The Influence of Nanoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Carpet Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
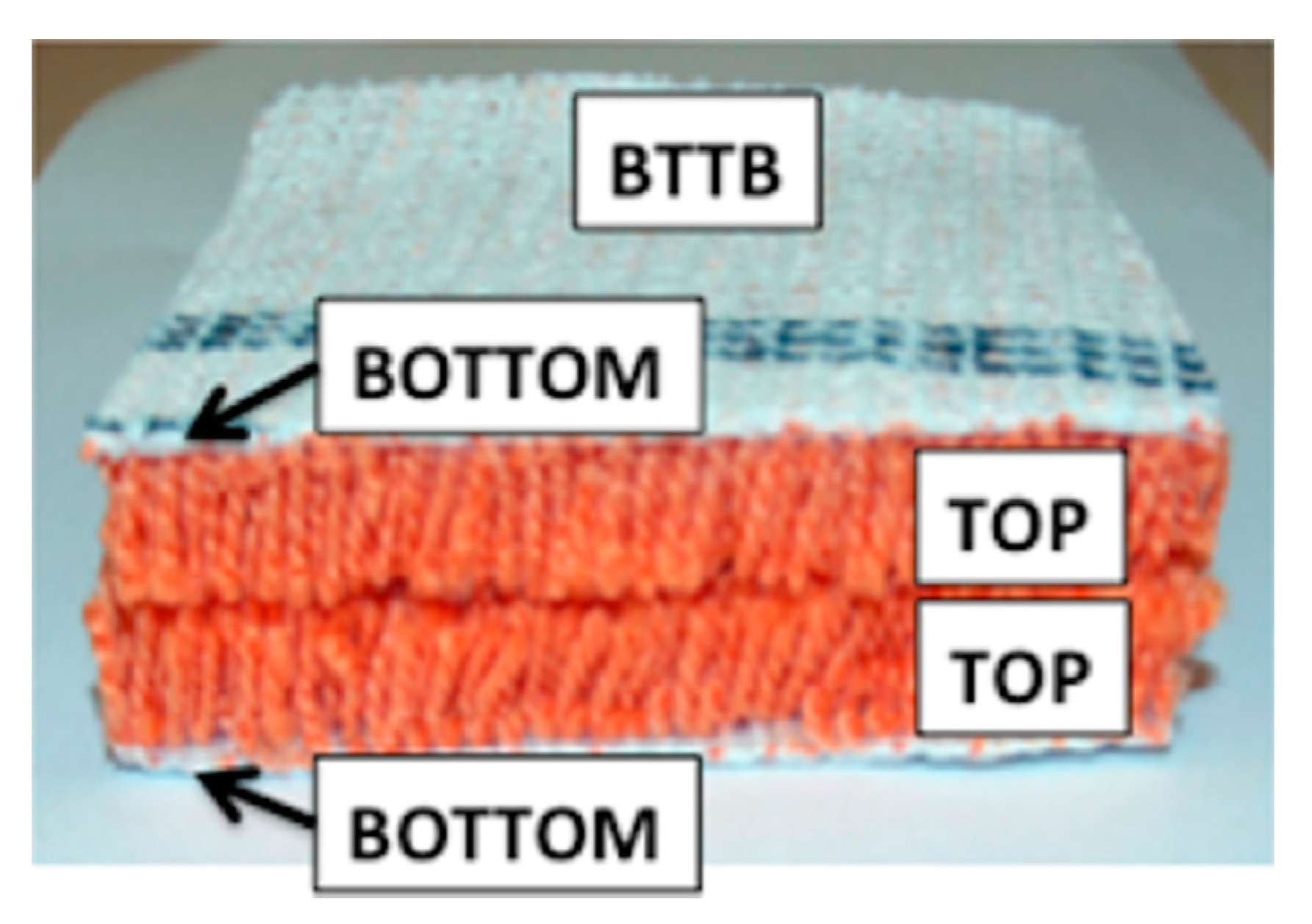
2.2. Fabrication of Carpet Composites
2.3. Moisture and UV Exposure
2.4. Characterization of Mechanical Properties
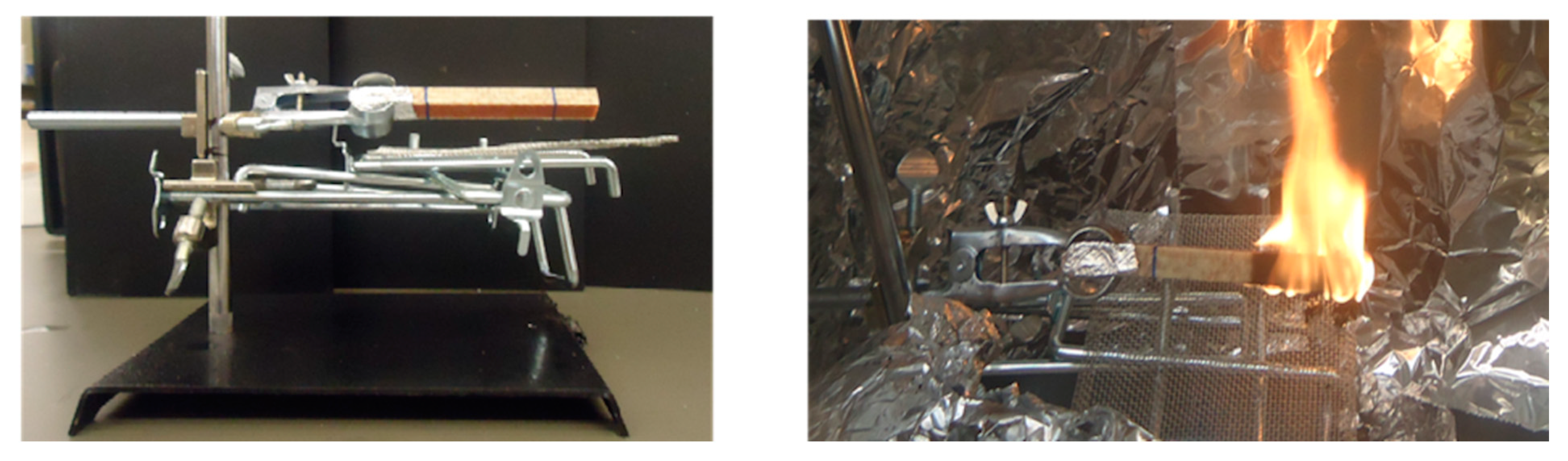
2.5. Flammability Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
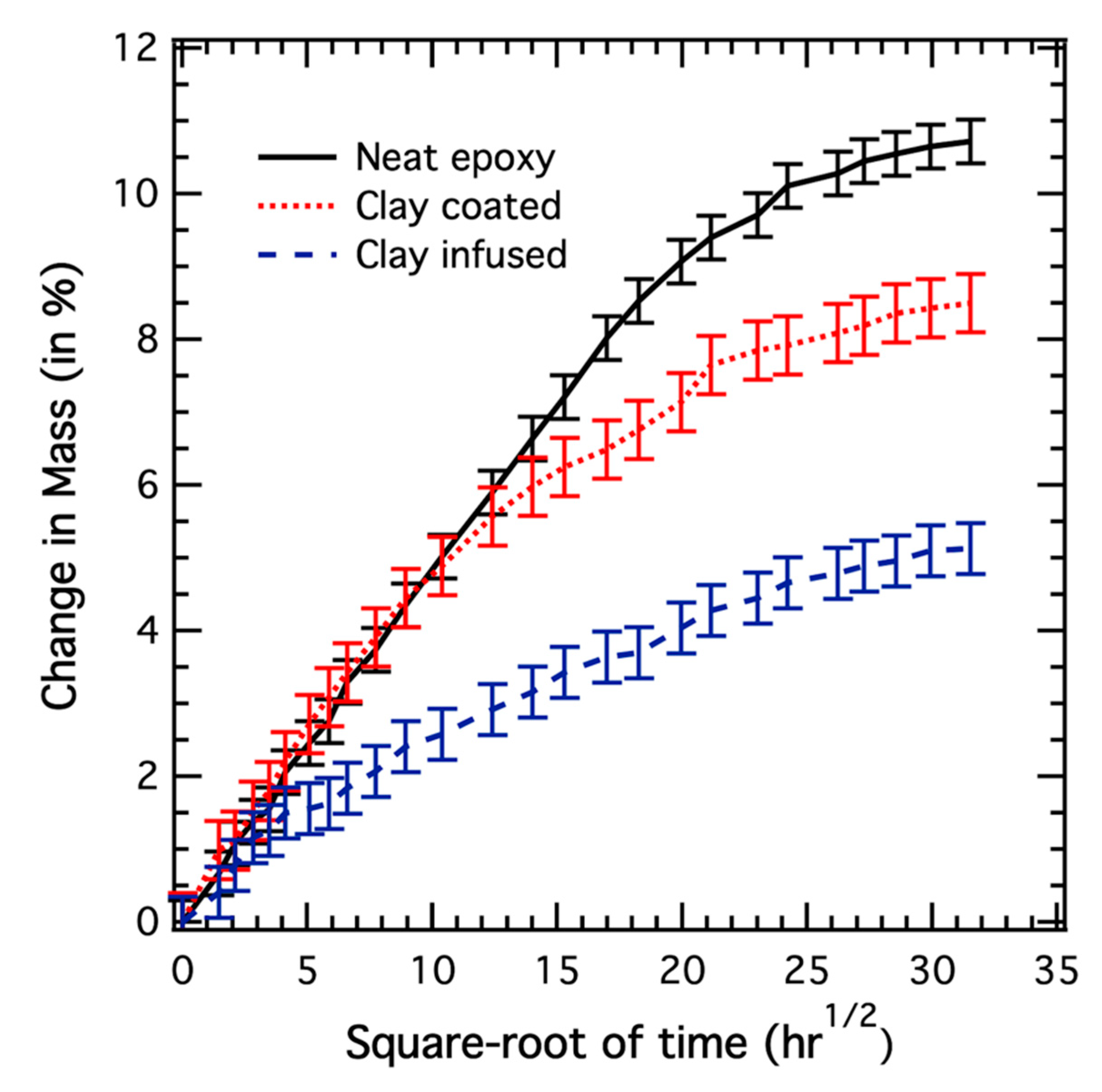
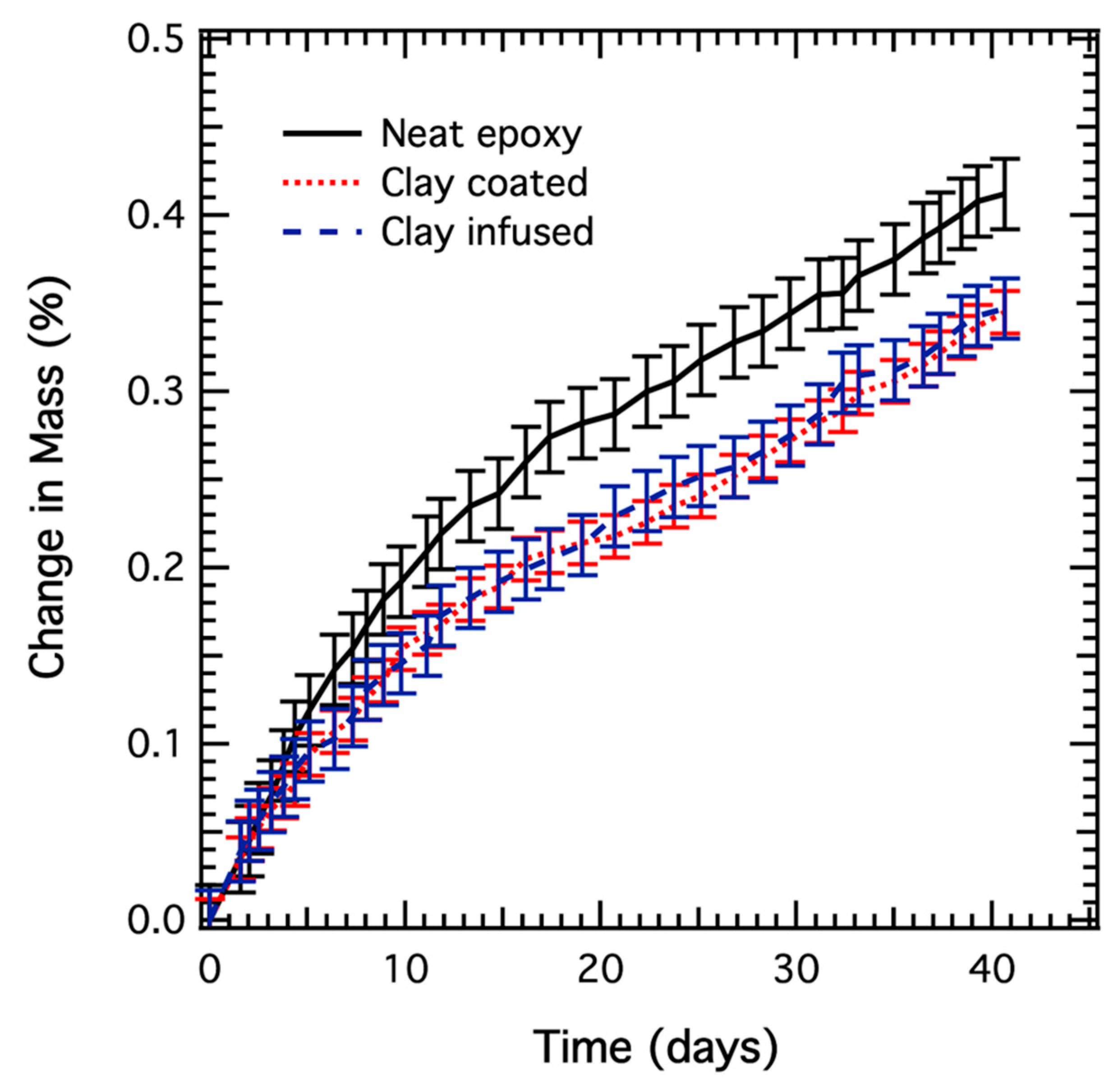
3.1. Gravimetric Analysis
3.2. Mechanical Properties
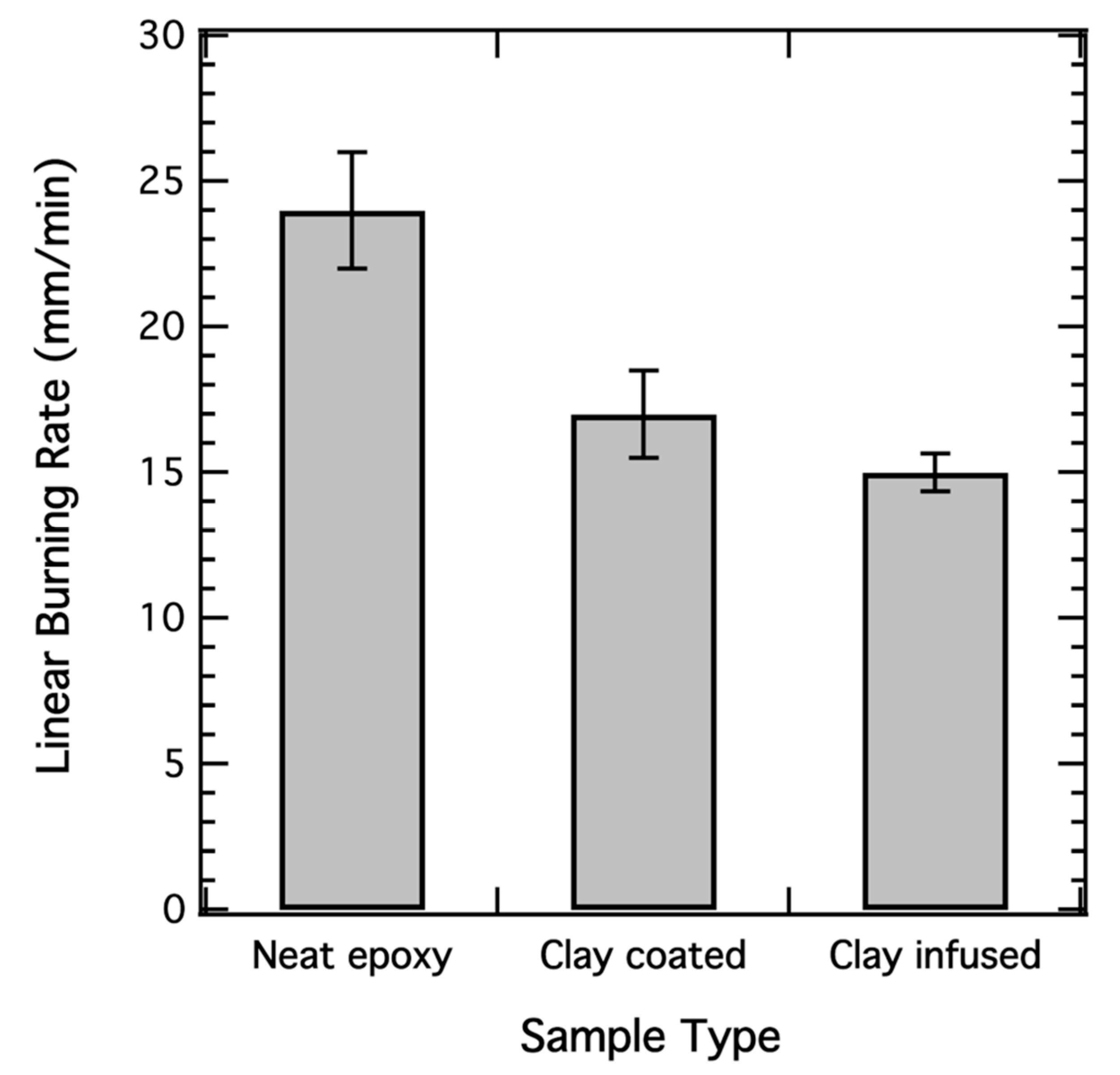
3.3. Flame Retardancy Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mihut, C.; Captain, D.K.; Gadala Maria, F.; Amiridis, M.D. Review: Recycling of nylon from carpet waste. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 1457–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.C.; Chlystek, S.J.; Malloy, R.; Rios, I.; Lear Corporation. Recycling of carpet scrap. US Patent 5,859,071, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salem, S.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, K.; Vaidyanathan, R.K. Application of Recycled Carpet Composite as a potential Noise Barrier in Infrastructure Applications. Recycling 2019, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Das, S.; Vaidyanathan, R. The Use of Recycled Carpet in Low-Cost Composite Tooling Materials. Recycling 2019, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Sims, D. Weathering of Polymers; Springer, Science & Business Media: Essex, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Abeysinghe, H.; Edwards, W.; Pritchard, G.; Swampillai, G. Degradation of crosslinked resins in water and electrolyte solutions. Polymer 1982, 23, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Hu, C.; Woo, R.S.C.; Sham, M.L. Moisture barrier characteristics of organoclay-epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soles, C.L.; Chang, F.T.; Bolan, B.A.; Hristov, H.A.; Gidley, D.W.; Yee, A.F. Contributions of the nanovoid structure to the moisture absorption properties of epoxy resins. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1998, 36, 3035–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soles, C.L.; Yee, A.F. A discussion of the molecular mechanisms of moisture transport in epoxy resins. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2000, 38, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, P.; Karasz, F. Epoxy-water interactions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, R.; Frontini, P.M.; Mai, Y.W. Effect of hygrothermal ageing on morphology and indentation modulus of injection moulded nylon 6/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, Z.; Berry, J. Hygrothermal aging studies of short carbon fiber reinforced nylon 6.6. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 51, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J. Environmental Effects on Crack Growth in Composites. In Comprehensive Structural Integrity; Milne, I., Ed.; Elsevier: Swansea, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, R.S.C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, J.; Kim, J.K.; Leung, C.K.Y. Environmental degradation of epoxy-organoclay nanocomposites due to UV exposure. Part I: Photo-degradation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 3448–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, W.; Tseng, F. The effect of long term ultraviolet light irradiation on polymer matrix composites. Polym. Compos. 1998, 19, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, C.; Pearce, E.; Bulkin, B.; Reimschuessel, H. FTIR spectroscopic study on the photo- and photooxidative degradation of nylons. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2003, 25, 2301–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, F. Clays, nanoclays, and montmorillonite minerals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Clay-reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 2216–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Lau, K.; Wong, T.; Ho, M.; Hui, D. Mechanism of reinforcement in a nanoclay/polymer composite. Compos. B Eng. 2011, 42, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerda, A.S.; Lesser, A.J. Intercalated clay nanocomposites: Morphology, mechanics, and fracture behavior. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudalakis, G.; Gotsis, A. Permeability of polymer/clay nanocomposites: A review. Europ. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.; Mather, P.; DeVries, K. Reinforcement and environmental degradation of nylon-6/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 2001, 42, 5849–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.B.; Wilkie, C.A. Flame Retardant Polymer Nanocomposites; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Castrovinci, A.; Camino, G. Fire-retardant mechanisms in polymer nanocomposite materials. In Multifunctional Barriers for Flexible Structure: Textile, Leather and Paper; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Nazare, S.; Kandola, B.; Horrocks, A. Flame retardant unsaturated polyester resin incorporating nanoclays. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G154-16. Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Light Apparatus for UV Expo- sure of Nonmetallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G154-16. Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Rein- forced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G154-16. Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Glaskova, T.; Aniskevich, A. Moisture absorption by epoxy/montmorillonite nanocomposite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2711–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, L.K.; Mishra, K.; Hamim, S.U.; Singh, R.P. Effect of excess silane on the viscoelastic behavior of epoxy under hygrothermal conditions. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 84, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.L.; Wu, M.D. Organoclay effect on mechanical responses of glass/epoxy nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2008, 42, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.S.; Parkinson, A. Ultraviolet derivative absorption spectra of nylon 6, 6: Effect of photolysis versus photo-induced oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1982, 4, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, L.K.; Mishra, K.; Singh, R.P. Near–fiber effects of UV irradiation on the fiber–matrix interphase: A combined experimental and numerical investigation. Mater. Des. 2018, 157, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Singh, R.P. Effect of APTMS modification on multiwall carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Comp. Part B 2019, 162, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Seo, D.I.; Lee, J.R. Surface modification of montmorillonite on surface acid- the base characteristics of clay and thermal stability of epoxy/clay nanocomposites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Type | As-Is | Flexural Strength (MPa) Hygrothermal Degraded | Cyclic UV Condensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | 27.1 ± 3.4 | 20.9 ± 1.1 | 37.3 ± 4.2 |
| Clay-coated | 27.9 ± 2.1 | 22.6 ± 1.4 | 36.4 ± 1.1 |
| Clay-infused | 30.6 ± 0.9 | 26.9 ± 1.1 | 37.1 ± 1.9 |
| Sample Type | As-Is | Flexural Modulus (GPa) Hygrothermal Degraded | Cyclic UV Condensation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | 1.84 ± 0.11 | 0.89 ± 0.04 | 2.03 ± 0.06 |
| Clay-coated | 1.87 ± 0.07 | 1.10 ± 0.04 | 2.18 ± 0.04 |
| Clay-infused | 1.96 ± 0.06 | 1.39 ± 0.16 | 2.17 ± 0.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mishra, K.; Vaidyanathan, R. The Influence of Nanoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Carpet Composites. Recycling 2019, 4, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020022
Mishra K, Vaidyanathan R. The Influence of Nanoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Carpet Composites. Recycling. 2019; 4(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMishra, Kunal, and Ranji Vaidyanathan. 2019. "The Influence of Nanoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Carpet Composites" Recycling 4, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020022
APA StyleMishra, K., & Vaidyanathan, R. (2019). The Influence of Nanoclay on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Performance of Recycled Carpet Composites. Recycling, 4(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020022





