Recycling of Egyptian Shammi Corn Stalks for Maintaining Sustainable Cement Industry: Scoring on Sustainable Development Goals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Mechanical and Physical Performance
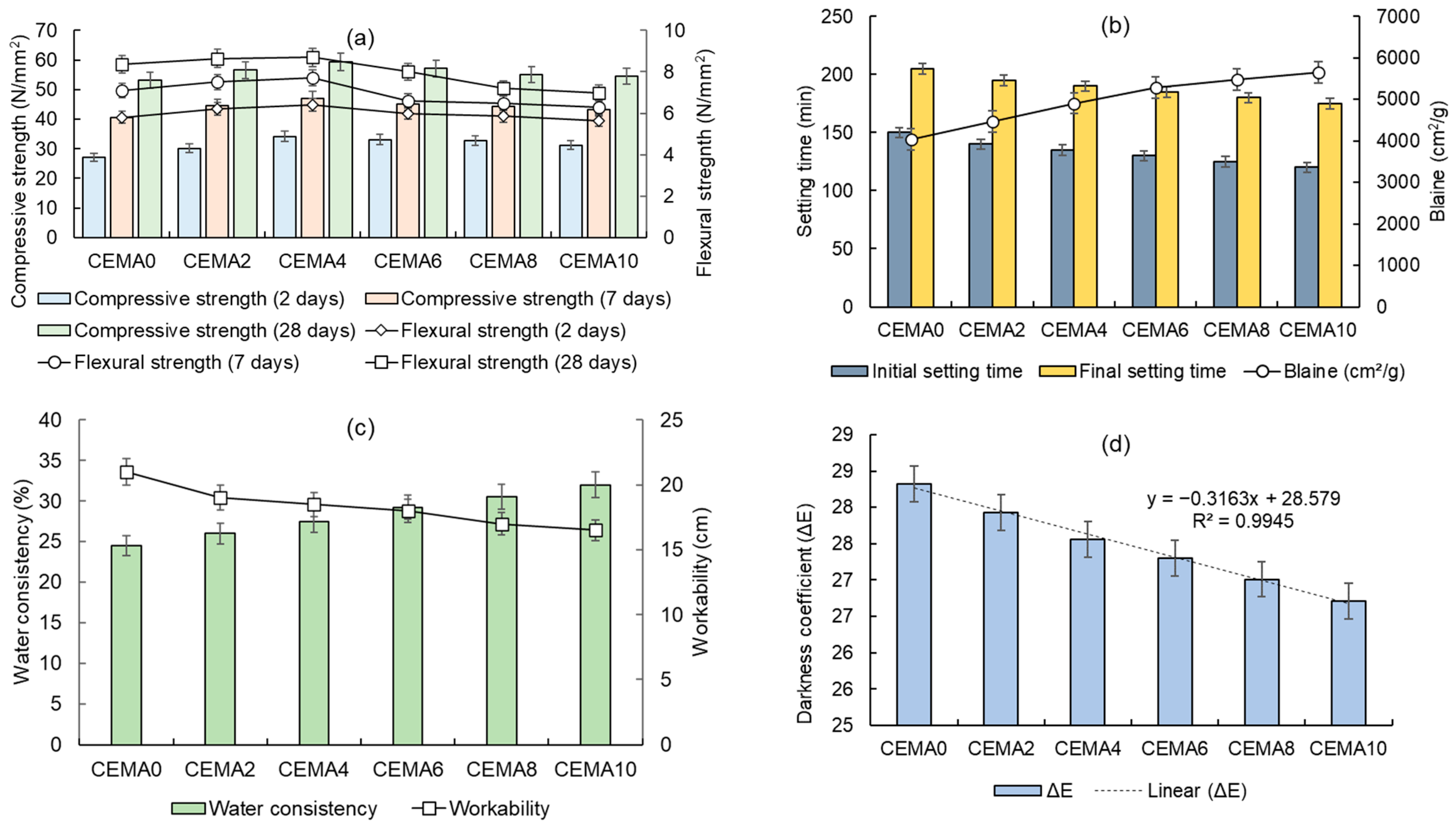
2.1.1. Compressive Strength
2.1.2. Flexural Strength
2.1.3. Blaine Value and Setting Time
2.1.4. Water Consistency
2.1.5. Darkness Coefficient (ΔE)
2.2. Characterization Results for the Cement Mixtures
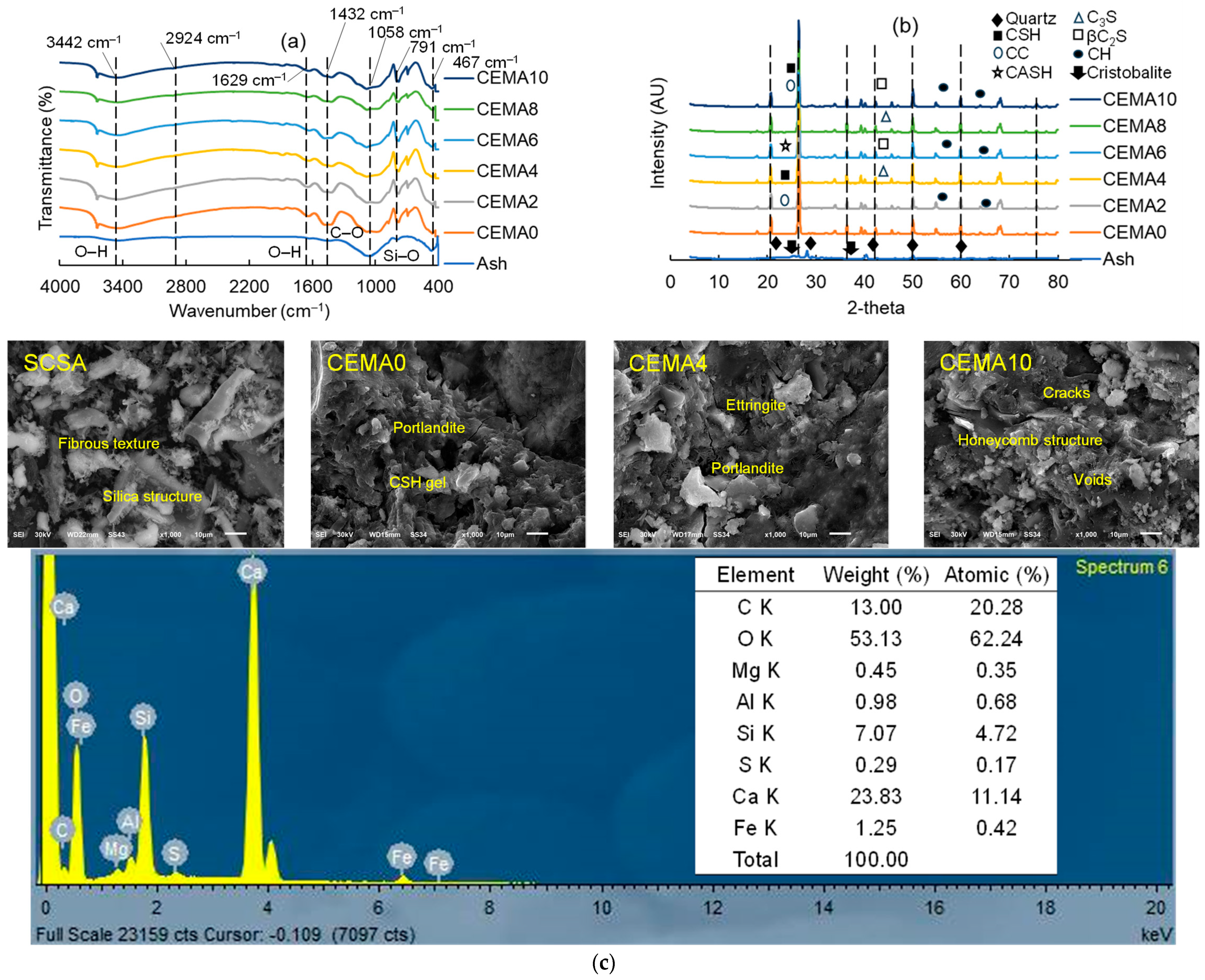
2.2.1. Surface Functional Groups
2.2.2. Crystallinity Degree
2.2.3. Surface Morphology
2.3. Decision of Alternatives Using AHP-TOPSIS
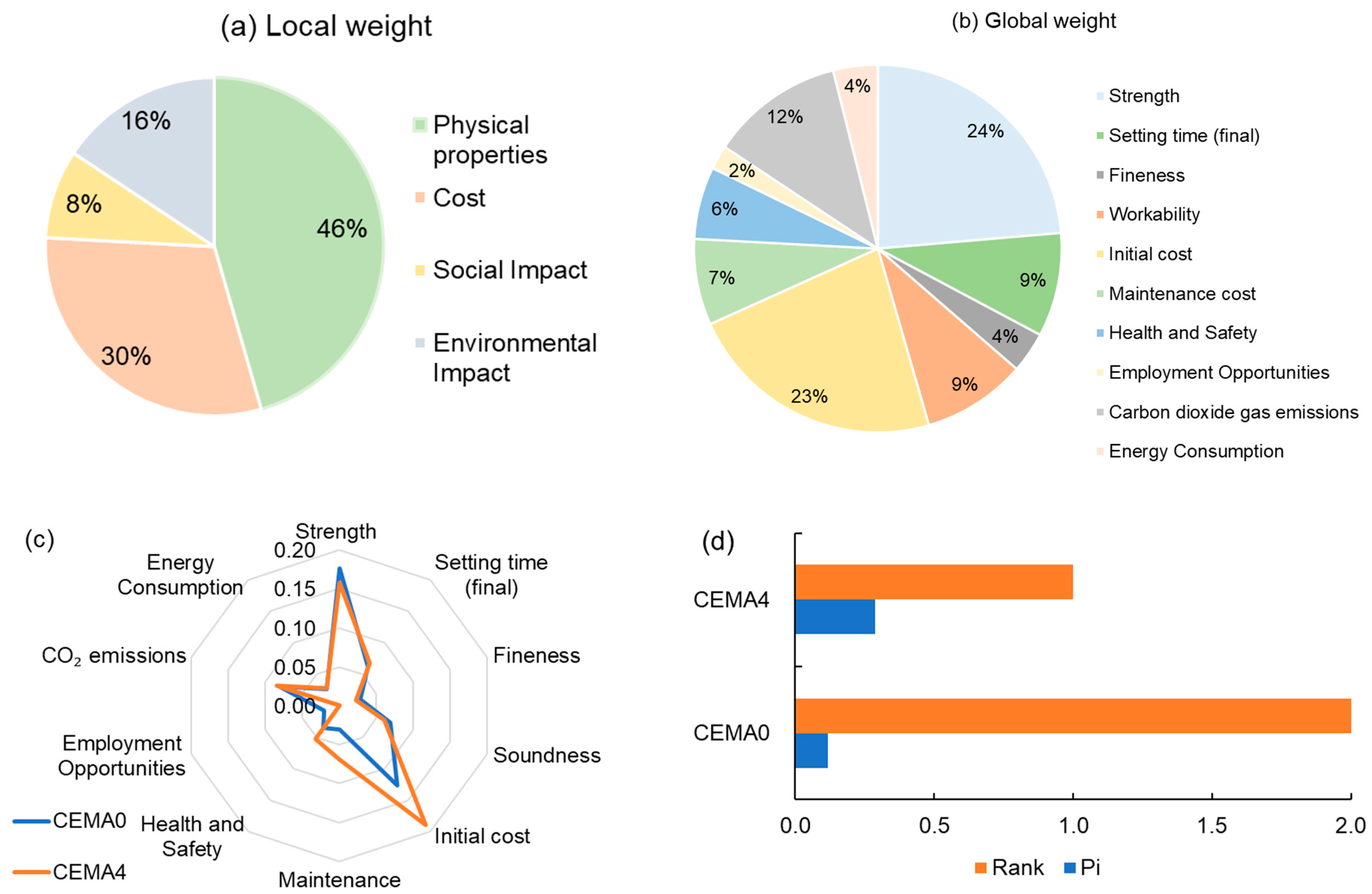
2.3.1. Categories and Sub-Categories Results and Weights
2.3.2. AHP-TOPSIS Decision on Alternatives
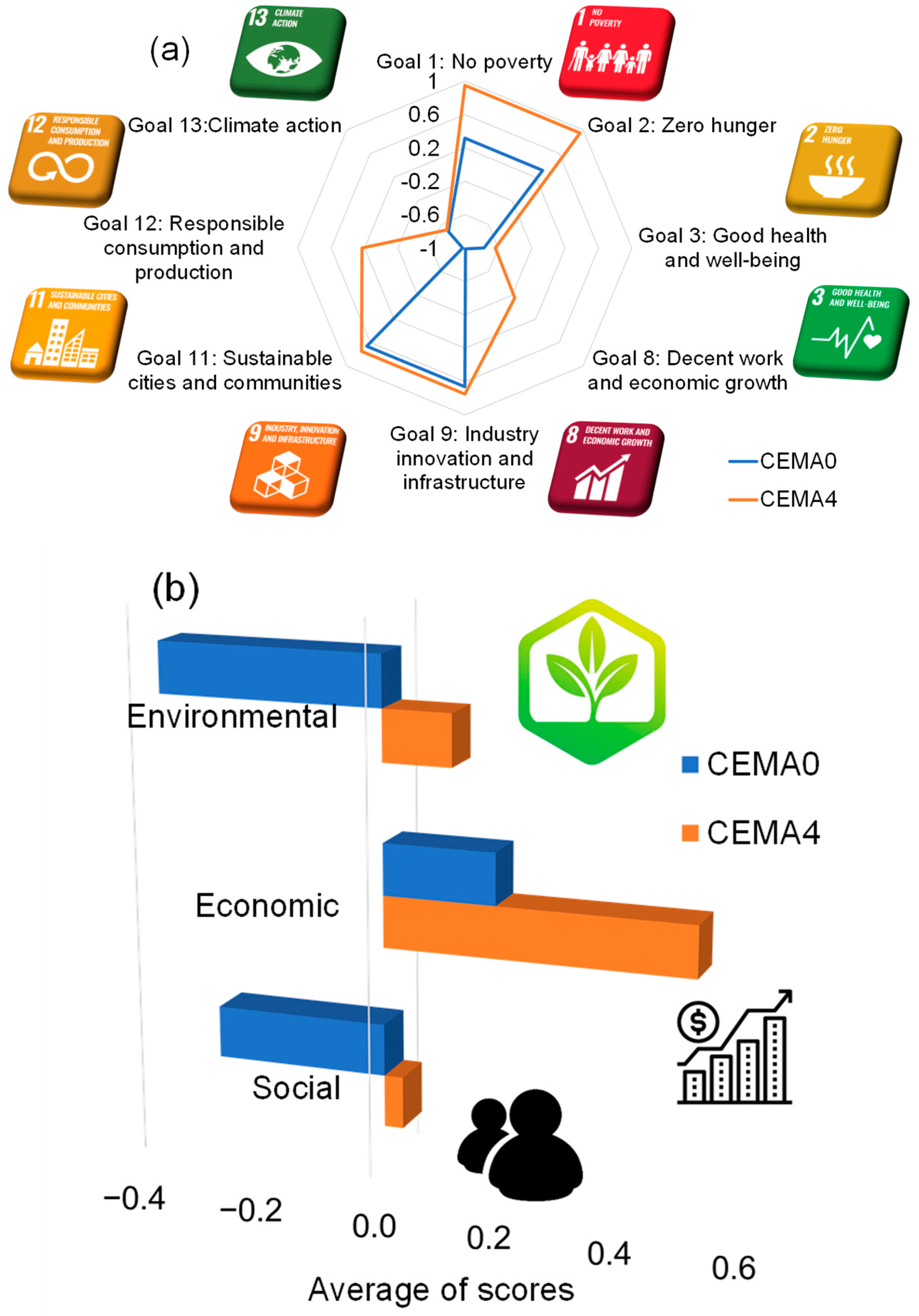
2.4. SDGs Integrated with AHP-TOPSIS
2.4.1. Social Impact Goals
2.4.2. Economic Impact Goals
2.4.3. Environmental Impact Goals
2.5. Study Limitations and Future Directions
- Optimization of Shammi corn cultivation location: It is essential to ensure that the location of corn-producing farms is not far from the cement-manufacturing industry, to minimize transportation costs and the utilization of fuel (e.g., petrol and diesel).
- Enhancing SCSA silica content: More research is required to increase the silica content in SCSA by optimizing and controlling the combustion conditions, which could further improve the Pozzolanic reaction of the cement binder and the aluminosilicate gel properties. Further studies are also required to provide an accurate measure of the amount of amorphous silica in the SCSA material, following the procedures reported earlier [48].
- More criteria for AHP-TOPSIS evaluation: Future studies are required to consider additional socio-economic factors, such as gender equality, protection of life on land, and clean energy usage, to improve the decision-making processes that determine the best agricultural waste-recycling strategy.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) model applications: The Fuzzy TOPSIS method could be incorporated into the decision-making process to evaluate the possible and available alternatives for cement mortar mixture selection. The best alternative selected by AI should confirm reduced CO2 emissions, a lower energy consumption, and cost-effectiveness.
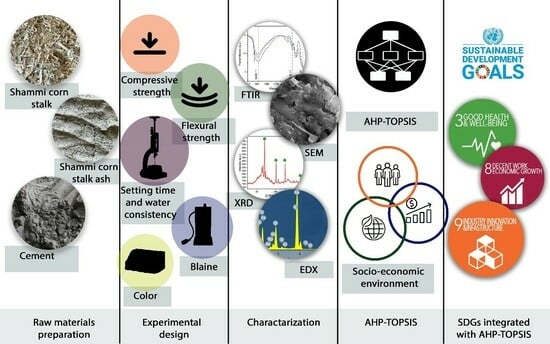
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Design
3.3. Testing Procedures
3.4. Analytical Analysis
3.5. Hybrid Methodology of Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS)
3.6. SDGs Integrated with AHP-TOPSIS for Determining Sustainability of Cement Material Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katman, H.Y.; Khai, W.J.; Bheel, N.; Kırgız, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Khatib, J.; Benjeddou, O. Workability, strength, modulus of elasticity, and permeability feature of wheat straw ash-incorporated hydraulic cement concrete. Buildings 2022, 12, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, H.; Mehrez, I.; Boumnijel, I.; Jemni, A.; Mihoubi, D. Sustainable Approach of Using Arundo donax Leaves Reinforced Cement Mortar/Fly Bottom Ash Composites. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 12039–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.; El-dek, S.; El-Gamal, S. Mechanical performance and thermal stability of hardened Portland cement-recycled sludge pastes containing MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Raman, S.; Lai, F.-C.; Zain, M.; Hamid, R. Synthesis of nano cementitious additives from agricultural wastes for the production of sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kutti, W.; Nasir, M.; Johari, M.A.; Islam, A.S.; Manda, A.A.; Blaisi, N.I. An overview and experimental study on hybrid binders containing date palm ash, fly ash, OPC and activator composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupić, S.; Malešev, M.; Radonjanin, V.; Bulatović, V.; Milović, T. Reactivity and pozzolanic properties of biomass ashes generated by wheat and soybean straw combustion. Materials 2021, 14, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakib, N.; Hasan, R.; Mutalib, A.A.; Jamil, M.; Raman, S.N.; Kaish, A. Utilization of Sugar Mill Waste Ash as Pozzolanic Material in Structural Mortar. Minerals 2023, 13, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, S.; Saranya, R.; Praveenkumar, S. Pozzolanic attributes of hydraulic cement paste hybridized with agricultural by-product and Nano-carbon. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, S.; Cheng, T.-W.; Luhar, I. Incorporation of natural waste from agricultural and aquacultural farming as Supplementary Materials with green concrete: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Khan, S.; Wahid, I.; Shestakova, Y.; Ashraf, M. Evaluating the effect of calcination and grinding of corn stalk ash on pozzolanic potential for sustainable cement-based materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1619480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, K.; Lee, H.-S.; Lim, S.; Song, H.; Hussin, M.W.; Ismail, M.A. Use of an agricultural by-product, nano sized Palm Oil Fuel Ash as a supplementary cementitious material. Constr. Build Mater. 2018, 183, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglad, A.M.; Amin, M.; Zeyad, A.M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Agwa, I.S. Engineering properties of ultra-high strength concrete containing sugarcane bagasse and corn stalk ashes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 3196–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.; Hamdy, Y.; Abdelraouf, E.-S.; Shazly, M. Towards sustainable concrete: Cement replacement using Egyptian cornstalk ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, P.; Mendes, R.; Marin, D.; Paes, J.; Cecchin, D.; Barbari, M. Agricultural Residues of Lignocellulosic Materials in Cement Composites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikanta, C.; Manikandan, P.; Duraimurugan, S.; Elavenil, S.; Vasugi, V. Pozzolanic properties of agro waste ashes for potential cement replacement predicted using ANN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1716, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.; Othman, M.H.; Khan, I.U.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Promoting sustainable cleaner production paradigms in palm oil fuel ash as an eco-friendly cementitious material: A critical analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Yang, J.; Mo, K.; Abdalla, J.; Hawileh, R.; Ariyachandra, E. Biomass ashes from agricultural wastes as supplementary cementitious materials or aggregate replacement in cement/geopolymer concrete: A comprehensive review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 40, 102332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, I.P.; Ranjbar, N.; Damø, A.J.; Jensen, L.S.; Canut, M.; Jensen, P.A. A review: Alkali-activated cement and concrete production technologies available in the industry. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To-On, P.; Wichapa, N.; Khanthirat, W. A novel TOPSIS linear programming model based on response surface methodology for determining optimal mixture proportions of lightweight concrete blocks containing sugarcane bagasse ash. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barišić, I.; Netinger Grubeša, I.; Hackenberger, D.; Palijan, G.; Glavić, S.; Trkmić, M. Multidisciplinary Approach to Agricultural Biomass Ash Usage for Earthworks in Road Construction. Materials 2022, 15, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-López, G.; Múnera, A.; Villegas, J. Multicriteria Decision-Making Tools for the Selection of Biomasses as Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 197-1:2000; Cement—Part 1: Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements; European Standard. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2000.
- Ananyachandran, P.; Vasugi, V. Development of a sustainable high early strength concrete incorporated with pozzolans, calcium nitrate and triethanolamine: An experimental study. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Z.; Rafiq, S. An experimental study on behavior of wood ash in concrete as partial replacement of cement. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 3426–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charitha, V.; Athira, V.; Jittin, V.; Bahurudeen, A.; Nanthagopalan, P. Use of different agro-waste ashes in concrete for effective upcycling of locally available resources. Constr. Build Mater. 2021, 285, 122851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudainiyan, J.; Kishore, K. A review on cement concrete strength incorporated with agricultural waste. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 78, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, M.; Behfarnia, K.; Soltanian, H. The effect of the blaine fineness on the mechanical properties of the alkali-activated slag cement. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 26, 100897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, A.H.; Darweesh, H.H. Setting and hardening of agro/cement composites. BioResources 2010, 5, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.R.; Chen, B.; Shah, S.F. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of bio-concrete prepared with optimized alternative green binders. Constr. Build Mater. 2021, 281, 122533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darweesh, H. Influence of sun flower stalk ash (SFSA) on the behavior of Portland cement pastes. Results Eng. 2020, 8, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Nivitha, M.; Krishnan, J.M.; Robinson, R. Characterization of cement stabilized pond ash using FTIR spectroscopy. Constr. Build Mater. 2020, 263, 120136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Qiao, H.; Li, Y.; Shu, X.; Cui, L. Effect of highland barley straw ash admixture on properties and microstructure of concrete. Constr. Build Mater. 2022, 315, 125802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ameer, S.; Abbas, S.; Abbass, W.; Razzaq, A.; Mohamed, A.; Mohamed, A. Effectiveness of Ternary Blend Incorporating Rice Husk Ash, Silica Fume, and Cement in Preparing ASR Resilient Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoğan, O.; Binici, H.; Ortlek, E. Durability of concrete made by partial replacement of fine aggregate by colemanite and barite and cement by ashes of corn stalk, wheat straw and sunflower stalk ashes. Constr. Build Mater. 2016, 106, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iheukwumere-Esotu, L.O.; Yunusa-Kaltungo, A. Knowledge criticality assessment and codification framework for major maintenance activities: A case study of cement rotary kiln plant. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunu, W.; Kativhu, T.; Moyo, P. An evaluation of the effectiveness of the Behaviour Based Safety Initiative card system at a cement manufacturing company in Zimbabwe. Saf. Health Work. 2018, 9, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, N.; Omidvari, M.; Meftahi, M. The effect of integrated management system on safety and productivity indices: Case study; Iranian cement industries. Saf. Sci. 2012, 50, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, N.C. Green Jobs: The Present and Future of the Building Industry. Evolution Analysis. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.K. Review on energy conservation and emission reduction approaches for cement industry. Environ. Dev. 2022, 44, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Khereby, M.A.; Ghorab, H.Y.; Elkhoshkhany, N. Preparation of geopolymer concrete using Egyptian kaolin clay and the study of its environmental effects and economic cost. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Mu, M.; Wang, Y. Comparison of CO2 emissions from OPC and recycled cement production. Constr. Build Mater. 2019, 211, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıoğlu Akan, M.; Dhavale, D.; Sarkis, J. Greenhouse gas emissions in the construction industry: An analysis and evaluation of a concrete supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Lovren, V.O.; Will, M.; Salvia, A.L.; Frankenberger, F. Poverty: A central barrier to the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 125, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, S.; Sharma, V.; Khan, N.; Chaurasia, D.; Ahmad, A.; Chauhan, S.; Singh, A.; You, S.; Pandey, A.; Bhargava, P.C. Sustainable biochar: A facile strategy for soil and environmental restoration, energy generation, mitigation of global climate change and circular bioeconomy. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, A.; Das, P.K.; Hashmi, A.W.; Yusuf, M.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S. Challenges and opportunities of utilizing municipal solid waste as alternative building materials for sustainable development goals: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 27, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Irfan, M.; Samad, S.; Ali, B.; Zhang, Y.; Badulescu, D.; Badulescu, A. The Relationship between Energy Consumption, CO2 Emissions, Economic Growth, and Health Indicators. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbasiouny, H.; Elbanna, B.A.; Al-Najoli, E.; Alsherief, A.; Negm, S.; Abou El-Nour, E.; Nofal, A.; Sharabash, S. Agricultural waste management for climate change mitigation: Some implications to Egypt. Waste Manag. MENA Reg. 2020, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payá, J.; Monzó, J.; Borrachero, M.; Mellado, A.; Ordoñez, L. Determination of amorphous silica in rice husk ash by a rapid analytical method. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, H.; Hafez, A.; Mohammed, M.; Sabry, R. Prepared and properties of filled and pozzolanic-filled cements from marble dust waste and granulated slag. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C128; Standard Test Method for Relative Density (Specific Gravity) and Absorption of Fine Aggregate. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. Available online: https://www.astm.org/c0128-22.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Topçu, S.S. Evaluation of Internal Stability of The CEN-Standard Sand Based on Different Gradation Methods. AS-Proceedings 2023, 1, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 196-1; Methods for Testing Cement. Part 1: Determination of Mechanical Strengths; E. Standard. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2010.
- 196-5; Methods for Testing Cement. Part 5: Pozzolanicity Test for Pozzolanic Cements; E. Standard. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2005.
- Galobardes, I.; Salvador, R.; Cavalaro, S.; Figueiredo, A.; Goodier, C. Adaptation of the standard EN 196-1 for mortar with accelerator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5513, I.; Vicat Apparatus—Specification. Bureau of Indian Standards: New Delhi, India, 1996.
- C191-21; Standard Test Methods for Time of Setting of Hydraulic Cement by Vicat Needle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/c0191-21.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- C187-16; Standard Test Method for Amount of Water Required for Normal Consistency of Hydraulic Cement Paste. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.astm.org/c0187-16.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- 1015-3; Methods of Test for Mortar for Masonry. Determination of Consistence of Fresh Mortar (by Flow Table). BSI: London, UK, 1999.
- C204-24; Standard Test Methods for Fineness of Hydraulic Cement by Air-Permeability Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.astm.org/standards/c204 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Jesus, C.; Junior, E.A.; Braga, N.; Junior, J.S.; Barata, M.S. Coloured concrete produced from low-carbon cements: Mechanical properties, chromatic stability and sustainability. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 67, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangiuli, D.; Calia, A.; Bianco, N. Novel multifunctional coatings with photocatalytic and hydrophobic properties for the preservation of the stone building heritage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T. The Analytic Hierarchy Process: Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Balsara, S.; Jain, P.; Ramesh, A. An integrated approach using AHP and DEMATEL for evaluating climate change mitigation strategies of the Indian cement manufacturing industry. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252 Pt A, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, N.; Mohamed, O.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Olabi, A. Geopolymer concrete as green building materials: Recent applications, sustainable development and circular economy potentials. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqr, A.; Nasr, M.; Fujii, M.; Yoshimura, C.; Ibrahim, M. Delineating suitable zones for solar-based groundwater exploitation using multi-criteria analysis: A techno-economic assessment for meeting sustainable development goals (SDGs). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 25, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiba, Y.; Ibrahim, M.; Mohamed, A.; Fujii, M.; Nasr, M. Developing smart sustainable irrigation matrix (SIM)-based model for selection of best irrigation techniques: A framework to achieve SDGs. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerbănoiu, A.A.; Grădinaru, C.M.; Muntean, R.; Cimpoeșu, N.; Șerbănoiu, B.V. Corn Cob Ash versus Sunflower Stalk Ash, Two Sustainable Raw Materials in an Analysis of Their Effects on the Concrete Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, P.; Parashar, A. Incorporation of Silica Fume and Waste Corn Cob Ash in Cement and Concrete for Sustainable Environment. Mater. Today: Proc. 2022, 62, 4151–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šupić, S.; Malešev, M.; Pantić, V.; Lukić, I.; Radonjanin, V.; Ognjanović, M.; Broćeta, G. Environmentally Friendly Masonry Mortar Blended with Fly Ash, Corn Cob Ash or Ceramic Waste Powder. Materials 2023, 16, 6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dimension | Cement | SCSA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lime (CaO) | % | 63.84 | 9.25 |
| Silica (SiO2) | % | 20.82 | 62.95 |
| Alumina (Al2O3) | % | 5.28 | 6.29 |
| Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) | % | 3.57 | 2.07 |
| Magnesia (MgO) | % | 1.54 | 3.29 |
| Sulphur Trioxide (SO3) | % | 2.4 | 1.37 |
| Alkalis (Na2O; K2O) | % | 0.48 | 3.94 |
| Phosphorus Pentoxide (P2O5) | % | UD * | 0.37 |
| Loss on Ignition (LOI) | % | 1.89 | 10.32 |
| Parameter | CEMA0 | CEMA2 | CEMA4 | CEMA6 | CEMA8 | CEMA10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCSA (w/w%) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Water (L) | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.225 | 0.225 |
| Cement (g) | 450 | 441 | 432 | 423 | 414 | 405 |
| SCSA (g) | 0 | 9 | 18 | 27 | 36 | 45 |
| CEN sand (g) | 1350 | 1350 | 1350 | 1350 | 1350 | 1350 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qasem, F.; Sharaan, M.; Fujii, M.; Nasr, M. Recycling of Egyptian Shammi Corn Stalks for Maintaining Sustainable Cement Industry: Scoring on Sustainable Development Goals. Recycling 2024, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9030034
Qasem F, Sharaan M, Fujii M, Nasr M. Recycling of Egyptian Shammi Corn Stalks for Maintaining Sustainable Cement Industry: Scoring on Sustainable Development Goals. Recycling. 2024; 9(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleQasem, Fajr, Mahmoud Sharaan, Manabu Fujii, and Mahmoud Nasr. 2024. "Recycling of Egyptian Shammi Corn Stalks for Maintaining Sustainable Cement Industry: Scoring on Sustainable Development Goals" Recycling 9, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9030034
APA StyleQasem, F., Sharaan, M., Fujii, M., & Nasr, M. (2024). Recycling of Egyptian Shammi Corn Stalks for Maintaining Sustainable Cement Industry: Scoring on Sustainable Development Goals. Recycling, 9(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling9030034