Inferring Body Measurements from 2D Images: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Method
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strings
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Selected Papers and Datasets
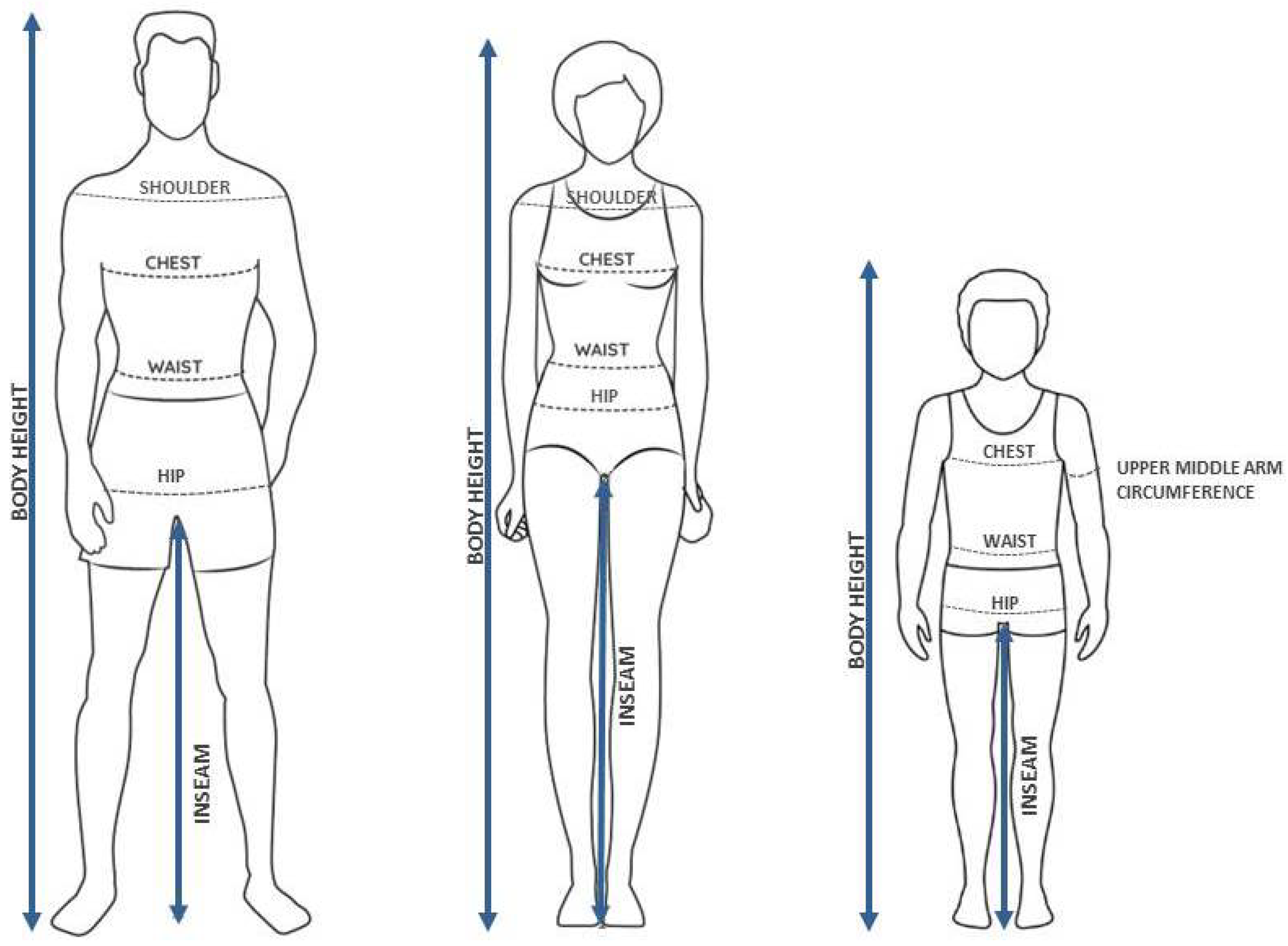
3. Three Types of Body-Shape Estimation Tasks
4. Body Measurement Estimation Methods
4.1. Traditional Machine-Learning Methods
Combining Traditional Machine-Learning and Deep-Learning Methods
4.2. Deep-Learning Methods
4.3. Limitations of CNN and the Rise of Alternative Architectures
5. Body Measurement Estimation Datasets
Preprocessing and Data Augmentation
6. Evaluation
7. Discussion
7.1. Methods
7.2. Datasets
7.3. Evaluation
7.4. Explainable AI
7.5. Readiness for Real-World Deployment
7.6. Ethics, Bias, and Privacy
8. Limitations and Conclusions
- Scope of applications: The review did not cover real-time or closed-loop systems such as digital twins, biomechanical or thermal simulations, or textile interaction modeling. These applications require edge-compatible architectures, low-latency inference, and integrated feedback mechanisms. Their implementation lies beyond the scope of current image-based body measurement models and remains a fertile ground for future research.
- Demographic fairness and policy: Achieving fairness across gender, ethnicity, and body types remains a critical challenge. The lack of globally representative datasets significantly constrains algorithmic generalization. Although this review addressed fairness conceptually, it did not cover tools for real-time bias monitoring or policy-enforced auditing. Emerging work on sample reweighting and fairness toolkits like AIF360 shows promise but has yet to be adapted for regression-based anthropometric prediction. The development of domain-specific fairness metrics and bias detection tools is urgently needed.
- Limitations related to cross-sector technologies and integration with Industry 5.0: Although our review is centered on AI-based methods for inferring body measurements from 2D images, primarily for child growth monitoring and nutritional assessment, it is important to acknowledge the growing relevance of body measurement estimation in Industry 5.0 initiatives, particularly in the garment sector. Recent research has shown how technologies such as digital human modeling (DHM), digital twins, and E-Libraries are being integrated to enable virtual sizing, customer-specific fit prediction, and sustainable production pipelines [104,105,106]. For example, e-body libraries can store user-specific measurements and 3D avatars, which are matched with garments using AI to reduce returns and enhance personalization. These systems often rely on body measurement data inserted by the user, but can also be inferred from images or scans, sometimes incorporating AI-based methods like the ones reviewed here. However, our paper does not address the engineering or implementation of such closed-loop systems. Instead, we focus on the methodological underpinnings of AI models for body measurement prediction. We see these industrial applications as complementary but distinct, and suggest that future interdisciplinary work could explore how AI models developed for healthcare may also serve as foundational components in garment technology platforms or digital twin systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casadei, K.; Kiel, J. Anthropometric Measurement StatPearls. 2019. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk537315 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Rumbo-Rodríguez, L.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Ferrer-Cascales, R.; García-D’Urso, N.; Hurtado-Sánchez, J.A.; Zaragoza-Martí, A. Comparison of body scanner and manual anthropometric measurements of body shape: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sowmya, A.; Khamis, H. Single camera multi-view anthropometric measurement of human height and mid-upper arm circumference using linear regression. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.D.; Jung, H.; Ebert, S.M.; Corner, B.D.; Reed, M.P. Efficient Model-Based Anthropometry under Clothing Using Low-Cost Depth Sensors. Sensors 2024, 24, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Moore, M.L.; Dellinger, J.R.; Adamson, B.T.; Benavides, M.L. Digital anthropometry via three-dimensional optical scanning: Evaluation of four commercially available systems. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocini, E.; Cammarota, C.; Frigerio, F.; Muzzioli, L.; Piciocchi, C.; Lacalaprice, D.; Buccolini, F.; Donini, L.M.; Pinto, A. Digital anthropometry: A systematic review on precision, reliability and accuracy of most popular existing technologies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.; Stocks, J.; Bonner, R.; Raywood, E.; Legg, S.; Lee, S.; Treleaven, P.; Lum, S. Acceptability, precision and accuracy of 3D photonic scanning for measurement of body shape in a multi-ethnic sample of children aged 5–11 years: The SLIC study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Bandoh, Y.; Kitahara, M.; Mikami, D. Calibration-Free Height Estimation for Person. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 19, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yang, X.; Hold-Geoffroy, Y.; Perazzi, F.; Eisenmann, J.; Sunkavalli, K.; Chandraker, M. Single view metrology in the wild. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 316–333. [Google Scholar]
- MohammedKhan, H.; Balvert, M.; Güven, C.; Postma, E. Predicting Human Body Dimensions from Single Images: A first step in automatic malnutrition detection. In Proceedings of the CAIP 2021: 1st International Conference on AI for People: Towards Sustainable AI, CAIP 2021, Bologna, Italy, 20–24 November 2021; European Alliance for Innovation: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2021; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- MohammedKhan, H.; Güven, C.; Balvert, M.; Postma, E. Image-Based Body Shape Estimation to Detect Malnutrition. In Proceedings of the SAI Intelligent Systems Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–8 September 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 577–590. [Google Scholar]
- Damberg, S. Predicting future use intention of fitness apps among fitness app users in the United Kingdom: The role of health consciousness. Int. J. Sport. Mark. Spons. 2022, 23, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntaner-Mas, A.; Martinez-Nicolas, A.; Lavie, C.J.; Blair, S.N.; Ross, R.; Arena, R. A Systematic Review of Fitness Apps and Their Potential Clinical and Sports Utility for Objective and Remote Assessment of Cardiorespiratory Fitness. Sport. Med. 2019, 49, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Forsythe, S. Adoption of virtual try-on technology for online apparel shopping. J. Interact. Mark. 2008, 22, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, A.; Müller, J.; Theissler, A. State-of-the-art on writing a literature review: An overview of types and components. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Tunis, Tunisia, 28–31 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi, R.; Javaid, S. Deep learning for pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images: A comprehensive survey. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loper, M.; Mahmood, N.; Romero, J.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. SMPL: A Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model. ACM Trans. Graph. Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia 2015, 34, 248:1–248:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohammedKhan, H.H.; Wanrooij, C.V.; Postma, E.O.; Güven, Ç.; Balvert, M.; Saeed, H.R.; Jaf, C.O.A.A. ARAN: Age-Restricted Anonymized Dataset of Children Images and Body Measurements. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, M.C.; Hadimaja, M.; Wong, J.; Mukherjee, S.S.; Foussat, A.; Chan, D.; Nandal, U.; Yap, F. Exploring the Use of a Length AI Algorithm to Estimate Children’s Length from Smartphone Images in a Real-World Setting: Algorithm Development and Usability Study. JMIR Pediatr. Parent. 2024, 7, e59564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Q. From prediction to measurement, an efficient method for digital human model obtainment. Int. J. Metrol. Qual. Eng. 2024, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Zou, X.; Wong, W. Learning Visual Body-shape-Aware Embeddings for Fashion Compatibility. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 8056–8065. [Google Scholar]
- Fadllullah, A.; Zulfia, R.; Pradana, A.; Akbar, M.A.Y. Automatic human height measurement system based on camera sensor with deep-learning and linear regression analysis. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2024, 35, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakina, M.; Muhammad, I.; Abdullahi, S.S. A multi-factor approach for height estimation of an individual using 2D image. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 231, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.D.B.; Teixeira, S.; Bordalo, V.; Lacoste, S.; Guimond, S.; Sousa, D.L.; Pinheiro, D.N.; Moreira, R.; Teles, A.S. A scale-equivariant CNN-based method for estimating human weight and height from multi-view clinic silhouette images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.A.; Hussain, M. A review of transformer-based models for computer vision tasks: Capturing global context and spatial relationships. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15178. [Google Scholar]
- Potamias, R.A.; Tarasiou, M.; Ploumpis, S.; Zafeiriou, S. Shapefusion: A 3d diffusion model for localized shape editing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 72–89. [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama, Y.; Endo, Y.; Kanamori, Y. DiffBody: Diffusion-Based Pose and Shape Editing of Human Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 6333–6342. [Google Scholar]
- Velesaca, H.O.; Vulgarin, J.; Vintimilla, B.X. Deep Learning-based Human Height Estimation from a Stereo Vision System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Systems (ICPRS), Guayaquil, Ecuador, 4–7 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Ha, E.J.; Choi, J.H. Human pose estimation using mediapipe pose and optimization method based on a humanoid model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, C.; Peleja, F.; Dotti, D.; de Santos, A. Human body shape classification based on a single image. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18480. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Feng, R.; Wu, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Z. 2D Human pose estimation: A survey. Multimed. Syst. 2023, 29, 3115–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Deshmukh, S.; Fernandes, F.; Patil, A.; Jabade, V. Poseanalyser: A survey on human pose estimation. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, E.; Hong, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Luo, P. DDP: Diffusion Model for Dense Visual Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 21741–21752. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, A.B.; Tahcfulloh, S. Digital Image Processing for Height Measurement Application Based on Python OpenCV and Regression Analysis. JOIV Int. J. Inf. Vis. 2022, 6, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Huang, J.; Xiong, A.; Pang, Y.; Wang, W.; Ding, B. Attention guided deep features for accurate body mass index estimation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 154, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartol, K.; Bojanić, D.; Petković, T.; Peharec, S.; Pribanić, T. Linear regression vs. deep learning: A simple yet effective baseline for human body measurement. Sensors 2022, 22, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Xiong, A.; Tan, X. Estimating Human Weight from A Single Image. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choutas, V.; Müller, L.; Huang, C.H.P.; Tang, S.; Tzionas, D.; Black, M.J. Accurate 3D Body Shape Regression using Metric and Semantic Attributes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maganti, S.; Yalamanchili, M.; Bandy, P.S.; J, S.K. Height and Weight Estimation of an Individual from Virtual Visuals. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), Lalitpur, Nepal, 20–22 July 2022; pp. 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, K.S.P.; Suh, S.; Zhou, B.; Lukowicz, P. Estimation of 3d body shape and clothing measurements from frontal-and side-view images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 2631–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Foysal, K.H.; Chang, H.J.; Bruess, F.; Chong, J.W. SmartFit: Smartphone application for garment fit detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.; Jain, M.; Gupta, N.K.; Hinsche, M.; Singh, P.; Matiaschek, M.; Behrens, T.; Militeri, M.; Birge, C.; Kaushik, S.; et al. Height Estimation of Children under Five Years using Depth Images. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 3886–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, S.; Hamada, M.; Sugimori, H. A deep-learning method using computed tomography scout images for estimating patient body weight. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, D. No-reference image quality assessment with convolutional neural networks and decision fusion. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wirta, J.; Kämäräinen, J.K. Silhouette body measurement benchmarks. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 7804–7809. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Kim, D.E. Body shape classification of Korean middle-aged women using 3D anthropometry. Fash. Text. 2020, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Zhu, S.; Shen, J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Shah, M. Deep learning-based human pose estimation: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.13392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlakos, G.; Choutas, V.; Ghorbani, N.; Bolkart, T.; Osman, A.A.; Tzionas, D.; Black, M.J. Expressive body capture: 3d hands, face, and body from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10975–10985. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Guo, G. Body Weight Analysis From Human Body Images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 2527–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunel, S.; Rhodin, H.; Fua, P. What face and body shapes can tell us about height. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1819–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Haritosh, A.; Gupta, A.; Chahal, E.S.; Misra, A.; Chandra, S. A novel method to estimate Height, Weight and Body Mass Index from face images. In Proceedings of the 2019 Twelfth International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3), Noida, India, 8–10 August 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dhikhi, T.; Suhas, A.N.; Reddy, G.R.; Vardhan, K.C. Measuring size of an object using computer vision. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 424–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmawi, S.; Alharbi, M.; Almaghrabi, A.; Alhothali, A. Fitme: Body measurement estimations using machine learning method. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 163, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantcheva, A.; Bremond, F.; Bilinski, P. Show me your face and I will tell you your height, weight and body mass index. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3555–3560. [Google Scholar]
- Kriz, P.; Riha, K.; Dutta, M.K.; Singh, A.; Marius, N. Determination of a Person’s Height from Images Using a Known Object Size. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Athens, Greece, 4–6 July 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, H.G.; Giorgi, G.; Eissfeller, B. Pose estimation and tracking of non-cooperative rocket bodies using time-of-flight cameras. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 139, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, J.; Sohn, K.A. Enhancing the performance of convolutional neural networks on quality degraded datasets. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Sydney, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Altinigne, C.Y.; Thanou, D.; Achanta, R. Height and Weight Estimation from Unconstrained Images. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibie, I.; Xu, W.; Mehta, D.; Pons-Moll, G.; Theobalt, C. In the wild human pose estimation using explicit 2d features and intermediate 3d representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10905–10914. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, A.; Black, M.J.; Jacobs, D.W.; Malik, J. End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7122–7131. [Google Scholar]
- Güler, R.A.; Neverova, N.; Kokkinos, I. Densepose: Dense human pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7297–7306. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Min, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Pan, L. Classification of female body shape based on two-dimensional image and computer vision technology. Text. Res. J. 2023, 93, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 466–481. [Google Scholar]
- Kajita, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Harada, K.; Yokoi, K. Introduction to Humanoid Robotics; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayati, S.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Hua, K.L.; Fu, J.; Cheng, W.H. What dress fits me best? Fashion recommendation on the clothing style for personal body shape. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 438–446. [Google Scholar]
- Keys, A.; Fidanza, F.; Karvonen, M.J.; Kimura, N.; Taylor, H.L. Indices of relative weight and obesity. J. Chronic Dis. 1972, 25, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guideline on the Prevention and Management of Wasting and Nutritional Oedema (Acute Malnutrition) in Infants and Children Under 5 Years; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Group, W.M.G.R.S. Reliability of anthropometric measurements in the WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 450, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knap, P. Human Modelling and Pose Estimation Overview. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.19290. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3.6M: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3D human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sooklal, S.; Hosein, P.; Teelucksingh, S. A review of human body shape detection techniques and their application to the prediction of health risks. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on e-Health, Madeira, Portugal, 1–4 July 2016; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Marr, D. Vision: A Computational Investigation into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information; Henry Holt and Co., Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.T.; Li, Y.W.; Chen, H.T.; Feng, S.Y.; Chien, T.T. A dynamic fitting room based on microsoft kinect and augmented reality technologies. In Proceedings of the Human-Computer Interaction. Interaction Modalities and Techniques: 15th International Conference, HCI International 2013, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 21–26 July 2013; Proceedings, Part IV 15. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.G.; Xie, H.J.; Niu, X.C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, S.W.; Shan, Y.Z. Transformer-based weakly supervised 3D human pose estimation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2025, 109, 104432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer New York Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, J.W.M.; Ohata, E.F.; Nascimento, N.M.; Alves, S.S.; Loureiro, L.L.; Bittencourt, V.Z.; Capistrano, V.L.; da Rocha, A.R.; Rebouças Filho, P.P. Estimating anthropometric measurements through 2D images using machine learning with gender-based analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Yokohama, Japan, 30 June–5 July 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pishchulin, L.; Wuhrer, S.; Helten, T.; Theobalt, C.; Schiele, B. Building Statistical Shape Spaces for 3D Human Modeling. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 67, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinette, K.M.; Blackwell, S.; Daanen, H.; Boehmer, M.; Fleming, S. Civilian American and European Surface Anthropometry Resource (CAESAR), Final Report. Volume 1. Summary; Technical Report; Sytronics Inc.: Beavercreek, OH, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, C.; Bradtmiller, B.; Corner, B.; Paquette, S. 2014 Anthropometric Survey (ANSUR II) of U.S. Army Personnel: Methods and Summary Statistics; Technical Report; US Army Natick Soldier Research, Development and Engineering Center: Natick, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- TC2: Textile and Clothing Technology Corporation. 2022. Available online: http://www.tc2.com/ (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- SCANative: Anthropometry of Indigenous Populations. 2020; available via academic collaboration only.
- CANDAT: Children’s Anthropometry Data. 2019; available via academic collaboration only.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. 1999–2005. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Ricanek, K.; Tesafaye, T. MORPH: A longitudinal image database of normal adult age-progression. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FGR06), Southampton, UK, 10–12 April 2006; pp. 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, N.; Baumgartner, S.; Gut, A.; Van Hedel, H.J.A. Concurrent Validity of a Custom Method for Markerless 3D Full-Body Motion Tracking of Children and Young Adults based on a Single RGB-D Camera. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 31, 1943–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hong, F.; Hu, T.; Pan, L.; Mei, H.; Xiao, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. HumanLiff: Layer-wise 3D Human Diffusion Model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühstück, A.; Singh, K.; Shechtman, E.; Mitra, N.; Wonka, P.; Lu, J. InsetGAN for Full-Body Image Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7723–7732. [Google Scholar]
- Biotonix Inc. Biotonix Health Solutions Dataset. 2024. Available online: https://biotonix.com/en/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Schaerf, L.; Postma, E.; Popovici, C. Art authentication with vision transformers. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 11849–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Taj, I.; Usman, S.M.; Shah, S.N.H.; Imran, A.S.; Khalid, S. A hybrid approach of vision transformers and CNNs for detection of ulcerative colitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Uncertainty-guided Diffusion Model for 3D Human Pose Estimation. Neurocomputing 2025, 641, 130306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Kang, B.; Jin, X.; Yang, L.; Lian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Feng, J. Deepvit: Towards deeper vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.11886. [Google Scholar]
- ACF International. SMART Methodology: Standardized Monitoring and Assessment of Relief and Transitions—Anthropometric Measurement Guidelines. Action Against Hunger. 2006. Available online: https://smartmethodology.org (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Alharthi, A.; Alqurashi, A.; Alharbi, T.; Alammar, M.; Aldosari, N.; Bouchekara, H.; Shaaban, Y.; Shahriar, M.S.; Ayidh, A.A. The Role of Explainable AI in Revolutionizing Human Health Monitoring. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.07347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ma, R.; Kuang, J.; Zhang, Y. How Decisions Are Made in Brains: Unpack “Black Box” of CNN With Ms. Pac-Man Video Game. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142446–142458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, E.M.; Ford, C.; Quinn, M.; Keane, M.T. Explaining black-box classifiers using post-hoc explanations-by-example: The effect of explanations and error-rates in XAI user studies. Artif. Intell. 2021, 294, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhore, V.; Bhat, A.; Nerlekar, V.; Chavhan, K.; Umare, A. Enhancing Explainable AI: A Hybrid Approach Combining GradCAM and LRP for CNN Interpretability. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.12175. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Li, J.; Wen, L.; Su, C.; Hao, F.; Zhang, C.J.; Chen, L. XPose: eXplainable Human Pose Estimation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.12370. [Google Scholar]
- Tempel, F.; Groos, D.; Ihlen, E.A.F.; Adde, L.; Strümke, I. Choose Your Explanation: A Comparison of SHAP and GradCAM in Human Activity Recognition. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.16003. [Google Scholar]
- MTailor. Custom Clothing Measured by Your Phone. Available online: https://www.mtailor.com/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Samy, T.M.; Asham, B.I.; Slim, S.O.; Abohany, A.A. Revolutionizing online shopping with FITMI: A realistic virtual try-on solution. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 6125–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soley, N.; Rattsev, I.; Speed, T.J.; Xie, A.; Ferryman, K.S.; Taylor, C.O. Predicting postoperative chronic opioid use with fair machine learning models integrating multi-modal data sources: A demonstration of ethical machine learning in healthcare. J. Am. Med Inf. Assoc. 2025, 32, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmezer, S.; Demircioglu, P.; Bogrekci, I.; Bas, G.; Durakbasa, M.N. Revolutionizing the garment industry 5.0: Embracing closed-loop design, E-libraries, and digital twins. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioglu, P.; Donmezer, S.; Bogrekci, I.; Durakbasa, N.M. Garment Industry 5.0: Transforming Through Digital Integration of 3D Virtual Measurement Data and Characteristics. In Illustrating Digital Innovations Towards Intelligent Fashion: Leveraging Information System Engineering and Digital Twins for Efficient Design of Next-Generation Fashion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 553–571. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, D.Ø; Slåtten, K.; Berg, T. From Industry 4.0 to Industry 6.0: Tracing the Evolution of Industrial Paradigms Through the Lens of Management Fashion Theory. Systems 2025, 13, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KhoKhar, F.A.; Shah, J.H.; Khan, M.A.; Sharif, M.; Tariq, U.; Kadry, S. A review on federated learning towards image processing. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 99, 107818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Author(s) | Title | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Mohammed Khan et al. [18] | ARAN: Age-restricted Anonymized Dataset of Children Images and Body Measurements | 2025 |
| Chua et al. [19] | Exploring the Use of a Length AI Algorithm to Estimate Children’s Length from Smartphone Images in a Real-World Setting | 2024 |
| Wang et al. [20] | From prediction to measurement, an efficient method for digital human model obtainment. | 2024 |
| Park et al. [4] | Efficient Model-Based Anthropometry under Clothing Using Low-Cost Depth Sensors. | 2024 |
| Pang et al. [21] | Learning Visual Body-shape-Aware Embeddings for Fashion Compatibility. | 2024 |
| Fadllullah et al. [22] | Automatic human height measurement system based on camera sensor with deep-learning and linear regression analysis. | 2024 |
| Sakina et al. [23] | A multi-factor approach for height estimation of an individual using 2D image. | 2024 |
| Lima et al. [24] | A scale-equivariant CNN-based method for estimating human weight and height from multi-view clinic silhouette images. | 2024 |
| Takeda, Toshiaki et al. [8] | Calibration-Free Height Estimation for Person | 2024 |
| Pereira and Hussain [25] | A review of transformer-based models for computer vision tasks: Capturing global context and spatial relationships | 2024 |
| Potamias et al. [26] | Shapefusion: A 3D diffusion model for localized shape editing | 2024 |
| Okuyama et al. [27] | DiffBody: Diffusion-Based Pose and Shape Editing of Human Images | 2024 |
| Velesaca et al. [28] | Deep Learning-based Human Height Estimation from a Stereo Vision System. | 2023 |
| Kim et al. [29] | Human pose estimation using mediapipe pose and optimization method based on a humanoid model. | 2023 |
| Trotter et al. [30] | Human body shape classification based on a single image. | 2023 |
| Chen et al. [31] | 2D Human Pose Estimation: A Survey | 2023 |
| Kulkarni et al. [32] | PoseAnalyser: A Survey on Human Pose Estimation | 2023 |
| MohammedKhan et al. [11] | Image-Based Body Shape Estimation to Detect Malnutrition | 2023 |
| Ji et al. [33] | DDP: Diffusion Model for Dense Visual Prediction | 2023 |
| Abadi et al. [34] | Digital Image Processing for Height Measurement Application Based on Python OpenCV and Regression Analysis | 2022 |
| Jin et al. [35] | Attention Guided Deep Features for Accurate Body Mass Index Estimation | 2022 |
| Bartol et al. [36] | Linear Regression vs. Deep Learning: A Simple Yet Effective Baseline for Human Body Measurement | 2022 |
| Jin et al. [37] | Estimating Human Weight from A Single Image | 2022 |
| Choutas et al. [38] | Accurate 3D Body Shape Regression using Metric and Semantic Attributes | 2022 |
| Maganti et al. [39] | Height and Weight Estimation of an Individual from Virtual Visuals | 2022 |
| Thota et al. [40] | Estimation of 3D Body Shape and Clothing Measurements from Frontal- and Side-View Images | 2022 |
| Mohammed Khan et al. [10] | Predicting Human Body Dimensions from Single Images: A First Step in Automatic Malnutrition Detection | 2021 |
| Foysal et al. [41] | SmartFit: Smartphone Application for Garment Fit Detection | 2021 |
| Trivedi et al. [42] | Height Estimation of Children Under Five Years Using Depth Images | 2021 |
| Ichikawa et al. [43] | A Deep-Learning Method Using Computed Tomography Scout Images for Estimating Patient Body Weight | 2021 |
| Varga [44] | No-Reference Image Quality Assessment with Convolutional Neural Networks and Decision Fusion | 2021 |
| Yan et al. [45] | Silhouette Body Measurement Benchmarks | 2021 |
| Tinsley et al. [5] | Digital Anthropometry via Three-Dimensional Optical Scanning: Evaluation of Four Commercially Available Systems | 2020 |
| Yu et al. [46] | Body Shape Classification of Korean Middle-Aged Women Using 3D Anthropometry | 2020 |
| Zheng et al. [47] | Deep Learning-Based Human Pose Estimation: A Survey | 2020 |
| Pavlakos et al. [48] | Expressive Body Capture: 3D Hands, Face, and Body from a Single Image | 2019 |
| Jiang [49] | Body Weight Analysis from Human Body Images | 2019 |
| Gunel et al. [50] | What Face and Body Shapes Can Tell Us About Height | 2019 |
| Haritosh et al. [51] | A Novel Method to Estimate Height, Weight and Body Mass Index from Face Images | 2019 |
| Dhikhi et al. [52] | Measuring Size of an Object Using Computer Vision | 2019 |
| Ashmawi et al. [53] | FitMe: Body Measurement Estimations Using Machine Learning Method | 2019 |
| Liu et al. [3] | Single Camera Multi-View Anthropometric Measurement of Human Height and Mid-Upper Arm Circumference Using Linear Regression | 2018 |
| Dantcheva et al. [54] | Show Me Your Face and I Will Tell You Your Height, Weight and Body Mass Index | 2018 |
| Kriz et al. [55] | Determination of a Person’s Height from Images Using a Known Object Size | 2018 |
| Martínez et al. [56] | Pose Estimation and Tracking of Non-Cooperative Rocket Bodies Using Time-of-Flight Cameras | 2017 |
| Cao et al. [57] | Realtime Multi-Person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields | 2017 |
| Yim et al. [58] | Enhancing the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks on Quality Degraded Datasets | 2017 |
| Dataset | # Images | # Subjects | Application | Labels | Children | Face/Body/Scan | Demographic Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAESAR [79] | N/A | 2400 | Ergonomics, apparel, healthcare | Yes | No | 3D Scans | North American and European |
| ANSUR [80] | N/A | 13,000 | Military, ergonomics, apparel | Yes | No | 3D Scans | US Military, mostly white |
| Human3.6M [71] | 3.6 m | 11 | Pose estimation, 3D modeling | No | No | Body pose | Limited |
| TC2 [81] | N/A | Variable | Apparel, ergonomics | Yes | Unknown | 3D Scans | Not specified |
| SCANative [82] | N/A | Unknown | Indigenous population anthropometry | Yes | Unknown | No | Indigenous populations (Canada) |
| CANDAT [83] | N/A | Unknown | Healthcare, nutrition, growth studies | Yes | Yes | No | Not specified |
| NHANES [84] | N/A | Unknown | Public health, nutrition, growth studies | Yes | Yes | No | Diverse U.S. population |
| IMDB-23K [50] | 23,000 | 12,104 | Age, gender prediction, height analysis | Yes (Height) | No | Face/Full body | Diverse western celebrities |
| MORPH-II [85] | 55k academic– 202k commercial | 55,000 | Age estimation, demographic studies | Yes (Age, Gender) | No | Facial Images | 77% black, 19% white, rest other |
| Body-Fit [45] | NA | 4149 | Body measurement estimation | Yes (16 body measurements) | No | Silhouette images | Not specified |
| Image-to-BMI [37] | 4189 | 3000 | BMI, gender, age, height, and weight estimation | Yes | No | Full body images | Diverse (unknown distribution) |
| ARAN [18] | 2048 | 512 | Pediatric growth and malnutrition monitoring | Yes (Height, weight, waist, head circ.) | Yes | Body (multi-view) | Kurdish |
| Publication | Dataset | H | W | WC | HC | TC | CC | WR | Comp. Diff. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (kg) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |||
| Mohammedkhan et al. [10] | CAESAR renders | 0.90 | – | 59 | – | – | – | – | M |
| Trivedi et al. [42] | CGM custom data | 1.40 | – | – | – | – | – | – | M |
| Lima et al. [24] | Botanic solution [89] | 3.68 | 3.77 | – | – | – | – | – | M |
| Sakina et al. [23] | Image-to-BMI | 6.20 | – | – | – | – | – | – | M |
| Maganti et al. [39] | Custom celebrity RGB | 6.90 | 3.20 | – | – | – | – | – | M |
| Gunel et al. [50] | IMDB-23K | 6.94 | – | – | – | – | – | – | H |
| Ichikawa et al. [43] | CT scans | – | 4.46 | – | – | – | – | – | H |
| Yilmaz & Achanta [59] | IMDB-23K | – | 9.80 | – | – | – | – | – | H |
| Thota et al. [40] | Synthetic 3D renders | – | – | 31.1 | 24.4 | – | 29.4 | – | M |
| Bartol et al. [36] | BODY-fit | – | – | 39.5 | 28.0 | 16.0 | 30.3 | 2.7 | L |
| Bartol et al. (alt) [36] | ANSUR | – | – | 37.9 | 21.6 | 17.0 | 29.1 | 4.4 | L |
| Mohammedkhan et al. [11] | CAESAR + AGORA | 1.14 | – | 24.3 | 10.3 | – | – | – | M |
| Yan et al. [45] | Silhouette dataset | – | – | 16.5 | 14.0 | 14.6 | 22.0 | 4.5 | M |
| Mohammedkhan et al. [18] | ARAN | 2.54 | 1.51 | 25.3 | 15.2 | – | – | – | M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammedkhan, H.; Fleuren, H.; Güven, Ç.; Postma, E. Inferring Body Measurements from 2D Images: A Comprehensive Review. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060205
Mohammedkhan H, Fleuren H, Güven Ç, Postma E. Inferring Body Measurements from 2D Images: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(6):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060205
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammedkhan, Hezha, Hein Fleuren, Çíçek Güven, and Eric Postma. 2025. "Inferring Body Measurements from 2D Images: A Comprehensive Review" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 6: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060205
APA StyleMohammedkhan, H., Fleuren, H., Güven, Ç., & Postma, E. (2025). Inferring Body Measurements from 2D Images: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Imaging, 11(6), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11060205







