2.1. Catalyst Characterization
Table 1 shows the results obtained from an initial wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence (WDXRF) analysis of the spent automotive catalytic converter (SACC) sample processed in this work.
The most abundant elements were Si, Al and Mg, in accordance with the catalyst fabrication process using honeycomb cordierite skeletons (2MgO·2Al
2O
3·5SiO
2). Cordierite is coated with a highly porous wash-coat composed by approximately 90% γ-Al
2O
3 and a mixture of base metals additives, mainly oxides of Ce, Zr, La, Ni, Fe, and alkaline-earths, in which PGMs are finely dispersed in metallic form [
17,
27,
28]. The Ce content was 3.28 wt%, whereas La only represents 0.066 wt%. The presence of these rare earth elements is due to the addition of Ce, Zr and La oxides as components of the wash-coat, to improve some properties of the catalysts [
28,
29]. Ce, Zr and La oxides promote Pt dispersion, reducing the particles agglomeration and providing more oxygen vacancy to enhance the catalytic activity [
30]. Recent studies have shown that the catalytic performance of PGMs can remarkably improve when Ce, La and Zr are used as electropositive promoters [
31].
The Pt content (0.257 wt%) was higher than the one reported previously [
28]. The amount of Pd was only 0.011 wt%.
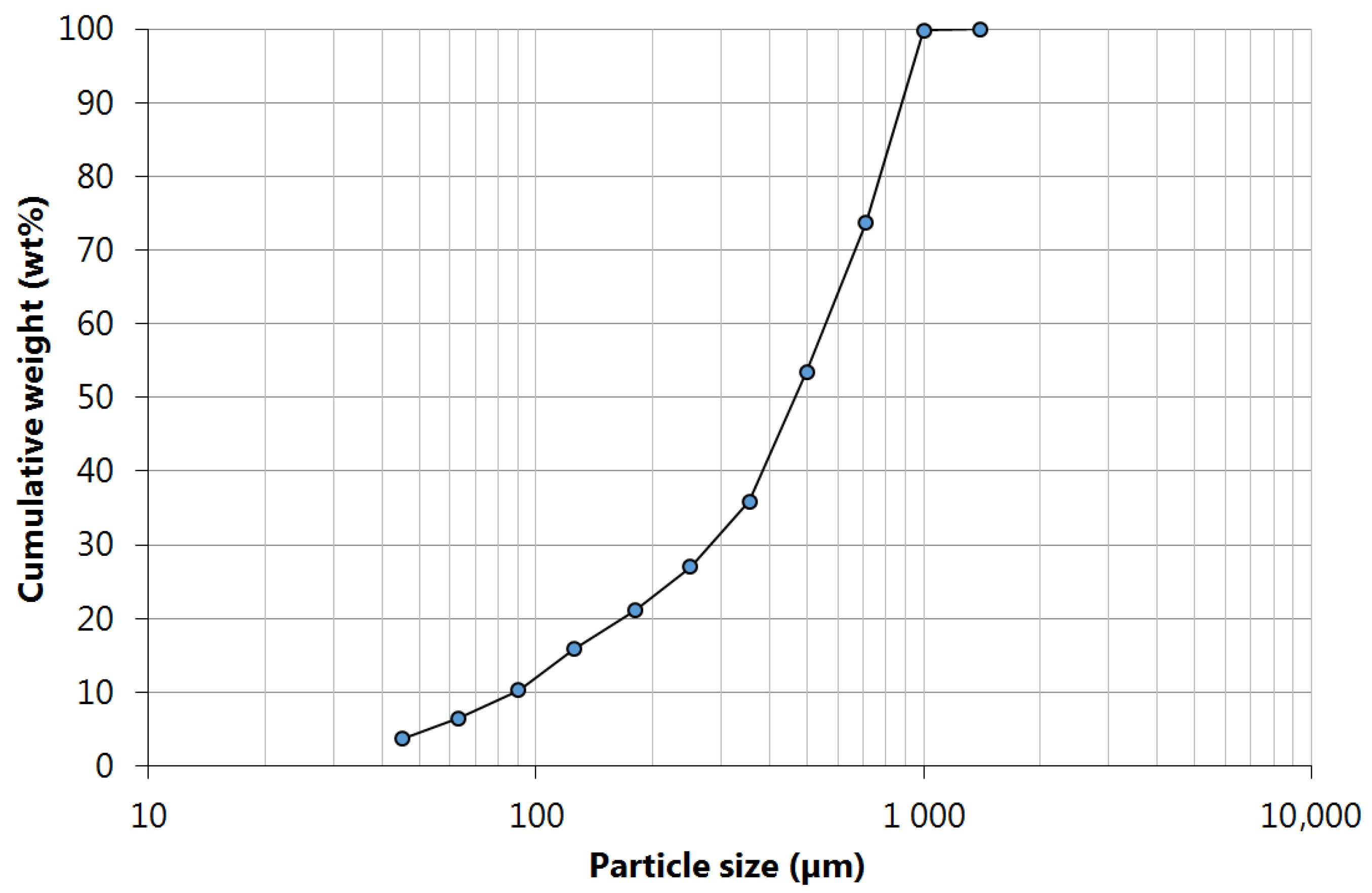
The particle size analysis of the ground samples (
Figure 1) led to the following characteristic diameters:
d10 = 85,
d50 = 485, and
d90 = 885 μm, respectively. The sample used in the leaching tests comprised all particle size fractions, therefore, being representative of the entire monolith, as this is the supposed situation that best fits industrial practice. Although PGMs contents are expected to be higher in fine fractions (as verified in previous unpublished work), all fractions should be used to avoid PGMs loss.
2.2. Leaching of Pt, Ce and Al
Pt recovery was the main target of the present work. However, due to the high content of Ce (~ 4%) in the SACC, its possible recovery was also considered. Regarding impurities, Al should be the most relevant, due to its high content in the catalyst, with a probable negative influence in the subsequent solvent extraction (SX) separation process. Although expecting a low Al leaching yield when considering the general adopted experimental conditions, its high content in the SACC can turn its concentration in the leaching liquor high. Therefore, the first objective was to select leaching conditions for which a better Pt leaching could be achieved with a lower Al contamination.
PGMs form soluble chloro-complex species in chloride media, hydrochloric acid being the most traditional source of chlorides for leaching. The replacement of a part of hydrochloric acid by another complexing agent, such as a non-volatile chloride salts (AlCl
3, NH
4Cl, MgCl
2) led to successful results according to different research works [
20,
32,
33]. For example, Lakshamanan and co-workers [
33] proposed that the addition of MgCl
2 to HCl solutions increased the activity of hydrogen ions, helping to improve metal extraction efficiency. Angelidis and Skoraki [
32] found that HCl replacement by AlCl
3 did not affect Pt leaching, whereas the volume of released gases was reduced by 60%. In the current investigation, HCl replacement by CaCl
2 was tested since its high solubility can provide high chloride concentrations in leaching solutions, being simultaneously a relatively low expensive reagent. Moreover, since Al is present in oxide form in the SAAC wash-coat layer, higher acid concentrations would dissolve it more. By substituting HCl by a soluble chloride salt, and simultaneously using a very high solid/liquid (S/L) ratio (1/2 kg/L), less Al concentration in the leachates would be expected, and therefore an improved selectivity towards the PGMs.
The chemical reaction of Pt leaching in chloride media, with hydrogen peroxide as oxidant precursor, can generally be expressed by Equation (1).
As a starting point, the use of high HCl concentrations and simultaneously high S/L ratios (i.e., concentrated pulp densities) would create conditions to decrease the solubility of aluminum chloride in leachates. Accordingly, a concentrated HCl solution (~12 M) was firstly chosen. Combinations of HCl with chloride salts, making a total 12 M chloride concentration, were therefore tested. Regarding temperature, values of 60 and 90 °C were selected, since lower temperatures lead to shorter PGMs recoveries [
19,
20] and, at the same time, temperatures close to the boiling point of water also cause high aluminum contaminations.
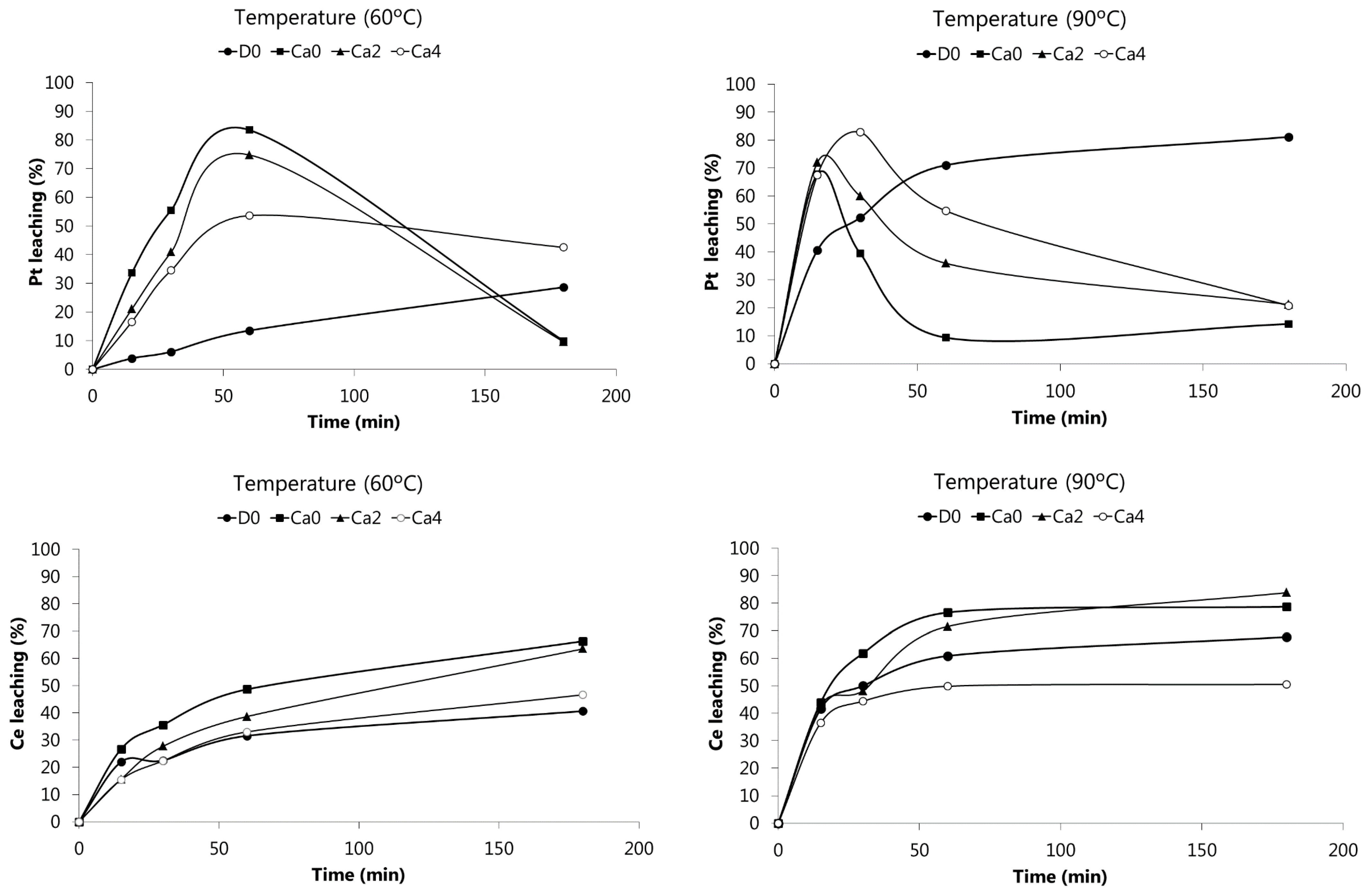
Figure 2 shows the leaching of Pt and Ce at 60 and 90 °C from the SACC powder using the solutions whose composition is summarized in the Materials and Methods section. Note that solutions Ca2 and Ca4 are combinations of HCl and CaCl
2 with constant total chloride concentration (~12 M), while solution D0 was used to evaluate the effect of acid without the presence of salt. Ca0 did not contain any CaCl
2, only HCl (~12 M) and H
2O
2.
The experimental results obtained showed that the percentage of Pt leaching greatly depend on the leaching solution used, on time and temperature. When 4 M HCl was used as leaching agent (solution D0, see Materials and Methods), the concentration of Pt in the leaching liquor increased with time and temperature, with a maximum value of 81% at 90 °C after 3 h of leaching. Leaching solutions with a higher chloride concentration (Ca0, Ca2, Ca4) turned Pt leaching faster (yields above 80% at 30 min for Ca4 at 90 °C, or 1 h for Ca0 at 60 °C). However, after a maximum value leaching, the concentration of Pt in solution significantly decreased (except for Ca0), probably due to a drop in the electrochemical potential leading to reduction and reprecipitation of Pt. This occurred as the oxidant (H2O2) was consumed by the chemical reactions, and also by decomposition. H2O2 decomposition helps to explain why the effect was more pronounced at higher temperatures, since the H2O2 decomposition phenomenon is also faster.
Concerning Ce, its dissolution at 60 °C increased over the leaching time. However, at 90 °C, Ce leaching reached maximum values using Ca0 (79%) and Ca2 solutions (84%). It is worthwhile to mention that leaching of Ce is also a H
2O
2 consumer since this metal is present in the catalyst as Ce(IV) oxide, requiring a reductant to transform Ce(IV) into soluble Ce(III) species. Therefore, H
2O
2 may act simultaneously as oxidant and reducer for different metals. These phenomena point out that leaching of SAACs is a quite complex process, involving a series of reactions that can interfere with each other, turning the interpretation of results difficult. It can however be concluded that the leaching of this SACC sample with Ca0 or Ca2 solutions made the recovery of Ce from the wash-coat possible. Cerium is a rare earth element, classified as CRM by the European Community, and it is being increasingly employed as a component of SACCs based on the high prices of PGMs and on its contribution to the improvement of PGMs catalytic properties [
15].
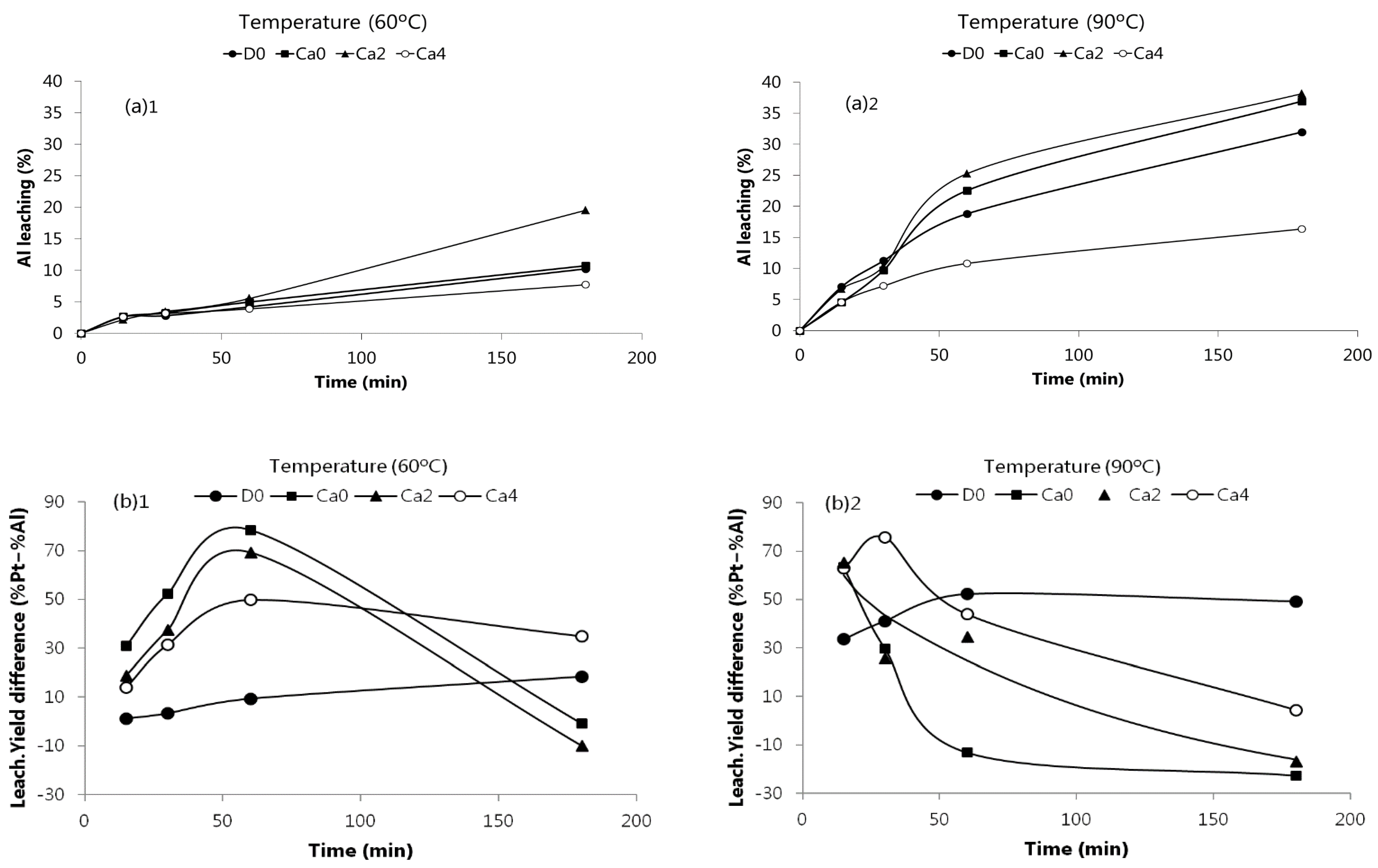
Figure 3 shows Al behavior at 60 and 90 °C using the leaching solutions summarized in Materials and Methods part. Al leaching significantly increased with time, and specially with temperature. At 90 °C, after 3 h leaching, the percentage of Al varied from 16 to 38%. Paiva et al. [
20] also observed similar trends.
Comparing
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, the optimal conditions for an improved leaching of Pt minimizing Al dissolution can be realized. At 60 °C and for 1 h of reaction time high recoveries of Pt can be achieved (75–85%) for the leaching solutions Ca0 and Ca2, with only near 5% Al dissolution. Alternatively, at 90 °C, similar Pt recoveries can be obtained for 20–30 min, but the dissolved Al increased up to 7–10%. The selectivity for Pt against Al can also be examined by plotting the leaching yields difference between these two metals, as depicted in
Figure 3b, in which the higher selectivity attained at 60 °C and for a reaction time of 60 min is shown. Therefore, lower temperatures seem to provide higher selectivity towards Pt. It is also proved that the replacement of part of HCl by CaCl
2, as leachant, is possible, without compromising Pt recovery, as found for the Ca2 mixture (2 M CaCl
2 + 8 M HCl) when compared to Ca0 (11.6 M HCl). The former alternative would present some possible advantages, such as the handling of less concentrated acid solutions and decreasing hazards, gaseous emissions, and corrosion effects. Dealing with concentrated HCl solutions also leads to energy inefficiency due to the volatile character of HCl, consuming latent heat for its evaporation; mixtures of HCl/CaCl
2 can therefore present some benefit in energy consumption, since they are less volatile. Nevertheless, strictly in terms of Pt recovery and Al co-dissolution, the option of using the mixture of calcium salt/acid did not show advantages as could be expected.
The leach liquor produced under the optimized conditions of Ca0 and Ca2 tests allowed the production of leachates with the following composition: 1.1 g L−1 Pt, 4.6 g L−1 Al, and 8.0 g L−1 Ce; 0.97 g L−1 Pt, 5.2 g L−1 Al and 6.4 g L−1 Ce, respectively. The Pt concentrations attained were relatively high, considering its low initial content in the catalyst, and this is the reason why the choice of a high pulp density (S/L ratio) was found appropriate. The concentration ratio Pt/Al obtained was about 1/5, which seems a good result regarding the selectivity of the leaching operation and considering the very high content of Al in the catalyst. Other contaminants (Ca, Mg, Fe) were also analyzed under these optimized conditions, resulting in the following concentrations: in Ca0 leachate, 0.41 g/L Ca, 1.70 g/L Mg and 1.37 g/L Fe; and in Ca2 leachate, 1.87 g/L Mg and 1.40 g/L Fe (Ca was not analyzed, since in Ca2 calcium is part of the leaching agent).
For the preparation of a batch of real SAAC leachate for the SX experiments, the conditions of 11.6 M HCl with 1%vol H2O2, at 60 °C for 1 h were selected. Hence, an experiment involving 170 g of SACC and 340 mL for the optimized leaching solution was then carried out. After filtration, the remaining solution was further diluted with distilled water—see Materials and Methods section.
2.3. Liquid-Liquid Extraction
The SX behavior of DMDCHTDGA towards Pt(IV) recovery from HCl solutions has been previously evaluated [
22,
23]. Generally it has been found that Pt(IV) is efficiently extracted (>95%) by DMDCHTDGA in 1,2-dichloroethane from 5 M or higher concentrated HCl aqueous phases, and that water or 1 M HCl are suitable stripping agents when Pt(IV) is loaded from concentrated HCl solutions [
23]. This extractant shows nevertheless a higher affinity for Pd(II) than for Pt(IV) [
22]. Generally, the selectivity outputs achieved for Pd(II) and Pt(IV) uptake against Al(III) are very promising, but Fe(III) co-extraction is a reality, particularly from the most HCl-concentrated aqueous solutions. Extraction of Fe(III) may not represent a serious drawback though, since its scrubbing from the loaded organic phases can be usually achieved by a simple contact with water [
22]. Additionally, although more efficient for Pd(II) stripping, thiourea in HCl also works for Pt(IV) stripping from the DMDCHTDGA solutions [
23].
Taking the above results into consideration, the testing of DMDCHTDGA performance when applied to the treatment of real leaching solutions coming from secondary resources [
20] was decided. Accordingly, and to find the best conditions to develop a suitable SX methodology to recover Pt effectively and selectively, a model 6 M HCl aqueous phase containing Pt(IV) and the most abundant metals in the SACC leaching solution, namely Fe(III), Al(III) and Ce(III) (having in mind the concentration profiles of those metals in the real SACC leaching solution) was preliminary subject to SX by DMDCHTDGA.
2.3.1. Model Solution with Pt(IV), Ce(III), Al(III) and Fe(III)
A series of experiments was planned to check the general SX behavior of DMDCHTDGA towards Pt(IV) recovery. Hence, a 6 M HCl feed aqueous solution containing about 500 mg L
−1 Pt(IV), 1000 mg L
−1 Fe(III), 1000 mg L
−1 Al(III) and 4000 mg L
−1 Ce(III) was extracted by DMDCHTDGA in toluene, and the loaded organic phase was sequentially contacted with distilled water, a 1 M HCl aqueous phase, and finally with a 0.1 M thiourea in 1 M HCl solution. The overall results achieved, expressed through the respective extraction, scrubbing, and stripping percentages, are displayed in
Table 2.
Regarding extraction, it can be observed that DMDCHTDGA showed a high affinity for Pt(IV) uptake, but also for Fe(III), as expected. On the other hand, Ce(III) and particularly Al(III) were not co-extracted. The first scrubbing of the loaded organic phase with water led to the removal of most part of Fe(III), while Pt(IV) stayed in the organic phase. Scrubbing with 1 M HCl caused a slight elimination of Pt(IV), but not significant. The thiourea solution allowed half recovery of Pt(IV) from the loaded organic phase. The general composition of the final thiourea aqueous solution contained 230.8 mg L−1 Pt(IV), 9.8 mg L−1 Fe(III), 0.5 mg L−1 Al(III) and 0.4 mg L−1 Ce(III).
The selective scrubbing of the extracted Fe(III) by water is an encouraging result, allowing its effective separation from Pt(IV), particularly because Pt(IV) in organic phase remained unaffected. The apparent traceable extraction of Al(III) and Ce(III) is also promising, but the incomplete Pt(IV) stripping by thiourea may compromise a good SX performance, and the finding of alternative stripping agents seems therefore justifiable.
The collected information served as basis for the test of performance of this DMDCHTDGA SX system to recover Pt(IV) from the SACC leaching solution. Hence, experiments to evaluate the loading capability of the organic solution towards Pt(IV), and also its recyclability potential, were envisaged.
2.3.2. SACC Leaching Solution
According to the results obtained from the preliminary experiments, high extractabilities towards Pt and Fe were therefore expected. However, there are much more metallic elements in the SACC leachate apart from the ones considered in the model solution, and that is why analyses of Mg and Ca were also considered, in addition to those of Al and Ce.
Considering the dilution factor, the SACC feed solution used for the experiments described in this section had approximately an 8 M HCl concentration, and the metallic contents were as follows (in mg L−1): Pt: 512; Fe: 718; Al: 2320; Ce: 3609; Ca: 244; Mg: 816.
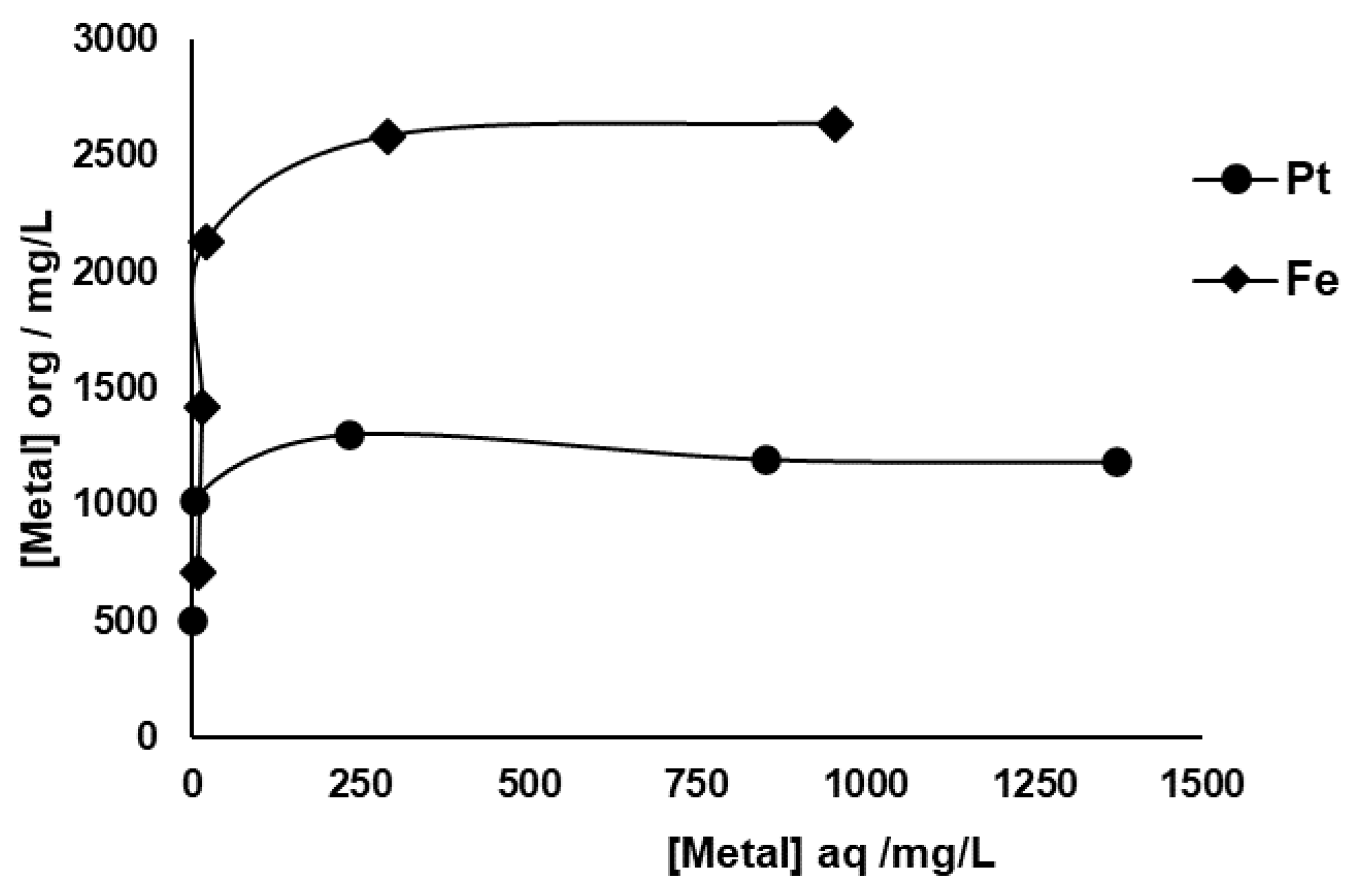
Equilibrium extraction isotherms for Pt and Fe are depicted in
Figure 4, and the data were obtained from the successive loading of the same portion of organic phase containing 0.25 M DMDCHTDGA in toluene with fresh SACC solution, following the experimental conditions described in the Materials and Methods section. The equilibrium metal concentrations in aqueous phase depicted in
Figure 4 are those obtained by the successive sum of the remaining metal portions after each extraction. DMDCHTDGA showed a high loading capacity for Pt and especially for Fe, with about 1303 (achieved at the 3
rd extraction stage) and 2636 mg L
−1, respectively, corresponding to 6.7×10
−3 M Pt and 4.7×10
−2 M Fe. The interference of the remaining metals that were analyzed did not seem notorious, but the analytical errors associated with the most concentrated ones was high, and fluctuations of ±100 mg L
−1 and ±200 mg L
−1, in relation to the initial contents of Al and Ce, respectively, were observed. Regarding Ca, the analytical data suggested that vestigial amounts of about 10 mg L
−1 seem to be extracted, and sequentially released to the aqueous phase. A similar situation is likely to occur with Mg.
Pt loading by DMDCHTDGA could most likely be enhanced by intermediate scrubbings with water, to remove co-extracted Fe from the organic phase. This assumption has not been tested in these experiments, but water may have the effect of co-removing significant amounts of Pt from the organic phase, as the acidity of the feed SACC is higher than in the model solution [
23]. Furthermore, recyclability experiments may or not confirm this hypothesis.
Aliquots of the final loaded organic solution from the equilibrium isotherm experiments were subject to successive contacts with distilled water and 0.1 M thiourea in 1 M HCl solution (2 contacts each). The results obtained were a bit surprising, although a similar tendency has been previously observed [
20]: from 1186 mg L
−1 Pt, only about 6 mg L
−1 Pt were removed by the four contacts. The situation was a bit better for Fe: 969 mg L
−1 (from 2636 mg L
−1) were caught up by the sum of the four solutions, the first contact with water removing 926 mg L
−1 Fe at once. These results suggest that it is much more difficult to strip the metal ions of interest from solutions with metal concentrations near saturation, and/or a bit “dirty” with traces of several contaminating metal ions. Amongst the other analyzed metals, only Ca summed 13.5 mg L
−1, all the others (Al, Mg, Ce) summed 1–2 mg L
−1 in all solutions. These observations may possibly confirm the selectivity of DMDCHTDGA towards Pt and Fe, leaving the other contaminant metals in the raffinate.
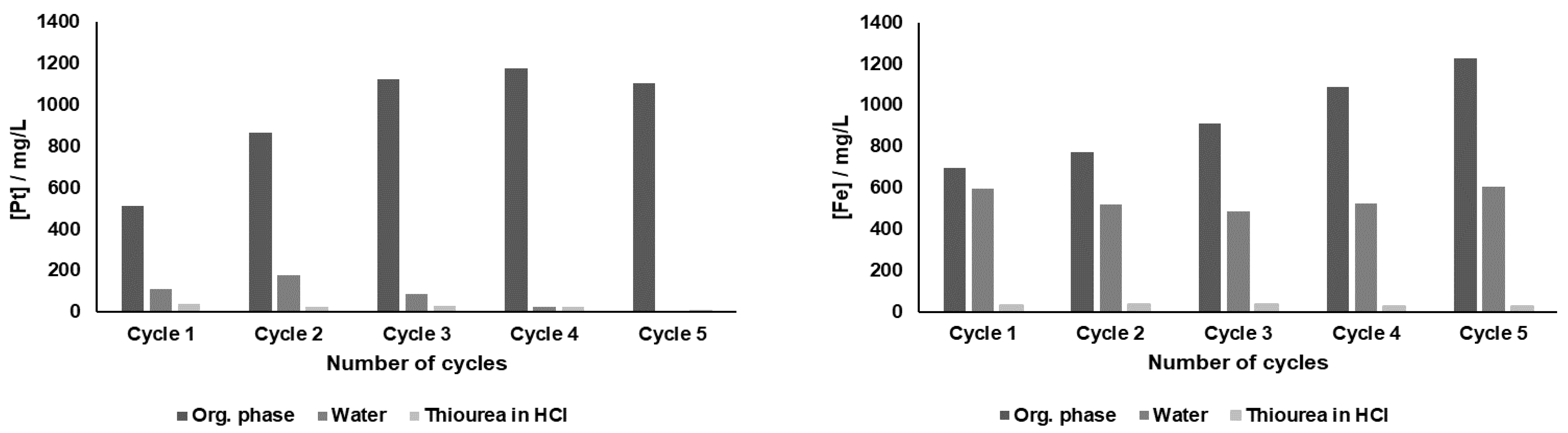
Reutilization experiments of DMDCHTDGA were also performed. In these tests, the same portion of 0.25 M DMDCHTDGA organic phase suffered five sequential extraction-scrubbing-stripping contacts. Each cycle included an extraction, a scrubbing equilibration with distilled water, and a stripping contact with 0.1 M thiourea in 1 M HCl. The data obtained for Pt and Fe is depicted in
Figure 5, in which the metallic concentrations in the organic phase, in water and in thiourea solution are presented.
Deficient Pt removal, both by water and particularly by thiourea in HCl, are the reasons why the recovery of Pt through reutilization of this SX system was not possible. The solvent has a very good saturation profile, and hence Pt was efficiently loaded until the 4th contact, being slightly released to the aqueous phase after the 5th contact. DMDCHTDGA did not reach saturation with Fe, since it increasingly accumulated in the organic phase; water was efficient to remove Fe in the 1st cycle but lost its efficacy for the more concentrated Fe solutions. All thiourea aqueous phases presented traces of Fe.
The profiles obtained for Al, Ce, Ca and Mg showed that there was some accumulation for all of them in DMDCHTDGA in the first two cycles, but from the third cycle onwards the analytical data provided some erratic results, being therefore not reliable.
Data obtained with the model solution, described in
Section 2.3.1, showed that thiourea could only strip half Pt from the organic phase, but these values became much more aggravated for the SACC solution, even for the 1st cycle. Water stripped 111 mg L
−1 and 178 mg L
−1 Pt in the 1st and 2nd cycles, and this did not occur in the SX experiments with the model solution. The high complexity provided by the different metallic species, probably present in the SACC leaching solution, should be the main reason justifying the different results obtained when the model and the SACC aqueous phases are compared, although the diverse HCl concentrations may also play a determinant role.
To find suitable stripping agents for Pt, the remaining loaded DMDCHTDGA organic solutions were additionally subject to additional contacts with alternative scrubbing/stripping agents, namely, 0.1 M NH
4Cl in 1 M NH
3 and 1 M HCl followed by 0.1 M NH
4Cl in 1 M NH
3 [
23]. During the contacts with the ammoniacal solutions, some precipitation occurred and, therefore, the mass balance to determine the metal concentrations cannot be used reliably. Even after separation of the aqueous phases some turbidity appeared, which had tendency to disappear with time. The ICP-AES results of the stripping aqueous solutions did not reveal any appreciable stripping, either for Pt or Fe. Accordingly, these alternative stripping agents for Pt should be tested with fresh DMDCHTDGA, loaded from a model solution, before their use could be extended to more complex situations.