The Use of Ca- and Mg-Rich Fly Ash as a Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus—Recycling and Reuse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Precipitants
2.1.2. Digestate from an Anaerobic Digestion Plant
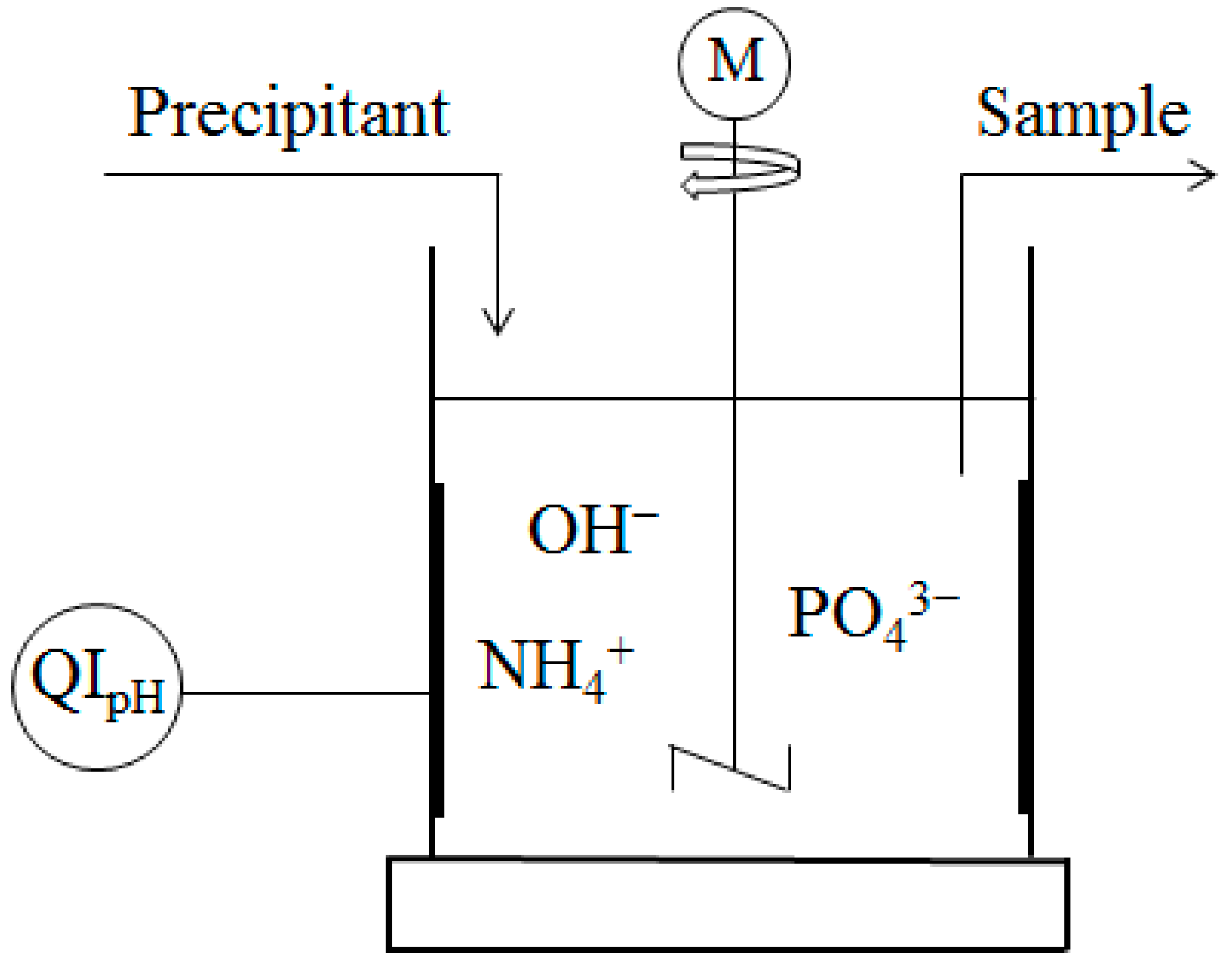
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Description of Analytical Equipment
3. Results
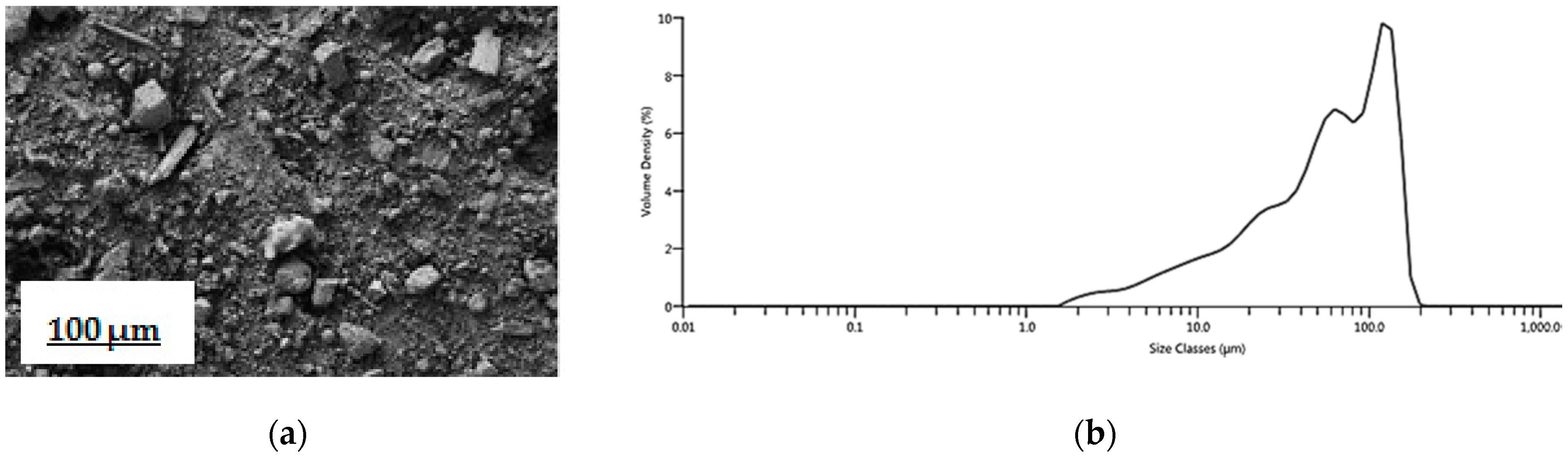
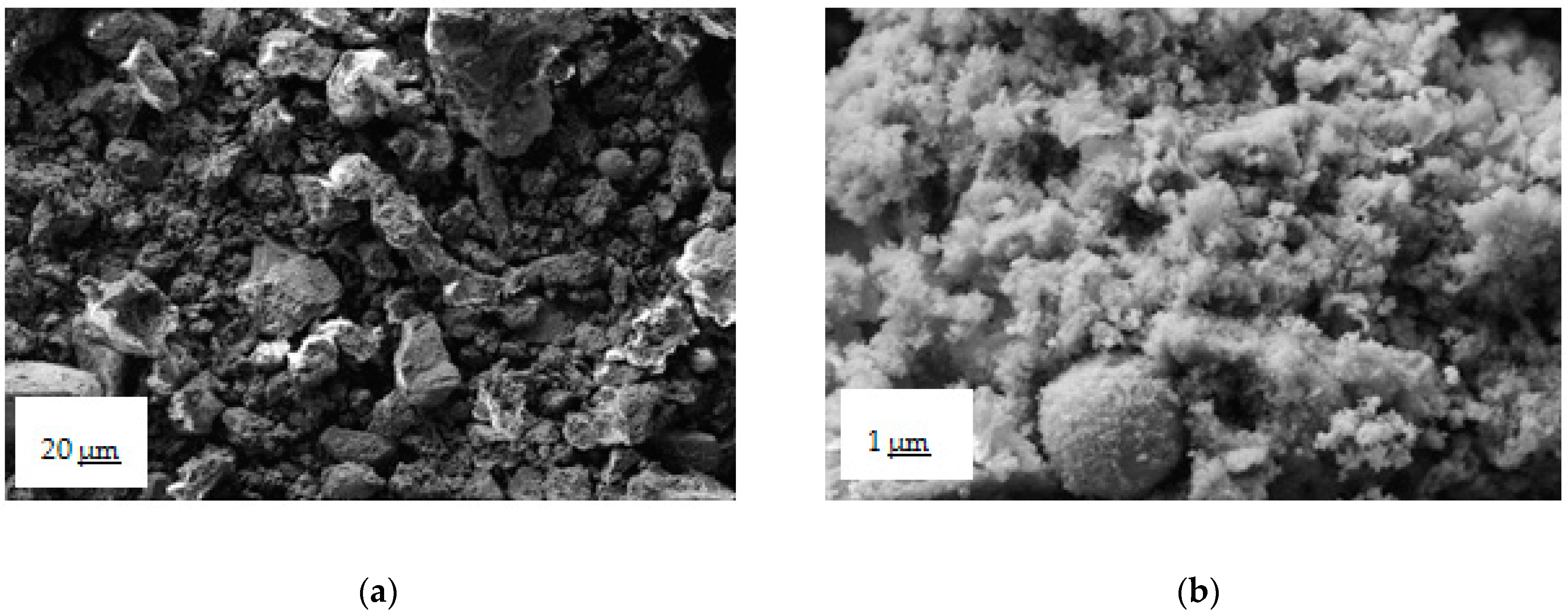
3.1. Fly Ash
3.2. Solid Phase and Liquid Phase of the Anaerobic Digestate
3.3. Results of the Synthetic Solution Experiments
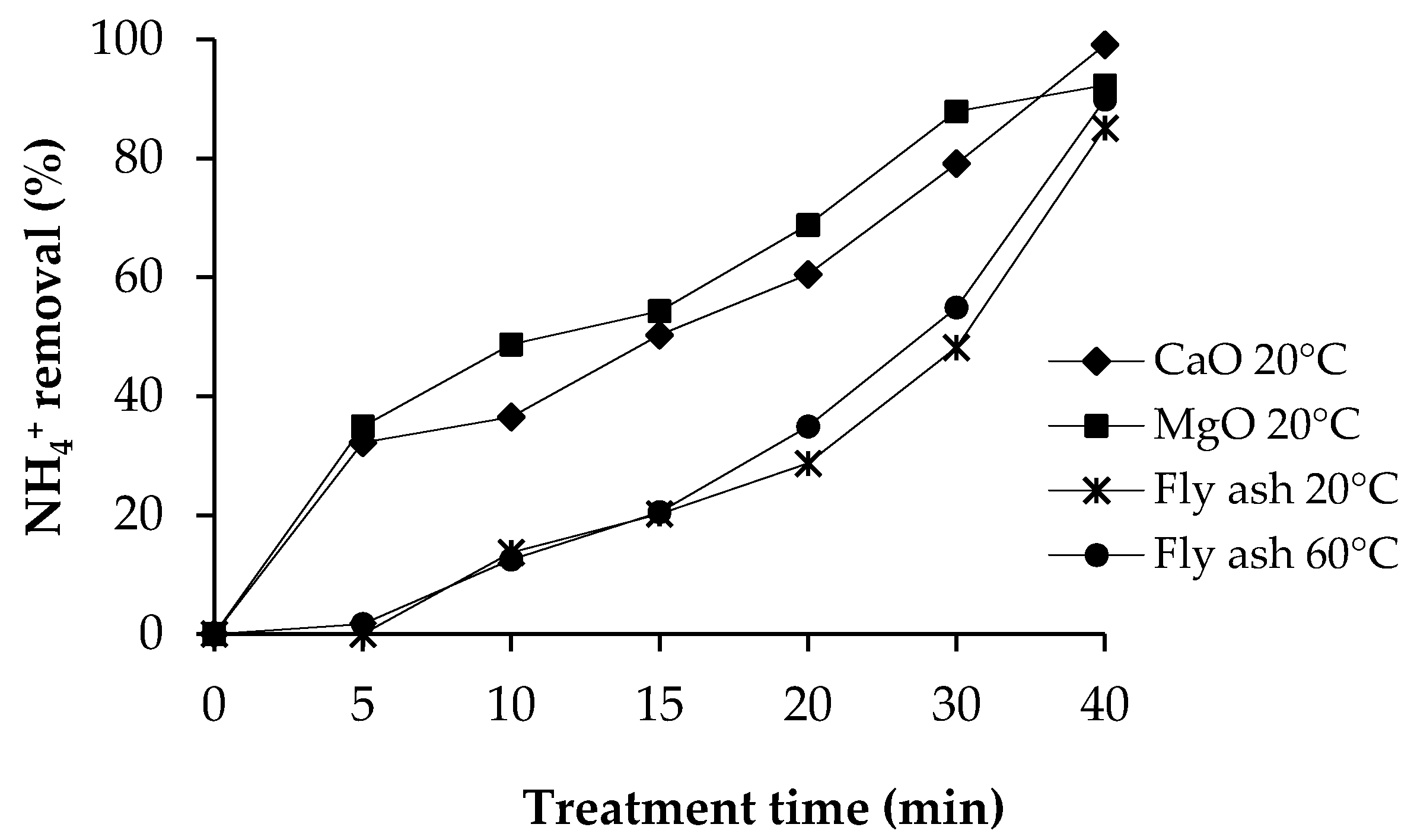
3.3.1. Ammonium Removal
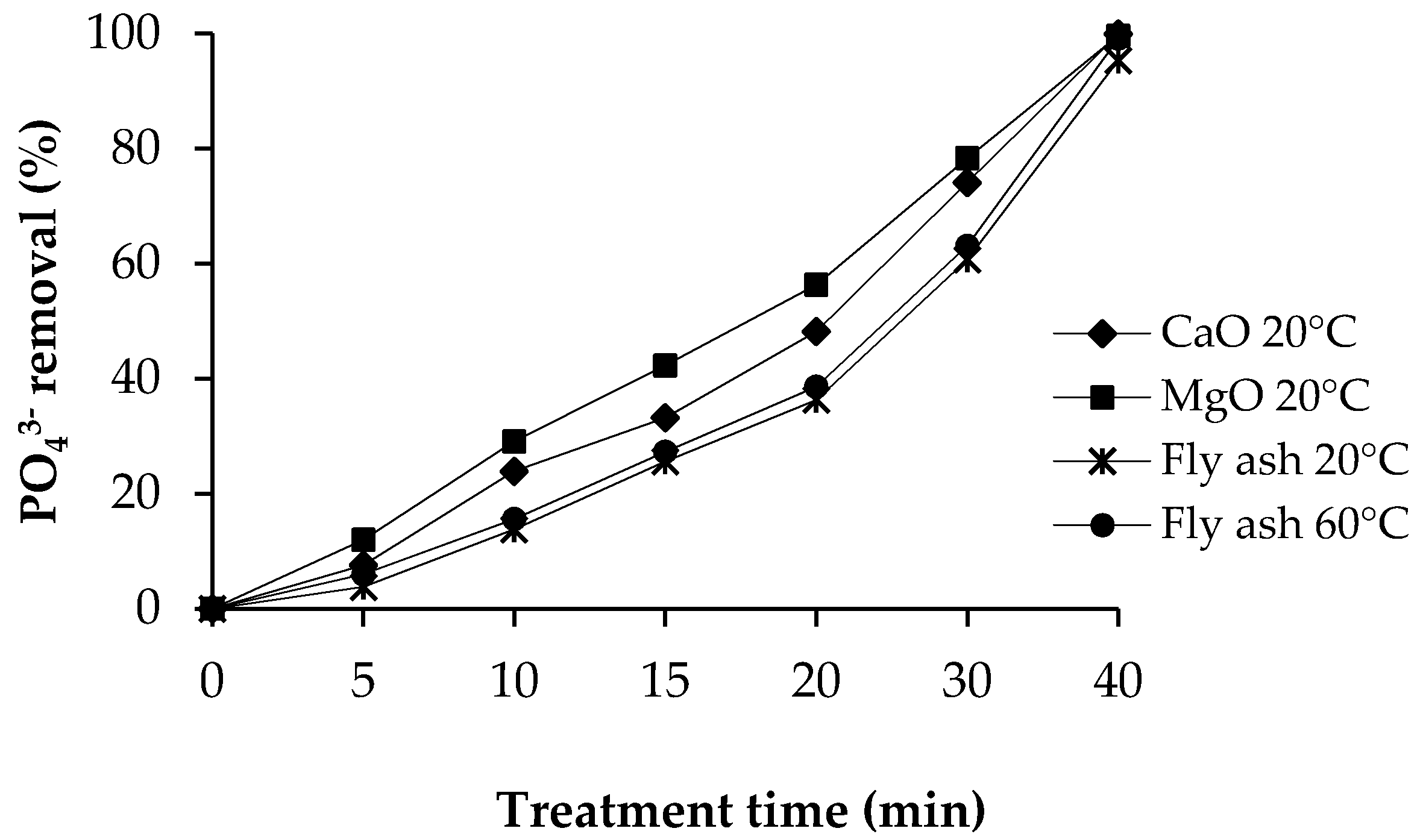
3.3.2. Phosphate Removal
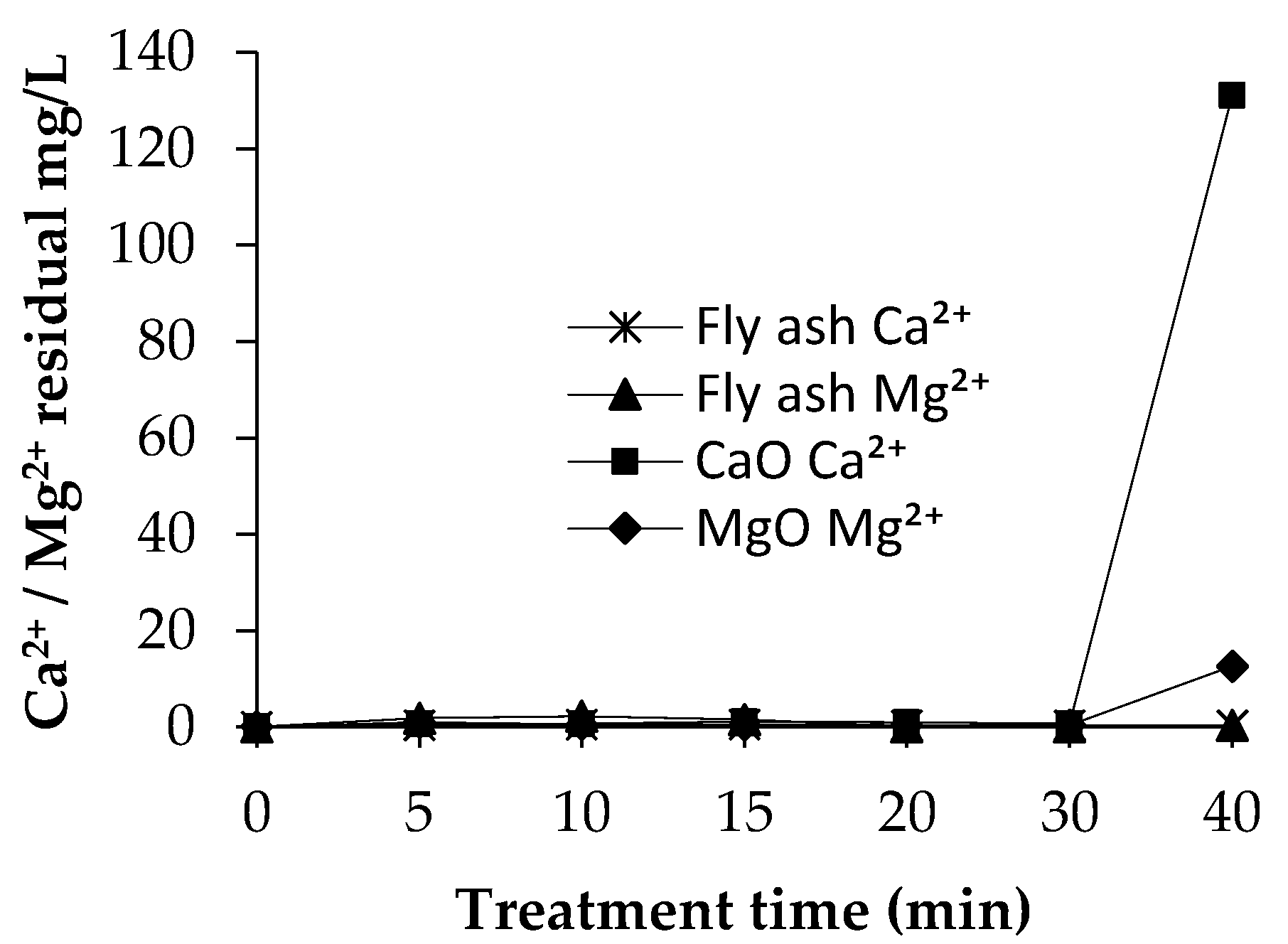
3.3.3. Residual Concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+
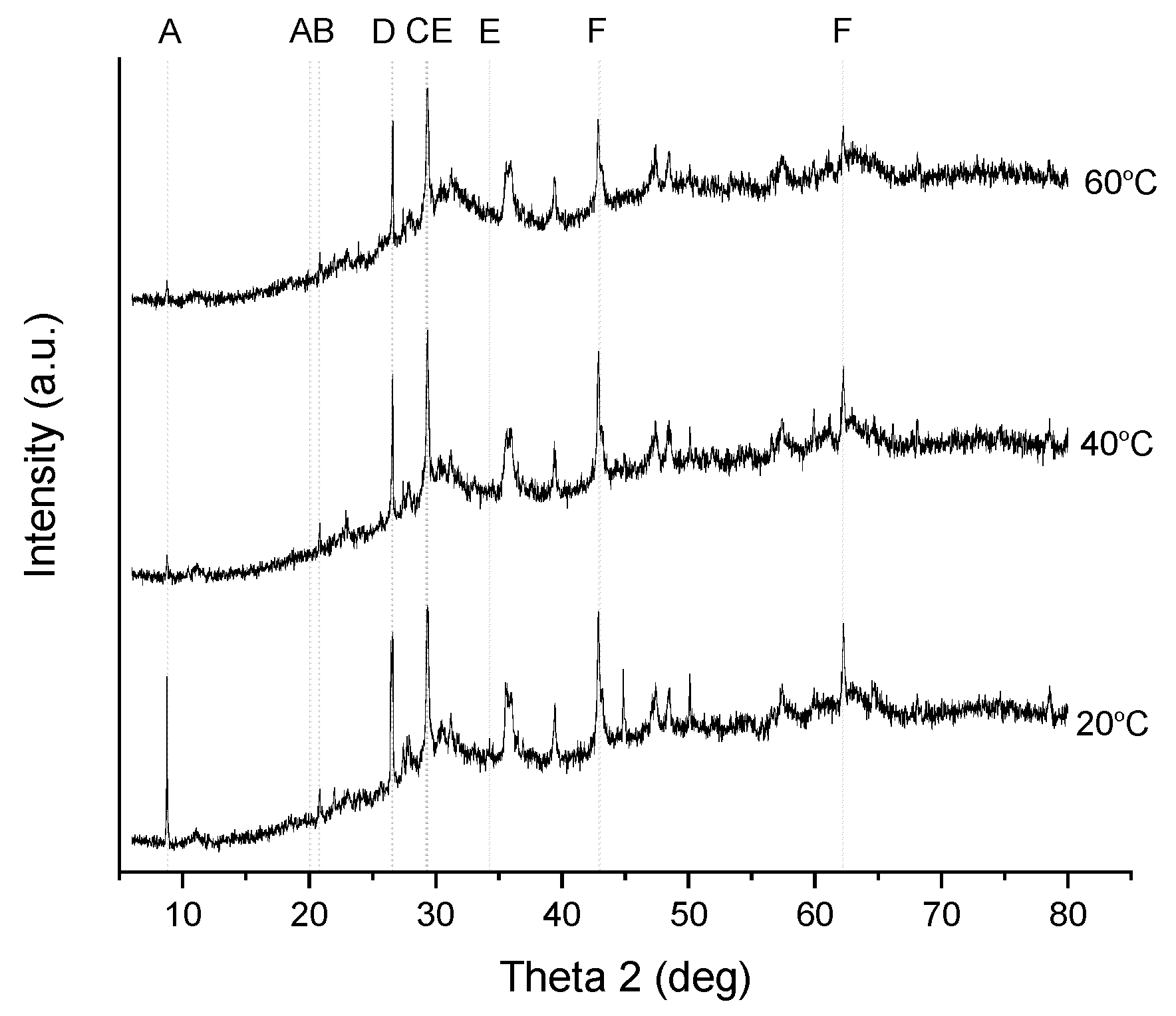
3.3.4. Characterization of Precipitates
3.4. Results of the Authentic Solution Experiments
3.4.1. Ammonium Nitrogen and Phosphate Removal
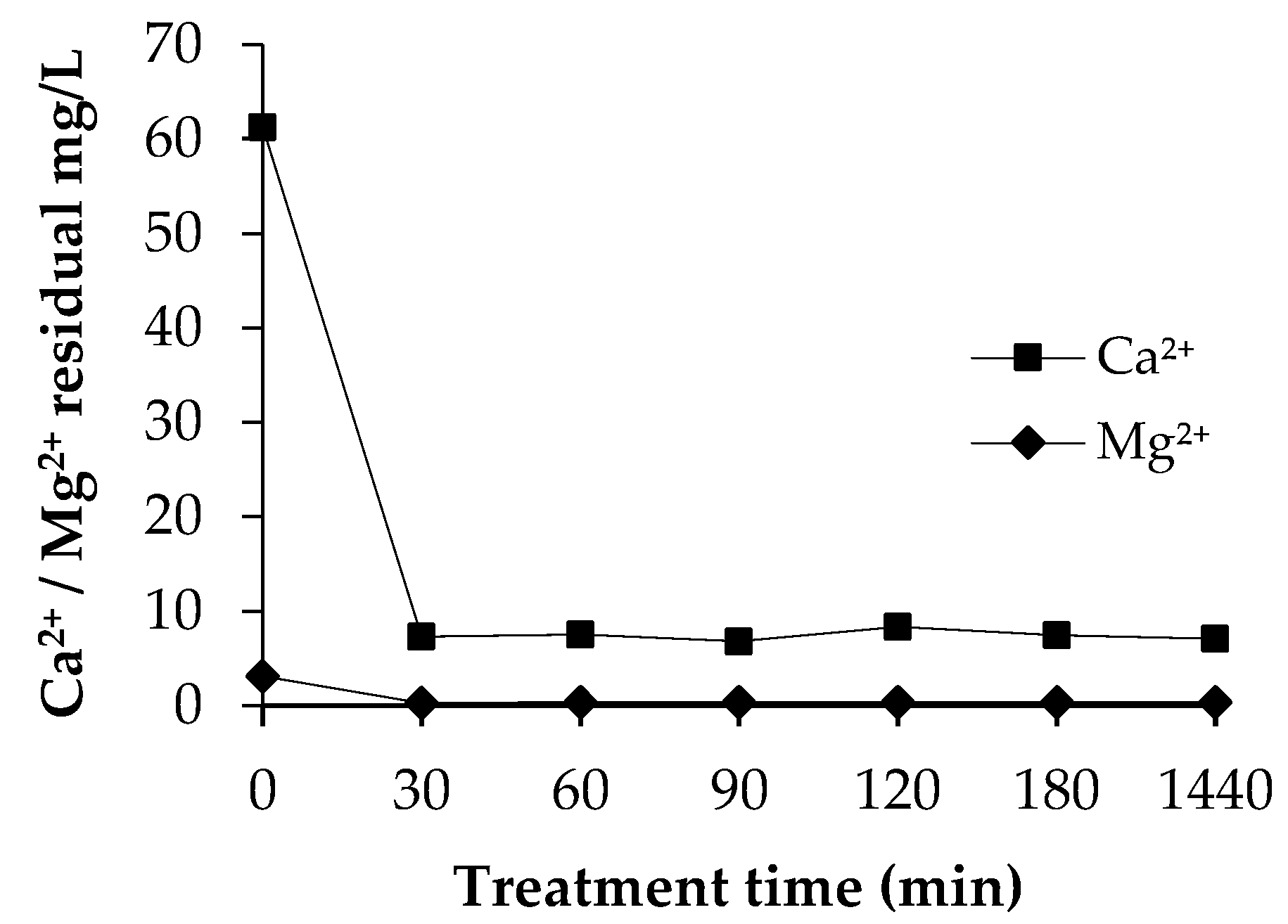
3.4.2. Residual Concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+
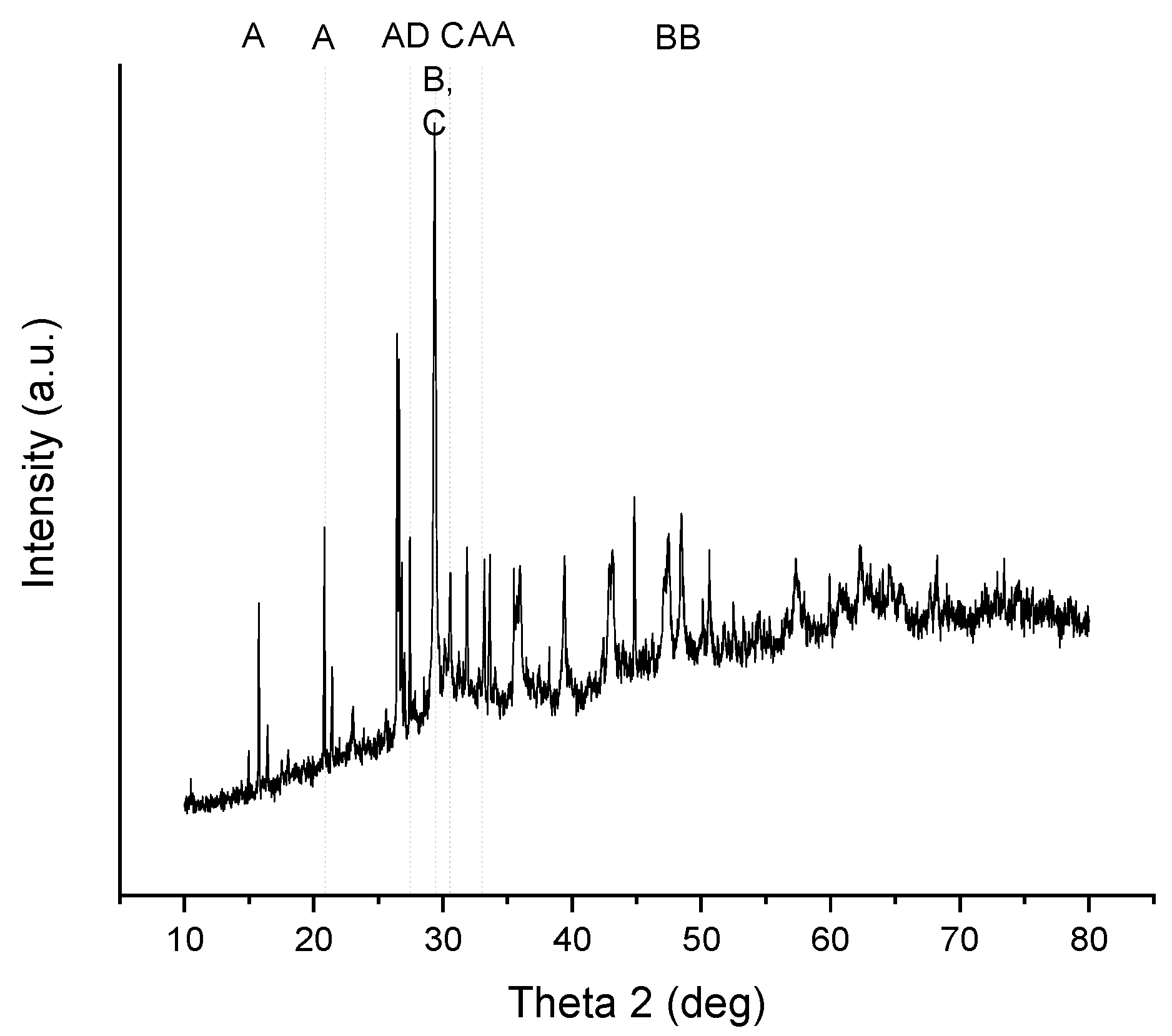
3.4.3. Characterization of Precipitates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission 2018: Circular Economy Strategy—Environment—European Commission. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/circular-economy/index_en.htm (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- European Commission 2018b: Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32008L0098 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Sokka, L.; Pakarinen, S.; Melanen, M. Industrial symbiosis contributing to more sustainable energy use—An example from the forest industry in Kymenlaakso, Finland. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, S.; Manninen, K.; Leskinen, P. Combining biogas LCA reviews with stakeholder interviews to analyse life cycle impacts at a practical level. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, S.; Venelampi, O.; Iho, A.; Koikkalainen, K.; Lehtonen, E.; Luostarinen, S.; Rasa, K.; Sarvi, M.; Tampio, E.; Turtola, E.; et al. Kohti Ravinteiden Kierrätyksen Läpimurtoa; Luonnonvara- ja biotalouden tutkimus 45/2017; Luonnonvarakeskus: Helsinki, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pan-in, S.; Sukasem, N. Methane production potential from anaerobic co-digestions of different animal dungs and sweet corn residuals. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latvala, M. Biokaasun Tuotanto Suomalaisessa Toimintaympäristössä; Suomen Ympäristö 24/2009; Suomen ympäristökeskus: Helsinki, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, J.; Herbes, C.; Nelles, M. Biogas digestate marketing: Qualitative insights into the supply side. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2015, 104, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission 2003: Regulation (EU) No 2003/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council Relating to Fertilizers. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/FI/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32003R2003&from=FI (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- European Commission 2009: Animal by-products Regulation (EU) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/FI/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32009R1069 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Finnish Legislation 2006: The Act on Fertilizer Products 539/2006. Available online: https://www.finlex.fi/fi/laki/ajantasa/2006/20060539 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Bolan, N.S.; Wong, L.; Adriano, D.C. Nutrient removal from farm effluents. Bioresource Technol. 2004, 94, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Zang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lei, S.; Xiao, R. Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, M. Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from eutrophic waters using natural calcium-rich attapulgite-based versatile adsorbent. Desalination 2014, 351, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektaş, N.; Akbulut, H.; Inan, H.; Dimoglo, A. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by electro-coagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, A.; Udert, K.M. Struvite precipitation from urine with electrochemical magnesium dosage. Water Res. 2013, 47, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos-Castillo, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Brillas, E.; Sirés, I. Removal of metals and phosphorus recovery from urban anaerobically digested sludge by electro-Fenton treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpimaa, S.; Runtti, H.; Kangas, T.; Lassi, U.; Kuokkanen, T. Physical activation of carbon residue from biomass gasification: Novel sorbent for the removal of phosphates and nitrates from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Veznikova, K.; Tolonen, E.T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2017, 39, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvers, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aho, M.; Pursula, T.; Saario, M.; Miller, T.; Kumpulainen, A.; Päällysaho, M.; Autio, M.; Hillgren, A.; Descombes, L. Ravinteiden Kierron Taloudellinen Arvo ja Mahdollisuudet Suomelle; Sitra: Helsinki, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kataki, S.; West, H.; Clarke, M.; Baruah, D.C. Phosphorus recovery as struvite: Recent concerns for use of seed, alternative Mg source, nitrogen conservation and fertilizer potential. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2016, 49, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Mavinic, D.S.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H.; Koch, F.A. Exploring the determination of struvite solubility product from analytical results. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, M.; Yao, M.; Tsuno, H.; Somiya, I. Removal and recovery of phosphate and ammonium as struvite from supernatant in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelen, I.; Türker, M. Recovery of Ammonia as Struvite from Anaerobic Digester Effluents. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O. Nutrient recovery by struvite precipitation, ion exchange and adsorption from source-separated human urine—A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2018, 7, 106–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.D.; Wang, C.C.; Lan, L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Struvite formation, analytical methods and effects of pH and Ca2+. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdalen, I. Phosphorus Recovery from Municipal Wastewater; Norwegian University of Science and Technology: Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, J.; Kwag, J.; Ra, C. Magnesium ammonium phosphate formation, recovery and its application as valuable resources: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, M.; Szara, E.; Sosulski, T.; Wąs, A.; van Pruissen, G.W.P.; Cornelissen, R.L.; Borowik, M.; Konkol, M. A Bio-Refinery Concept for N and P Recovery—A Chance for Biogas Plant Development. Energies 2019, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRM Alliance. Critical Raw Materials. Available online: www.criticalrawmaterials.org/critical-raw-materials.OK (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Gunay, A.; Karadag, D.; Tosun, I.; Ozturk, M. Use of magnesit as a magnesium source for ammonium removal from leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.M.; Xiao, X.M.; Yang, L.P.; Yan, B. Removal of ammonium from rare-earth wastewater using natural brucite as a magnesium source of struvite precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A.; De Rosa, S. Recovery of ammonia in digestates of calf manure through a struvite precipitation process using unconventional reagents. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, L. Treatment of swine wastewater combined with MgO-saponification wastewater by struvite precipitation technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchik, D.; Sánchez, A.; Garrido, J.M. Simulation and experimental validation of multiple phosphate precipitates in a saline industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.; Wang, J. Characterization of induced struvite formation from source-separated urine using seawater and brine as magnesium sources. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.R.; Tilley, E.; Udert, K.M. Wood ash as a magnesium source for phosphorus recovery from source-separated urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 419, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.W.; Lehr, J.R.; Smith, J.P. Calcium Ammonium Orthophosphates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1964, 12, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Decree on Fertilizer Products 24/2011; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Helsinki, Finland, 2011.
- Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Perämäki, P.; Kuokkanen, T.; Välimäki, I. Leachability of metals in fly ash from a pulp and paper mill complex and environmental risk characterization for eco-efficient utilization of the fly ash as a fertilizer. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2005, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, T.; Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Rämö, J. Sequential leaching of heavy metals and sulfur in bottom ash and fly ash from the co-combustion of wood and peat at a municipal district heating plant. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2006, 18, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M.; Kuokkanen, T.; Lassi, U. Stabilization/solidification of fly ash from fluidized bed combustion of recovered fuel and biofuel using alkali activation and cement addition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Kuokkanen, T.; Rautio, P.; Lassi, U. Bioavailability of nutrients and harmful elements in ash fertilizers: Effect of granulation. Biomass Bioenerg. 2017, 100, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepua: Jepuan Biokaasu. Available online: https://jeppobiogas.fi/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/TUOTESELOSTE-2018.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Wäger-Baumann, F. Physical and Biological Methods for the Treatment of the Liquid Fraction of Anaerobic Digester Effluent; University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yunqin Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Tan, S. Ammonium removal from digested effluent of swine wastewater by using solid residue from magnesium-hydroxide flue gas desulfurization process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Yuan, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen recovery from anaerobically digested sludge using a hybrid system coupling hydrothermal pretreatment with MAP precipitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, M.Y.; Yildiz, E. Phosphate removal from water by fly ash: Factorial experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B135, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.; Aris, A.; Puteh, M.H.; Jusoh, M.N.H.; Kadir, A.A. Waste bones ash as an alternative source of P for struvite preciptation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L. Industrial by-products and natural substrata as phosphorus sorbents. Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K.; Kojima, T.; Minawa, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakamachi, K. Development of artificial seed crystal for crystallization of calcium phosphate. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Substance | CaO (wt%) | SiO2 (wt%) | MgO (wt%) | FeO (wt%) | Al2O3 (wt%) | K2O (wt%) | P2O5 (wt%) | S (wt%) | TiO2 (wt%) | Others (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34.6 | 22.4 | 14.7 | 8.7 | 7.7 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 5.8 |
| As (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | <10 | <10 | <60 | 80 | <20 | <70 | 600 |
| Limit value field fertilizers/forest fertilizers | 25/40 | 1.5/25 | 300 | 600/700 | 100/150 | 100/150 | 1500/4500 |
| Wet Basis (kg/m3) | Dry Basis (g/kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 5.0 | 138 |
| Soluble nitrogen (N) | 3.1 | 84 |
| Phosphorus | 0.8 | 21 |
| Soluble phosphorus (P) | 0.083 | 2.3 |
| Potassium (K) | 1.4 | 39 |
| pH | NH4+ (mg/L) | PO43− (mg/L) | Ca (mg/L) | Mg (mg/L) | K (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.7 | 700 | 470 | 61.2 | 3.1 | 69.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Myllymäki, P.; Pesonen, J.; Romar, H.; Hu, T.; Tynjälä, P.; Lassi, U. The Use of Ca- and Mg-Rich Fly Ash as a Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus—Recycling and Reuse. Recycling 2019, 4, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020014
Myllymäki P, Pesonen J, Romar H, Hu T, Tynjälä P, Lassi U. The Use of Ca- and Mg-Rich Fly Ash as a Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus—Recycling and Reuse. Recycling. 2019; 4(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMyllymäki, Pekka, Janne Pesonen, Henrik Romar, Tao Hu, Pekka Tynjälä, and Ulla Lassi. 2019. "The Use of Ca- and Mg-Rich Fly Ash as a Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus—Recycling and Reuse" Recycling 4, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020014
APA StyleMyllymäki, P., Pesonen, J., Romar, H., Hu, T., Tynjälä, P., & Lassi, U. (2019). The Use of Ca- and Mg-Rich Fly Ash as a Chemical Precipitant in the Simultaneous Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus—Recycling and Reuse. Recycling, 4(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling4020014






