Abstract
Polymer-bonded magnets are increasingly being used in terms of applications in drive technology and, more specifically, in new concepts based on reluctance motors. The increasing demand for polymer-bonded magnets, especially in the context of electromobility, is leading to a shortage of materials, mainly in terms of the finite resource neodymium–iron–boron (NdFeB). So far, the recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets is pyrolysis, which leads to either a massive reduction of the magnetic properties or a high energy requirement. Therefore, the paper investigates an alternative recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets based on the reusage of shreds. Several influencing factors such as the form of the carrier material and the temperature level were varied in order to find a suitable recycling method. It was found that the magnetic properties were reduced by at least 15% compared to the pure material. The required energy and the CO2 emission were reduced by 90% compared to the pyrolysis. Thus, the strategy of recycling polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets by the reusage of shreds leads to improved conditions compared to pyrolysis and is, therefore, a suitable alternative.
1. Introduction
1.1. Polymer-Bonded Magnets: Material, Processing and Application
The material development in terms of permanent magnets began in the 20th century. Within a few years, different groups of materials were found, such as aluminum–nickel alloys (AlNi) in 1933 and hard ferrites in 1950 [1]. In 1970, polymer-bonded magnets expanded the application possibilities of permanent magnets due to new fabrication methods [2]. These new manufacturing methods were based on the material setting, after which polymer-bonded magnets are made out of a matrix material (polymer) and a hard magnetic filler [3]. This enabled the injection molding of bonded magnets, leading to a higher degree of freedom and the possibility of functional integration [2]. However, the matrix material strongly defines the processing method that can be applied. With that, thermoplastic-based polymer-bonded magnets are mainly fabricated by the injection molding process with a maximum filler grade of 65 vol.-% [4]. Thermoset-based polymer-bonded magnets are mainly processed by pressing with filler grades of up to 85 vol.-% [2]. First attempts were made to fabricate thermoset-based polymer-bonded magnets by injection molding to combine the advantages of the processing method with the material ones in terms of the low viscosity and the high filler orientation as well as the high temperature and chemical resistance [5,6].
In terms of the hard magnetic fillers, two main groups can be distinguished for polymer-bonded magnets: the hard ferrites and the raw earth materials. These fillers highly define the magnetic properties of the sample but differ in terms of the geometry, particle size and initial magnetic properties [7]. The hard ferrites like strontium ferrite (SrFeO) depict a particle size of 1 to 10 µm with a hexagonal geometry, whereas neodymium–iron–boron (NdFeB) has a size of 100 to 400 µm and a plate-like structure [8]. In terms of the magnetic properties, NdFeB reveals a remanence BR, which is about three times higher, and resistance against demagnetization, which is about two to three times higher, compared to SrFeO. Hard magnetic fillers can be used in an isotropic or anisotropic form. In terms of anisotropic fillers, the remanence BR reaches up to 85% of the saturation flux density BS, whereas isotropic fillers attain only 50% [3]. To use the material potential of anisotropic fillers, the fillers have to be orientated during the fabrication process along the preferred direction, which requires a certain movability of the fillers. Besides the physical orientation of the fillers, the magnetic moments within the dipoles (smallest magnetic unit) have to be magnetized as well. This can take place after the fabrication process, for example, by using an impulse magnetizer [9]. In terms of the properties, the magnetic flux density as a key characteristic value has to be distinguished in terms of an orientated sample (permanence Bperm) and a fully magnetized sample (remanence BR) [3].
The application of polymer-bonded magnets can be divided into the following two main groups: the sensor and the actuator implementation. In the automotive sector, thermoplastic-based polymer-bonded magnets reach a few million magnets per year [10,11]. In 2007, hard ferrites were applied in 95% of polymer-bonded magnets, mainly because of the low price [12]. With respect to the creation of value, NdFeB depicts a market share of 62% relative to 34% for hard ferrites [13]. The focus of recent research activities is the implementation of polymer-bonded magnets in drive motors within electromobility by the integration into electro-metal stacks. New concepts rely on the principles of reluctance and the change of the magnetic resistance [14]. Until 2030, an undersupply of about 48,000 tons of NdFeB in the application field of electromobility is expected, which corresponds to 25 million electro-vehicles [15]. Therefore, new concepts are required either to reduce the usage of NdFeB or to implement recycling strategies to overcome the massive gap between the resources available and those claimed. The new concept in terms of reluctance reveals the possibility of replacing rare earths within pump motors with ferrites [16]. However, at the moment, motors with greater performance can not be substituted by hard ferrites. Therefore, the gap can only be filled by new recycling strategies.
1.2. Urgent Requirements for New Recycling Methods in Terms of Polymer-Bonded Magnets
In terms of polymer-bonded magnets, the focus of the recycling strategy is mainly based on hard magnetic fillers and is more precise on rare earths. This goes along with the economic aspects, as hard ferrites are not a limited resource and reveal a comparable low price. With that, recycling strategies would increase the price too much in terms of hard ferrites.
NdFeB is the third leading rare earth material with the highest magnetic properties in terms of the remanence BR so far [17]. In total, 90% of the worldwide production of NdFeB is implemented in permanent magnets, and, in 2018, 89% of NdFeB was utilized in drive technologies like electric motors in the industry or wind energy. However, within the drive technology, only 6% of NdFeB is used in terms of polymer-bonded magnets [18]. The recent demand in terms of electromobility can only be reached by implementing bonded magnets, due to the required multipolar and complex magnetic field structures. With that, the recycling strategy in terms of permanent magnets should focus on bonded magnets and the reusage of fillers, especially NdFeB.
In 2020, the demand for NdFeB magnets reached 120,000 t and was doubled within 6 years. In 2014, Germany used about 1000 t in drive applications; only 4% of this stock could be used for recycling strategies within the same year. It is assumed that, by 2030, about 10% could be utilized. These long return times are caused by the durability of samples in drive application, which last up to 10 to 15 years. Additionally, a large amount of possible returns is sold in foreign countries [13]. Nevertheless, the two driving forces of the increasing demand for rare earth magnets and the increasing awareness of resource-saving consumption lead to the establishment of a recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets. The returns will increase alongside this.
1.3. Possibilities of the Recycling for Polymer-Bonded Magnets
To satisfy the rising demand for rare earth materials in magnets, three main routes are possible. First, the material input can be reduced by efficiency enhancements, for example, by implementing the injection molding process in the fabrication of permanent magnets and using geometry freedom [16,18]. Second, rare earth materials can be substituted by other chemical elements, different materials or by new technologies [3]. Third, polymer-bonded magnets can be recycled, with the primary goal of regaining the hard magnetic fillers.
Table 1 summarizes the main recycling strategies that are currently used in terms of thermosets and thermoplastics. It has to be taken into account that these strategies are applied to unfilled polymers or filled polymers without the target of reusing the fillers. For thermoplastics, the typical recycling strategy is the reusage of shreds. It has to be taken into account that the fusing of shreds several times reduces the length of the polymer chains and causes aging effects in the polymer [19]. In terms of thermosets, the main recycling strategy is energy recovery so far. However, new attempts were made to find different methods in terms of thermosets, by which the three-dimensional chemical cured network in thermosets is broken to reuse the components.

Table 1.
Overview of main recycling strategies in terms of thermoplastic or thermoset as polymer.
In terms of polymer-bonded magnets and the aspect of regaining the hard magnetic filler primarily, pyrolysis would be the most suitable recycling method. However, the first attempts in terms of thermoset-based polymer-bonded magnets were made to regain the filler by pyrolysis. It was shown that pure pyrolysis under an oxygen atmosphere leads to oxidation of the hard magnetic fillers and, with that, a reduction of the magnetic properties of up to 90%. This reduction can be lowered by the process conditions of the pyrolysis as a cover, and, with that, less oxygen flow can be implemented or a nitrogen atmosphere can be used. As a result, the reduction of the magnetic properties lies between 20 and 30%. However, the implementation of both methods is quite expensive and therefore is not suitable in terms of a realistic circular economy. In addition, different processes in terms of a chemical recycling strategy were invested in thermoset-based polymer-bonded magnets. The main idea of these methods is the generation of the possibility to separate the resin and the hardener after the curing process, in order to redo this step similar to the reheating in terms of thermoplastics. However, this idea can only be realized in terms of special thermosets, which are built with unique resin and hardeners. As a result, this method has not been widely used, as the material options are very limited and quite expensive.
For thermoplastic-based polymer-bonded magnets, the reusage of shreds is another possible recycling strategy. Although the fillers themselves are not extracted, the matrix material allows a second fusing and, with that, another orientation of the fillers. The magnetic properties are reduced by 20% and the recycling strategy leads to different flow conditions, which has an influence on the pole accuracy. It was assumed that the reduction of the magnetic properties is mainly caused by the change in the flow conditions and, with that, by the aging in the matrix material [20].
In terms of permanent magnets, recycling strategies have so far been focused on sintered samples. For example, ref. [21] proved the chemical route based on a metallurgical treatment to be the best one in terms of recycling sintered permanent magnets in electro-motors. Ref. [22] invested in different ways, like the hydrogen decrepitation process, to recycle sintered magnets based on NdFeB. Through this method, the remanence was reduced by 10% [22]. The importance of an expensive powder treatment after the recycling step was shown in [23] in terms of sintered NdFeB magnets. Further, ref. [24] showed a theoretical way of successfully regaining fillers out of the matrix in terms of polymer-bonded magnets without proving this method or adopting it to an application. With that, a concrete solution for a recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets especially based on thermosets is not available yet. Pyrolysis, which so far has been the main recycling strategy in terms of polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets, reveals either very low remaining magnetic properties or a high effort in terms of the process and, with that, high costs. On the other hand, the recycling strategy for thermoplastic-based polymer-bonded magnets based on the reusage of shreds shows a promising solution, even if the aging of the matrix material would be further reduced.
The aim of this paper was to investigate a mechanical recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets to overcome the lack and disadvantages of the methods for thermosets. A new strategy of reusing shreds based on thermosets was found, taking the challenge into account that a thermoset can not be fuzzed again. Further, the influence of different carrier materials, the amount of recycled material, the temperature level and the filler orientation have been investigated. In addition, the required energy has been compared relative to the pyrolysis to evaluate the different mechanical strategies for recycling polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets, not only relative to the magnetic properties but also in terms of the economic efficiency.
2. Results
2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Following DIN EN ISO 11357 [25]
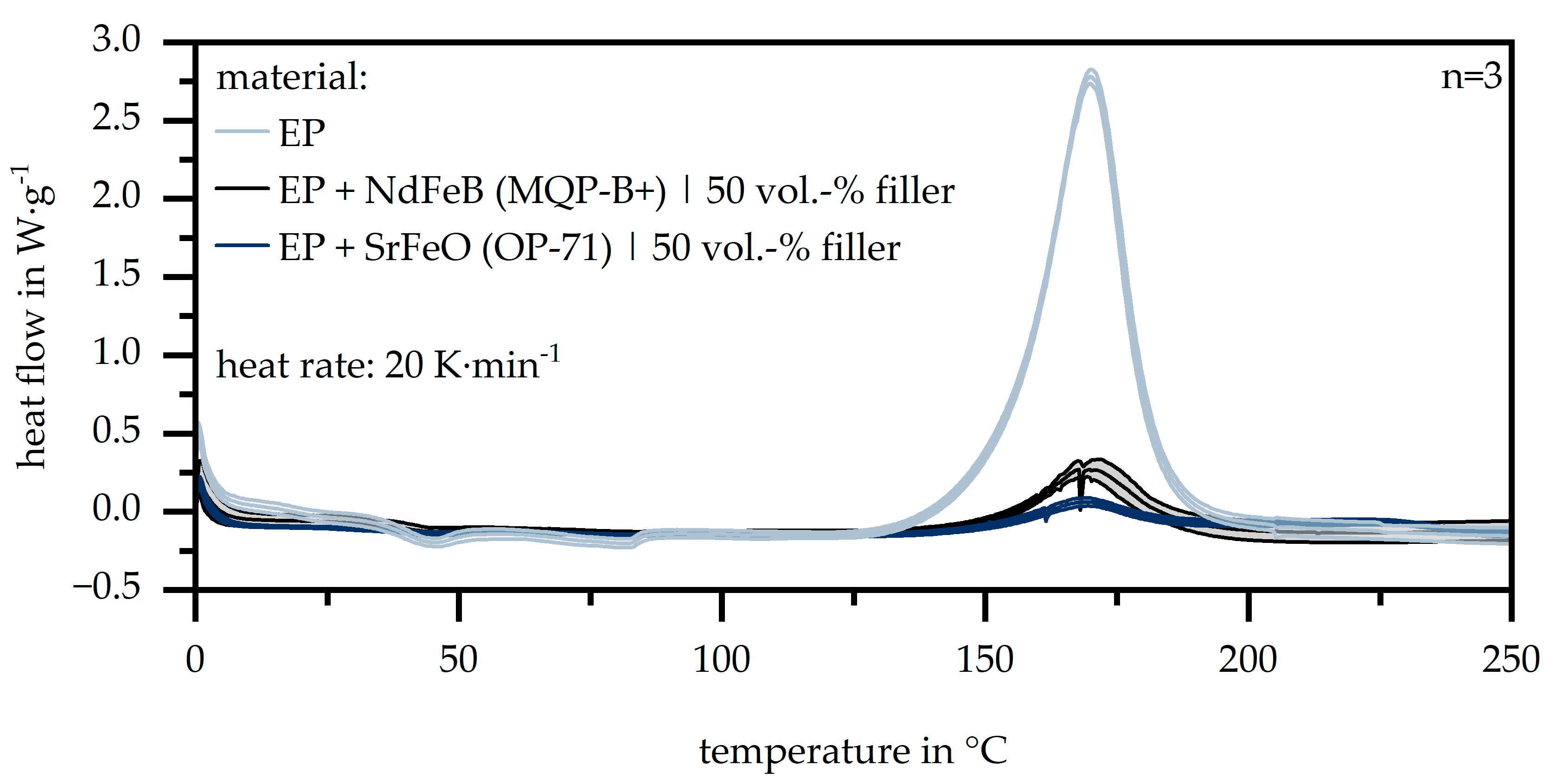
To evaluate the chosen temperature levels within the sample preparation, as well as to define the enthalpy behavior of the different carrier materials with respect to the temperature, Figure 1 shows the route of the DSC measurements. Especially in terms of the required enthalpy, the filled materials differ highly compared to the pure epoxy resin, as the values for the filled materials are six times lower. After the amount of the matrix materials is highly reduced in terms of the filled materials, less enthalpy is required to cure the sample. Further, the higher thermal conductivity within iron-based fillers increases heat integration, which reduces the demand for energy in terms of the curing process as well. The peak temperatures show a similar level for each carrier material.
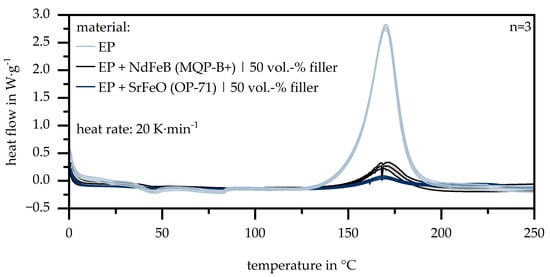
Figure 1.
Route of the DSC measurement for the carrier material (EP: epoxy resin | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron | SrFeO: strontium ferrite).
With respect to the chosen temperature levels for the fabrication of the samples, the reference setting of 200 °C fits with the offset temperature of the DSC measurements. The lower (180 °C) and higher (220 °C) temperatures relative to the reference reveal the influence of the possible amount of curing within the matrix material. A lower temperature level reduces the velocity of the curing process and gives the particles more time to orientate.
2.2. Magnetic Properties
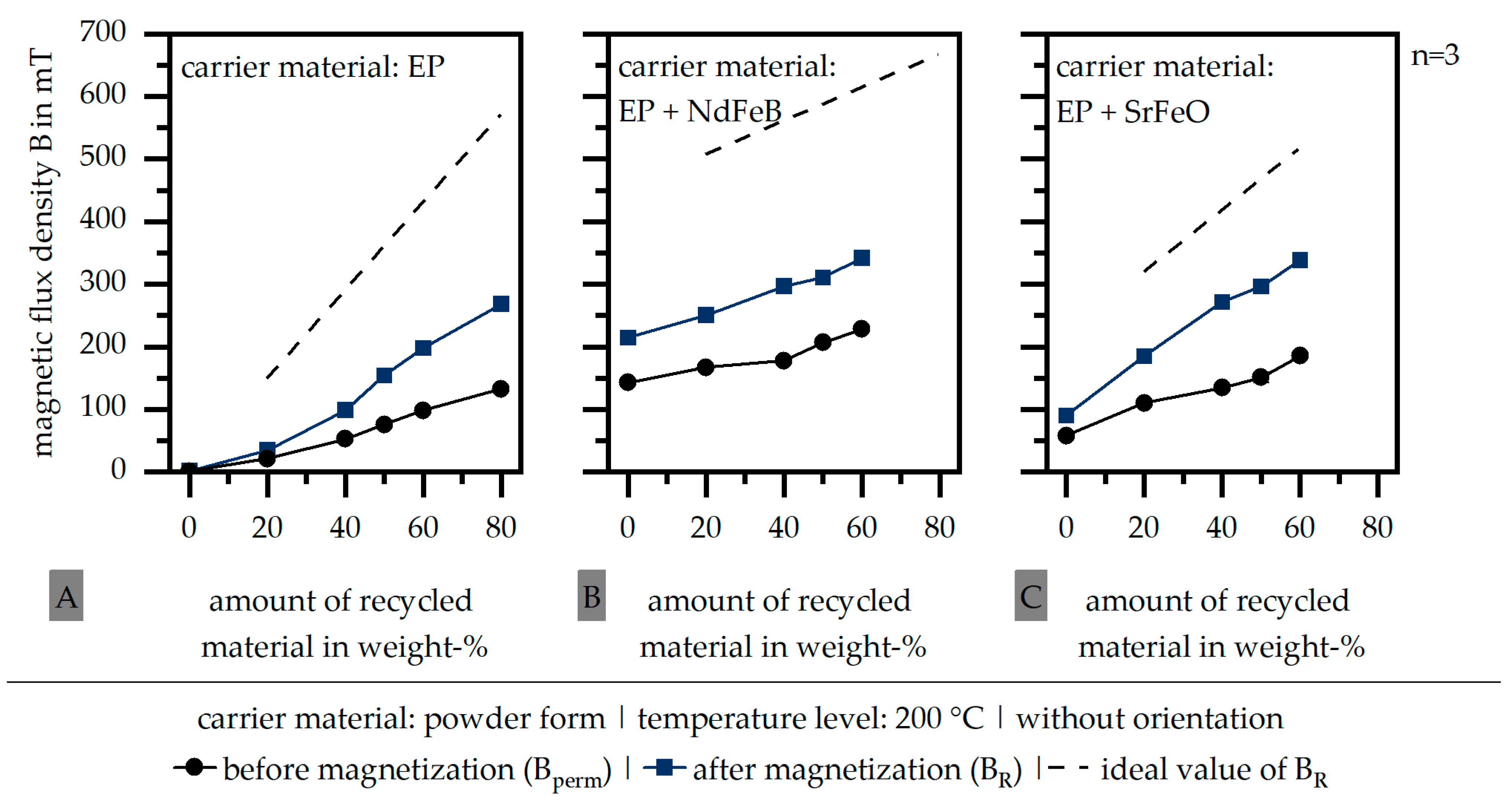
Figure 2 shows the influence of the magnetization step after the fabrication in terms of the three different carrier materials of EP (A), EP + NdFeB (B) and EP + SrFeO (C) for a constant temperature level of 200 °C. After the magnetization step is differentiated in Figure 2, the magnetic flux density has to be distinguished between parameter Bperm (before magnetization) and BR (after magnetization). Further, a line represents the ideal value of the remanence BR. This ideal value goes along with the theoretical magnetic properties of the pure filler and the amount of filler in the recycled material as well as the carrier material. It has to be taken into account that the standard deviation is so low that it is not visible in terms of the scale chosen. The magnetic flux density increases through the magnetization step. In terms of the carrier material EP + SrFeO, the highest increase can be seen. However, independent of the chosen carrier material, the magnetic properties are significantly lower compared to the ideal values. This mainly follows along with the missing orientation of the fillers within the process.
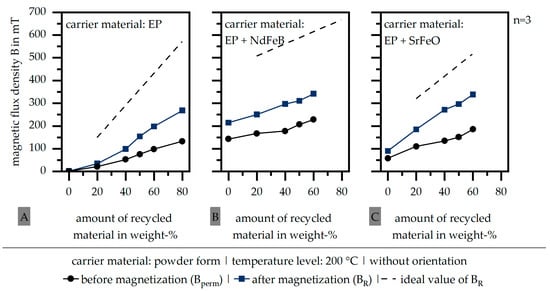
Figure 2.
Influence of the carrier material on the magnetic flux density B (before and after magnetization | without orientation of the fillers in the process) (EP: epoxy resin (A) | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron (B) | SrFeO: strontium ferrite (C)).
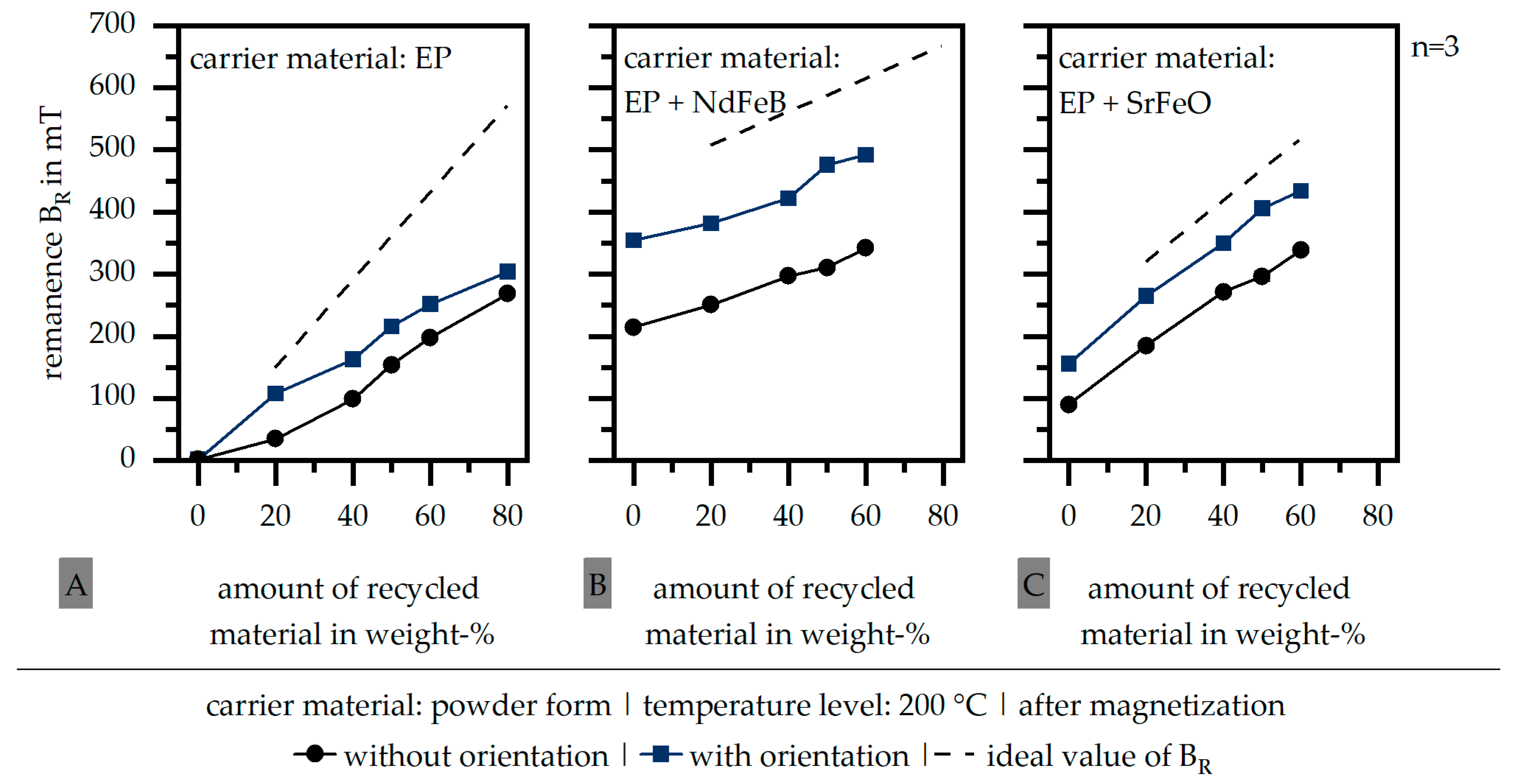
Relative to the findings of Figure 2 in terms of the required orientation, Figure 3 depicts the influence of this orientation step during the fabrication of the samples in terms of the magnetic properties after magnetization. Again, the line representing the ideal values of the remanence BR is shown. Further, the standard deviation is very low. Particularly in terms of the carrier material based on the filled materials (EP + NdFeB | EP + SrFeO), a significant increase in the remanence BR can be realized by adding the orientation step. In terms of the carrier material EP + SrFeO, the remanence BR reaches about 85% of the ideal values, whereas EP + NdFeB reaches only 75% and EP only 55%. It can be assumed that the smaller particles of SrFeO are more likely to be orientated within the recycled material compared to the larger particle size of NdFeB in the carrier material. This follows the theory that the combination of small and large particles increases the magnetic properties further after the smaller particles are able to close gaps between the larger particles [26]. After the grinding process, the fillers might not be fully extracted from the matrix material of the recycled material. Therefore, a smaller particle in the carrier material improves the magnetic properties overall, as this particle has the opportunity to fill the gaps between the larger fillers. The same behavior can be reached by the pure EP; however, an increase in the magnetic properties is not likely, as the carrier material itself has no magnetic properties.
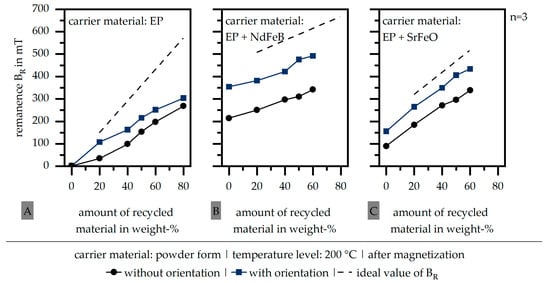
Figure 3.
Influence of the orientation in the process on the remanence BR (after magnetization) (EP: epoxy resin (A) | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron (B) | SrFeO: strontium ferrite (C)).
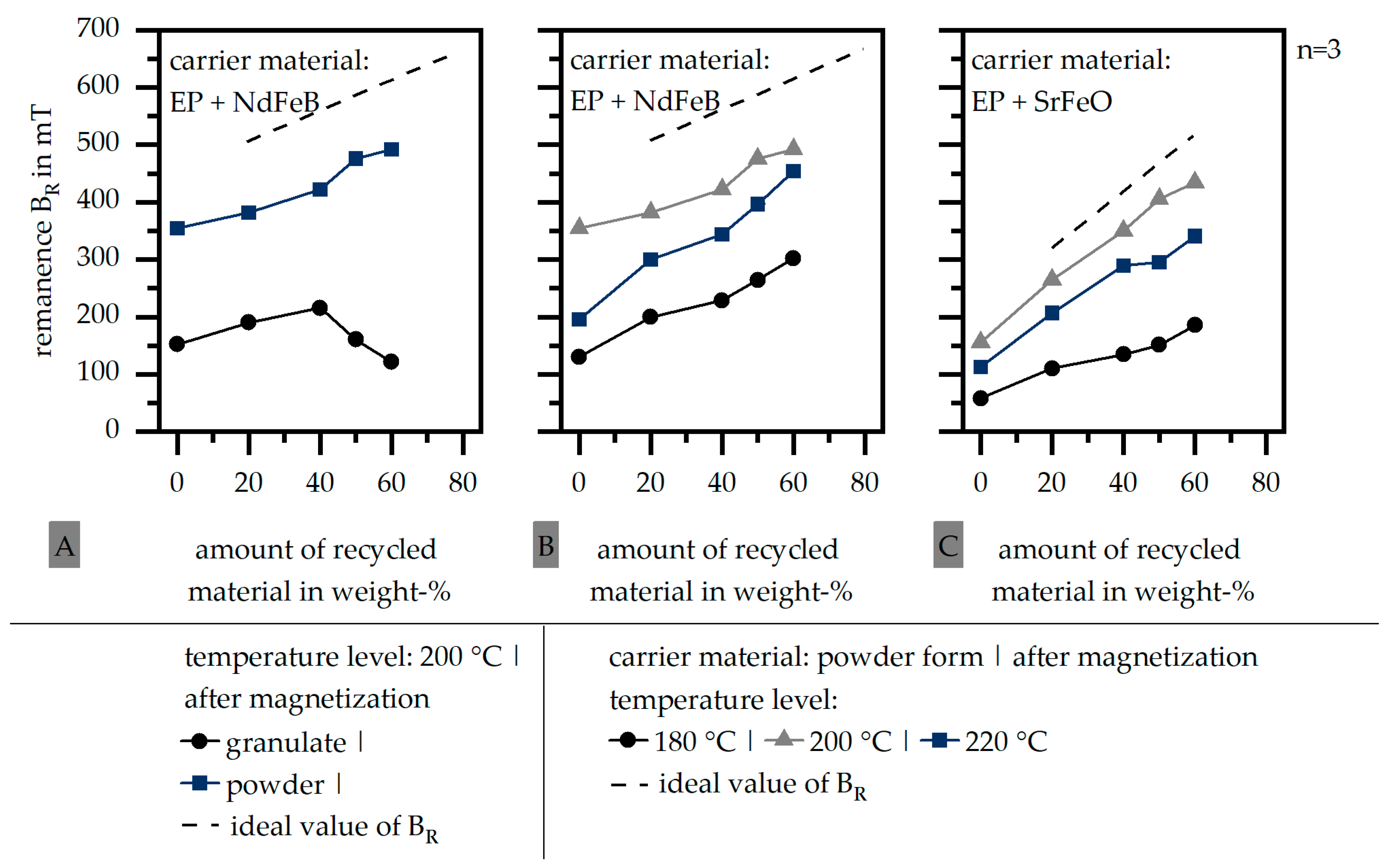
To evaluate the possibilities to further increase the magnetic properties within the samples, Figure 4 shows the impact of the form of the carrier material in terms of a granulate and a powder for the carrier material EP + NdFeB (A). Additionally, it depicts the influence of the temperature level, which is used to fabricate the samples, for the carrier material EP + NdFeB (B) and EP + SrFeO (C). Again, the ideal values of the remanence BR are portrayed in terms of a line and the standard deviation is low.
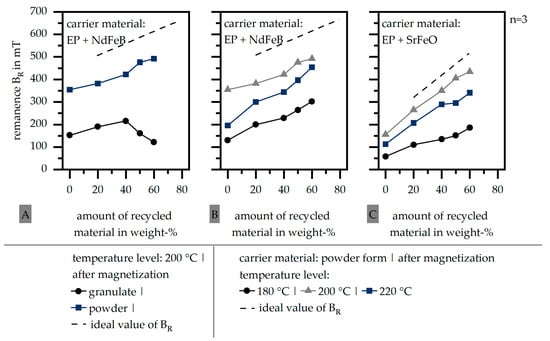
Figure 4.
Influence of the form of the carrier material (A) and the temperature level (B,C) on the remanence BR (after magnetization | with orientation) (EP: epoxy resin | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron | SrFeO: strontium ferrite).
The behavior of the magnetic properties in terms of the different forms of the carrier material is similar for granulate and powder forms within the amount of up to 40 weight-% of the recycled material. A further increase in the recycled material in terms of the granulate decreases the magnetic properties significantly. It is assumed that a large amount of recycled material in granulate forms hinders the carrier material in between the recycled material to be orientated. After the fillers in the recycled material are trapped by the surrounding matrix material, it is assumed that only the carrier material can be orientated, and, with that, contributes a large amount of the resulting magnetic properties in the sample. With that, the additional step of the grinding should be executed in terms of the recycling strategy of polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets in order to use most of the material’s potential not only within the carrier material but also in the recycled material.
Further, the impact of the temperature level during the curing process of the samples was investigated. For both carrier materials based on a compound (EP + NdFeB (B) and EP + SrFeO (C)), the reduced temperature level of 180 °C (relative to the reference level of 200 °C) leads to lower magnetic properties. This effect is more significant in terms of SrFeO as a hard magnetic filler within the carrier material. It can be assumed that the lower temperature reduces the movability of the fillers after the lowest viscosity level can not be reached. With that, a certain level of temperature is needed in order to ensure the full orientation of the hard magnetic fillers. In terms of the higher temperature level (220 °C), the magnetic properties decrease in terms of EP + NdFeB and EP + SrFeO. After the required enthalpy for EP + SrFeO (relative to Figure 1) is lower compared to EP + NdFeB, the higher temperature leads to fast curing without giving the fillers enough time to orientate. With respect to the temperature level, only a small range can be chosen to ensure a good orientation by enough movability of the fillers without fast curing, which reduces the level of possible orientation.
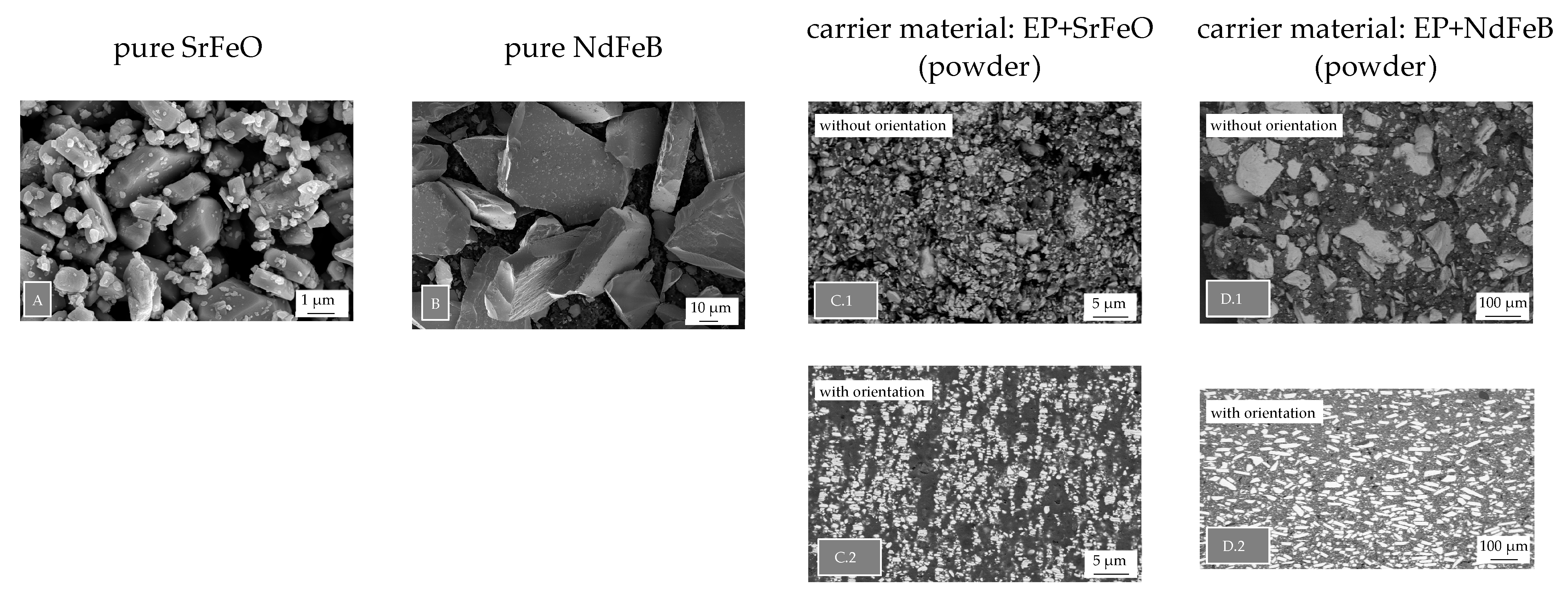
2.3. Filler Distribution and Microstructure of the Pure Filler
As shown in Figure 5, the two pure fillers of the carrier material (SrFeO (A) and NdFeB (B)) highly differ in terms of the filler size and geometry. Further, the influence of the orientation is shown in terms of the recycled samples and the carrier material in powder form. For both carrier materials, a clear difference between the orientation step can be seen, e.g., comparing C.1 and C.2 in terms of SrFeO. Due to the orientation step, the fillers are aligned in build areas in which the orientated particles are stacked. Besides these areas, the pure matrix material can be found, which suggests segregation in terms of SrFeO, to some extent. The images are shown exemplarily for the temperature level of 200 °C and a 50 weight-% of recycled material.
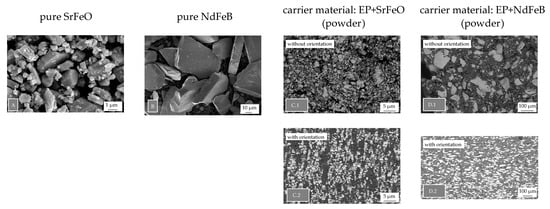
Figure 5.
Microstructure of the pure fillers ((A) SrFeO, (B) NdFeB) and filler distribution relative to the orientation (SrFeO: without, with orientation—(C.1,C.2); NdFeB: without, with orientation—(D.1,D.2)) (NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron, SrFeO: strontium ferrite).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material
The experiments were based on samples, which were shredded after their fabrication, and, with that, the initial product was a post-industrial product. This post-industrial product was provided by the project partner Magnetworld AG (Jena, Germany) and was based on the matrix material epoxy resin (EP) and the hard magnetic filler neodymium–iron–boron (NdFeB; anisotropic). Neither the exact composition nor the fabrication parameters were known. In the following, the material based on this initial post-industrial product is called recycled material.
Further, a so-called carrier material was used, which can be divided into the following three groups: a pure epoxy resin (EP) of the type EPOXIDUR EP 3681 E (company: Raschig GmbH; Ludwigshafen, Germany) and two compounds based on the same EP. Within the compounds, the hard magnetic filler was changed by using the isotropic NdFeB of the type MQP-B+ (company: Neo Magnet Quench GmbH; Tübingen, Germany) and the anisotropic SrFeO of the type OP-71 (company: Dowa Holdings Co.; Tokyo, Japan). NdFeB was chosen to be similar to the recycled material; SrFeO has the opportunity to increase the magnetic properties in the recycled material further and, after, the smaller particles might increase the packing density of the sample. The filler grade of the compound was kept constant at 50 vol.-%.
3.2. Fabrication of the Samples
The carrier material and the recycled material were mixed in the first place before the samples were fabricated. Further, the carrier material in terms of the compound was grinded partly before to investigate the influence of a preferably fine distribution of the carrier and the recycled material. The carrier material based on the pure EP was already in powder form. The grinding step was carried out by using an RWP 700-type press (company: ATM Deutschland GmbH; Blieskastel, Germany). Figure 6 depicts the carrier material within the two modes of grinded (powder form) and not grinded (granulate form). It can be clearly seen that the particle size decreased due to the grinding step.
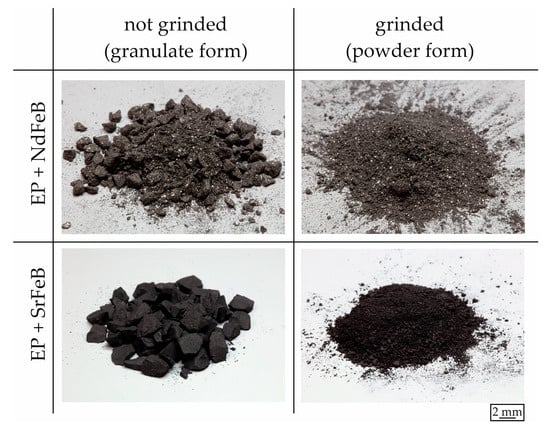

Figure 6.
Modes of carrier material (granulate form—left side | powder form—right side) (EP: epoxy resin | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron | SrFeO: strontium ferrite).
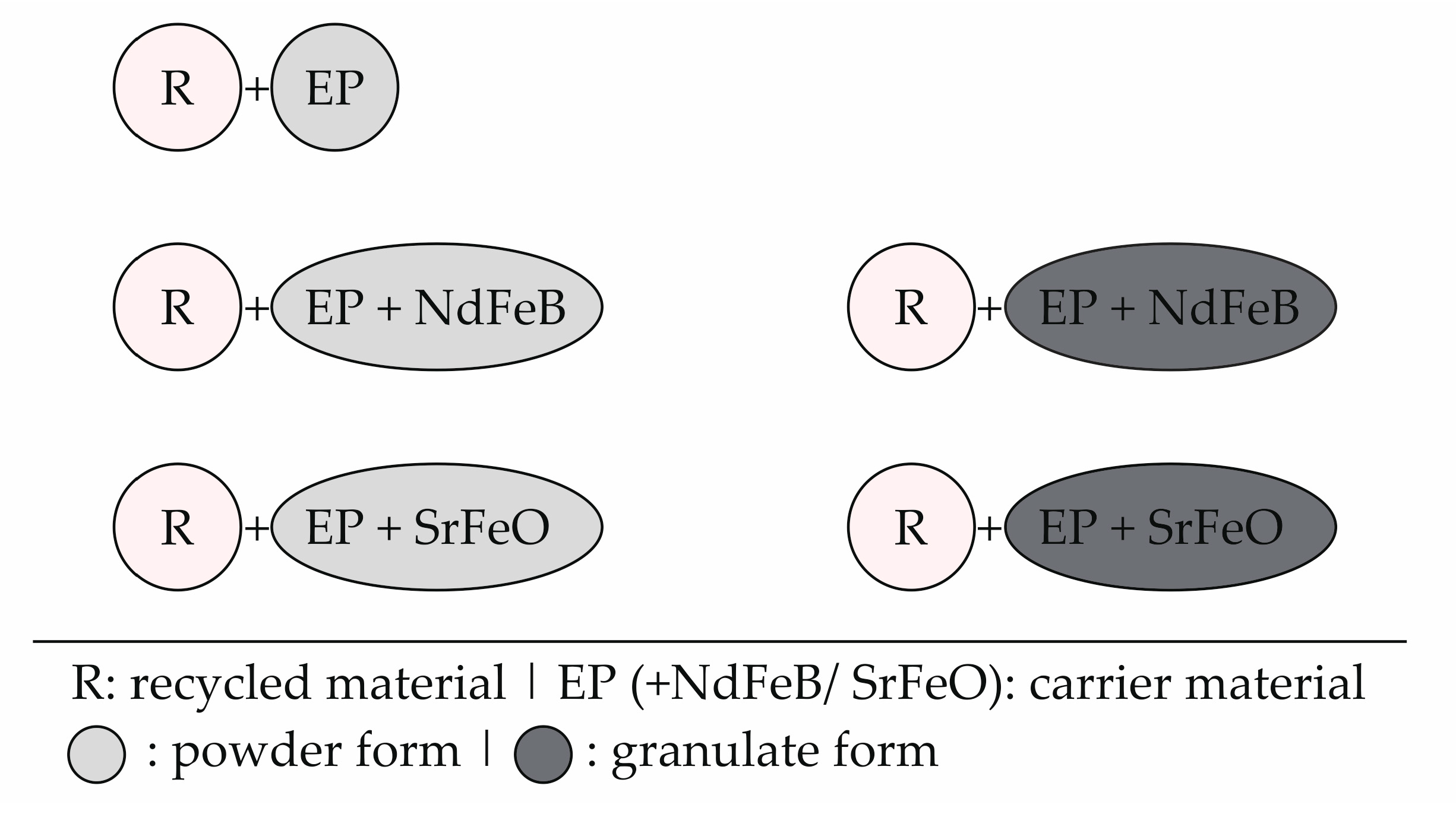
The different combinations of the material are summarized in Figure 7.
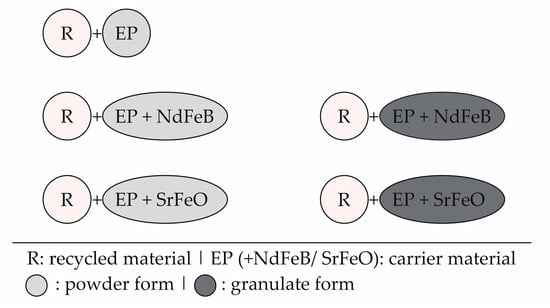
Figure 7.
Overview of the different material combinations (mixture of recycled material (R) and carrier material (EP: epoxy resin | NdFeB: neodymium–iron–boron | SrFeO: strontium ferrite).
Afterwards, the carrier and the recycled material were manually mixed with the proportion of 0 to 80 weight-% of the recycled material in 20 weight-% steps and an intermediate level with 50 weight-%. In terms of the carrier material based on the compound, a sample preparation with a proportion of 80 weight-% of recycled material was not possible. The samples were fabricated by pressing a defined amount of material in a device using an RWP 700-type press. The samples had a diameter of 28 mm and a height of 3 mm. The pressure of the pressing process was kept constant at the level of 100 bar. The device was temperated at the level of 200 °C (reference). Further, the temperature level was changed to 180 and 220 °C. Additionally, a magnetic field was integrated by using permanent magnets to evaluate the influence of the orientation of the hard magnetic fillers within the mixed sample on the magnetic properties. The curing time was kept constant for 90 s. Table 2 summarizes the different parameters that were analyzed.

Table 2.
Overview of the different parameters analyzed (type and condition of the carrier material, amount of recycled material, temperature level and orientation of the fillers).
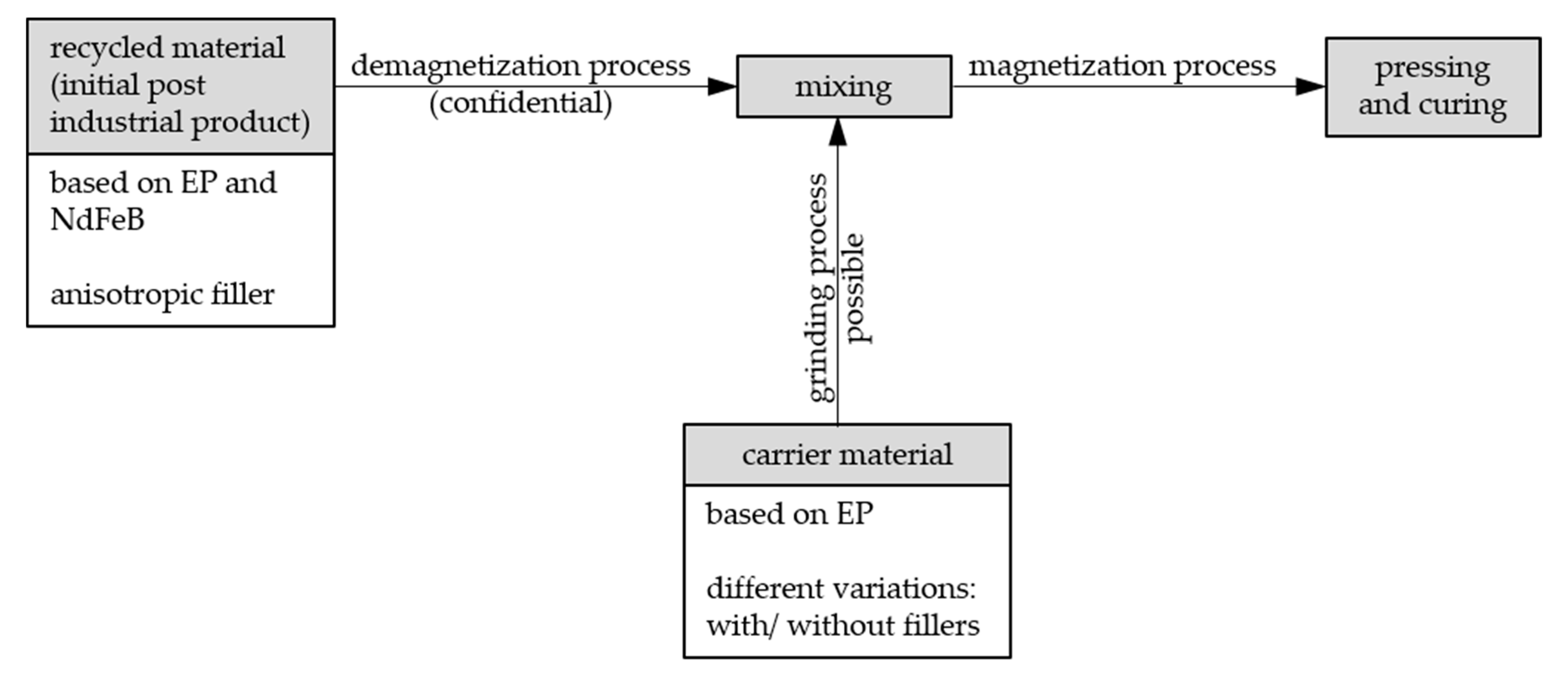
Figure 8 summarizes the process of the sample fabrication in terms of the material components, the (de)magnetization process and the pressing as well as curing step in the end.
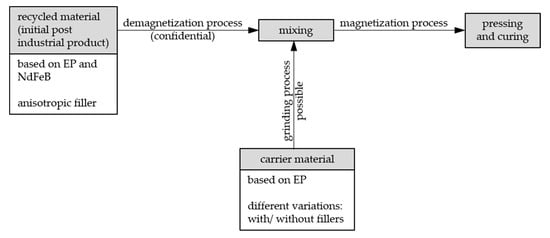
Figure 8.
Schematic summary of the sample fabrication process.
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Following DIN EN ISO 11357 [24]
To define the reaction behavior of the carrier material relative to temperature and time, DSC measurements were carried out based on the DIN EN ISO 11357 [24] standard. By using the DSC (company: TA Instruments; New Castle, DE, USA) about 10 mg of the material was heated from 0 °C to 250 °C with a heat rate of 20 K per minute. The peak temperature as well as the enthalpy were analyzed.
3.3.2. Magnetic Properties
The magnetic properties were defined by a permagraph of the type C-300 (company: Magnet-Physik Dr. Steingroever GmbH; Cologne, Germany). Thereby, a magnetic field strength H is applied onto the sample to (de)magnetize the material. The response of the sample in terms of the magnetic flux density B is measured. To distinguish between the orientation of the fillers and the full magnetization, the samples were magnetized by using a pulse magnetizer of the type Im-12220-U-MA-C (company: Magnet-Physik Dr. Steingroever GmbH; Cologne, Germany) and a magnetic device of the type MVD 30 × 30 mm F-TC (company: Magnet-Physik Dr. Steingroever GmbH; Cologne, Germany) after the first measurement at the permagraph. With that, the different magnetic properties before and after magnetization were analyzed relative to the two parameters of permanence Bperm and remanence BR.
3.3.3. Filler Distribution and Microstructure of the Pure Filler
The behavior of the pure filler and the filler within the carrier material was depicted by a scanning electron microscope SEM of the Gemini Ultra-plus type (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany). The magnification was chosen in terms of the size of the filler and varies.
4. Conclusions
Within this paper, a recycling strategy in terms of polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets was evaluated. It was shown that several factors influence the remaining magnetic properties within samples. An additional grinding step is needed to ensure a powder form of the recycled material. This form is especially required to further fabricate recycled material and reach proper magnetic properties. Further, an orientation of the fillers within the fabrication has to be ensured in terms of the temperature level and an outer magnetic field. In addition, smaller particles in the carrier material increase the magnetic properties, and after that, can close gaps between greater particles. Based on the investigations, the following parameters, as shown in Table 3, should be chosen in terms of implementing the mechanical recycling strategy for thermoset-based polymer-bonded magnets.

Table 3.
Overview of the recommended parameters to realize the mechanical recycling strategy for polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets.
With respect to pyrolysis as the common recycling strategy in terms of thermosets, and especially filled thermoset systems, the different strategy prevents the fillers from oxidation, which reduces the magnetic properties. The pyrolysis under a nitrogen atmosphere would also allow the reduction of the oxidation; however, this method is quite expensive. Within the mechanical strategy, the required energy and the CO2 emission can be reduced by 90% compared to the pyrolysis method [27]. With that, the mechanical strategy of grinding and pressing by implementing a carrier material reveals the opportunity of recycling polymer-bonded magnets based on thermosets with only a little reduction of the magnetic properties relative to the ideal values of the material and suitable impact of required energy as well as CO2 emission. It has to be taken into account that the new method always requires a carrier material to some extent and, with that, new resin. This reduces the magnetic properties in comparison to the original.
Author Contributions
U.R.: conceptualization, methodology, validation, investigation, writing—original draft and visualization; D.D.: writing—review and editing and project supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt” within the project “Recycling von Magnetwerkstoffen für die Verwendung in kunststoffgebundenen Dauermagneten” (reference number: 38099/01-31).
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data are available with the permission of the author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank you the project partner Magnetworld AG for providing the post-industrial products, which were essential in terms of the investigations portrayed in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Cassing, W.; Kuntze, K.; Ross, G. Dauermagnete: Mess- und Magnetisierungstechnik, 3rd ed.; Expert-Verlag: Renningen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod, J.; Constantinides, S. Bonded permanent magnets: Current status and future opportunities (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 4816–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalowsky, L.; Schneider, J. Magnettechnik: Grundlagen, Werkstoffe, Anwendungen, 3rd ed.; Vulkan Verlag: Essen, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Drummer, D. Verarbeitung und Eigenschaften Kunststoffgebundener Dauermagnete. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rösel, U. Zum Spritzgießen multipolarer kunststoffgebundener Dauermagnete auf Duroplast-Basis. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Alexander University, Erlangen, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maenz, T. Spritzgießtechnische Herstellung Duroplastgebundener Dauermagnete. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität, Chemnitz, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, E.; Martin, R.; Stohrer, M. Physik für Ingenieure, 12th ed.; Springer Vieweg: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ivers-Tiffée, E.; Münch, W. Werkstoffe der Elektrotechnik, 10th ed.; B. G. Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Grönefeld, M. Polymergebundene hartmagnetische Werkstoffe. In Magnetwerkstoffe für Technische Anwendungen; Haus der Technik e.V.: Essen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cassing, W. Elektromagnetische Wandler und Sensoren: Grundlagen, Feldnumerische Berechnungen Elektromagnetischer Fel-der und Anwendungen in der Mechatronik, 2nd ed.; Expert-Verlag: Renningen, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schliesch, T. Kunststoffgebundener Rotor für Gleichstrommotoren mit unterschiedlichen Werkstoffen und Feldbereichen. In Kunststoffgebundene Dauermagnete; Springer: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2004; pp. 68–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto, S. Current status and recent topics of rare-earth permanent magnets. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchert, M.; Manhart, A.; Suttler, J. Untersuchung zu Seltenen Erden: Permanentmagnete im industriellen Einsatz in Baden-Württemberg; Öko-Institut eV: Freiburg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchling, H. Taschenbuch der Physik, 15th ed.; Fachbuchverl.: Leipzig, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, H. Seltene Erden Werden Selten: Magnete für E-Autos Könnten Knapp Warden. 2020. Available online: https://www.elektroniknet.de/automotive/wirtschaft/magnete-fuer-e-autos-koennten-knapp-werden.179916.html (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Dolgirev, J.; Kalter, M.; Urschel, S.; Funck, R.; Jung, J.; Schimmelpfennig, V. Resource-saving Cirulating Pump on basis of an Integrated Synchronous-Reluctance Drive System. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Future Energy Electronics Conference (IFEEC), Singapore, 25–28 November 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Willard, M.A.; Brück, E.; Chen, C.H.; Sankar, S.G.; Liu, J.P. Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: Stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 9506–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glöser-Chahoud, S.; Kühn, A.; Espinoza, L.A.T. Globale Verwendungsstrukturen der Magnetwerkstoffe Neodym und Dysprosium: Eine Szenariobasierte Analyse der Auswirkung der Diffusion der Elektromobilität auf den Bedarf an Seltenen Erden, Working Paper Sustainability and Innovation. Working Paper Sustainability and Innovation No. S 05/2016. 2016. Available online: https://www.isi.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/isi/dokumente/ccn/2016/KSE-WorkingPaper_Globale-Verwendungsstrukturen.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Baur, E.; Brinkmann, S.; Osswald, T.; Rudolph, N. Schmachtenberg, Saechtling Kunststoff Taschenbuch, 31st ed.; Carl Hanser Verlag: München, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rösel, U.; Drummer, D. Possibilities in Recycling Magnetic Materials in Applications of Polymer-Bonded Magnets. Magnetism 2022, 2, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, U.; Blank, R.; Buchert, M.; Elwert, T.; Finsterwalder, F.; Hörnig, G.; Klier, T.; Langkau, S.; Marscheider-Weidermann, F.; Müller, J.-O.; et al. Recycling von Komponenten und Strategische Metallen aus Elektrischen Fahrantrieben: Kennwort: MORE (Motor Recycling). FKZ: 03X4622, Abschlussbericht. 2014. Available online: https://edocs.tib.eu/files/e01fb15/826920594.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2024).
- Zakotnik, M.; Harris, I.R.; Williams, A.J. Possible methods of recycling NdFeB-type sintered magnets using HD/degrassing process. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 450, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Yin, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, Q. Progress in recycling of NdFeB sintered magnet wastes. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 77506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EP1096517 B 1; Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Wiederverwendeten Pulvers für die Benutzung in einem Verbundmagnet und Verfahren zur Wiederverwendung eines Verbundmagneten. Matsushita Electric Industrial Co. Ltd.: Osaka, Japan, 2005.
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V. Kunststoffe—Dynamische Differenz-Thermoanalyse (DSC): Teil 5: Bestimmung von Charakteristischen Reaktionstemperaturen und-Zeiten, Reaktionsenthalpie und Umsatz; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lucarini, S.; Hossain, M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D. Recent advances in hard-magnetic soft composites: Synthesis, characterisation, computational modelling, and applications. Compos. Struct. 2022, 279, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, D.; Rösel, U. Zwischenbericht: Recycling von Magnetwerkstoffen für die Verwendung in Kunststoffgebundenen Dauermagneten; Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU): Erlangen, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).