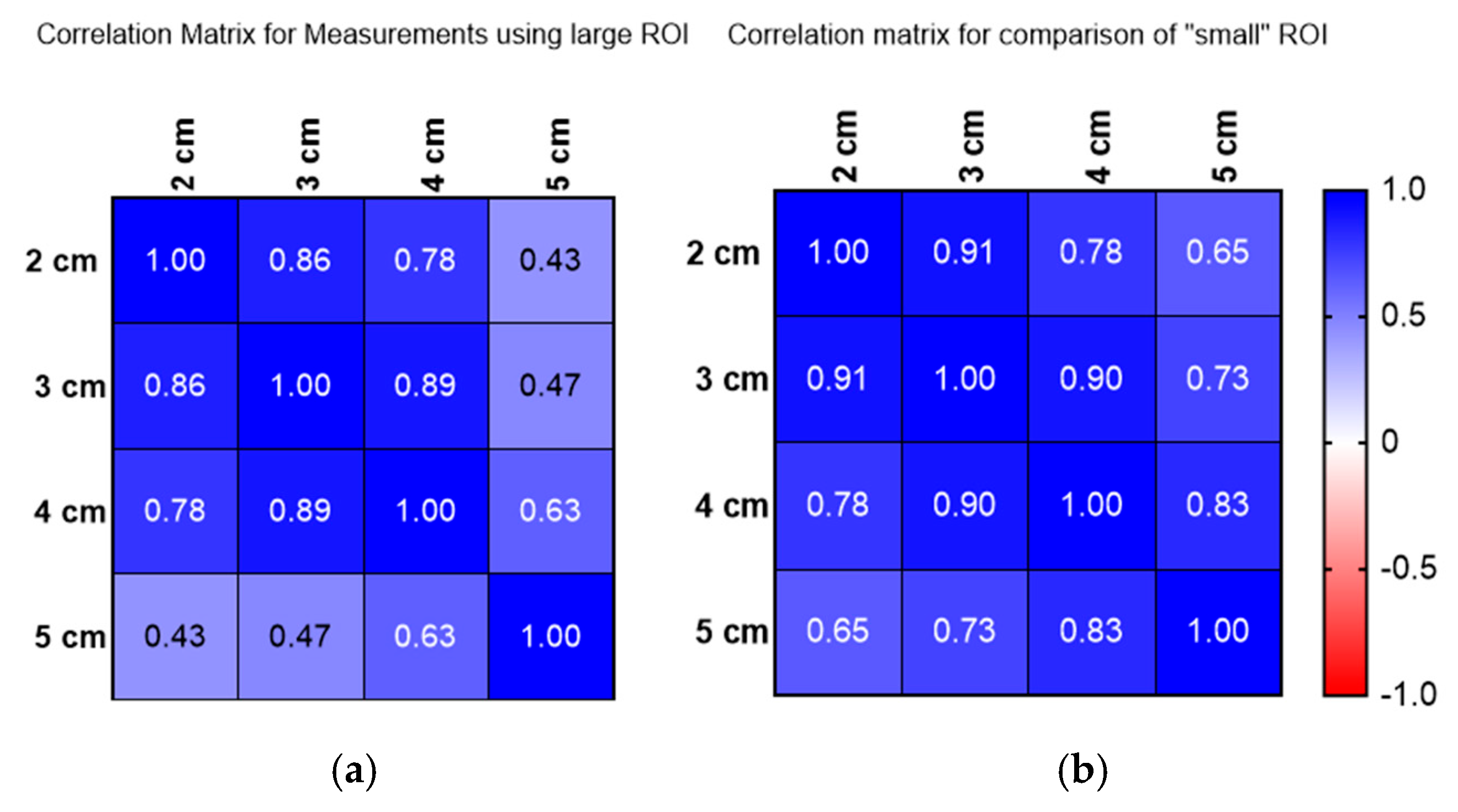
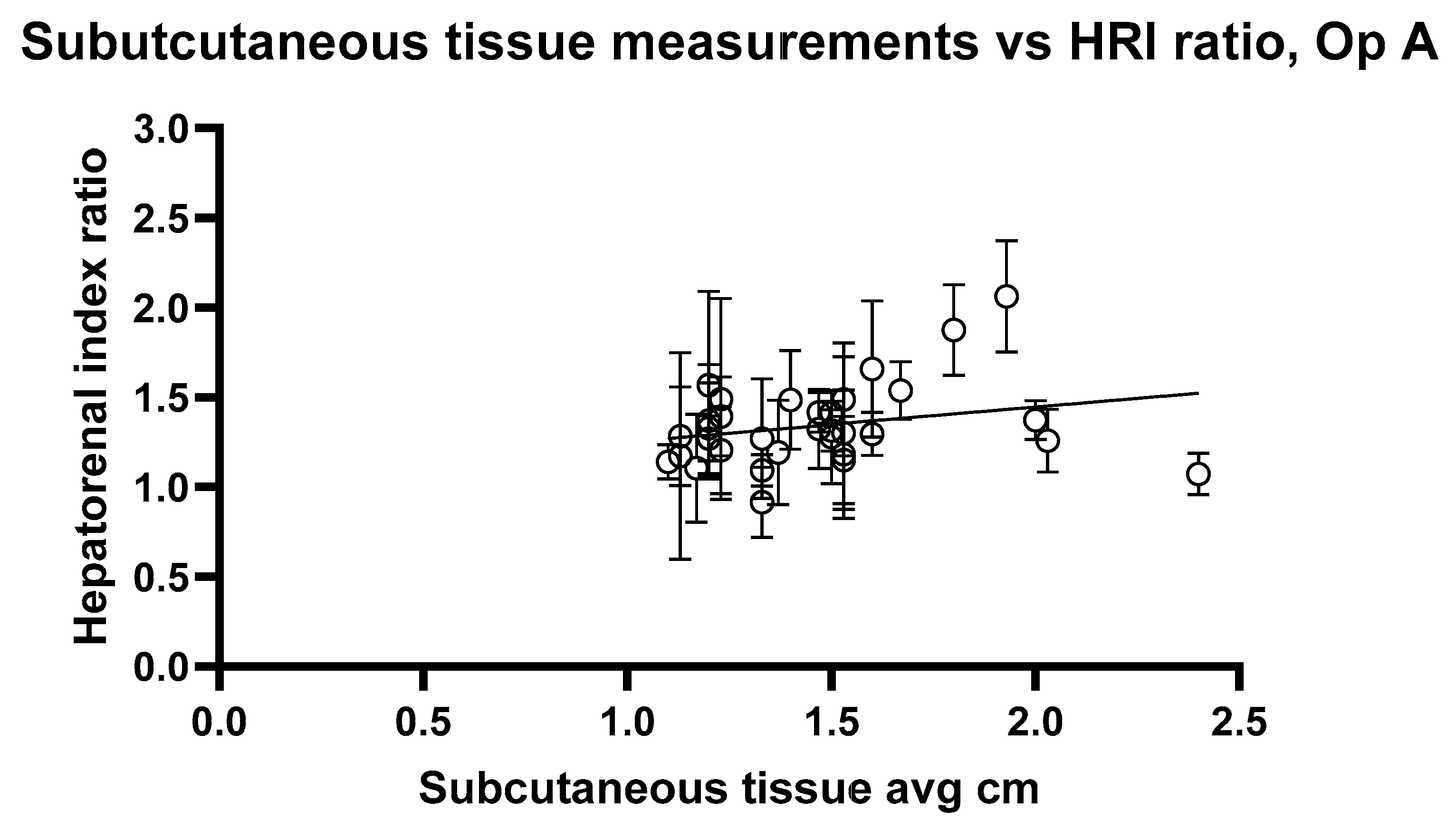
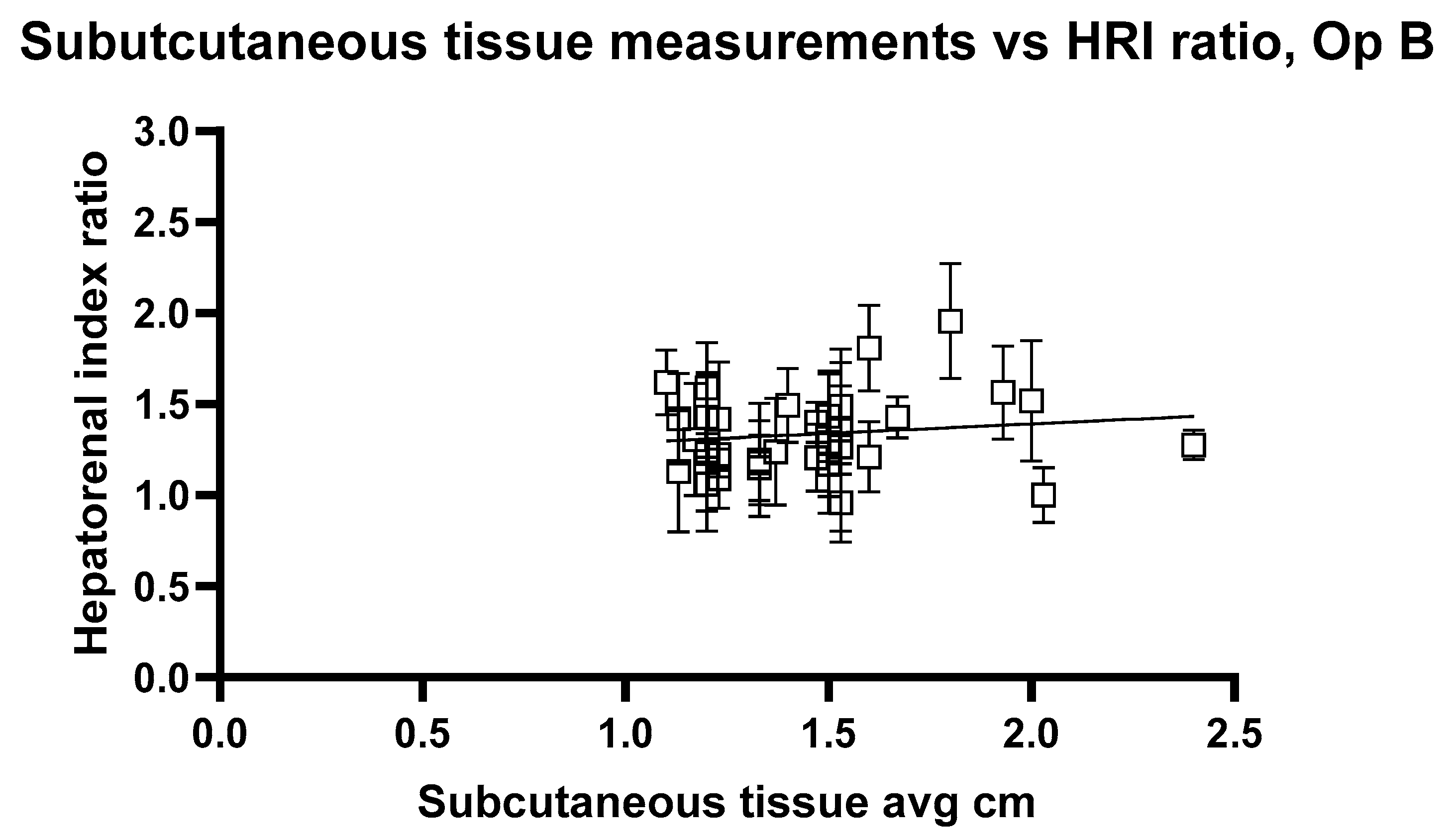
2.2. Depth and ROI Size Analysis
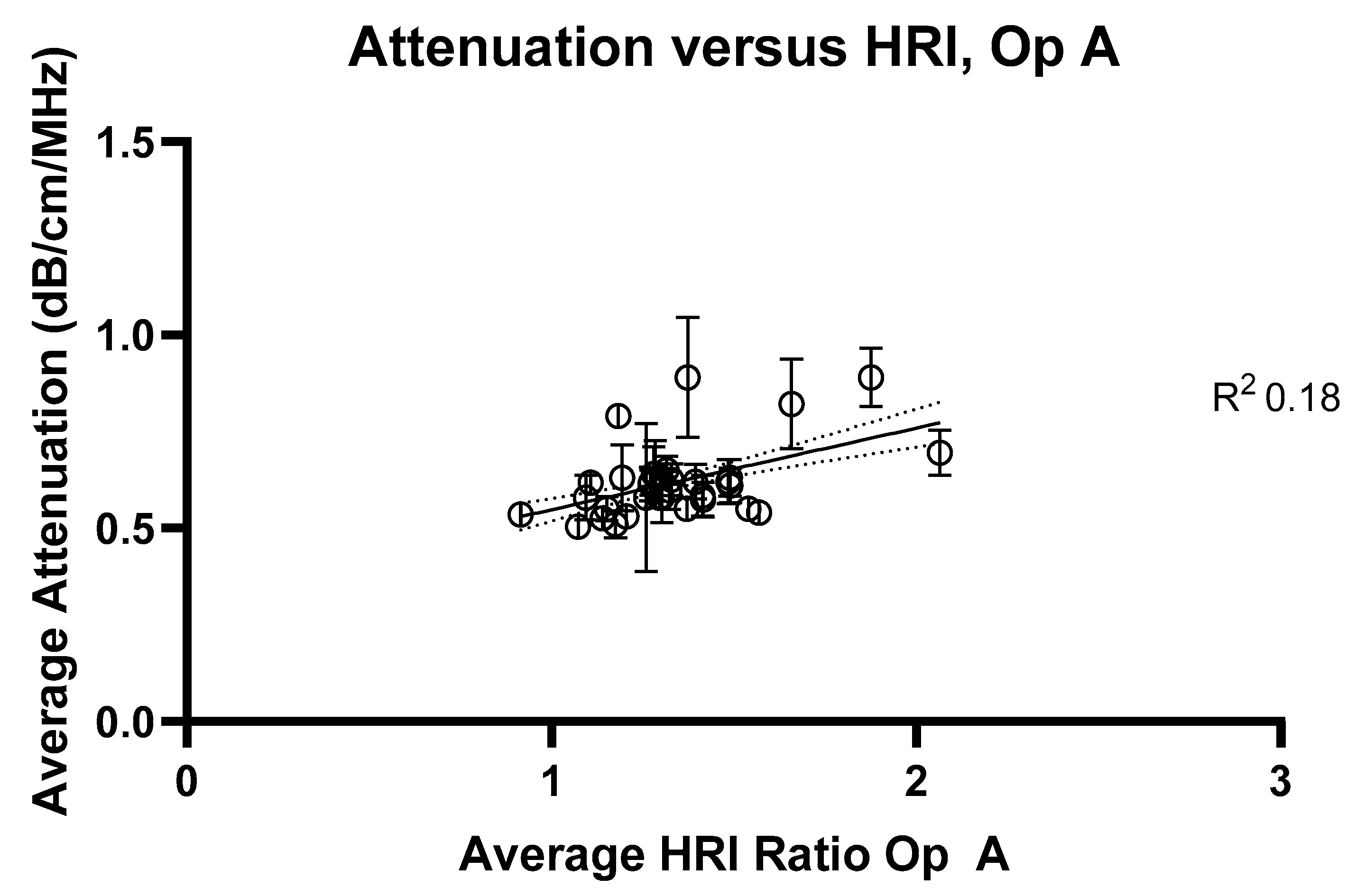
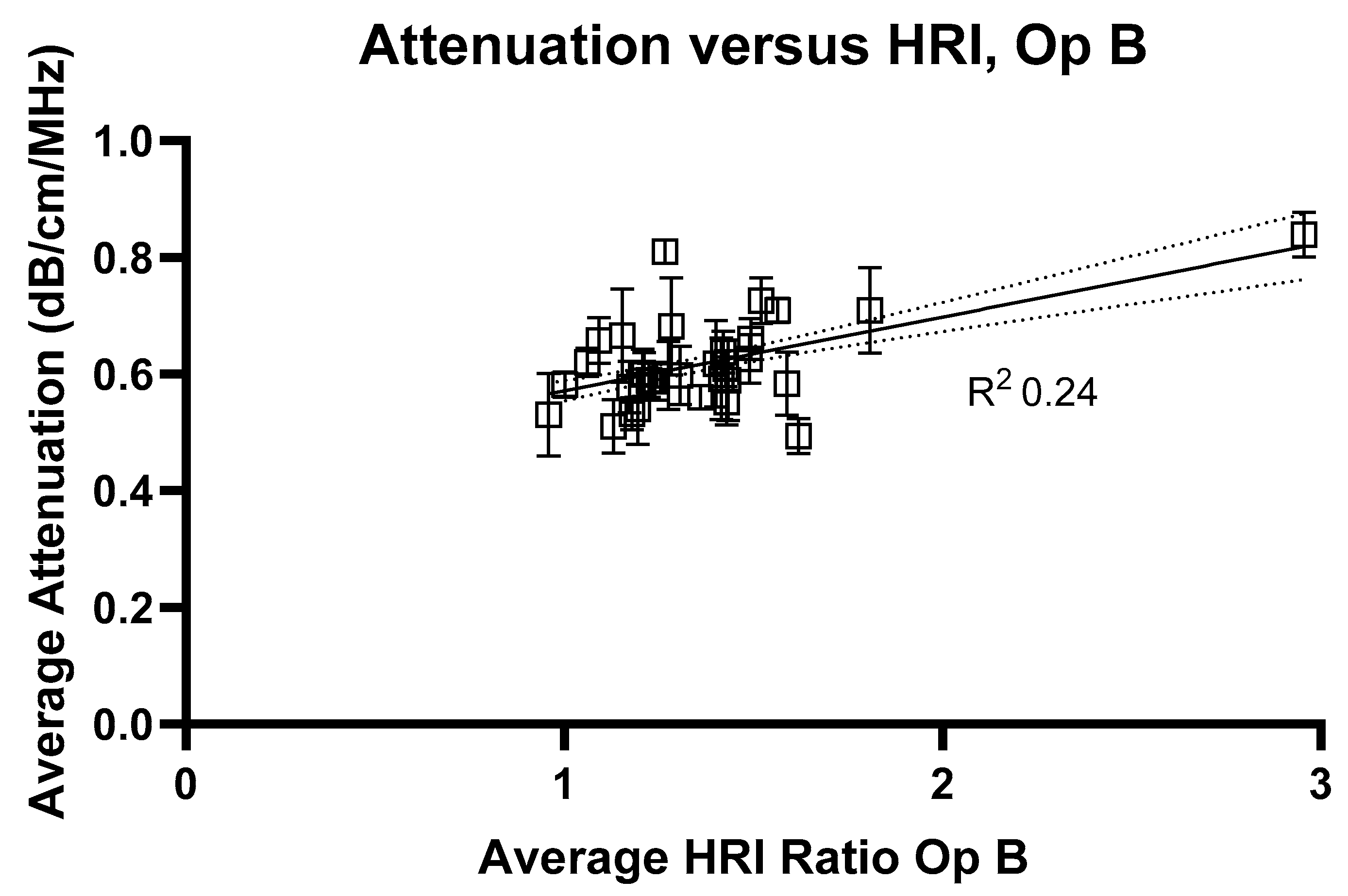
2.3. HRI Versus Attenuation Coefficient
2.4. Statistics
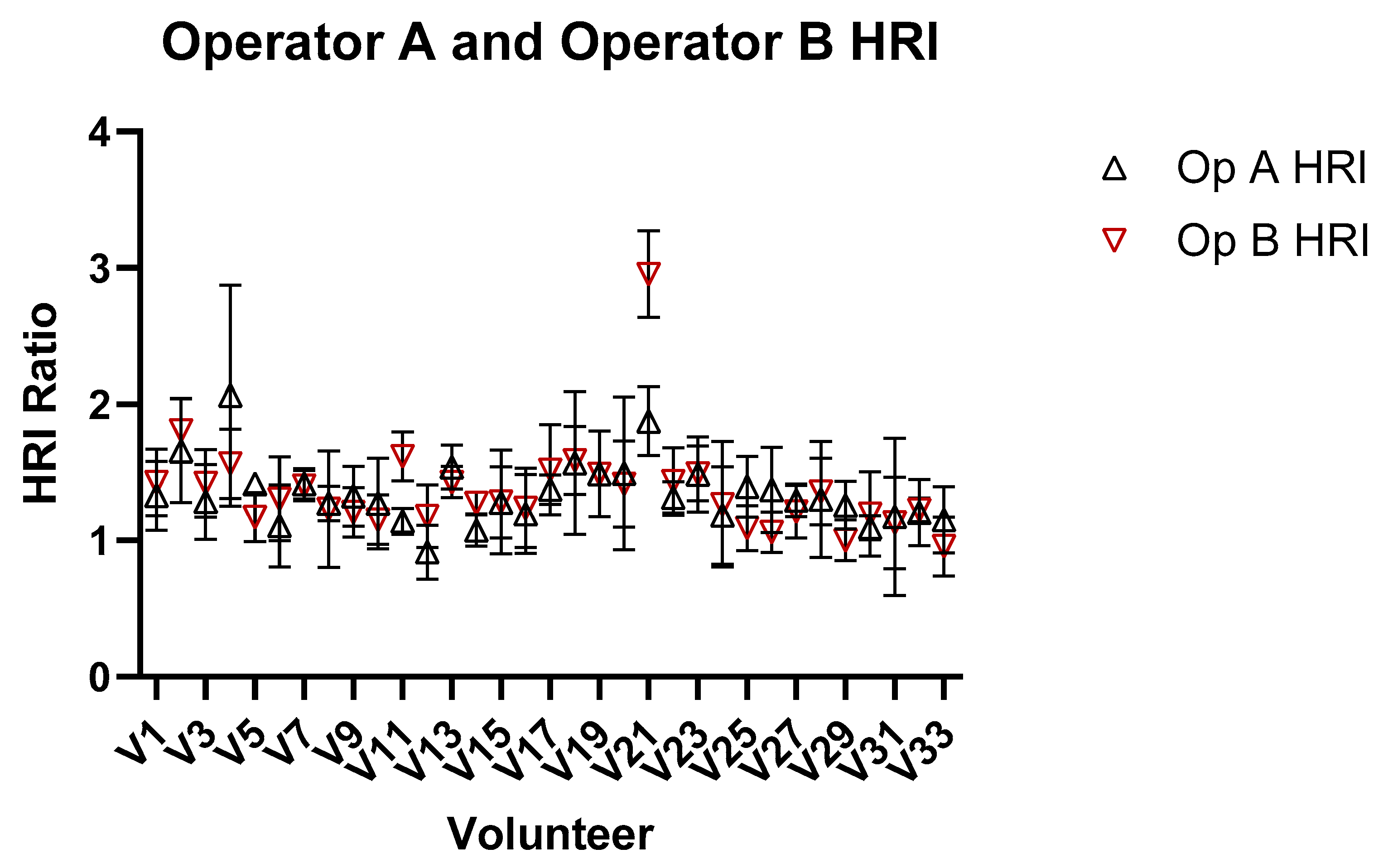
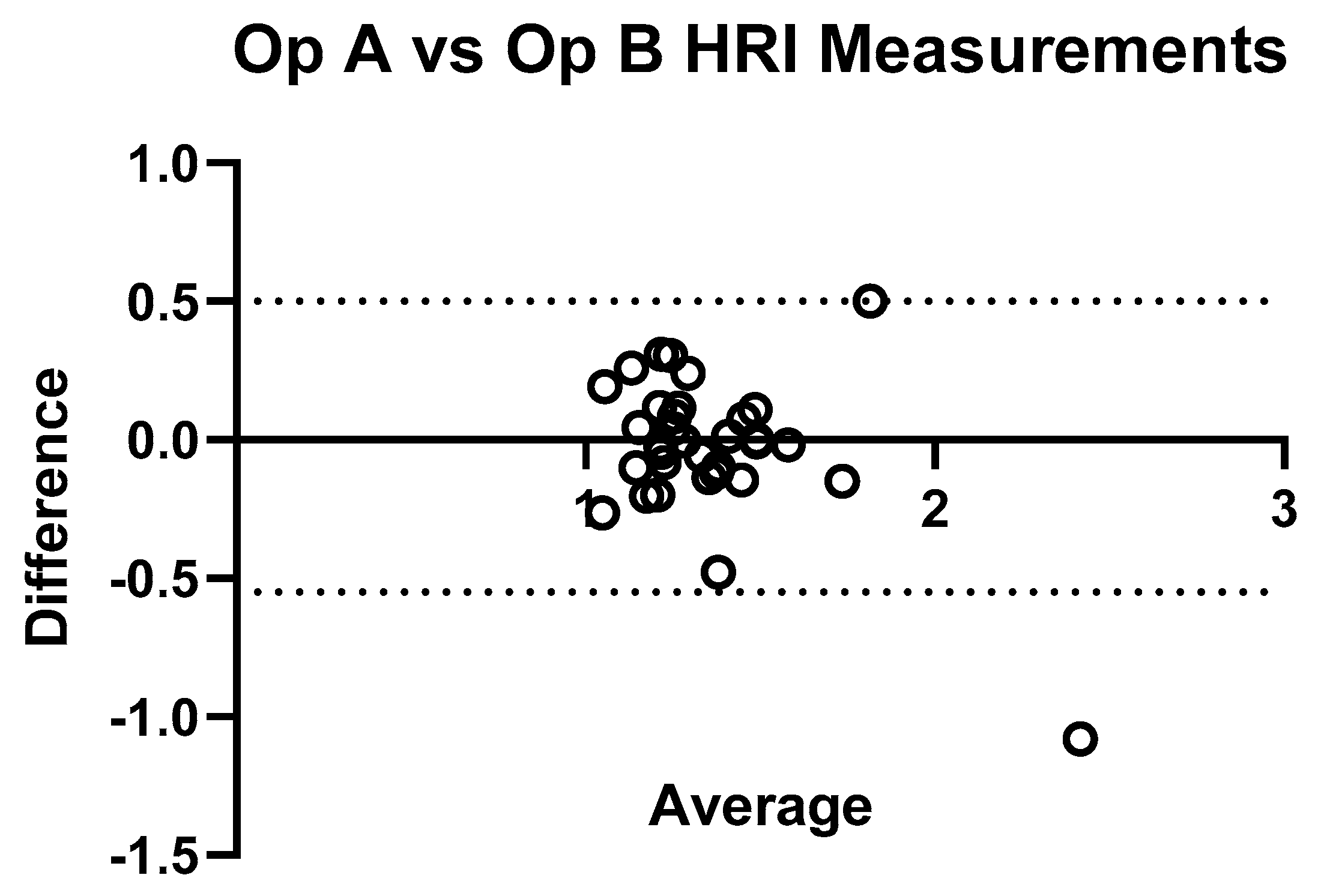
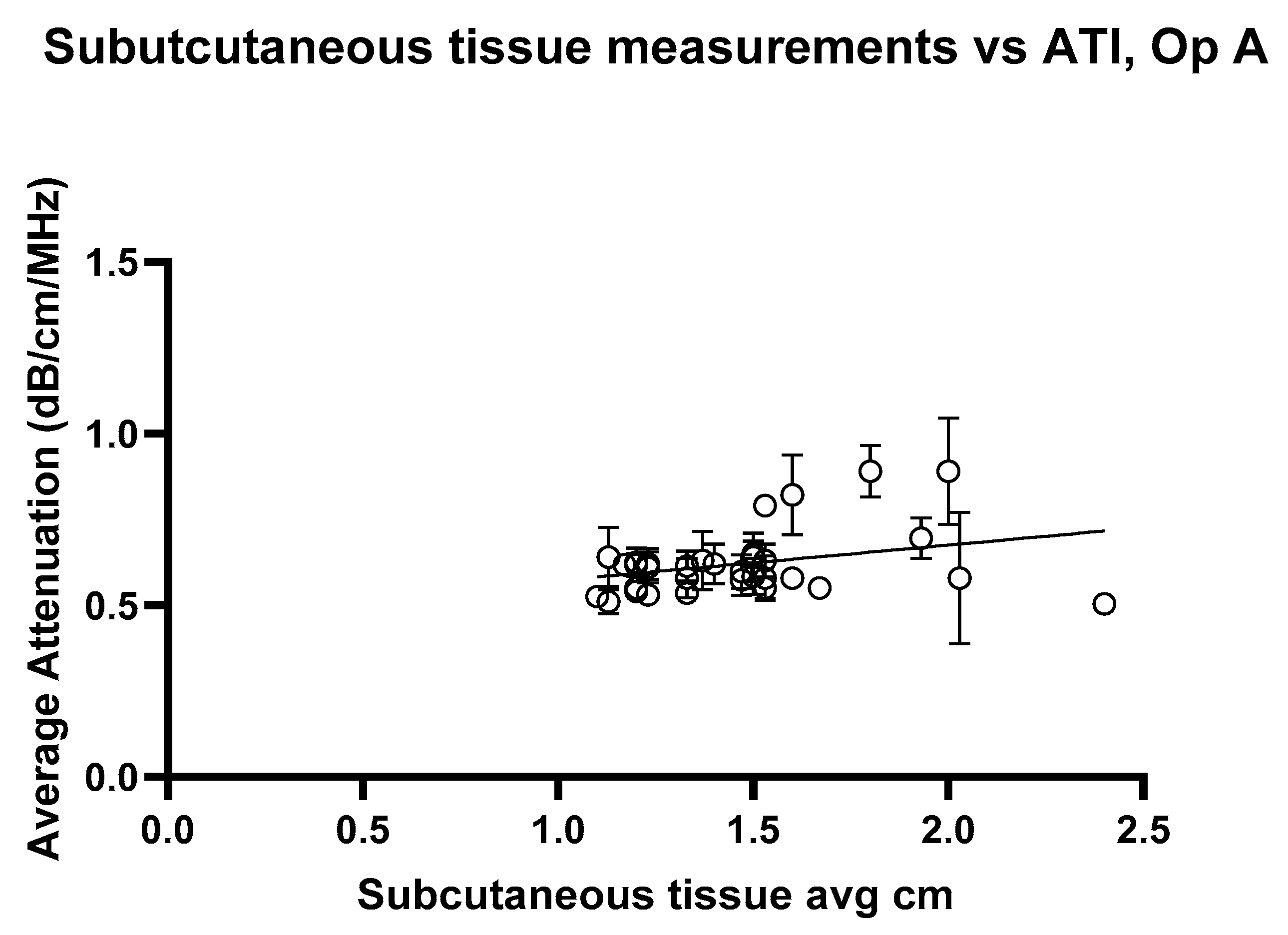
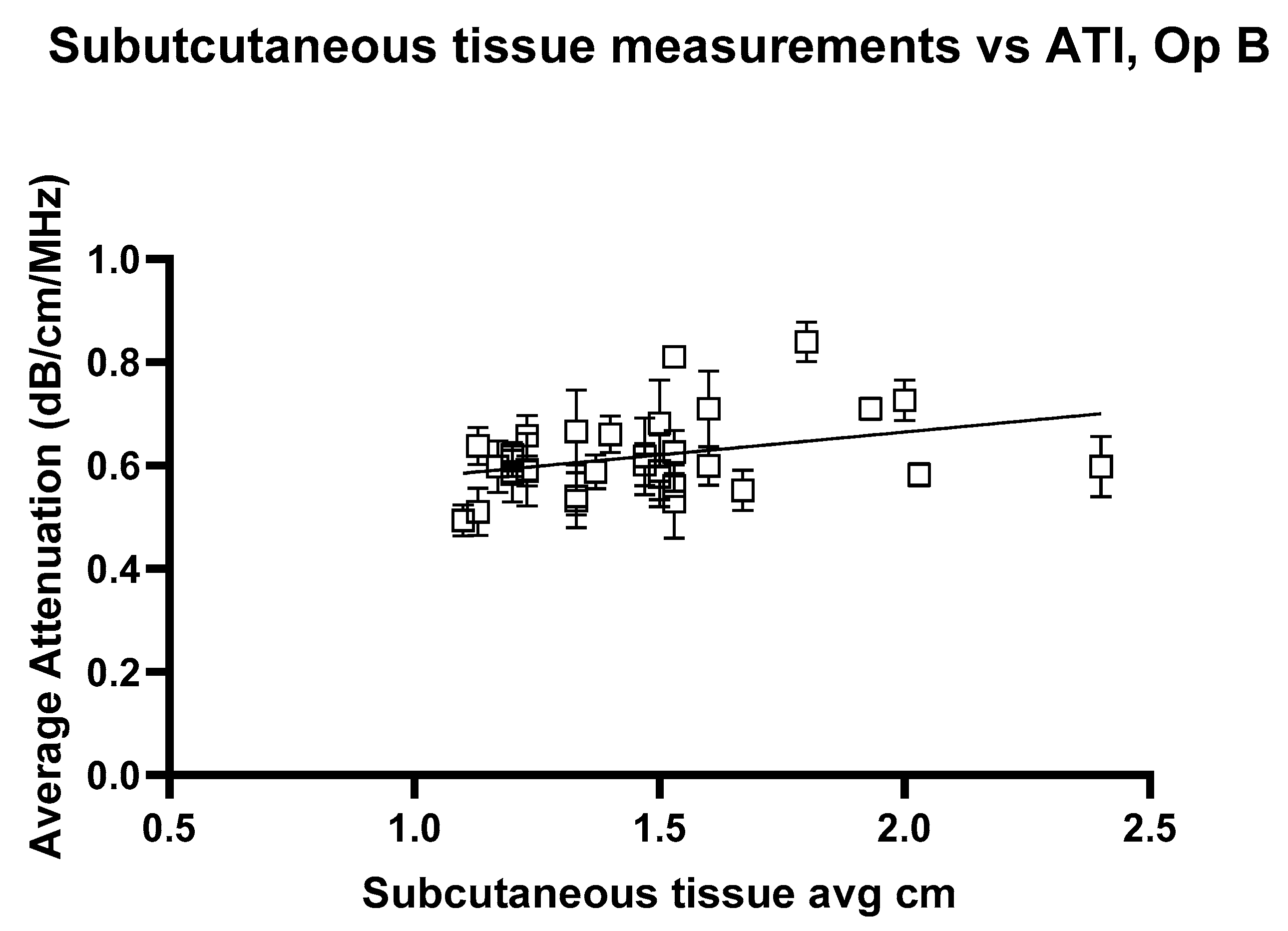
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATI | Ultrasound attenuation imaging |
| HRI | Hepatorenal Index |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| AOI | Area of Interest |
| MRI | Magnet resonance imaging |
| MRI-PDFF | MRI proton density fat fraction |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
References
- Huang, D.Q.; Wong, V.W.S.; Rinella, M.E.; Boursier, J.; Lazarus, J.V.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Loomba, R. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in adults. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2025, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, G.J.K.; Tan, F.X.N.; Sasikumar, N.A.; Tham, E.K.J.; Ko, D.; Kim, D.H.; Yeo, Y.H.; Srivastava, S.; Thongngarm, T.; Wong, V.W.S.; et al. High Global Prevalence of Steatotic Liver Disease and Associated Subtypes: A Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Yilmaz, Y.; Yu, M.L.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Fernandez, M.C.; Isakov, V.A.; Charlton, M.; Loomba, R.; Bugianesi, E.; Ratiu, V.; et al. Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes From Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Across the World: Data From the Global Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)/Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Registry. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2296–2306.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockey, D.C.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.D.; Nelson, R.C.; Smith, A.D. Liver biopsy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1017–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibulpolprasert, P.; Subpinyo, B.; Chirnaksorn, S.; Chattranukulchai Shantavasinkul, P.; Putadechakum, S.; Phongkitkarun, S.; Sritara, C.; Angkathunyakul, N.; Sumritpradit, P. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and liver biopsy to assess hepatic steatosis in obesity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 57324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Reeder, S.B.; Sirlin, C.B.; Loomba, R. Non-invasive, quantitative assessment of liver fat by MRI-PDFF as an endpoint in NASH trials. Hepatology 2018, 68, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatos, I.; Drazinos, P.; Yarmenitis, S.; Theotokas, I.; Koskinas, J.; Koullias, E.; Krokidis, M.; Diamantopoulos, S.; Angelopoulos, P.; Koulouris, N.; et al. Liver Ultrasound Attenuation: An Ultrasound Attenuation Index for Liver Steatosis Assessment. Ultrasound Q. 2022, 38, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, Y.; Wakui, N.; Nagai, H.; Igarashi, Y. The ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter is useful in quantification of hepatic steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. JGH Open 2021, 5, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesper, D.; Klett, D.; Schellhaas, B.; Pfeifer, L.; Leppkes, M.; Waldner, M.; Schlottmann, S.; Kratzer, A.; Dietrich, C.F.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Ultrasound-Based Attenuation Imaging for the Non-Invasive Quantification of Liver Fat—A Pilot Study on Feasibility and Inter-Observer Variability. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2020, 8, 1800409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi Burgio, M.; Ronot, M.; Reizine, E.; Rautou, P.E.; Castera, L.; Paradis, V.; Lebigot, J.; Bouattour, M.; Nault, J.C.; Vilgrain, V.; et al. Quantification of hepatic steatosis with ultrasound: Promising role of attenuation imaging coefficient in a biopsy-proven cohort. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, R.H.; Eissa, M.; Bluth, E.I.; Gulotta, P.M.; Davis, N.K. Hepatorenal index as an accurate, simple, and effective tool in screening for steatosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlschmidt, F.L.; Tafarel, J.R.; Menini-Stahlschmidt, C.M.; Baena, C.P. Hepatorenal index for grading liver steatosis with concomitant fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Soares Monteiro, L.B. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Raimondi, A.; Maiocchi, L.; De Silvestri, A.; Poma, G.; Kumar, V.; Copetti, M. Liver Fat Quantification With Ultrasound: Depth Dependence of Attenuation Coefficient. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 42, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Savietto, G.; Tinelli, C.; Nichetti, M.; Rondanelli, M.; Sasso, F.C. Performance of the Attenuation Imaging Technology in the Detection of Liver Steatosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 40, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, G.; Maiocchi, L.; Raciti, M.V.; Tinelli, C.; de Silvestri, A.; Nichetti, M.; De Cata, P.; Rondanelli, M.; Chiovato, L.; Calliada, F.; et al. Detection of Liver Steatosis with a Novel Ultrasound-Based Technique: A Pilot Study Using MRI-Derived Proton Density Fat Fraction as the Gold Standard. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivers, R.C.; Hill, C.R. Ultrasonic attenuation in human tissue. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1975, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooi, F.M.; Kripfgans, O.; Carson, P.L. Acoustic attenuation imaging of tissue bulk properties with a priori information. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, G.H. Computerized time-of-flight ultrasonic tomography for breast examination. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1977, 3, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, I.W.; Cho, Y.B.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, D.H. Diagnostic performance of ultrasound attenuation imaging for assessing low-grade hepatic steatosis. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Bian, H.; Zhu, Y.L.; Yan, H.M.; Wang, W.P.; Xia, M.F.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, R.; et al. Quantitative Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging in a Biopsy-Proven Cohort. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, S155–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Abe, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nagasawa, T.; Takikawa, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter as a noninvasive test for steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 48, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.X.; Mehta, B.; Kusel, K.; Seow, J.; Zelesco, M.; Abbott, S.; Clark, S.; Moran, J.; Mitchell, S.; Duryea, J.; et al. Hepatic steatosis: Qualitative and quantitative sonographic assessment in comparison to histology. Australas. J. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 27, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welman, C.J.; Saunders, J.; Zelesco, M.; Abbott, S.; Boardman, G.; Ayonrinde, O.T. Hepatic steatosis: Ultrasound assessment using attenuation imaging (ATI) with liver biopsy correlation. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 67, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraioli, G.; Barr, R.G.; Berzigotti, A.; Sporea, I.; Wong, V.W.; Reiberger, T.; Yoon, J.H.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Cui, X.W.; Sirli, R.; et al. WFUMB Guidelines/Guidance on Liver Multiparametric Ultrasound. Part 2: Guidance on Liver Fat Quantification. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2024, 50, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Abe, M.; Oshiro, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kakegawa, T.; Tomita, Y.; Ohno, N.; Ichikawa, T.; Otsuka, M.; Imai, Y.; et al. The most appropriate region-of-interest position for attenuation coefficient measurement in the evaluation of liver steatosis. J. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 48, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, A.; Grajo, J.R.; Gee, M.S.; Benjamin, A.; Zubajlo, R.E.; Thomenius, K.E.; Sirlin, C.B. Quantitative Hepatic Fat Quantification in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Using Ultrasound-Based Techniques: A Review of Literature and Their Diagnostic Performance. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 2461–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicle, O. Artificial intelligence in diagnostic ultrasonography. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 29, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed Central]
- Ko, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Na, H.; Hong, E.; Han, K.; Jung, I.; Kim, E.K.; Moon, H.J.; Park, V.Y.; et al. Deep convolutional neural network for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules on ultrasound. Head. Neck. 2019, 41, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; et al. Diagnosis of thyroid cancer using deep convolutional neural networks: A multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, T.; Kubota, K.; Mori, M.; Nitta, N.; Kato, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Togashi, K. Using deep learning to distinguish between benign and malignant breast masses on ultrasound. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2019, 37, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmauch, B.; Herent, P.; Jehanno, P.; Edeline, J.; Chammas, M.; Tubach, F.; Hervé, L. Diagnosis of focal liver lesions from ultrasound using deep learning. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| n (Range) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.52 (24.5–63.3) |
| Sex | 19 (f)/14 (m) |
| Weight (kg) | 67.3 (52–86) |
| Height (m) | 1.72 (1.53–1.90) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.6 (18.0–28.0) |
| Alcohol > 14 units/week | 3 yes/30 no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, A.; Hurni, O.; Paverd, C.; Hänni, O.; Ruby, L.; Frauenfelder, T.; Huber, F.A. Depth-Dependent Variability in Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging for Hepatic Steatosis: A Pilot Study of ATI and HRI in Healthy Volunteers. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070229
Martin A, Hurni O, Paverd C, Hänni O, Ruby L, Frauenfelder T, Huber FA. Depth-Dependent Variability in Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging for Hepatic Steatosis: A Pilot Study of ATI and HRI in Healthy Volunteers. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(7):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Alexander, Oliver Hurni, Catherine Paverd, Olivia Hänni, Lisa Ruby, Thomas Frauenfelder, and Florian A. Huber. 2025. "Depth-Dependent Variability in Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging for Hepatic Steatosis: A Pilot Study of ATI and HRI in Healthy Volunteers" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 7: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070229
APA StyleMartin, A., Hurni, O., Paverd, C., Hänni, O., Ruby, L., Frauenfelder, T., & Huber, F. A. (2025). Depth-Dependent Variability in Ultrasound Attenuation Imaging for Hepatic Steatosis: A Pilot Study of ATI and HRI in Healthy Volunteers. Journal of Imaging, 11(7), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11070229







