Abstract
Rapid industrialization has led to a substantial increase in waste salts containing Na2SO4/NaCl mixtures, posing significant challenges for their phase separation and resource recovery. This study pioneers an integrated process combining frozen crystallization with stepwise decompression evaporation for Na2SO4/NaCl separation. Through the systematic investigation of phase transition behaviors under varying ionic ratios, the optimal combined processes corresponding to mixed salts with different compositions were identified. The experimental results demonstrate that brines with NaCl > 80.0% should preferentially undergo vacuum evaporation, while those below this threshold are suitable for prioritizing frozen crystallization for Na2SO4 recovery. Utilizing the complementary advantages of both processes, the mixture was prepared with a mass ratio of NaCl to Na2SO4 of 3:1. The frozen crystallization of the brine yielded 90.0% pure Na2SO4 crystals while concentrating NaCl to 92.0% in the residual liquor. Subsequent stepwise evaporation yielded 98.5% pure NaCl crystals. Finally, the removal effect and lifecycle evaluation of the process for impurity ions provide new insights for the zero liquid discharge system in industrial waste salt management.
1. Introduction
Rapid advancements in petrochemical [1], pharmaceutical, pesticide, seawater desalination [2], and fine chemical industries [3] have led to an unprecedented surge in high-concentration saline wastewater generation. The salted waste generated from wastewater treatment primarily consists of Na2SO4 and NaCl, along with other soluble inorganic salt ions such as NH+ and Ca2+. The direct discharge of untreated waste salts can lead to soil acidification, vegetation destruction, aquatic ecosystem imbalance, the failure of biological treatment systems, and severe threats to marine ecology and economy [4,5,6,7,8,9]. To prevent environmental damage and achieve resource recovery, the efficient separation and recovery of salts from waste salts has emerged as a critical strategy.
Currently, conventional separation methods for Na2SO4 and NaCl rely heavily on eutectic frozen crystallization [10], evaporative distillation [11,12,13,14], membrane separation [11], and antisolvent crystallization techniques [15,16,17]. Both frozen crystallization and evaporative distillation are based on the varying solubility of the two salts with temperature [18,19,20,21,22,23]. For instance, frozen crystallization uses low temperatures (e.g., 5 °C) to precipitate Na2SO4 as decahydrate (Na2SO4·10H2O). Yet, in practice, strict temperature control is needed, and when the NaCl content in the solution is high, the energy efficiency and costeffectiveness of this method drop significantly. Although evaporative distillation effectively crystallizes NaCl, it is energy-intensive. When the NaCl content is below 75.0%, the cocrystallization of the two salts during evaporation results in a product purity of only 50–80%, falling short of highpurity requirements [24,25,26,27,28,29]. Membrane separation technology, which is based on the selective permeation of ions through membrane pores, can separate salt components. Youngkwon Choi et al. employed a fractional submerged membrane distillation crystallizer (F-SMDC) to recover Na2SO4 from reverse osmosis brine [11]. However, in actual operation, salt deposition on the membrane surface affects membrane performance, and the regular replacement of membranes increases disposal costs. Antisolvent crystallization separates salts based on the different solubilities of NaCl and Na2SO4 in a specific solvent. However, its efficiency is highly susceptible to interference from impurity ions. In complex salt systems, the separation efficiency drops markedly [30,31]. These methods, which rely on single processes for the separation of NaCl and Na2SO4, still face issues such as co-crystallization and susceptibility to impurity ions.
Studies have shown that single processes, due to cocrystallization issues, cannot achieve highselectivity separation. This causes traditional methods to still face major challenges in waste salt resource utilization [32]. Therefore, developing efficient, lowenergy, combined separation processes has become a key focus of current research. Given the significant limitations of single-process approaches in mixed-salt separation, researchers have proposed various combined processes to achieve efficient separation. For instance, the study by Balis et al. indicates that while the combination of membrane distillation (MD) and evaporation crystallization can recover solid salts and generate high-purity water, it still faces challenges such as membrane fouling, high operational costs, and solution concentration limitations [33]. Bhatti et al. integrated antisolvent crystallization with evaporation crystallization to selectively recover Na2SO4 and NaCl [30]. However, due to the use of a large amount of ecotoxic organic solvents in the process, even with solvent recovery, a significant environmental burden remains. Currently, evaporative crystallization and frozen crystallization are more extensively utilized in the valorization of salt wastes compared to membrane distillation and antisolvent crystallization, with their industrial-scale infrastructure being more advanced and well established.
Building on existing evaporation and frozen crystallization technologies, this study innovatively proposes a hybrid process combining frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation for Na2SO4/NaCl separation. Tailored to the physicochemical properties of salt waste solutions and industrial-scale equipment, the process dynamically selects between frozen and evaporation steps based on the NaCl content (e.g., NaCl content above 80% triggers decompression evaporation) and incorporates salt-washing purification to achieve high-purity industrial-grade salts (>98.5% NaCl, >90% Na2SO4). Compared to single-process evaporative distillation, the hybrid process reduces energy consumption. The pre-concentration of NaCl through frozen crystallization minimizes co-crystallization, ensuring stable product purity. Unlike organic solvent crystallization, this method eliminates the use of toxic solvents and reduces carbon emissions. Utilizing well-established industrial technologies, it offers a scalable and sustainable alternative.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Separation of Sodium Sulfate by Frozen Crystallization
2.1.1. Effect of Reaction Time on Crystallization Purity
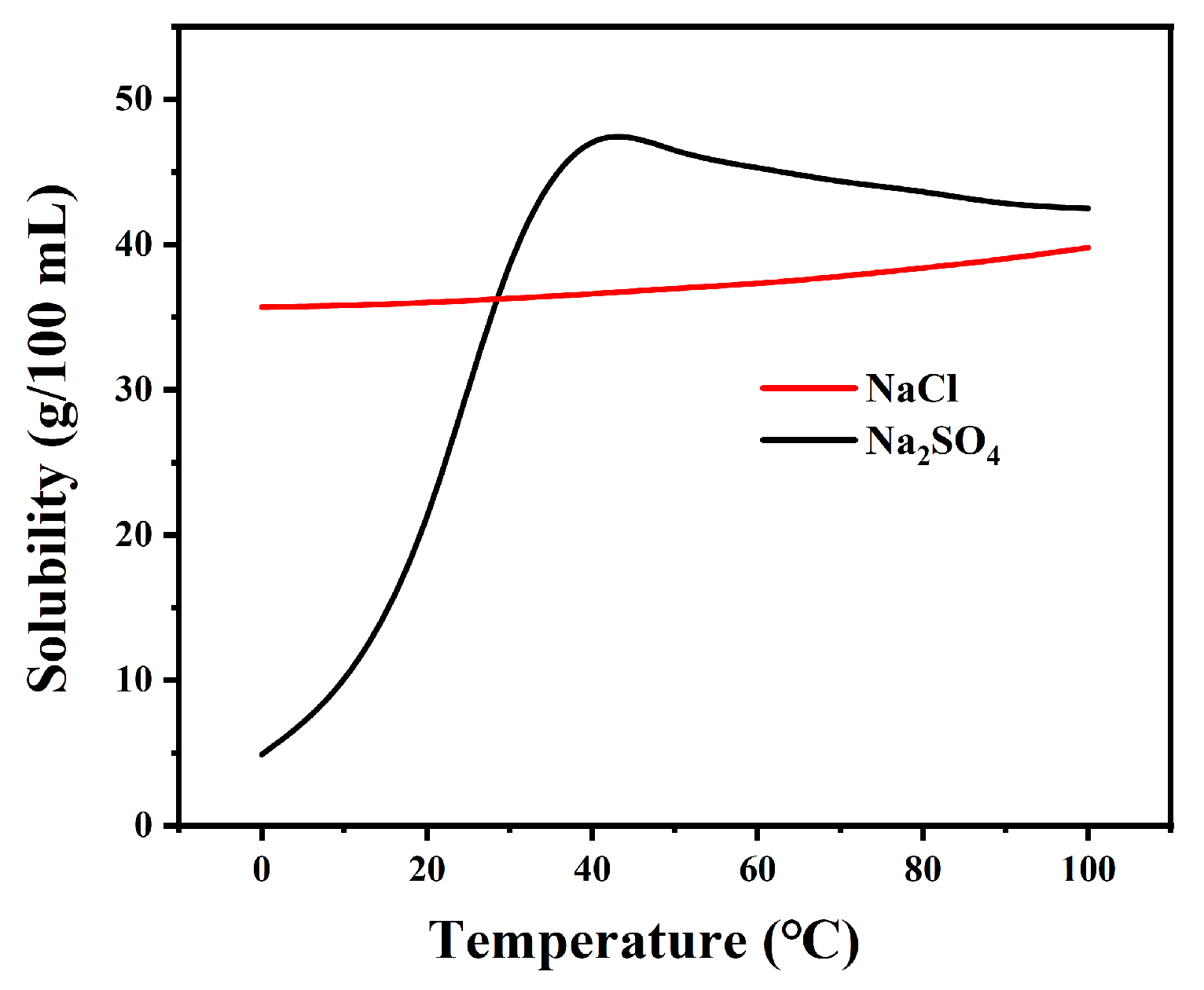
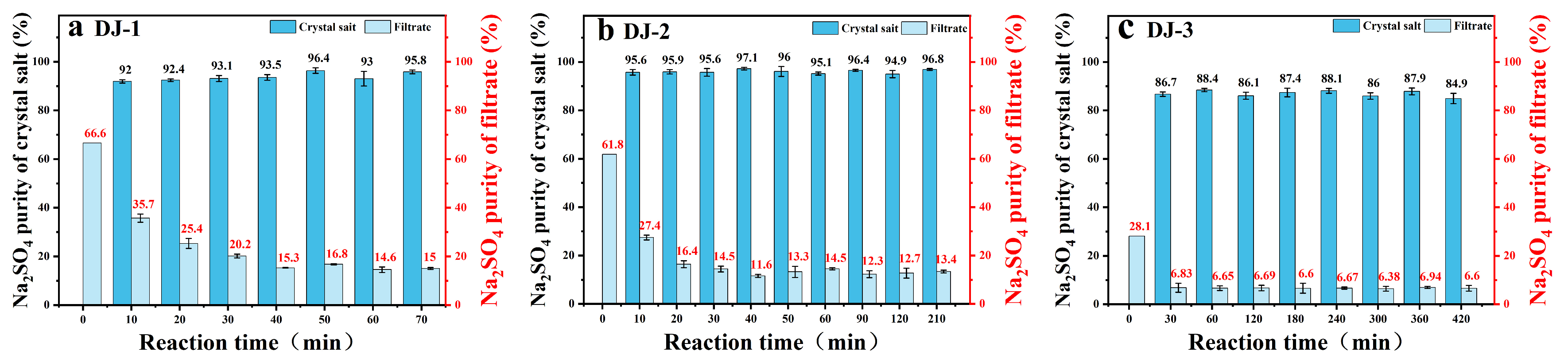
The effect of reaction time on purity was investigated by measuring the compositional changes of the precipitated crystalline salts. Since the solubility of Na2SO4 is much lower than that of NaCl at low temperatures (as shown in Figure 1), the impurity incorporation is minimal and the purity enhancement rate is rapid. As shown in Figure 2, the experiment can be divided into two stages. In the initial rapid crystallization stage, the purity of Na2SO4 in the precipitated crystalline salts increased significantly within 30 min (DJ-1 reached 91.95%, DJ-2 reached 95.64%, and DJ-3 reached 86.71%). This is attributed to the high concentration of Na2SO4 in the solution, which provides a strong driving force for crystallization.
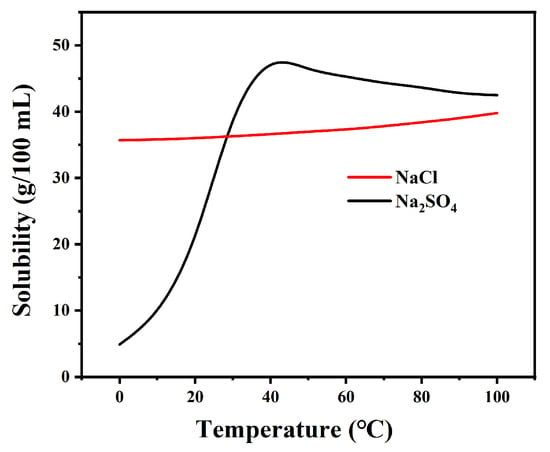
Figure 1.
Solubility curve of Na2SO4 and NaCl.
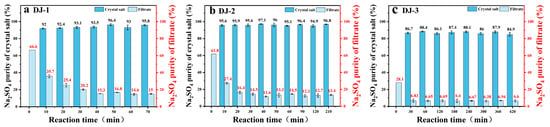
Figure 2.
Effect of reaction time on Na2SO4 purity.
In the subsequent equilibrium stage, the rate of purity increase of the precipitated crystalline salts slowed down, with an increase of less than 3% after 30 min. This is primarily due to the reduced concentration of Na2SO4 in the solution, which weakens the crystallization driving force. Meanwhile, the higher solubility of NaCl (as evidenced by the relatively flat solubility curve in the phase diagram) increases the probability of its incorporation into the crystalline salts, and the system gradually approaches phase equilibrium.
By adjusting the reaction time, the disadvantage of a lower initial concentration can be compensated for. High-concentration systems tend to crystallize rapidly with higher purity (as shown in Figure 2b), while low-concentration systems rely on extended reaction time to accumulate the amount of crystallized product (as shown in Figure 2c). However, the purity increase of less than 3% after 30 min indicates that the system has already approached phase equilibrium, and further prolonging the reaction time only yields marginal benefits. The 420 min long-duration reaction further validates the stability of the crystalline salt purity, ruling out the interference of impurity redissolution or secondary crystallization.
Based on the above conclusions and the characteristics of the phase diagram, an optimal reaction time of 30 min is recommended. During this period, the low solubility of Na2SO4 at low temperatures can be fully utilized to avoid the risk of impurity incorporation, achieving a balance between high purity (>90%) and low energy consumption.
2.1.2. Effect of Initial Concentration on Crystallization Efficiency at Low Temperatures
Seven groups of saturated solutions with different salt component ratios were prepared to analyze the change in the mass fraction of the crystalline salts precipitated in the low-temperature environment and to explore the application range of the low-temperature crystallization method.
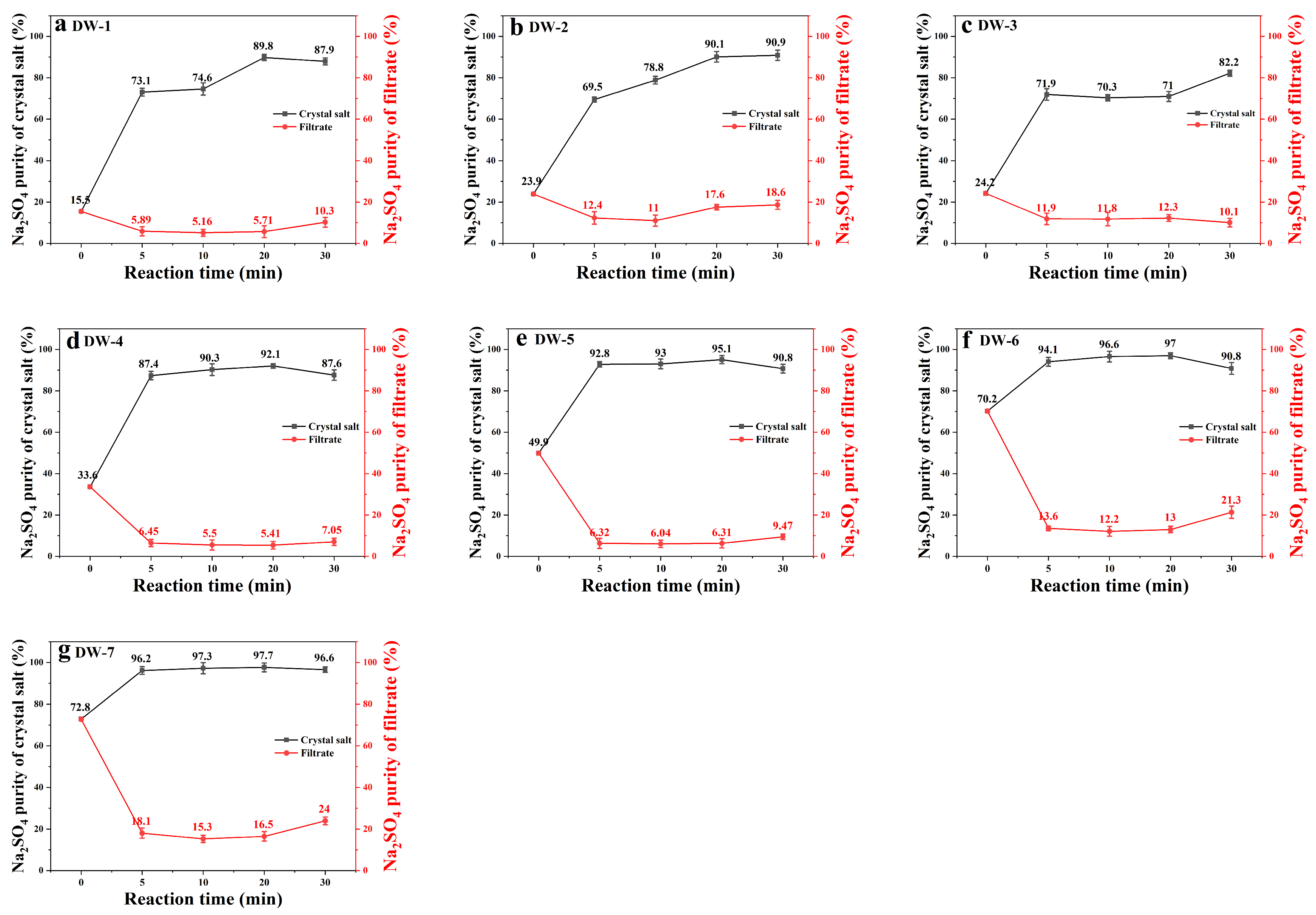
As evidenced by Figure 3, the initial Na2SO4 concentration exhibits a significant correlation with crystal purity enhancement. High-sulfate systems (DW-6/DW-7: >70% initial) achieved exceptional phase separation efficiency, reaching 96.6–97.3% Na2SO4 purity within 10 min of frozen crystallization. Comparatively, low-sulfate systems (DW-1: 15.5%) required extended processing (30 min) to attain 87.9% purity, demonstrating composition-dependent crystallization kinetics. This divergence originates from sulfate’s low-temperature dominance—at >70%, Na2SO4’s eutectic depression (−1.2 °C) promotes preferential nucleation, while chloride-rich systems require longer equilibration to overcome ionic hydration barriers.
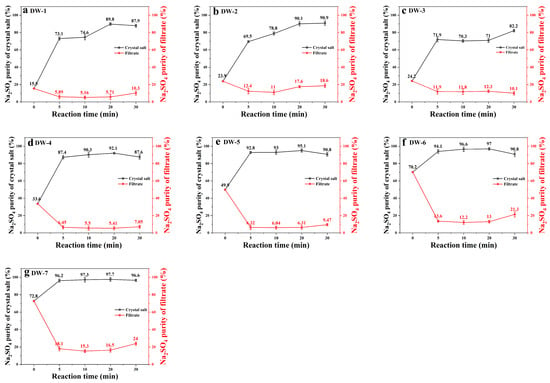
Figure 3.
Variation of Na2SO4 purity with reaction time in samples DW-1 to DW-7 (a–g).
2.2. Stepwise Decompression Evaporation Crystallization Separates Sodium Chloride
2.2.1. Effect of Solute Composition on Evaporation Purity
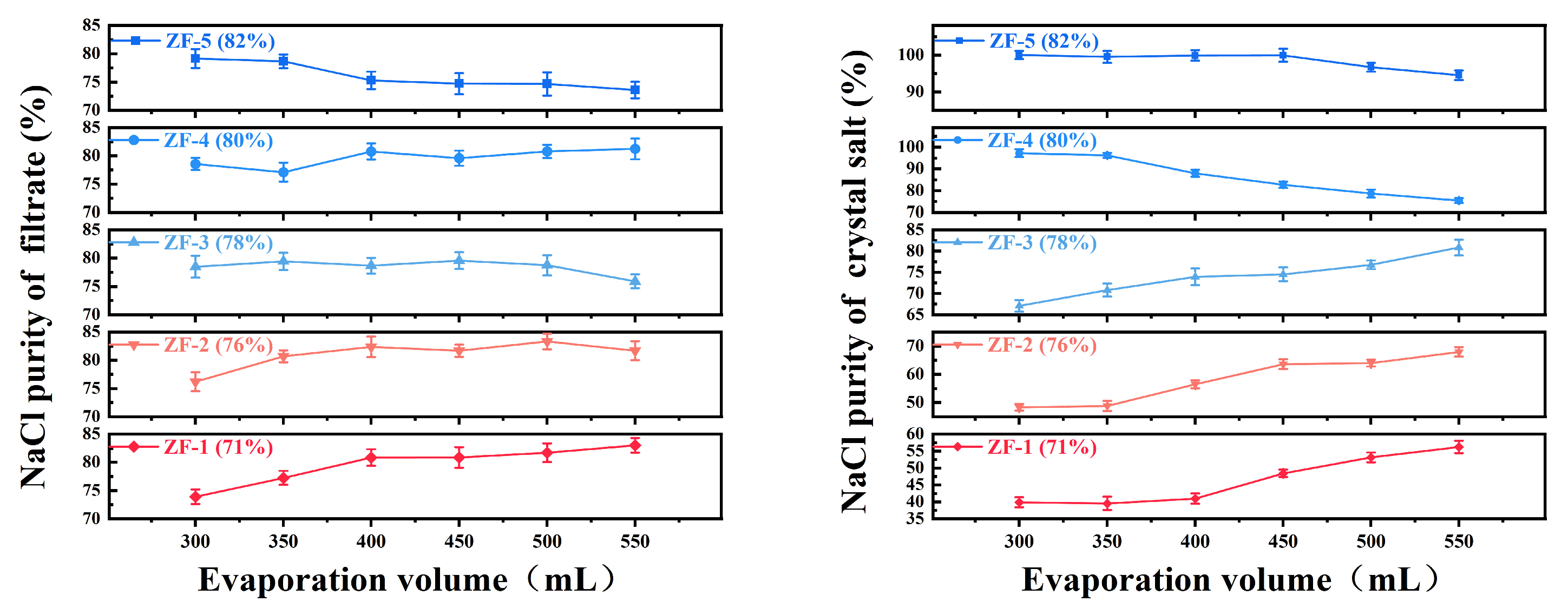
This study conducted evaporation–crystallization experiments on five custom-prepared mixed-salt solutions using an evaporation–crystallization setup. The crystallization behavior of NaCl under varying evaporation volumes (300, 350, 400, 450, 500, and 550 mL) was systematically investigated, with the corresponding results illustrated in Figure 4.
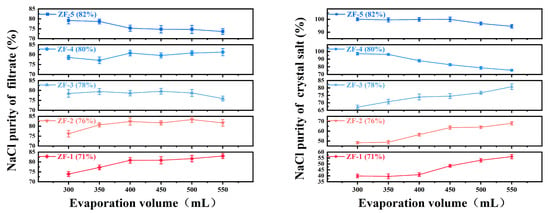
Figure 4.
Variation of NaCl purity with evaporation volume (filtrate and crystalline salt).
Experimental data revealed that when the initial NaCl purity in mixed salts fell within the 71.4–78.0% range, the crystallized salt purity exhibited a gradual decline (from 82.0% to 74.0%) with increasing evaporation volume. This phenomenon indicates preferential crystallization of the Na2SO4 phase under these compositional conditions, consistent with sodium sulfate’s characteristic temperature-dependent solubility behavior. Notably, a phase transition occurred when the initial NaCl purity exceeded 78.0–82.0%, where crystallized salt purity demonstrated significant enhancement with elevated evaporation volume (reaching 96.2% at 350 mL), confirming NaCl as the dominant crystalline phase and in accordance with its relatively temperature-insensitive solubility properties.
Based on industrial specifications requiring ≥90.0% NaCl purity, critical process parameters were identified through data analysis: For initial 80.0% NaCl purity systems, high-purity crystallized salt (96.2%) was achieved at 350 mL evaporation volume, whereas purity dramatically decreased to 87.9% at 400 mL, suggesting the existence of critical operational thresholds. Systems with 78% initial purity consistently produced substandard products (<90.0% purity) across all tested evaporation volumes, while 82.0% purity systems maintained exceptional purity levels (>95.0%) throughout the experimental parameter range (300–400 mL). Thermodynamic phase diagram analysis attributes these phenomena to co-saturation point migration mechanisms in the NaCl-Na2SO4-H2O ternary system.
The optimized process parameters derived from this research recommend maintaining initial NaCl purity within 80.0–82.0% in raw materials and controlling evaporation volume between 350 and 380 mL to ensure the stable production of NaCl crystals exceeding 90.0% purity. These findings provide essential phase equilibrium data and process optimization guidelines for the sustainable resource utilization of mixed-salt systems.
2.2.2. Select the Node for Crystallization Mode
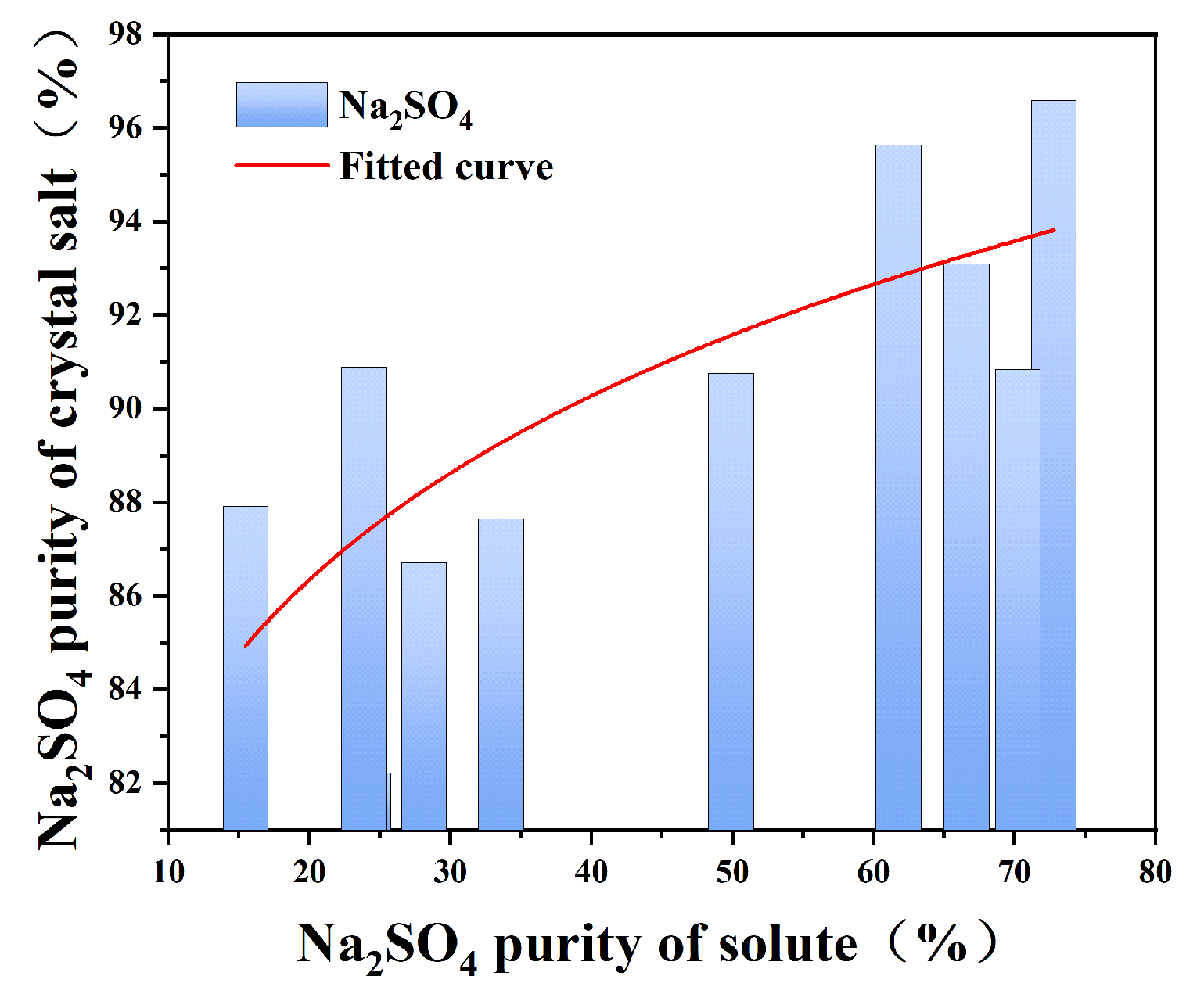
The frozen crystallization experiments revealed distinct phase separation characteristics governed by sodium sulfate’s cryohydric properties. As depicted in Figure 5, the systematic investigation of NaCl-Na2SO4-H2O ternary systems demonstrated critical threshold behavior: when initial Na2SO4 concentration exceeded 15%, low-temperature crystallization (0 °C, 30 min agitation) yielded Na2SO4 crystals with ≥80% purity. This phase selectivity originates from the marked solubility differential—Na2SO4 exhibits 5.2 g/100 g H2O solubility at 0 °C (NaCl’s 35.7 g/100 g H2O), driving preferential nucleation through freeze concentration effects. The crystallization pathway follows Ostwald’s step rule, where metastable Na2SO4 forms prior to NaCl due to a lower nucleation activation energy.
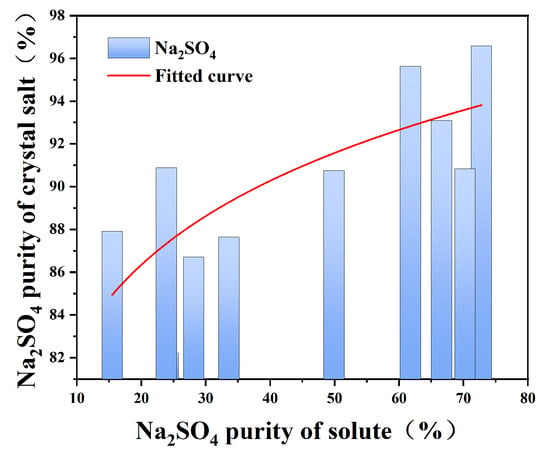
Figure 5.
Purity diagram of Na2SO4 in solution and corresponding crystallization salt when stirring for 30 min in low-temperature crystallization.
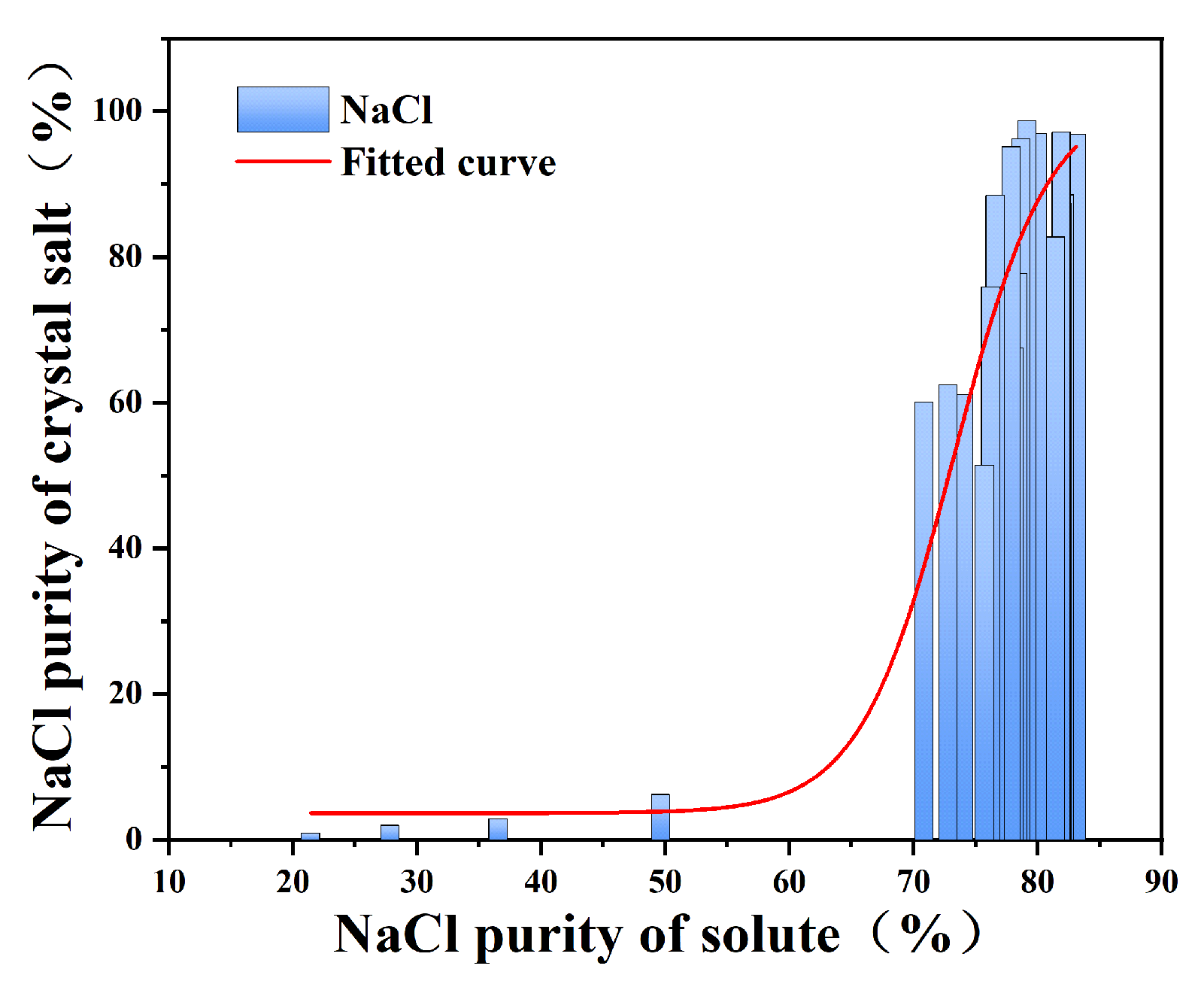
In the stepwise decompression evaporation experiment, the saturated solution is evaporated and precipitated by rotary evaporator in stages in the form of constant evaporation, and the purity of the crystalline salt precipitated in part of the evaporation stage can be improved. The solute in the saturated salt solution and the NaCl mass fraction in the corresponding crystallization salt at the evaporation crystallization stage were collated and plotted into a fitting curve.
As fitting curves such as Figure 6 show, in the stepwise decompression evaporation experiment, the solute NaCl mass fraction directly affected the crystal purity (Figure 6): NaCl > 80%: the crystallization purity was stable > 80%, which was in line with the positive correlation of NaCl solubility with increasing temperature;
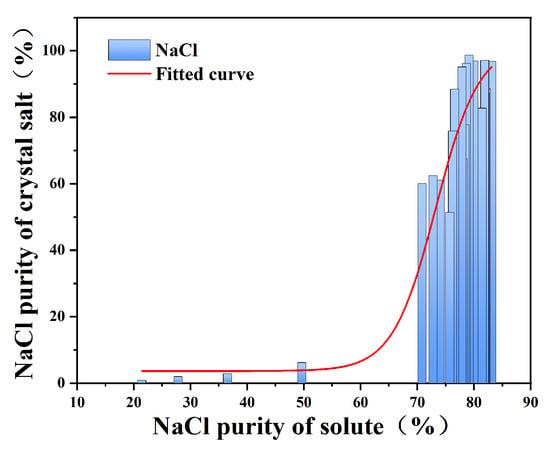
Figure 6.
Purity diagram of NaCl in solution and corresponding crystallization salt when stirring for 30 min in stepwise evaporation crystallization.
NaCl ranges from approximately 70 to 80%: the purity fluctuates significantly (50~80%), mainly due to the intermittent eutectic analysis of Na2SO4; NaCl < 70%: Pre-separation is required to increase the proportion of sodium chloride to avoid inefficient evaporation.
2.3. Frozen Crystallization–Stepwise Decompression Evaporation Combined Separation Process
Combined Process Test Results
Combined with the advantages and disadvantages of frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation, the salt component separation experiment was carried out by using a combination of frozen crystallization to precipitate sodium sulfate and stepwise decompression evaporation crystallization to precipitate sodium chloride. During the reaction process, when the NaCl content is <80%, frozen crystallization is first employed to precipitate Na2SO4, thereby increasing the NaCl concentration in the solution. When the NaCl content exceeds 80%, the process no longer utilizes frozen crystallization for Na2SO4 precipitation but instead switches to stepwise decompression evaporation to primarily crystallize out NaCl. In many industrial production processes, the ratio of sodium chloride to sodium sulfate is close to 3:1. Setting the ratio of 3:1 can better simulate the composition of actual industrial waste salt and ensure that our research results have practical application value and relevance. The experimental results showed the following:
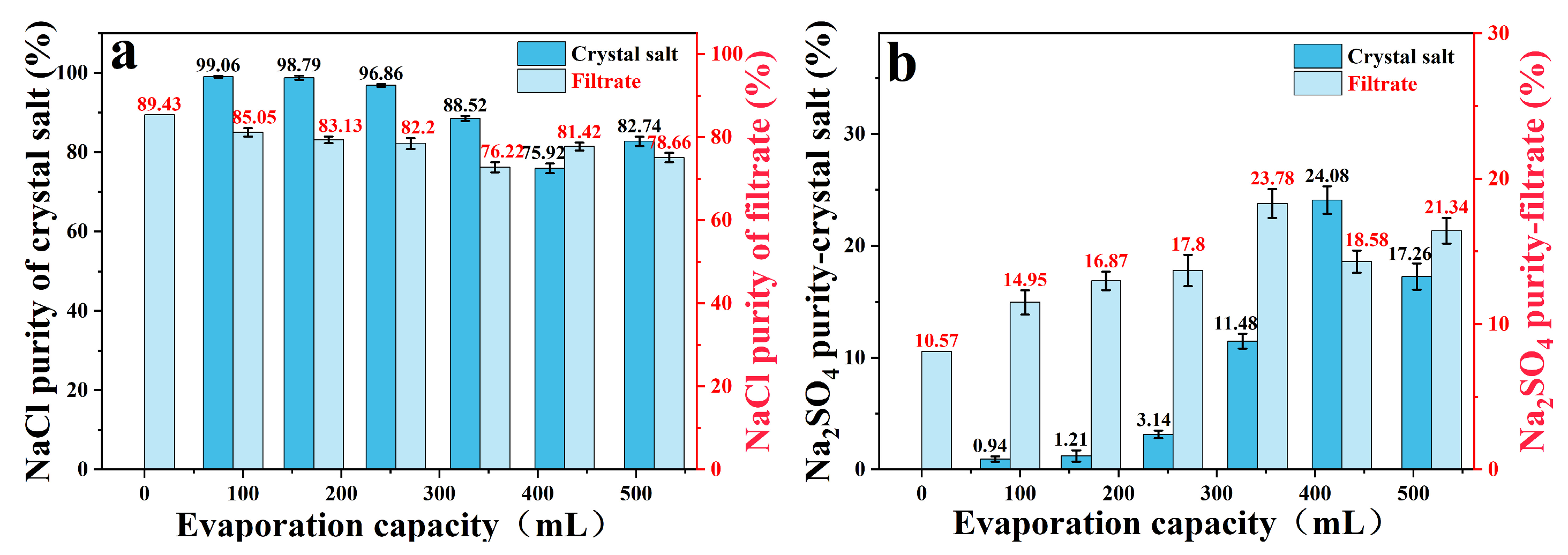
In the frozen crystallization stage, the purity of the crystalline salt of sodium sulfate was 89.99%, and the NaCl content in the filtrate increased from 76.18% to 89.43%, which laid the foundation for subsequent evaporation and enrichment (Table 1). In the stepwise decompression evaporation stage, it can be known that the crystal purity of sodium chloride changes with the evaporation amount in the staged evaporation using the filtrate: the first three evaporations (cumulative evaporation ≤ 255.5 mL) precipitate high-purity NaCl (99.06%, 98.79%, 96.86%); in the subsequent stage, the proportion of NaCl in the filtrate decreased (82.20% → 76.22%), and the purity decreased to 75.92~88.52% (Table 1, Figure 7). Finally, the total yield of sodium chloride was 75.38%, of which high-purity (≥98.5%) crystallization accounted for a significant proportion. The crystallization yield of sodium sulfate is 72.88%, and the purity is stable at about 90%, which meets the industrial application standard. Further optimization of experimental parameters could increase the yield of sodium chloride without damaging the purity of salt.

Table 1.
Experimental data of the combined process.
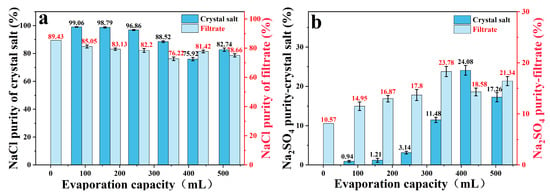
Figure 7.
In the combined process, NaCl (a) and Na2SO4 (b) as a function of evaporation.
In our study, we evaluated the effectiveness of three different processes for the recovery of NaCl and Na2SO4: single evaporation, single frozen crystallization, and a combined process of frozen crystallization followed by stepwise decompression evaporation. The results indicate that the single processes are only effective for the recovery of one type of salt, whereas the combined process achieves high-purity recovery for both salts. Specifically, this combined method yields Na2SO4 with 90% purity and a 72.8% yield, as well as NaCl with 98.5% purity and a 75.4% yield, thereby not only enhancing the overall efficiency but also improving the effectiveness of the separation and recovery of both salts.
2.4. Salt Washing and Purification of Sodium Chloride
2.4.1. Investigation of Wash Liquor Reusability
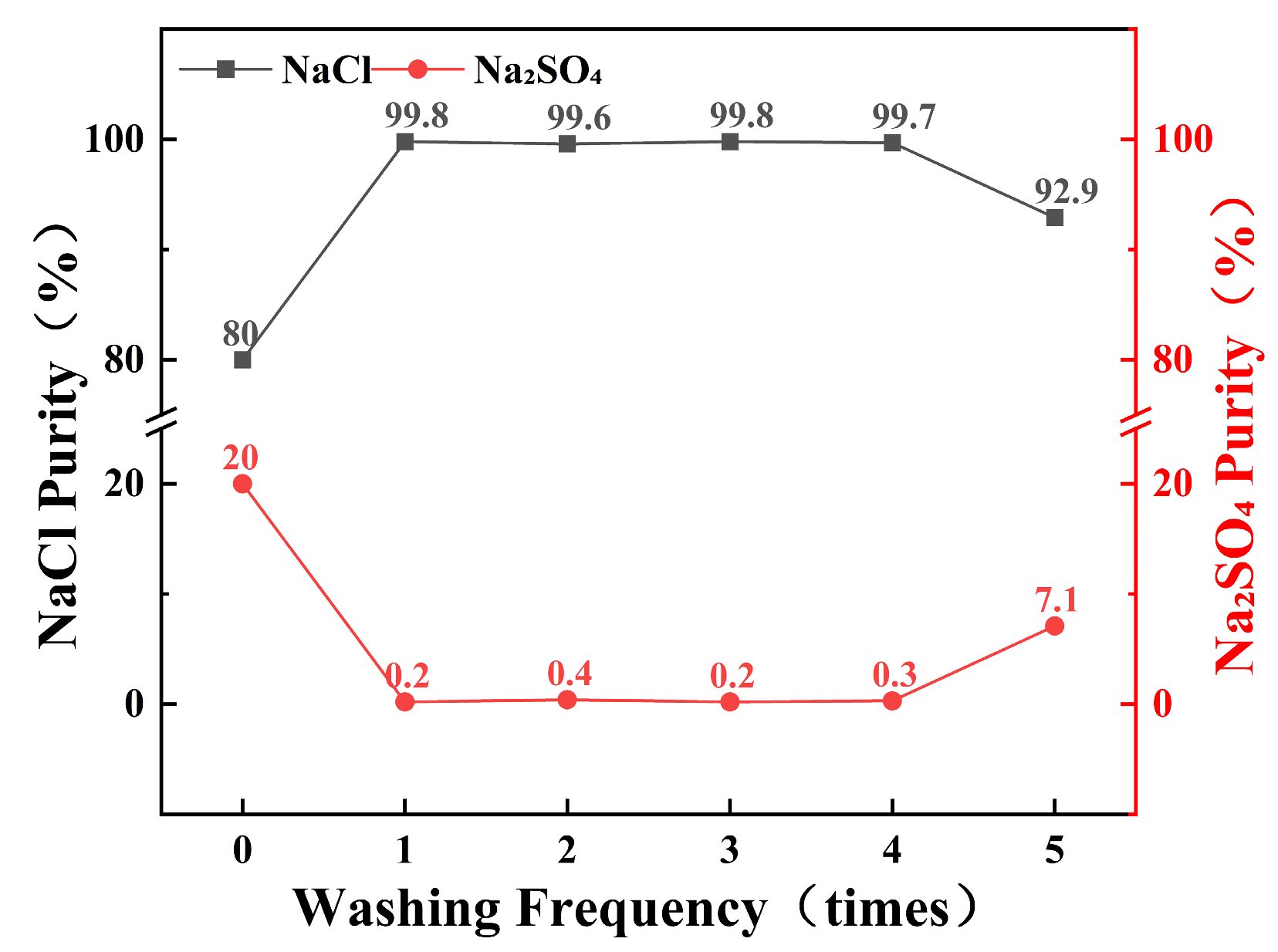
To determine the number of times the wash liquor can be reused, saturated sodium chloride solution was employed as the wash liquor to purify multiple samples of salt with an initial purity of 80%. The results are shown in Figure 8. The wash liquor effectively increased the purity of sodium chloride in the samples. Within four reuses, the wash liquor consistently purified the samples to a purity of over 99.6%. However, when the wash liquor was used for the fifth time, the purification efficiency significantly decreased, resulting in a purity of only 92.9% after washing. This shows that the saturated sodium chloride solution can be reused as washing liquid up to four times, and the original sodium chloride salt with 80% purity is purified to more than 99% each time, which reduces waste and does not affect the salt purity of the product. After using it four times, the wash solution can be reused as a waste salt solution after the combined frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation process.
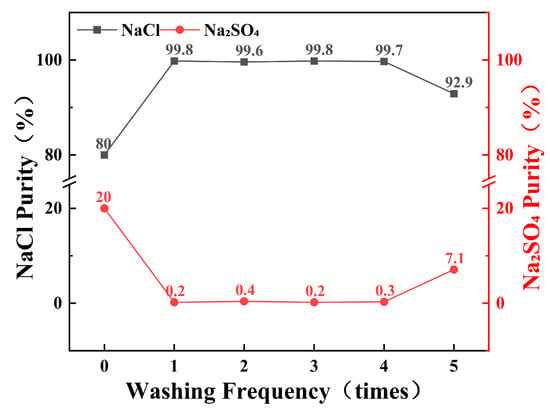
Figure 8.
Effect of wash solution reuse cycles on purification performance.
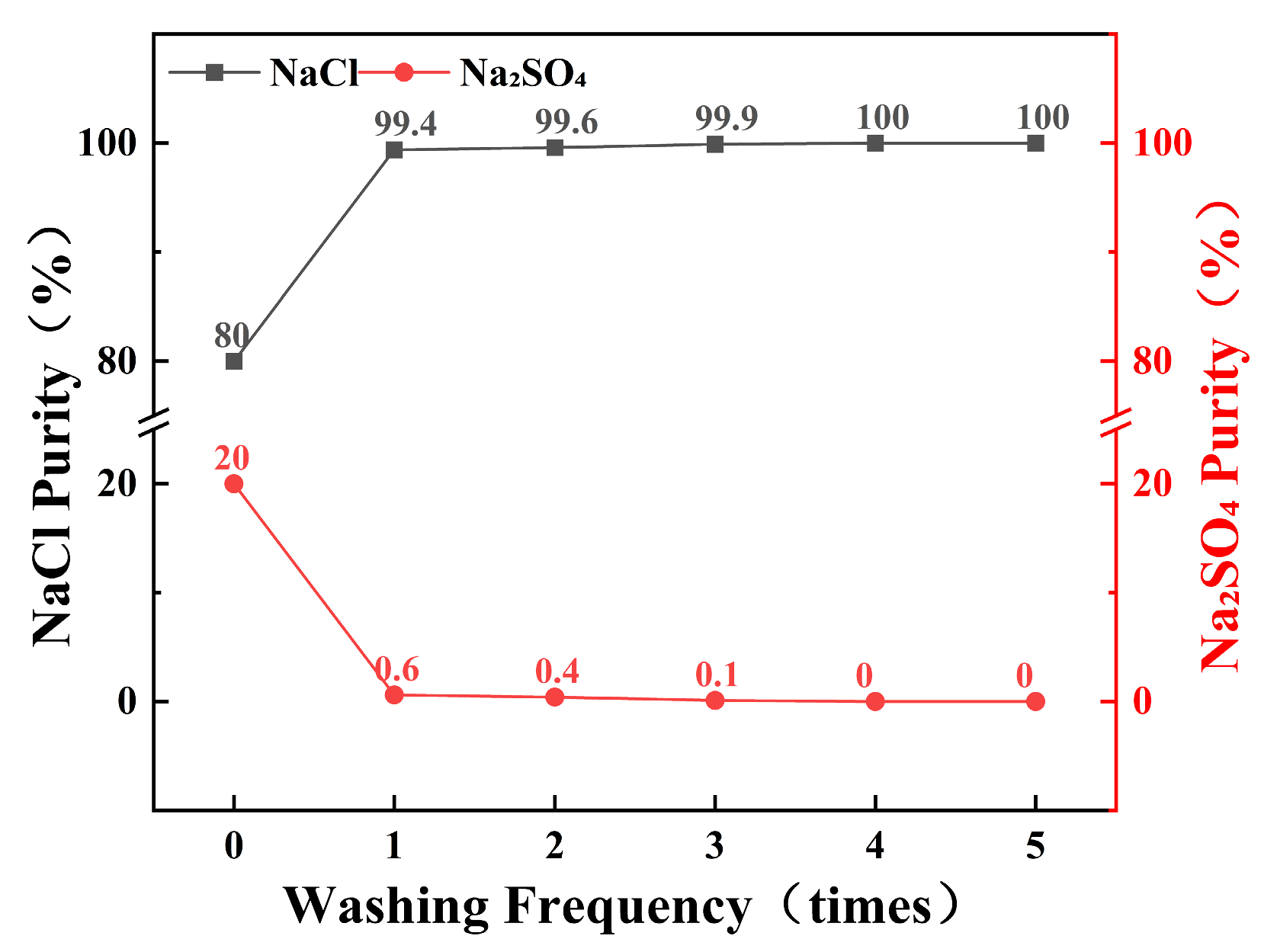
2.4.2. Wash the Same Batch of Salt Many Times
As illustrated in Figure 9, the initial washing of mixed salts with a saturated NaCl solution resulted in a substantial increase in NaCl purity, with 80% of the NaCl achieving a purity of 99.4%. Subsequent multiple washings with fresh saturated NaCl solution further enhanced the purity of NaCl. As the number of wash cycles increased, the purity of NaCl continued to improve, eventually reaching 100%. These results indicate that within a limited stirring duration, the target purity of the product salt can be achieved by increasing the number of washing cycles.
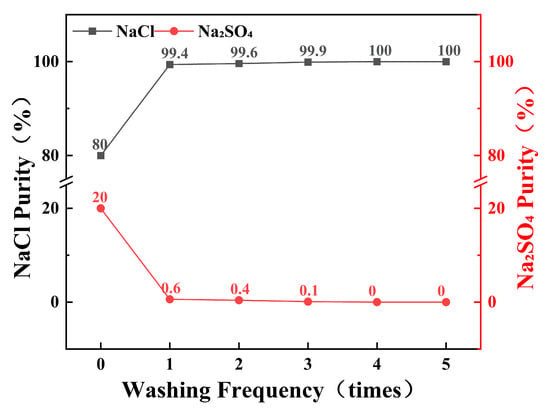
Figure 9.
Purity of NaCl and Na2SO4 in the same batch of salt-wash used many times.
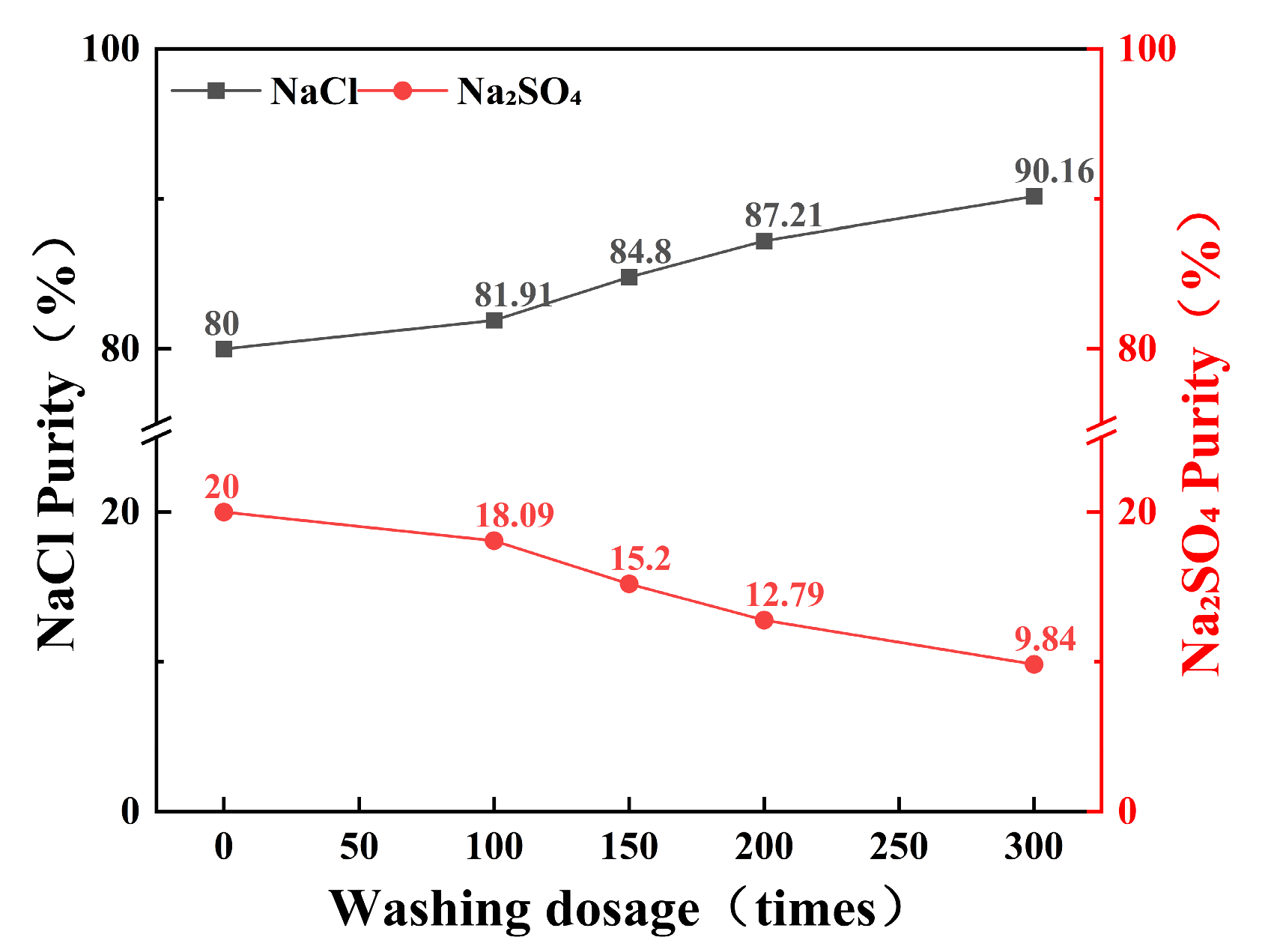
2.4.3. Influence of Lotion Amount on Solubility
The effect of wash liquor volume on the content of NaCl and Na2SO4 in 100 g of prepared salt (NaCl:Na2SO4 = 1:4) after 5 h of stirring is illustrated in Figure 10. During the purification process using the salt-washing method, increasing the volume of wash liquor from 50.0 mL to 300.0 mL can enhance the purity of NaCl in the crystallized salt from 80% to 90.16%. The purification efficiency is directly proportional to the volume of wash liquor used. Salt-washing purification efficiency improves with multiple small-volume washes or increased wash liquor volume.
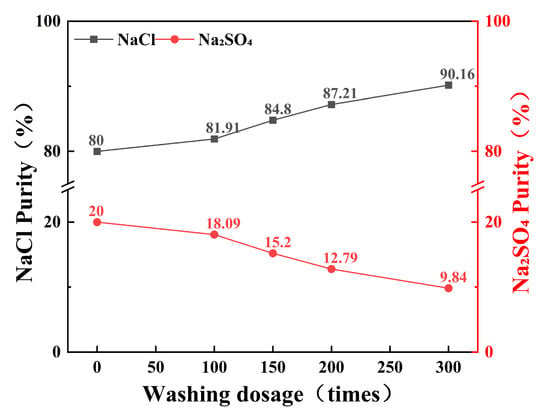
Figure 10.
Effect of lotion amount on the purity of NaCl and Na2SO4.
2.5. X-Ray Diffraction Fluorescence Spectroscopic Analysis
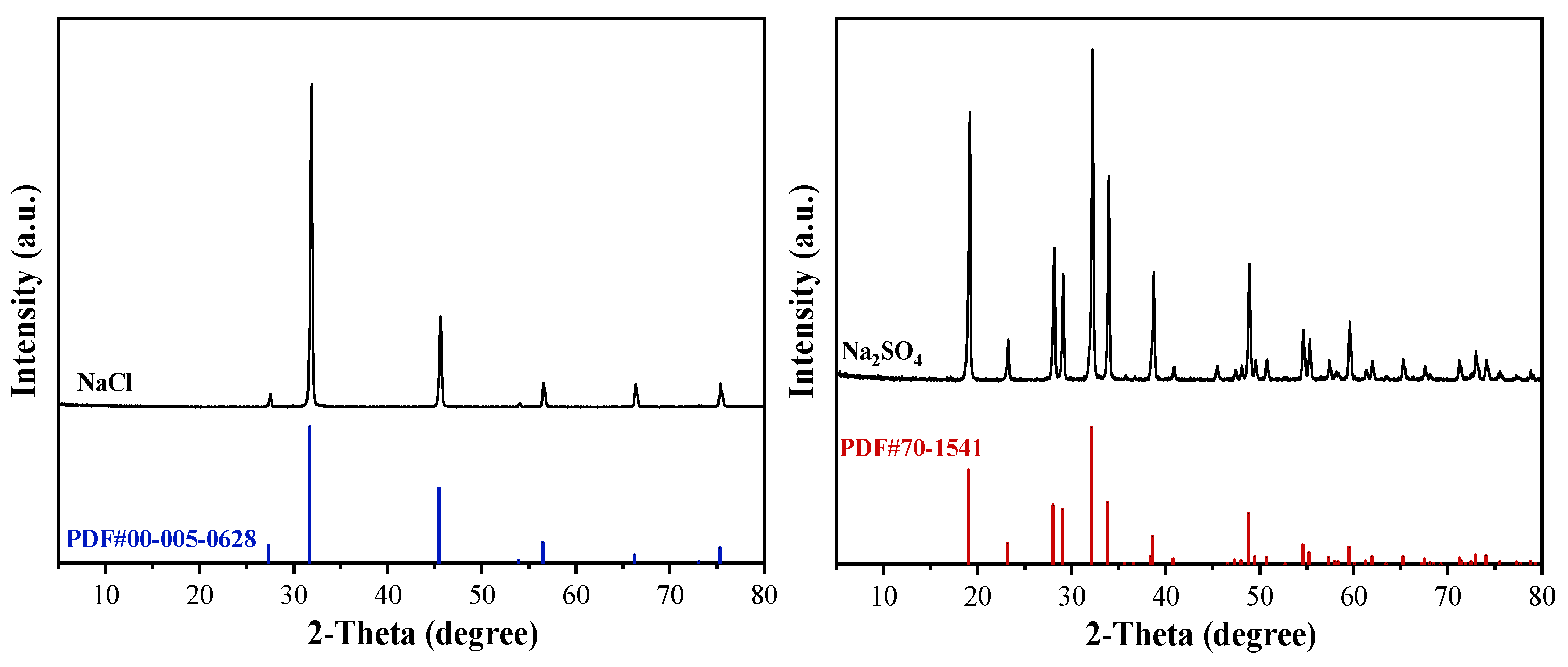
To further verify the chemical composition of solid products obtained through frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation processes, XRD spectroscopy was employed.
Figure 11 presents the chemical composition of products obtained via combined frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation. Characteristic peaks for NaCl (2θ = 31.7°, (200)) and Na2SO4 (2θ = 20.7°, 26.6°, 33.4°) were observed (Figure 11), demonstrating the coexistence of both phases. The higher intensity of the Na2SO4 peaks aligns with its elevated initial concentration, validating the separation efficacy of the proposed process. These results provide critical insights for further optimization and industrial applications.
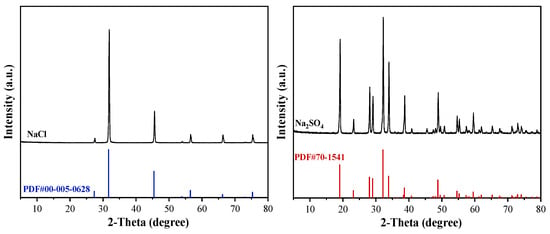
Figure 11.
XRD spectral profile of the resulting products.
2.6. Impact of Impurity Ions
The influence of impurity ions should be considered in the process of recovering waste salt. To evaluate the removal efficiency of impurity ions from waste salts by the combined process, this study referenced the characteristics of actual waste salts from an industrial park in Zhejiang Province. Two representative impurity ions (K+ and NO3−) were selected for in-depth investigation. Custom-prepared mixed salts containing these impurities were subjected to evaporative crystallization and frozen crystallization experiments to assess their removal efficiency. Seven groups of mixed salts with varying impurity ratios were tested under a 40% evaporation rate. As shown in Table 2, the results demonstrated significant impurity removal. The results indicate that the evaporation crystallization process was highly effective in removing K+, with complete removal (100%) achieved in all groups except one, which showed a removal rate of 74.67%. For the NO3− impurity ion, only one group exhibited a removal rate of 81.52%, while the remaining groups consistently exceeded 90% removal efficiency. In conclusion, the evaporative crystallization process exhibited remarkable efficiency in removing impurity ions, highlighting its potential for industrial-scale waste salt purification.

Table 2.
Table of K+ and NO3− removal rates in evaporative crystallization process.
Table 3 presents the ion distribution in crystallized salts from seven groups of mixed salts after 1 h of frozen crystallization. The results demonstrate that the frozen crystallization process also exhibits significant removal efficiency for impurity ions (K+ and NO3−), with K+ removal rates exceeding 97.33% and NO3− removal rates surpassing 78.60%. Compared to the evaporative crystallization process, frozen crystallization demonstrates superior performance in removing impurity ions. Additionally, both processes show higher removal efficiency for K+ than for NO3−. Overall, the combined frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation process achieves remarkable effectiveness in removing impurity ions (K+ and NO3−) when treating real industrial waste salts.

Table 3.
K+ and NO3− removal rates in frozen crystallization process.
2.7. Analysis of Industrial Application Potential
Existing industrial-scale evaporation and freezing equipment for 0 °C has been proven applicable for sodium chloride and sodium sulfate crystallization, respectively. In fact, as long as the temperature of frozen crystallization is kept close to 0 °C, the effect of massive precipitation of Na2SO4 crystals can be achieved, and the effect of frozen crystallizer on the market can be achieved. When applying this combined process, selecting evaporation or freeze crystallization based on the wastesalt purity can enhance the crystalsalt purity and yield. Compared with other saltseparation methods, membrane separation is only suitable for lowsalinity brine (<5% TDS). It is prone to irreversible membrane fouling when treating highsalinity wastewater and is thus unsuitable for wastesalt treatment. The antisolvent crystallization saltseparation process has not been widely applied on a large scale. Moreover, organic solvents (like methanol) are highly toxic. Their use involves risks and demands highstandard equipment sealing, which restricts their largescale application.
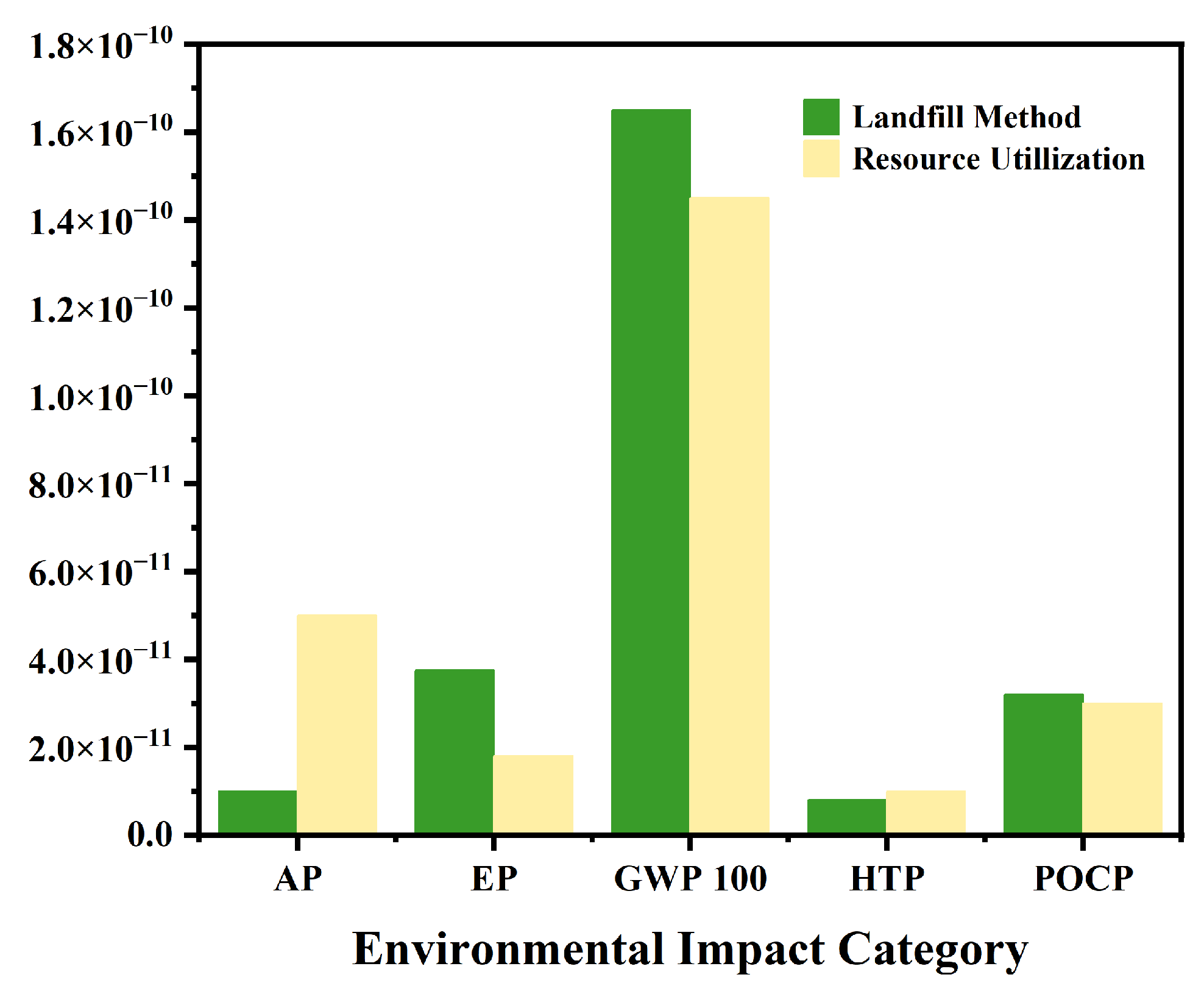
This study performed a lifecycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental performance of the proposed frozen-stepwise evaporation crystallization combined process against conventional landfill disposal. The results reveal substantial reductions in most environmental impact categories for the combined process, as illustrated in Figure 12: global warming potential (GWP100), 12.5% reduction; eutrophication potential (EP), 83.9% reduction; photochemical ozone creation potential (POCP), moderate decrease (6.8%). These reductions underscore the environmental viability of the combined process. However, two impact categories showed elevated values: acidification potential (AP) increased by 18.2%, and human toxicity potential (HTP) rose by 9.7%, attributed primarily to the energy-intensive pyrolysis of waste salts (high electricity/natural gas demand) and pyrolysis off-gas emissions (e.g., NOx, SO2). Future research should prioritize optimizing pyrolysis parameters (e.g., temperature control, residence time, and gas scrubbing) to mitigate these adverse effects.
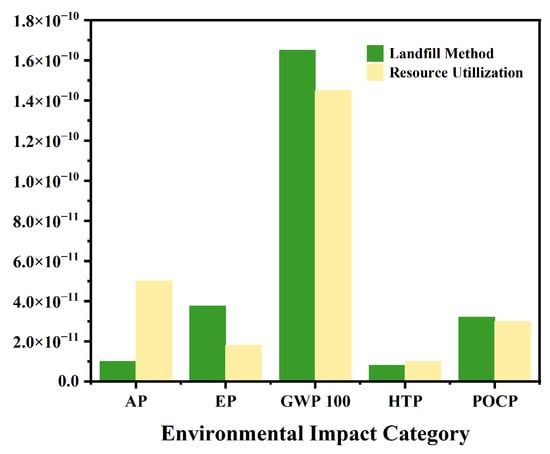
Figure 12.
Comparison chart of LCA between combined process and traditional landfill method.
Additionally, the current LCA assumes the single-cycle treatment of 1 ton of waste salt, where post-washing brine is discharged after wastewater treatment. This simplification overestimates environmental burdens, as industrial applications would recycle the brine into the washing system for continuous salt recovery, drastically reducing wastewater discharge. Consequently, while HTP increases marginally in practice, it remains within controllable thresholds.
3. Experimental Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
Chemical reagents: sodium chloride (NaCl, AR grade) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4, AR grade) were procured from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Deionized water (18.2 MΩ·cm) was obtained from a Milli-Q water purification system (Shanghai, China).
Sample preparation: To prepare the samples with a mass ratio of NaCl to Na2SO4 of 7:3 and a concentration of 100 mg/L, 60.0000 g of NaCl and 25.7145 g of Na2SO4 were dissolved in 400.0 mL of pure water. This method ensured the desired concentration and composition for the subsequent experiments.
The experimental setup comprised the following: A low-temperature circulator (BILON-T-1000, Shanghai Bilon Instruments Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China) for frozen crystallization temperature control (±0.5 °C), a rotary evaporator (RE-2000B, Shanghai Yarong Biochemical Instrument Factory Shanghai, China) with vacuum regulation (1–100 kPa), and an ion chromatograph (ICS600, Thermo Fisher Shanghai, China) equipped with a autosampler(CETAC ASX-520 Shanghai, China) (Na2SO4: LOD = 0.15 mg/L, LOQ = 0.50 mg/L, NaCl: LOD = 0.10 mg/L, LOQ = 0.35 mg/L).
3.2. Experimental Methods
3.2.1. Sodium Sulfate Crystals Were Precipitated by Frozen Crystallization
The systematic investigation into the impact of reaction time on the purity of sodium sulfate in the filtrate and crystallized salt during the frozen crystallization process is presented. Mixed solutions of NaCl and Na2SO4 (Table 4) were agitated in a mechanically stirred low-temperature water bath for durations of 70, 210, and 420 min. Samples of the filtrate and crystalline phases were collected at set intervals to measure the redistribution of components. The primary distinctions between the DJ-1 and DJ-2 experiments lie in the sampling methodology, experimental procedures, and error control. As far as the sampling method is concerned, DJ-1 involves dividing the solution into seven parts and treating them at different times before mixing, while DJ-2 takes samples from the same beaker at different times. As for the experimental procedures, DJ-1 improved the accuracy of the data by batch processing and merging crystallized salts; DJ-2, on the other hand, is simpler in operation but may suffer from uneven sampling. In terms of error control, DJ-1 reduces such errors by batch processing, thereby increasing the reliability of the results; DJ-2 might introduce errors due to uneven sampling.

Table 4.
Experimental conditions of NaCl-Na2SO4.
To determine the crystallization thresholds under low-temperature conditions (0 °C), concurrent experiments were conducted using saturated solutions with varying ionic ratios. The salt ratios represented by DW were established based on the varying concentrations of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) found in different types of industrial waste salts. The concentration of Na2SO4 in these waste salts ranges from 15% to 70%. To comprehensively cover this range and to simulate the compositions of waste salts generated in various industrial processes, we selected a series of initial Na2SO4 purities in our experiments, ranging from 15.5% to 72.8%. The experiments involved seven groups of saturated solutions, each with distinct initial Na2SO4 purities (DW-1 at 15.5%, DW-2 at 23.9%, DW-3 at 24.2%, DW-4 at 33.6%, DW-5 at 49.9%, DW-6 at 70.2%, and DW-7 at 72.8%). The solutions were subjected to controlled agitation at a constant speed of 200 rpm within a cryostat bath equipped with mechanical stirring. Samples were collected at predetermined intervals of 5, 10, 20, and 30 min to quantify the redistribution of components.
Each experiment was repeated three times to ensure the reproducibility and reliability of the results. The purity of the final products (Na2SO4 and NaCl) was measured after thorough drying to ensure accurate quantification. These procedures were applied consistently across all experiments described in this study. This parametric analysis established operational boundaries for optimal salt recovery efficiency through frozen crystallization protocols.
Filtrate and crystalline salt samples were diluted to <100 mg/L for ion chromatography (IC) analysis, and a standard curve solution was prepared to detect the Na2SO4 content using IC. Based on the data measured by IC, the content of Na2SO4 in the filtrate and bottom crystalline salt at each time was calculated, and its trend over time was plotted.
3.2.2. Stepwise Decompression Evaporation Crystallization Method
In the stepwise decompression evaporation process, the objective is to separate NaCl and Na2SO4 from mixed-salt solutions through controlled evaporation under reduced pressure. The study utilized analytical-grade NaCl and Na2SO4 to prepare five groups of double-saturated salt solutions with NaCl purities varying between 71.43% and 82% (ZF-1 at 71.43%, ZF-2 at 76.00%, ZF-3 at 78.00%, ZF-4 at 80.00%, and ZF-5 at 82.00%), each with a total volume of 1 L. The evaporation was conducted at a water bath temperature of 60 °C, with evaporation parameters set to 300–550 mL. Following evaporation, the supernatant liquid and crystallized salts were subjected to filtration, drying, and weighing to quantitatively analyze their purities.
3.2.3. Frozen Crystallization–Stepwise Decompression Evaporation Combined Separation Process
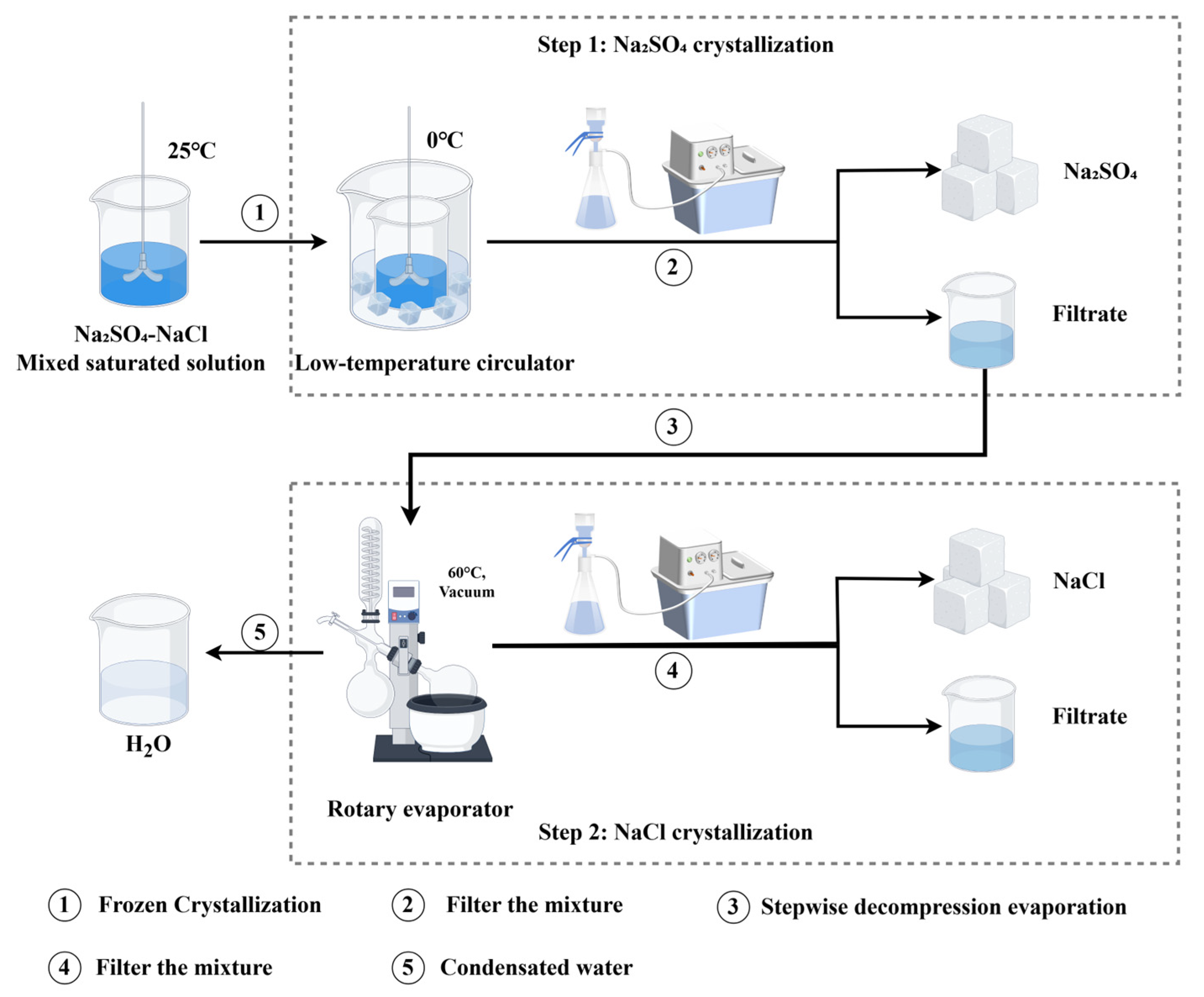
The solubility of sodium chloride (NaCl) and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) varies with temperature. Based on these solubility characteristics, a mixed saturated solution of NaCl and Na2SO4 is first subjected to frozen crystallization to precipitate Na2SO4 crystals, followed by stepwise decompression evaporation to precipitate NaCl crystals. As depicted in Figure 13, the prepared mixed solution was placed in a constant-temperature water bath at 25 °C and stirred using a mechanical stirrer until all salts were completely dissolved. Subsequently, the solution was transferred to a low-temperature circulator for frozen crystallization. After stirring for 30 min, the mixture was filtered. A 1.0 mL aliquot of the filtrate was diluted and analyzed for NaCl and Na2SO4 content. The filtrate was then transferred to the evaporation flask of a rotary evaporator. The rotary evaporator was set to 60 °C at 130 rpm, and the vacuum pump was activated until the vacuum gauge stabilized (typically between −0.08 and −0.09 MPa). When the evaporation volume approached 80.0 mL, the heating was stopped, and the system was allowed to rest for 5 min to ensure complete condensation of water vapor. The evaporation flask was then removed, filtered, and the filtrate density was measured. A 4.0 mL sample was taken for NaCl and Na2SO4 analysis. The precipitated salts were dissolved and diluted for further NaCl and Na2SO4 content analysis. To assess the impact of residual salts on salt loss, the evaporation flask was rinsed four times, and the rinse solution was made up to 1000.0 mL.
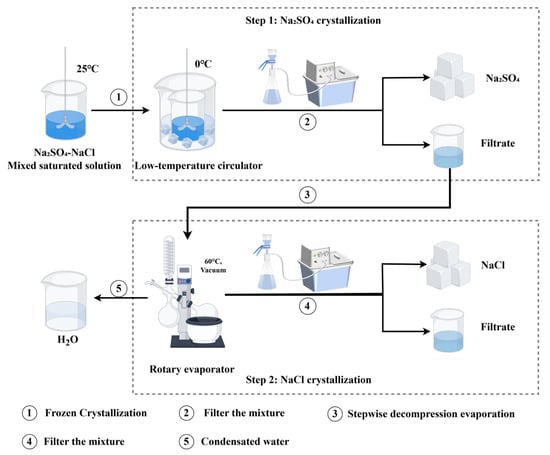
Figure 13.
Combined process experiment operation flowchart.
3.2.4. Salt Washing and Purification
A prepared salt mixture (NaCl:Na2SO4 = 1:4) was used. One hundred grams of the prepared salt was added to 1 L of saturated NaCl solution and stirred for 1 h, after which it was filtered. The filtrate and filter cake were treated separately. The filtrate was subjected to the same procedure four more times, with 100 g of prepared salt added each time. The filter cakes from the five filtrations were dried to constant weight. The filter cakes were then placed in a new 100 mL saturated NaCl solution, and the stirring and filtration process was repeated five times. One hundred grams of prepared salt was washed with 100, 150, 200, and 300 mL of saturated NaCl solution, respectively. After stirring for 5 h, it was filtered, and the filter cake was dried to constant weight and analyzed by ion chromatography to determine the salt composition.
3.2.5. Analytical Methods
The concentrations of Cl− and SO42− were determined by ion chromatography (IC, Metrohm, Shanghai, China). In the detection process, an anion chromatographic column was used, the eluent was composed of 3.6 mM Na2CO3 and 4.5 mM NaHCO3, the inhibitor was composed of a 10% H2SO4 solution, the IC injection flow rate was 1.5 mL/min, and the pressure was 3.6 MPa. The concentration range of chloride ion and sulfate ion standard solution was 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 mg/L, and the standard curve was drawn. The sample to be tested was diluted and measured on the machine. The crystalline phase of the product salt was identified by X-ray diffractometer (XRD).
3.2.6. Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
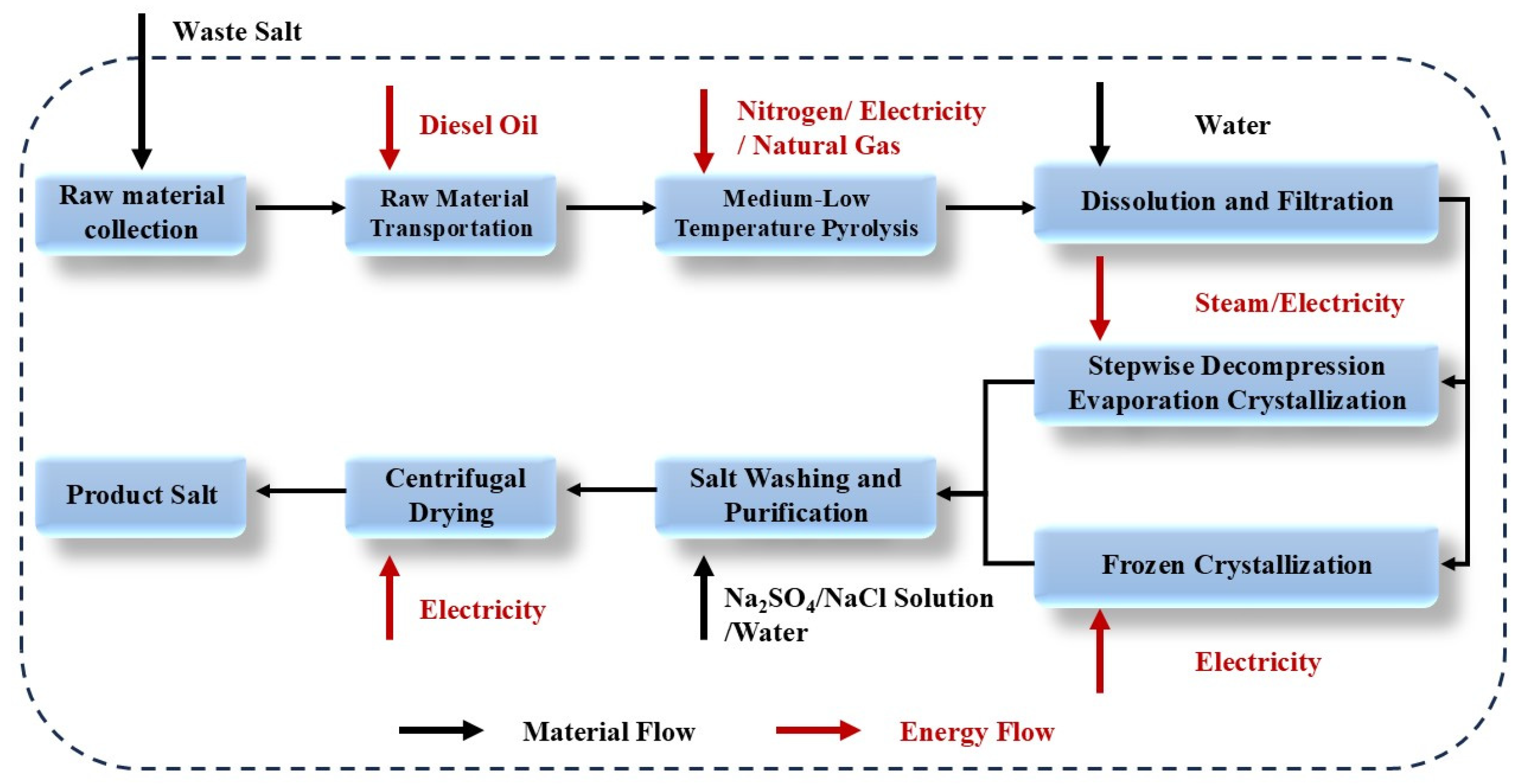
The lifecycle assessment (LCA) of the preliminary experimental data from the process combining frozen crystallization with stepwise decompression evaporation was conducted using GaBi 10 software. As illustrated in Figure 14 below, the system boundary spans from the transportation of waste salts to the production of industrial-grade salt products. The process encompasses the following stages: transportation of waste salts; pyrolysis of waste salts; dissolution and filtration of waste salts; crystallization of NaCl and Na2SO4; purification of crystallized salts; production of salt products; emission of flue gases; and discharge of wastewater.
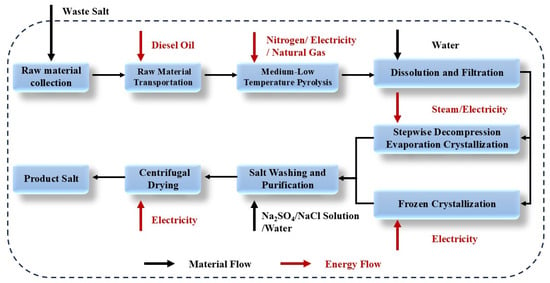
Figure 14.
Boundary of combined process system.
In this waste-salt valorization scenario, the data on salt pyrolysis, crystallization/purification, and energy consumption during the process were derived from experimental procedures. Additionally, fundamental inventory data for electricity, water, and other basic materials were sourced from established databases, based on the lifecycle inventory of the studied system. The compiled input–output inventory is presented in Table 5. Following the CML2001 methodology for environmental impact categories, this study selected the following indicators for in-depth analysis: acidification potential (AP), global warming potential (GWP100), eutrophication potential (EP), photochemical ozone creation potential (POCP), and human toxicity potential (HTP).

Table 5.
Input and output data list table.
4. Conclusions
This study successfully developed a process that combines frozen crystallization and stepwise decompression evaporation to effectively separate sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and sodium chloride (NaCl) from mixed salts, achieving the resource utilization of waste salts. For mixed salts with sodium chloride content exceeding 80%, evaporative crystallization is the preferred method; for lower contents, frozen crystallization yields higher purity and recovery rates. The concrete results include treating the solution containing 75% sodium chloride to obtain sodium sulfate with a purity of 89.9% and a recovery of 72.8%, and sodium chloride with a purity of 98.5% and a recovery of 75.4%. Additionally, the salt washing process can enhance the purity of sodium chloride from 80% to over 99%, meeting industrial standards. This study provides a theoretical basis for the recovery of high-purity salts from mixed salts using the combined process. Future research should focus more on the industrial application of this combined process to real waste salts and further explore the types of nucleation inhibitors that can be used to reduce eutectic contamination during crystallization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.W.; methodology, C.W.; software, H.W.; validation, C.W., X.H. and H.W.; formal analysis, X.H.; investigation, R.C.; resources, C.W.; data curation, R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.W.; writing—review and editing, C.W. and X.H.; visualization, C.W. and X.H.; supervision, X.R.; project administration, X.R.; funding acquisition, X.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Pilot-scale treatment of hypersaline coal chemical wastewater with zero liquid discharge. Desalination 2021, 518, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, T.; Klungsøyr, J.; Sanni, S. Environmental impacts of produced water and drilling waste discharges from the Norwegian offshore petroleum industry. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 92, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessa, Y.W.; Lang, Q.; Yan, B.; Kuang, S.; Mao, D.; Shu, L.; Zhang, Y. Anion exchange membrane organic fouling and mitigation in salt valorization process from high salinity textile wastewater by bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Desalination 2019, 465, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Tian, B.; Zhu, M.; Yang, M. Current progresses in the analysis, treatment and resource utilization of industrial waste salt in China: A comprehensive review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 217, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress on Zero Discharge and Resource Utilization of Industrial High-Salt Wastewater. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2021, 49, 2000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Heterogeneous impact of soil acidification on crop yield reduction and its regulatory variables: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 319, 109643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.; Refaat, A.; Munshi, F.; El-Said, M.A.; El-Shafai, S.A. Influence of Salinity Level on the Treatment Performance and Membrane Fouling of MBRs Treating Saline Industrial Effluent. Water 2024, 16, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, X.; Hua, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, L.; Dai, X. Biological treatment processes for saline organic wastewater and related inhibition mechanisms and facilitation techniques: A comprehensive review. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ismail, S.; Wang, Z.-B.; Ni, S.-Q. Salt-tolerant marine sludge is more suitable for stable and efficient high-salinity wastewater treatment than activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.T.; Lewis, A.E.; Witkamp, G.J.; Kramer, H.J.M.; van Spronsen, J. Recovery of Na2SO4·10H2O from a reverse osmosis retentate by eutectic freeze crystallisation technology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Lee, S.; Vigneswaran, S. Recovery of sodium sulfate from seawater brine using fractional submerged membrane distillation crystallizer. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Huang, X. Optimization design analysis on sodium chloride solution evaporative crystallization system driven by high-temperature heat pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 254, 123860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Chang, J.; Chung, T.-S. Cooling Crystallization of Sodium Chloride via Hollow Fiber Devices to Convert Waste Concentrated Brines to Useful Products. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 10183–10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penha, F.M.; Andrade, F.R.D.; Lanzotti, A.S.; Moreira Junior, P.F.; Zago, G.P.; Seckler, M.M. In Situ Observation of Epitaxial Growth during Evaporative Simultaneous Crystallization from Aqueous Electrolytes in Droplets. Crystals 2021, 11, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FernÁNdez-Lozano, J.A. Sodium Sulphate from Bittern by Methanol. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1996, 154, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Gao, B.; Bhatti, S.; Capellades, G.; Yenkie, K.M. Process Design Framework for Inorganic Salt Recovery Using Antisolvent Crystallization (ASC). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-L.; Wei, C.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, M.; Fan, G. Optimization of NaOH–Na2CO3 brine purification method: From laboratory experiments to industrial application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzer, K.S.; Murdzek, J.S. Thermodynamics of aqueous sodium sulfate. J. Solut. Chem. 1982, 11, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmoria, P.; Gehlot, P.S.; Gupta, H.; Kumar, A. Temperature-Dependent Solubility Transition of Na2SO4 in Water and the Effect of NaCl Therein: Solution Structures and Salt Water Dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 12734–12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. The apparent and partial molal volume of aqueous sodium chloride solutions at various temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. 1970, 74, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharmoria, P.; Gupta, H.; Mohandas, V.P.; Ghosh, P.K.; Kumar, A. Temperature Invariance of NaCl Solubility in Water: Inferences from Salt–Water Cluster Behavior of NaCl, KCl, and NH4Cl. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 11712–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Lei, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, J.; Fang, T. Experimental Determination and Modeling of the Solubility of Sodium Chloride in Subcritical Water from (568 to 598) K and (10 to 25) MPa. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 3374–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Explanation and Exploration of the Isothermal Titration Curve for the NaCl + Na2SO4 + H2O System at 298.15 K and 102.2 kPa. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25811–25821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.; Xu, L.; Horseman, T.; Westerhoff, P.; Xu, P.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Alghanayem, R.; Lin, S. Brine management with zero and minimal liquid discharge. Nat. Rev. Clean Technol. 2025, 1, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Deng, R. Directional salt crystallization system for high-efficiency solar-driven evaporation to achieve zero-liquid discharge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Tong, Z.; Huang, K. Recent advances in solar-driven interfacial evaporation coupling systems: Energy conversion, water purification, and seawater resource extraction. Nano Energy 2024, 120, 109180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Jing, L.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Multi-interface engineering of solar evaporation devices via scalable, synchronous thermal shrinkage and foaming. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semblante, G.U.; Lee, J.Z.; Lee, L.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Brine pre-treatment technologies for zero liquid discharge systems. Desalination 2018, 441, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Bian, H.; Liu, X.; Rong, R.; Song, D.; Peng, C. Feasibility of effective separation of NaCl and Na2SO4 after simultaneous crystallization from solution. Powder Technol. 2024, 444, 120053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, S.; Sahu, P.; Masani, H.R.; Dinesh, A.K.; Upadhyay, S.C.; Vyas, B.G.; Kumar, A. Process integration and techno-economic assessment of crystallization techniques for Na2SO4 and NaCl recovery from saline effluents. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2024, 203, 109879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, A.V.; Podupu, P.K.R.; Coliaie, P.; Singh, M.R. Three-Step Mechanism of Antisolvent Crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Deng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, S.; Huang, X. Recovery of NaCl and Na2SO4 from high salinity brine by purification and evaporation. Desalination 2022, 530, 115631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balis, E.; Griffin, J.C.; Hiibel, S.R. Membrane Distillation-Crystallization for inland desalination brine treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).