Imaging-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Desmoid Tumor Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Input Data
2.3. Manual Lesion Segmentation
2.4. Model Training
2.5. Data Splitting
2.6. Network Architecture
2.7. Transfer Learning
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Algorithm Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board PPTE. Childhood Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment (PDQ®). Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/soft-tissue-sarcoma/hp/child-soft-tissue-treatment-pdq (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Lv, A.; Tian, X.; Hao, C. En bloc resection for intra-abdominal/retroperitoneal desmoidtype fibromatosis with adjacent organ involvement: A case series and literature review. Biosci. Trends 2018, 12, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, M.R.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; Long, N.; Qin, L.X.; Kirane, A.; Sbaity, E.; Hameed, M.; Coit, D.G.; Brennan, M.F.; Singer, S.; et al. Association of MRI T2 Signal Intensity with Desmoid Tumor Progression during Active Observation: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshan, D.; Amini, B.; Nikolaidis, P.; Assing, M.; Vikram, R. Current Update on Desmoid Fibromatosis. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2019, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shido, Y.; Nishida, Y.; Nakashima, H.; Katagiri, H.; Sugiura, H.; Yamada, Y.; Ishiguro, N. Surgical treatment for local control of extremity and trunk desmoid tumors. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2009, 129, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timbergen, M.J.M.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Grünhagen, D.J.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Sleijfer, S.; Verhoef, C.; Husson, O. Identification and assessment of health-related quality of life issues in patients with sporadic desmoid-type fibromatosis: A literature review and focus group study. Qual. Life Res. 2018, 27, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto Netto, S.D.; Teixeira, F.; Menegozzo, C.A.M.; Leão-Filho, H.M.; Albertini, A.; Ferreira, F.O.; Akaishi, E.H.; Utiyama, E.M. Sporadic Abdominal Wall Desmoid type Fibromatosis: Treatment paradigm after thirty two years. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenhuis, M.H.; Casparie, M.; Mathus-Vliegen, L.M.H.; Dekkers, O.M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; Vasen, H.F.A. A nation-wide study comparing sporadic and familial adenomatous polyposis-related desmoid-type fibromatoses. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Camargo, V.P.; Keohan, M.L.; D’Adamo, D.R.; Antonescu, C.R.; Brennan, M.F.; Singer, S.; Ahn, L.S.; Maki, R.G. Clinical outcomes of systemic therapy for patients with deep fibromatosis (desmoid tumor). Cancer 2010, 116, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, M.; MacNeill, A.; Gronchi, A.; Colombo, C. Desmoid-Type Fibromatosis: Evolving Treatment Standards. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 803–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alman, B.; Attia, S.; Baumgarten, C.; Benson, C.; Blay, J.Y.; Bonvalot, S.; Breuing, J.; Cardona, K.; Casali, P.G.; van Coevorden, F.; et al. The management of desmoid tumours: A joint global consensus-based guideline approach for adult and paediatric patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 127, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounder, M.M.; Mahoney, M.R.; Van Tine, B.A.; Ravi, V.; Attia, S.; Deshpande, H.A.; Gupta, A.A.; Milhem, M.M.; Conry, R.M.; Movva, S.; et al. Sorafenib for Advanced and Refractory Desmoid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, B.; Baumgarten, C.; Bonvalot, S.; Haas, R.; Haller, F.; Hohenberger, P.; Moreau, G.; Van Der Graaf, W.T.A.; Gronchi, A. Management of sporadic desmoid-type fibromatosis: A European consensus approach based on patients’ and professionals’ expertise—A Sarcoma Patients EuroNet and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group initiative. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarville, M.B.; Hotter, F.A.; Adelman, C.S.; Khoury, J.D.; Li, C.; Skapek, S.X. MRI and biologic behavior of desmoid tumors in children. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Thomas, J.M.; Phillips, S.; Fisher, C.; Moskovic, E. Aggressive fibromatosis: MRI features with pathologic correlation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 186, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinauer, P.A.; Brixey, C.J.; Moncur, J.T.; Fanburg-Smith, J.C.; Murphey, M.D. Pathologic and MR imaging features of benign fibrous soft-tissue tumors in adults. Radiographics 2007, 27, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmi, G.; Cifaratti, A.; Scalzo, G.; Magarelli, N. Imaging of superficial and deep fibromatosis. Radiol. Med. 2009, 114, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbin, M.R.; Murphey, M.D.; Temple, H.T.; Kransdorf, M.J.; Choi, J.J. Imaging of musculoskeletal fibromatosis. Radiographics 2001, 21, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.C.; Li, X.T.; Ji, W.Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.S. Desmoid-type fibromatosis: Tumour response assessment using magnetic resonance imaging signal and size criteria. Clin. Imaging 2020, 68, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efrima, B.; Ovadia, J.; Drukman, I.; Khoury, A.; Rath, E.; Dadia, S.; Gortzak, Y.; Albagli, A.; Sternheim, A.; Segal, O. Cryo-surgery for symptomatic extra-abdominal desmoids. A proof of concept study. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 124, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnekave, E.; Atar, E.; Amar, S.; Bruckheimer, E.; Knizhnik, M.; Yaniv, I.; Dujovny, T.; Feinmesser, M.; Ash, S. Doxorubicin-Eluting Intra-Arterial Therapy for Pediatric Extra-Abdominal Desmoid Fibromatoses: A Promising Approach for a Perplexing Disease. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombé, A.; Kind, M.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Isambert, N.; Chevreau, C.; André, T.; Lebbe, C.; Le Cesne, A.; Bompas, E.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; et al. Progressive Desmoid Tumor: Radiomics Compared with Conventional Response Criteria for Predicting Progression during Systemic Therapy—A Multicenter Study by the French Sarcoma Group. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhawong, T.K.; Feister, K.; Sweet, K.; Alperin, N.; Kwon, D.; Rosenberg, A.; Trent, J.; Wilky, B.A. MRI volumetrics and image texture analysis in assessing systemic treatment response in extra-abdominal desmoid fibromatosis. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e210016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019; International Machine Learning Society (IMLS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 5–19 June 2019; Volume 2019, pp. 10691–10700. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Yi, Z.; Xie, M.; Xie, Y.; Tang, X.; Tu, B.; Gao, Y.; Wan, M. Machine learning-based radiomics analysis for predicting local recurrence of primary dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans after surgical treatment. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 186, 109737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malenfer, M.; Sarrey, M.; Clerté, J.; Hery, M.; Bieri, M.; Braunschweig, B.; Chatellier, R.; Fates, N.; Halluin, S.; de Jouvenel, F.; et al. Artificial intelligence in the service of health and safety at work: Perspectives and challenges from now to 2035—A prospective study. Qeios 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 Encoder Pre-Trained on ImageNet for Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.L.H.; Chong, E.K.P.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Automated Pavement Crack Segmentation Using U-Net-Based Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 114892–114899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, N.; Gyftopoulos, S. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Musculoskeletal Imaging: From the Request to the Report. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021, 72, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkhoff, D.C.; van Dalen, A.S.H.M.; Schijven, M.P. A Review on the Current Applications of Artificial Intelligence in the Operating Room. Surg. Innov. 2021, 28, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikawa, K.; Hirasawa, T.; Yoshio, T.; Fujisaki, J.; Ozawa, T.; Ishihara, S.; Aoki, T.; Yamada, A.; Koike, K.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Utilizing artificial intelligence in endoscopy: A clinician’s guide. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 14, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehralivand, S.; Yang, D.; Harmon, S.A.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z.; Roth, H.; Masoudi, S.; Kesani, D.; Lay, N.; Merino, M.J.; et al. Deep learning-based artificial intelligence for prostate cancer detection at biparametric MRI. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Desai, J.; Lazarakis, S.; Gyorki, D. Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes Following Various Treatment Options for Patients with Extraabdominal Desmoid Tumors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penel, N.; Chibon, F.; Salas, S. Adult desmoid tumors: Biology, management and ongoing trials. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2017, 29, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bree, E.; Keus, R.; Mellissas, J.; Tsiftsis, D.; van Coevorden, F. Desmoid tumors: Need for an individualized approach. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2009, 9, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Tanzi, P.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Akahane, M.; Kido, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Cesari, M.; Donati, D.M.; Longhi, A.; Errani, C. Upfront surgery is not advantageous compared to more conservative treatments such as observation or medical treatment for patients with desmoid tumors. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schut, A.R.W.; Timbergen, M.J.M.; Lidington, E.; Grünhagen, D.J.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Sleijfer, S.; van Houdt, W.J.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; Younger, E.; Dunlop, A.; et al. The evaluation of health-related quality of life issues experienced by patients with desmoid-type fibromatosis (The qualified study)—A protocol for an international cohort study. Cancers 2021, 13, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhao, B.; Zang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Yu, H.; Sui, X. Diagnostic Performance of Radiomics and Deep Learning to Identify Benign and Malignant Soft Tissue Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.; Calisto, F.M.; Santiago, C.; Aleluia, C.; Nascimento, J.C. Classification of Breast Cancer in Mri with Multimodal Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Cartagena, Colombia, 18–21 April 2023; Volume 2023. [Google Scholar]

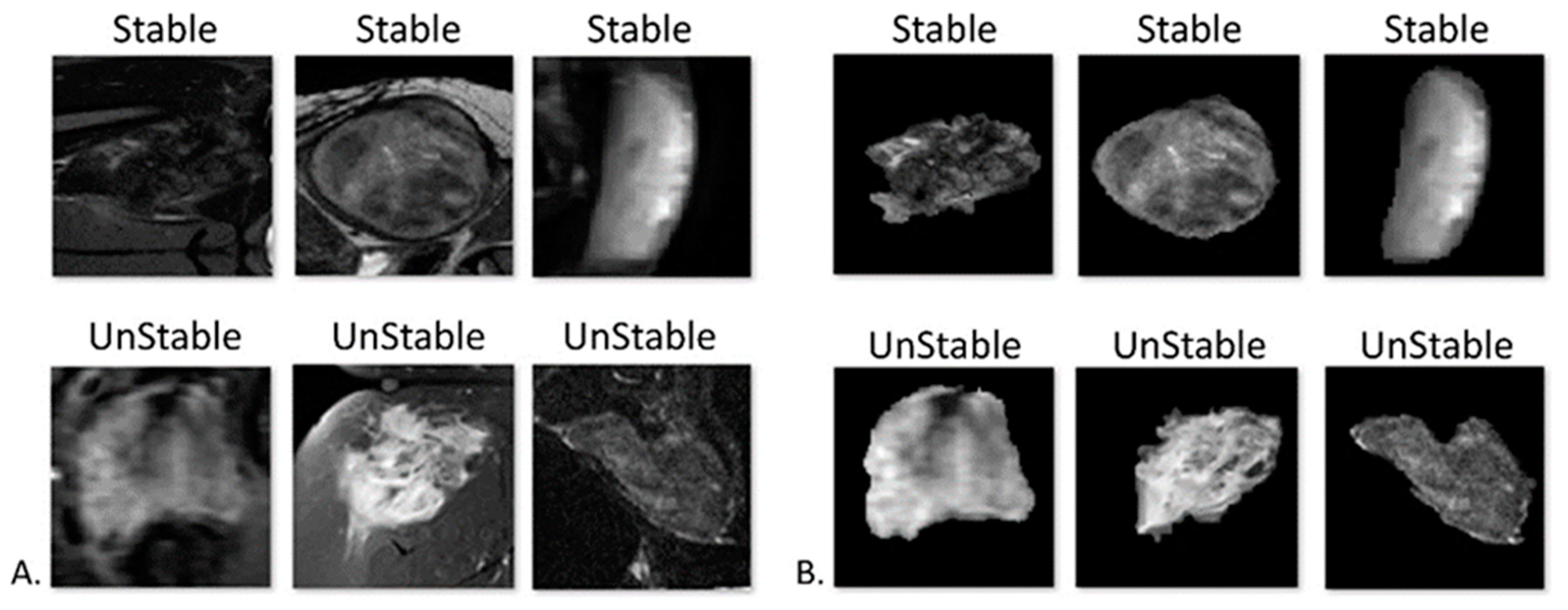
| Stable | Unstable | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Male, 28 | 13 (46.4%) | 15 (65.2%) | N.S. | |
| Female, 23 | 15 (53.6%) | 8 (34.8%) | N.S. | |
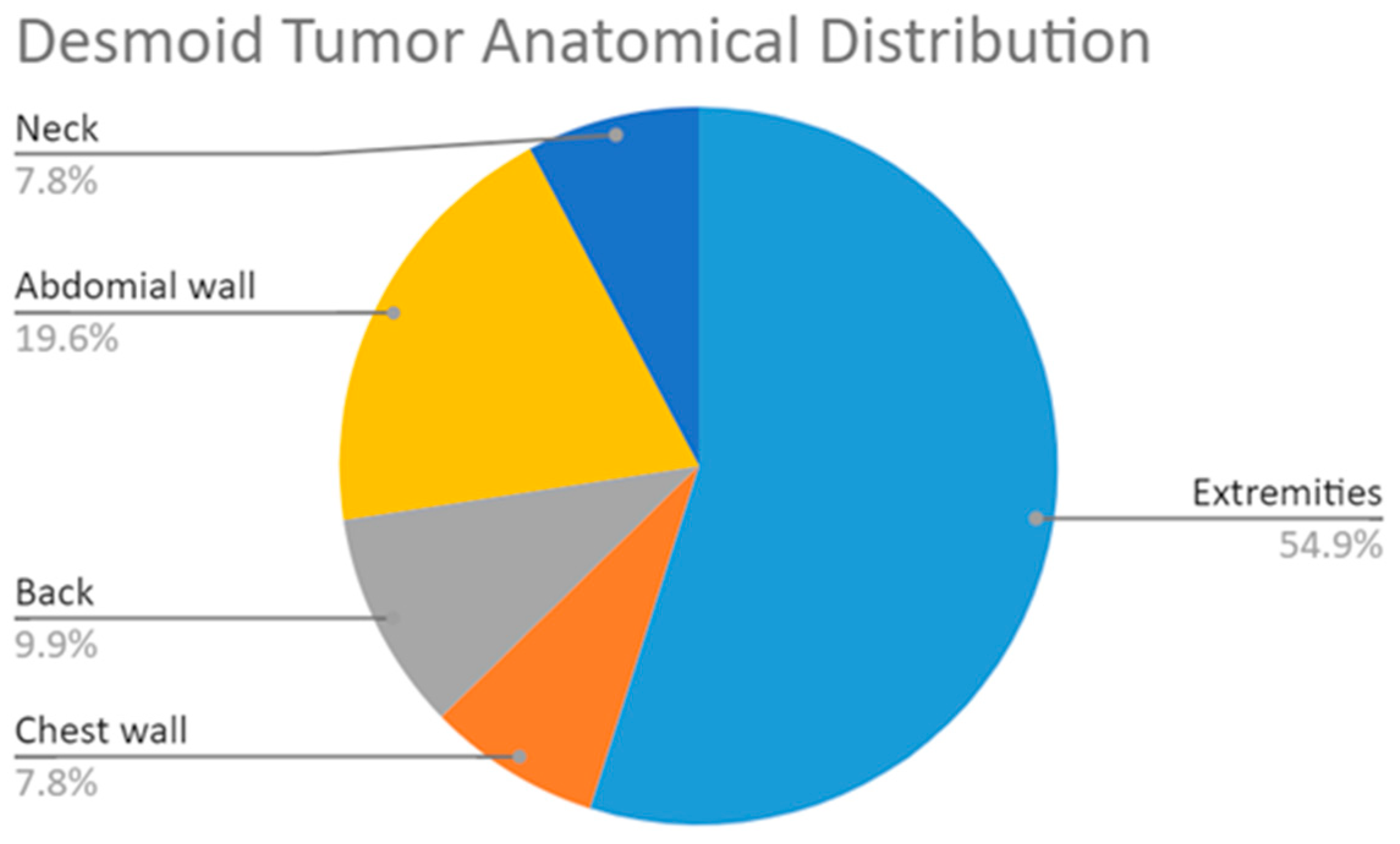
| Anatomic location of the DT | ||||
| Extremities, 31 | 16 (57.15) | 15 (65.2%) | N.S. | |
| Chest wall, 5 | 3 (10.7%) | 2 (8.7%) | N.S. | |
| Back, 4 | 2 (7.1%) | 2 (8.7%) | N.S. | |
| Abdominal wall, 8 | 6 (21.4%) | 2 (8.7%) | N.S. | |
| Neck, 3 | 1 (3.6%) | 2 (8.7%) | N.S. | |
| Weight (Kg) | 67.5 | 72 | N.S. | |
| Height (cm) | 168 | 175.5 | N.S. | |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 31.76 | 26.67 | N.S. | |
| Follow-up time (months) | 45.63 | 31.99 | N.S. |
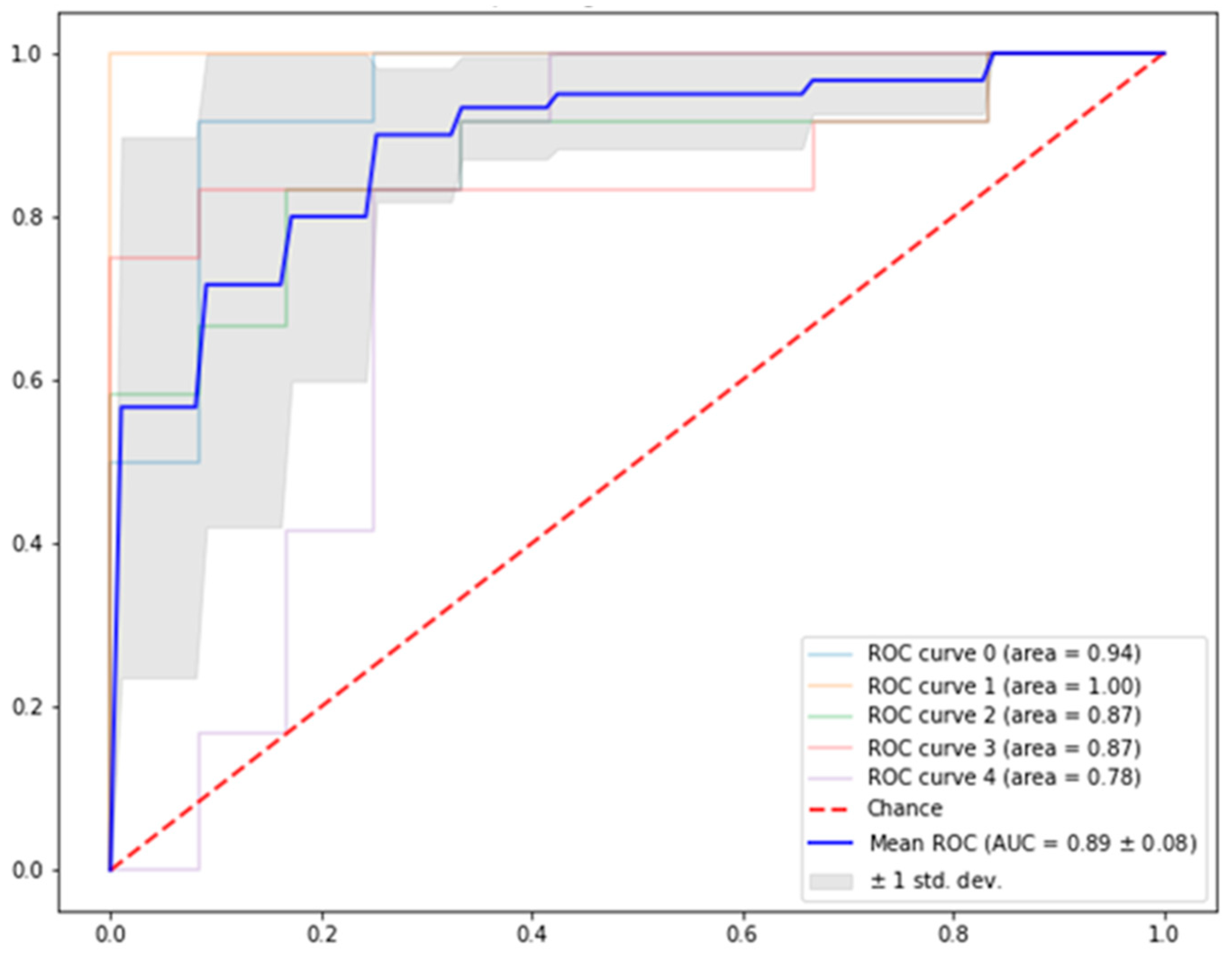
| Precision | Recall | F_Score | Accuracy | ROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stable | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.06 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.08 |
| Unstable | 0.77 ± 0.11 | 0.91 ± 0.10 | 0.82 ± 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fares, R.; Atlan, L.D.; Druckmann, I.; Factor, S.; Gortzak, Y.; Segal, O.; Artzi, M.; Sternheim, A. Imaging-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Desmoid Tumor Progression. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10050122
Fares R, Atlan LD, Druckmann I, Factor S, Gortzak Y, Segal O, Artzi M, Sternheim A. Imaging-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Desmoid Tumor Progression. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(5):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10050122
Chicago/Turabian StyleFares, Rabih, Lilian D. Atlan, Ido Druckmann, Shai Factor, Yair Gortzak, Ortal Segal, Moran Artzi, and Amir Sternheim. 2024. "Imaging-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Desmoid Tumor Progression" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 5: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10050122
APA StyleFares, R., Atlan, L. D., Druckmann, I., Factor, S., Gortzak, Y., Segal, O., Artzi, M., & Sternheim, A. (2024). Imaging-Based Deep Learning for Predicting Desmoid Tumor Progression. Journal of Imaging, 10(5), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10050122








