Conditioning Solid-State Anode-Less Cells for the Next Generation of Batteries
Abstract
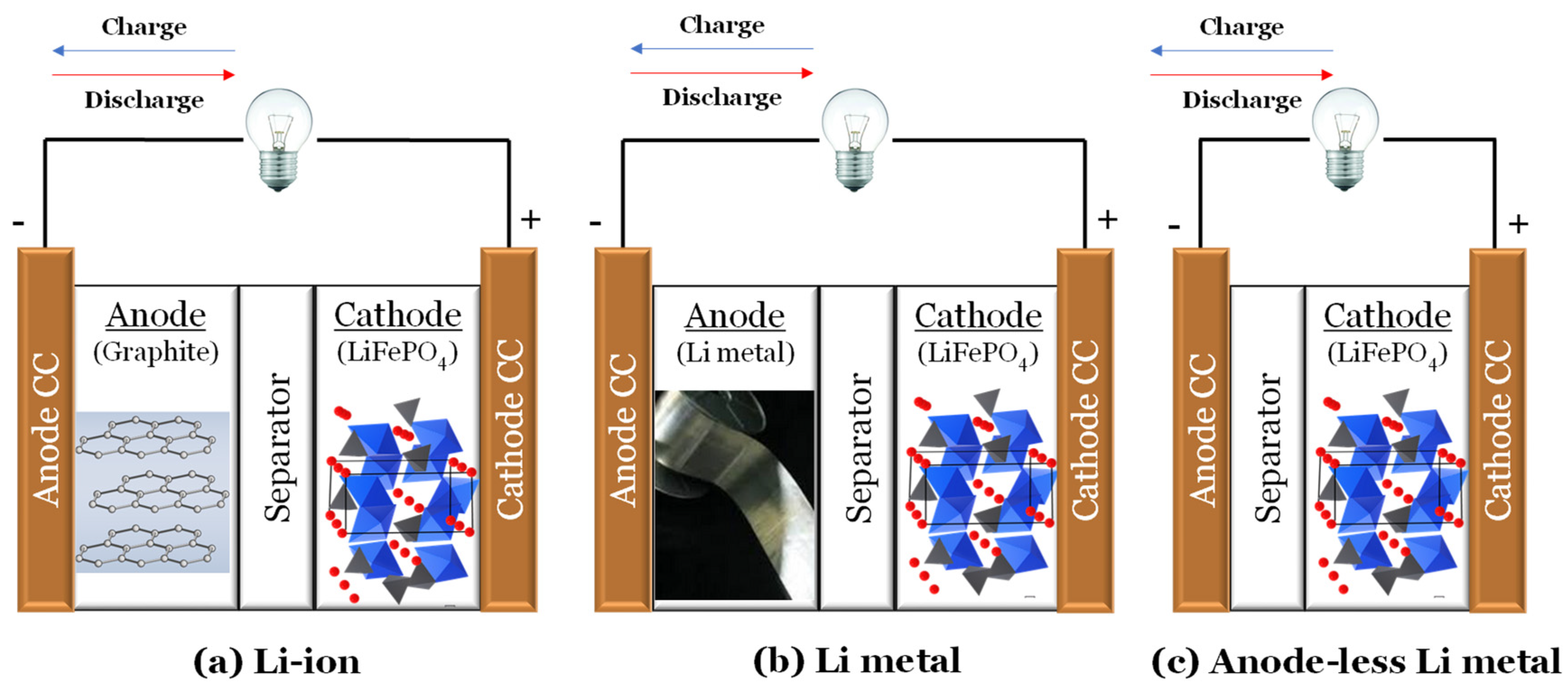
1. Introduction
While there are relatively few original papers on anode-less cells in the solid state, notable references include the work of Neudecker et al. (2000) [19], who presented a novel lithium-free thin-film battery with an in situ Li coating on the Cu anode current collector during the charging step. This work was later cited by Bates et al. (2000) [20]. Lee, Liu, and Tracy (2003) [21] assembled an anode-free solid-state battery (AFSSB) with a different configuration, namely SS/LiPON/Li1.3V2O5/Cu, fabricated on a stainless steel (SS) substrate using sequential thin-film deposition methods. Westover et al. (2019) [22] worked with a solid LiPON electrolyte, highlighting the importance of achieving a homogeneous, pore-free morphology for anode-less battery success. Zegeye et al. (2020) [23] developed a surface-rolled ultrafine polymer solid-state electrolyte for anode-free solid-state batteries. Wang et al. (2020) [24] presented a “Li-free” battery using the solid electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO). The cell was fabricated by depositing lithium directly from a composite cathode of NCA/PEO onto a copper current collector through the LLZO electrolyte. This cell underwent 50 cycles at a C/19 rate, showing initial capacities of 0.8 mAh cm−2 and nearly 100% coulombic efficiency. In 2022/2023, numerous interdisciplinary studies focused on advancing anode-less or anode-free cell configurations across multiple fields [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Current Collector: Copper
2.1.2. Surface-Coating Layer: ZnO Solution Deposition
2.1.3. Cathode: LiFePO4
2.1.4. Separator: Cellulose with Solid Electrolyte Li2.99Ba0.005ClO
2.1.5. Laminated Film
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Pouch Cells Fabrication
2.2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.2.3. Samples Preparation for XPS, SEM, EDX, and LIBS Analysis
2.2.4. XPS, SE()M, and EDX Analysis
2.2.5. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of the Cu/Li2.99Ba0.005ClO Composite in Cellulose/LiFePO4/Cu Pouch Cell with Cu as a Negative Current Collector
3.1.1. Electrochemical Cycling
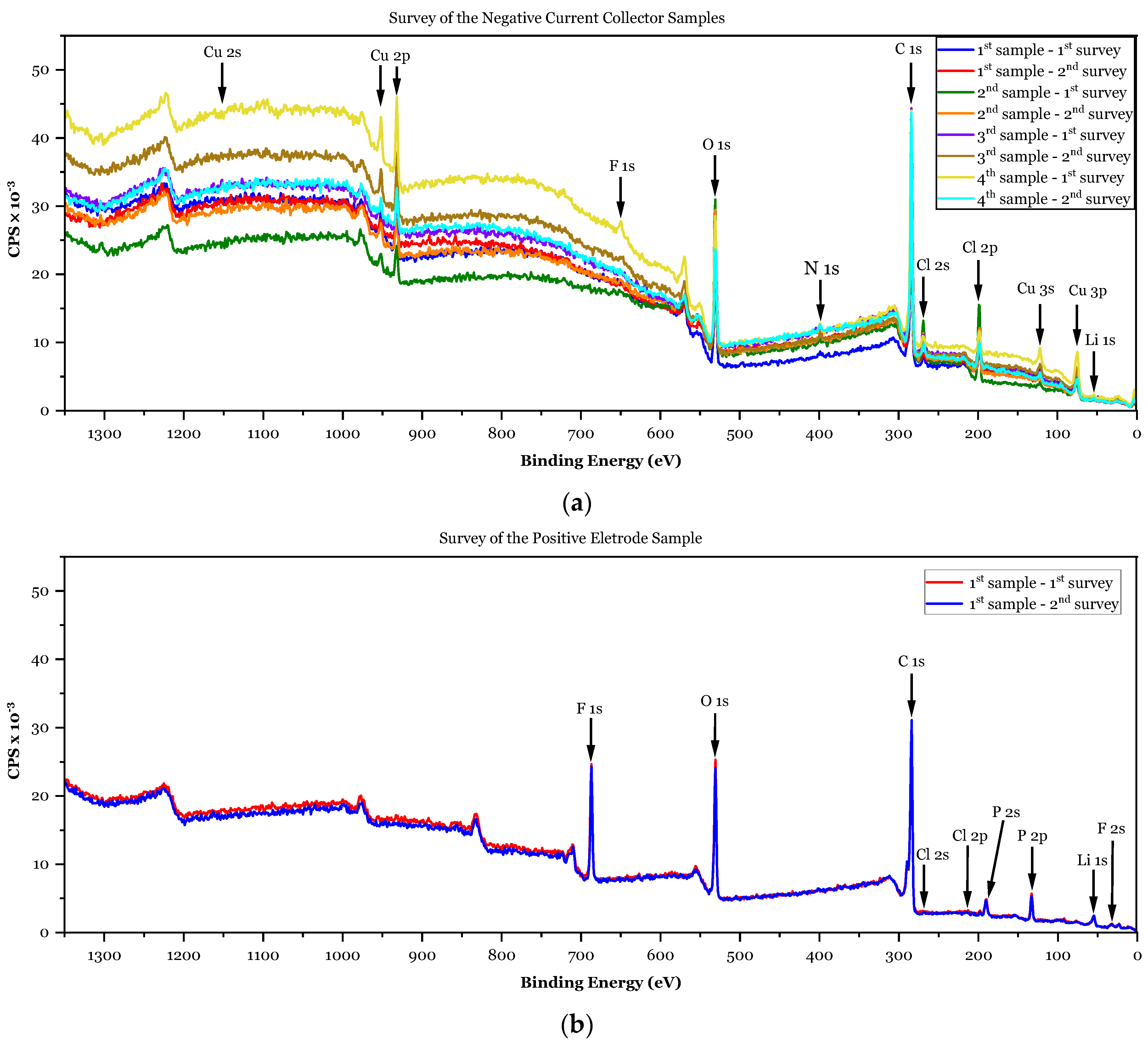
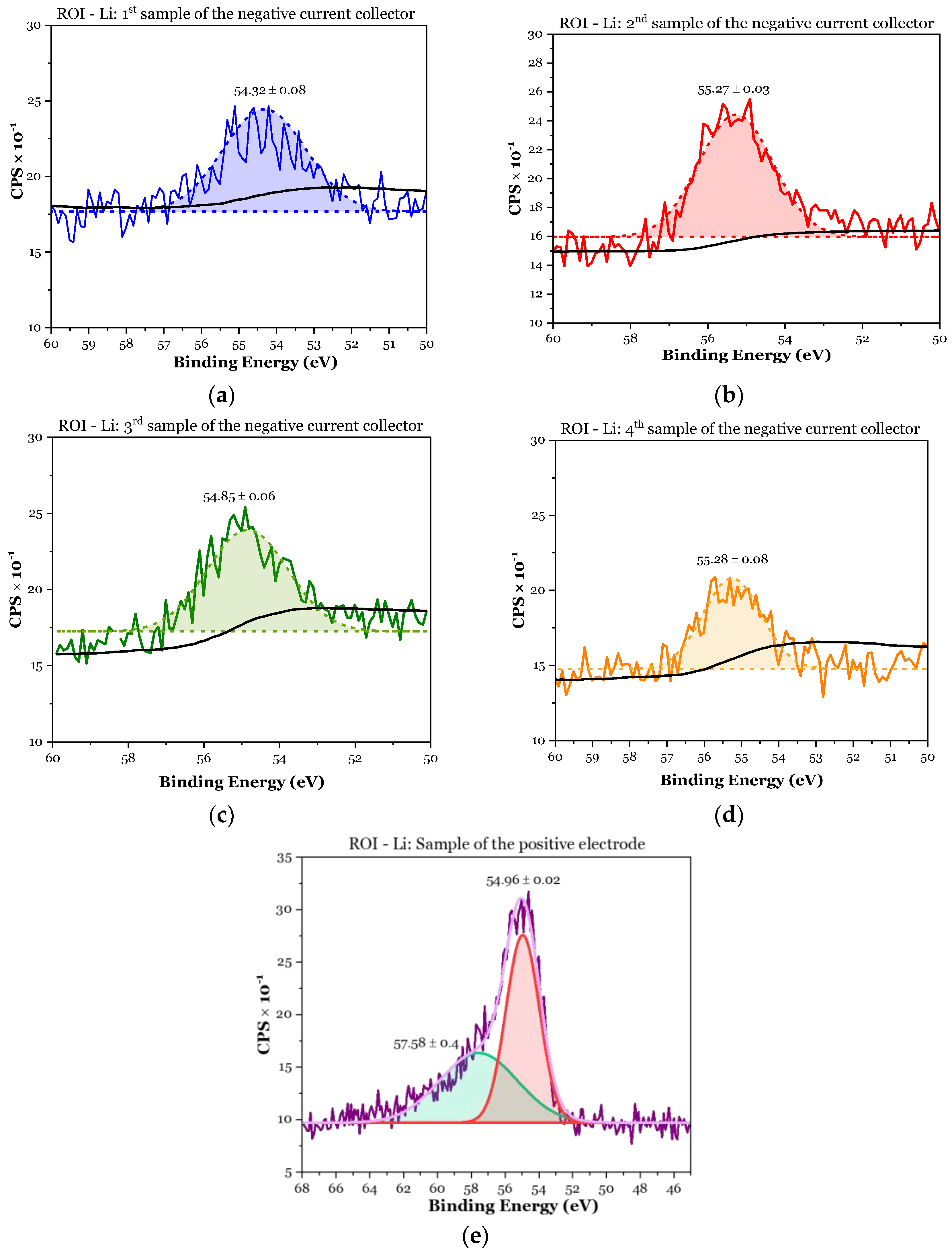
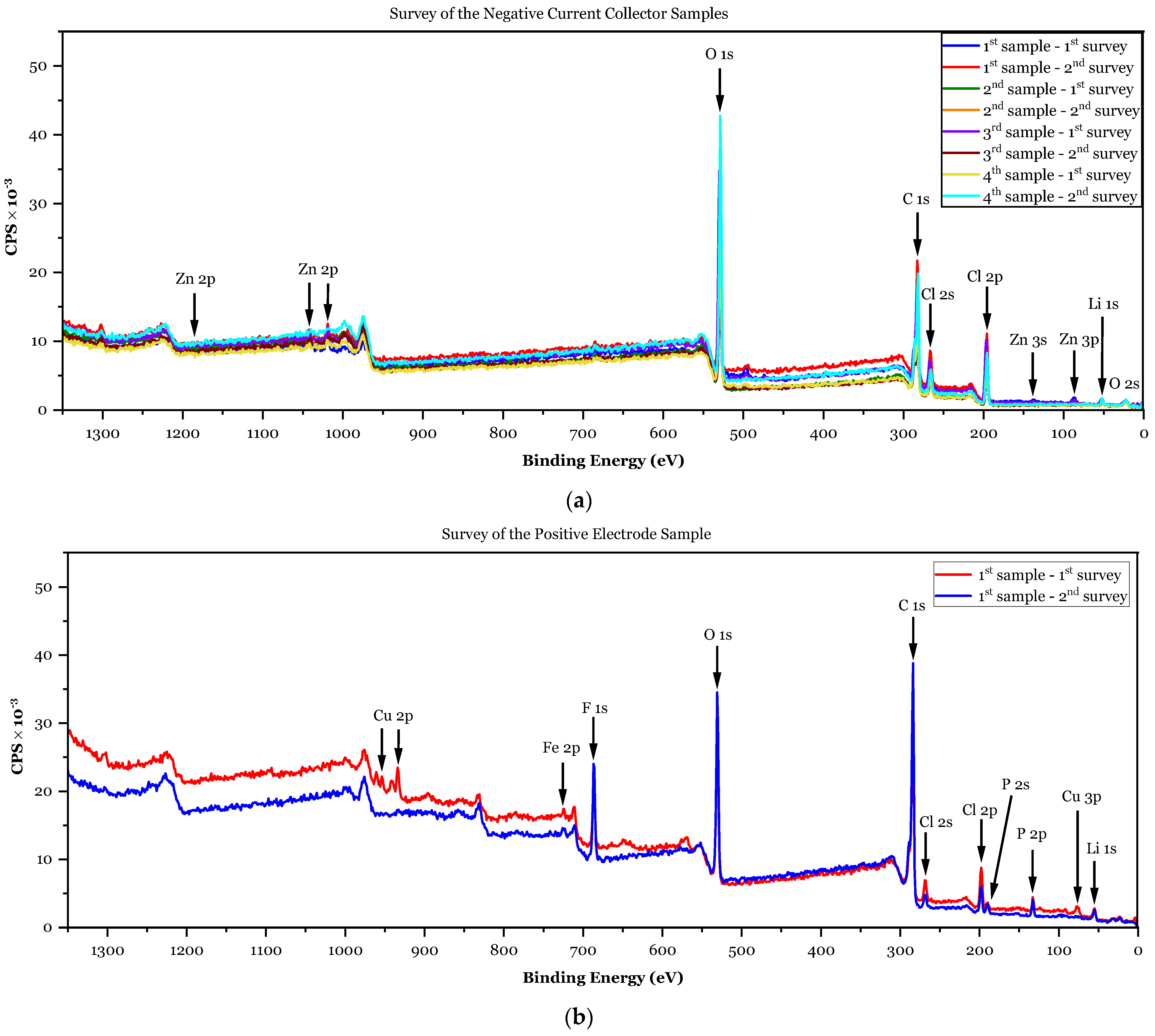
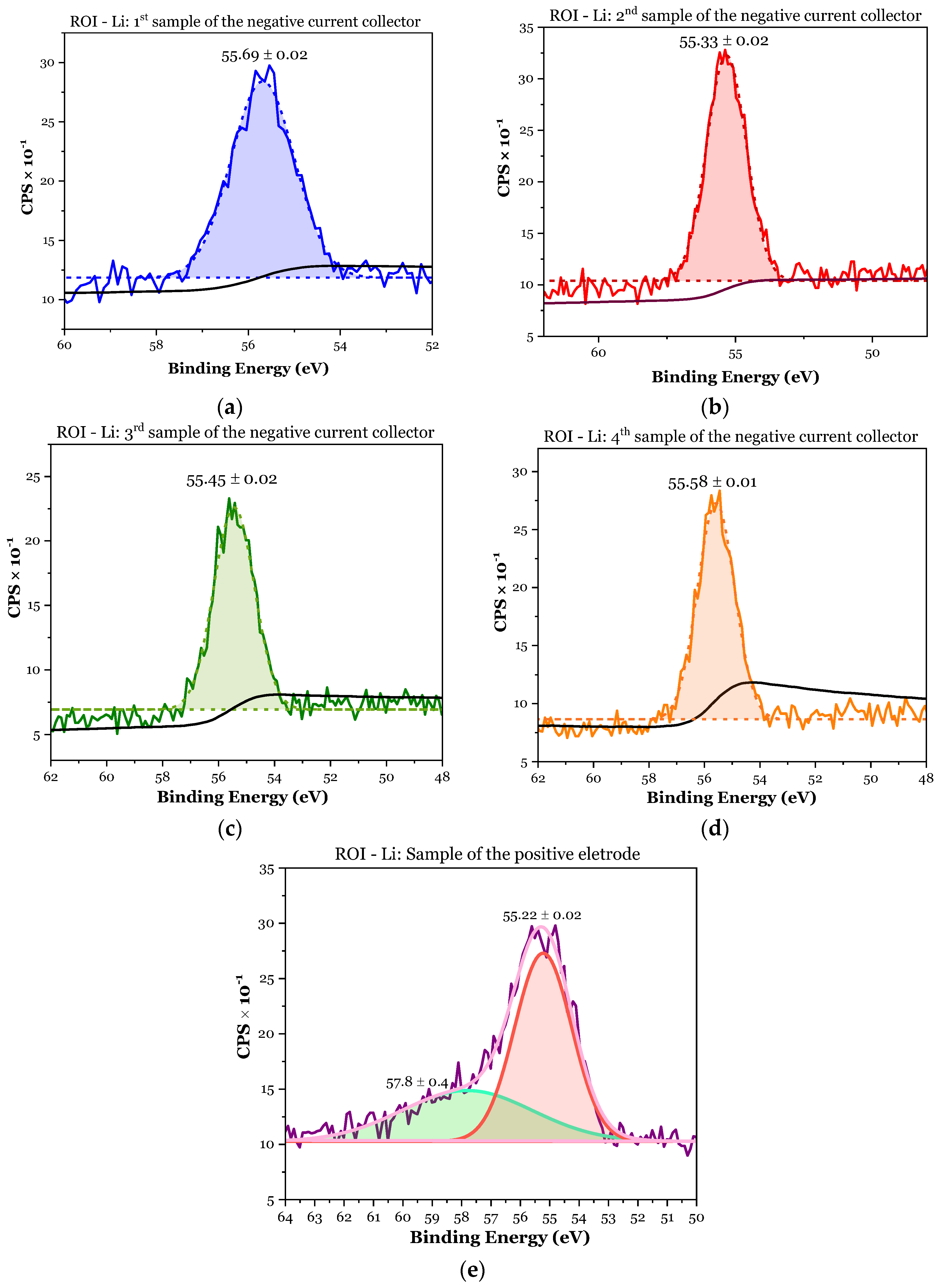
3.1.2. XPS Analyses
- ✓
- First sample (negative CC): 8.8 at.% > 2.99 × 1.2 at.% = 3.6 at.%;
- ✓
- Second sample (negative CC): 12.6 at.% > 2.99 × 3.9 at.% = 11.7 at.%;
- ✓
- Third sample (negative CC): 12.6 at.% > 2.99 × 2.8 at.% = 8.4 at.%;
- ✓
- Fourth sample (negative CC): 8.1 at.% > 2.99 × 2.2 at.% = 6.6 at.%;
- ✓
- First sample (positive electrode): .
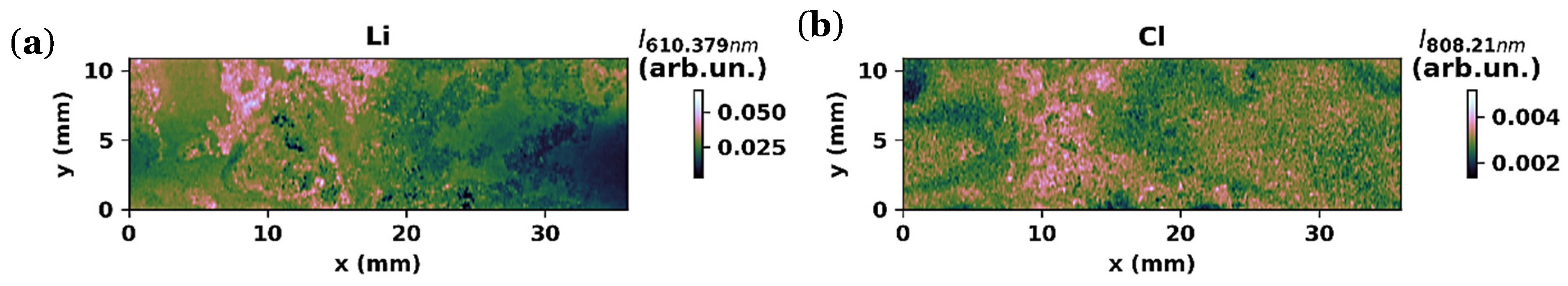
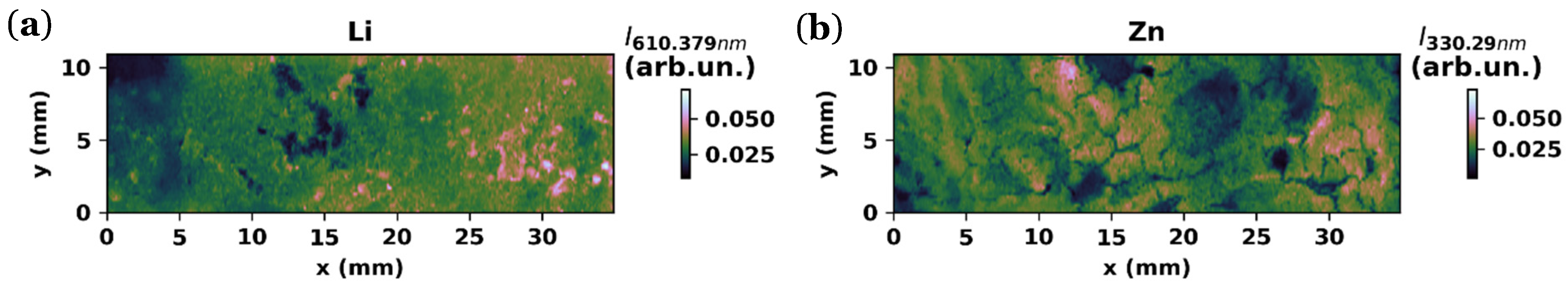
3.1.3. LIBS Maps
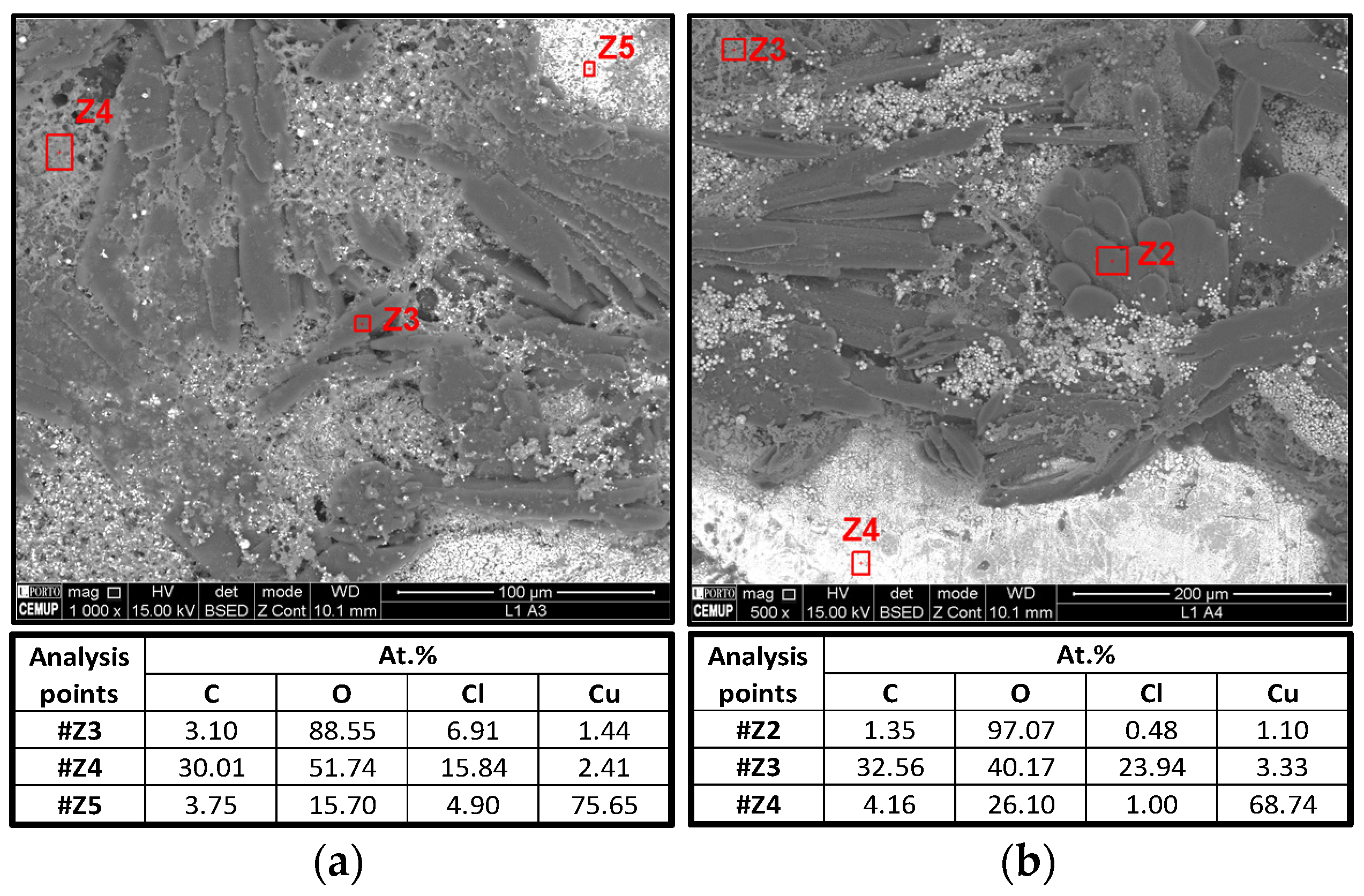
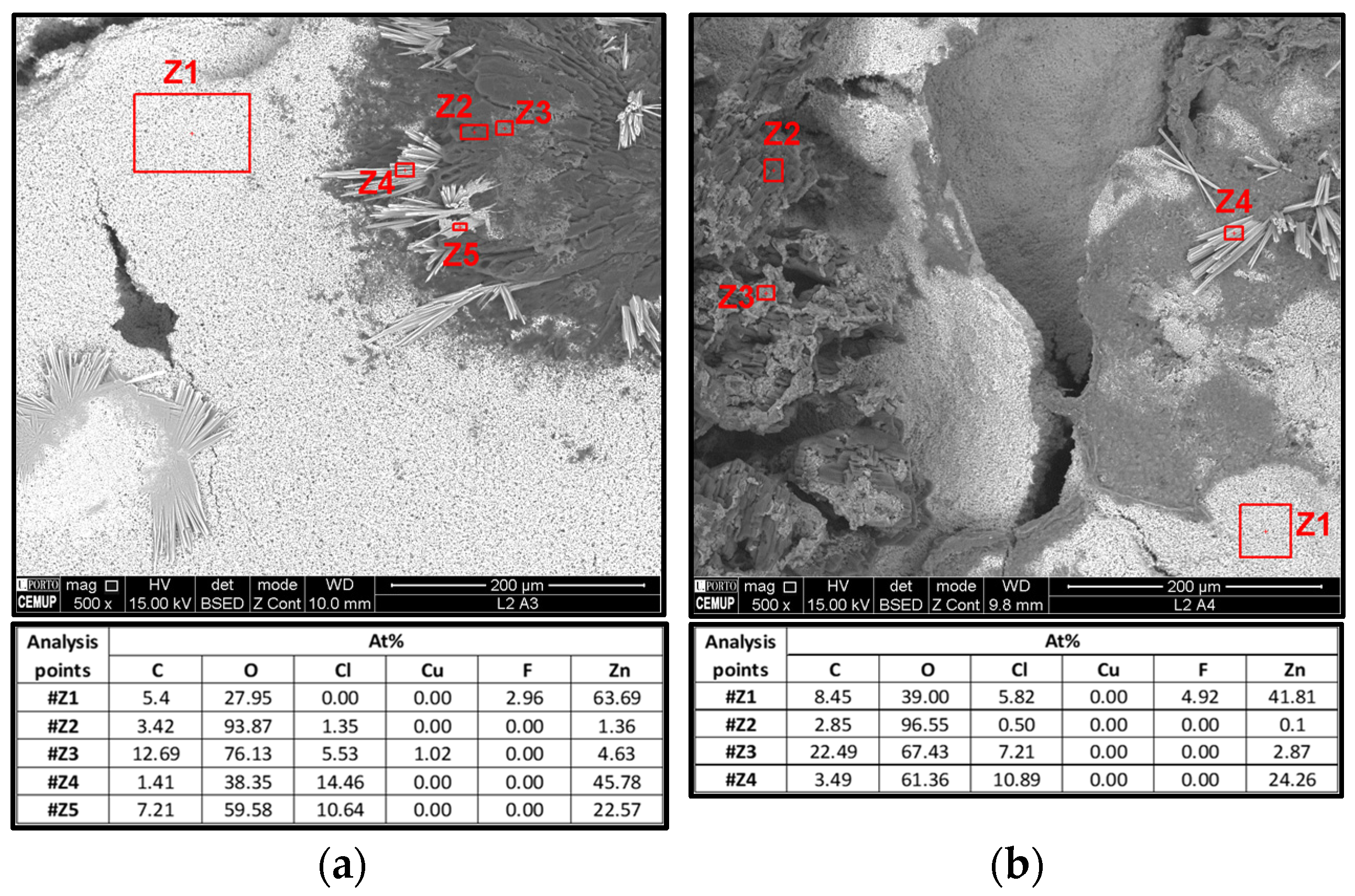
3.1.4. SEM and EDS Analysis
- 1.
- Z3 (left) and Z2 (right) almost only show oxygen, likely corresponding to Li metal oxidation;
- 2.
- Z4 (left) and Z3 (right) show an unequivocal amount of Cl that ought to be from the electrolyte, Li2.99Ba0.005ClO;
- 3.
- Z5 (left) and Z4 (right) are the current collector base, i.e., Cu.
3.2. Performance of the Cu/ZnO/Li2.99Ba0.005ClO Composite in Cellulose/LiFePO4/Cu Pouch Cell with ZnO@Cu as a Negative Current Collector
3.2.1. Electrochemical Cycling
3.2.2. XPS Analysis
- ✓
- First sample (negative CC): 17.3 at.% < 2.99 × 8.3 at.% = 24.8 at.%;
- ✓
- Second sample (negative CC): 20.9 at.% > 2.99 × 3.8 at.% = 11.4 at.%;
- ✓
- Third sample (negative CC): 23.7 at.% > 2.99 × 5.2 at.% = 15.5 at.%;
- ✓
- Fourth sample (negative CC): 21.8 at.% > 2.99 × 4.9 at.% = 14.7 at.%;
- ✓
- First sample (positive electrode): .
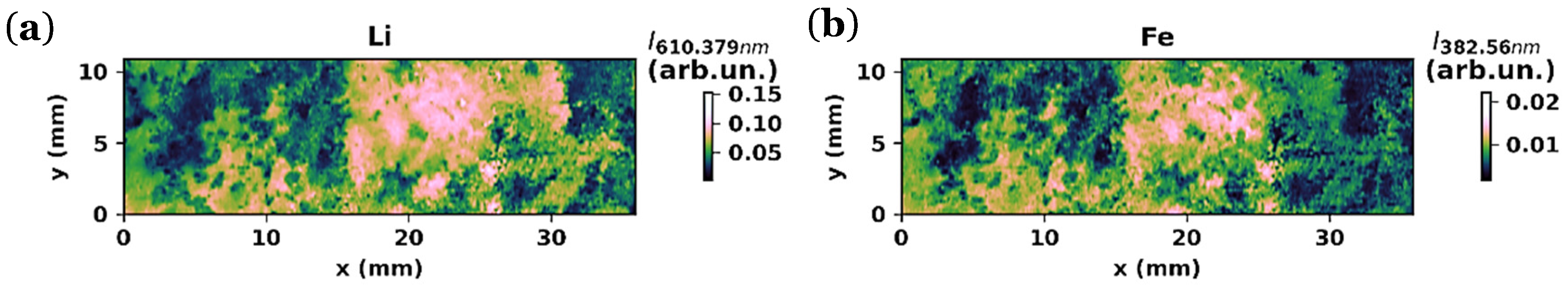
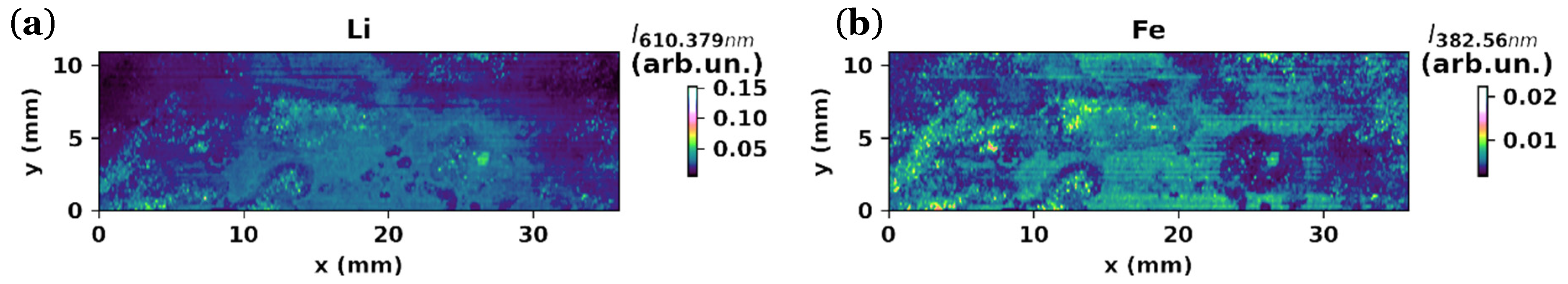
3.2.3. LIBS Maps
3.2.4. SEM and EDX Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rume, T.; Islam, S.M.D.U. Environmental Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic and Potential Strategies of Sustainability. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppez, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Chowdhury, S.P. The Importance of Energy Storage in Renewable Power Generation: A Review. In Proceedings of the 45th International Universities Power Engineering Conference UPEC2010, Cardiff, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, M.H.; Murchison, A.J.; Ferreira, J.A.; Singh, P.; Goodenough, J.B. Glass-Amorphous Alkali-Ion Solid Electrolytes and Their Performance in Symmetrical Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, R.; Chen, W.; And, J.T.-A.E. What Can Be Expected from “Anode-Free” Lithium Metal Batteries? Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Zhang, X.; Babu, B.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Vlad, A. Materials, Electrodes and Electrolytes Advances for next-Generation Lithium-Based Anode-Free Batteries. Oxf. Open Mater. Sci. 2022, 2, itac005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.G. Anode-Less. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kim, H.; Ming, J.; Jung, H.-G.; Belharouak, I.; Sun, Y.-K. Quasi-Compensatory Effect in Emerging Anode-Free Lithium Batteries. eScience 2021, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; An, Y.; Wei, C.; Jiang, H.; Xiong, S.; Feng, J.; Qian, Y. Recently Advances and Perspectives of Anode-Free Rechargeable Batteries. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, Z.; An, X.; Yue, X.; Wang, J.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Anode-Free Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries: Progress and Prospects. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 32, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Bazri, B.; Hu, S.-F.; Liu, R.-S. Interfacial Chemistry in Anode-Free Batteries: Challenges and Strategies. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2021, 9, 7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Maletti, S.; Auer, H.; Hüttl, J.; Voigt, K.; Lohrberg, O.; Nikolowski, K.; Partsch, M.; Michaelis, A. From Lithium-Metal toward Anode-Free Solid-State Batteries: Current Developments, Issues, and Challenges. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Jun, D.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, Y.J. Toward High-Performance Anodeless Batteries Based on Controlled Lithium Metal Deposition: A Review. J. Mater Chem. A Mater. 2021, 9, 14656–14681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, A.; Tang, X.; Zhang, M.; Bai, M.; Ma, Y. Challenges, Strategies, and Prospects of the Anode-Free Lithium Metal Batteries. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Zou, P.; Wang, M.; Zhan, H.; Kang, F.; Yang, C. Design Principle, Optimization Strategies, and Future Perspectives of Anode-Free Configurations for High-Energy Rechargeable Metal Batteries. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2021, 4, 601–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Gupta, A.; Manthiram, A. Anode-Free Full Cells: A Pathway to High-Energy Density Lithium-Metal Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 11, 2000804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, M.; Armand, P. Zaghib Building Better Batteries in the Solid State: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, C.; Raijmakers, L.H.J.; Liu, J.; Danilov, D.L.; Eichel, R.-A.; Notten, P.H.L. Li-Growth and SEI Engineering for Anode-Free Li-Metal Rechargeable Batteries: A Review of Current Advances. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 57, 508–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Anode-Free Sodium Metal Batteries as Rising Stars for Lithium-Ion Alternatives. iScience 2023, 26, 105982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudecker, B.J.; Dudney, N.J.; Bates, J.B. “Lithium-Free” Thin-Film Battery with In Situ Plated Li Anode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2000, 147, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.B.; Dudney, N.J.; Neudecker, B.; Ueda, A.; Evans, C.D. Thin-Film Lithium and Lithium-Ion Batteries. Solid State Ion. 2000, 135, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Liu, P.; Tracy, C.E. Lithium Thin-Film Battery with a Reversed Structural Configuration SS/Li/Lipon/LixV2O5/Cu. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2003, 6, A275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, A.S.; Dudney, N.J.; Sacci, R.L.; Kalnaus, S. Deposition and Confinement of Li Metal along an Artificial Lipon-Lipon Interface. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, T.A.; Su, W.N.; Fenta, F.W.; Zeleke, T.S.; Jiang, S.K.; Hwang, B.J. Ultrathin Li6.75La3Zr1.75Ta0.25O12-Based Composite Solid Electrolytes Laminated on Anode and Cathode Surfaces for Anode-Free Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 11713–11723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Carmona, E.; Gupta, A.; Albertus, P.; Sakamoto, J. Enabling “Lithium-Free” Manufacturing of Pure Lithium Metal Solid-State Batteries through in Situ Plating. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, S. Surface-Roughened Current Collectors for Anode-Free All-Solid-State Batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 70, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-Z.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Xu, P.; Kong, W.-J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Shi, P.; Wu, P.; Zhao, C.-Z.; Yuan, H.; Huang, J.-Q. High-Areal-Capacity Anode-Free All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries Enabled by Interconnected Carbon-Reinforced Ionic-Electronic Composites. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2023, 11, 12713–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrberg, O.; Voigt, K.; Maletti, S.; Auer, H.; Nikolowski, K.; Heubner, C.; Michaelis, A. Benchmarking and Critical Design Considerations of Zero-Excess Li-Metal Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, H.; Liu, J.; Ueno, K.; Dokko, K.; Kojima, T.; Takeichi, N.; Miyuki, T.; Yamakawa, Y.; Watanabe, M. Enhancing the Reversibility of Li Deposition/Dissolution in Sulfur Batteries Using High-Concentration Electrolytes to Develop Anode-Less Batteries with Lithium Sulfide Cathode. J. Power Sources 2023, 554, 232323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Luo, R.; Xu, K.; Si, M.; Kang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Ahmad, T. Constructing Robust Heterostructured Interface for Anode-Free Zinc Batteries with Ultrahigh Capacities. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.; Becker, J.; Haslam, C.G.; Lerch, C.; Sakamoto, J.; Richter, F.H.; Janek, J. Current-Dependent Lithium Metal Growth Modes in “Anode-Free” Solid-State Batteries at the Cu| LLZO Interface. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, T.-H.; Wang, M.-C.; Liu, S.-E.; Wu, B.-H.; Li, Y.-C.; Tsai, D.-G.; Chang, S.-M.; Shiue, A.; Chin, K.-Y. Sputtered Silver on the Current Collector for Anode-Less NMC111 Gel Polymer Electrolyte Lithium Batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2023, 150, 107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, S.; Xie, J. Space-Confined Guest Synthesis to Fabricate Sn-monodispersed N-doped Mesoporous Host toward Anode-Free Na Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2023, 2301967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahunsi, O.J.; Gao, S.; Kaelin, J.; Li, B.; Razak, I.B.A.; An, B.; Cheng, Y. Anode-Free Na Metal Batteries Developed by Nearly Fully Reversible Na Plating on the Zn Surface. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahunsi, O.J.; Li, B.; An, B.; Abdul Razak, I.B.; Xia, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Cheng, Y. Directing High-Efficiency Na Plating with Carbon–Aluminum Junction Interfaces for Anode-Free Na Metal Batteries. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 7522–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Guo, S.; Yang, Q.-H.; Zhou, H. Toward High Performance Anodes for Sodium-Ion Batteries: From Hard Carbons to Anode-Free Systems. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.-H.; Sohn, K.-S.; Myung, S.-T. Feasible Approaches for Anode-Free Lithium-Metal Batteries as Next Generation Energy Storage Systems. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 57, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Lieu, W.Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ghosh, T.; Thakur, A.; Wyatt, B.C.; Anasori, B.; Liu, W. MXene-Based Anode-Free Magnesium Metal Battery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2303067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, R.; He, W.; Li, K.; Yan, S.; Cui, J.; Fang, X.; Yan, J. Robust Anode-Free Sodium Metal Batteries Enabled by Artificial Sodium Formate Interface. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2204125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, F.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Emwas, A.-H.; Liang, H.; Cui, Y.; Alshareef, H.N. Co-Solvent Electrolyte Engineering for Stable Anode-Free Zinc Metal Batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7160–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jiao, K.; Yan, J. Prospective Strategies for Extending Long-Term Cycling Performance of Anode-Free Lithium Metal Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 54, 689–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Sun, H.; Huang, C.; Zhu, G.; Tai, H.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, S. A Nonflammable High-Voltage 4.7 V Anode-Free Lithium Battery. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2207361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Fujiki, S.; Jung, C.; Suzuki, N.; Yashiro, N.; Omoda, R.; Ko, D.S.; Shiratsuchi, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Ryu, S.; et al. High-Energy Long-Cycling All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries Enabled by Silver–Carbon Composite Anodes. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, A.; McCalla, E. The Role of Metal Substitutions in the Development of Li Batteries, Part I: Cathodes. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3474–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.M.; Danzi, F.; Oliveira, J.E.; El-Azab, A.; Camanho, P.P.; Braga, M.H. The Latest Trends in Electric Vehicles Batteries. Molecules 2021, 26, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.H.; Oliveira, J.E.; Murchison, A.J.; Goodenough, J.B. Performance of a Ferroelectric Glass Electrolyte in a Self-Charging Electrochemical Cell with Negative Capacitance and Resistance. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.H. Coherence in the Ferroelectric A3ClO (A = Li, Na) Family of Electrolytes. Materials 2021, 14, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.H.; Ferreira, J.A.; Stockhausen, V.; Oliveira, J.E.; El-Azab, A. Novel Li3ClO Based Glasses with Superionic Properties for Lithium Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2014, 2, 5470–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, A.N.; Baptista, M.C.; Maia, B.A.; Braga, M.H. Interfacial Chemistry with ZnO: In Operando Work Functions in Hetero Cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 9811–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, R.; Melikechi, N.; Abdel-Salam, Z.A.; Harith, M.A.; Palleschi, V.; Motto-Ros, V.; Busser, B. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for Human and Animal Health: A Review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2019, 152, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.F.S.; Capela, D.; Silva, N.A.; Gonçalves, F.; Lima, A.; Guimarães, D.; Jorge, P.A.S. Comprehensive Comparison of Linear and Non-Linear Methodologies for Lithium Quantification in Geological Samples Using LIBS. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2022, 195, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglos, D.; Detalle, V. Cultural Heritage Applications of LIBS. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Theory and Applications. Springer Ser. Opt. Sci. 2014, 182, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyrek, P.; Bergfeldt, T.; Seifert, H.J.; Pfleging, W. Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy for the Quantitative Measurement of Lithium Concentration Profiles in Structured and Unstructured Electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2019, 7, 5656–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Sun, D.; Su, M.; Han, J.; Dong, C. Rapid Analysis on the Heavy Metal Content of Spent Zinc–Manganese Batteries by Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2012, 44, 2469–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzi, F.; Camanho, P.P.; Braga, M.H. An All-Solid-State Coaxial Structural Battery Using Sodium-Based Electrolyte. Molecules 2021, 26, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.C.; Khalifa, H.; Araújo, A.; Maia, B.A.; Souto, M.; Braga, M.H. Giant Polarization in Quasi-Adiabatic Ferroelectric Na+ Electrolyte for Solid-State Energy Harvesting and Storage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2212344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, A.N.; Maia, B.A.; Khalifa, H.; Baptista, M.C.; Braga, M.H. What Differentiates Dielectric Oxides and Solid Electrolytes on the Pathway toward More Efficient Energy Storage? Batteries 2022, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, M.L.; Hrbek, J.; Sham, T.K.; Xu, G.-Q. A Soft X-Ray Study of the Interaction of Oxygen with Li. Surf. Sci. 1990, 234, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contour, J.P.; Salesse, A.; Froment, M.; Garreau, M.; Thevenin, J.; Warin, D. Analysis by Electron-Microscopy and XPS of Lithium Surfaces Polarized in Anhydrous Organic Electrolytes. J. De Microsc. Et De Spectrosc. Electron. 1979, 4, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Contarini, S.; Rabalais, J.W. Ion Bombardment-Induced Decomposition of Li and Ba Sulfates and Carbonates Studied by X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Electron. Spectros. Relat. Phenomena. 1985, 35, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wren, A.G.; Phillips, R.W.; Tolentino, L.U. Surface Reactions of Chlorine Molecules and Atoms with Water and Sulfuric Acid at Low Temperatures. J. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 1979, 70, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
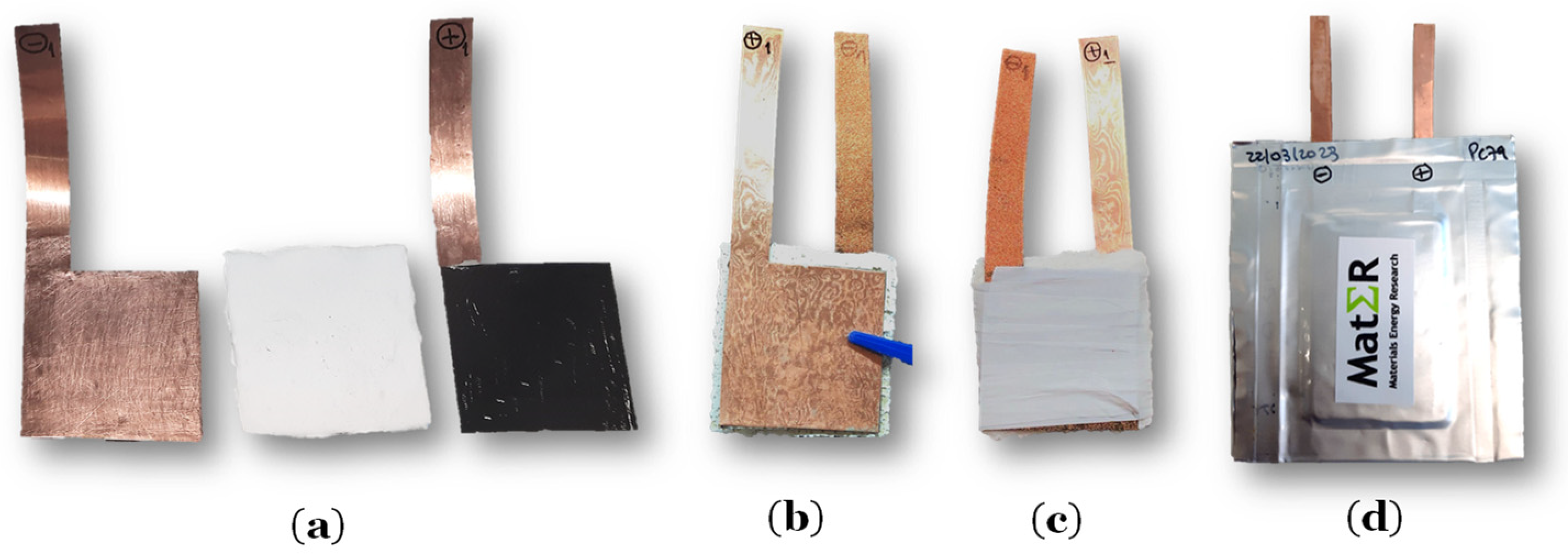




| Measurements | Current Collector (Cu Foil) | Coated Layer on Negative Collector | Cellulose With 80% Li2.99Ba0.005ClO + 20% PVAC | Positive Electrode | Active Cathode (LiFePO4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu/Li2.99Ba0.005ClO composite in cellulose/LiFePO4/Cu pouch cell with Cu as a negative current collector | |||||
| Contact area (mm2) | 1600 | -- | 2025 | 1600 | 1600 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.127 | -- | 1.60 | 0.10 | -- |
| Weight (mg) | N/A | -- | 736.6 (cellulose: 41.4) Li2.99Ba0.005ClO: 556.2 (27 mg cm−2) | 188.4 | 150.7 |
| Cu/ZnO/Li2.99Ba0.005ClO composite in cellulose/LiFePO4/Cu pouch cell with ZnO@Cu as a negative current collector | |||||
| Contact area (mm2) | 1600 | 1600 | 2025 | 1600 | 1600 |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.127 | 0.05 | 1.65 | 0.15 | -- |
| Weight (mg) | N/A | 112.7 (7 mg cm−2) | 882.7 (cellulose: 42.3) Li2.99Ba0.005ClO: 672.3 (33 mg cm−2) | 501.6 | 210.1 |
| External Resistor Rext (kΩ) | Cycle | Discharge Time | Maximum Discharge Potential | Average Discharge Potential | Discharged Capacity | Discharged Li Mass | Discharged Li Volume | Discharged Li Thickness * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time (h) | ∆Vmax (V) | ∆Vav (V) | QRext (mAh) | mLi (mg) | V’Li (mm3) | dLi (μm) | ||
| 980 | 6th | 42 | 3.20 | 0.86 | 0.037 | 0.010 | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| 7th | 16 | 2.53 | 0.90 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.005 | |
| 684 | 8th | 107 | 1.83 | 0.72 | 0.112 | 0.029 | 0.054 | 0.034 |
| 9th | 44 | 2.37 | 0.76 | 0.049 | 0.013 | 0.024 | 0.015 | |
| 10th | 293 | 2.41 | 0.66 | 0.283 | 0.073 | 0.137 | 0.086 | |
| 11th | 79 | 2.51 | 0.76 | 0.087 | 0.023 | 0.042 | 0.026 | |
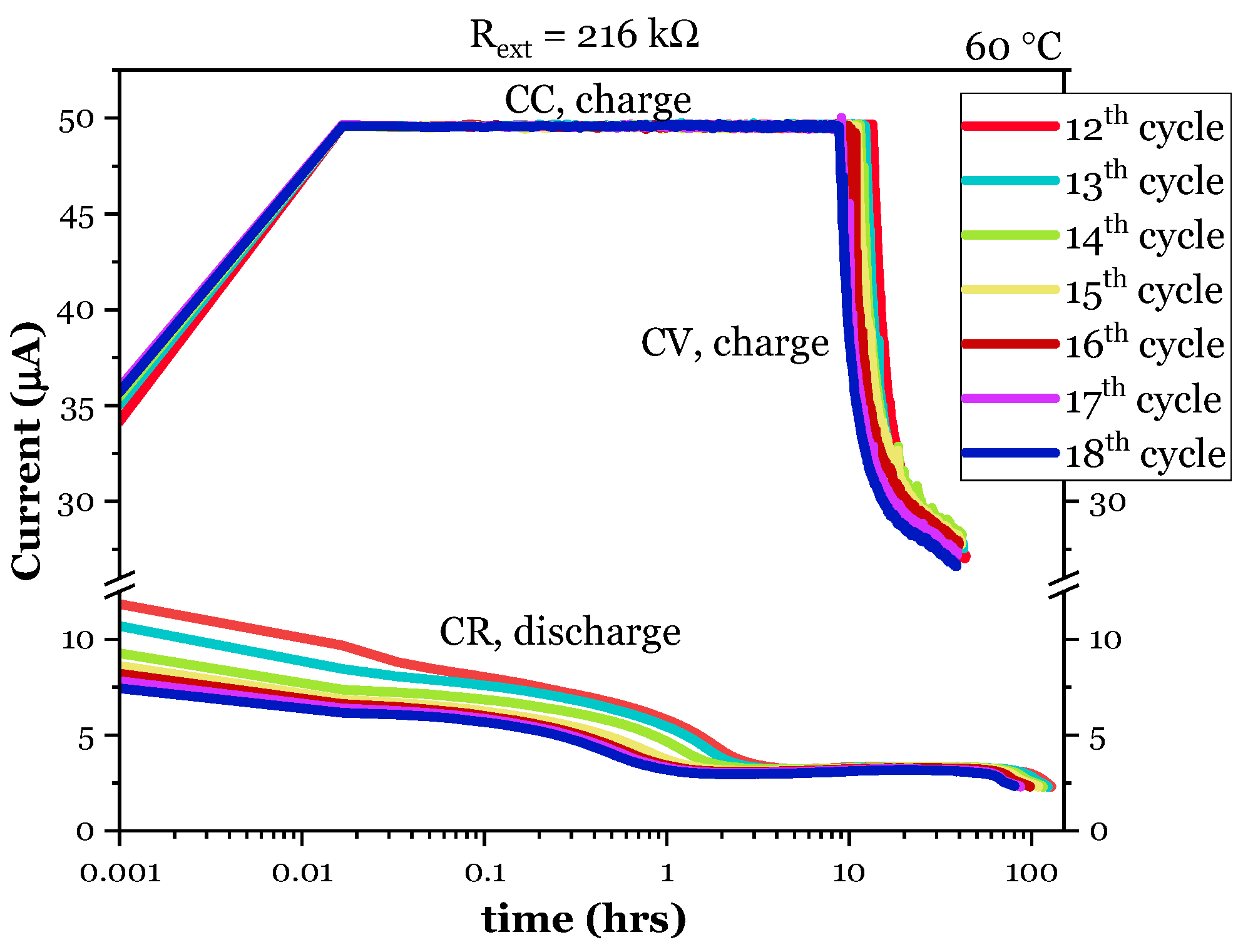
| 216 | 12th | 128 | 2.56 | 0.68 | 0.404 | 0.105 | 0.196 | 0.122 |
| 13th | 123 | 2.31 | 0.68 | 0.386 | 0.100 | 0.187 | 0.117 | |
| 14th | 115 | 2.00 | 0.67 | 0.358 | 0.093 | 0.173 | 0.108 | |
| 15th | 109 | 1.86 | 0.66 | 0.334 | 0.087 | 0.162 | 0.101 | |
| 16th | 98 | 1.77 | 0.66 | 0.299 | 0.078 | 0.145 | 0.091 | |
| 17th | 87 | 1.69 | 0.65 | 0.260 | 0.067 | 0.126 | 0.079 | |
| 18th | 81 | 1.61 | 0.64 | 0.240 | 0.062 | 0.117 | 0.073 |
| Element | Sensitivity Factor | 1st Sample Negative CC at.% | 2nd Sample Negative CC at.% | 3rd Sample Negative CC at.% | 4th Sample Negative CC at.% | 1st Sample Positive Electrode at.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li 1s | 0.025 | 8.8 | 12.6 | 12.6 | 8.1 | 33.4 |
| C 1s | 0.278 | 74.2 | 65.6 | 65.9 | 75.2 | 47.0 |
| N 1s | 0.477 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| O 1s | 0.78 | 13.2 | 15.4 | 15.1 | 12.1 | 9.9 |
| F 1s | 1 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | 7.1 |
| P 2p | 0.486 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | 2.3 |
| Cl 2p | 0.891 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 0.1 |
| Cu 2p | 5.32 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 1.2 | N.D. * |
| Ba 3d | 12.4 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * |
| Cycle | Charged Capacity | Plated Li | Mass of Li | Volume of Li | Thickness of Li |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q (mAh) | xLi (mmol) | mLi (mg) | V’Li (mm3) | dLi (μm) | |
| 1st | 4.222 | 0.158 | 1.095 | 2.047 | 1.279 |
| 2nd | 3.686 | 0.138 | 0.956 | 1.787 | 1.117 |
| 3rd | 3.388 | 0.127 | 0.879 | 1.642 | 1.026 |
| 4th | 3.244 | 0.121 | 0.841 | 1.573 | 0.983 |
| 5th | 3.086 | 0.115 | 0.800 | 1.496 | 0.935 |
| 6th | 3.349 | 0.125 | 0.869 | 1.623 | 1.015 |
| 7th | 4.420 | 0.165 | 1.146 | 2.143 | 1.339 |
| 8th | 4.968 | 0.186 | 1.288 | 2.408 | 1.505 |
| 9th | 5.008 | 0.187 | 1.299 | 2.428 | 1.517 |
| 10th | 5.230 | 0.195 | 1.356 | 2.535 | 1.584 |
| 11th | 4.933 | 0.184 | 1.279 | 2.391 | 1.495 |
| 12th | 4.985 | 0.186 | 1.293 | 2.416 | 1.510 |
| 13th | 4.731 | 0.177 | 1.227 | 2.293 | 1.433 |
| 14th | 5.529 | 0.207 | 1.434 | 2.680 | 1.675 |
| 15th | 6.278 | 0.235 | 1.628 | 3.043 | 1.902 |
| 16th | 9.646 | 0.360 | 2.502 | 4.676 | 2.922 |
| 17th | 6.467 | 0.242 | 1.677 | 3.135 | 1.959 |
| External Resistor | Cycle | Discharge Time | Maximum Discharge Potential | Average Discharge Potential | Discharged Current | Discharged Capacity | Thickness of Li |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rext (kΩ) | time (h) | ΔVmax (V) | ΔVav (V) | IRext (μA) | QRext (μAh) | dLi (μm) | |
| 4700 | 1st | 21 | 2.09 | 0.879 | 0.2 | 3.9 | 0.001 |
| 2nd | 48 | 2.12 | 0.872 | 0.2 | 8.9 | 0.003 | |
| 3rd | 48 | 2.12 | 0.966 | 0.2 | 9.9 | 0.003 | |
| 4th | 48 | 2.20 | 1.114 | 0.2 | 11.4 | 0.003 | |
| 5th | 48 | 2.21 | 1.177 | 0.3 | 12.0 | 0.004 | |
| 6th | 48 | 2.21 | 1.265 | 0.3 | 12.9 | 0.004 | |
| 980 | 7th | 48 | 2.09 | 1.004 | 1.0 | 49.2 | 0.015 |
| 8th | 48 | 2.13 | 1.107 | 1.1 | 54.3 | 0.016 | |
| 9th | 48 | 2.14 | 1.199 | 1.2 | 58.7 | 0.018 | |
| 550 | 10th | 48 | 2.07 | 1.057 | 1.9 | 92.2 | 0.028 |
| 11th | 48 | 2.15 | 1.091 | 2.0 | 95.2 | 0.029 | |
| 12th | 48 | 2.15 | 1.095 | 2.0 | 95.6 | 0.029 | |
| 217 | 13th | 2.9 | 2.15 | 1.674 | 7.7 | 22.1 | 0.007 |
| 14th | 6.0 | 2.06 | 1.277 | 5.9 | 35.6 | 0.011 | |
| 15th | 21 | 1.97 | 0.940 | 4.3 | 91.6 | 0.028 | |
| 16th | 4.6 | 2.00 | 1.443 | 6.6 | 30.5 | 0.009 | |
| 17th | 17 | 2.01 | 0.962 | 4.4 | 73.6 | 0.022 |
| Element | Sensitivity Factor | 1st Sample Negative CC at.% | 2nd Sample Negative CC at.% | 3rd Sample Negative CC at.% | 4th Sample Negative CC at.% | 1st Sample Positive Electrode at.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li 1s | 0.025 | 17.3 | 20.9 | 23.7 | 21.8 | 24.2 |
| C 1s | 0.278 | 51.7 | 46.7 | 40.3 | 45.3 | 52.5 |
| N 1s | 0.477 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| O 1s | 0.78 | 21.7 | 28.3 | 30.3 | 27.5 | 13.1 |
| F 1s | 1 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | 6.0 |
| P 2p | 0.486 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | 1.7 |
| Cl 2p | 0.891 | 8.3 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 4.9 | 1.6 |
| Fe 2p | 2.96 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * | 0.6 |
| Zn 2p | 3.73 | 0.4 | N.D. * | 0.1 | 0.03 | N.D. * |
| Ba 3d | 12.4 | N.D. * | 0.05 | N.D. * | N.D. * | N.D. * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baptista, M.C.; Gomes, B.M.; Capela, D.; Ferreira, M.F.S.; Guimarães, D.; Silva, N.A.; Jorge, P.A.S.; Silva, J.J.; Braga, M.H. Conditioning Solid-State Anode-Less Cells for the Next Generation of Batteries. Batteries 2023, 9, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9080402
Baptista MC, Gomes BM, Capela D, Ferreira MFS, Guimarães D, Silva NA, Jorge PAS, Silva JJ, Braga MH. Conditioning Solid-State Anode-Less Cells for the Next Generation of Batteries. Batteries. 2023; 9(8):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9080402
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaptista, Manuela C., Beatriz Moura Gomes, Diana Capela, Miguel F. S. Ferreira, Diana Guimarães, Nuno A. Silva, Pedro A. S. Jorge, José J. Silva, and Maria Helena Braga. 2023. "Conditioning Solid-State Anode-Less Cells for the Next Generation of Batteries" Batteries 9, no. 8: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9080402
APA StyleBaptista, M. C., Gomes, B. M., Capela, D., Ferreira, M. F. S., Guimarães, D., Silva, N. A., Jorge, P. A. S., Silva, J. J., & Braga, M. H. (2023). Conditioning Solid-State Anode-Less Cells for the Next Generation of Batteries. Batteries, 9(8), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9080402











