Abstract
The optical quality of an image depends on both the optical properties of the imaging system and the physical properties of the medium the light passes while travelling from the object to the image plane. The computation of the point spread function (PSF) associated to the optical system is often used to assess the image quality. In a non-ideal optical system, the PSF is affected by aberrations that distort the final image. Moreover, in the presence of turbid media, the scattering phenomena spread the light at wide angular distributions that contribute to reduce contrast and sharpness. If the mathematical degradation operator affecting the recorded image is known, the image can be restored through deconvolution methods. In some scenarios, no (or partial) information on the PSF is available. In those cases, blind deconvolution approaches arise as useful solutions for image restoration. In this work, a new blind deconvolution method is proposed to restore images using spherical aberration (SA) and scatter-based kernel filters. The procedure was evaluated in different microscopy images. The results show the capability of the algorithm to detect both degradation coefficients (i.e., SA and scattering) and to restore images without information on the real PSF.
1. Introduction
Confocal and multiphoton (MP) scanning microscopy are widespread techniques used for imaging biological tissues both in ex vivo [1,2] and living [3,4] conditions. The quality of the images acquired with these instruments is often limited by the presence of optical aberrations and scattering. Whereas the former distorts the image through the loss of high-spatial frequency contents [2,3], the latter reduces the overall contrast [5]. The combination of both leads to image degradation (i.e., reduced resolution and low contrast).
A method to assess image quality is based on the calculation of the point spread function (PSF) of the optical system under study. In scanning microscopy, this PSF is affected by off-axis optical aberrations such as coma or field curvature, as well as astigmatism, and spherical (SA) and chromatic aberrations. These can be minimised with appropriate apochromatic objectives [6], correction collars [7], deformable mirrors [2,3,8,9], or spatial light modulators [2,10].
Moreover, when thick biological samples are involved, the image quality reduces significantly at deeper locations due to an increase in both scattering and aberrations (mainly SA) [5,8,10,11]. Therefore, the combination of SA and scattering degrades the PSF of the microscope, limiting the penetration depth within the tissue [8,9,10,11,12]. To overcome aberrations (or to increase the penetration depth), adaptive optics (AO) procedures have been implemented into confocal [3] and MP [2,8,9,10,11,13] microscopes to compensate for these effects and provide enhanced images.
Although charaterizing light scattering effects in biological tissues is challenging, different AO-based tools have been reported for scattering compensation in biomedical imaging [11,14,15]. However, after the SA correction, residual aberrations and uncompensated scattering might be enough to degrade the optical resolution and prevent proper image analysis [16].
Deconvolution is an alternative mathematical method used in digital image processing to restore optical degradation effects [17]. However, to perform a deterministic deconvolution process, it is essential to have previous information about the operator responsible for image degradation, that is, the PSF.
Unfortunately, the access to this information is not always easily available. In this sense, blind deconvolution algorithms [18] allow restoring blurred images, using as a starting point an approximate geometrical distribution of the PSF. Blind deconvolution has been succesfully applied to restore the optical quality of images in clinical and research fields [19,20].
In this work, we present a new blind deconvolution algorithm based on an iterative-optimization process of both SA and wide-angle scattering PSF compensation. This approach can be used to restore and improve microscopy images without the need of previous information on the optical properties of the imaging systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spherical Aberration Point Spread Function
The wave aberration (WA) of an optical system can be represented by the Zernike polynomial expansion. This is defined in a circular pupil, and its units can be expressed in wavelengths (λ) or microns. According to the widely accepted double-index convention of the Optical Society of America (now Optica) [21], this WA(ρ, θ) can be expressed in polar coordinates as:
where and are the Zernike polynomials and their corresponding coefficients, respectively. This notation uses a sub-index n to indicate the radial order and a super-index m for the frequency. In this Equation (1), θ ranges between 0 and 2π, and ρ is the normalized pupil size.
In addition, the pupil function of an optical system P(ρ, θ) can be expressed as
with A being the amplitude and k = 2π/λ the wave number defined as the spatial frequency of the wave (over a specific unit distance). The squared modulus of the Fourier transform of this pupil function is the associated PSF:
In particular, the SA term of the WA in the Zernike expansion is defined as [21]:
SA term has been reported to present a dominant contribution in certain research fields such as Microscopy, Astronomy or Physiological Optics, among others [6,7,8,9,10]. Altough any aberration mode can be included in the developed algorithm, previous literature has reported the benefit of compensating for this dominant SA aberration terms in microscopy, biomedical imaging, and physiological optics [8,9,10].
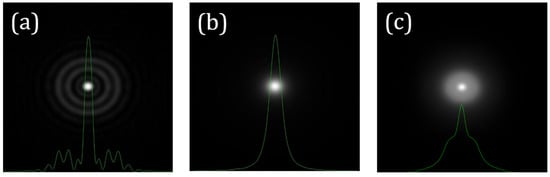
If the WASA of an optical system is known, its PSFSA can be directly computed from Equation (3). As an illustrative example, Figure 1 presents the PSFSA corresponding to a SA value of +0.20 µm (λ = 800 nm and 6 mm of pupil size). This can be directly compared to a diffraction-limited PSF (i.e., no aberrations).
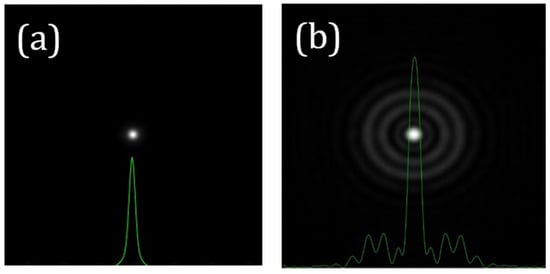
Figure 1.
Example of computer generated PSFs for 0 (i.e., diffraction-limitted) (a) and +0.20 μm (b) of SA. The corresponding cross-sectional intensity profiles are overlayed in green. Image size: 256 × 256 μm2.
2.2. Wide-Angle Scattering PSF
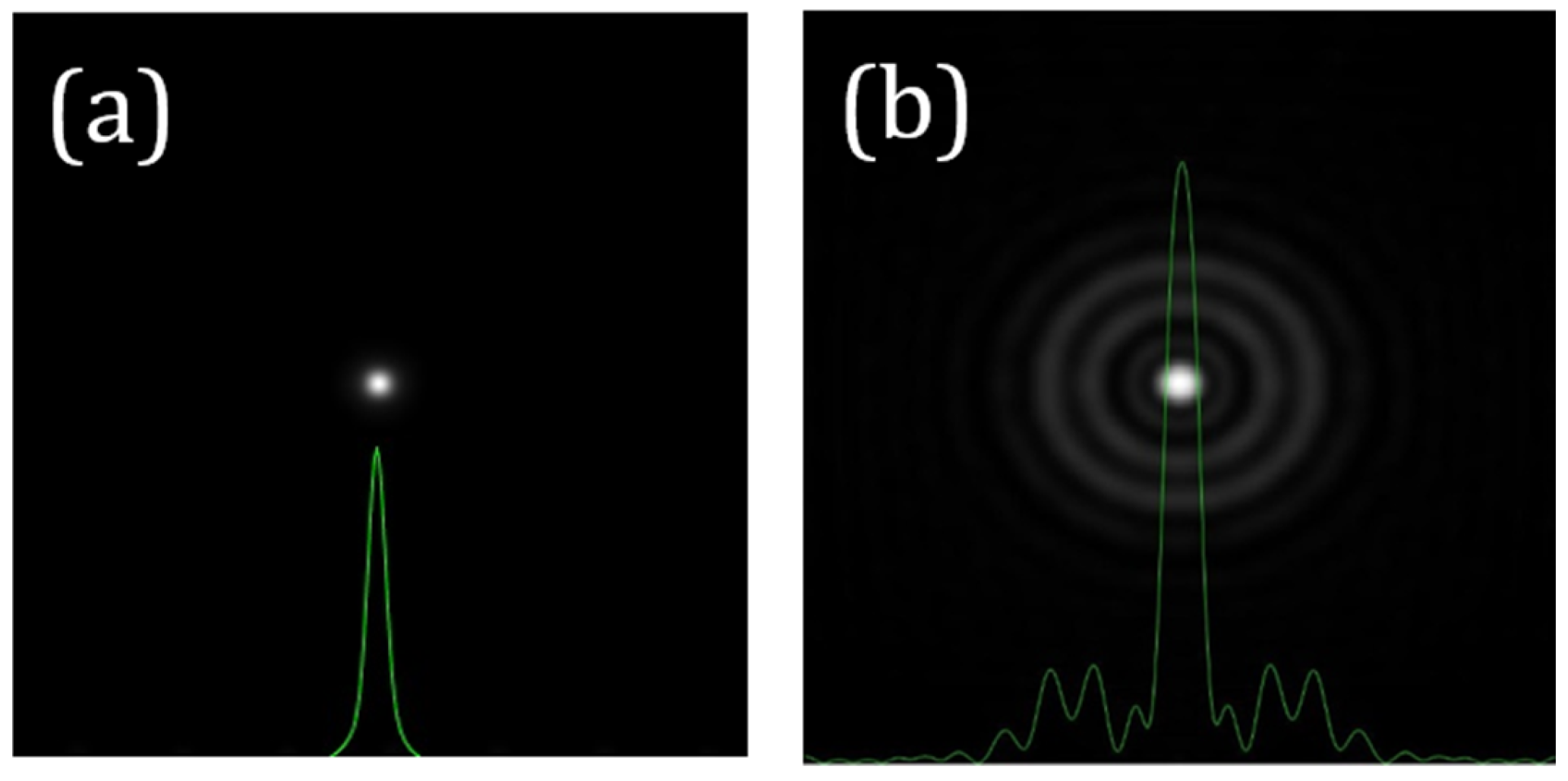
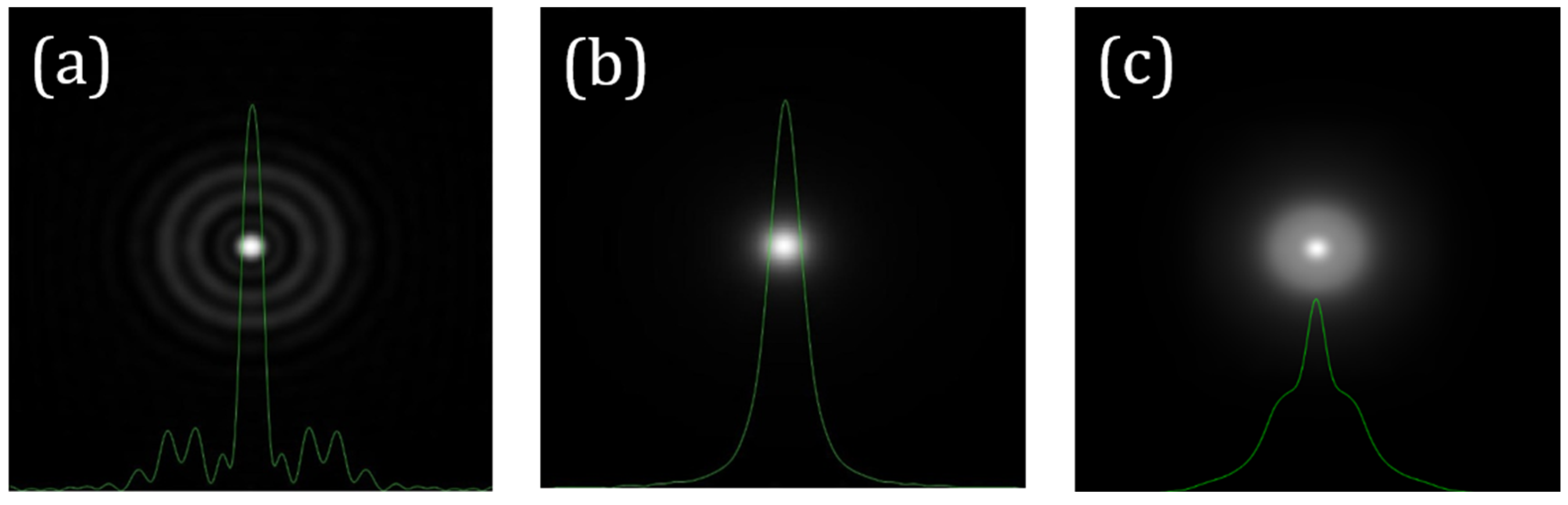
Scattering effects in an optical system are usually characterized by a veiling glare distributed over the acquired image [22]. In this work, the glare spread function (GSF) according to the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) standards was used [23]. This is defined as
According to this model, the wide-angle scattered PSF (GSF or PSFscatt) depends on the veiling glare angle (α) and other parameters related to the imaging system [23] that are considered to remain constant within this work (Age and pigment factor, PF). Mathematically, the PSFscatt associated with an optical system in the presence of scattering is the kernel of the response during image acquisition. Figure 2b depicts an example of a PSFscatt for α = 4°. For a direct comparison, the PSFSA (+0.20 μm, Figure 2a) and the PSFSA+scatt combining SA and scattering (α = 4°) are also shown (Figure 2c).
2.3. Deconvolution Procedure
Any non-diffraction limited imaging system is affected by aberrations. In addition, if during image formation the light travels through non-transparent media, the effects of scattering are also present.
Let us suppose an imaging system with a degradation operator with a double contribution: (1) the SA with an associated PSFSA and (2) the scattering effects characterized by the corresponding veiling glare function (PSFscatt). If PSFSA+scatt is the PSF containing both contributions, the image i′ of an object i through this optical system can be modelled by a convolution operation expressed as
The problem of obtaining the restored image i from this Equation (6) might be easily solved by a simple division in the Fourier domain. However, if the Fourier transform of the PSF contains zeros, the division would be impossible. To overpass this limitation, blind deconvolution can be used [18,19].
The blind deconvolution algorithm proposed herein is an inverse mathematical method for image restoration that assumes some information about the PSF (or the equivalent combined effect of both PSFSA and PSFscatt, i.e., PSFSA+scatt). The approach is based on the maximum likelihood estimates [24], being the first input the original image together with an initial theoretical PSF. Then, an iterative procedure begins, where for each Nth iteration, the estimated image and the PSF(N) (either PSFSA, PSFscatt or the combination of both) ensures non-zero components in its Fourier transform due to the imposition of frequency band-limited constraints. These are calculated as [24]
where PSF* and N are the flipped PSF and the iteration number, respectively.
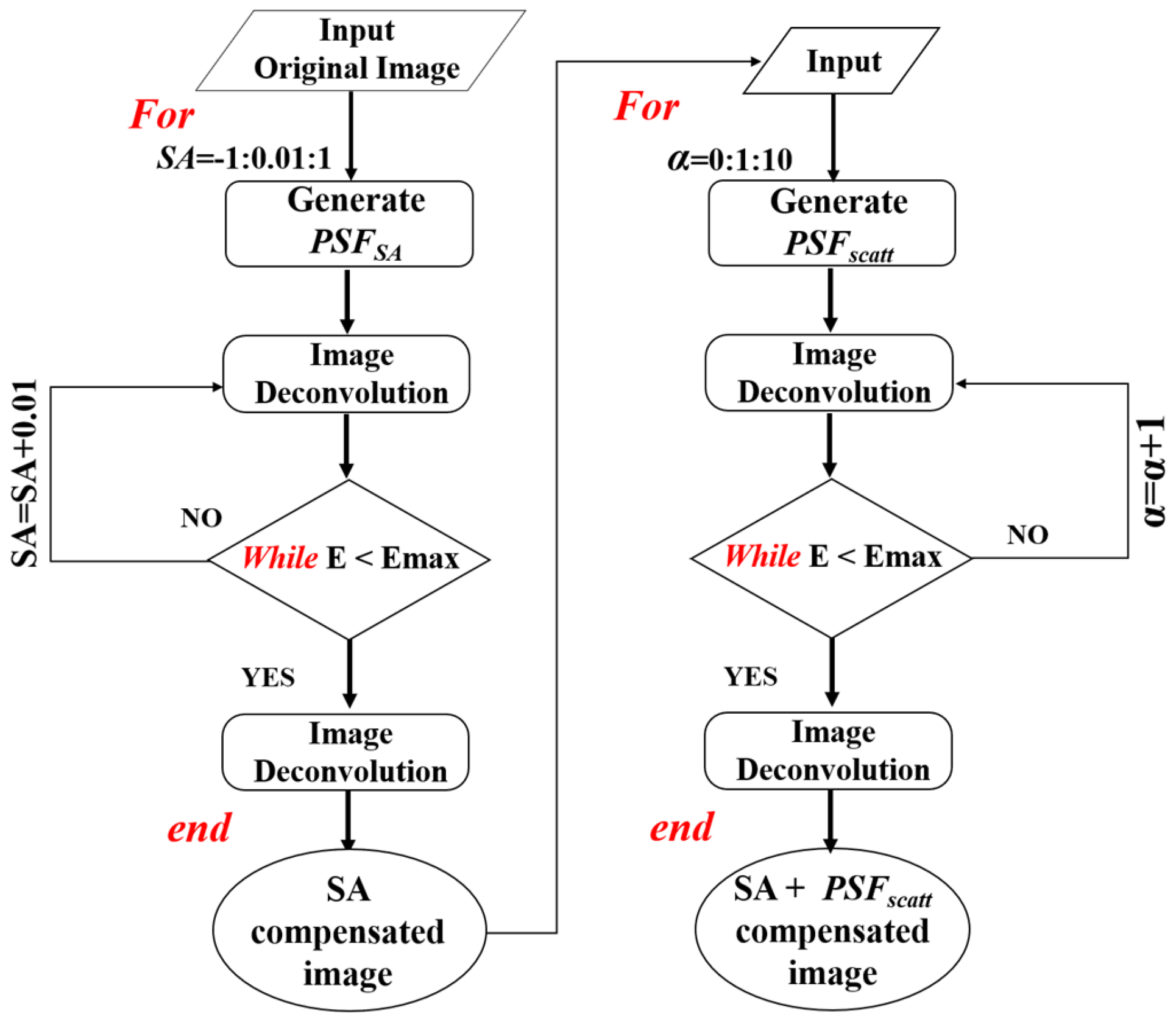
2.4. Algorithm Description
The algorithm here developed is divided into 2 steps. The first one (#1) is based on a through-focus sampling PSF optimization. The second one (#2) is the iterative-optimized deconvolution processing itself. Both parts are described in the following sections. The algorithm was written in Matlab (MatlabTM 2021b, The MathWorks, Inc., Torrance, CA, USA).
During the image optimization process, an image quality metric is required. In particular, throughout this work, the metric “entropy” (E) was used. According to the theory of communication, the concept of entropy of an image can be understood as the degree of randomness of the information within an image. Therefore, E is an appropriate metric since it provides information on the presence of details and features within an image [25]. In previously reported iterative deconvolution approaches, image entropy has been proposed as an efficient tool to optimize the density distribution of the estimated PSF and restored images [26,27]. This work employs this image quality metric as a quantitative measure of the improved spatial resolution of the restored images. For its calculation, the Shannon Entropy MatlabTM function was used.
2.4.1. Step #1: Sampling PSF Optimization
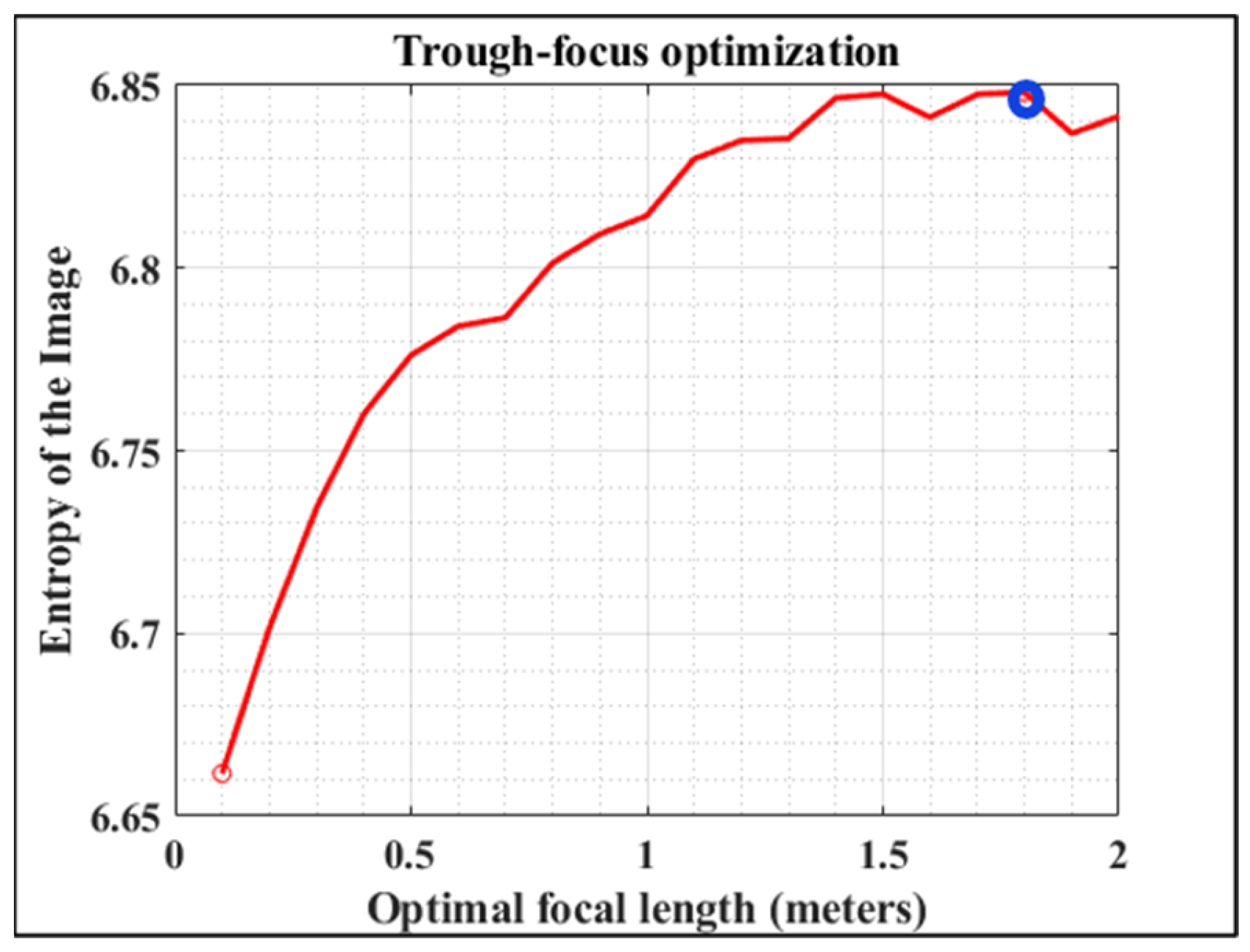
This step #1 is based on an optimization process by direct search of the optimum focal length (FL) (i.e., defocus minimization) (see Figure 3). The algorithm requires the values of some initial parameters such as the number of pixels of the image (N), the size of each pixel (Pixelsize), the wavelength (λ), the aperture radius (AR), and the ratio FL/AR. If the information about the optical system is completely unknown, the input parameters are exclusively reduced to provide the image size.
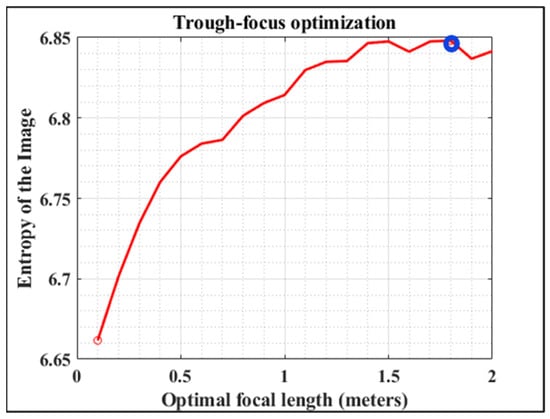
Figure 3.
Representative example of entropy evolution as a function of FL (step #1 of the algorithm). For the sense of completeness, both minimum (red dot) and maximum (blue dot) values are marked within the plot.
Then, the SA Zernike coefficient (C40) is set to a negligible value (0.001 in our case). The algorithm begins with a hill-climbing searching for the optimal FL within an interval ranging between 0 and 5 m, in steps of 0.1 m. For each step, a simple blind deconvolution is performed and the E value of each deconvolved image calculated. In general, the higher the E value, the higher the image sharpness (i.e., more details are visualized). Once the entire closed-loop is completed, the FL value of the image with maximum E is chosen as the optimum one (Figure 3) [28].
2.4.2. Step #2: Deconvolution through PSFSA and PSFscatt
Once the optimal FL has been found (and therefore the focal plane according to the initial parameters is known), step #2 begins using the image with the optimal FL as the input image. As depicted in Figure 4, this part of the procedure includes two sequential iterative-optimized deconvolution subroutines intended to compute the SA coefficient and the α value that maximize the image quality. These will provide the final restored image through the calculation of the optimal PSFSA and PSFscatt (i.e., PSFSA+scatt).
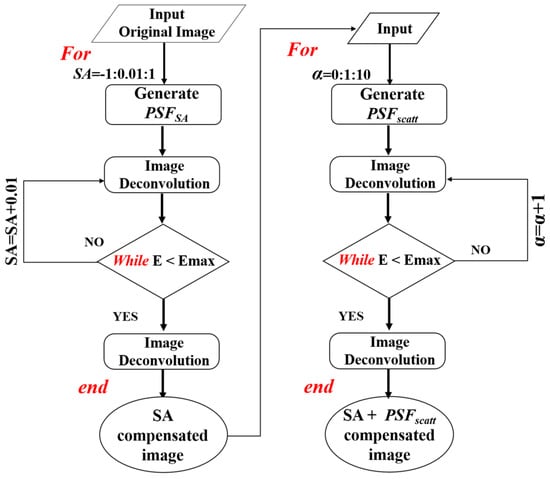
Figure 4.
Flowchart describing the deconvolution process (step #2) here developed.
After this deconvolution process, each final image was evaluated by means of the Image Sharpness (S) metric defined as
with Gx and Gy being the gradients of the image along X- and Y- directions
The Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) (also provided by MatlabTM 2021b Toolbox) computes the similarity between pixels within an image based on neighborhood relationships. Then, the SSIM function compares the similarity between a test and a reference image considering three characteristics: luminance, contrast, and structural information.
2.5. Samples and Images
Different images were used to test the proposed algorithm. As a proof of concept, an artificial image was firstly used. This corresponded to an image of the 1951 USAF resolution test. This original image was degraded through a convolution operation involving different amounts of SA and scattering. The main reasons for chosing an artificial image were the absence of noise sources and the null SA and scatterning contributions before the computer-controlled degradation.
The second set of measurements involved images of the human optic nerve head acquired with a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope (CSLO). The instrument included a polymer dispersed liquid crystal cell (PDLC) to acquire images affected by different amounts of scattering. Further details on this setup can be found in [29]. A PDLC is a device able to modify its transparency as a function of the voltage. If a null voltage is applied, the internal molecules are randomly orientated, the cell appears cloudy, and the maximum scattering level is produced. When the voltage increases, the amount of scattered light decreases (i.e., PDLC transparency increases). For this experiment, CSLO images of two young healthy subjects and three scattering levels were used. This were named as SCL0 (transparent, i.e., maximum voltage applied to the PDLC), SCL1 (moderate scattering level), and SCL2 (high scattering level).
The last set corresponded to images of different ex vivo ocular tissues recorded with an AO-MP microscope [10]: a rat retina (sample #1) and a porcine cornea (sample #2). The microscope used herein incorporates a liquid-crystal SLM (used as AO element) to compensate for the SA. The AO algorithm uses a hill-climbing procedure to get the optimum SA value. Deconvolved images here obtained were compared to those experimentally acquired using the AO procedure. Real images (i.e., the above mentioned three sets of images) were filtered in both spatial and frequency domains, as a pre-processing step before deconvolution, to avoid introducing noise artifacts in the proposed restoration procedure.
3. Results
3.1. Validation of the Algorithm with Degradation-Controlled Artificial Images: A Proof of Concept
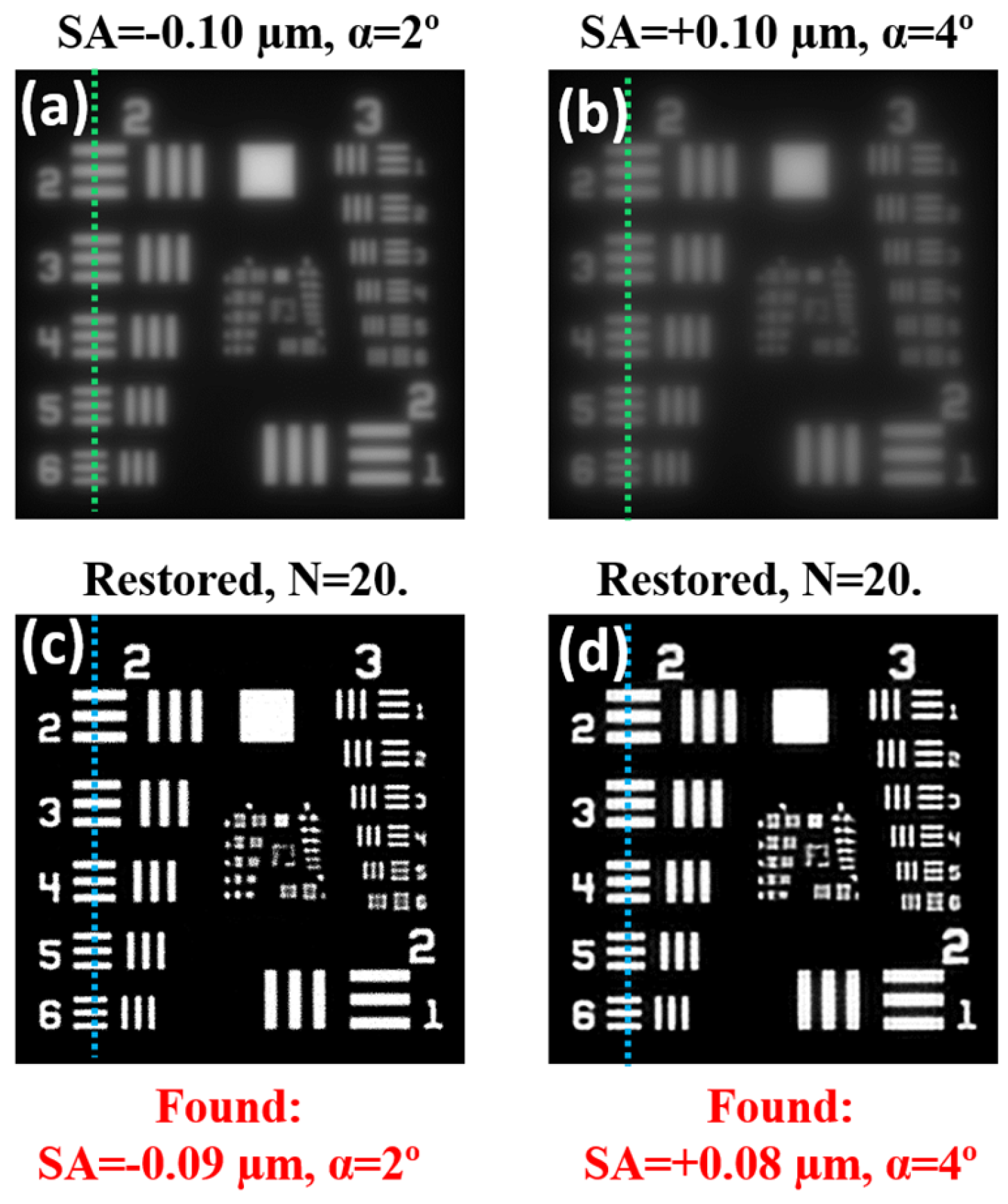
The original image of the USAF resolution test was degraded through a convolution operation involving two PSFSA+scatt with different values of SA and α glare angles. Figure 5a,b shows the corresponding degraded images. The deconvolution method was applied to those images, and the corresponding restored ones are depicted in Figure 5c,d.
Details on the restoration process for image in Figure 5b are presented in Figure 6. This shows the evolution of the metric E as a function of the amount of SA (Figure 6a) and glare α (Figure 6b) during deconvolution. Blue dots represent the values of both parameters (SA and α) that maximized the metric. For this work, the optimum number of iterations (N) during the procedure was chosen as the point where E and S improvement curves intersect (Figure 6c).
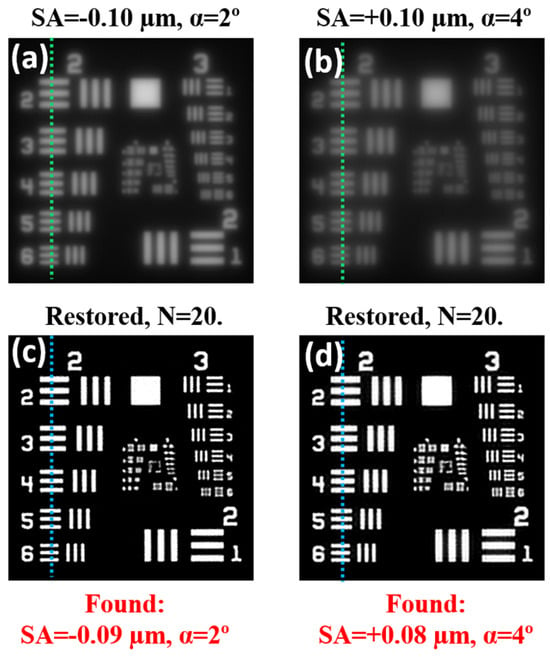
Figure 5.
Degraded images combining different amounts of the SA and glare angle α: (a) SA = −0.10 μm, α = 2°; (b) SA = +0.10 μm; and α = 4°. (c,d) Corresponding restored images using the deconvolution method here described (N = 20). Green and blue dotted lines correspond to the intensity profiles shown in Figure 7.
Figure 5.
Degraded images combining different amounts of the SA and glare angle α: (a) SA = −0.10 μm, α = 2°; (b) SA = +0.10 μm; and α = 4°. (c,d) Corresponding restored images using the deconvolution method here described (N = 20). Green and blue dotted lines correspond to the intensity profiles shown in Figure 7.
Experimentally, the intersection point was found as the threshold from which the optical quality either decreased or did not improve significantly as the number of iterations raises.
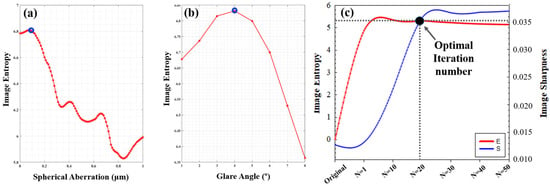
Figure 6.
Example of the calculation of SA (a) glare angle α (b) values during the deconvolution procedure using E as an image quality metric. (c) Experimental determination of the optimal iteration number, N. These data correspond to the restoration of image in Figure 5b. Dotted lines intersect the coordinates (E,S) for the optimal iteration number, N.
Figure 6.
Example of the calculation of SA (a) glare angle α (b) values during the deconvolution procedure using E as an image quality metric. (c) Experimental determination of the optimal iteration number, N. These data correspond to the restoration of image in Figure 5b. Dotted lines intersect the coordinates (E,S) for the optimal iteration number, N.
Our algorithm can be directly validated by comparing the nominal values of SA and α used to generate the input degraded images (see legends in Figure 5a,b) and those obtained from the optimization procedure (see red legends in Figure 5c,d). These experimental (nominal) values were −0.09 (−0.10), +0.08 (+0.10) μm for SA, and 2° (2°), 4° (4°) for α. They agreed well, which corroborates the accuracy of the method here shown.
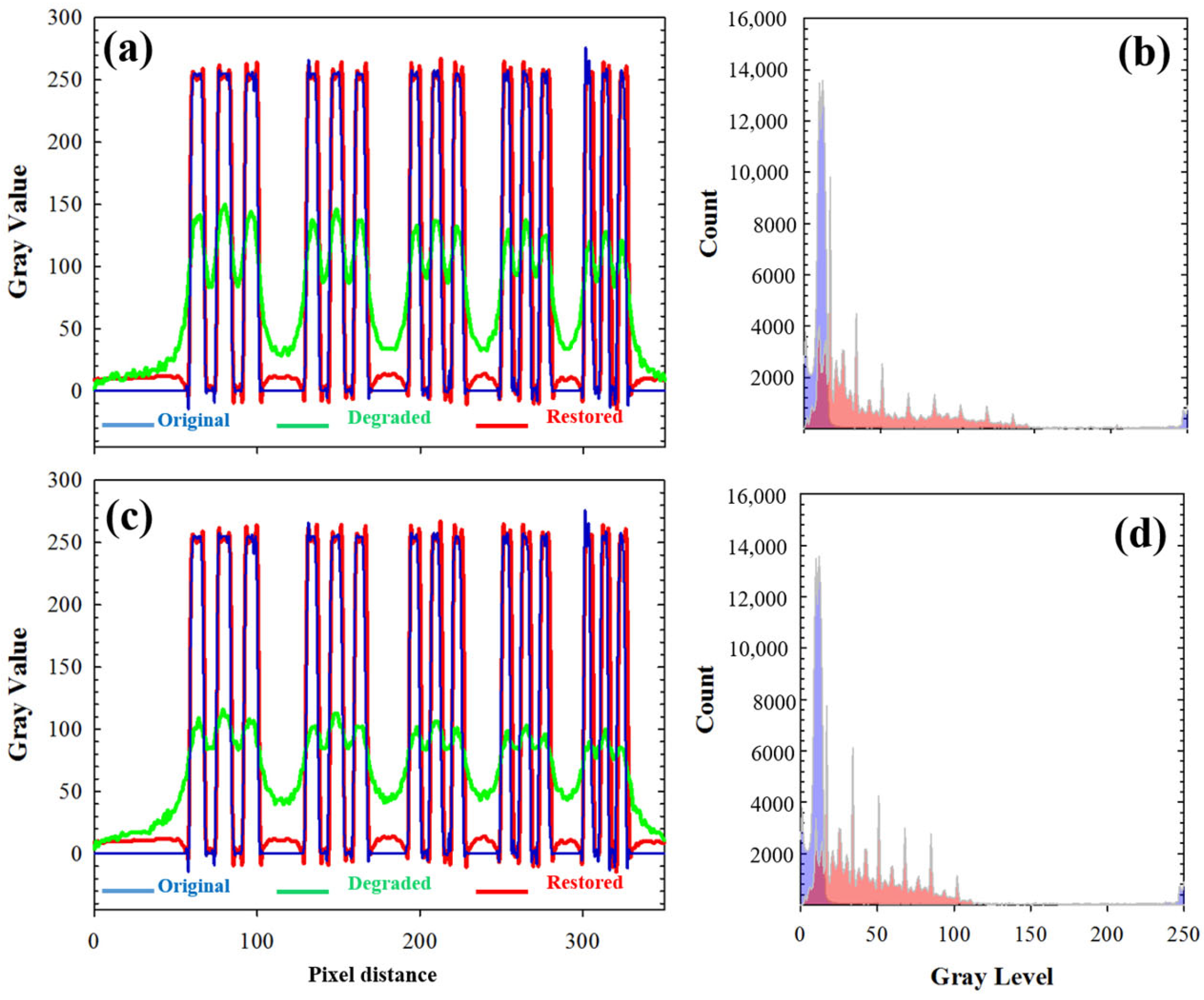
For the sense of completeness, Figure 7a,c depicts the intensity profiles along the vertical dotted lines of Figure 5a–d. Profiles from restored (blue lines) and original images (red lines) did not show statistically significant differences (as shown by a t-test). In addition, Figure 7b,d presents the histograms for the original degraded (purple distribution) and restored (red distribution) images. As expected, after deconvolution, an equalization of the histogram was observed, which ensured energy conservation during the operation.
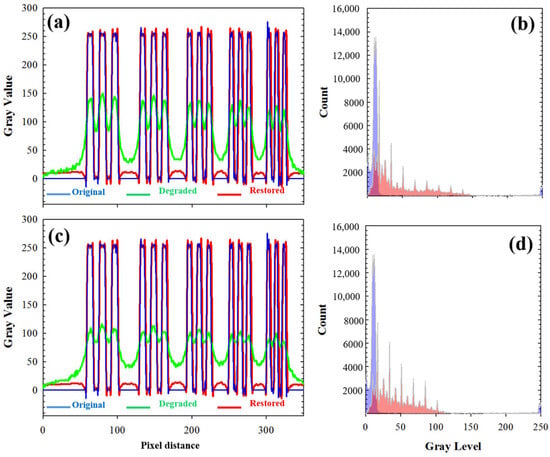
Figure 7.
(a,c) Local intensity profiles along the vertical dotted lines in Figure 5a–d. See text for details. (b,d) Comparison of the histograms of the degraded (purple) and restored (red) images.
Figure 7.
(a,c) Local intensity profiles along the vertical dotted lines in Figure 5a–d. See text for details. (b,d) Comparison of the histograms of the degraded (purple) and restored (red) images.
3.2. Deconvolution of Human Retinal Images with Induced Scattering
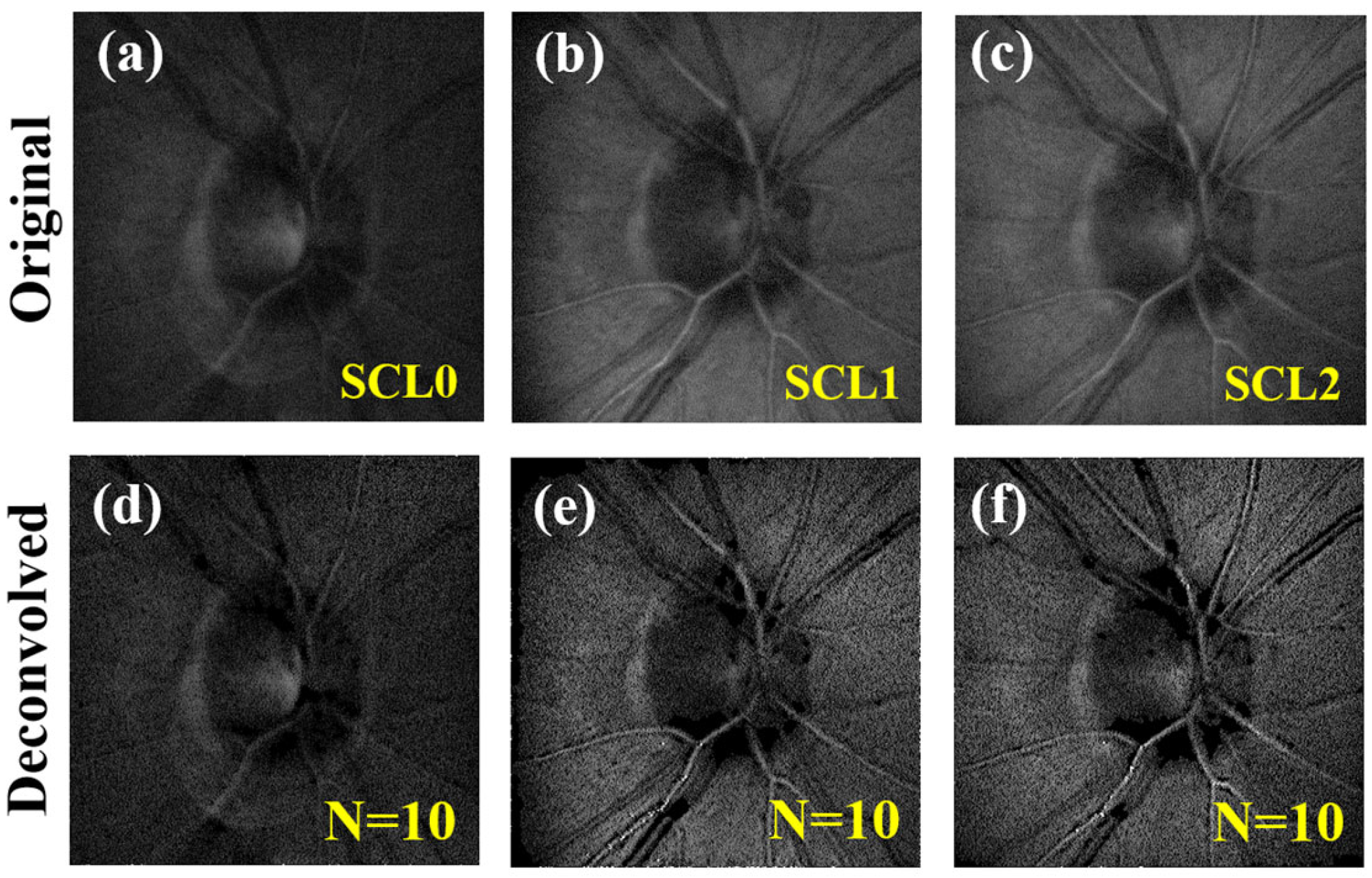
In this section, the degradation coefficient related to scattering effects (i.e., α) was controlled by means of a variable PDLC. Upper panels in Figure 8 show, for one of the subjects involved in the experiment, the original CSLO retinal images acquired for different scattering-induced levels SCL0, SCL1, and SCL2 (see Section 2 for further details). The corresponding restored images after N = 10 iterations are presented at the bottom row.
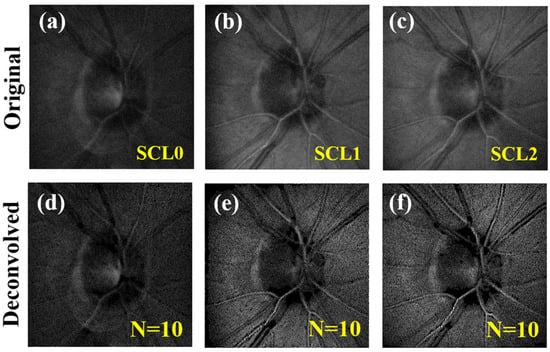
Figure 8.
CSLO retinal images for three different scattering-induced values (as indicated in the upper images) in subject #1. (a–c) Original acquired images. (d–f) Corresponding deconvolved images. Images subtend 15° of visual field.
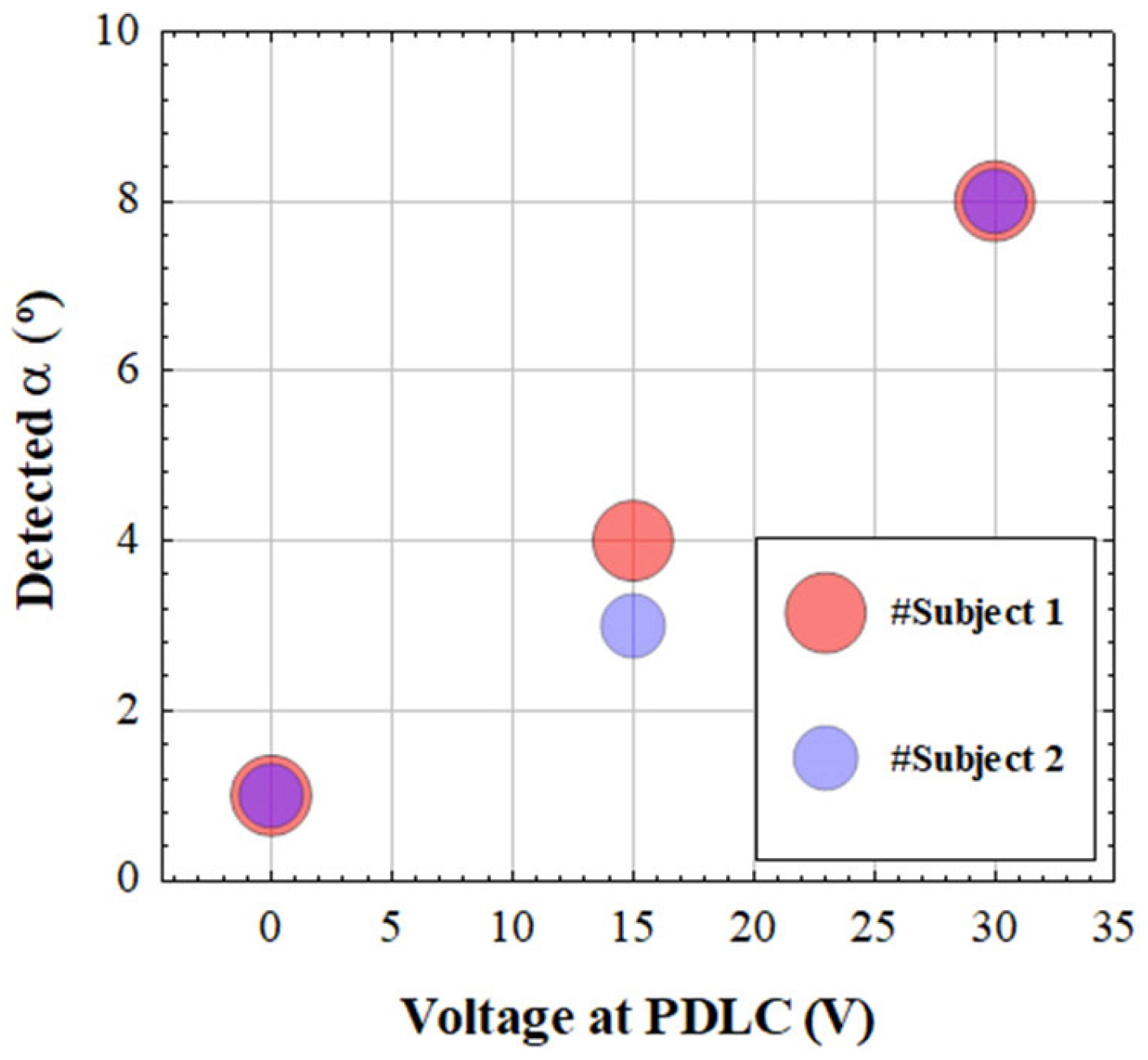
For each experimental scattering condition, Figure 9 shows the glare angles α obtained when applying the present algorithm to the CSLO images from two subjects. It is interesting to notice that for both subjects, given a scattering-induced level, the computed α values were similar. Since the subjects involved were young and healthy, the natural ocular scattering was low [22,23]. Then, the amount of scattering found corresponded exclusively to the induced counter-part, which is coherent with the results found here. The improvements in E (S) when comparing final restored and initial images were 97 (176), 101 (165), and 111 (109)% for SCL0, SCL1, and SCL2 images, respectively.
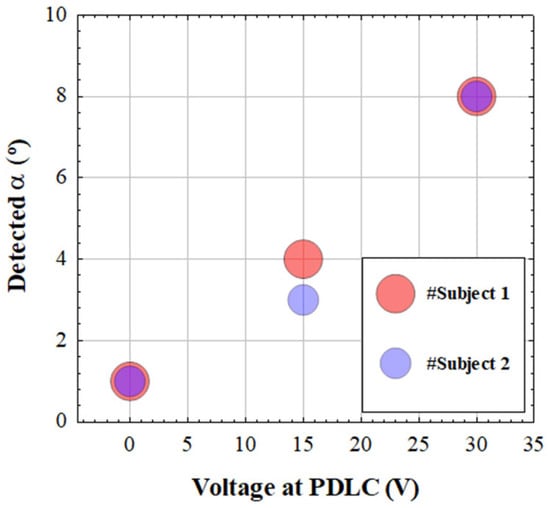
Figure 9.
Values of the glare angles α obtained through deconvolution as a function of the induced scattering level.
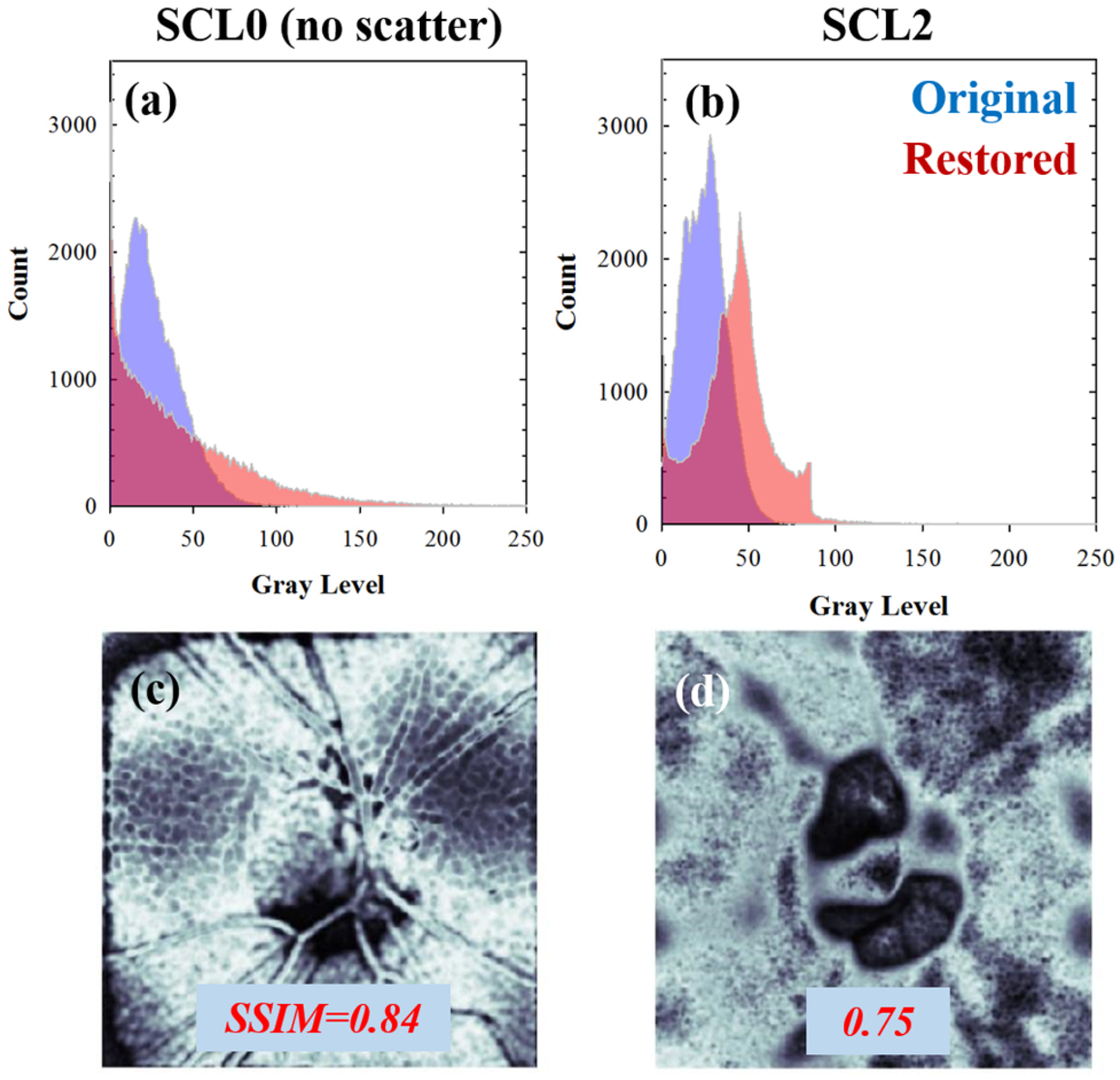
The results of the deconvolution process can be seen not only in the enhanced image quality (as measured by E and S) but also in terms of histogram equalization and recovered structural information, as Figure 10 depicts. SSIM maps (Figure 10c,d) represent the differences between the original and restored images in terms of image luminance, resolved structure (spatial resolution), and image contrast.
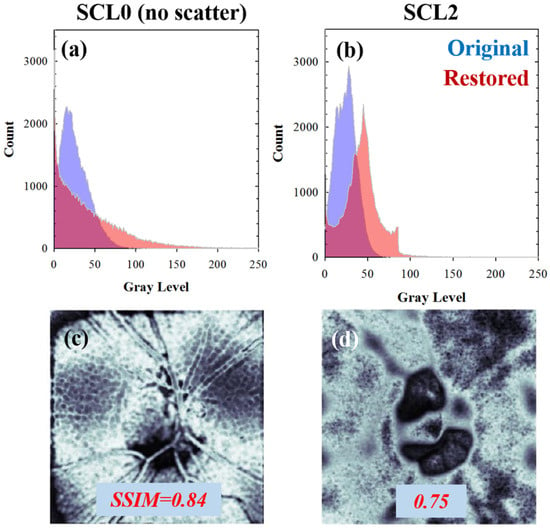
Figure 10.
(a,b) Gray level histograms of the original (purple) and restored (red) CSLO images from Figure 8. The corresponding SSIM maps (included as a comparison) are scaled between zero (no similarity) and 1 (total similarity) (c,d).
For high scattering levels, fine details and features of retinal images would be hidden by the superimposed veiling glare. If the algorithms properly find and restore this degradation mathematical operator, then the structural differences between original and restored images would impact the computed SSIM values, as a greater amount of spatial resolution was recovered, as shown in Figure 10.
3.3. Deconvolution of Multiphoton Microscopy Images
It is worth noting that CSLO images shown in the previous section were acquired from living human eyes, and therefore the intrinsic SA of the human cornea was present (also detected by our algorithm) in the degradation operator that combines SA and scattering contributions. In this sense, this section deals with the evaluation of the algorithm with AO-MP images of thick scattering biological tissues (see Section 2 above). Further details on this AO technique can be seen in [10].
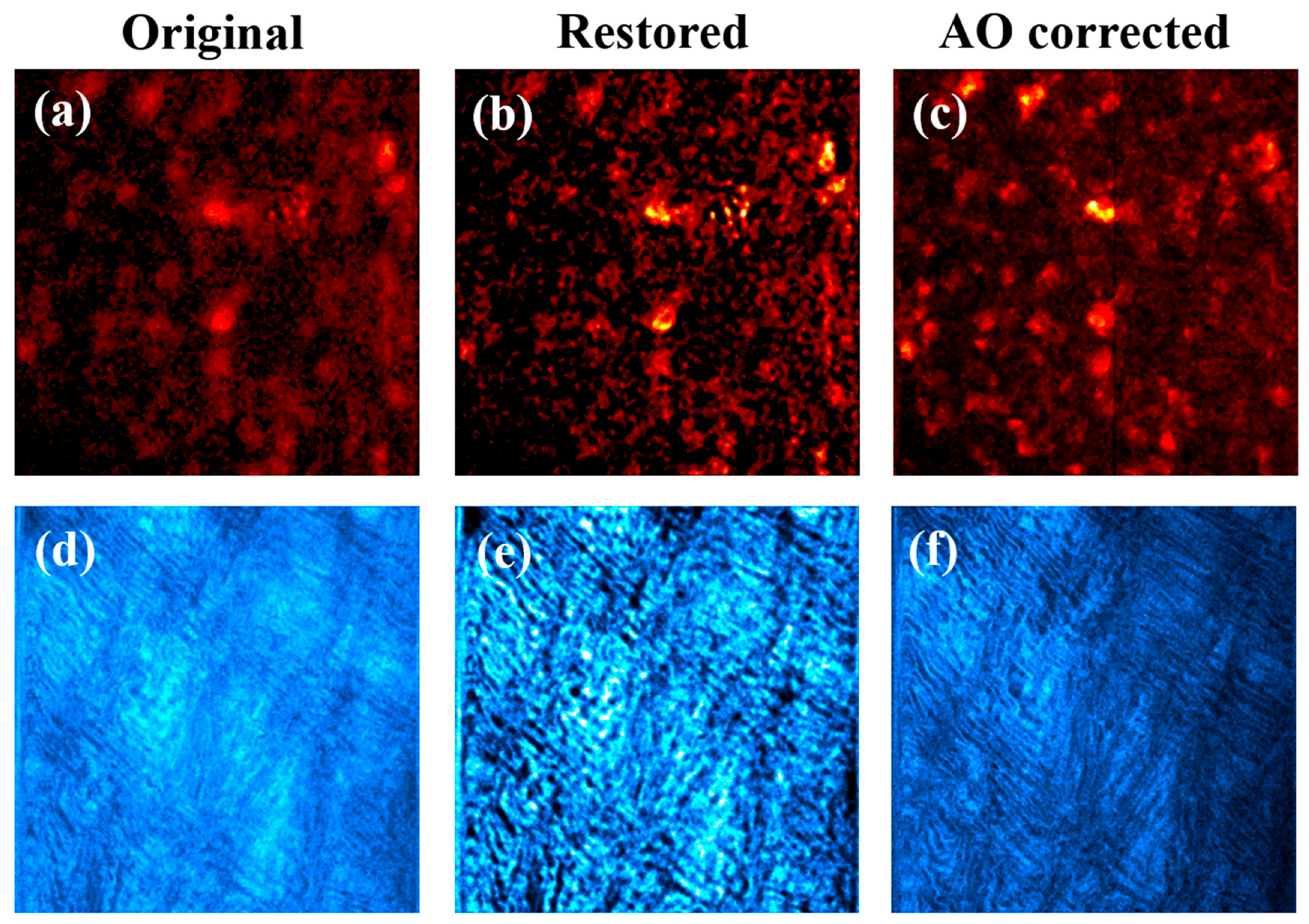
The left column of Figure 11 presents MP images acquired in sample #1 (top) and sample #2 (bottom). As expected, these original MP images were of limited quality due to the effect of SA and scattering. Cells (in Figure 11a) and collagen fibers (in Figure 11d) were hardy distinguished due to the reduced contrast and resolution of the original images. After deconvolution, a noticeable improvement in the images was obtained (middle column).
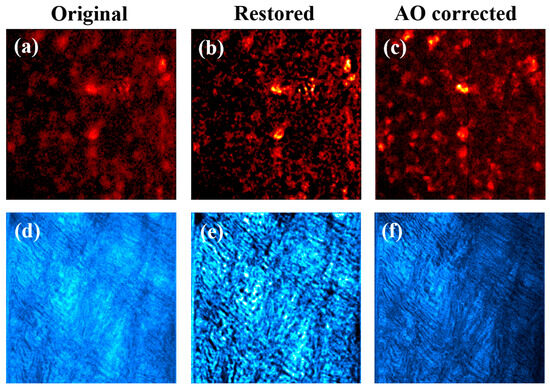
Figure 11.
Experimentally recorded MP microscopy images (a,d) corresponding to a rat retina (a) and a porcine cornea (d). Restored images using the deconvolution method (b,e). AO-MP images with compensation for SA (i.e., AO on; right panels (c,f)). Images within a row share the same color scale. Image size: 210 × 210 μm2.
For the sense of completeness, the images experimentally recorded through AO (i.e., just SA compensation) are also depicted (right column). A simple visualization indicates that MP images obtained through deconvolution were better that those obtained after using AO-SA compensation. This might be mainly due to two reasons: (1) SA values differ among both techniques (see Table 1) and (2) our algorithm is also capable of detecting non-negligible α values (Table 1) that further improve the quality of the restored images (this scattering was not compensated with experimental AO). Those qualitative appreciations are corroborated with the computational results of Figure 12.

Table 1.
Comparison of SA values for MP images in Figure 11 obtained with deconvolution (N iterations as indicated) and AO. Values of α provided by the algorithm are also shown.
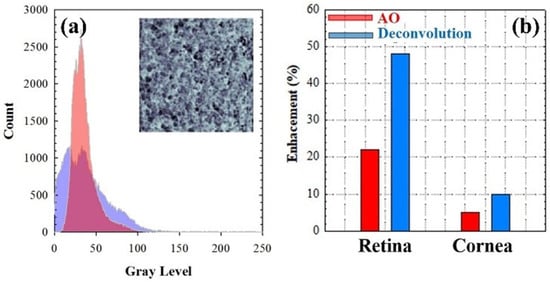
Figure 12.
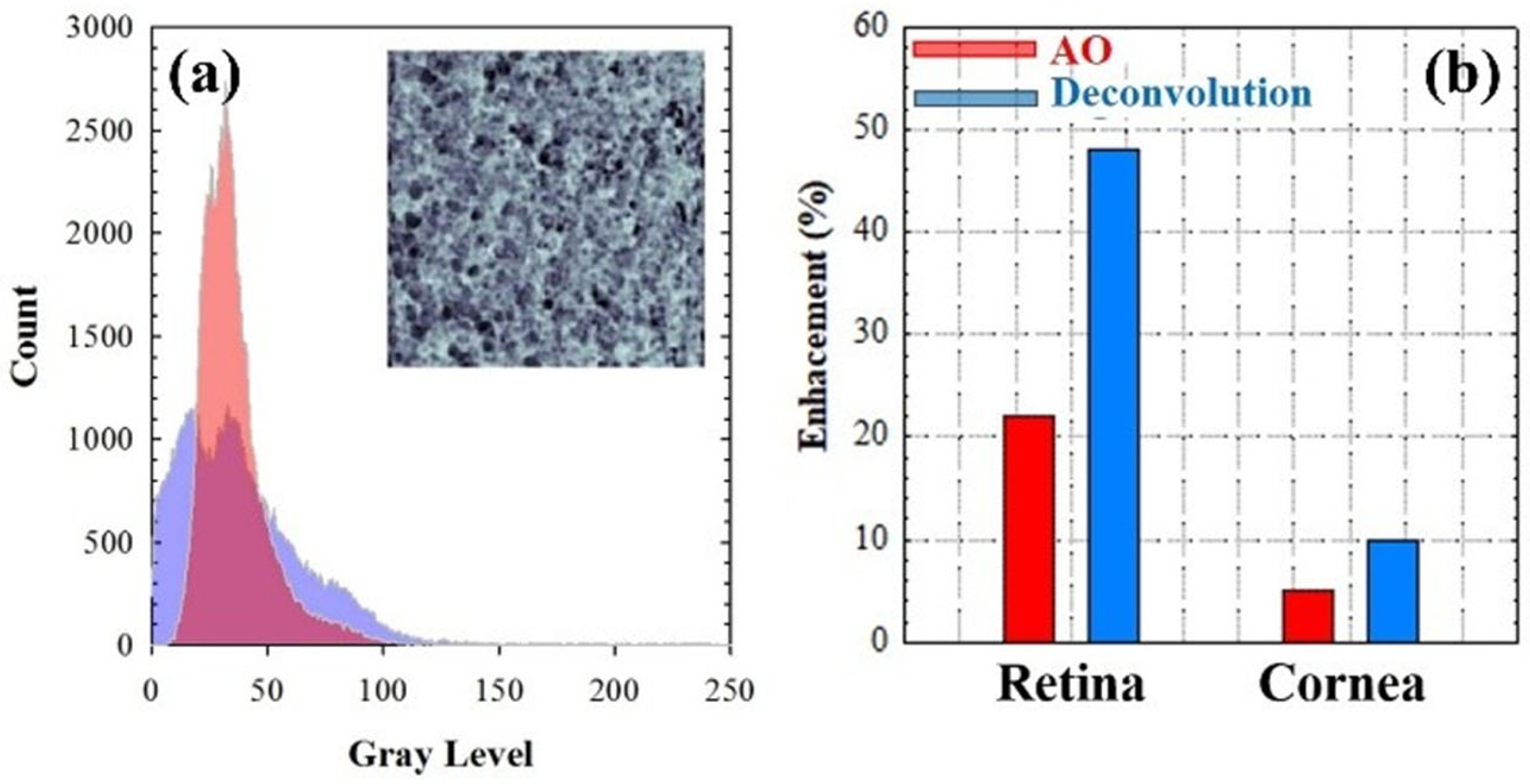
(a) Histograms of the AO-SA compensated (red) and deconvolution restored (purple) MP images (sample #1) and the corresponding SSIM map. (b) Enhancement in image quality (E) when comparing the original images (Figure 11a,d) and those obtained after SA correction (red bars; Figure 11c,f) and deconvolution (blue bars; Figure 11b,e).
Figure 12a compares the intensity histograms of the images using deconvolution (blue) and after the experimental SA correction (red). The differences in the SSIM values (see map inserted) were mainly due to the uncorrected scattering contribution that remained residual after AO operation. Image enhancement (%, in terms of E) when comparing the original acquired images and those obtained with AO-SA compensation (red bars) and after deconvolution (blue bars) are depicted in Figure 12b.
3.4. Contribution of SA and Scattering to Image Quality Degradation
The algorithm here reported takes into account SA and scattering, both inherent contributions to the image formation process. This was tested in CSLO and MP images, where the final restored images were a result of the optimum SA and α coefficients. Whereas in the former, the amount of induced scattering was controlled, in the latter, only the SA was compensated through AO. However, CSLO images might also be affected by the ocular SA, and scattering effects were also present in thick biological tissues during MP imaging. In this sense, at this point it is interesting to quantify the individual contribution of every coefficient (SA and α) to the degradation factor defined in this work.
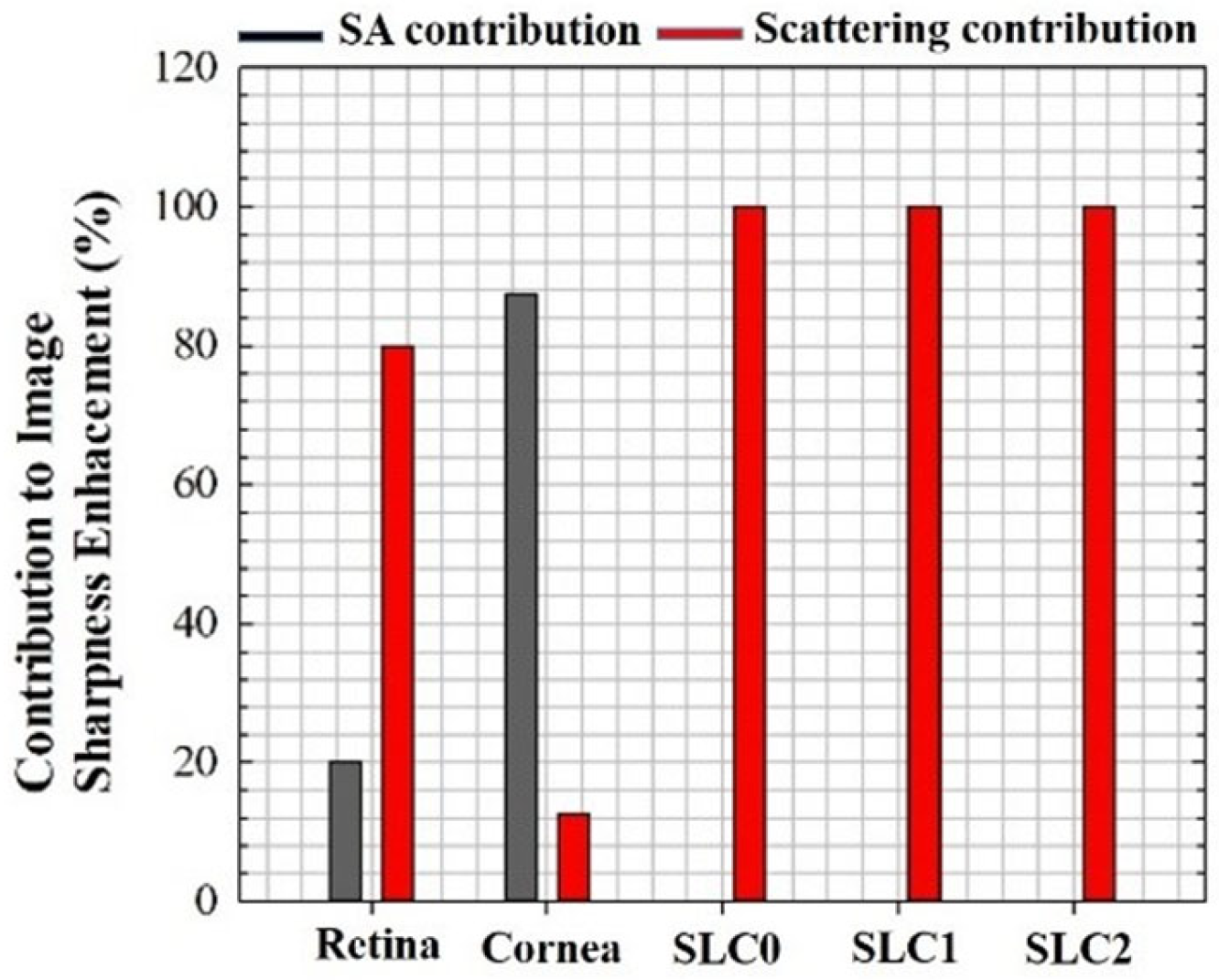
Figure 13 shows the contribution (in %) to the final image enhancement (using S as a metric) after individually compensating SA and scattering for different images used in this work. The results show that for CSLO images, the α coefficient was the dominant contribution to image improvement (i.e., SA’s was nearly negigible). On the other hand, for MP imaging, the weight of each contribution depended on the sample, that is, the improvement when combining both was better than that corresponding to the use of SA or α separately.
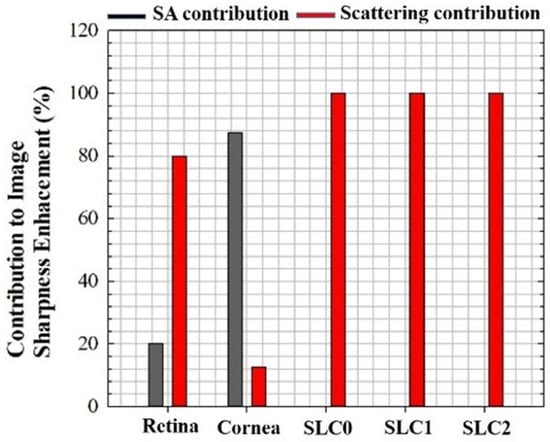
Figure 13.
Individual contribution (in %, based on E values) of SA (black bars) and scattering (red bars) to image enhancement in restored images.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Image deconvolution algorithms have been widely used to enhance the resolution of blurred images in fluorescence [30] and MP microscopy [31,32], retinal imaging [33], and astronomy [34], among others.
Under some experimental conditions, the PSF of the optical system required for the deconvolution procedure is unknown. Then, blind (or myopic) deconvolution methods are required to obtain a solution. These are based on aberration compensation. Other previous studies have employed regularization deconvolution to compensate for scattering effects in biological microscopy [35] or diffuse light and halos [36,37] in astronomic images.
Deep learning algorithms based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have provided new horizons in optical deblurring during the last years [38]; however, those approaches require large image datasets (as well as training processing) that may not be readily available.
However, to the best of our knowledge, blind deconvolution procedures to compensate both aberrations and scattering (or veiling glare) effects have not been reported yet. Unlike previous literature, the present work takes a step forward and merges both effects.
The algorithm incorporates a hill-climbing optimization method that searches for the SA and α coefficients that optimize the image quality using E as a metric. Considering that even in blind deconvolution algorithms a minimal prior knowledge of the PSF is required (such as the imposition of the non-negativity of the energy distribution of the deconvolution kernel), the use of the image entropy as the image quality optimization ensures the non-negativity of the estimated PSF within the iterative process [39].
As a proof of concept, this was firstly tested in computer-generated images generated by convolving a resolution USAF test and PSFs with different amounts of SA and α parametrization (see the accurate performance in Figure 5 and Figure 7). Then, biological images affected by SA and scattering were used to evaluate the capabilities of the algorithm. This provided restored images with measurable improvements, where structural details that remained hidden in the original images could be visualized after deconvolution (see for instance Figure 8 and Figure 11).
Our results revealed the proposed algorithm as a useful tool to successfully restore images by accurately obtaining both the SA and α optimal coefficients. The most interesting finding reported herein is that image enhancement is higher than that reached when using SA or scattering compensation separately.
The main limitation of the procedure proposed herein occurs when the spatial resolution of the original image is not enough to obtain an improved image with better entropy. In these cases, the iteration number exceeds the point of optimal convergence (i.e., the intersection E,S, Figure 6c), and the signal-to-noise ratio increases at the cost of introducing image artifacts as the deconvolution process runs ahead.
To conclude, we developed a blind deconvolution algorithm to compensate for both SA and scattering effects. This approach has been carried out defining PSFSA and PSFscatt according to the well-established previous publications [21,23]. The algorithm does not require information about the original PSF of the optical system used to obtain the image under study. The effectiveness of the approach was demonstrated in microscopy images of different nature.
Future applications of this approach might be of interest in different microscopy imaging applications, ranging from forensic sciences to biomedical environments, in particular in those critical situations where the information on the PSF responsible for image formation is not available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J.Á.; methodology, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; software, F.J.Á.; validation, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; formal analysis, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; investigation, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; resources, J.M.B.; data curation, F.J.Á.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; writing—review and editing, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; visualization, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; supervision, F.J.Á. and J.M.B.; project administration, J.M.B.; funding acquisition, J.M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Agencia Estatal de Investigación, Spain (grant PID2020-113919RB-I00/AEI/10.13039/501100011033).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Murcia (Protocol ID-3114/2020, 8 March 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
The subjects involved in the experiment were informed on the details and goals of the imaging procedure and signed a written consent form.
Data Availability Statement
The algorithm presented in this study is available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Melanie C. W. Campbell for allowing the use of the CSLO images.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jonkman, J.; Brown, C.M.; Wright, G.D.; Anderson, K.I.; North, A.J. Tutorial: Guidance for quantitative confocal microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1585–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Ji, N. Adaptive optical microscopy for neurobiology. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2018, 50, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, S.A.; Elsner, A.E.; Sapoznik, K.A.; Warner, R.L.; Gast, T.J. Adaptive optics imaging of the human retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 68, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, F.J.; Gambín, A.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. In vivo two photon microscopy of the human eye. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, J. Optical aberrations of the microscope. In Understanding Light Microscopy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, W.; Sun, Y.; Lin, S.-J.; Jee, S.-H.; Dong, C.-Y. Spherical aberration correction in multiphoton fluorescence imaging using objective correction collar. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 034006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Débarre, D.; Botcherby, E.J.; Watanabe, T.; Srinivas, S.; Booth, M.J.; Wilson, T. Image-based adaptive optics for two-photon microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2495–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M.; Skorsetz, M.; Palacios, R.; Gualda, E.J.; Artal, P. Multiphoton imaging microscopy at deeper layers with adaptive optics control of spherical aberration. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorsetz, M.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. Performance evaluation of a sensorless adaptive optics multiphoton microscope. J. Microsc. 2016, 261, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Sun, W.; Cui, M. High-resolution in vivo imaging of mouse brain through the intact skull. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9236–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaigneau, E.; Wright, A.J.; Poland, S.P.; Girkin, J.M.; Silver, R.A. Silver, Impact of wavefront distortion and scattering on 2-photon microscopy in mammalian brain tissue. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 22755–22774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinefeld, D.; Paudel, H.P.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Bifano, T.G.; Xu, C. Adaptive optics in multiphoton microscopy: Comparison of two, three and four photon fluorescence. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 31472–31483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, I.N.; Jouhanneau, J.-S.; Poulet, J.F.A.; Judkewitz, B. Scattering compensation by focus scanning holographic aberration probing (F-SHARP). Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, P.; Gandolfi, D.; Porro, C.A.; Bigiani, A.; Mapelli, J. Scattering compensation for deep brain microscopy: The long road to get proper images. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DBurke, D.; Patton, B.; Huang, F.; Bewersdorf, J.; Booth, M.J. Adaptive optics correction of specimen-induced aberrations in single-molecule switching microscopy. Optica 2015, 2, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Starck, J.L.; Pantin, E.; Murtagh, F. Deconvolution in astronomy: A review. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2002, 114, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Weiss, Y.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. Understanding and evaluating blind deconvolution algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1964–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Michailovich, O.; Tannenbaum, A. Blind deconvolution of medical ultrasound images: A parametric inverse filtering approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 3005–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ameen, Z.; Bin Sulong, G.; Johar, G.M. Computer forensics and image deblurring: An inclusive investigation. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 2013, 5, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thibos, L.N.; A Applegate, R.; Schwiegerling, J.T.; Webb, R. Standards for reporting the optical aberrations of eyes. J. Refract. Surg. 2002, 18, S652–S660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, T.J.; IJspeert, J.K.; de Waard, P.W. Dependence of intraocular straylight on pigmentation and light transmission through the ocular wall. Vis. Res. 1991, 31, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.; van den Berg, T.J. Report on Disability Glare. CIE Collect. 1999, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sibarita, J. Deconvolution Microscopy. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2005, 95, 201–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E.; Eddins, S.L. Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Chapter 11. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, R.; Nityananda, R. Maximum entropy image restoration in astronomy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 24, 127–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skilling, J.; Bryan, R.K. Maximum entropy image reconstruction: General algorithm. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1984, 211, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, J.J.; Cookson, C.J.; Kisilak, M.; Bueno, J.M.; Campell, M.C.W. Characterizing image quality in a scanning laser ophthalmoscope with different pinholes and induced scattered light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2007, 24, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedlow, J.R. Quantitative fluorescence microscopy and image deconvolution. Methods Cell Biol. 2013, 114, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doi, A.; Oketani, R.; Nawa, Y.; Fujita, K. High-resolution imaging in two-photon excitation microscopy using in situ estimations of the point spread function. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Mugnier, L.M.; Artal, P.; Bueno, J.M. Blind deconvolution of second harmonic microscopy images of the living human eye. Biomed. Opt. Express 2023, 14, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, L.; Mugnier, L.M. Marginal blind deconvolution of adaptive optics retinal images. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 23227–23239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fétick, R.J.-L.; Mugnier, L.M.; Fusco, T.; Neichel, B. Blind deconvolution in astronomy with adaptive optics: The parametric marginal approach. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 496, 4209–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benno, K.-S.; Lars, O.; Tobias, S.-M.; Timo, M.; Vasilis, N. Scattering correction through a space-variant blind deconvolution algorithm. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 096005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.A.; Nalcioglu, O.; Roeck, W. Removal of image intensifier veiling glare by mathematical deconvolution techniques. Med. Phys. 1985, 12, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabal, E.; Duc, P.-A.; Kuntschner, H.; Chanial, P.; Cuillandre, J.-C.; Gwyn, S. A deconvolution technique to correct deep images of galaxies from instrumental scattered light. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 601, A86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajkofci, A.; Liebling, M. Spatially-variant CNN-based point spread function estimation for blind deconvolution and depth estimation in optical microscopy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5848–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, M.F.; Raheem, G.M.A.; Mohammed, U.S.; Fahmy, O.F. A fast iterative blind image restoration algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 28th National Radio Science Conference (NRSC), Cairo, Egypt, 26–28 April 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).