Synergetic Treatment of BOF Slag and Copper Slag via Oxidation–Magnetic Separation for MgFe2O4 Preparation and Non-Magnetic Slag Stabilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phase Transformation and MgFe2O4 Morphology During Oxidation Process
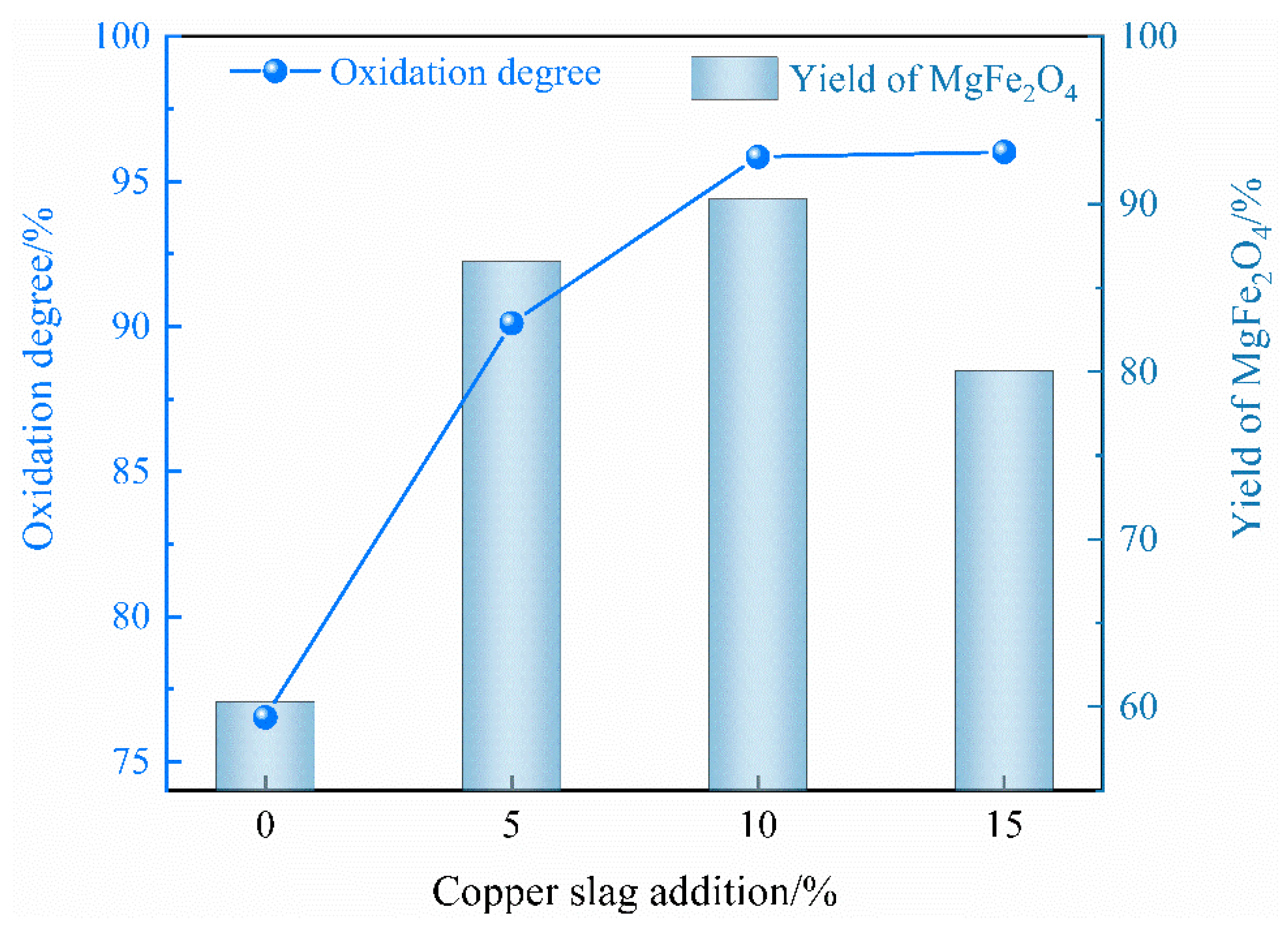
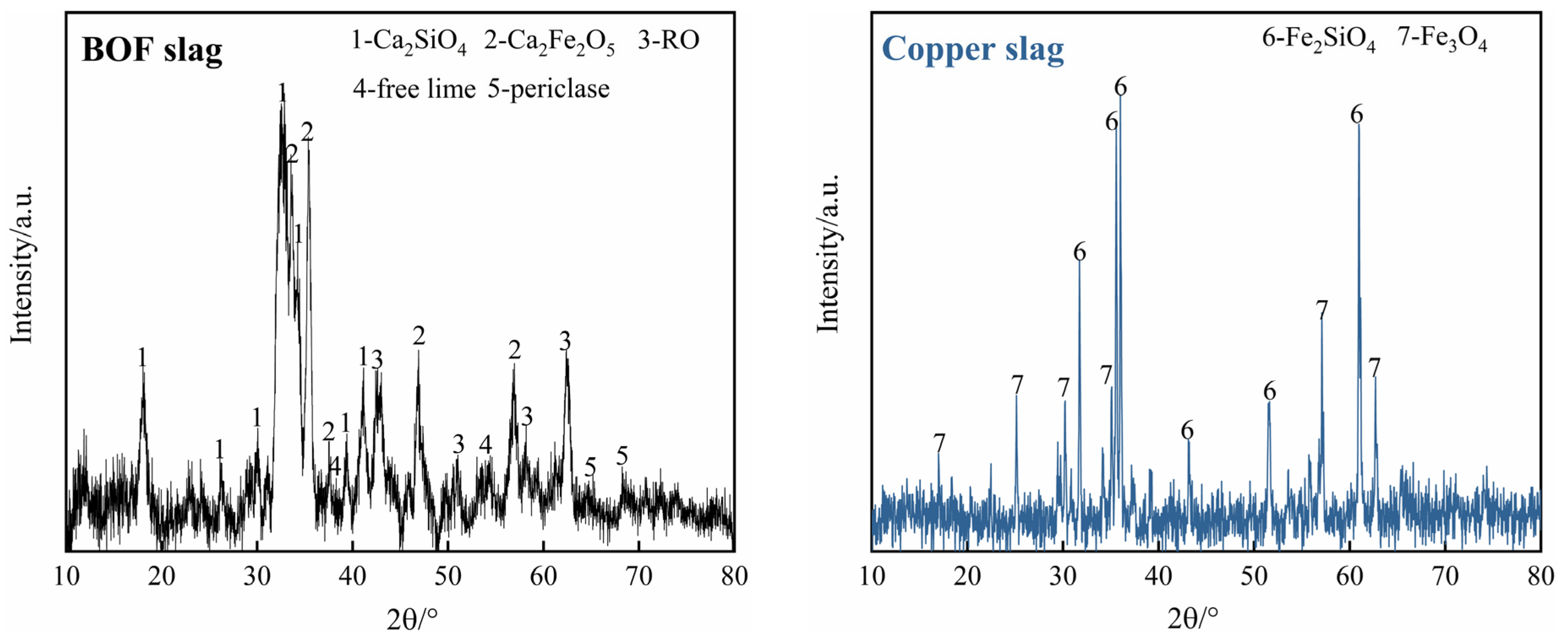
2.1.1. Effect of Copper Slag Addition
2.1.2. Effect of Oxidation Temperature
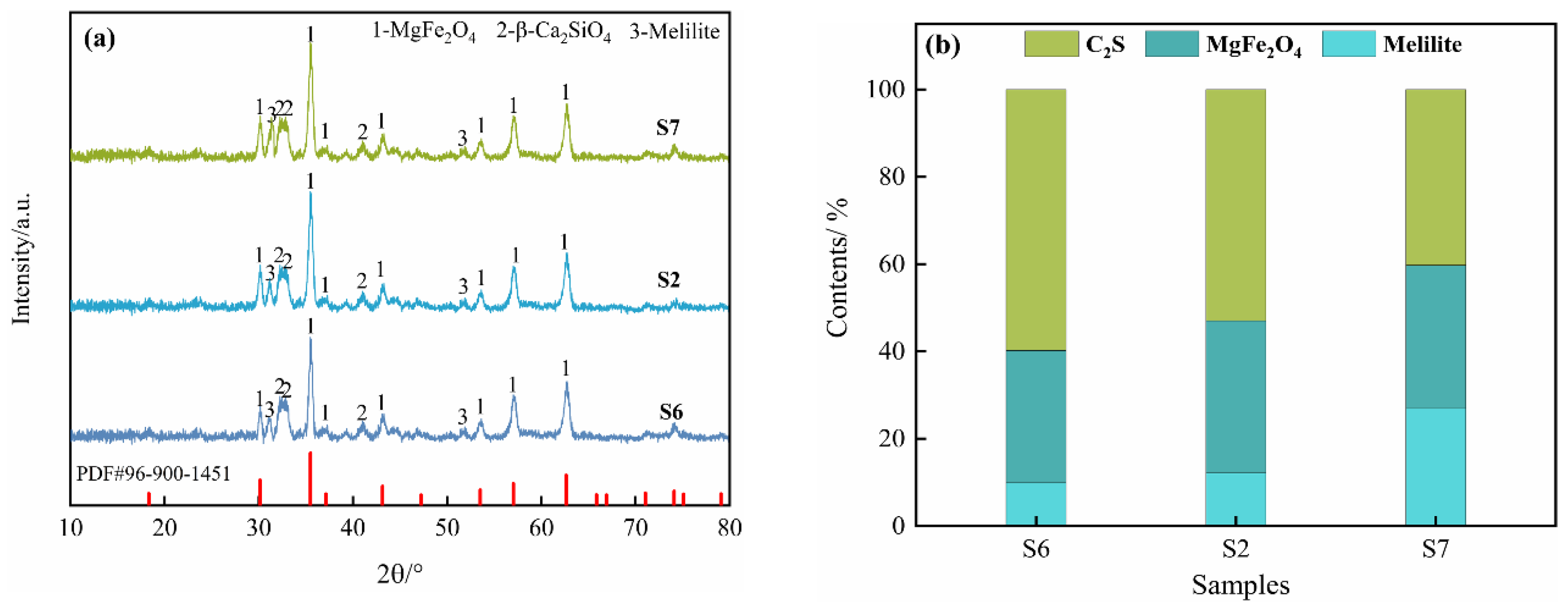
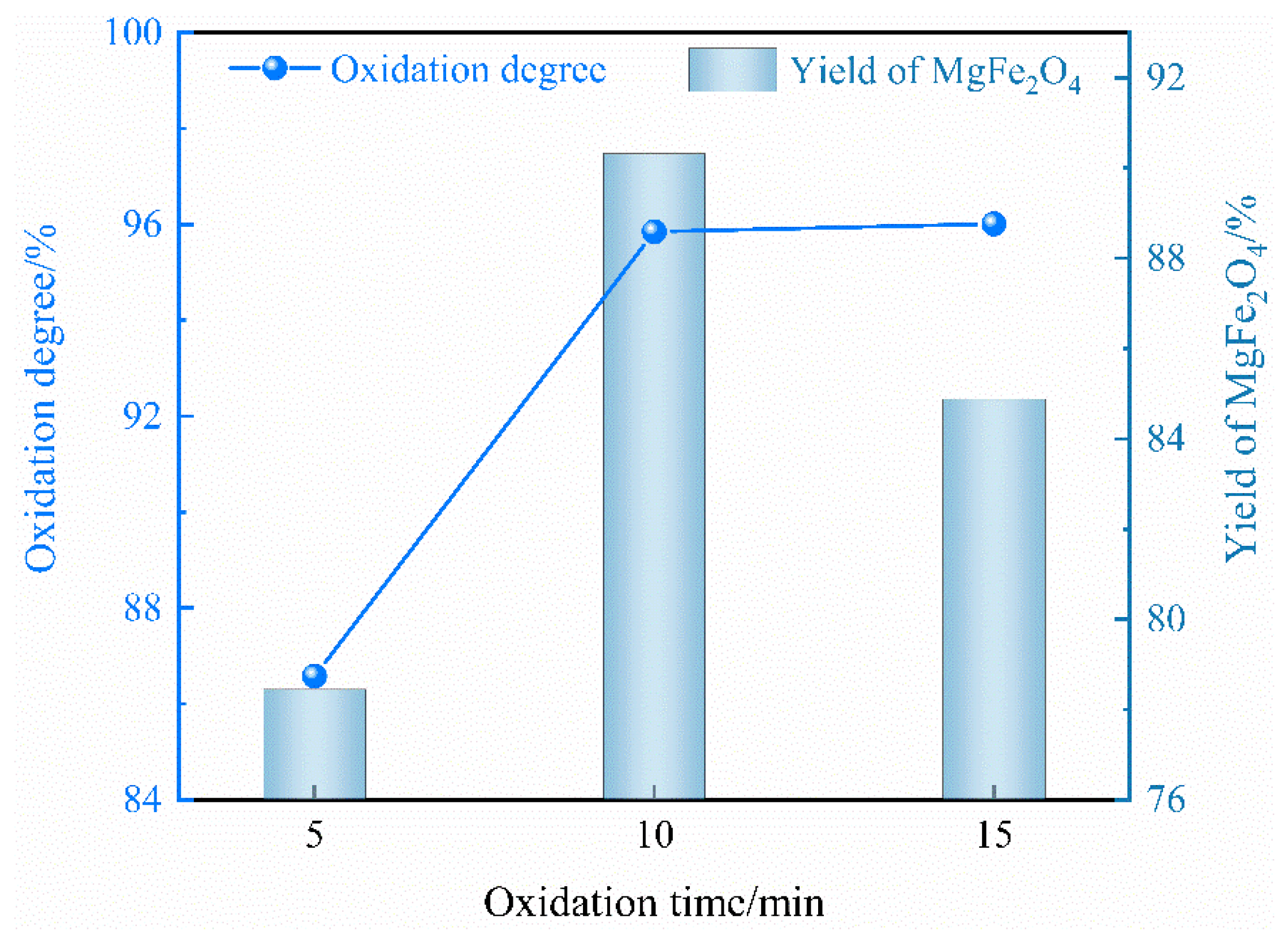
2.1.3. Effect of Oxidation Time
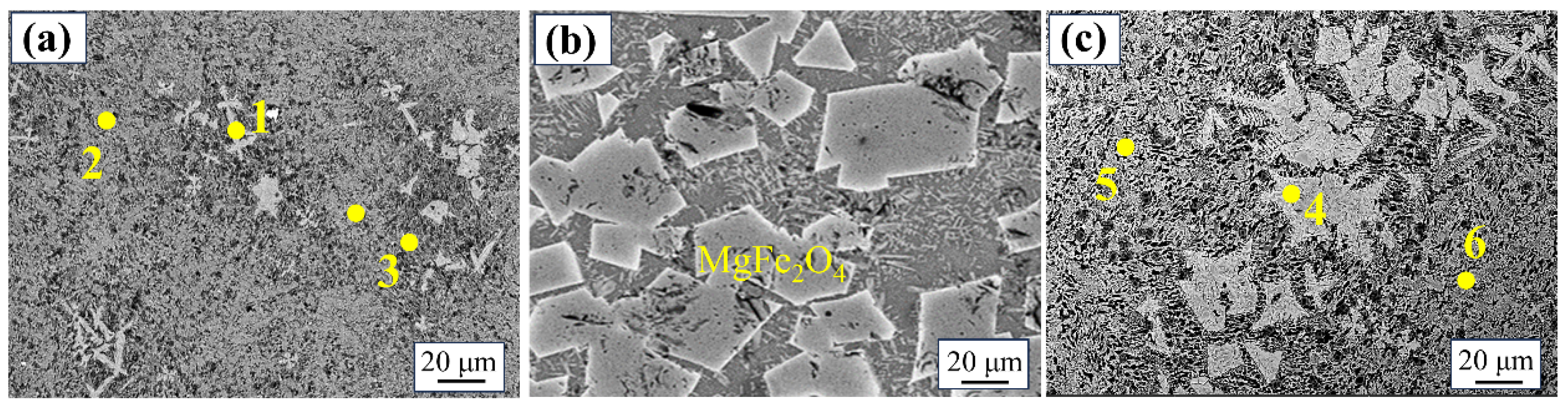
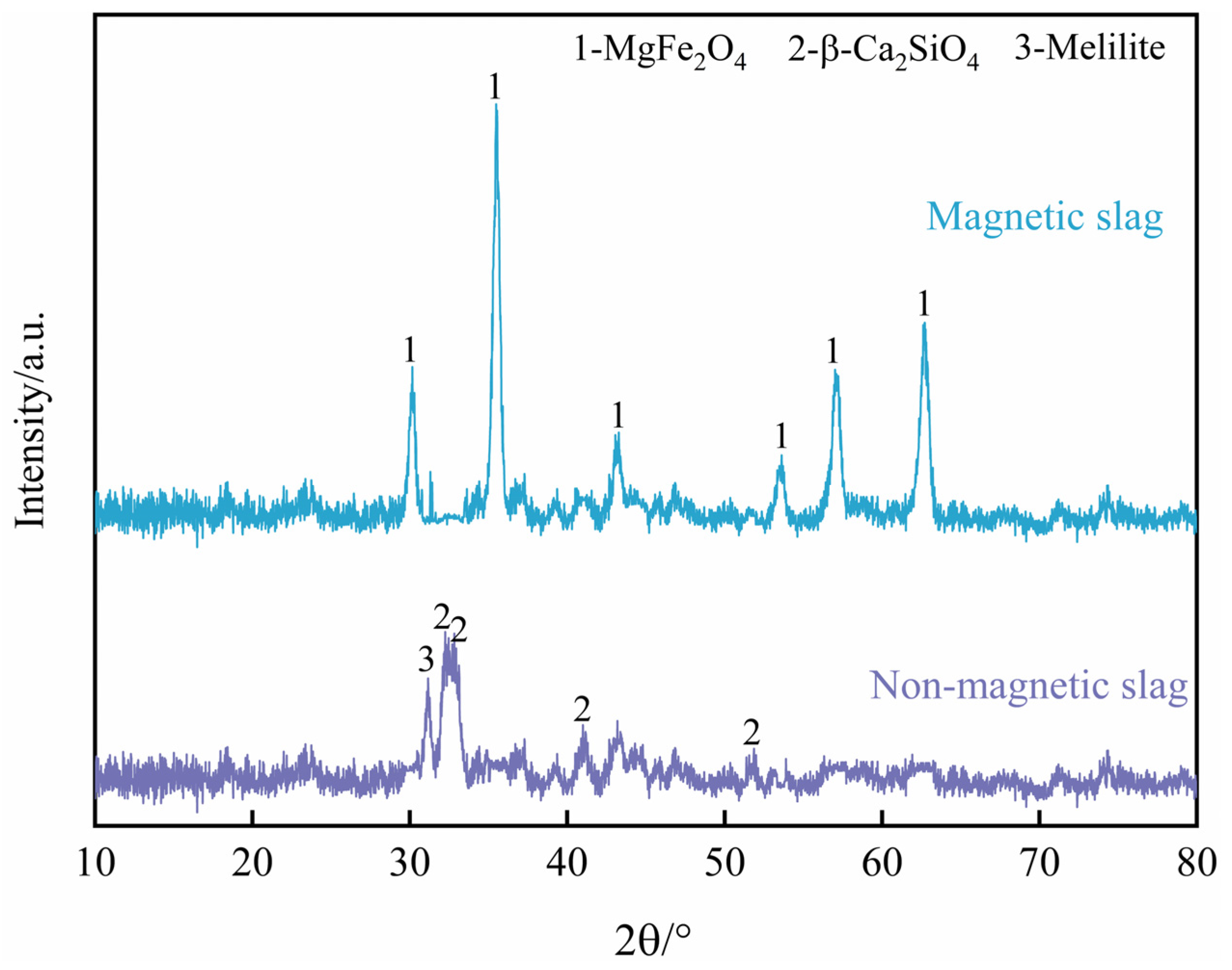
2.2. Magnetic Separation Product Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Procedure
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of copper slag can facilitate the dicalcium ferrite in BOF slag and fayalite in copper slag to release simple iron oxides of FeO and Fe2O3, and it promotes the formation of magnetic MgFe2O4.
- (2)
- An increase in both the oxidation temperature and oxidation time resulted in an increase in the size of the MgFe2O4 particles, which is conducive to the separation of the magnetic MgFe2O4.
- (3)
- The optimal oxidation conditions include 10% addition of copper slag, an oxidation temperature of 1450 °C and a 10 min oxidation time, resulting in a maximum oxidation degree of Fe2+ and yield of MgFe2O4 of 95.85% and 90.31%, respectively.
- (4)
- This process results in the removal of free CaO and free MgO from the BOF slag, and the non-magnetic slag is predominantly composed of Ca2SiO4, which can be utilized as a construction material.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, K.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Review of the energy consumption and production structure of China’s steel industry: Current situation and future development. Metals 2020, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, I.Z.; Prezzi, M. Chemical, mineralogical, and morphological properties of steel slag. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2011, 2011, 463638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel slag in China: Treatment, recycling, and management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Comprehensive utilization of steel slag: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harichandan, B.; Venugopal, R. Effect of design parameters of magnetic separator on recovery of metal values from slag waste. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2023, 31, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegas, I.; Oleaga, A.; García, C.V.; Santamaria, A.; Tomas San, J.J. Assessment of steelmaking slags subjected to accelerated carbonation. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102790–102804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, T.C.; Mucsi, G.; Venugopalan, T.; Kumar, S. BOF steel slag: Critical assessment and integrated Approach for Utilization. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Steel furnace slag aggregate expansion and hardened concrete properties. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.B.F.; Fredericci, C.; Faria, J.O.G.; Chotoli, F.F.; Ribeiro, T.R.; Malynowskyj, A.; Silva, A.L.N.; Quarcioni, V.A.; Lotto, A.A. Modification of basic oxygen furnace slag for cement manufacturing. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naakase, K.; Matsui, A.; Nakai, Y.; Kikuchi, N.; Kishimoto, Y.; Tetsuyama, I. Development of Iron Recovery Technique from Steelmaking Slag by Reduction at High Temperature. ISIJ Int. 2023, 63, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Hirata, H.; Arai, T.; Toh, T.; Yamada, T. Development of the Molten Slag Reduction Process-1 Characteristics of Closed Type DC arc Furnace for Molten Slag Reduction. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yin, S.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F. Iron recovery and active residue production from basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag for supplementary cementitious materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Luo, G.; Wang, L.; An, S.; Chai, Y.; Song, W. Preparation of cementing material and recovery of iron resources using converter slag. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Li, Y.; Cang, D.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y. BOF Slag Glass-ceramics Prepared in Different Atmospheres from Parents Glasses with Various Reduction Degree. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; He, Z.; Hu, X. Optimization of Iron Recovery from BOF Slag by Oxidation and Magnetic Separation. Metals 2022, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; He, D.; Xu, A.; Gu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Engström, F.; Björkman, B. Modification of industrial BOF slag: Formation of MgFe2O4 and recycling of iron. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Hu, X.; Chou, K.-C. Oxidative modification of industrial basic oxygen furnace slag for recover iron-containing phase: Study on phase transformation and mineral structure evolution. Process. Saf. Environ. 2023, 171, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, W. Modifying hot slag and converting it into value-added materials: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Guo, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.; Yang, C.; Xue, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, D. Comprehensive review on metallurgical recycling and cleaning of copper slag. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Chen, M. Co-modification of BOF slag and copper slag to recover valuable metals by carbothermal reduction. JOM 2023, 75, 3568–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal Uddin, M.; Jeong, Y.K. Application of magnesium ferrite nanomaterials for adsorptive removal of arsenic from water: Effects of Mg and Fe ratio. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, N.; Kaur, M.; Singh, D. Fabrication of mesoporous nanocomposite of graphene oxide with magnesium ferrite for efficient sequestration of Ni (II) and Pb (II) ions: Adsorption, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, X. Fabrication of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/porous magnesium ferrite@silica dioxide composite with excellent dual-band electromagnetic absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, S.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. Optimization of mineralogy and microstructure of solidified basic oxygen furnace slag through SiO2 addition or atmosphere control during hot-stage slag treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 50, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y. Thermodynamics and kinetics on hot state modification of BOF slag by adding SiO2. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2023, 54, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talero, R.; Trusilewicz, L.; Delgado, A.; Pedrajas, C.; Lannegrand, R.; Rahhal, V.; Mejía, R.; Delvasto, S.; Ramírez, F.A. Comparative and semi-quantitative XRD analysis of Friedel’s salt originating from pozzolan and Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J.; Cabrera, M.Á.; Fernández, C.; Mota-Heredia, C.; Fernández, R.; Torres, E.; Turrero, M.J.; Ruiz, A.I. Bentonite Powder XRD Quantitative Analysis Using Rietveld Refinement: Revisiting and Updating Bulk Semiquantitative Mineralogical Compositions. Minerals 2022, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chou, K.; Shu, Q. Effects of oxygen atmosphere, FeOx and basicity on mineralogical phases of CaO–SiO2–MgO–Al2O3–FetO–P2O5 steelmaking slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 46, 1470362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Du, X. Influence of CaO addition, FeO/SiO2, and MgO/SiO2 on the melting characteristic temperatures of FeO-SiO2-MgO-CaO System. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duée, C.; Bourgel, C.; Véron, E.; Allix, M.; Fayon, F.; Bodénan, F.; Poirier, J. Phosphorus speciation in dicalcium silicate phases: Application to the basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 73, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, M.; Poirier, J.; Bodénan, F.; Franceschini, G.; Véron, E. Basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag cooling: Laboratory characteristics and prediction calculations. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 123, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, G.B.; Lucchesi, S. Intersite distribution of Fe2+ and Mg in the spinel (sensu stricto)–hercynite series by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Am. Miner. 2002, 87, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 6730.65-2009; Iron Ores—Determination of Total Iron Content-Titanium (III) Chloride Reduction Potassium Dichromate Titration Methods (Routine Methods). Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 6730.8-2016; Iron Ores—Determination of Iron (II) Content—Potassium Dichromate Titrimetric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 176-2017; Methods for Chemical Analysis of Cement. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Uehara, N.; Takita, M. Extraction of free magnesia from steelmaking slags using Iodine–Ethanol solutions. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K.; Inose, M.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, K.; Fujimoto, K. Development of analytical methods for free-MgO in steelmaking slag. Tetsu Hagane-J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2016, 102, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

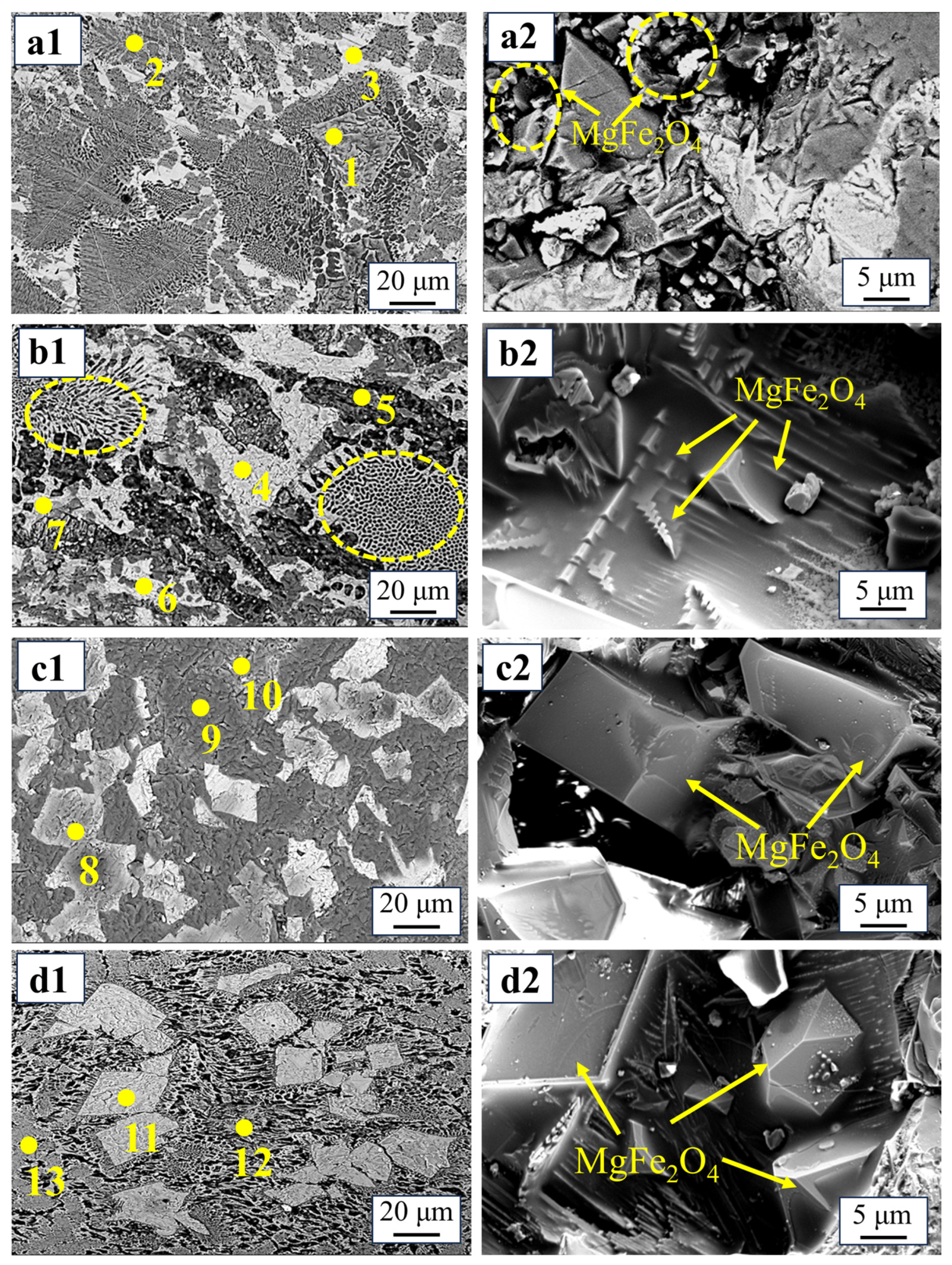




| Sample | Point | Phase | O | Mg | Fe | Ca | Si | Mn | Al | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 1 | MgFe2O4 | 52.04 | 15.64 | 29.13 | / | / | 2.14 | 1.05 | / |
| 2 | Ca2SiO4 | 43.66 | / | 0.84 | 37.20 | 16.70 | / | 0.36 | 1.23 | |
| 3 | Ca2Fe2O5 | 50.80 | / | 21.48 | 23.34 | 3.22 | / | 1.16 | / | |
| S1 | 4 | MgFe2O4 | 57.33 | 13.59 | 26.12 | / | / | 1.40 | 1.56 | / |
| 5 | Ca2SiO4 | 57.37 | / | / | 25.35 | 13.62 | / | / | 1.66 | |
| 6 | Ca2Fe2O5 | 44.94 | / | 23.69 | 28.63 | 1.52 | / | 1.22 | / | |
| 7 | Melilite | 52.21 | 7.55 | 5.03 | 16.28 | 10.39 | / | 8.54 | / | |
| S2 | 8 | MgFe2O4 | 49.57 | 15.57 | 31.45 | / | / | 1.68 | 1.73 | / |
| 9 | Ca2SiO4 | 58.30 | / | 0.77 | 27.50 | 12.43 | / | / | 0.99 | |
| 10 | Melilite | 48.15 | 8.28 | 6.90 | 15.28 | 10.50 | 0.61 | 10.28 | / | |
| S3 | 11 | MgFe2O4 | 46.74 | 13.92 | 31.50 | / | / | 1.74 | 6.10 | / |
| 12 | Ca2SiO4 | 54.20 | / | 0.64 | 30.21 | 13.20 | / | / | 1.75 | |
| 13 | Melilite | 43.84 | 7.51 | 10.48 | 18.77 | 9.23 | / | 10.17 | / |
| Sample | Point | Phase | O | Mg | Fe | Ca | Si | Mn | Al | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S4 | 1 | MgFe2O4 | 48.83 | 14.80 | 32.72 | 0.19 | / | 1.80 | 1.66 | / |
| 2 | Ca2SiO4 | 52.63 | / | / | 29.56 | 16.21 | / | / | 1.60 | |
| 3 | Melilite | 47.28 | 8.97 | 6.37 | 18.73 | 9.44 | / | 9.21 | / | |
| S5 | 4 | MgFe2O4 | 53.18 | 13.10 | 23.32 | / | / | 1.55 | 8.85 | / |
| 5 | Ca2SiO4 | 51.91 | / | 0.32 | 30.51 | 15.74 | / | / | 1.52 | |
| 6 | Melilite | 41.11 | 9.46 | 12.39 | 17.53 | 8.30 | / | 11.21 | / |
| Sample | Point | Phase | O | Mg | Fe | Ca | Si | Mn | Al | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S6 | 1 | MgFe2O4 | 54.46 | 13.52 | 28.63 | / | / | 1.69 | 1.70 | / |
| 2 | Ca2SiO4 | 51.93 | / | 0.22 | 30.66 | 15.46 | / | / | 1.73 | |
| 3 | Melilite | 42.98 | 6.41 | 6.17 | 20.39 | 15.58 | / | 8.47 | / | |
| S7 | 4 | MgFe2O4 | 46.36 | 14.87 | 30.23 | / | / | 1.64 | 6.89 | / |
| 5 | Ca2SiO4 | 57.87 | / | 0.48 | 27.44 | 11.49 | / | / | 2.72 | |
| 6 | Melilite | 45.33 | 8.06 | 8.99 | 18.47 | 8.83 | / | 10.32 | / |
| Copper Slag Addition/Mass % | TFe | FeO | Fe2O3 | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | MnO | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 17.76 | 5.27 | 19.52 | 45.98 | 11.96 | 8.23 | 5.63 | 2.03 | 1.78 |
| 5 | 18.69 | 0.23 | 26.44 | 44.49 | 13.07 | 8.05 | 4.10 | 1.94 | 1.70 |
| 10 | 19.88 | 0.09 | 28.30 | 42.61 | 13.86 | 7.79 | 4.02 | 1.81 | 1.61 |
| 15 | 21.23 | 0.08 | 30.24 | 40.49 | 14.76 | 7.50 | 3.76 | 1.70 | 1.52 |
| Composition | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | FeO | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | MnO | P2O5 | f-CaO | f-MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic product | 1.12 | 1.03 | 28.93 | - | 62.81 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.10 | - | - |
| Non-magnetic slag | 47.65 | 18.91 | 4.86 | 0.05 | 1.07 | 4.76 | 1.36 | 1.24 | 0.81 | 0.68 |
| TFe | FeO | Cu | CaO | SiO2 | MgO | Al2O3 | MnO | P2O5 | f-CaO | f-MgO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOF slag | 17.76 | 15.56 | - | 43.69 | 12.48 | 6.77 | 6.08 | 2.12 | 1.86 | 4.30 | 1.82 |
| Copper slag | 44.73 | 37.31 | 0.32 | 2.63 | 30.31 | 2.21 | 3.56 | - | - | - | - |
| Oxidation Slag Sample | Copper Slag Addition /Mass % | Oxidation Temperature/°C | Oxidation Time/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 0 | 1450 | 10 |
| S1 | 5 | 1450 | 10 |
| S2 | 10 | 1450 | 10 |
| S3 | 15 | 1450 | 10 |
| S4 | 10 | 1400 | 10 |
| S5 | 10 | 1500 | 10 |
| S6 | 10 | 1450 | 5 |
| S7 | 10 | 1450 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, M. Synergetic Treatment of BOF Slag and Copper Slag via Oxidation–Magnetic Separation for MgFe2O4 Preparation and Non-Magnetic Slag Stabilization. Recycling 2025, 10, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10030081
Cao B, Wang N, Chen M. Synergetic Treatment of BOF Slag and Copper Slag via Oxidation–Magnetic Separation for MgFe2O4 Preparation and Non-Magnetic Slag Stabilization. Recycling. 2025; 10(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Bowen, Nan Wang, and Min Chen. 2025. "Synergetic Treatment of BOF Slag and Copper Slag via Oxidation–Magnetic Separation for MgFe2O4 Preparation and Non-Magnetic Slag Stabilization" Recycling 10, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10030081
APA StyleCao, B., Wang, N., & Chen, M. (2025). Synergetic Treatment of BOF Slag and Copper Slag via Oxidation–Magnetic Separation for MgFe2O4 Preparation and Non-Magnetic Slag Stabilization. Recycling, 10(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10030081






