Interface Engineering of a NASICON-Type Electrolyte Using Ultrathin CuS Film for Lithium Metal Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of LAGP Pellets
2.2. Preparation of CuS Film Attached to the LAGP Pellet by MS
2.3. SSLMB Assembly
2.4. Material Characterizations
2.5. Electrochemical Measurement
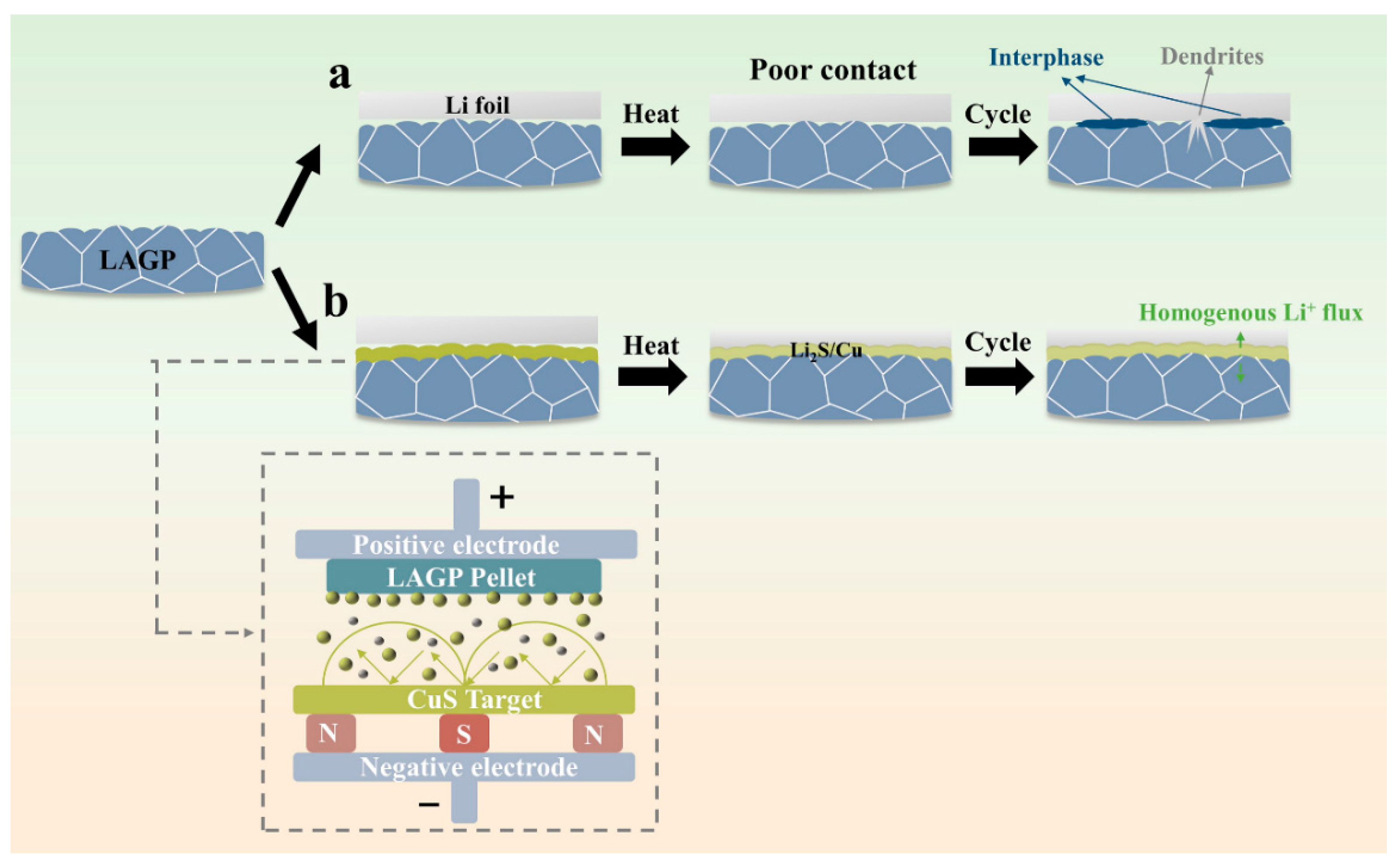
3. Results and Discussion
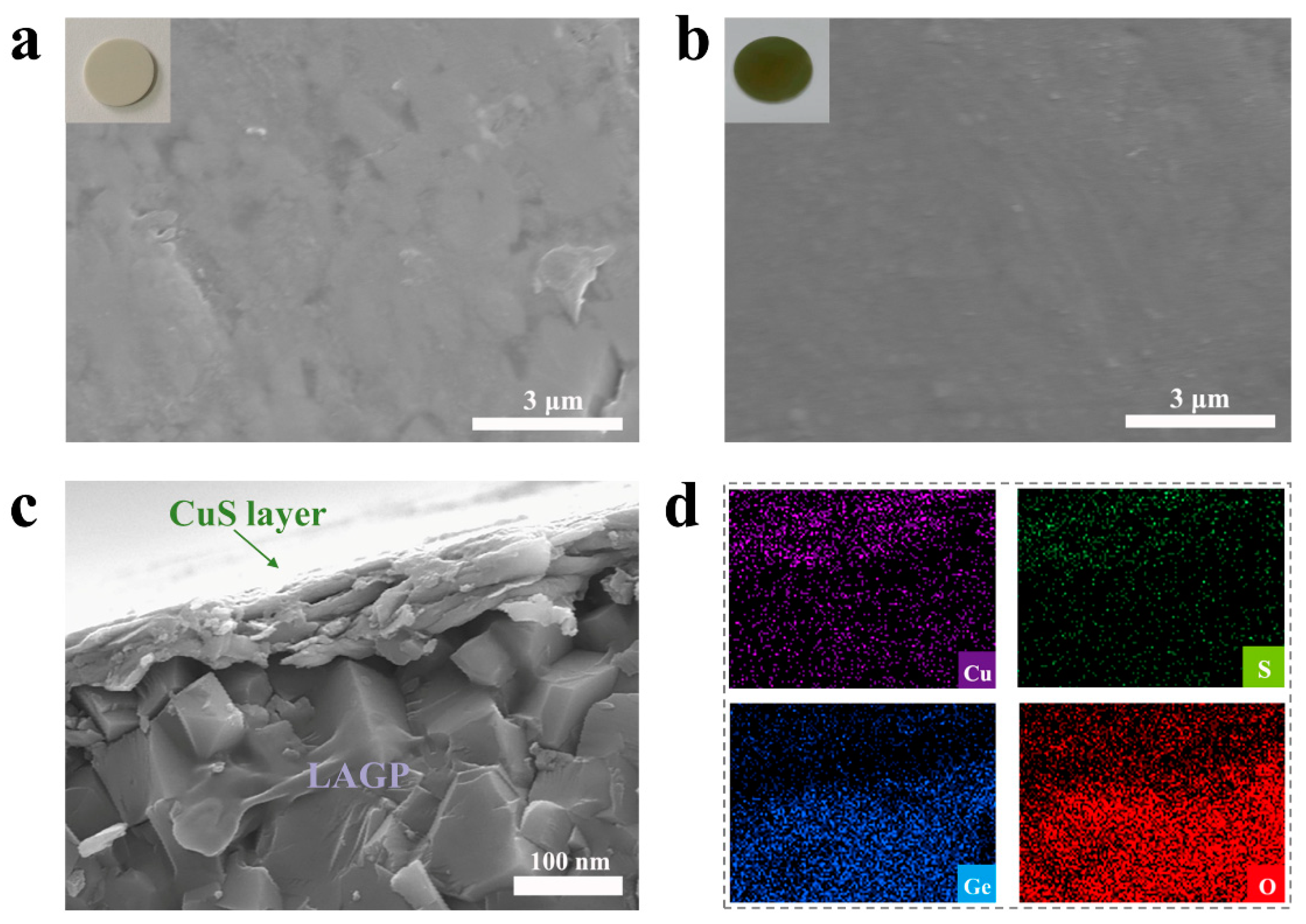
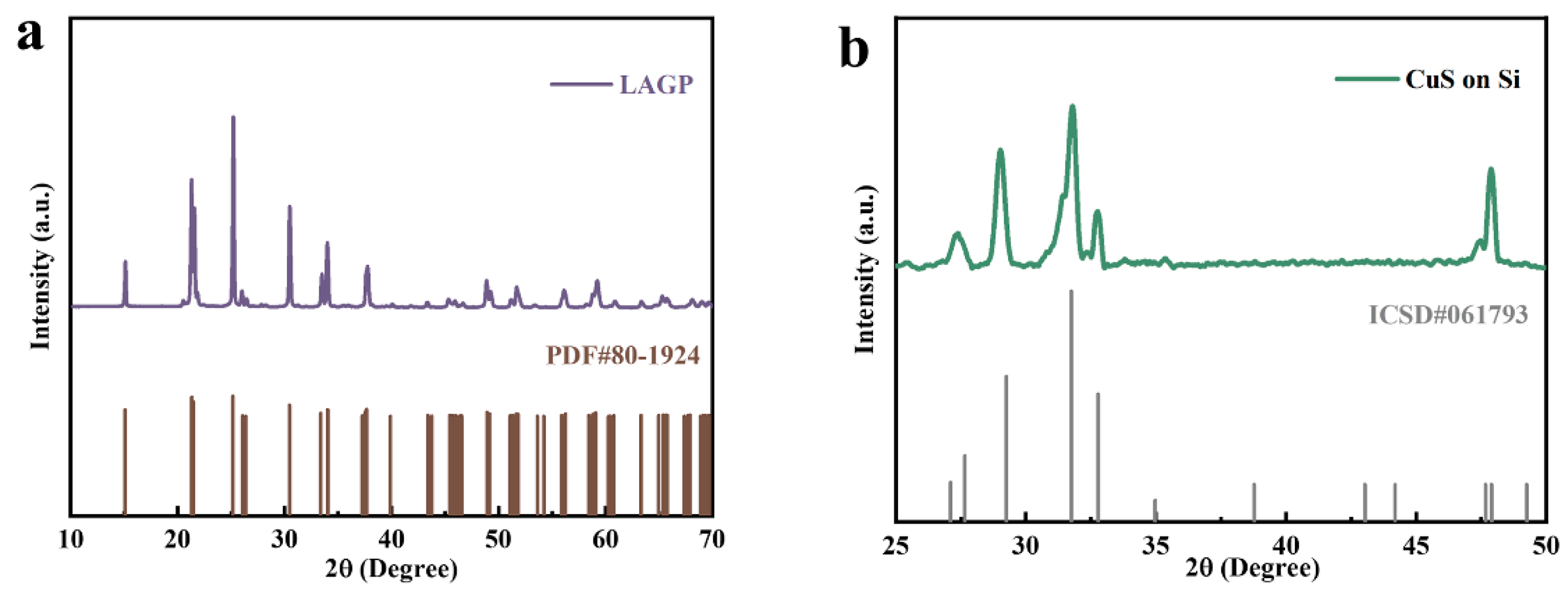
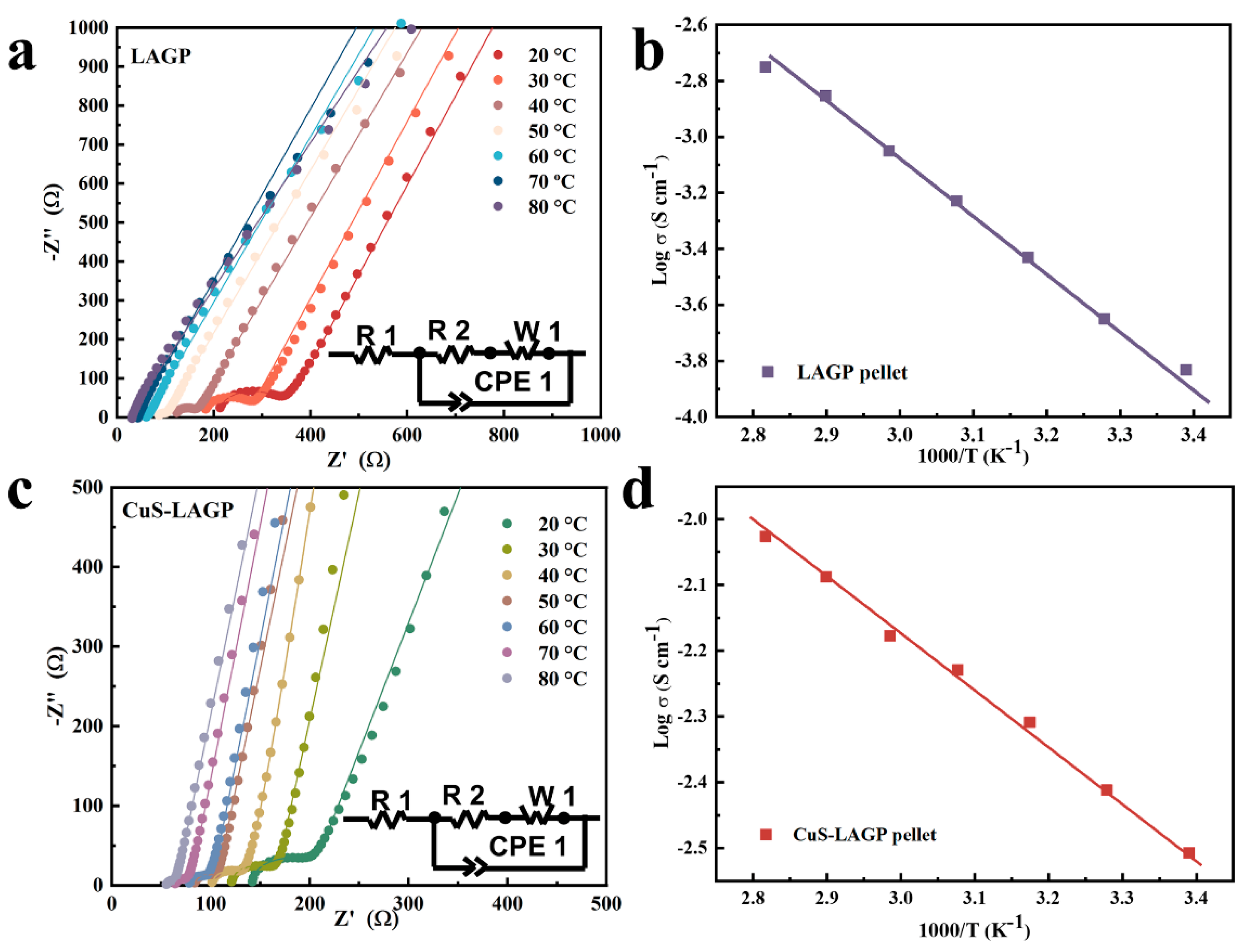
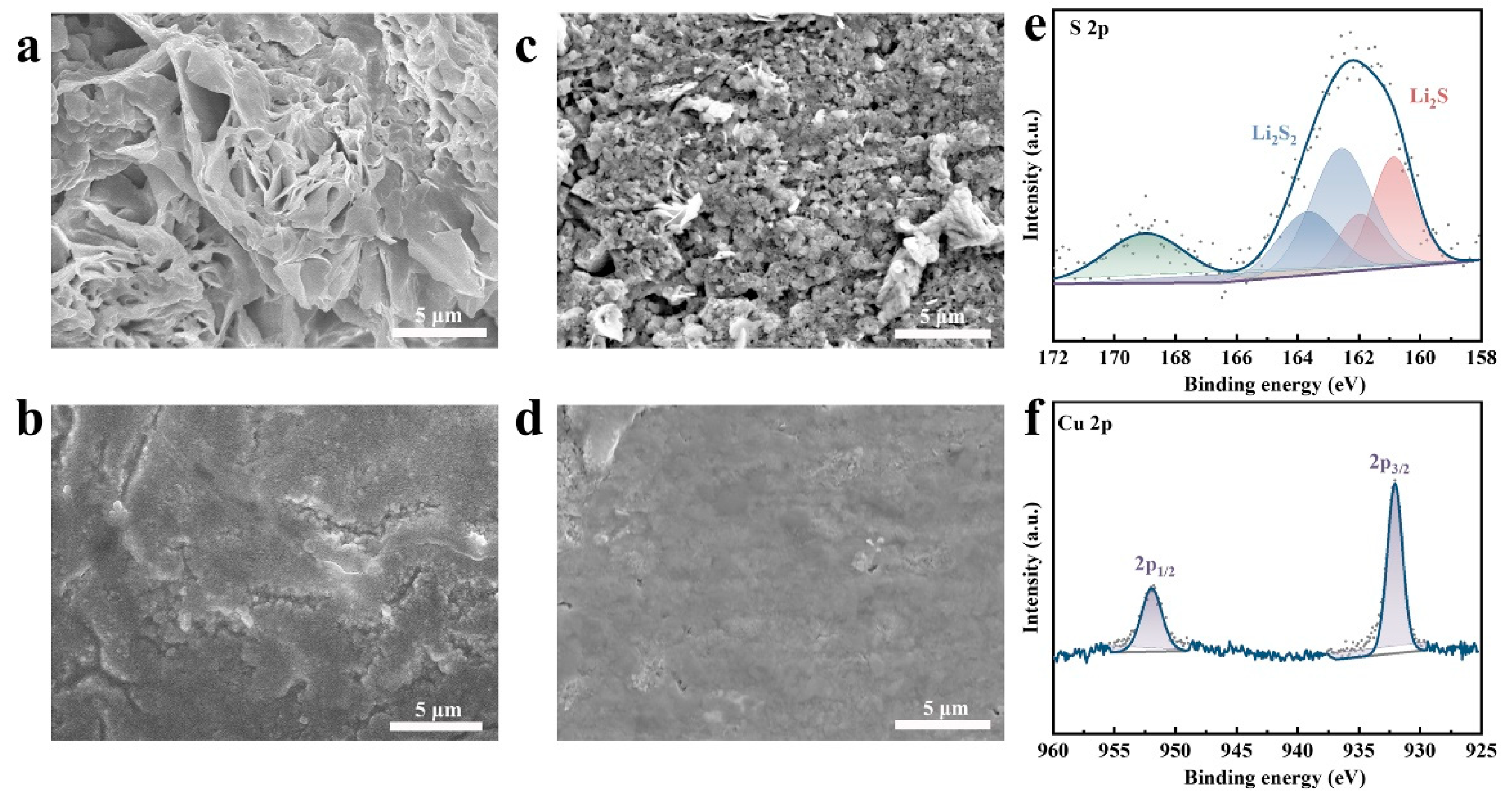
3.1. Morphology and Structure of CuS@LAGP Pellets
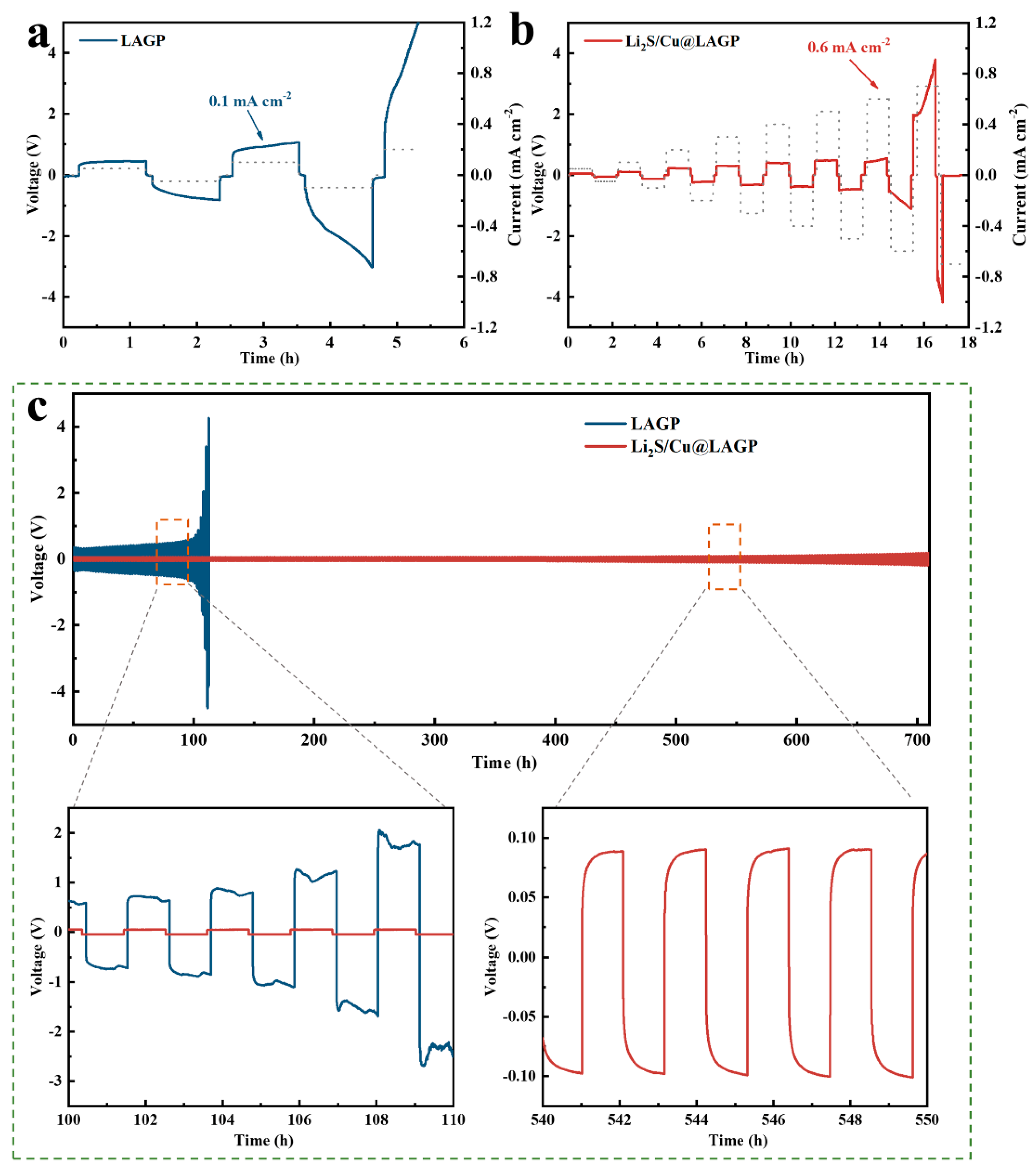
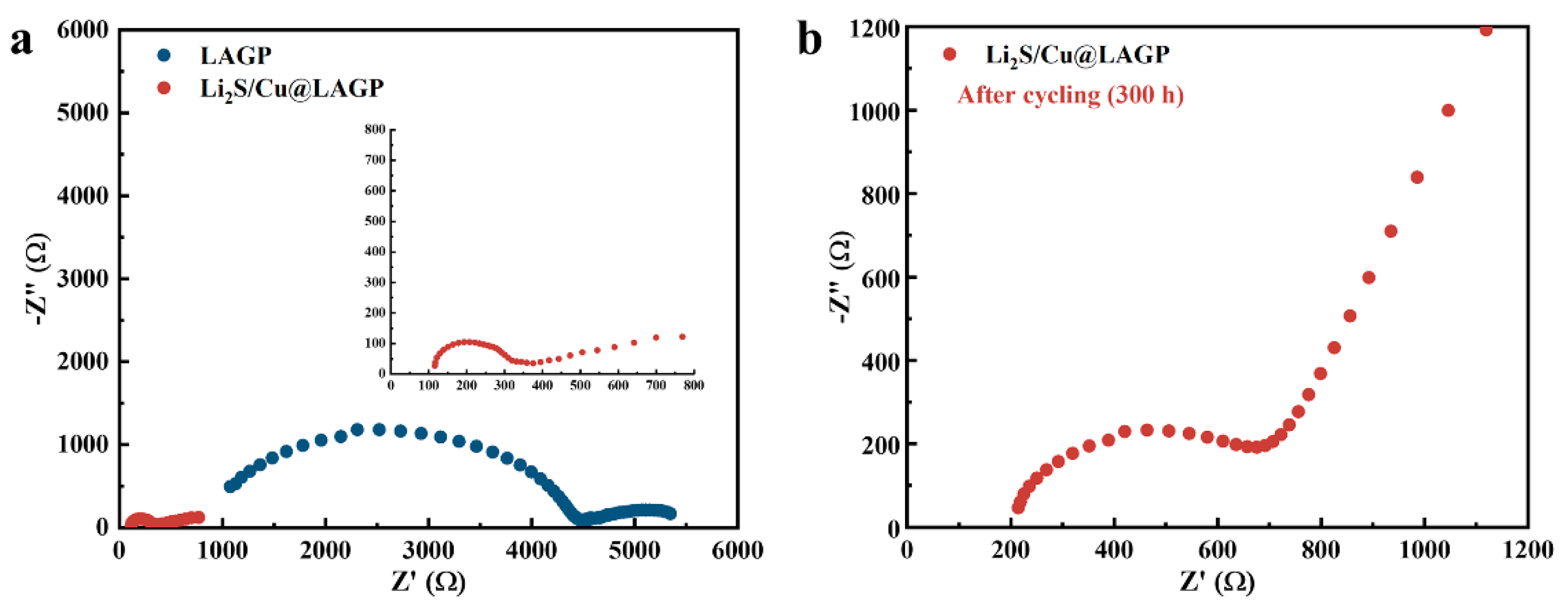
3.2. Interface Stability of Li2S/Cu@LAGP
3.3. Electrochemical Performance of SSLMBs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, Y.-M. Building a Better Battery. Science 2010, 330, 1485–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Stalin, S.; Zhao, C.Z.; Archer, L.A. Designing solid-state electrolytes for safe, energy-dense batteries. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaya, N.; Homma, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Kanno, R.; Yonemura, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Kato, Y.; Hama, S.; Kawamoto, K.; et al. A lithium superionic conductor. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M.; Paolella, A.; Armand, M.; Zaghib, K. Building Better Batteries in the Solid State: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Dendrites in Lithium Metal Anodes: Suppression, Regulation, and Elimination. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3223–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, A.; Armand, M.; Julien, C.M.; Zaghib, K. Challenges and issues facing lithium metal for solid-state rechargeable batteries. J. Power Source 2017, 353, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Pang, Q.; Kochetkov, I.R.; Sempere, M.S.; Huang, H.; Sun, X.; Nazar, L.F. A facile surface chemistry route to a stabilized lithium metal anode. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.J.; Liang, F.; Chen, K.F.; Dai, Y.N.; Xue, D.F. Challenges and perspectives of NASICON-type solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 132003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badami, P.; Weller, J.M.; Wahab, A.; Redhammer, G.; Ladenstein, L.; Rettenwander, D.; Wilkening, M.; Chan, C.K.; Kannan, A.N.M. Highly Conductive Garnet-Type Electrolytes: Access to Li6.5La3Zr1.5Ta0.5O12 Prepared by Molten Salt and Solid-State Methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 48580–48590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; DeBlock, R.H.; Butts, D.M.; Ashby, D.S.; Choi, C.S.; Dunn, B.S. Sulfide Solid Electrolytes for Lithium Battery Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Chien, P.-H.; Li, Y.; Dolocan, A.; Xu, H.; Xu, B.; Grundish, N.S.; Jin, H.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Goodenough, J.B. Fast Li+ Conduction Mechanism and Interfacial Chemistry of a NASICON/Polymer Composite Electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.K.; Jalem, R.; Gao, B.; Yamamoto, Y.; Muto, S.; Sakakura, M.; Iriyama, Y.; Tateyama, Y. Electron and Ion Transfer across Interfaces of the NASICON-Type LATP Solid Electrolyte with Electrodes in All-Solid-State Batteries: A Density Functional Theory Study via an Explicit Interface Model. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54752–54762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Zhai, W.; Hou, G.; Chen, L.; Ci, L. Bifunctional In Situ Polymerized Interface for Stable LAGP-Based Lithium Metal Batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 210072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharamulu, N.; Rao, K.K.; Rambabu, G.; Kumar, B.V.; Radha, V.; Vithal, M. A wide-ranging review on Nasicon type materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2821–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Tamura, S.; Imanaka, N. New Calcium Ion Conducting Solid Electrolyte with NASICON-type Structure. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Sun, Q.; Chen, C.; Oh, J.A.S.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Tu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, K.; Lu, L. Failure Mechanism and Interface Engineering for NASICON-Structured All-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20895–20904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Han, D.; Lu, Q.; He, Y.-B.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Han, C.; Kang, F.; Li, B. Constructing Effective Interfaces for Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 Pellets to Achieve Room-Temperature Hybrid Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9911–9918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Oh, Y.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, C.S. Characterization of Sputter-Deposited LiCoO2 Thin Film Grown on NASICON-type Electrolyte for Application in All-Solid-State Rechargeable Lithium Battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16063–16070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Ma, N.; Wang, A.; Ran, Y.; Song, T.; He, B.; Ye, A.; Mi, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; et al. Identifying Migration Channels and Bottlenecks in Monoclinic NASICON-Type Solid Electrolytes with Hierarchical Ion-Transport Algorithms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 202107747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhl, C.; Fingerle, M.; Hausbrand, R. Process related effects upon formation of composite electrolyte interfaces: Nitridation and reduction of NASICON-type electrolytes by deposition of LiPON. J. Power Source 2017, 362, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Q.; Li, T.; Li, B.-Q.; Zhang, R.; Shi, P.; Yan, C.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, Q. A Sustainable Solid Electrolyte Interphase for High-Energy-Density Lithium Metal Batteries Under Practical Conditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3252–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, T.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Gu, C.; Tu, J. A Stretchable and Safe Polymer Electrolyte with a Protecting-Layer Strategy for Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J.; Hou, G.M.; Li, D.P.; Han, G.F.; Ci, L.J. Spontaneous In Situ Surface Alloying of Li-Zn Derived from a Novel Zn2+-Containing Solid Polymer Electrolyte for Steady Cycling of Li Metal Battery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 4282–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Peng, H.L.; Yan, Y.A.; Bai, Y.Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, N.N.; Dou, S.X.; Huang, F.Q. Solid-state batteries designed with high ion conductive composite polymer electrolyte and silicon anode. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 43, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Li, C.; Li, B.J.; Song, H.C.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, M.R.; He, P.; Zhou, H.S. Germanium Thin Film Protected Lithium Aluminum Germanium Phosphate for Solid-State Li Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Sang, L.; Ding, F.; Song, J.; Mai, Y. Conformation of lithium-aluminium alloy interphase-layer on lithium metal anode used for solid state batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 277, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Q.; Xi, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ci, L. In situ construction of a flexible interlayer for durable solid-state lithium metal batteries. Carbon 2022, 187, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-K.; Tong, Z.; Fang, C.-C.; Liao, S.-C.; Chen, J.-M.; Liu, R.-S.; Hu, S.-F. Extensively Reducing Interfacial Resistance by the Ultrathin Pt Layer between the Garnet-Type Solid-State Electrolyte and Li-Metal Anode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 56181–56190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.; Weng, W.; Jiang, M.; Liu, G.; Yao, X.; He, H. In Situ Formed Li-Ag Alloy Interface Enables Li10GeP2S12-Based All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 50076–50082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, X.-B.; Huang, J.-Q.; Yuan, H.; Lu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhu, G.-L.; Xu, R.; Zhao, C.-Z.; Hou, L.-P.; et al. Controlling Dendrite Growth in Solid-State Electrolytes. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Yao, X.; Cui, P.; Duan, J.; Luo, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X. Enabling high-areal-capacity all-solid-state lithium-metal batteries by tri-layer electrolyte architectures. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 24, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ju, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Cui, L.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, G. In Situ Polymerization Permeated Three-Dimensional Li+-Percolated Porous Oxide Ceramic Framework Boosting All Solid-State Lithium Metal Battery. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Wu, X.; Xiang, J.; Li, M.; Su, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Gu, C.; Tu, J. Ionic-liquid-containing polymer interlayer modified PEO-based electrolyte for stable high-voltage solid-state lithium metal battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.Y.; Zhao, N.; Luo, J.; da Silva, J.G.P.; Mucke, R.; Kaghazchi, P.; Guo, X.X.; Sun, X.L. Design of a mixed conductive garnet/Li interface for dendrite-free solid lithium metal batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.P.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, S.Z.; Sun, W.W.; Zheng, C.M.; Xie, K. Flame Retardant and Stable Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3-Supported Ionic Liquid Gel Polymer Electrolytes for High Safety Rechargeable Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 10334–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, D.; Holmes, N.G.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Fu, J.; Li, R.; Guo, X.; et al. A flexible electron-blocking interfacial shield for dendrite-free solid lithium metal batteries. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, A.M.; Wachsman, E.D.; Mo, Y. Computation-guided discovery of coating materials to stabilize the interface between lithium garnet solid electrolyte and high-energy cathodes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 41, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Yu, B.-C.; Jung, J.-W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H.; Son, S.; Goodenough, J.B. Electrochemical Nature of the Cathode Interface for a Solid-State Lithium-Ion Battery: Interface between LiCoO2 and Garnet-Li7La3Zr2O12. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8051–8059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Schmieg, J.; Dierickx, S.; Joos, J.; Weber, A.; Gerthsen, D.; Ivers-Tiffee, E. Reducing Impedance at a Li-Metal Anode/Garnet-Type Electrolyte Interface Implementing Chemically Resolvable In Layers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 14739–14752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yu, P.; Zhang, N.; Ren, G.; Zheng, S.; Huang, W.; Long, X.; Li, H.; Liu, X. In situ formation of a bifunctional interlayer enabled by a conversion reaction to initiatively prevent lithium dendrites in a garnet solid electrolyte. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ma, W.; Li, B.; Hu, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J. A fast and low-cost interface modification method to achieve high-performance garnet-based solid-state lithium metal batteries. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Vincent, C.A.; Bruce, P.G. Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 1987, 28, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugmann, S.; Fleischmann, M.; Amereller, M.; Gschwind, R.M.; Wiemhoefer, H.D.; Gores, H.J. Measurement of transference numbers for lithium ion electrolytes via four different methods, a comparative study. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 3926–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Duan, J.; Zhang, B.; Luo, W.; Ji, X.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Song, Z.; Wen, J.; et al. A self-regulated gradient interphase for dendrite-free solid-state Li batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pei, A.; Lin, D.; Xie, J.; Yang, A.; Xu, J.; Lin, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, F.; et al. Uniform High Ionic Conducting Lithium Sulfide Protection Layer for Stable Lithium Metal Anode. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1900858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Cheng, X.-B.; Yao, Y.-X.; Shen, X.; Li, B.-Q.; Li, W.-J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J.-Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. An Armored Mixed Conductor Interphase on a Dendrite-Free Lithium-Metal Anode. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Ci, L.; Min, G. Interface Engineering of a NASICON-Type Electrolyte Using Ultrathin CuS Film for Lithium Metal Batteries. Batteries 2023, 9, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040194
Zhang S, Liu D, Zhang L, Li J, Zhao G, Ci L, Min G. Interface Engineering of a NASICON-Type Electrolyte Using Ultrathin CuS Film for Lithium Metal Batteries. Batteries. 2023; 9(4):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040194
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shengnan, Dongming Liu, Lin Zhang, Jianwei Li, Guoqing Zhao, Lijie Ci, and Guanghui Min. 2023. "Interface Engineering of a NASICON-Type Electrolyte Using Ultrathin CuS Film for Lithium Metal Batteries" Batteries 9, no. 4: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040194
APA StyleZhang, S., Liu, D., Zhang, L., Li, J., Zhao, G., Ci, L., & Min, G. (2023). Interface Engineering of a NASICON-Type Electrolyte Using Ultrathin CuS Film for Lithium Metal Batteries. Batteries, 9(4), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9040194







