Benchmarking of Multispectral Pansharpening: Reproducibility, Assessment, and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Notation
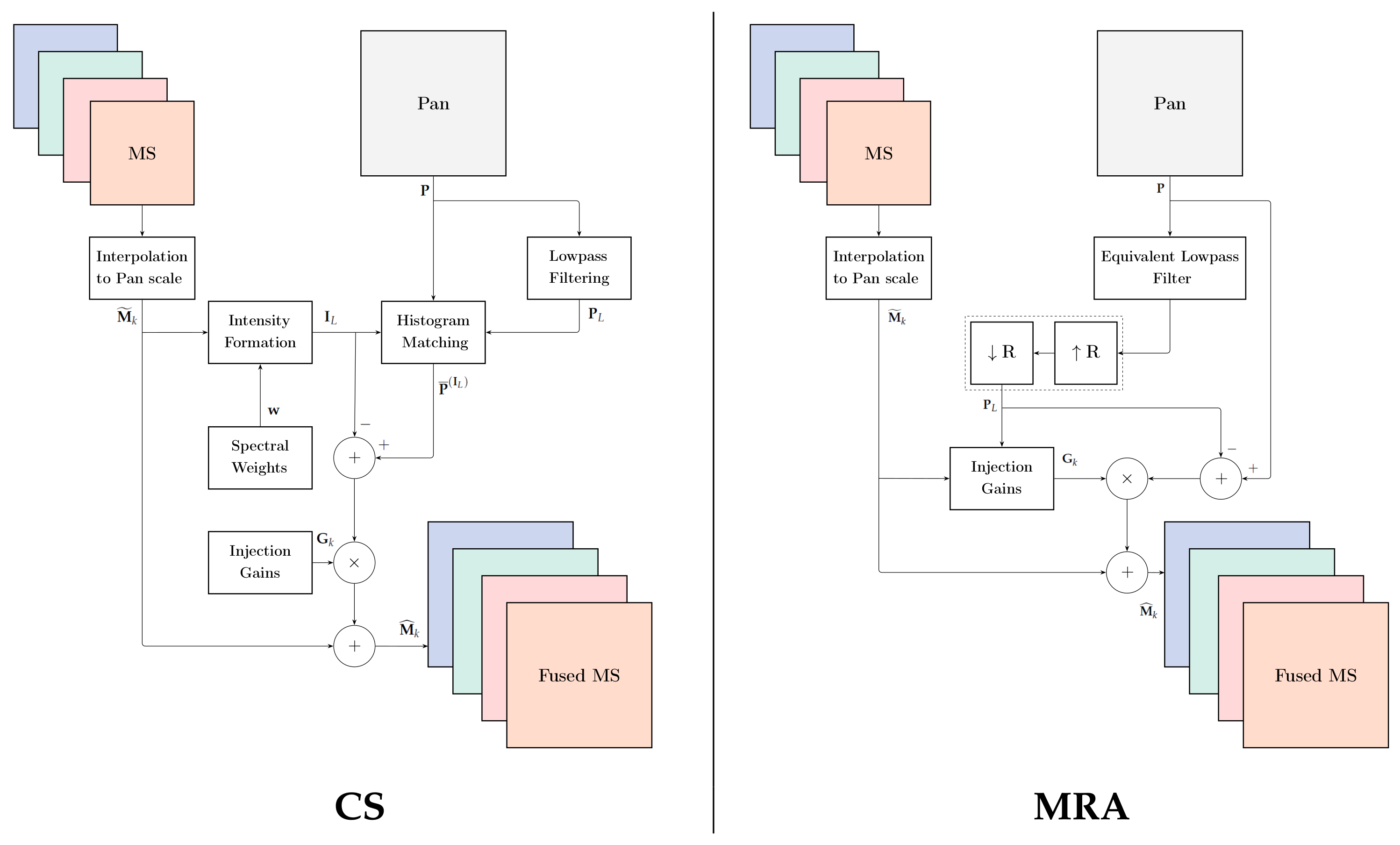
2.2. Component Substitution Methods
2.3. Multiresolution Analysis Methods
2.4. Hybrid Methods
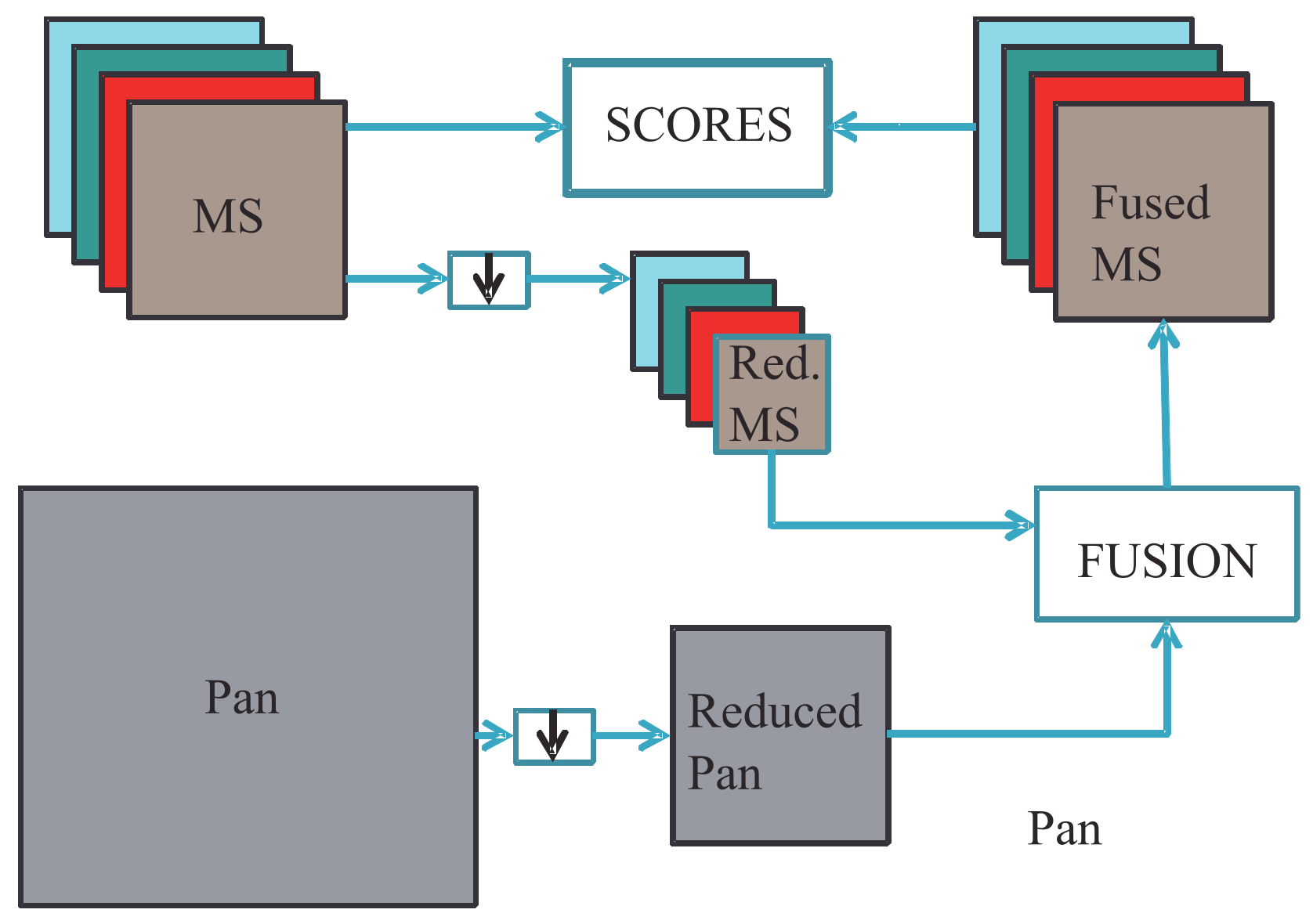
2.5. Assessment
- Consistency, checked at the spatial scale of the fusion product.
- Synthesis, checked at a spatial scale that is r times greater than that of the original Pan (with r in the MS-to-Pan scale ratio), as outlined in Figure 3.
2.6. Reproducibility
2.7. Meta-Analysis
2.8. Benchmarking
- Choose at least two different datasets, not two parts of the same image, coming from two different instruments; at least one should have a 4:1 MS-to-Pan scale ratio. A different number of bands between the two datasets is also desirable.
- Choose performance indexes that are obviously different for reduced resolution and full resolution. The performance indexes should be fairly independent of one another, specific for pansharpening, exhibit good discrimination capability, and be reasonably in-trend. It is important not to use too many indexes in order to avoid confusion. In particular, low-confidence indexes that have never been validated for pansharpening evaluations should be avoided, e.g., entropy, mutual information, average gradients, etc., as they might compromise the success of the comparative assessment.
- Whenever possible, use a standard implementation of CS, MRA, and hybrid methods such as those provided in [9], in which a few algorithms stand out for performance and efficiency. Comparisons with up-to-date top-performing methods, though not very efficient in terms of the performance–cost tradeoff, should be performed through meta-analysis, as we demonstrate in Section 3.
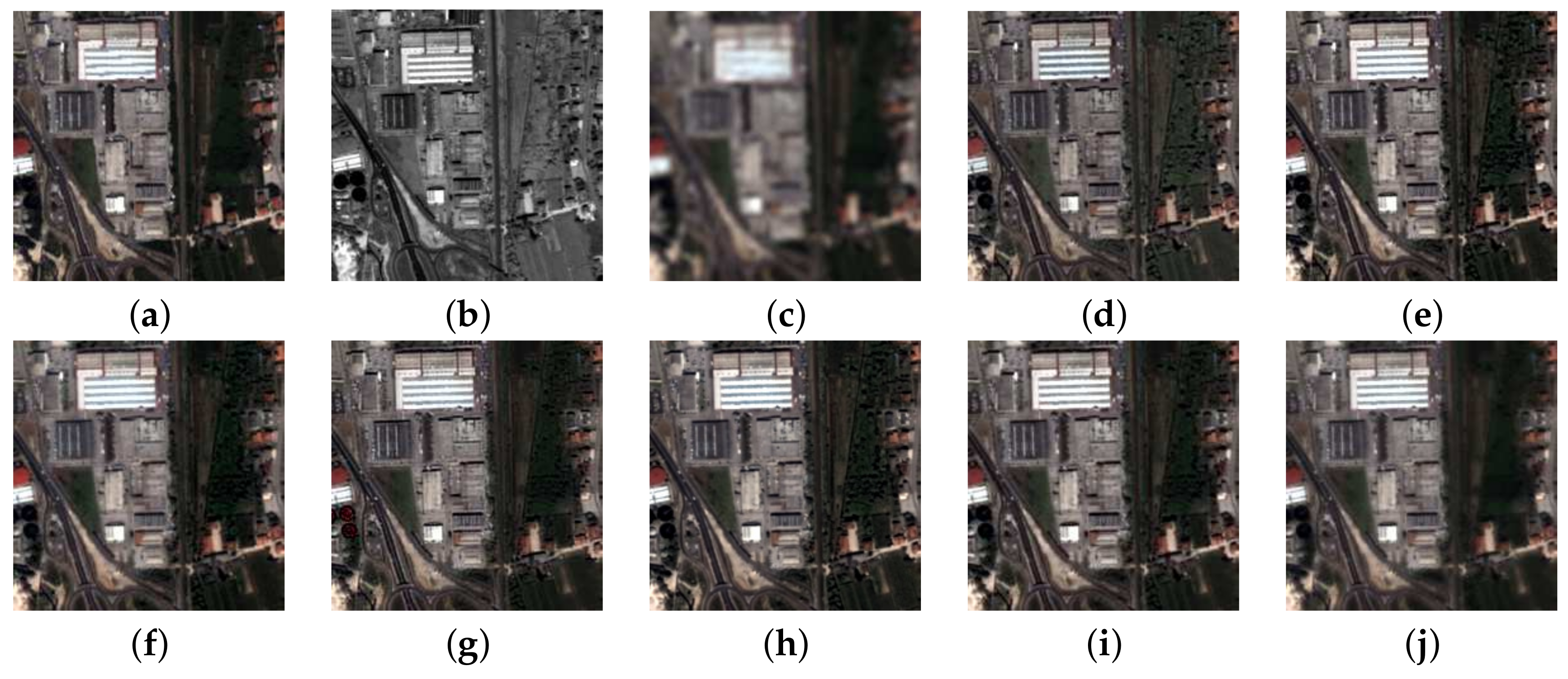
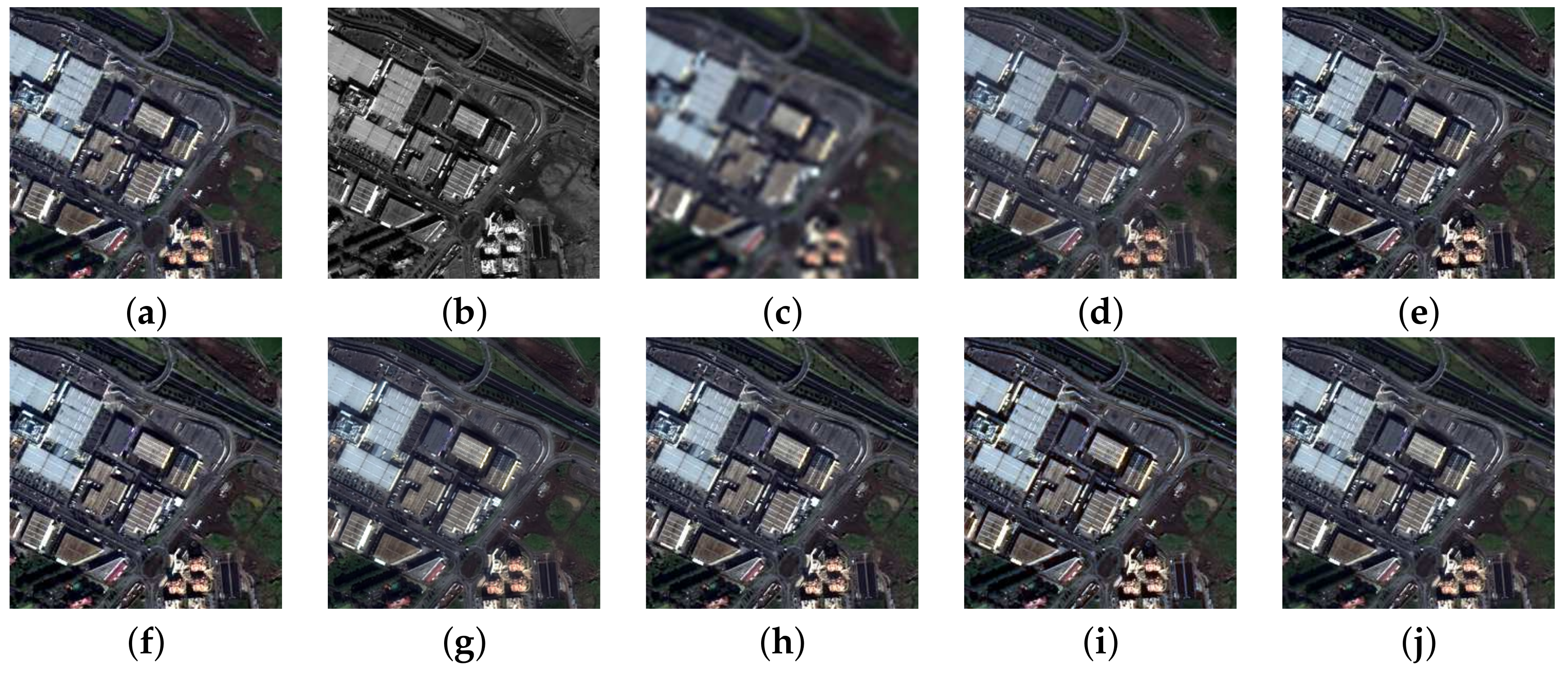
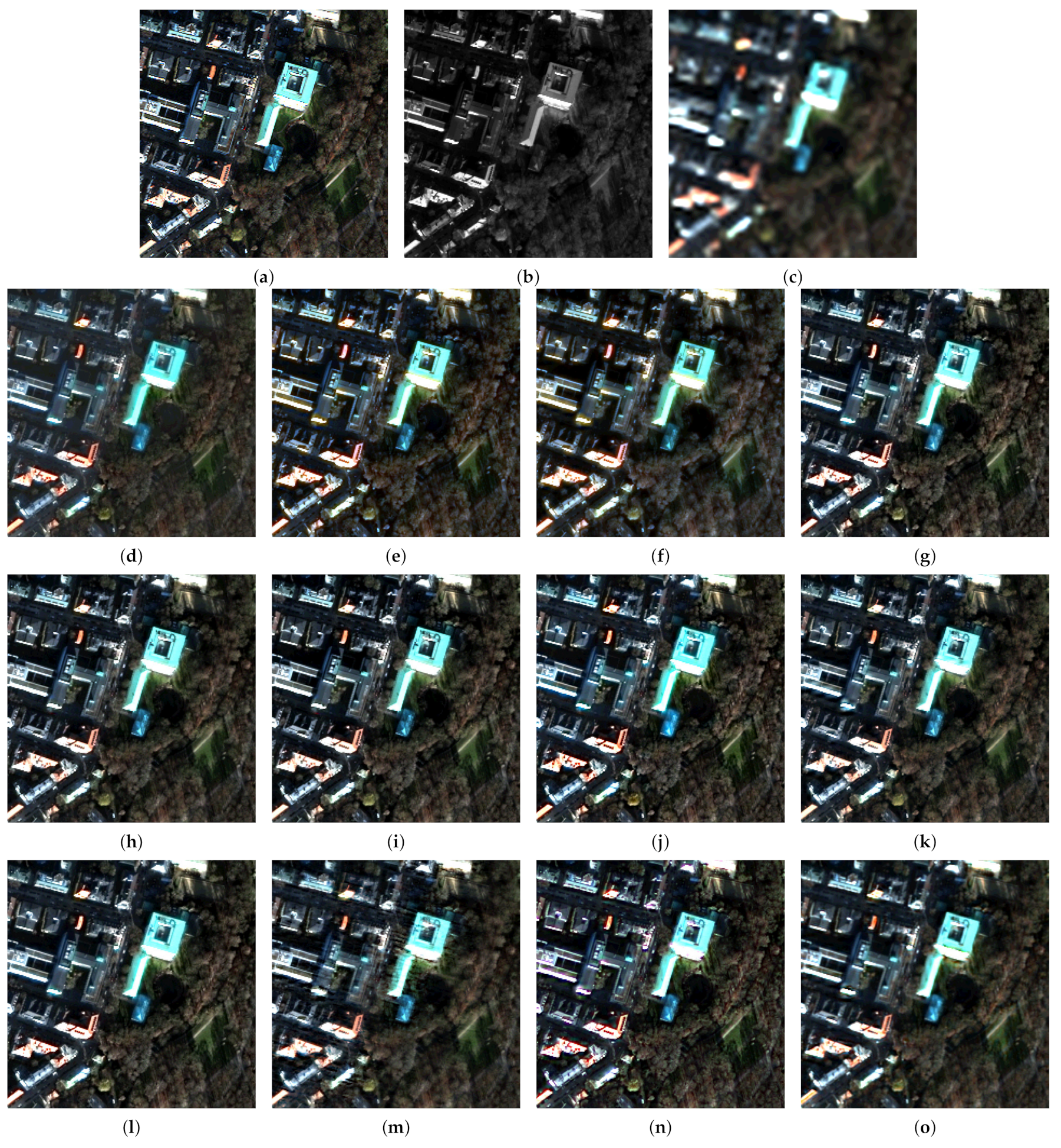
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Benchmarks
- MS image interpolated with a 23-taps kernel (EXP) [15].
- Gram–Schmidt (GS) spectral sharpening method [11].
- Fast fusion with hyperspherical color space (HCS) [95].
- Optimized BT with haze correction (BT-H) [33].
- Fast fusion with hyper-ellipsoidal color space (HECS) [13].
- Original AWLP approach proposed in [38].
- GLP with MTF filters and full-scale detail injection modeling (MTF-GLP-FS) [98].
- Sparse representation dictionary learning pansharpening (SRDLP) [46].
- Joint sparse and low-rank pansharpening (JSLRP) [44].
- Fusion based on sparse representation of spatial details (SR-D) [42].
- Fusion based on total-variation (TV) optimization [41].
- Advanced pansharpening with neural networks and fine tuning (A-PNN-FT) [55].
3.2. Setup
- Data format; we used the spectral radiance unpacked to floating-point values,
- Interpolation filters; we used 23-tap filters [15].
- RR or FR assessment; we adopted RR assessment.
- In the case of RR assessment, we specified the reduction filters using MTF-matched Gaussian filters [24] with two cascaded stages of filtering and decimation by two.
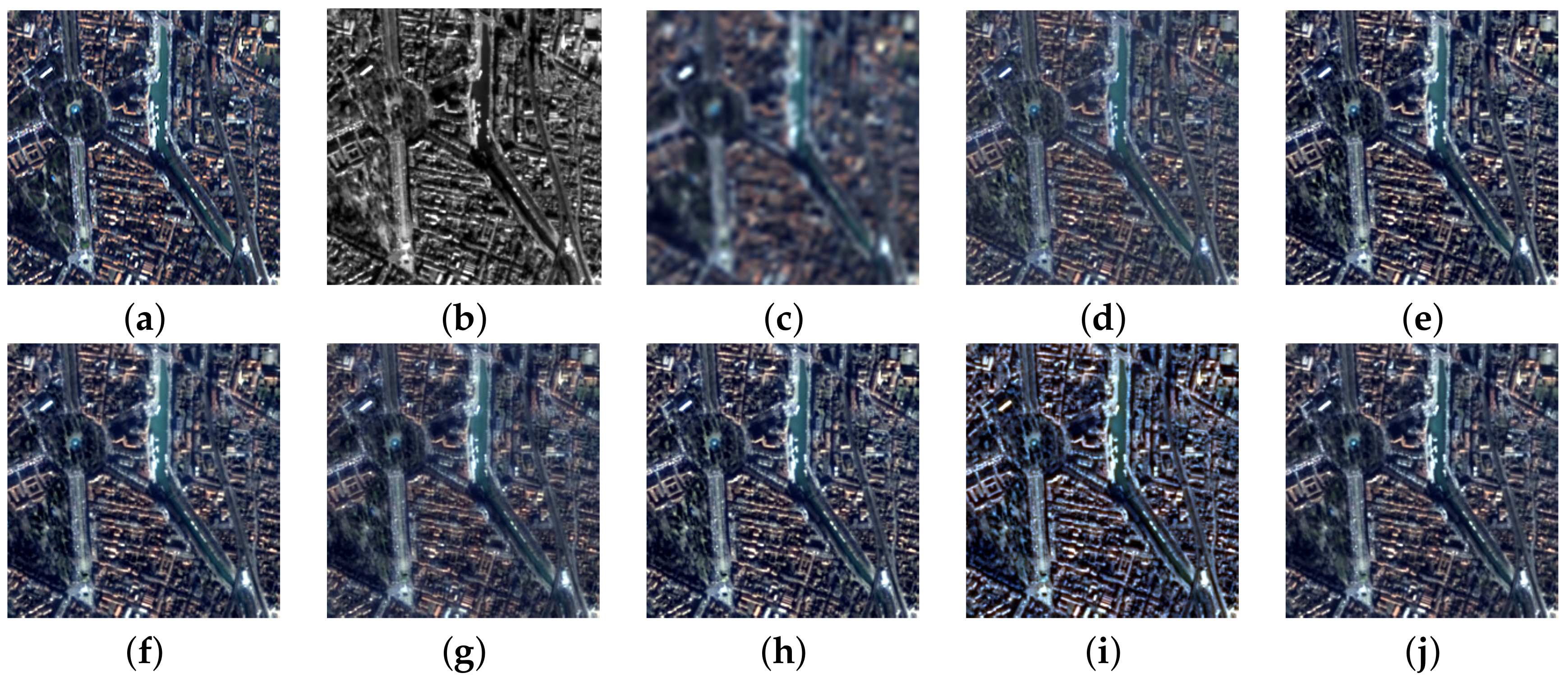
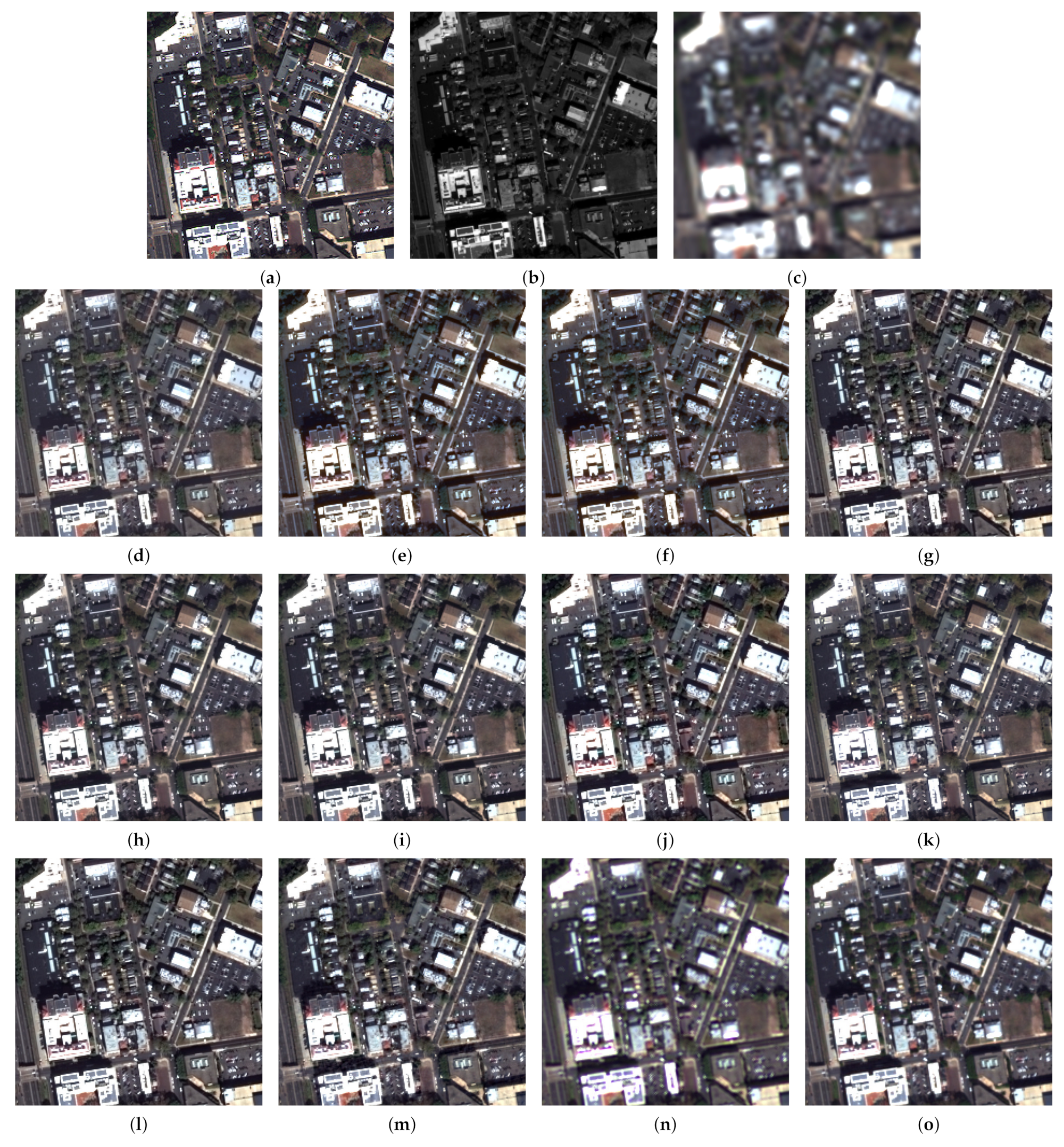
3.3. Fusion Simulations
3.4. Meta-Analysis
- GS: 7.12% Munich, 7.67% Trenton.
- BT: 4.69% Munich, 4.90% Trenton.
- AWLP-H: 3.19% Munich, 3.18% Trenton.
- HECS: 3.14% Munich, 3.13% Trenton.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| BDSD | Band-Dependent Spatial Detail |
| CS | Component Substitution |
| EHR | Extremely High Resolution |
| EO | Earth Observation |
| ERGAS | Erreur Relative Globale Adimensionnelle de Synthèse |
| FR | Full Resolution |
| GLP | Generalized Laplacian Pyramid |
| GS | Gram–Schmidt |
| HCS | Hyperspherical Color Space |
| HECS | Hyper-Ellipsoidal Color Space |
| HPM | High-Pass Modulation |
| IHS | Intensity–Hue–Saturation |
| LiDAR | Light Detection And Ranging |
| LP | Laplacian Pyramid |
| MMSE | Minimum Mean Square Error |
| MRA | Multi-Resolution Analysis |
| MS | Multi-Spectral |
| MSE | Mean Square Error |
| MTF | Modulation Transfer Function |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
| NIR | Near Infra-Red |
| OLI | Operational Land Imager |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| QNR | Quality with No Reference |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RR | Reduced Resolution |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| SAM | Spectral Angle Mapper |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SPOT | Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre |
| SSI | Spatial Sampling Interval |
| SWIR | Short-Wave Infra-Red |
| TIR | Thermal Infra-Red |
| UIQI | Universal Image Quality Index |
| VHR | Very High Resolution |
| VNIR | Visible Near-Infra-Red |
References
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A. Remote Sensing Image Fusion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Zoppetti, C. Fusion of VNIR optical and C-band polarimetric SAR satellite data for accurate detection of temporal changes in vegetated areas. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S. Information-theoretic heterogeneity measurement for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, C.; Ruscino, S.; Abbate, M.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. SAR image classification through information-theoretic textural features, MRF segmentation, and object-oriented learning vector quantization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Selva, M.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Butera, F.; Chiarantini, L. Signal-dependent noise modelling and estimation of new-generation imaging spectrometers. In Proceedings of the WHISPERS ’09—1st Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing, Grenoble, France, 26–28 August 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L. Some terms of reference in data fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Restaino, R.; Scarpa, G.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J. A new benchmark based on recent advances in multispectral pansharpening: Revisiting pansharpening with classical and emerging pansharpening methods. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 53–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Ranchin, T.; Wald, L.; Chanussot, J. Synthesis of multispectral images to high spatial resolution: A critical review of fusion methods based on remote sensing physics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Licciardi, G.A.; Restaino, R.; Wald, L. A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Carlà, R. Assessment of pyramid-based multisensor image data fusion. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing IV; Serpico, S.B., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1998; Volume 3500, pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laben, C.A.; Brower, B.V. Process for Enhancing the Spatial Resolution of Multispectral Imagery Using Pan-Sharpening. U.S. Patent # 6,011,875, 4 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Padwick, C.; Deskevich, M.; Pacifici, F.; Smallwood, S. WorldView-2 pan-sharpening. In Proceedings of the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Annual Conference 2010: Opportunities for Emerging Geospatial Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–30 April 2010; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Arienzo, A.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Lolli, S. Advantages of nonlinear intensity components for contrast-based multispectral pansharpening. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L.; Ranchin, T.; Mangolini, M. Fusion of satellite images of different spatial resolutions: Assessing the quality of resulting images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Selva, M.; Alparone, L. Bi-cubic interpolation for shift-free pan-sharpening. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 86, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S.; He, L. Near real-time automatic sub-pixel registration of panchromatic and multispectral images for pan-sharpening. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, A.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A. Improved regression-based component-substitution pansharpening of Worldview-2/3 data through automatic realignment of spectrometers. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024—2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. Fusion of panchromatic and multispectral images by genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 3810–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. Panchromatic sharpening of remote sensing images using a multiscale Kalman filter. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Argenti, F.; Baronti, S. Wavelet and pyramid techniques for multisensor data fusion: A performance comparison varying with scale ratios. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing V; Serpico, S.B., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3871, pp. 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Selva, M. Advantages of Laplacian pyramids over “à trous” wavelet transforms for pansharpening of multispectral images. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XVIII; Bruzzone, L., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8537, pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S. Multiresolution fusion of multispectral and panchromatic images through the curvelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 29 July 2005; pp. 2838–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocky, D.A. Artifacts in wavelet image merging. Opt. Eng. 1996, 35, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A. Spatial methods for multispectral pansharpening: Multiresolution analysis demystified. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, S.; Aiazzi, B.; Selva, M.; Garzelli, A.; Alparone, L. A theoretical analysis of the effects of aliasing and misregistration on pansharpened imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2011, 5, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Santurri, L. Blind correction of local misalignments between multispectral and panchromatic images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Carlà, R.; Garzelli, A.; Santurri, L. Sensitivity of pansharpening methods to temporal and instrumental changes between multispectral and panchromatic data sets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, R.; Vivone, G.; Addesso, P.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral sharpening approaches using satellite multiplatform data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Arienzo, A.; Garzelli, A. Spatial resolution enhancement of satellite hyperspectral data via nested hypersharpening with Sentinel-2 multispectral data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 10956–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, C.; Carfagni, M.; Alparone, L.; Arienzo, A.; Argenti, F. Multimodal fusion of tomographic sequences of medical images: MRE spatially enhanced by MRI. Comput. Meth. Progr. Biomed. 2022, 223, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Vivone, G. Intersensor statistical matching for pansharpening: Theoretical issues and practical solutions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4682–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jing, L. Improvement of a pansharpening method taking into account haze. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5039–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Vivone, G. Haze correction for contrast-based multispectral pansharpening. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2255–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, F.; Longbotham, N.; Emery, W.J. The importance of physical quantities for the analysis of multitemporal and multiangular optical very high spatial resolution images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6241–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Santurri, L.; Selva, M. Spatial resolution enhancement of ASTER thermal bands. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XI; Bruzzone, L., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5982, p. 59821G. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Lotti, F.; Selva, M. A comparison between global and context-adaptive pansharpening of multispectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, R.; Dalla Mura, M.; Vivone, G.; Chanussot, J. Context-adaptive pansharpening based on image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otazu, X.; González-Audícana, M.; Fors, O.; Núñez, J. Introduction of sensor spectral response into image fusion methods. Application to wavelet-based methods. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Wald, L.; Chanussot, J.; Thomas, C.; Gamba, P.; Bruce, L.M. Comparison of pansharpening algorithms: Outcome of the 2006 GRS-S data fusion contest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasbender, D.; Radoux, J.; Bogaert, P. Bayesian data fusion for adaptable image pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O. A new pansharpening algorithm based on total variation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, M.R.; Restaino, R.; Vivone, G.; Dalla Mura, M.; Chanussot, J. A pansharpening method based on the sparse representation of injected details. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Grohnfeld, C.; Bamler, R. Exploiting joint sparsity for pan-sharpening: The J-sparseFI algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 2664–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H. A joint sparse and low-rank decomposition for pansharpening of multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3545–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yu, J.; Huang, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, A.; Ma, H.; Sun, W. Super-resolution based on compressive sensing and structural self-similarity for remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4864–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, H.; Fang, L. Remote sensing image fusion via sparse representations over learned dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4779–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. A sparse image fusion algorithm with application to pan-sharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A. A review of image fusion algorithms based on the super-resolution paradigm. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shen, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Fu, R. Review of the pansharpening methods for remote sensing images based on the idea of meta-analysis. Inform. Fusion 2019, 46, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.A.; Sharma, G. A regularized model-based optimization framework for pan-sharpening. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 2596–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addesso, P.; Longo, M.; Restaino, R.; Vivone, G. Sequential Bayesian methods for resolution enhancement of TIR image sequences. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, G.; Vitale, S.; Cozzolino, D. Target-adaptive CNN-based pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5443–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Liang, P.; Guo, X.; Jiang, J. Pan-GAN: An unsupervised pan-sharpening method for remote sensing image fusion. Inform. Fusion 2020, 62, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abady, L.; Barni, M.; Garzelli, A.; Tondi, B. GAN generation of synthetic multispectral satellite images. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXVI; Bruzzone, L., Bovolo, F., Santi, E., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11533, p. 115330L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Scarpa, G. Pansharpening by convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inform. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Lolli, S.; Vivone, G. Multispectral pansharpening with radiative transfer-based detail-injection modeling for preserving changes in vegetation cover. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Lolli, S. Fast reproducible pansharpening based on instrument and acquisition modeling: AWLP revisited. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Selva, M.; Alparone, L. Enhanced Gram-Schmidt spectral sharpening based on multivariate regression of MS and Pan data. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 3806–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Kahle, A.B.; Walker, R.E. Color enhancement of highly correlated images-II. Channel ratio and “Chromaticity” Transform techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A. Wavelet-based fusion of optical and SAR image data over urban area. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Symposium of ISPRS Commission III on Photogrammetric Computer Vision, PCV 2002, Graz, Austria, 9–13 September 2022; International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Hannover, Germany, 2002; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S. A reduced Laplacian pyramid for lossless and progressive image communication. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1996, 44, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowengerdt, R.A. Remote Sensing: Models and Methods for Image Processing, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G. Smoothing filter based intensity modulation: A spectral preserve image fusion technique for improving spatial details. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Younan, N.H.; King, R.L. An efficient pan-sharpening method via a combined adaptive-PCA approach and contourlets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, G.; Vivone, G.; Dalla Mura, M.; Restaino, R.; Chanussot, J. Multi-resolution analysis techniques and nonlinear PCA for hybrid pansharpening applications. Multidim. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 27, 807–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S., Jr. An improved dark-object subtraction technique for atmospheric scattering correction of multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argenti, F.; Alparone, L. Filterbanks design for multisensor data fusion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2000, 7, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Pippi, I.; Selva, M. Generalised Laplacian pyramid-based fusion of MS + P image data with spectral distortion minimisation. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Symposium of ISPRS Commission III on Photogrammetric Computer Vision, PCV 2002, Graz, Austria, 9–13 September 2022; International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: Hannover, Germany, 2002; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Alparone, L.; Arienzo, A.; Garzelli, A. Spatial resolution enhancement of vegetation indexes via fusion of hyperspectral and multispectral satellite data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Benediktsson, J.A. Quantitative quality evaluation of pansharpened imagery: Consistency versus synthesis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Younan, N.H.; King, R.L.; Shah, V.P. On the performance evaluation of pan-sharpening techniques. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Selva, M.; Arienzo, A.; Baronti, S. Influence of the system MTF on the on-board lossless compression of hyperspectral raw data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Civco, D.L.; Silander, J.A. A wavelet transform method to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Selva, M. Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J. Pansharpening quality assessment using the modulation transfer functions of instruments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3880–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, M.; Santurri, L.; Baronti, S. On the use of the expanded image in quality ssessment of pansharpened images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Vivone, G. Spatial consistency for full-scale assessment of pansharpening. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 5132–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, A.; Vivone, G.; Garzelli, A.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J. Full-resolution quality assessment of pansharpening: Theoretical and hands-on approaches. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, R.; Santurri, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S. Full-scale assessment of pansharpening through polynomial fitting of multiscale measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 6344–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Restaino, R.; Chanussot, J. A Bayesian procedure for full resolution quality assessment of pansharpened products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4820–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Arienzo, A.; Garzelli, A. Automatic fine co-registration of datasets from extremely high resolution satellite multispectral scanners by means of injection of residues of multivariate regression. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A.; Lolli, S.; Zoppetti, C. Full-scale assessment of pansharpening: Why literature indexes may give contradictory results and how to avoid such an inconvenience. In Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIX; Bruzzone, L., Bovolo, F., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023; Volume 12733, p. 1273302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L. Data Fusion: Definitions and Architectures—Fusion of Images of Different Spatial Resolutions; Les Presses de l’École des Mines: Paris, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas, R.H.; Goetz, A.F.H.; Boardman, J.W. Discrimination among semi-arid landscape endmembers using the Spectral Angle Mapper (SAM) algorithm. In Summaries of the 3rd Annual JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop; NASA-JPL: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1992; pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. A global quality measurement of pan-sharpened multispectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. Hypercomplex quality assessment of multi-/hyper-spectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, A.; Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A. Reproducibility of pansharpening methods and quality indexes versus data formats. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A. Coherence estimation from multilook incoherent SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Sauvage, L.; Loaec, S.; Lardier, M. EZ LidarTM: A new compact autonomous eye-safe scanning aerosol Lidar for extinction measurements and PBL height detection. Validation of the performances against other instruments and intercomparison campaigns. Opt. Pura Apl. 2011, 44, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.; Higgins, J.; Rothstein, H. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; Wiley Online Library: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laporterie-Déjean, F.; de Boissezon, H.; Flouzat, G.; Lefèvre-Fonollosa, M.J. Thematic and statistical evaluations of five panchromatic/multispectral fusion methods on simulated PLEIADES-HR images. Inform. Fusion 2005, 6, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Pacifici, F. A benchmarking protocol for pansharpening: Dataset, preprocessing, and quality assessment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6102–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.M.; Hsu, C.L.; Tu, P.Y.; Lee, C.H. An adjustable pan-sharpening approach for IKONOS/QuickBird/GeoEye-1/WorldView-2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A. Context-driven fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images based on oversampled multiresolution analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2300–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Capobianco, L. Optimal MMSE Pan sharpening of very high resolution multispectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Restaino, R.; Chanussot, J. Full scale regression-based injection coefficients for panchromatic sharpening. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3418–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Dataset | Satellite | Location & Date | SSI [m] | Spectral Bands | Scene Size | Format |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IKONOS | Toulouse, France | 1.0 | Panchromatic | 2048 × 2048 | TOA Spectral Radiance |
| 15 May 2000 | 4.0 | B, G, R, NIR | 512 × 512 | from 11-b DNs | ||
| 2 | QuickBird | Trento, Italy | 0.7 | Panchromatic | 1024 × 1024 | TOA Spectral Radiance |
| October 2005 | 2.8 | B, G, R, NIR | 256 × 256 | from 11-b DNs | ||
| 3 | WorldView-2 | Rome, Italy | 0.5 | Panchromatic | 1200 × 1200 | TOA Spectral Radiance |
| 18 September 2013 | 2.0 | B, G, R, NIR | 300 × 300 | from 11-b DNs | ||
| C, Y, RE, NIR2 | 300 × 300 | |||||
| 4 | WorldView-3 | Munich, Germany | 0.4 | Panchromatic | 2048 × 2048 | TOA Spectral Radiance |
| 10 January 2020 | 1.6 | B, G, R, NIR | 512 × 512 | from 11-b DNs | ||
| C, Y, RE, NIR2 | 512 × 512 | |||||
| 5 | GeoEye-1 | Trenton, NJ, USA | 0.5 | Panchromatic | 2048 × 2048 | TOA Spectral Radiance |
| 27 September 2019 | 2.0 | B, G, R, NIR | 512 × 512 | from 11-b DNs |
| Dataset | Toulouse | Trento | Rome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | Q8 | SAM | ERGAS | |
| GT | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| EXP | 0.519 | 4.840 | 5.879 | 0.785 | 3.343 | 3.645 | 0.715 | 4.982 | 5.479 |
| GS | 0.808 | 4.260 | 4.191 | 0.766 | 5.110 | 3.923 | 0.830 | 4.907 | 4.052 |
| GSA | 0.932 | 3.021 | 2.586 | 0.833 | 4.193 | 3.316 | 0.890 | 4.157 | 3.398 |
| BDSD | 0.931 | 2.800 | 2.467 | 0.862 | 3.663 | 2.979 | 0.875 | 4.973 | 3.866 |
| SFIM | 0.866 | 3.615 | 3.519 | 0.841 | 3.835 | 5.951 | 0.891 | 4.146 | 3.449 |
| CBD | 0.933 | 3.016 | 2.566 | 0.849 | 4.040 | 3.059 | 0.893 | 4.159 | 3.354 |
| AWLP | 0.897 | 4.840 | 3.262 | 0.861 | 3.343 | 2.937 | 0.799 | 4.982 | 3.563 |
| AWLP-H | 0.936 | 2.756 | 2.433 | 0.889 | 3.093 | 2.637 | 0.917 | 3.605 | 3.114 |
| Dataset | Toulouse | Trento | Rome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | Q8 | SAM | ERGAS | |
| GT | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| EXP | 0.519 | 4.840 | 5.879 | 0.785 | 3.343 | 3.645 | 0.715 | 4.982 | 5.479 |
| GS | 0.808 | 4.260 | 4.191 | 0.766 | 5.110 | 3.923 | 0.830 | 4.907 | 4.052 |
| GSA | 0.932 | 3.021 | 2.586 | 0.833 | 4.193 | 3.316 | 0.890 | 4.157 | 3.398 |
| BDSD | 0.931 | 2.800 | 2.467 | 0.862 | 3.663 | 2.979 | 0.875 | 4.973 | 3.866 |
| SFIM | 0.866 | 3.615 | 3.519 | 0.841 | 3.835 | 5.951 | 0.891 | 4.146 | 3.449 |
| CBD | 0.933 | 3.016 | 2.566 | 0.849 | 4.040 | 3.059 | 0.893 | 4.159 | 3.354 |
| AWLP | 0.897 | 4.840 | 3.262 | 0.861 | 3.343 | 2.937 | 0.799 | 4.982 | 3.563 |
| AWLP-H | 0.936 | 2.756 | 2.433 | 0.889 | 3.093 | 2.637 | 0.917 | 3.605 | 3.114 |
| SRDLP | 0.890 | 3.286 | 3.822 | 0.844 | 3.941 | 3.578 | 0.914 | 3.785 | 3.696 |
| JSRLP | 0.908 | 3.020 | 3.124 | 0.860 | 3.622 | 2.924 | 0.932 | 3.479 | 3.020 |
| Dataset | Munich | Trenton | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8 | SAM | ERGAS | Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | |
| GT | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| EXP | 0.6311 | 4.7548 | 10.8511 | 0.5826 | 6.6167 | 10.2034 |
| BT | 0.8803 | 4.7548 | 5.5754 | 0.9000 | 6.6167 | 5.3655 |
| GS | 0.8028 | 4.2535 | 6.9518 | 0.8461 | 6.2997 | 6.6388 |
| HCS | 0.8906 | 4.7548 | 6.1731 | 0.8969 | 6.6167 | 5.4681 |
| BT-H | 0.9236 | 2.9309 | 4.2466 | 0.9025 | 4.9937 | 4.9978 |
| GSA | 0.9204 | 3.2007 | 4.4250 | 0.8985 | 6.0420 | 5.2664 |
| HECS | 0.9287 | 2.9078 | 4.1268 | 0.9066 | 4.9565 | 4.9609 |
| BDSD | 0.9245 | 3.2388 | 4.1748 | 0.9054 | 6.0254 | 5.1267 |
| AWLP-H | 0.9154 | 2.9794 | 4.3915 | 0.8928 | 5.2913 | 5.2182 |
| MTF-GLP-FS | 0.9200 | 3.1876 | 4.4465 | 0.9030 | 6.0093 | 5.1501 |
| SR-D | 0.8936 | 3.4386 | 5.3399 | 0.8915 | 5.4449 | 5.3810 |
| TV | 0.9164 | 3.4225 | 4.6557 | 0.7693 | 6.1318 | 7.7066 |
| A-PNN-FT | 0.8747 | 3.6465 | 5.8899 | 0.8857 | 4.3841 | 5.4262 |
| Dataset | Munich | Trenton | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8 | SAM | ERGAS | Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | |
| EXP | 0.5973 | 3.7257 | 8.5869 | 0.6155 | 8.4443 | 12.8938 |
| BT | 0.9228 | 3.7257 | 4.5155 | 0.8586 | 8.4443 | 6.625 |
| GS | 0.8675 | 3.5472 | 5.587 | 0.783 | 7.5541 | 8.2605 |
| HCS | 0.9196 | 3.7257 | 4.6018 | 0.8686 | 8.4443 | 7.3352 |
| BT-H | 0.9253 | 2.8118 | 4.206 | 0.9008 | 5.2052 | 5.046 |
| GSA | 0.9212 | 3.4021 | 4.4321 | 0.8977 | 5.6843 | 5.258 |
| HECS | 0.9295 | 2.7909 | 4.175 | 0.9058 | 5.1641 | 4.9037 |
| BDSD | 0.9283 | 3.3928 | 4.3145 | 0.9017 | 5.752 | 4.9607 |
| AWLP-H | 0.9154 | 2.9794 | 4.3915 | 0.8928 | 5.2913 | 5.2182 |
| MTF-GLP-FS | 0.9259 | 3.3837 | 4.3342 | 0.8973 | 5.6611 | 5.2836 |
| SR-D | 0.9141 | 3.0659 | 4.5285 | 0.8715 | 6.1068 | 6.3451 |
| TV | 0.7888 | 3.4527 | 6.4857 | 0.8938 | 6.0782 | 5.5321 |
| A-PNN-FT | 0.9081 | 2.4686 | 4.5665 | 0.8531 | 6.476 | 6.9987 |
| Dataset | Munich | Trenton | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8 | SAM | ERGAS | Q4 | SAM | ERGAS | |
| EXP | −0.0338 | −1.0291 | −2.2642 | 0.0329 | 1.8276 | 2.6904 |
| BT | 0.0425 | −1.0291 | −1.0599 | −0.0414 | 1.8276 | 1.2595 |
| GS | 0.0647 | −0.7063 | −1.3648 | −0.0631 | 1.2544 | 1.6217 |
| HCS | 0.0290 | −1.0291 | −1.5713 | −0.0283 | 1.8276 | 1.8671 |
| BT-H | 0.0017 | −0.1191 | −0.0406 | −0.0017 | 0.2115 | 0.0482 |
| GSA | 0.0008 | 0.2014 | 0.0071 | −0.0008 | −0.3577 | −0.0084 |
| HECS | 0.0008 | −0.1169 | 0.0482 | −0.0008 | 0.2076 | −0.0572 |
| BDSD | 0.0038 | 0.1540 | 0.1397 | −0.0037 | −0.2734 | −0.1660 |
| AWLP-H | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MTF-GLP-FS | 0.0059 | 0.1961 | −0.1123 | −0.0057 | −0.3482 | 0.1335 |
| SR-D | 0.0205 | −0.3727 | −0.8114 | −0.0200 | 0.6619 | 0.9641 |
| TV | −0.1276 | 0.0302 | 1.8300 | 0.1245 | −0.0536 | −2.1745 |
| A-PNN-FT | 0.0334 | −1.1779 | −1.3234 | −0.0326 | 2.0919 | 1.5725 |
| NMAE % | 3.19 | 12.98 | 14.84 | 3.18 | 14.51 | 16.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alparone, L.; Garzelli, A. Benchmarking of Multispectral Pansharpening: Reproducibility, Assessment, and Meta-Analysis. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11010001
Alparone L, Garzelli A. Benchmarking of Multispectral Pansharpening: Reproducibility, Assessment, and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Imaging. 2025; 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlparone, Luciano, and Andrea Garzelli. 2025. "Benchmarking of Multispectral Pansharpening: Reproducibility, Assessment, and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Imaging 11, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11010001
APA StyleAlparone, L., & Garzelli, A. (2025). Benchmarking of Multispectral Pansharpening: Reproducibility, Assessment, and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Imaging, 11(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging11010001











