Abstract
The demand for new sources of energy is one of the main quests for humans. At the same time, there is a growing need to eliminate or recover a set of industrial or agroforestry waste sources. In this context, several options may be of interest, especially given the amounts produced and environmental impacts caused. Olive pomace can be considered one of these options. Portugal, as one of the most prominent producers of olive oil, therefore, also faces the problem of dealing with the waste of the olive oil industry. Olive pomace energy recovery is a subject referenced in many different studies and reports since long ago. However, traditional forms of recovery, such as direct combustion, did not prove to be the best solution, mainly due to its fuel properties and other characteristics, which cause difficulties in its storage and transportation as well. Torrefaction and pyrolysis can contribute to a volume reduction, optimizing storage and transportation. In this preliminary study, were carried out torrefaction and pyrolysis tests on olive pomace samples, processed at 300 °C, 400 °C, and 500 °C, followed by laboratory characterization of the materials. It was verified an improvement in the energy content of the materials, demonstrating that there is potential for the use of these thermochemical conversion technologies for the energy recovery of olive pomace.
1. Introduction
Olive oil production is an activity of vital economic importance in Mediterranean countries [1]. Portugal is a reference in modern olive growing, and is expected during next decade to be the third largest producer of olive oil in the world and the seventh largest in terms of occupied area [2]. This growth is sustained by the evolution in the country and, in particular, in Alentejo, Southern Portugal, with the contribution of Alqueva dam that provided the irrigation for intensive crops [3]. For example, in 2018, which saw adverse weather conditions, the results presented in SIAZ—Olive Oil and Table Olives Information System-https://www.gpp.pt—indicated a 30% drop in oil production compared to the previous campaign. Despite this, production was 4% higher than the average production in the last four campaigns. Currently, as the ninth producer in the world, Portugal has 361 thousand hectares of olive groves, and 135 thousand tons of oil extracted.
Olive oil production is associated with the generation of residues, olive pomace, and red waters, which present potentially toxic compositions and are harmful to ecosystems when improperly discharged into the environment [4]. Due to the high levels of oils and fats, the chemical deficiency of oxygen, total solids, polyphenols, and red waters, in order to be able to be sent either to emissaries or directly to the receiving environment, need extremely efficient treatments, with significant investment and operating costs that can make the mills unfeasible. Within these residues, olive pomace has viable forms of recovery already known and in use [5,6,7]. This olive pomace, resulting from the recently introduced two-stage centrifugation system, is a semi-solid, moderately acidic residue formed by pieces of olive stone, olive pulp, and water [8]. Its composition varies according to the variety of olives, fruit ripeness, climatic conditions, and cultivation practices [9]. In general, it consists of high amounts of water (60–70%), residual oil retained in the pulp (2.5–3%), inorganic compounds, and appreciable amounts of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose, as well as other organic matter including proteins, polyalcohols, fatty acids, sugars, polyphenols, and pigments [9,10]. This organic load is responsible for its phytotoxic and antimicrobial characteristics, as well as its high moisture content, making it difficult to handle, store, and transport [11,12].
In recent years, many efforts have been made to find a way to efficiently recover olive pomace in order to add commercial value to this waste [13,14]. Within the forms of recovery already studied and mentioned in the literature, bioconversion of these residues into fertilizers can be highlighted, including application in the production of animal feed, the use as a substrate for the production of bioethanol/biomethane and biohydrogen, and bioconversion in some biopolymers or enzymes for other industries [15].
Despite all the advantages that are described in the literature for these conversion technologies, as capable of processing residual biomass mainly due to its ability to homogenize different types of raw materials with different qualities, these technologies still present restrictions, namely with regard to its scalability, and the fact that large production units must operate continuously. Many recent developments have been achieved, mainly with regard to process control and stability. However, it cannot yet be considered a mature technology, so a large investment in R&D is still needed.
Torrefaction and pyrolysis are thermochemical conversion technologies that present as main difference the temperature range where occur, being, respectively, 220 °C to 320 °C for torrefaction, and 320 °C to 600 °C for pyrolysis [16]. Both processes take place at atmospheric pressure, in an oxygen-poor environment, where residence times vary according to the purpose for which the process is intended, and in the case of roasting, the final yield tends towards the solid fraction, whereas in pyrolysis, this yield tends normally to the liquid fraction [17]. The use of these technologies for the processing of agroforestry residues is already widely documented in the bibliography, with some previous work already dedicated specifically to the thermo-conversion of olive pomace, mainly because these processes allow a very significant volume reduction, at the same time that confer properties such as hydrophobicity, thus allowing a more efficient storage without the risk of reaction with water or withstanding biological activity [18,19,20,21].
This work aims to evaluate the potential of using olive pomace as a renewable energy source in the perspective of circular economy, where waste is reused and incorporated into a new production cycle. For this, the research was divided into different stages, starting with the characterization of olive pomace, namely with regard to its original properties that will serve as a standard, followed by torrefaction and pyrolysis in a muffle at different temperatures, respectively, 300 °C, 400 °C, and 500 °C, followed by the determination of a set of characteristics, which allow the evaluation of the potential to improved energy recovery processes, optimizing circular economy in olive oil industrial sector, assuming definitively the potential that these materials present, provided that the initial disadvantages as a fuel are overcome, for example, with the use of technologies such as torrefaction or pyrolysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection and Preparation
In this study, several analyses were carried out to characterize the evolution of the olive pomace properties resulting from the torrefaction and pyrolysis processes. Thus, different techniques were used, such as thermogravimetric analysis, elemental analysis, and heating value. The olive pomace samples analyzed, were collected in an olive oil extraction plant that operates in a two stages process, in the region of Vila Real (Northern Portugal), in the 2019 campaign.
Olive pomace samples were dried at a temperature of 90 °C for 6 h. Samples were weighed to be approximately 500 g and wrapped in aluminum foil to ensure an atmosphere with low oxygen content, as presented in Figure 1. Tests were carried out in duplicate, placing two samples at the same time in each batch, to guarantee their reproducibility.

Figure 1.
Assemblage of the samples in aluminum foil for torrefaction and pyrolysis tests.
For torrefaction and pyrolysis, the experimental protocol described by Ribeiro et al. (2018) [22] was applied, which proposed using a high-temperature oven for thermochemical processes used already in other previous studies, such as that one presented by Sá et al. (2020) [23]. The samples were torrefied and pyrolyzed in the muffle, which was programmed according to temperature (°C) and residence time (minutes) as presented in Table 1. The selection of parameters was done in a sequential manner, taking into account the results obtained for each one of the tests carried out. Initial and processed materials are presented in Figure 2.

Table 1.
First series of conversion tests.
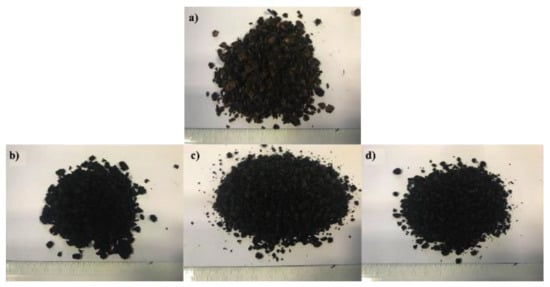
Figure 2.
(a) Dried sample; (b) 300 °C; (c) 400 °C; and (d) 500 °C.
2.2. Determination of Elemental Composition
To determine the elemental composition was used a CHN analyzer in accordance with the procedure described in the standard EN 15104: 2011—Solid Biofuels—Determination of Total Content of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen—Instrumental Methods. After obtaining the results for carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen content, the following equation was used to calculate the oxygen content:
where w(O) is the oxygen content (%), w(C) is the carbon content (%), w(H) is the hydrogen content (%), and w(N) is the nitrogen content (%).
w(O) = 100 − w(C) − w(H) − w(N)
2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was conducted in accordance with the procedures described in the standards EN 14775: 2009—Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content, EN 15148: 2009—Solid Biofuels—Determination of Volatiles Content and EN 14774-3: 2009—Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content. The entire procedure requires ground materials before being introduced into the melting pots, which were loaded with approximately 1 g of material.
2.4. Determination of Heating Value
To determine HHV, the equation deduced by Parikh et al. (2005) was used as follows [24]:
where HHV(db) is the High Heating Value (MJ.kg−1) on a dry basis, FC is the Fixed Carbon (%) content, V is the Volatile content (%), and A is the Ash content (%).
HHV(db) = 0.3536FC + 0.1559V − 0.0078A
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elemental Analysis
The results obtained in the analysis of the elemental composition are shown in Table 2. As already mentioned, all analyses were performed in duplicate, so the value presented is the average, and the same applies to all the following results.

Table 2.
Ultimate analysis for the different process temperatures.
The determined sulfur (S) content proved to be lower than the lower detection limit of the equipment used in the analysis, so it was considered, for the purposes of calculating other parameters, to be equal to the referred limit value, which was 0.01% on a dry basis. However, in relation to the S content present in olive pomace, a more rigorous determination of the levels that can be found in these residues will be necessary, since there are very different opinions among other works on the subject [25,26,27,28,29,30].
In the elemental analysis, there is a decrease in the levels of hydrogen and oxygen, which is understood as normal, due to the fact that with the increase in temperature there is a devolatilization of hydrogenated and oxygenated compounds, mainly related to the depolymerization of hemicellulose, when the process takes place at 300 °C, and lignin and cellulose, when the temperature is increased to 400 °C and 500 °C.
The nitrogen content remains practically unchanged during the different tests at different temperatures, with a small concentration at 400 °C. Nitrogen is eliminated from the solid yield when 500 °C is reached, most likely due to the formation of some compounds, such as light nitriles (acetonitrile, propanenitrile), long chain nitriles and amides, pyrrolic and pyrrolidinic compounds, and diketopiperazines (DKPs), as stated in several previous research works [31,32,33], and that are emitted at this stage.
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
The results obtained in the analysis of the proximate composition are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Proximate composition for the different process temperatures.
The TGA results highlight the evolution of fixed carbon, which increases significantly from 18.84% to 82.14%. This fact indicates, first, a directly proportional increase in heating value, but it also opens the door to the creation of products with more added value, which may even justify other studies. Concerning the ashes, there is also an increase in the content, from the initial 1.31%, to 3.51% at 500 °C, which is due to the fact that the loss of mass leads to this concentration of the mineral fraction, which is not lost through the volatilization of oxygenated compounds. Volatile content also presents an expected behavior, since it decreases throughout the process, being minimal in the material produced at 500 °C, with a value of 14.36%.
3.3. Heating Value
The results obtained for the calculation of High Heating Value (HHV) are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
High Heating Value (HHV) calculated for the different process temperatures.
The determination of HHV by the method described by Parikh et al. (2005) [24] allows the evaluation of the energy content of a fuel by knowing other properties, such as fixed carbon, volatile and ash content. Thus, the initial heating value of the thermally untreated sample, of 19.20 MJ.kg−1, increases up to 31.26 MJ.kg−1. These values are in accordance to those presented in previous studies, such as the presented by Guizani et al. (2016), where a two-step process based on torrefaction and combustion is proposed for olive pomace recovery and where is concluded that torrefaction improves strongly the combustion properties [20].
The mass loss verified during the tests was, respectively, 37%, 76%, and 78%. This result can be interesting if associated with the energy recovery is also the environmental issue of reducing the volume of waste generated. Previous studies such as those from Bridgeman et al. (2008) found yields for torrefaction of Phalaris arundinacea, processed in a range of temperatures comprised from 230 to 290 °C, with mass losses of 7% to 32% [34]. Bergman and Kiel (2005) report typical values of 20% for mass loss [35]. Felfli et al. (2005) found mass losses from 6% to 46%, respectively for temperatures from 220 °C to 270 °C, for wooden briquettes processed for a period of 60 min [36]. Concerning higher temperature tests can be found several in the literature available [37,38,39]. However, once in these studies the technology used was fast high temperature pyrolysis, the main objective was to obtain a gaseous yield the highest possible, being in the majority of the cases reached 95% [37]. When comparing the results obtained in the tests conducted in the present study with those found in the referred literature, mass loss results for torrefaction temperature range can be considered similar. For the pyrolysis temperature range, above 300 °C, it was not possible to find comparable results, once the procedures used to the obtention of the samples were considerably different from the one used here.
4. Conclusions
Torrefaction and pyrolysis are thermochemical conversion processes that can be the starting point for the development of other conversion technologies. That is, can act as pre-processing technologies before the use of other processes for the production of energy and for a more efficient methodology to reduce waste volumes. It is already possible to find many cases in the literature in reference to the use of these materials in biomass gasification and liquefaction processes, where olive pomace can be included.
The results obtained in this preliminary study showed a significant increase of 11.5%, 57%, and 63% for the heating value, respectively, for the tests performed at 300 °C, 400 °C, and 500 °C, with mass losses of 37%, 76%, and 78%. In this way, the options defined by the tests at 400 °C and 500 °C are potentially interesting, since mass loss, although significant, may allow the process to become viable. However, it is necessary to carry out further tests, namely, using a torrefaction unit on a pilot-industrial scale, in order to confirm the feasibility of the processes.
It is possible to see that there is a strong probability that these technologies can contribute to the resolution of a set of problems, namely, through the elimination and recovery of a set of waste, such as those resulting from the olive oil industry, which are responsible for great environmental concerns, but also because can be an alternative to the production of renewable fuels that allow, for example, the replacement of others with fossil origin, guaranteeing the continuity of its operation, and thus the existence of backup units that ensure the stability of the energy supply, when other renewable sources, more intermittent, are unable to assure it.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.J.R.N.; methodology, L.J.R.N. and H.F.C.S.; validation, L.J.R.N., L.C.R.S. and L.M.E.F.L.; formal analysis, L.J.R.N.; investigation, L.J.R.N., L.C.R.S., L.M.E.F.L.; resources, H.F.C.S.; data curation, L.J.R.N., L.C.R.S. and L.M.E.F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.J.R.N.; writing—review and editing, L.J.R.N. and H.F.C.S.; supervision, L.J.R.N.; funding acquisition, H.F.C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Portuguese companies YGE—Yser Green Energy SA, and AFS—Advanced Fuel Solutions SA, both in Portugal, for the execution of the laboratory tests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Visioli, F.; Bellosta, S.; Galli, C. Oleuropein, the bitter principle of olives, enhances nitric oxide production by mouse macrophages. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekaj, M.; Hernández, P.; Fonseca, A.; Rivera, M.; Żmija, K.; Żmija, D. Uncovering Production Flows from Small Farms: Results from Poland and Portugal Case Studies. Rocz. Nauk. Stowarzyszenia Ekon. Rol. I Agrobiz. 2019, 21, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Jiménez-Morillo, N.T.; Freitas, F.; Garcia, R.; da Silva, M.G.; Cabrita, M.J. Revisiting 3D van Krevelen diagrams as a tool for the visualization of volatile profile of varietal olive oils from Alentejo region, Portugal. Talanta 2020, 207, 120276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azbar, N.; Bayram, A.; Filibeli, A.; Muezzinoglu, A.; Sengul, F.; Ozer, A. A review of waste management options in olive oil production. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 34, 209–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarian, B.; Casazza, A.A.; Perego, P. Valorization of olive oil solid waste using high pressure–high temperature reactor. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, M.S.; Abdulrahim, S.M.; Al-Khawaldeh, G.Y.; Robinson, R.K. Solid state fermentation of waste pomace from olive processing. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 1999, 74, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, A.; Cayuela, M.L.; Sánchez-Monedero, M. An overview on olive mill wastes and their valorisation methods. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Caranfa, L. Improvement of soil properties by application of olive oil waste. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Albarrán, A.; Nunes, J.R.; Barreto, C. Short and medium-term effects of two-phase olive mill waste application on olive grove production and soil properties under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7982–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantila, N.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic properties of olive oil and olive pomace polar extracts in rabbits. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 36204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, J.; Antizar-Ladislao, B.; Monteoliva-Sánchez, M.; Ramos-Cormenzana, A.; Russell, N. Bioremediation and biovalorisation of olive-mill wastes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, L.; Asses, N.; Chammem, N.; Othman, N.B.; Hamdi, M. Advanced oxidation process and biological treatments for table olive processing wastewaters: Constraints and a novel approach to integrated recycling process: A review. Biodegradation 2017, 28, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanakis, C.M. Recovery of high added-value components from food wastes: Conventional, emerging technologies and commercialized applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Martínez, M.; Miralles, N.; Poch, J.; Serarols, J. Sorption of Pb (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solution by olive stone waste. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J. A Case Study about Biomass Torrefaction on an Industrial Scale: Solutions to Problems Related to Self-Heating, Difficulties in Pelletizing, and Excessive Wear of Production Equipment. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Matias, J.; Catalão, J. Torrefied Biomass Pellets: An alternative fuel for coal power plants. In Proceedings of the 2016 13th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Porto, Portugal, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Brachi, P.; Chirone, R.; Miccio, M.; Ruoppolo, G. Fluidized bed torrefaction of biomass pellets: A comparison between oxidative and inert atmosphere. Powder Technol. 2019, 357, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barskov, S.; Zappi, M.; Buchireddy, P.; Dufreche, S.; Guillory, J.; Gang, D.; Hernandez, R.; Bajpai, R.; Baudier, J.; Cooper, R. Torrefaction of biomass: A review of production methods for biocoal from cultured and waste linocellulosic feedstocks. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 624–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizani, C.; Haddad, K.; Jeguirim, M.; Colin, B.; Limousy, L. Combustion characteristics and kinetics of torrefied olive pomace. Energy 2016, 107, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellatoğlu, N.; İlkan, M. Effects of torrefaction on carbonization characteristics of solid olive mill residue. BioResources 2016, 11, 6286–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Godina, R.; Matias, J.C.d.O.; Nunes, L.J.R. Future perspectives of biomass torrefaction: Review of the current state-of-the-art and research development. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá, L.C.; Loureiro, L.M.; Nunes, L.J.; Mendes, A.M. Torrefaction as a pretreatment technology for chlorine elimination from biomass: A case study using Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Resources 2020, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, J.; Channiwala, S.; Ghosal, G. A correlation for calculating HHV from proximate analysis of solid fuels. Fuel 2005, 84, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.; Arranz, J.; Montero, I.; Román, S.; Rojas, C.; Nogales, S. Characterization and combustion of olive pomace and forest residue pellets. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 103, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliche-Quesada, D.; Leite-Costa, J. Use of bottom ash from olive pomace combustion in the production of eco-friendly fired clay bricks. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.; Nogales, S.; Román, S.; Montero, I.; Arranz, J.I.; Sepúlveda, F.J. Control of several emissions during olive pomace thermal degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18349–18361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, T.; Román, S.; Arranz, J.; Rojas, S.; González, J.; Montero, I. Emissions from thermal degradation of pellets with different contents of olive waste and forest residues. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Papalia, T.; Settineri, G.; Romeo, F.; Mallamaci, C. Three different methods for turning olive pomace in resource: Benefits of the end products for agricultural purpose. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranchi, M.; Giannetto, C.; De Pascale, A. Economic analysis and energy valorization of by-products of the olive oil process:“Valdemone DOP” extra virgin olive oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, O.; Villot, A. Nitrogen products and reaction pathway of nitrogen compounds during the pyrolysis of various organic wastes. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 114, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wen, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, N. Nitrogen transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 5088–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Ko, J.-E. Analysis of cyclic pyrolysis products formed from amino acid monomer. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8443–8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgeman, T.; Jones, J.; Shield, I.; Williams, P. Torrefaction of reed canary grass, wheat straw and willow to enhance solid fuel qualities and combustion properties. Fuel 2008, 87, 844–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.C.; Kiel, J.H. Torrefaction for biomass upgrading. In Proceedings of the 14th European Biomass Conference, Paris, France, 17–21 October 2005; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Felfli, F.F.; Luengo, C.A.; Beat n, P.A. Wood briquette torrefaction. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2005, 9, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakcı, S.B.; Aydemir, H. Pyrolysis of olive pomace and copyrolysis of olive pomace with refuse derived fuel. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, R.; Messineo, A.; Millan, M.; Volpe, M.; Kandiyoti, R. Assessment of olive wastes as energy source: Pyrolysis, torrefaction and the key role of H loss in thermal breakdown. Energy 2015, 82, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounas, A.; Aboulkas, A.; Bacaoui, A.; Yaacoubi, A. Pyrolysis of olive residue and sugar cane bagasse: Non-isothermal thermogravimetric kinetic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11234–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).