Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Image Processing and Analysis in Medical Diagnostics
1.2. Objectives and Scope of the Review
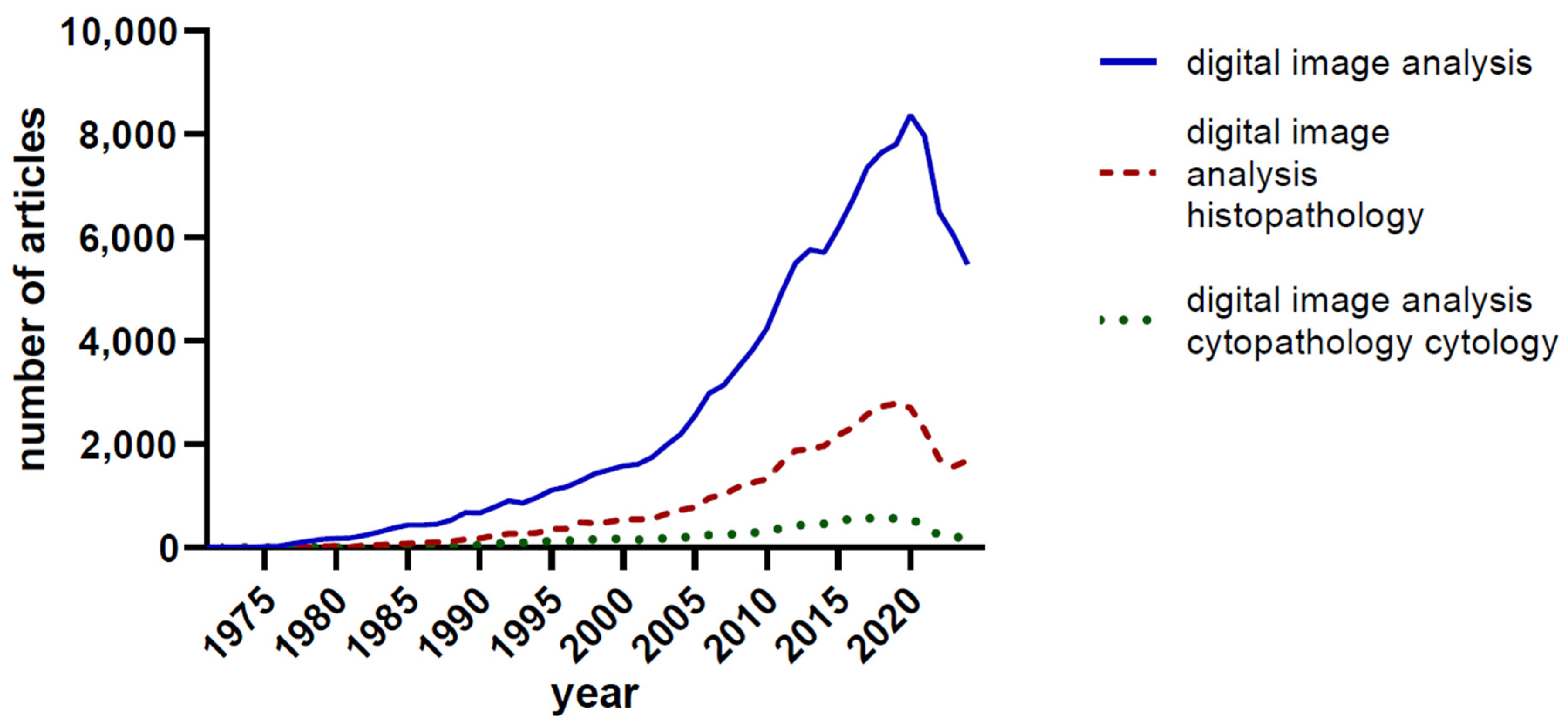
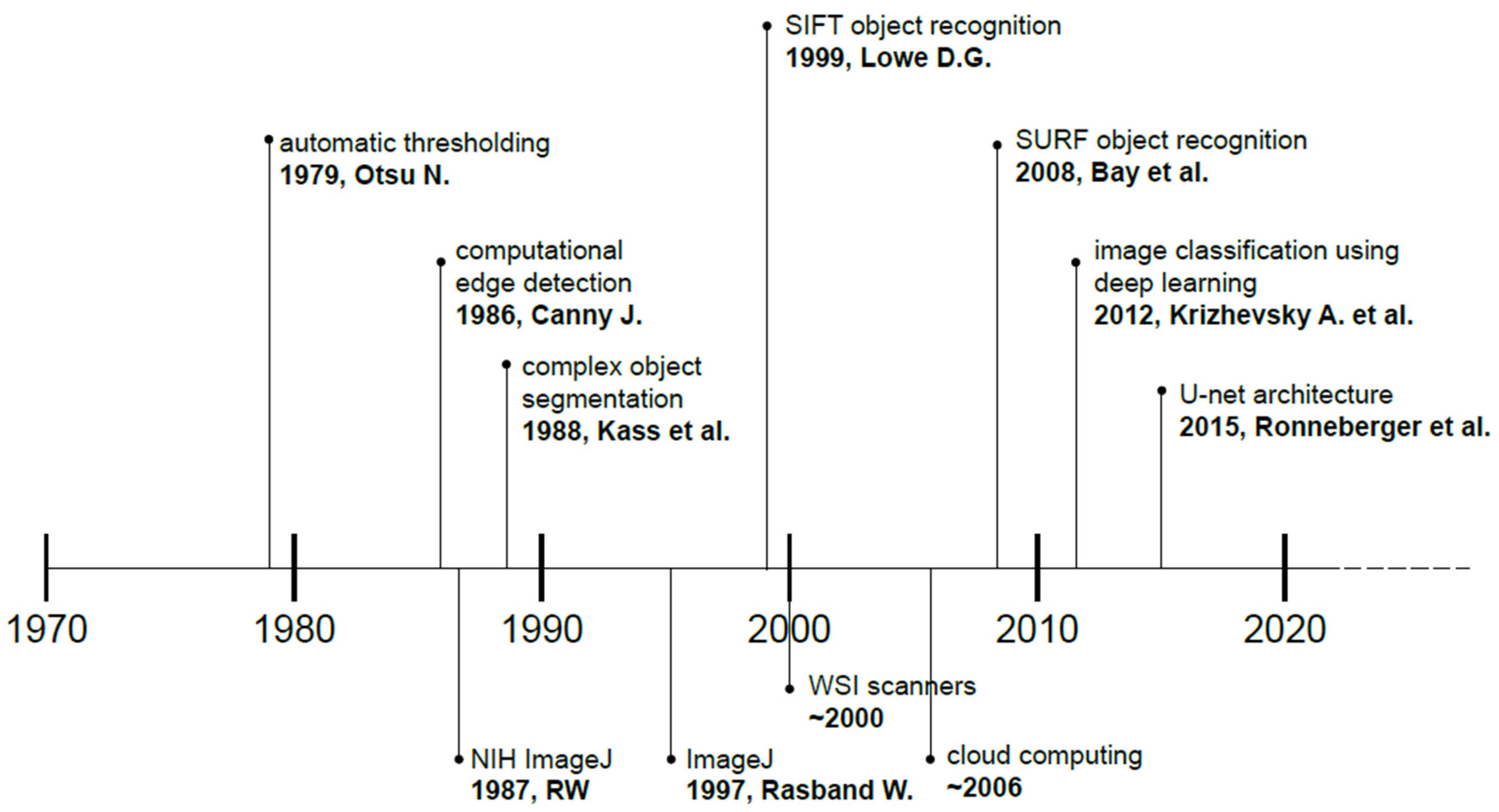
2. Historical Developments
3. Current Techniques and Technologies in Image Analysis
3.1. Digital Pathology
3.1.1. Whole Slide Imaging
3.1.2. Image Storage and Retrieval Systems
3.2. Digital and Automated Image Analysis
3.2.1. Segmentation Techniques
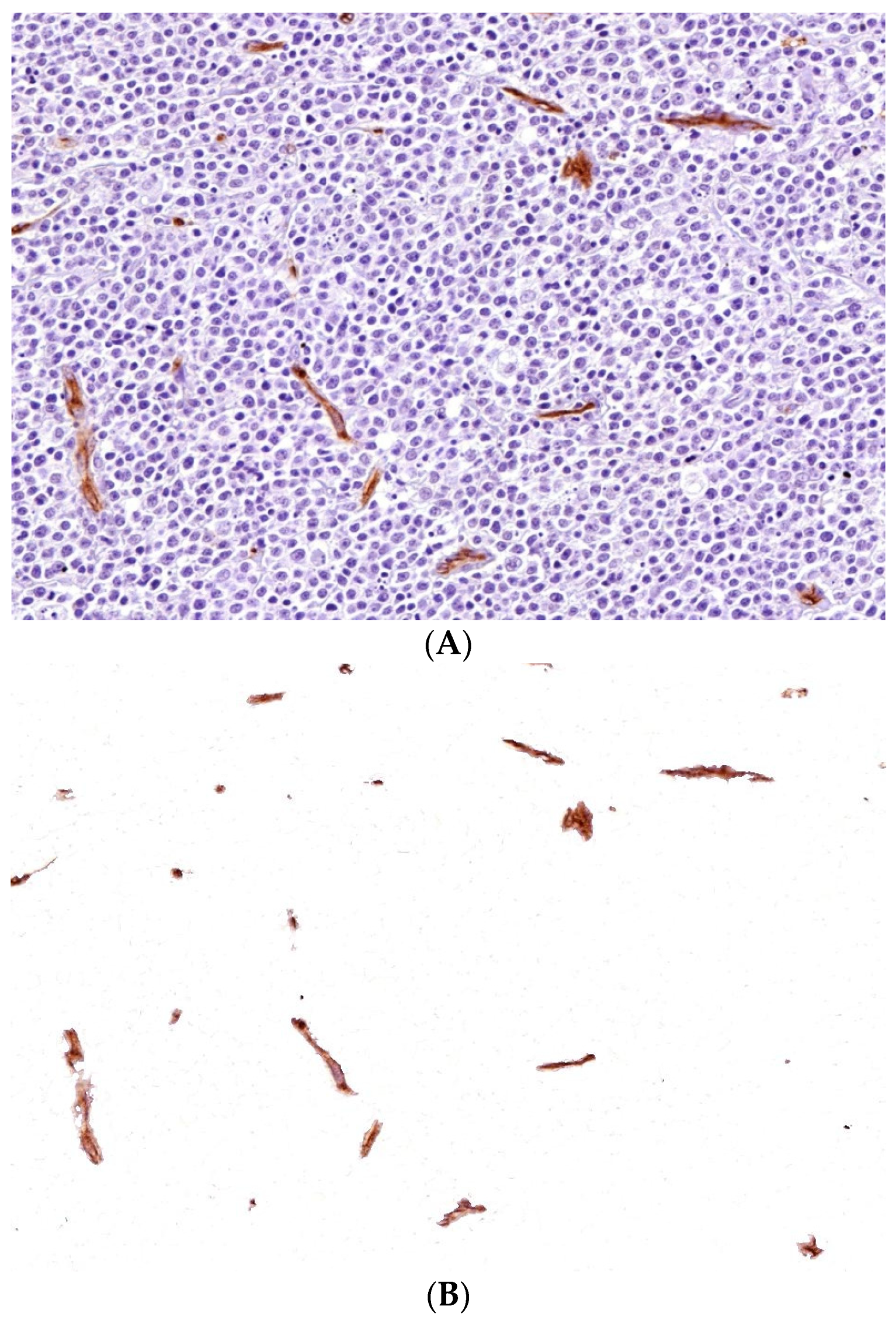
3.2.2. Feature Extraction and Quantification
3.2.3. Classification and Pattern Recognition
3.3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Image Analysis
3.4. 3D Imaging and Advanced Visualization Techniques
3.5. Virtual Staining and Deep Learning
4. Applications in Clinical Diagnostics
4.1. Histopathological Image Analysis for Cancer Detection and Grading
4.2. Cytological Image Analysis for Early Detection of Disease
4.3. Other Applications
5. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
5.1. Patient Confidentiality and Data Privacy
5.2. Bias in Training Data
5.3. Regulation of AI-Based Tools
5.4. Human vs. Machine Debate
6. Interoperability and Integration Challenges
7. Future Perspectives
7.1. Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
7.2. Explainable AI
7.3. AI for Predictive and Preventive Diagnostics
7.4. Emerging Technologies
7.5. The Role of Image Analysis in Telemedicine
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ASC | American Society of Cytopathology |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| LIME | Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations |
| LSFM | Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| OPT | Optical Projection Tomography |
| SAM | Segment Anything Model |
| SIFT | Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) |
| WSI | Whole Slide Imaging |
| XAI | Explainable AI |
References
- Araki, T. The History of Optical Microscope. Mech. Eng. Rev. 2017, 4, 16–00242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittekind, D. Traditional Staining for Routine Diagnostic Pathology Including the Role of Tannic Acid. 1. Value and Limitations of the Hematoxylin-Eosin Stain. Biotech. Histochem. 2003, 78, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titford, M. Progress in the Development of Microscopical Techniques for Diagnostic Pathology. J. Histotechnol. 2009, 32, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.C. The Wonderful Colors of the Hematoxylin-Eosin Stain in Diagnostic Surgical Pathology. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 22, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafts, K.P.; Pambuccian, S.E. Romanowsky Staining in Cytopathology: History, Advantages and Limitations. Biotech. Histochem. 2011, 86, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantziantoniou, N.; Donnelly, A.D.; Mukherjee, M.; Boon, M.E.; Austin, R.M. Inception and Development of the Papanicolaou Stain Method. Acta Cytol. 2017, 61, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucar, E. Diagnostic Decision-Making in Anatomic Pathology. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 116 (Suppl. S1), S21–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, R.S.; Naus, G.J.; Stewart, J., 3rd; Friedman, C.P. Development of Visual Diagnostic Expertise in Pathology—An Information-Processing Study. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2003, 10, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallua, J.D.; Brunner, A.; Zelger, B.; Schirmer, M.; Haybaeck, J. The Future of Pathology Is Digital. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Chou, K.; Yeung, S.; Naik, N.; Madani, A.; Mottaghi, A.; Liu, Y.; Topol, E.; Dean, J.; Socher, R. Deep Learning-Enabled Medical Computer Vision. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, L.; Nivala, M.; Kronqvist, P.; Ericsson, K.A.; Lehtinen, E. Do Prior Knowledge, Personality and Visual Perceptual Ability Predict Student Performance in Microscopic Pathology?: Predicting Student Performance in Microscopic Pathology. Med. Educ. 2010, 44, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaarsma, T.; Jarodzka, H.; Nap, M.; van Merrienboer, J.J.G.; Boshuizen, H.P.A. Expertise under the Microscope: Processing Histopathological Slides. Med. Educ. 2014, 48, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaarsma, T.; Jarodzka, H.; Nap, M.; van Merriënboer, J.J.G.; Boshuizen, H.P.A. Expertise in Clinical Pathology: Combining the Visual and Cognitive Perspective. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 2015, 20, 1089–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, P.W.; van Diest, P.J.; Williams, R.; Gallagher, A.G. Do We See What We Think We See? The Complexities of Morphological Assessment. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandel, T.M.; Pfnür, M.; Schäfer, S.C.; Bacchetti, P.; Mast, F.W.; Corinth, C.; Ansorge, M.; Melchior, S.W.; Thüroff, J.W.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; et al. Do We Truly See What We Think We See? The Role of Cognitive Bias in Pathological Interpretation. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Rahaman, M.M.; Yao, Y.; Ai, S.; Sun, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. A Comprehensive Review for Breast Histopathology Image Analysis Using Classical and Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90931–90956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowski, P.; Strzelecki, M.; Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E.; Zalewska, A. Computer Analysis of Normal and Basal Cell Carcinoma Mast Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2001, 7, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.; Minsky, M.L.; Rochester, N.; Shannon, C.E. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, August 31, 1955. AIMag 2006, 27, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechter, R. Learning While Searching in Constraint-Satisfaction-Problems. Available online: https://cdn.aaai.org/AAAI/1986/AAAI86-029.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Cooper, M.; Ji, Z.; Krishnan, R.G. Machine Learning in Computational Histopathology: Challenges and Opportunities. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2023, 62, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.; Witkin, A.; Terzopoulos, D. Snakes: Active Contour Models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1988, 1, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Object Recognition from Local Scale-Invariant Features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Corfu, Greece, 25 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2012, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015, Proceedings, Part III. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. ISBN 9783319245737. [Google Scholar]
- Komura, D.; Ishikawa, S. Machine Learning Methods for Histopathological Image Analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaggoune, K.; Al Masry, Z.; Ma, J.; Devalland, C.; Mouss, L.H.; Zerhouni, N. A Deep Learning Pipeline for Breast Cancer Ki-67 Proliferation Index Scoring. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.07452. [Google Scholar]
- Pantanowitz, L.; Hornish, M.; Goulart, R.A. The Impact of Digital Imaging in the Field of Cytopathology. Cytojournal 2009, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Das, N.; Dey, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Nasipuri, M.; Naskar, M.K. Cytology Image Analysis Techniques Toward Automation: Systematically Revisited. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyssoux, A.; Jarnouen, K.; Lallement, L.; Fezzani, R.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C. Automated Staining Analysis in Digital Cytopathology and Applications. Cytometry A 2022, 101, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khan, M. Advances in Biomedical Imaging Techniques: A Comprehensive Review. Significances Bioeng. Biosci. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Feldman, M.D.; Abels, E.; Ashfaq, R.; Beltaifa, S.; Cacciabeve, N.G.; Cathro, H.P.; Cheng, L.; Cooper, K.; Dickey, G.E.; et al. Whole Slide Imaging versus Microscopy for Primary Diagnosis in Surgical Pathology: A Multicenter Blinded Randomized Noninferiority Study of 1992 Cases (pivotal Study). Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.G.; Monaco, S.E.; Cuda, J.; Xing, J.; Ahmed, I.; Pantanowitz, L. Comparison of Glass Slides and Various Digital-Slide Modalities for Cytopathology Screening and Interpretation. Cancer 2017, 125, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; An, Y.; Li, C. Intelligent Segmentation and Recognition Method of Breast Cancer Based on Digital Image Processing Technology. Proc. Int. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. Conf. 2021, 2021, 2256316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, N.; Parwani, A.V.; Pantanowitz, L. Whole Slide Imaging in Pathology: Advantages, Limitations, and Emerging Perspectives. Pathol. Lab. Med. Int. 2015, 2015, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.J.; Salama, M.E.; Henricks, W.H.; Pantanowitz, L. Implementation of Whole Slide Imaging for Clinical Purposes: Issues to Consider from the Perspective of Early Adopters. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarella, M.D.; Bowman, D.; Aeffner, F.; Farahani, N.; Xthona, A.; Absar, S.F.; Parwani, A.; Bui, M.; Hartman, D.J. A Practical Guide to Whole Slide Imaging: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Thrall, M.J.; Michelow, P.; Schmitt, F.C.; Vielh, P.R.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Sundling, K.E.; Virk, R.; Alperstein, S.; Bui, M.M.; et al. The Current State of Digital Cytology and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Global Survey Results from the American Society of Cytopathology Digital Cytology Task Force. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2024, 13, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalkar, P.; Talmale, G. Review Paper on Histopathological Image Analysis Approach for Automatic Detection of Glandular Structures in Human Tissue. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Pervasive Computing (ICPC), Pune, India, 8–10 January 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Salpea, N.; Tzouveli, P.; Kollias, D. Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Modern Architectures. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 691–708. ISBN 9783031250811. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Han, L.; You, C.; Wang, B. Segment Anything in Medical Images. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment Anything. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.02643. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Yao, T.; Remedios, L.W.; Bao, S.; Landman, B.A.; Wheless, L.E.; Coburn, L.A.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Digital Pathology: Assess Zero-Shot Segmentation on Whole Slide Imaging. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04155. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, D.D.; Sonal, G. Medical Image Segmentation: A Review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 2013, 2, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, A.; Rahim, M.S.M.; Altameem, A.; Saba, T.; Rad, A.E.; Rehman, A.; Uddin, M. Medical Image Segmentation Methods, Algorithms, and Applications. IETE Tech. Rev. 2014, 31, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.K.D.; Kumar, G.; Swapna, K.; Datta, D.; Rajest, S. A Review of Medical Image Segmentation Algorithms. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 2018, 7, 169184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Rauland, A.; Jia, Y.; Avval, A.H.; Bozorgpour, A.; Karimijafarbigloo, S.; Cohen, J.P.; Adeli, E.; Merhof, D. Medical Image Segmentation Review: The Success of U-Net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenster, A.; Chiu, B. Evaluation of Segmentation Algorithms for Medical Imaging. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2005, 2005, 7186–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, T.; Szakács, M.; Dénes, L.; Jung, J.; Egyed-Zsigmond, I. Semiautomated Image Analysis of High Contrast Tissue Areas Using Hue/Saturation/ Brightness Based Color Filtering. Available online: https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A3%3A1312531/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A75120032&crl=c (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Pluim, J.P.W.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Heng, P.-A.; Guo, Y.B.; Wang, L.Y.; Matuszewski, B.J.; Bruni, E.; Sanchez, U.; et al. Gland Segmentation in Colon Histology Images: The Glas Challenge Contest. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatnik de Sousa, I.; Maria Bernardes Rebuzzi Vellasco, M.; Costa da Silva, E. Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations for Classification of Lymph Node Metastases. Sensors 2019, 19, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexhepaj, E.; Agnarsdóttir, M.; Bergman, J.; Edqvist, P.-H.; Bergqvist, M.; Uhlén, M.; Gallagher, W.M.; Lundberg, E.; Ponten, F. A Texture Based Pattern Recognition Approach to Distinguish Melanoma from Non-Melanoma Cells in Histopathological Tissue Microarray Sections. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazab, N.; Gab Allah, W.; Elmogy, M. Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Grading Brain Tumor Using Histopathology Images Based on Color and Texture Features. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurcan, M.N.; Boucheron, L.E.; Can, A.; Madabhushi, A.; Rajpoot, N.M.; Yener, B. Histopathological Image Analysis: A Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; You, F.; Li, H. Automatic Classification Method of Thyroid Pathological Images Using Multiple Magnification Factors. Neurocomputing 2021, 460, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, S.; Moffitt, R.A.; Chaudry, Q.; Young, A.N.; Wang, M.D. Computer Aided Histopathological Classification of Cancer Subtypes. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 7th International Symposium on BioInformatics and BioEngineering, Boston, MA, USA, 14–17 October 2007; pp. 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Kalaw, E.M.; Jie, W.; Al-Shabi, M.; Wong, C.F.; Giron, D.M.; Chong, K.-T.; Tan, M.; Zeng, Z.; Lee, H.K. Cribriform Pattern Detection in Prostate Histopathological Images Using Deep Learning Models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.04030. [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath, A.; Corredor, G.; Li, L.; Leo, P.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Elliott, R.; Purysko, A.; Shiradkar, R.; Madabhushi, A. An Integrated Radiology-Pathology Machine Learning Classifier for Outcome Prediction Following Radical Prostatectomy: Preliminary Findings. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Bandi, P.; Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Geessink, O.; Balkenhol, M.; Bult, P.; Halilovic, A.; Hermsen, M.; van de Loo, R.; Vogels, R.; et al. 1399 H&E-Stained Sentinel Lymph Node Sections of Breast Cancer Patients: The CAMELYON Dataset. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veta, M.; Heng, Y.J.; Stathonikos, N.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Beca, F.; Wollmann, T.; Rohr, K.; Shah, M.A.; Wang, D.; Rousson, M.; et al. Predicting Breast Tumor Proliferation from Whole-Slide Images: The TUPAC16 Challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 54, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Islam, S.M.S.; Akhtar, N.; Janjua, N.K. Going Deep in Medical Image Analysis: Concepts, Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 99540–99572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Marostica, E.; Yuan, W.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Tang, H.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; et al. A Pathology Foundation Model for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis Prediction. Nature 2024, 1–9, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowczyk, A.; Madabhushi, A. Deep Learning for Digital Pathology Image Analysis: A Comprehensive Tutorial with Selected Use Cases. J. Pathol. Inform. 2016, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madabhushi, A.; Lee, G. Image Analysis and Machine Learning in Digital Pathology: Challenges and Opportunities. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 33, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Chan, L.; Tse, G.; Tang, M.; Deng, J.; Norouzi, S.; Rowsell, C.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Damaskinos, S. Atlas of Digital Pathology: A Generalized Hierarchical Histological Tissue Type-Annotated Database for Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11739–11748. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Veta, M.; Johannes van Diest, P.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; the CAMELYON16 Consortium; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women with Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gadepalli, K.; Norouzi, M.; Dahl, G.E.; Kohlberger, T.; Boyko, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Timofeev, A.; Nelson, P.Q.; Corrado, G.S.; et al. Detecting Cancer Metastases on Gigapixel Pathology Images. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.02442. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Li, C.; Wu, X.; Yao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Qi, S. A Survey for Cervical Cytopathology Image Analysis Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 61687–61710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakovic, K.; Colling, R.; Browning, L.; Dolton, M.; Horton, M.R.; Protheroe, A.; Lamb, A.D.; Bryant, R.J.; Scheffer, R.; Crofts, J.; et al. The Use of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence in Histopathological Diagnostic Assessment of Prostate Cancer: A Survey of Prostate Cancer UK Supporters. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, N.; Marchesin, S.; Otálora, S.; Wodzinski, M.; Caputo, A.; van Rijthoven, M.; Aswolinskiy, W.; Bokhorst, J.-M.; Podareanu, D.; Petters, E.; et al. Unleashing the Potential of Digital Pathology Data by Training Computer-Aided Diagnosis Models without Human Annotations. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Alam, M.R.; Abdul-Ghafar, J.; Chong, Y. Recent Application of Artificial Intelligence in Non-Gynecological Cancer Cytopathology: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, N.; Braun, A.; Jutt, D.; Huffman, T.; Reder, N.; Liu, Z.; Yagi, Y.; Pantanowitz, L. Three-Dimensional Imaging and Scanning: Current and Future Applications for Pathology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2017, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelzer, V.H.; Gisler, A.; Hanhart, J.C.; Griss, J.; Wagner, S.N.; Willi, N.; Cathomas, G.; Sachs, M.; Kempf, W.; Thommen, D.S.; et al. Digital Image Analysis Improves Precision of PD-L1 Scoring in Cutaneous Melanoma. Histopathology 2018, 73, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenson, Y.; de Haan, K.; Wallace, W.D.; Ozcan, A. Emerging Advances to Transform Histopathology Using Virtual Staining. BME Front. 2020, 2020, 9647163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pillar, N.; Ozcan, A. Deep Learning-Enabled Virtual Histological Staining of Biological Samples. Light Sci. Appl. 2023, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latonen, L.; Koivukoski, S.; Khan, U.; Ruusuvuori, P. Virtual Staining for Histology by Deep Learning. Trends Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Hui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, W.; Tian, F.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J. Deep Learning for Virtual Histological Staining of Bright-Field Microscopic Images of Unlabeled Carotid Artery Tissue. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillar, N.; Ozcan, A. Virtual Tissue Staining in Pathology Using Machine Learning. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 22, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Park, E.; Misra, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Baik, J.W.; Kim, K.G.; Jung, C.K.; Kim, C. Deep Learning-Based Virtual Staining, Segmentation, and Classification in Label-Free Photoacoustic Histology of Human Specimens. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Roa, A.; Basavanhally, A.; González, F.; Gilmore, H.; Feldman, M.; Ganesan, S.; Shih, N.; Tomaszewski, J.; Madabhushi, A. Automatic Detection of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma in Whole Slide Images with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2014: Digital Pathology, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 20 March 2014; Volume 9041, p. 904103. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.; Zerbe, N.; Klempert, I.; Hellwich, O.; Hufnagl, P. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Gastric Carcinoma Using Whole Slide Images in Digital Histopathology. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 61, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceachi, B.; Cioplea, M.; Mustatea, P.; Gerald Dcruz, J.; Zurac, S.; Cauni, V.; Popp, C.; Mogodici, C.; Sticlaru, L.; Cioroianu, A.; et al. A New Method of Artificial-Intelligence-Based Automatic Identification of Lymphovascular Invasion in Urothelial Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, T.J.; Buhmann, J.M. Computational Pathology: Challenges and Promises for Tissue Analysis. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2011, 35, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G.; Ciompi, F. Deep Learning in Histopathology: The Path to the Clinic. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, D.Y. Artificial Intelligence and Computational Pathology. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.H.; Jaume, G.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Lu, M.Y.; Vaidya, A.; Miller, T.R.; Mahmood, F. Artificial Intelligence for Digital and Computational Pathology. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 930–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, B.; Tahir, M.; Hu, Y.; Kellough, D.; Lujan, G.; Sun, S.; Parwani, A.V.; Li, Z. Artificial Intelligence-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Lymph Node Metastasis on Histologic Slides in a Digital Workflow. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kohlberger, T.; Norouzi, M.; Dahl, G.E.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Olson, N.; Peng, L.H.; Hipp, J.D.; Stumpe, M.C. Artificial Intelligence-Based Breast Cancer Nodal Metastasis Detection: Insights into the Black Box for Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, D.F.; MacDonald, R.; Liu, Y.; Truszkowski, P.; Hipp, J.D.; Gammage, C.; Thng, F.; Peng, L.; Stumpe, M.C. Impact of Deep Learning Assistance on the Histopathologic Review of Lymph Nodes for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Fedorov, A.; Fennessy, F.; Kikinis, R.; Gao, Y. Large Scale Digital Prostate Pathology Image Analysis Combining Feature Extraction and Deep Neural Network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02678. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, L.; Osinski, B.L.; Ho, I.Y.; Tan, T.L.; Willis, C.; Weiss, H.; Beaubier, N.; Mahon, B.M.; Taxter, T.J.; Yip, S.S.F. Multi-Field-of-View Deep Learning Model Predicts Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Status from Whole-Slide Hematoxylin and Eosin Images. J. Pathol. Inform. 2019, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabyarmohammadi, S.; Leo, P.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Janowczyk, A.; Corredor, G.; Fu, P.; Meyerson, H.; Metheny, L.; Madabhushi, A. Machine Learning to Predict Risk of Relapse Using Cytologic Image Markers in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Posthematopoietic Cell Transplantation. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2022, 6, e2100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, J.K.; Ilyas, A.M.; Walke, V.; Gupta, V.; Kapoor, N. The Role of Cytomorphometric Image Analysis in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules. Cureus 2023, 15, e37872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Ali, S.Z. Brief Overview of the Updated Third Edition of the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Diagn. Histopathol. 2023, 29, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.-R.; Jan, I.-S.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chuang, W.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-L.; Chang, T.-C.; Chen, A. Computerized Cytological Features for Papillary Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis-Preliminary Report. Cancers 2019, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, V.; Pizzimenti, C.; Franchina, M.; Micali, M.G.; Russotto, F.; Pepe, L.; Militi, G.B.; Tralongo, P.; Pierconti, F.; Ieni, A.; et al. The Minefield of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: Could Artificial Intelligence Be a Suitable Diagnostic Tool? Diagn. Histopathol. 2023, 29, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, P. Meta-Analysis on the Utility of Morphometry in the Cytological Differential Diagnosis of Thyroid Neoplasms. MGM J. Med. Sci. 2024, 11, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koss, L.G.; Lin, E.; Schreiber, K.; Elgert, P.; Mango, L. Evaluation of the PAPNET Cytologic Screening System for Quality Control of Cervical Smears. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 101, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Sundling, K.E.; Virk, R.; Thrall, M.J.; Alperstein, S.; Bui, M.M.; Chen-Yost, H.; Donnelly, A.D.; Lin, O.; Liu, X.; et al. Digital Cytology Part 2: Artificial Intelligence in Cytology: A Concept Paper with Review and Recommendations from the American Society of Cytopathology Digital Cytology Task Force. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2024, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudray, N.; Ocampo, P.S.; Sakellaropoulos, T.; Narula, N.; Snuderl, M.; Fenyö, D.; Moreira, A.L.; Razavian, N.; Tsirigos, A. Classification and Mutation Prediction from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology Images Using Deep Learning. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saillard, C.; Schmauch, B.; Laifa, O.; Moarii, M.; Toldo, S.; Zaslavskiy, M.; Pronier, E.; Laurent, A.; Amaddeo, G.; Regnault, H.; et al. Predicting Survival after Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resection Using Deep Learning on Histological Slides. Hepatology 2020, 72, 2000–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulczyn, E.; Steiner, D.F.; Xu, Z.; Sadhwani, A.; Wang, H.; Flament-Auvigne, I.; Mermel, C.H.; Chen, P.-H.C.; Liu, Y.; Stumpe, M.C. Deep Learning-Based Survival Prediction for Multiple Cancer Types Using Histopathology Images. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, F.; Schmitt, M.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Kather, J.N.; Nientiedt, M.; Kriegmair, M.C.; Worst, T.S.; Neuberger, M.; Steeg, M.; Popovic, Z.V.; et al. Deep Learning Can Predict Survival Directly from Histology in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.R.; Dariush, A.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.; Abraham, J.E.; Iddawela, M.; Vallier, A.-L.; Hiller, L.; Dunn, J.A.; Bowden, S.J.; et al. Computational Pathology of Pre-Treatment Biopsies Identifies Lymphocyte Density as a Predictor of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannet, P.; Coudray, N.; Donnelly, D.M.; Jour, G.; Illa-Bochaca, I.; Xia, Y.; Johnson, D.B.; Wheless, L.; Patrinely, J.R.; Nomikou, S.; et al. Using Machine Learning Algorithms to Predict Immunotherapy Response in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laury, A.R.; Blom, S.; Ropponen, T.; Virtanen, A.; Carpén, O.M. Artificial Intelligence-Based Image Analysis Can Predict Outcome in High-Grade Serous Carcinoma via Histology Alone. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.-T.; Dinstag, G.; Shulman, E.D.; Hermida, L.C.; Ben-Zvi, D.S.; Elis, E.; Caley, K.; Sammut, S.-J.; Sinha, S.; Sinha, N.; et al. A Deep-Learning Framework to Predict Cancer Treatment Response from Histopathology Images through Imputed Transcriptomics. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 1305–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, C.; Gullapalli, R.R. Ethics of AI in Pathology: Current Paradigms and Emerging Issues. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlematter, U.J.; Daniore, P.; Vokinger, K.N. Approval of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning-Based Medical Devices in the USA and Europe (2015-20): A Comparative Analysis. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e195–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Jain, A.; Araveeti, S.R.; Adhikari, S.; Garg, H.; Bhandari, M. FDA-Approved Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)-Enabled Medical Devices: An Updated Landscape. Electronics 2024, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, M.A. Health Privacy in the Electronic Age. J. Leg. Med. 2007, 28, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Rushefsky, M.E. Health Care Policy in an Age of New Technologies; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2015; ISBN 9781317468868. [Google Scholar]
- Sundholm, B. Strict Liability for Genetic Privacy Violations in the Age of Big Data. Univ. Memphis Law Rev. 2018. Available online: https://www.memphis.edu/law/documents/03_sundholm_no_banner.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Brazell, N.E. The Significance and Applications of Informed Consent. AORN J. 1997, 65, 377–380, 382, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, L.A.; Durant, J.; Brantley, P.R. A Modern History of Informed Consent and the Role of Key Information. Ochsner J. 2021, 21, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrazabal, A.J.; Nieto, N.; Peterson, V.; Milone, D.H.; Ferrante, E. Gender Imbalance in Medical Imaging Datasets Produces Biased Classifiers for Computer-Aided Diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12592–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Majumder, S.; Menzies, T. Bias in Machine Learning Software: Why? How? What to Do? In Proceedings of the 29th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, Athens, Greece, 23–28 August 2021; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Risser, L.; Picard, A.; Hervier, L.; Loubes, J.-M. A Survey of Identification and Mitigation of Machine Learning Algorithmic Biases in Image Analysis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.04491. [Google Scholar]
- Wesarg, S.; Antón, E.P.; Baxter, J.S.H.; Erdt, M.; Drechsler, K.; Laura, C.O.; Freiman, M.; Chen, Y.; Rekik, I.; Eagleson, R.; et al. Clinical Image-Based Procedures, Fairness of AI in Medical Imaging, and Ethical and Philosophical Issues in Medical Imaging: 12th International Workshop, CLIP 2023 1st International Workshop, FAIMI 2023 and 2nd International Workshop, EPIMI 2023 Vancouver, BC, Canada, October 8 and October 12, 2023 Proceedings; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2023; ISBN 9783031452499. [Google Scholar]
- Char, D.S.; Shah, N.H.; Magnus, D. Implementing Machine Learning in Health Care—Addressing Ethical Challenges. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, G.; Hanna, M.G.; Geneslaw, L.; Miraflor, A.; Werneck Krauss Silva, V.; Busam, K.J.; Brogi, E.; Reuter, V.E.; Klimstra, D.S.; Fuchs, T.J. Clinical-Grade Computational Pathology Using Weakly Supervised Deep Learning on Whole Slide Images. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panch, T.; Mattie, H.; Atun, R. Artificial Intelligence and Algorithmic Bias: Implications for Health Systems. J. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 010318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Rajpoot, N.; Treanor, D.; Magee, D. A Nonlinear Mapping Approach to Stain Normalization in Digital Histopathology Images Using Image-Specific Color Deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bel, T.; Hermsen, M.; Kers, J.; van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G. Stain-Transforming Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks for Improved Segmentation of Renal Histopathology. 2018. Available online: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=BkxJkgSlx4 (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Roy, S.; Kumar Jain, A.; Lal, S.; Kini, J. A Study about Color Normalization Methods for Histopathology Images. Micron 2018, 114, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.Z.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Nyberg, P.; Seppänen, T. Stain Normalization Methods for Histopathology Image Analysis: A Comprehensive Review and Experimental Comparison. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, A.J. Artificial Intelligence and Black-Box Medical Decisions: Accuracy versus Explainability. Hastings Cent. Rep. 2019, 49, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artificial Intelligence Workplan to Guide Use of AI in Medicines Regulation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/artificial-intelligence-workplan-guide-use-ai-medicines-regulation (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Center for Devices. Radiological Health Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/software-medical-device-samd/artificial-intelligence-and-machine-learning-software-medical-device (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Fraggetta, F.; L’Imperio, V.; Ameisen, D.; Carvalho, R.; Leh, S.; Kiehl, T.-R.; Serbanescu, M.; Racoceanu, D.; Della Mea, V.; Polonia, A.; et al. Best Practice Recommendations for the Implementation of a Digital Pathology Workflow in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory by the European Society of Digital and Integrative Pathology (ESDIP). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Sundling, K.E.; Virk, R.; Thrall, M.J.; Alperstein, S.; Bui, M.M.; Chen-Yost, H.; Donnelly, A.D.; Lin, O.; Liu, X.; et al. Digital Cytology Part 1: Digital Cytology Implementation for Practice: A Concept Paper with Review and Recommendations from the American Society of Cytopathology Digital Cytology Task Force. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2024, 13, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, J.; Hodson, H. Google DeepMind and Healthcare in an Age of Algorithms. Health Technol. 2017, 7, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Househ, M.; Kushniruk, A.W.; Borycki, E.M. Big Data, Big Challenges: A Healthcare Perspective: Background, Issues, Solutions and Research Directions; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 9783030061098. [Google Scholar]
- Topol, E.J. High-Performance Medicine: The Convergence of Human and Artificial Intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbastathis, G.; Ozcan, A.; Situ, G. On the Use of Deep Learning for Computational Imaging. Optica 2019, 6, 921–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-B.; Xie, B.-K.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Zhang, M.-X.; Xu, J.-C.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.-H. Deep Learning Enables Parallel Camera with Enhanced- Resolution and Computational Zoom Imaging. PhotoniX 2023, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Moukheiber, L.; Celi, L.A.; Patel, M.; Mahmood, F.; Gondim, D.; Hogarth, M.; Levenson, R. AI in Pathology: What Could Possibly Go Wrong? Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 40, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, R.; Monreale, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Turini, F.; Giannotti, F.; Pedreschi, D. A Survey of Methods for Explaining Black Box Models. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarakulasinghe, N.B.; Blomberg, T.; Liu, J.; Leao, A.S.; Papapetrou, P. Evaluating Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations on Clinical Machine Learning Classification Models. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MI, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Barredo Arrieta, A.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; Garcia, S.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, Taxonomies, Opportunities and Challenges toward Responsible AI. Inf. Fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjoa, E.; Guan, C. A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Toward Medical XAI. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 2021, 32, 4793–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abuhmed, T.; El-Sappagh, S.; Muhammad, K.; Alonso-Moral, J.M.; Confalonieri, R.; Guidotti, R.; Del Ser, J.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Herrera, F. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): What We Know and What Is Left to Attain Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, L.; Brcic, M.; Cabitza, F.; Choi, J.; Confalonieri, R.; Ser, J.D.; Guidotti, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Herrera, F.; Holzinger, A.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) 2.0: A Manifesto of Open Challenges and Interdisciplinary Research Directions. Inf. Fusion 2024, 106, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M.S.; Pantanowitz, L. Artificial Intelligence in Cytopathology: A Review of the Literature and Overview of Commercial Landscape. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2019, 8, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Bi, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhou, D.; You, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Cytology for Detection of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or Invasive Cancer: A Multicenter, Clinical-Based, Observational Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrafiah, A.R. Application and Performance of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Cytopathology. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlpine, E.D.; Michelow, P. The Cytopathologist’s Role in Developing and Evaluating Artificial Intelligence in Cytopathology Practice. Cytopathology 2020, 31, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guan, S.; Ou, Z.; Li, W.; Yan, L.; Situ, B. Advances in AI-based Cancer Cytopathology. Interdiscip. Med. 2023, 1, e20230013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Robicquet, A.; Ramsundar, B.; Kuleshov, V.; DePristo, M.; Chou, K.; Cui, C.; Corrado, G.; Thrun, S.; Dean, J. A Guide to Deep Learning in Healthcare. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, S.W. Far-Field Optical Nanoscopy. Science 2007, 316, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaña-Loaiza, O.S.; Boyd, R.W. Quantum Imaging and Information. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2019, 82, 124401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilaberte Basset, M.; Setzpfandt, F.; Steinlechner, F.; Beckert, E.; Pertsch, T.; Gräfe, M. Perspectives for Applications of Quantum Imaging. Laser Photon. Rev. 2019, 13, 1900097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermelleh, L.; Ferrand, A.; Huser, T.; Eggeling, C.; Sauer, M.; Biehlmaier, O.; Drummen, G.P.C. Super-Resolution Microscopy Demystified. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemet, G.; Carisey, A.F.; Hamidi, H.; Henriques, R.; Leterrier, C. The Cell Biologist’s Guide to Super-Resolution Microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, 240713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujan, G.; Quigley, J.C.; Hartman, D.; Parwani, A.; Roehmholdt, B.; Van Meter, B.; Ardon, O.; Hanna, M.G.; Kelly, D.; Sowards, C.; et al. Dissecting the Business Case for Adoption and Implementation of Digital Pathology: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. Inform. 2021, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.G.; Ardon, O.; Reuter, V.E.; Sirintrapun, S.J.; England, C.; Klimstra, D.S.; Hameed, M.R. Integrating Digital Pathology into Clinical Practice. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mezei, T.; Kolcsár, M.; Joó, A.; Gurzu, S. Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100252
Mezei T, Kolcsár M, Joó A, Gurzu S. Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(10):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100252
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezei, Tibor, Melinda Kolcsár, András Joó, and Simona Gurzu. 2024. "Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 10: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100252
APA StyleMezei, T., Kolcsár, M., Joó, A., & Gurzu, S. (2024). Image Analysis in Histopathology and Cytopathology: From Early Days to Current Perspectives. Journal of Imaging, 10(10), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10100252






