Relationship among Vulcanization, Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Blends Containing Recycled EPDM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Milling and Characterization of EPDM-r
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of the Blends
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of EPDM-r
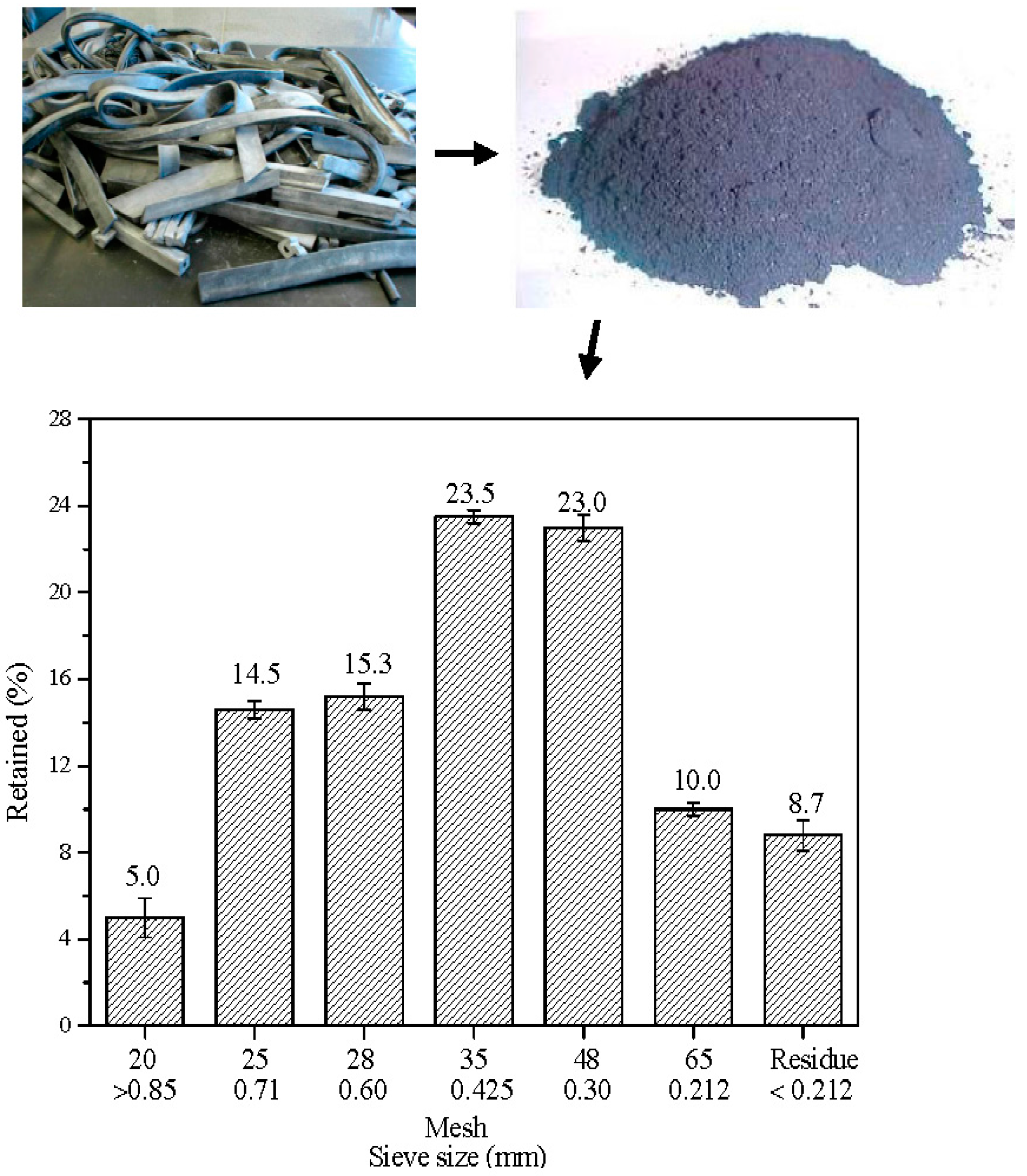
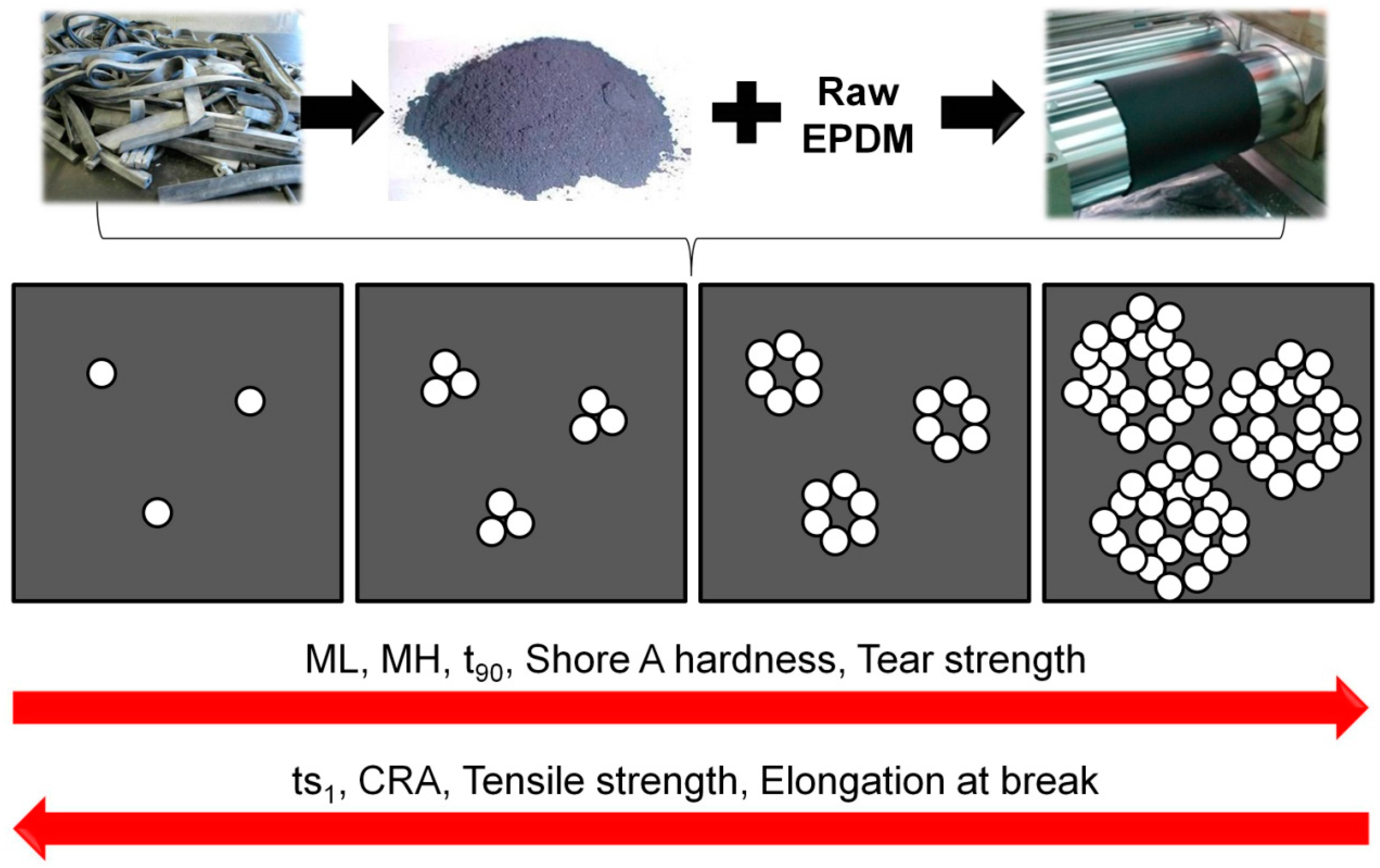
3.1.1. Milling and Particle Size Distribution
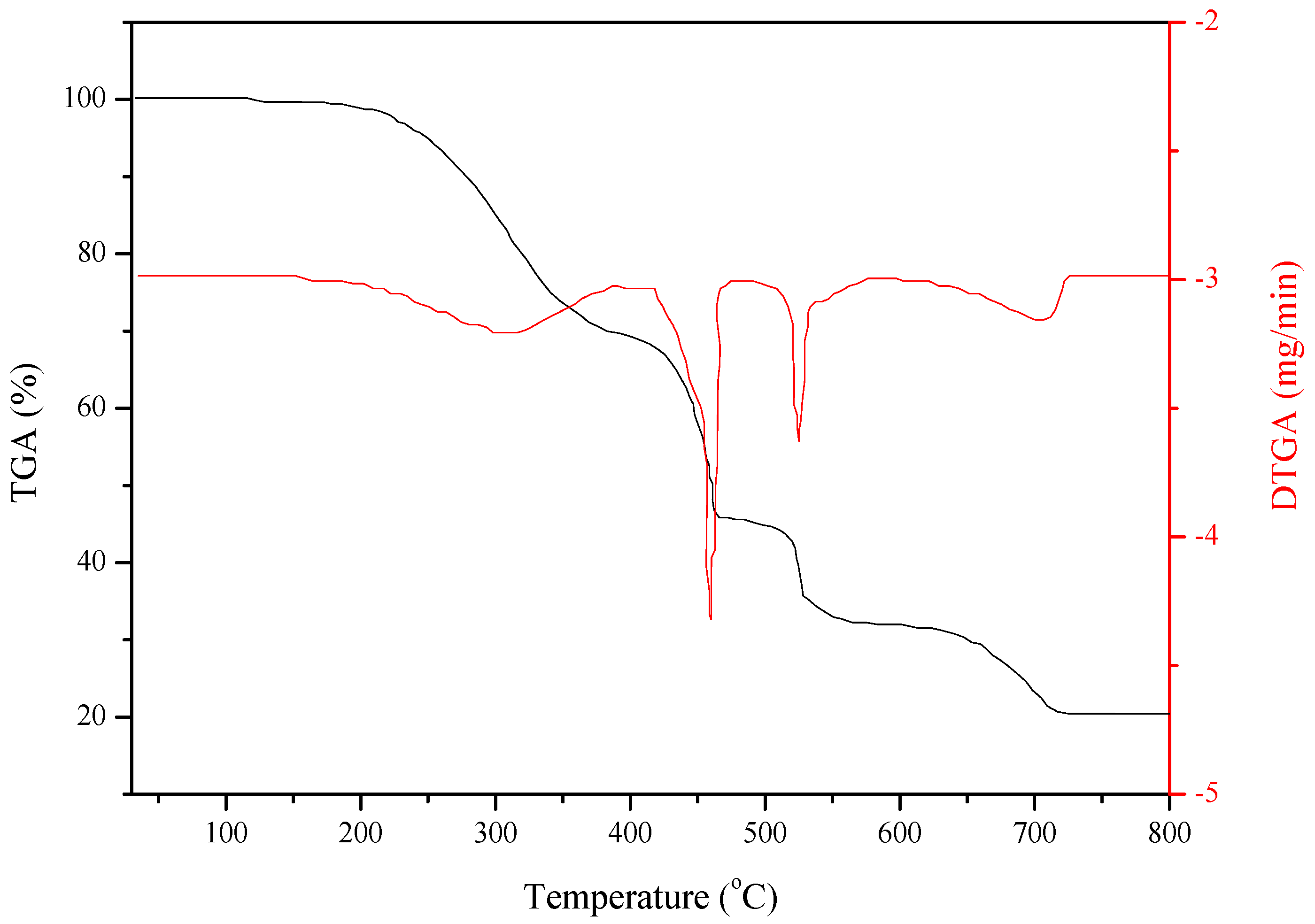
3.1.2. Thermo-Oxidative Degradation
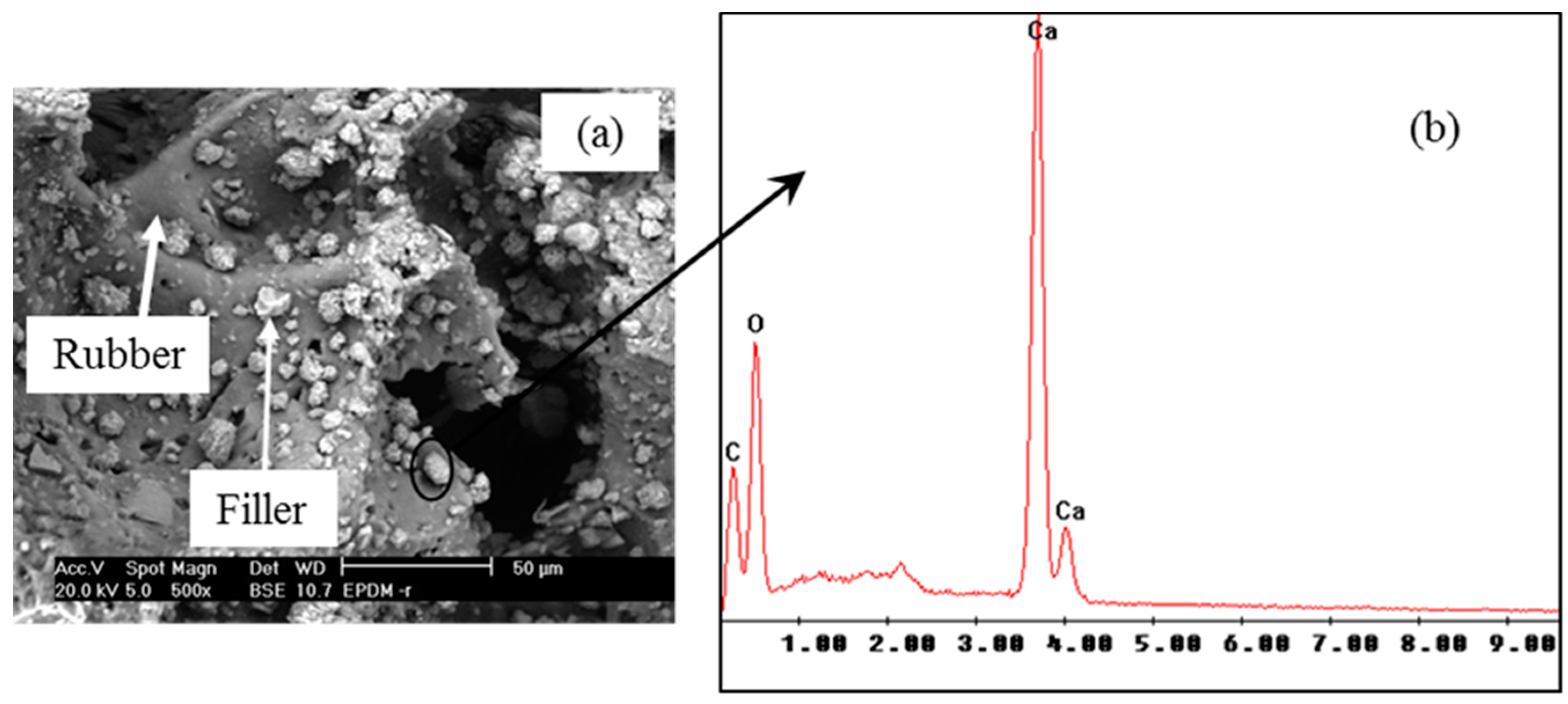
3.1.3. Morphology
3.2. Characterization of the Blends
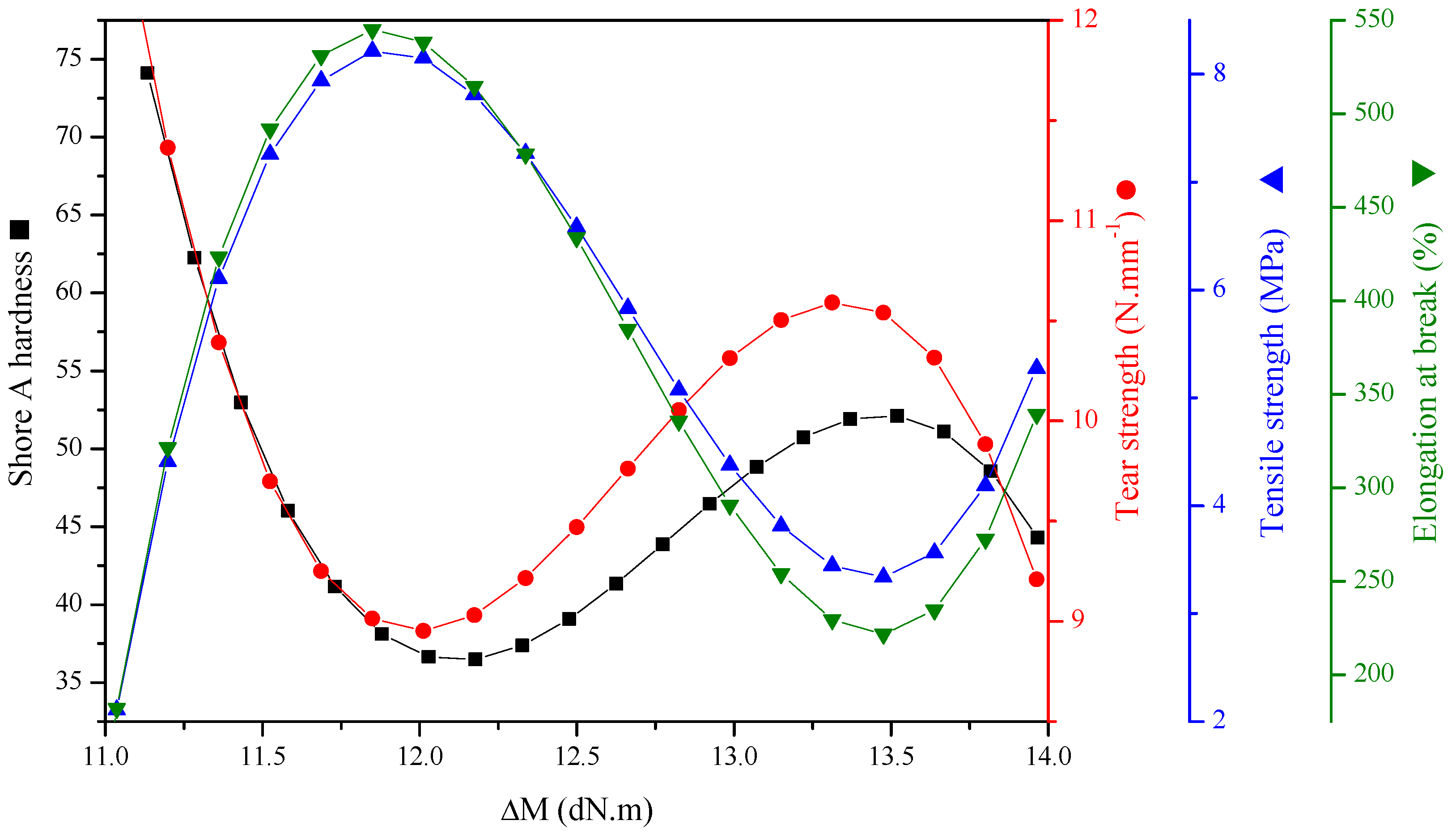
3.2.1. Vulcanization Characteristics
3.2.2. Density and Hardness
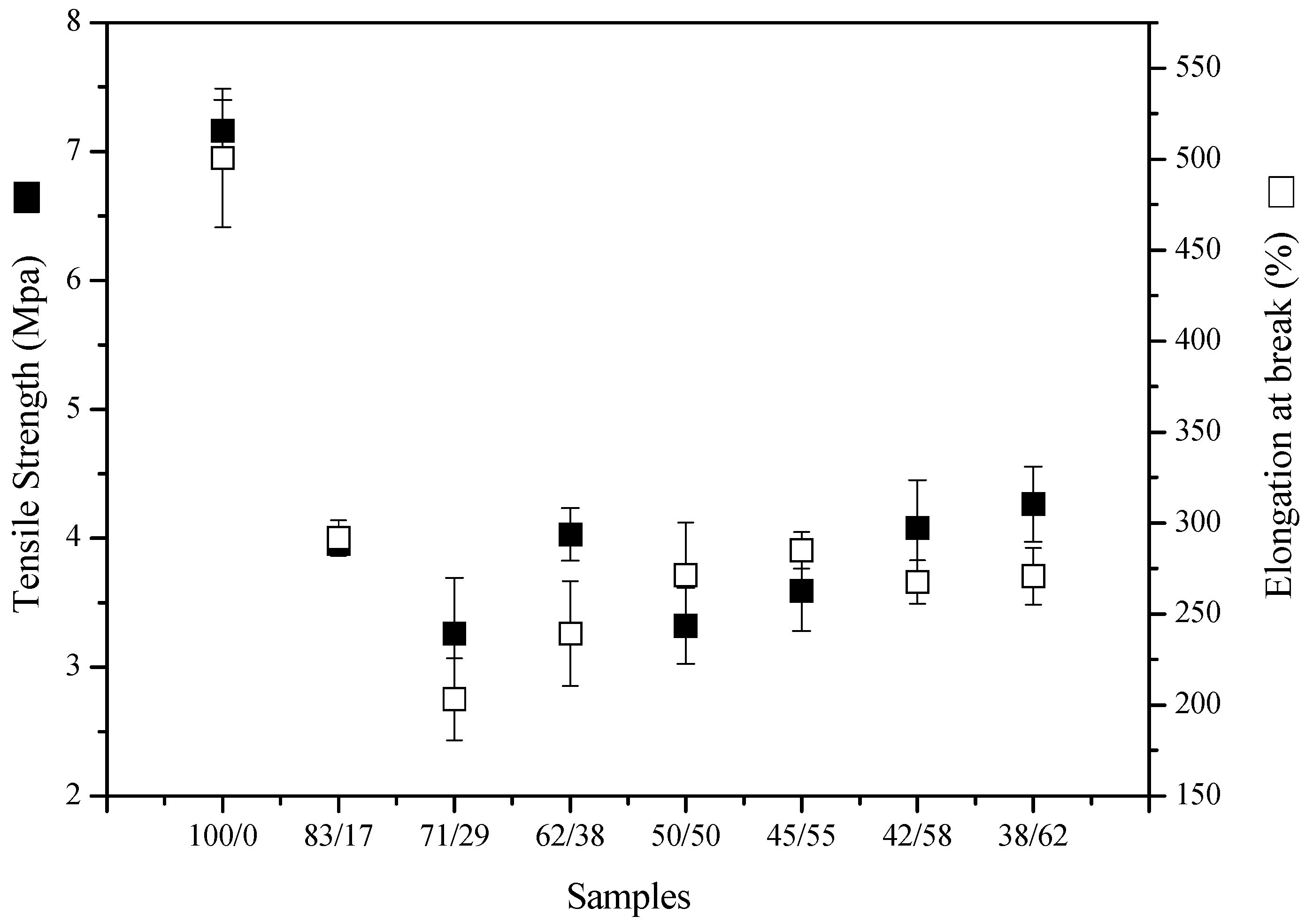
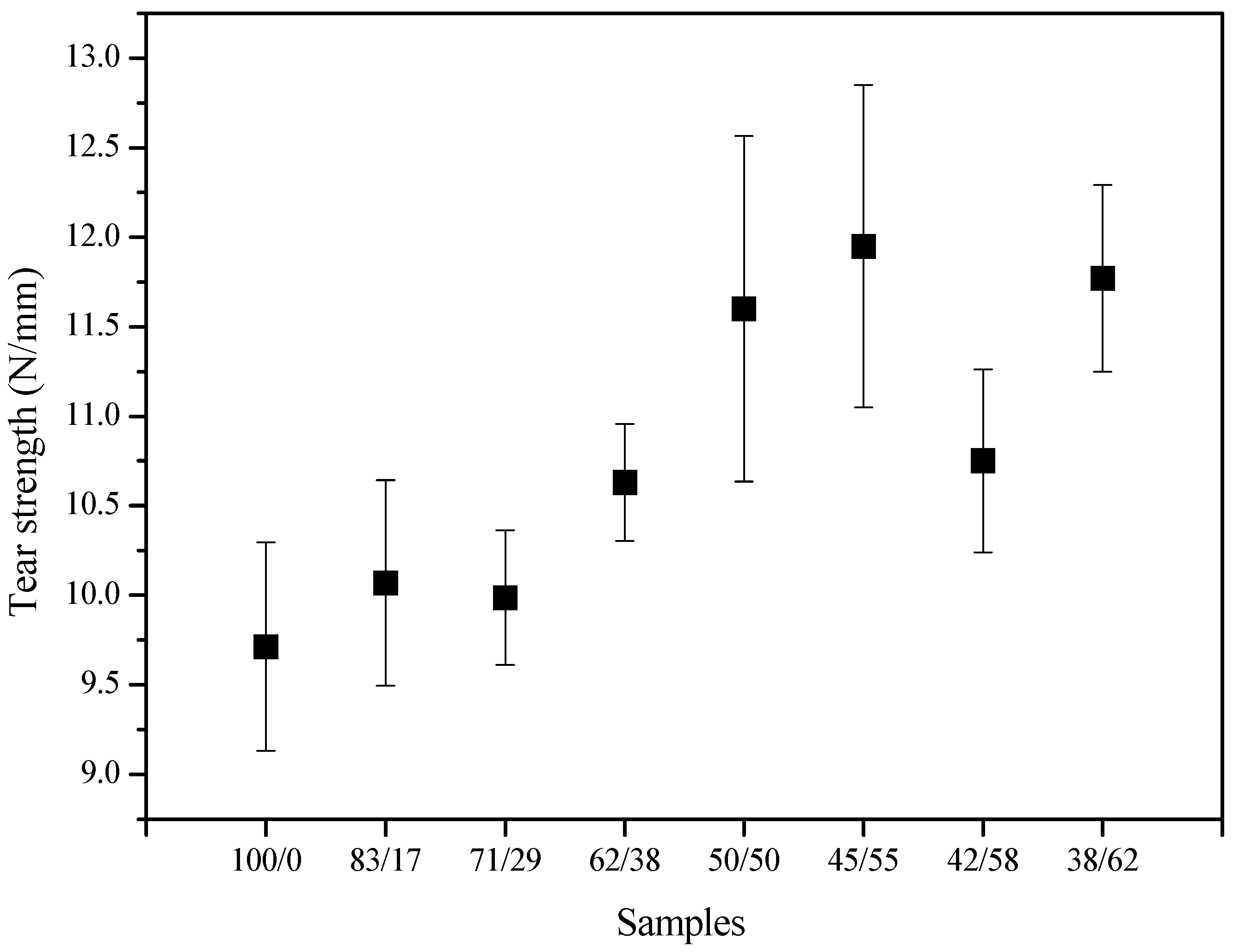
3.2.3. Mechanical Properties
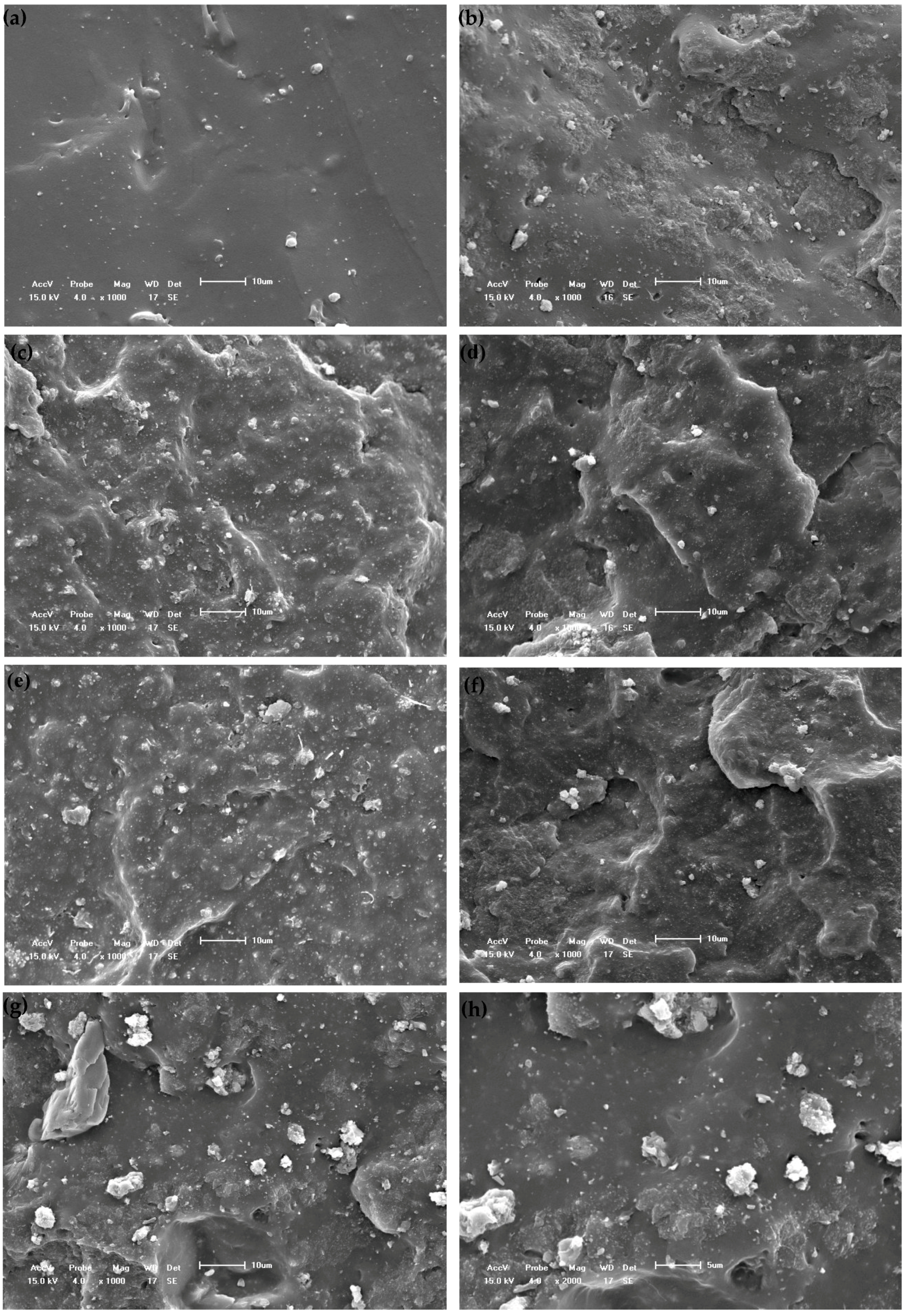
3.2.4. Morphology
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imbernon, L.; Norvez, S. From landfilling to vitrimer chemistry in rubber life cycle. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Zanchet, A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Influence of reversion in compounds containing recycled natural rubber: In search of sustainable processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; De, D.; Maiti, S. Reclamation and recycling of waste rubber. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 909–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuracchio, C.H.; Waki, D.A.; Da Silva, M.L.C.P. Thermal analysis of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polgar, L.M.; Van Duin, M.; Broekhuis, A.A.; Picchioni, F. Use of Diels-Alder Chemistry for Thermoreversible Cross-Linking of Rubbers: The Next Step toward Recycling of Rubber Products? Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7096–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, H.M.; Ramos, V.D.; da Silva, W.S.; Sirqueira, A.S. Analysis and optimization of polypropylene (PP)/ethylene–propylene–diene monomer (EPDM)/scrap rubber tire (SRT) mixtures using RSM methodology. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadane, P.A.; Cheng, J.; Ellul, M.D.; Favis, B.D. Decoupling of reactions in reactive polymer blending for nanoscale morphology control. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papautsky, D. Recuperação e Regeneração. Borracha Atual. 2003, 46, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Crespo, J.S.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Nunes, R.C. Characterization of Microwave-Devulcanized Composites of Ground SBR Scraps. J. Elastomers Plast. 2009, 41, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujel, A.A.; Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Carli, L.N.; Brandalise, R.N.; Crespo, J.S. Development of bus body rubber profiles with additives from renewable sources: Part I—Additives characterization and processing and cure properties of elastomeric compositions. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhan, M.; Wang, Y. The status of recycling of waste rubber. Mater. Des. 2001, 22, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.; Ismail, H.; Azura, A.R. Comparison of thermo-oxidative ageing and thermal analysis of carbon black-filled NR/Virgin EPDM and NR/Recycled EPDM blends. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, H.; Ismail, H.; Azura, A.R. Optimisation of accelerators and vulcanising systems on thermal stability of natural rubber/recycled ethylene-propylene-diene-monomer blends. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Bianchi, O.; Mauler, R.S.; Crespo, J.S. Crosslinking kinetics of SBR composites containing vulcanized ground scraps as filler. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, D.; Hamed, G.R. Cure and mechanical behavior of rubber compounds containing ground vulcanizates. Part I-Cure behavior. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1994, 67, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, D.; Laohapisitpanich, K.; Thomas, D.; Hamed, G.R. Cure and mechanical behavior of rubber compounds containing ground vulcanizates. Part II-Mooney viscosity. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibala, D.; Thomas, D.; Hamed, G.R. Cure and mechanical behavior of rubber compounds containing ground vulcanizates: Part III. Tensile and tear strength. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, K.; Natchimuthu, N. Vulcanization characteristics and mechanical properties of natural rubber-scrap rubber compositions filled with leather particles. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.; De, P.P.; Bhowmick, A.K.; De, S.K. Recycling of EPDM waste. I. Effect of ground EPDM vulcanizate on properties of EPDM rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 3293–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, P.; Picchioni, F.; Janssen, L.P.B.M.; Dijkhuis, K.A.J.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W. State of the art: Recycling of EPDM rubber vulcanizates. Int. Polym. Process. 2006, 21, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Dal’Acqua, N.; Weber, T.; Crespo, J.S.; Brandalise, R.N.; Nunes, R.C. Propriedades reométricas e mecânicas e morfologia de compósitos desenvolvidos com resíduos elastoméricos vulcanizados. Polim E Tecnol. 2007, 17, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H. Vulcanization behavior of NBR with organically modified clay. J. Elastomers Plast. 2012, 44, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Brandalise, R.N.; Crespo, J.S.; Nunes, R.C. Grinding and Characterization of Scrap Rubbers Powders. J. Elastomers Plast. 2008, 40, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Crespo, J.S.; Oliveira, M.G.; Suarez, J.; Nunes, R.C. Caracterização de Artefatos Elastoméricos obtidos por Revulcanização de Resíduo Industrial de SBR (Copolímero de Butadieno e Estireno) Characterization of Elastomeric Artifacts obtained by Revulcanization of SBR Industrial Waste. Polim E Tecnol. 2011, 21, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchet, A.; Carli, L.N.; Giovanela, M.; Brandalise, R.N.; Crespo, J.S. Use of styrene butadiene rubber industrial waste devulcanized by microwave in rubber composites for automotive application. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomide, R. Operações Unitárias: Operações com Sistemas Sólidos Granulares; Editora LTC: São Paulo, Brazil, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgili, E.; Arastoopour, H.; Bernstein, B. Pulverization of rubber granulates using the solid state shear extrusion process Part II. Powder characterization. Powder Technol. 2001, 115, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.S.; de Sousa, F.D.B.; de Lima, J.A.; Cruz, S.A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Devulcanization of ground tire rubber: Physical and chemical changes after different microwave exposure times. eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2015, 91, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Devulcanization of waste tire rubber by microwaves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 138, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunthonpagasit, N.; Duffey, M.R. Scrap tires to crumb rubber: Feasibility analysis for processing facilities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2004, 40, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, K.C.; Stephens, H.L. Basic Elastomer Technology; Rubber Division: Akron, OH, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.A.; Kutty, S.K.N. Cure Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Maleic Anhydride Grafted Reclaimed Rubber/Styrene Butadiene Rubber Blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2004, 43, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usberco, J.; Salvador, E. Química; Editora Saraiva: São Paulo, Brazil, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.S.; Isayev, A.I. Continuous ultrasonic devulcanization of unfilled butadiene rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Ghose, S.; Isayev, A.I. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on unfilled butadiene rubber. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2003, 41, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Ishak, S.; Hamid, Z.A.A. Effect of blend ratio on cure characteristics, tensile properties, thermal and swelling properties of mica-filled (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer)/(recycled ethylene-propylene-diene monomer) (EPDM/r-EPDM) blends. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2015, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maridass, B.; Gupta, B.R. Effect of Carbon Black on Devulcanized Ground Rubber Tire—Natural Rubber Vulcanizates: Cure Characteristics and Mechanical Properties. J. Elastomers Plast. 2006, 38, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coran, A.Y. Vulcanization. In Science and Technology of Rubber, 3rd ed.; Mark, J.E., Erman, B., Eirich, F.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 321–366. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Gouveia, J.R.; de Camargo Filho, P.M.F.; Vidotti, S.E.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Amurin, L.G.; Valera, T.S. Blends of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves/HDPE—Part A: Influence of devulcanization process. Polím. Ciênc. Tecnol. 2015, 25, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H.; Hu, G.H.; Hoppe, S. Effects of processing parameters on the properties of microwave-devulcanized ground tire rubber/polyethylene dynamically revulcanized blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavate, J.; Casas, P.; Colom, X.; Nogues, F. Formulations for thermoplastic vulcanizates based on high density polyethylene, ethylene-propylene-diene monomer, and ground tyre rubber. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magioli, M.; Sirqueira, A.S.; Soares, B.G. The effect of dynamic vulcanization on the mechanical, dynamic mechanical and fatigue properties of TPV based on polypropylene and ground tire rubber. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Bhowmick, A.K. Thermal ageing, degradation and swelling of acrylate rubber, fluororubber and their blends containing polyfunctional acrylates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B. Vulcanization of Natural Rubber: Past, Present and Future Perspectives. In Natural Rubber: Properties, Behavior and Applications; Hamilton, J.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publichers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 47–88. [Google Scholar]
- Coran, A.Y. Vulcanization: Conventional and Dynamic. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1995, 68, 351–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.D.B.; Scuracchio, C.H. The role of carbon black on devulcanization of natural rubber by microwaves. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Zanchet, A.; Crespo, J.S.; Oliveira, M.G.; Suarez, J.; Nunes, R.C. Caracterização de artefatos elastoméricos obtidos por revulcanização de resíduo industrial de SBR (copolímero de butadieno e estireno). Polim E Tecnol. 2011, 21, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Boniatti, R.; Teixeira, C.E.; Nunes, R.C.; Crespo, J.S. Development and characterization of composites with ground elastomeric vulcanized scraps as filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Amount (phr) a |
|---|---|
| EPDM (4770/4703) | 100 |
| ZnO | 5 |
| Stearic acid | 1 |
| TMTD | 1 |
| MBT | 0.5 |
| Sulphur | 1.5 |
| Carbon black | 14 |
| Partial Composition | Weight Loss (%) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil | 30.10 | 291.6 |
| EPDM | 23.87 | 447.4 |
| Carbon black | 13.28 | 522.5 |
| CaCO3 | 11.42 | 682.5 |
| Residue at 800 °C | 21.33 | − |
| Sample | ML (dN·m) | MH (dN·m) | ∆M (dN·m) | ts1 (min) | t90 (min) | CRA (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100/0 | 3.58 | 15.28 | 11.70 | 1.86 | 4.46 | 0.38 |
| 83/17 | 3.59 | 16.92 | 13.33 | 1.57 | 4.81 | 0.31 |
| 71/29 | 4.24 | 17.97 | 13.73 | 1.49 | 10.00 | 0.12 |
| 62/38 | 5.28 | 18.34 | 13.06 | 1.46 | 10.03 | 0.12 |
| 50/50 | 8.09 | 19.47 | 11.38 | 1.16 | 12.59 | 0.09 |
| 45/55 | 8.88 | 20.25 | 11.37 | 1.24 | 10.43 | 0.11 |
| 42/58 | 9.35 | 23.01 | 13.66 | 1.13 | 25.20 | 0.04 |
| 38/62 | 9.95 | 21.35 | 11.40 | 1.26 | 24.18 | 0.04 |
| Sample | Shore A Hardness | Density (g·cm−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unvulcanized | Vulcanized | ||
| 100/0 | 41.3 ± 1 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.67 ± 0.09 |
| 83/17 | 48.1± 2 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.64 ± 0.06 |
| 71/29 | 48.3± 1 | 0.37 ± 0.10 | 0.55 ± 0.01 |
| 62/38 | 51.4 ± 1 | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 0.51 ± 0.01 |
| 50/50 | 53.3 ± 1 | 0.47 ± 0.07 | 0.47 ± 0.06 |
| 45/55 | 55.2 ± 1 | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.52 ± 0.05 |
| 42/58 | 55.4 ± 1 | 0.52 ± 0.05 | 0.58 ± 0.01 |
| 38/62 | 60.3 ± 1 | 0.54 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.03 |
| Sample | CS |
|---|---|
| 100/0 | 1.9 ± 0.3 |
| 83/17 | 3.9 ± 1.8 |
| 71/29 | 5.6 ± 4.2 |
| 62/38 | 4.5 ± 0.9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanchet, A.; Bandeira Dotta, A.L.; D. Bastos de Sousa, F. Relationship among Vulcanization, Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Blends Containing Recycled EPDM. Recycling 2017, 2, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling2030016
Zanchet A, Bandeira Dotta AL, D. Bastos de Sousa F. Relationship among Vulcanization, Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Blends Containing Recycled EPDM. Recycling. 2017; 2(3):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling2030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanchet, Aline, Aline L. Bandeira Dotta, and Fabiula D. Bastos de Sousa. 2017. "Relationship among Vulcanization, Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Blends Containing Recycled EPDM" Recycling 2, no. 3: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling2030016
APA StyleZanchet, A., Bandeira Dotta, A. L., & D. Bastos de Sousa, F. (2017). Relationship among Vulcanization, Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Blends Containing Recycled EPDM. Recycling, 2(3), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling2030016





