Abstract
Biofuel cells have been in the spotlight for the past century because of their potential and promise as a unique platform for sustainable energy harvesting from the human body and the environment. Because biofuel cells are typically developed in a small platform serving as a primary battery with limited fuel or as a rechargeable battery with repeated refueling, they have been interchangeably named biobatteries. Despite continuous advancements and creative proof-of-concept, however, the technique has been mired in its infancy for the past 100 years, which has provoked increasing doubts about its commercial viability. Low performance, instability, difficulties in operation, and unreliable and inconsistent power generation question the sustainable development of biofuel cells. However, the advancement in bioelectrocatalysis revolutionizes the electricity-producing capability of biofuel cells, promising an attractive, practical technique for specific applications. This perspective article will identify the misconceptions about biofuel cells that have led us in the wrong development direction and revisit their potential applications that can be realizable soon. Then, it will discuss the critical challenges that need to be immediately addressed for the commercialization of the selected applications. Finally, potential solutions will be provided. The article is intended to inspire the community so that fruitful commercial products can be developed soon.
1. Introduction
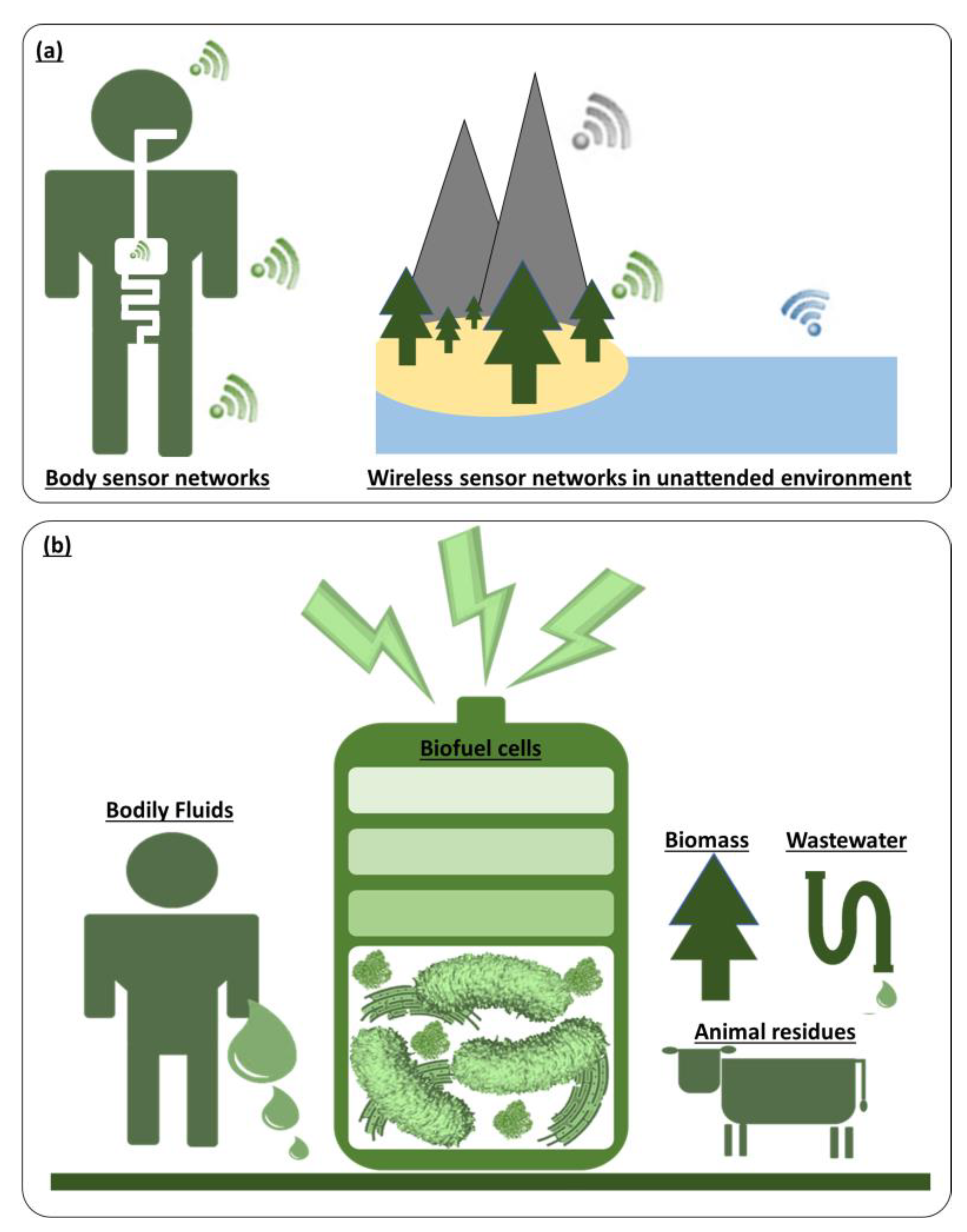
Radical technological innovations and significant size reductions in electronics are allowing for massive improvements in speed, energy efficiency, and integration density [1,2,3]. Furthermore, with advances in manufacturing and materials science, electronics are evolving into new flexible and stretchable forms [4,5,6,7]. This trend has allowed these rapidly-becoming ubiquitous devices to be seamlessly integrated into the human body and our environmental surroundings, collecting real-time information and creating a more connected world (Figure 1a) [8,9,10]. For the untethered and independent operation of these electronics to be deployed in our everyday life, an integrable, autonomous, self-sustainable, miniaturized power source that does not require human intervention and maintenance is the most critical necessity [11,12,13,14,15]. While traditional battery-operated electronic devices suffer from a limited energy budget, bulky size, and toxic compounds of the integrated battery, harvesting energy from the human body and ambient environment has emerged as a promising power solution for these applications [16,17,18,19]. The power scavenged from external sources (e.g., thermal, mechanical, solar, and moisture) is relatively small, irregular, and inefficiently converted [13,14,20]. However, because the energy resources are potentially infinite, they can help achieve the longstanding vision of long-lived deployments of stand-alone, always-on electronics with the aid of energy storage devices and advanced electronic circuits [19,21]. Among many micro- and nano-sized energy harvesting techniques, biological fuel cells or biofuel cells are considered the most suitable power solution, especially when chemical or biochemical energy resources are available [22,23,24]. Biochemical energy is stored within all formats of human bodily fluids, including tears, sweat, saliva, urine, and blood, and even in organic substrates available throughout the gastrointestinal tract [22,23,25]. All forms of environmental organic water, wastewater, and biomass contain chemical or biochemical energy convertible to electricity [26,27,28]. Biofuel cells can use enzymes, organelles, or microorganisms as an eco-friendly biocatalyst to convert that chemical or biological energy into electrical energy, allowing for portable, wearable, implantable, or ingestible power generation in a sustainable manner, or offering a long-term power solution for unattended environmental electronics (Figure 1b) [29,30]. Although there is a distinct difference in the technical definition of fuel cells and batteries [31,32], the terminology of biofuel cells and biobatteries have been used interchangeably when the fuel cells are applied as a random energy source for low-power distributed electronics [33,34,35,36]. The limited short-term operation of the biofuel cells resembles the behavior of a primary battery and the replenishment of the fuel for a longer-term operation can be considered as a form of recharging. In this perspective article, we will not technically differentiate these two words when it comes to their role as an energy harvesting technique in a miniaturized platform.
Figure 1.
(a) Future electronics deployed within the human body and in unattended environments. (b) Biofuel cells as a self-sustainable power source for those electronics.
Because of the outstanding energy harvesting mechanism of biofuel cells with biodegradable organic substrates, these techniques have attracted much attention from scientists and have been explored for the past 100 years [37,38]. Many ideas based on scientific curiosity have been proposed and published in important journals, demonstrating potential as a permanent power solution by exploiting abundant renewable energy resources [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. Enzymatic fuel cells (EFCs) have been implanted into many living creatures self-sustainably generating meaningful power from their body fluids [49], while ingestible microbial fuel cells (MFCs) have been proposed by using the biodegradable organic fuels in the human intestine [50,51]. Wearable biofuel cells that can be fueled by sweat or interstitial fluid have drawn valuable attention from the scientific community as a potential power solution for body sensor networks [22,23]. Many miniaturized biofuel cells, which can be readily activated by any organic liquid, have been innovatively leveraged as a portable power supply for in vitro point-of-care biosensors [52,53,54,55] or, revolutionarily, have been developed as self-powered biosensors because their power output can be sensitively used as a transducing signal for specific biomarkers [26,56,57,58]. MFCs or photosynthetic MFCs have been proposed as the most suitable power source for wireless sensor networks (WSNs) deployed in unattended working environments in order to connect the world in the context of the Internet of Things (IoT) [59,60,61]. Obviously, these attempts are conceivable real-world applications with large upside promise and potential. However, given that research on biobatteries has remained in an early stage for the past century without commercial success [26,38,62,63,64,65], we need to correct our misconceptions about biofuel cells, re-examine opportunities, and identify the challenges. This perspective article will reveal new insights into biofuel cells, or biobatteries, and set the stage for future directions.
2. Misconceptions
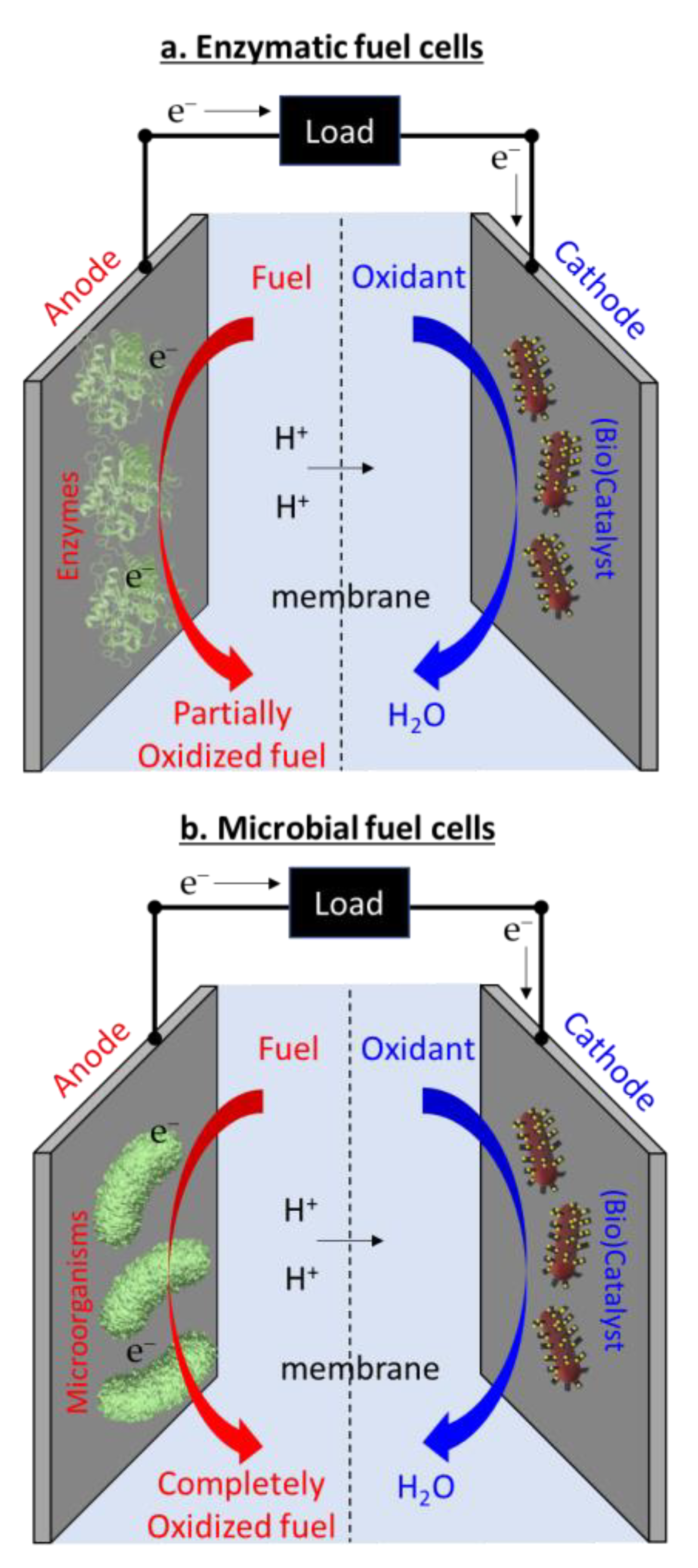
Biofuel cells can be largely categorized into EFCs and MFCs. EFCs use enzymes to partially oxidize fuels, while MFCs employ microorganisms that can completely oxidize fuel but require continued maintenance and support for microbial sustenance (Figure 2) [29,30,66]. As another format of biofuel cells, organelle (e.g., mitochondria)-based fuel cells have also been demonstrated to improve the oxidation reaction and stability of EFCs [67], and other organelle (i.e., sub-cellular) photosynthetic fuel cells have been developed as an environmental power solution [68,69]. However, in this report, we will focus mainly on two biofuel cell platforms, EFCs and MFCs, because organelle-based fuel cells generally belong to EFCs and the technique has not well been established compared with the others. Usually, EFCs are considered a power source for wearable or implantable applications because of their excellent capability of miniaturization, integration into various form factors, and biosafe operation [30]. On the other hand, MFC developments have been centered around macro-scale platforms for sustaining power generation from ambient environments, and are capable of applications such as wastewater treatment that have minimal power demand. Because MFCs require continuous nutrient introduction through a complicated energy-intensive fluidic system and potential microbial cytotoxicity may pose a threat [32], MFCs are not being used in the human body. In this section, our misconceptions about EFCs and MFCs will be identified and corrected so as to enable versatile new avenues for unique applications.
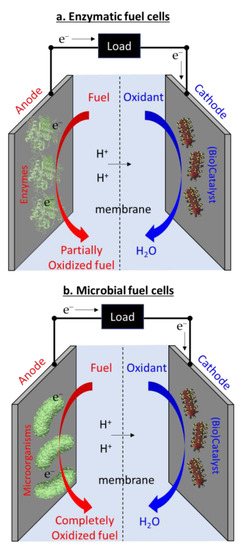
Figure 2.
Working principles of (a) enzymatic fuel cells and (b) microbial fuel cells.
2.1. Misconceptions about EFCs
Applications: In 2007 at the 234th American Chemical Society National Meeting and Exposition in Boston, SONY announced the development of an EFC powering a Walkman music player. Their biobattery was a pioneering achievement that showed practical efficacy as a simple power source with readily available organic substances (e.g., sugar). However, its demonstration as a replacement for conventional batteries was an incorrect start and failed to identify the unique applications and future directions of EFCs. An EFC is an energy harvesting technology that can generate relatively low power, but works as a potentially infinite chemical energy supply so that the EFC theoretically runs forever. Its power performance cannot be compared to other high-power batteries, chemical fuel cells, and energy storage devices because the application of the EFC is very specific and unique for unattended environments where battery replacement or recharging is not practical.
Cost and renewability: EFCs are a subclass of green and renewable fuel cells that do not generate greenhouse gases [30]. Moreover, nonrenewable and noble metals that are catalysts in conventional fuel cells can be replaced with renewable and eco-friendly enzymes in EFCs [30]. Therefore, many research articles have introduce EFCs as an alternative energy technique. However, this claim is misleading and illogical because it is difficult to see how small-scale EFCs can meaningfully become a green and renewable energy technique only offering micro-watt level power [38,64,65]. EFCs cannot be a significant contributor to solving energy crises and environmental pollution. Even the claim that EFCs are cost-effective and an inexpensive energy technique is misleading [65]. The extraction, isolation, purification, and immobilization of enzymes are generally expensive requiring labor-intensive and time-consuming steps. Moreover, considering the low energy conversion efficiency and low power generation of EFCs, their cost performance can be much worse than other energy techniques.
Operating conditions: Usually, conventional fuel cells require relatively high temperatures and non-neutral pHs to maximize the activity and stability of noble metal catalysts [30,37]. On the other hand, EFCs are an easy-to-handle technique because of their less stringent requirements for operating conditions with room temperature and neutral pH [70]. This allows EFCs to be effectively applied to the human body, where the operating conditions are generally favorable because the body usually maintains a steady temperature and neutral pH [23,25]. Depending on the type of enzymes, however, their activities are dramatically affected by minute changes in those conditions. When the anode and the cathode of the EFC use different enzymes in a common body fluid, the performance and stability of the EFCs must significantly decrease [64]. For example, the most common glucose/oxygen EFC uses glucose oxidase on the anode and laccase on the cathode. While glucose oxidase has its maximum activity at pH 5.5 and 40 °C, laccase shows its best stability at pH 7.4 and 30 °C. In addition to temperature and pH, the type of fuel is another critical factor that has often been overlooked [25,64,66]. Especially when the EFCs use bodily fluids, the low ionic strength and the low concentration of redox substrates (e.g., glucose, lactate, etc.) can significantly reduce the EFC performance and stability [64,66].
2.2. Misconceptions about MFCs
Applications: Since the electrogenic capability of microorganisms was discovered, the majority of microbial energy research has focused on the development of macroscopic MFC systems for wastewater treatment and simultaneous power generation [32]. Mesoscopic MFC systems have been developed for self-sustainable power generation in sediments [32,71]. For the past several decades, we have observed significant developments and performance improvements in these macro- and meso-level MFC technologies. These advances are reflected in the considerably increasing number of scientific literature and patents [28,62,63]. Even many governmental agencies and companies have regarded MFCs as promising alternative clean energy that can solve our global energy and environmental issues. MFC was in TIME Magazine’s list of the 50 Best Inventions for 2009 [72]. However, the MFC technique has never gone further than a pilot-scale laboratory experiment and has not produced any commercial success. Now, many leading researchers are raising questions about its practicability [32,62,63,73]. Although the MFC technique for these attractive macroscale applications must be continuously explored, the nature and definition of the MFC must be re-evaluated and MFC miniaturization needs to be considered for more feasible applications. MFC is obviously an energy harvesting technique similar to EFC that can convert chemical or biological energy waste into electricity.
Carbon neutrality: In many cases, MFC has been promoted as a clean and green energy technology. However, MFCs generate a large amount of carbon dioxide during their operation. Only when the technique uses biomass to fuel the photosynthesis of natural components will it consume existing carbon dioxide on a human timescale, making the energy and power production a weapon against the rise of atmospheric carbon dioxide. If the time from energy generation to photosynthesis is not short enough, net-zero emissions cannot be achieved by the MFC technique. In particular, with recent unprecedented environmental destruction through rash human logging or wildfires, it is really difficult to balance CO2 emissions from MFC and removal by plants. For the specific purpose of CO2 reduction, photosynthetic MFCs can be particularly considered.
Operating conditions: Similarly to EFCs, the performance of MFCs is sensitive to environmental operating conditions such as temperature, salinity, and pH [74,75]. Although one advantage of MFCs over typical fuel cells is to require much less strict operating conditions, their performance may not be optimized for use in practical field applications. The effects of those environmental conditions on MFC performance have been intensively explored. However, many reports on MFCs are misleading because they highlight their ideal applications in natural settings without considering extreme weather conditions. As the effects of environmental conditions have been well-researched, researchers must now extensively explore and discuss the availability and suitability of electricity-producing bacteria (i.e., exoelectrogens) in natural environments. Unfortunately, to date, only about 100 microbial species have been found as exoelectrogens [76,77]. Although more and more exoelectrogens and other electron transfer mechanisms are being discovered [78,79,80], we are jumping to conclusions by claiming that microorganisms can be the next generation of sustainable energy.
3. Opportunities
Many interesting and innovative biobatteries and biofuel cells have been proposed. With further improvements, these reports claim that ideally long-lived EFCs for wearable and implantable electronics or high-power MFCs for wastewater treatment, renewable energy generation, and remediation will be soon realized. However, similar conditional demonstrations have been around for the past century without ensuring their practical efficacy. In this section, by correcting our misconceptions about biofuel cells or biobatteries and re-visiting their definitions and outstanding features that the other techniques cannot supply, we will propose the most feasible, potential applications that can quickly open new avenues for commercialization.
3.1. EFCs
Because of the mild operating conditions, various redox enzymes for selective substrates in body fluids, and the miniaturable and integrable features of EFCs, particular attention has been paid to the development of wearable and implantable EFCs for self-sustainable, long-standing power generation harvesting from physiological body fluids [23,30,39,81,82,83]. In parallel, excellent fuel diversity and availability have enabled EFCs to be considered as an alternative power source to conventional batteries to power portable electronic applications such as mobile phones, laptop computers, and other handheld devices [30,84,85]. However, EFC technology has long been limited by many problems such as intrinsic low stability, biodeterioration, inefficient and partial electrocatalytic activities, low reliability, oversensitive reactions to environments, and biofouling issues of enzymes [24,29,30,37,49,70]. Although EFCs have been experimentally implanted in many living creatures such as cockroaches, snails, lobsters, clams, and rats, it is very hard to believe that the EFC technique can replace conventional up-to-date implantable batteries now lasting up to 25 years [64,66]. Moreover, as we discussed in the previous section, the low and unreliable power generation of EFCs will limit their ability to power useful electronic applications in practice.
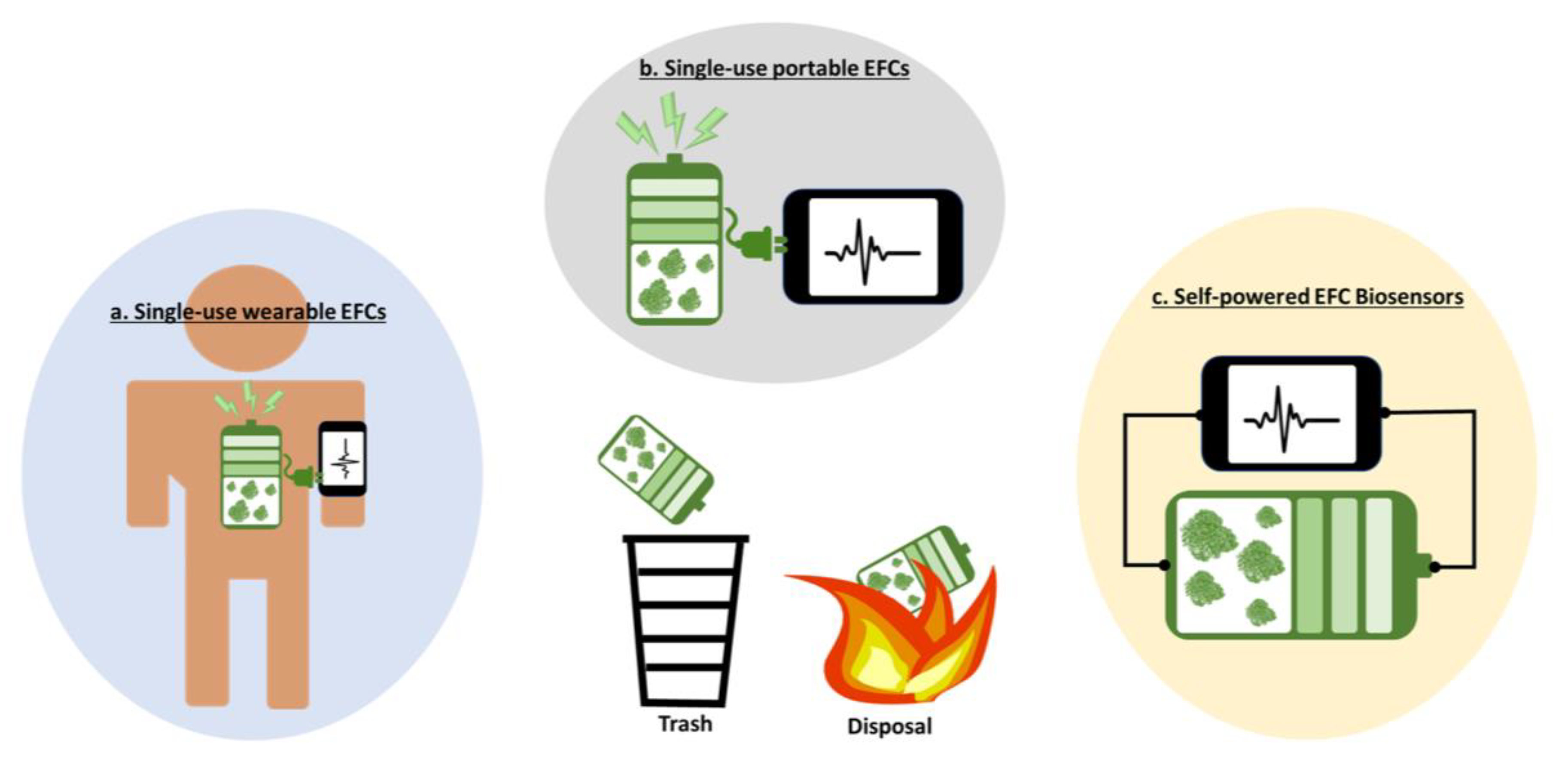
Single-use wearable EFCs: While implantable EFCs have a long way to go for practical applications [64], the EFC technique has been considered a realizable sweat-based power solution for wearable applications, with actual demonstrations on human subjects [22,23,86,87]. Many reports have featured wearable EFCs as a new way to accomplish the longstanding dream of self-powered, self-sustainable, and always-on wearable systems [88,89]. The systems will collect valuable real-time health information, perform multiple therapeutic functions, and monitor potential chemical or biological threats, which can create an intelligent and autonomic body sensor network [90]. Although wearable EFCs require much less stringent development and operational conditions than their implantable counterparts, there are critical hurdles to overcome. Generally, wearable EFCs have been intensively explored for three objectives: (i) long-lived, stable power generation; (ii) continuous operation during irregular perspiration; and (iii) excellent durability under mechanical deformation. With the significant advances in material sciences, more stretchable and flexible EFCs have been successfully developed without compromising performance under mechanical deformation [22,23,86,87]. Textile-, fiber-, tattoo-, and island-bridge-based EFCs have been demonstrated to have a high durability with high power generation under rigorous mechanical deformations [91]. However, the long-term and stable power generation of EFCs have not been achieved because of their unstable and denaturing enzymatic activities. Even the latest advances in EFCs through protein engineering, immobilization of the enzymes, or employment of nanoparticles have not improved their lifespan for more than several hours [29,30,49]. Moreover, the continuous power generation of sweat-based EFCs has been another critical issue. Continuously securing a sufficient amount of sweat for reliable and constant power generation is very difficult because of irregular human perspiration [92]. Although the use of pharmacological agents or iontophoresis has been proposed to trigger sweat excretion [93], and energy storage devices have been added to store excess energy when sweat is available [89], practical and reliable wearable EFCs for long-term, stable, and continuous power generation have not been demonstrated because of the complicated system design and integration, as well as extra power demand for additional functions. If the biggest challenges that prevent the practical applications of wearable EFCs are intrinsic enzymatic instability and limited sweat access, then a single-use, disposable battery-type EFC platform is potentially realizable (Figure 3a). A disposable patch-type EFC can be readily attached to dry skin and sufficient sweat will be available from exercise to generate enough power to run other functional devices. Monitoring sweat composition will provide the wearer with important health information. After exercise, the patch can be readily thrown away. This one-time use platform may be preferable for wearable applications considering that humans feel uncomfortable with wearable gadgets and tend not to wear them all the time. Rather, intermittent or on-demand use may be a more appropriate target for wearable applications.
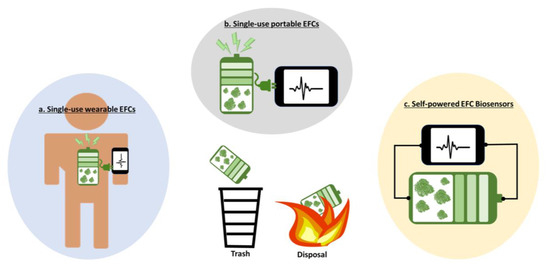
Figure 3.
Opportunities of EFCs.
Single-use portable EFCs: Similarly, disposable, portable, single-use, low-powered EFCs can be a great application target because they do not require stable and long-lived power generation (Figure 3b). Eco-friendly disposable power sources are required to serve the increasing market for disposable electronics and sensors [94,95,96]. Furthermore, a new paradigm of the Internet of Things (IoT), named the Internet of Disposable Things (IoDT), has been developed for various applications in point-of-care testing, shipment tracking, and food/groceries monitoring [26], which means a realistic and accessible power source is needed. EFCs can be the most suitable power source that can be easily integrated into these disposable devices and be readily activated by any biodegradable substrate (e.g., body fluids, ethanol, organic acids, and sugars), which are easily available in our environment. Paper-based EFCs are great examples of those inexpensive and disposable applications [52,97,98]. Paper has recently emerged as a low-cost, disposable game-changing substrate for next-generation disposable electronics and sensors [99,100]. A self-sustainable paper-based power source allows for the creation of an eco-friendly all-paper device that can be easily disposed of through incineration [98]. Usually, microwatt-level power sources are more attractive for the short-term operation of those disposable applications and EFCs are most suitable as a low-power generator.
EFCs for self-powered point-of-care biosensing: As the electrical outputs of EFCs are based on the specific bonding between the biocatalytic enzymes pre-loaded in the EFC and the substrates available in the analytes, EFCs can function as a biosensor to selectively monitor the presence or the concentration of the substrates (Figure 3c) [56,101,102,103,104,105]. The electricity generation that can be measured in various forms, such as current, voltage, and power, will be proportional to the concentration of the substrate specific to the enzyme. As the anode of the EFC serves as a transducer and the enzymes act as a bioreceptor, the EFC does not require any additional transducers or external power sources, leading to the development of a simple-to-operate and easy-to-miniaturize self-powered biosensor. If EFCs serve as the only power sources for potential applications (as shown in the previous sections), they are expected to provide a sufficient electrical performance, but the intrinsic limitations of low output voltage and power need to be addressed for practical applications. However, when EFCs are used as self-powered biosensors, even minute electrical outputs are enough to precisely monitor health parameters without further design modification and functional additions. Many proof-of-concept devices have been demonstrated as in vivo wearable or in vitro point-of-care platforms [56,103,104]. However, considering the instability and unreliability of the enzymes, single-use and disposable formats will be much more probable for commercial success. Ideally, a drop of body fluid containing many valuable substrate-type biomarkers will be enough to activate the EFC and allow for a meaningful electrical output that indicates the patients’ physiological states. Many reports have demonstrated that EFCs can be applied to a self-powered drug delivery system. An iontophoretic device with a built-in EFC or a redox polymer-mediated EFC has been proven feasible for controlled drug release [101,106,107]. However, power generation for continuous drug release requires implantable or microneedle-type EFCs that use blood or interstitial fluids, while a smart on-demand drug release function needs an energy-intensive feedback system. EFC-based drug delivery systems may not be realized as a practical example soon.
3.2. MFCs
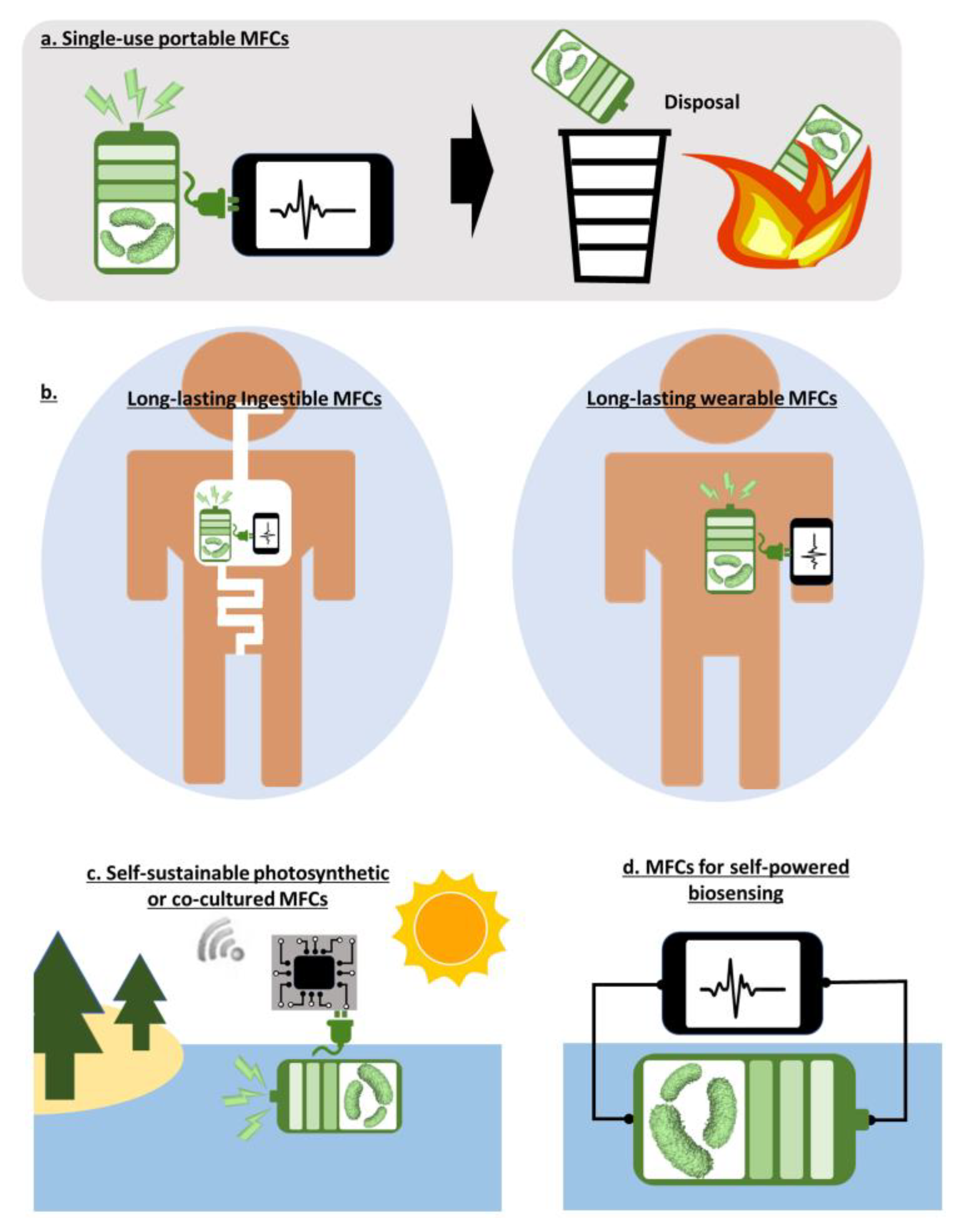
The outstanding capability of microbes to break down renewable organic substrates and produce electricity simultaneously appear fascinating as a solution for environmental sustainability and preservation [108]. To this end, this technique has been advanced mainly with an MFC platform at large scales to meaningfully address environmental issues and the energy crisis [32,73]. Typically, natural microorganisms are used in MFCs. However, it has been very challenging to control the viability of natural microorganisms in the context of consortia and to optimize their performance for practical large-scale applications. Even worse, scaling challenges, energy-intensive maintenance and operation, biofouling issues, relatively expensive materials, and low performance keep raising questions about the sustainable development of MFCs [32]. Although there is no doubt that MFCs will somehow become a meaningful renewable energy and wastewater treatment technique, this will not happen soon. Rather, miniaturized platforms with selected microorganisms for low-power applications will be more applicable, realizable, and feasible [109,110]. Similar to EFCs with preloaded enzymes, small-scale MFCs pre-inoculated with selected microorganisms are more controllable for operation and optimization, and their outputs are more predictable than those with a microbial consortia available in nature [111,112,113]. One of the biggest arguments for those miniature MFCs is a self-contained system that produces the intensive energy needed to maintain microbial vitality. With those systems, many strategic plans can be proposed for specific realizable applications (Figure 4a–d).
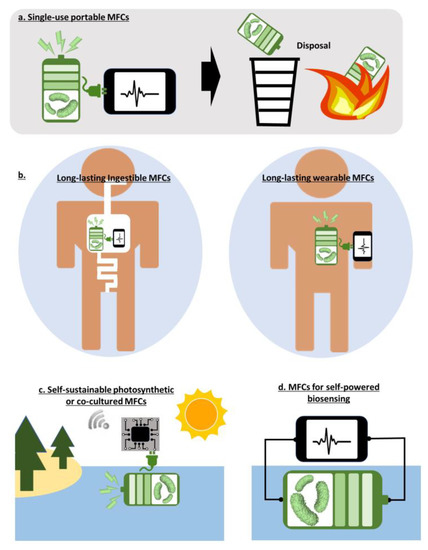
Figure 4.
Opportunities of MFCs.
Single-use portable MFCs: Quality diagnostics and adequate disease surveillance are quite limited in developing countries that lack basic access to testing resources [114]. The World Health Organization (WHO) issued seven criteria named “ASSURED” to provide guidelines for the development of ideal point-of-care biosensors, “affordable, sensitive, specific, user-friendly, rapid and robust, equipment-free, and deliverable to end users” [114]. However, as conventional colorimetric biosensors that meet the criteria require additional transducing functions for sensitivity improvement, an integrated power source is demanded [98,115]. Moreover, future diagnostic platforms require two additional criteria of Real-time connectivity and Ease of sample collection, making the acronym “REASSURED”, which necessitates an additional power source [116]. That power source must meet the REASSURED criteria and be accessible in resource-limited settings. Because of the one-time point-of-care operation of the biosensors, a small and disposable power source will be more attractive when conventional batteries or other energy-storage devices are not available or are wasteful for single-use low-power applications. Miniaturized MFCs are very suitable as a power source because a wide range of waste and renewable biomasses for microbial metabolism and their consequent electricity generation are readily available in resource-limited environments [115,117]. Their power will be enough to run practical biosensors in a cost-effective and eco-friendly manner (Figure 4a). Even in dry, desert climates where these biomasses are not available, human body fluids will be easily accessible as an organic fuel to active the MFCs [118,119].
Long-lasting MFCs for powering wearable or ingestible electronics: As discussed in the section about EFCs, unstable and denaturing enzymatic activities require fundamental breakthroughs to achieve self-sustaining, long-lived power generation within the human body, limiting their immediate potential uses to single-use applications for only a short period. On the other hand, microorganisms as biocatalysts can provide exceptional, self-sustaining, long-term stability as they regenerate enzymes as part of their metabolism [120,121]. Consequently, microbial biocatalytic activities in an MFC are self-maintaining, self-repairing, and self-assembling, which can provide long-lasting, self-sustaining power for wearable or ingestible applications while continuously feeding off human sweat or gut organic substrates (Figure 4b). Recently, the increasing number of reports revealing the electrogenic capability of human skin and gut bacteria suggest their potential use as novel microbial power supplies [79,80,122]. The immediate use of human-body inhabiting bacteria for practical and reliable power generation remains a challenge. However, the direct use of non-toxic, non-human exoelectrogens as a power resource interdependently with the human body may provide a quicker path to commercially successful wearable or ingestible electronics. In particular, reported work on spore-forming microbial energy harvesting possibilities creates the opportunity for wearable and ingestible MFC realization [119,123,124,125,126]. This novel MFC technique improves its storage stability by exploiting bacterial natural survival strategy to become endospores under adverse environments and to germinate when nutrients are sufficiently available.
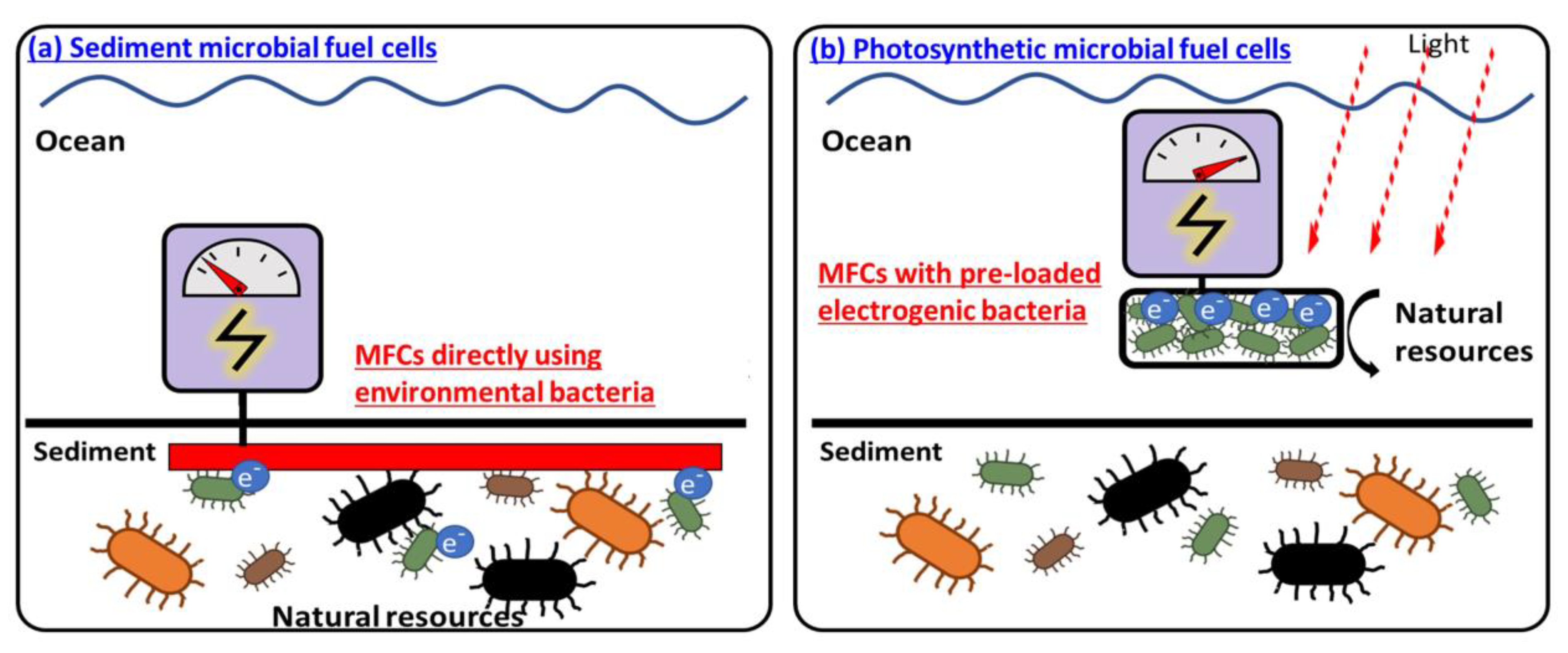
Self-sustainable photosynthetic or co-cultured MFCs: With a significant size reduction in electronics and rapid advances in IoT technology, miniature wireless sensors are expected to connect every corner of the world [127]. A miniature power source is the most critical requirement for the independent and sustaining function of sensors (Figure 4c) [127,128]. MFCs have attracted much attention as one of the proper power sources for such devices as every environment generally hosts various microorganisms that can self-sustainably run MFCs [59]. In particular, a natural sediment rich in microorganisms and organic substrates is considered the best location to install an MFC where the anode is buried in the anaerobic sediment and the cathode is put in the overlying aerobic water (Figure 5a) [71]. However, the low performance of MFC using a limited number of exoelectrogens in unoptimized natural environments require a significant increase in size, which eventually does not guarantee performance improvement and develops critical challenges when anchoring, running, and maintaining the large-scale MFC in the sediment [32]. Moreover, the sediment MFCs cannot be provided in a small-scale platform for the next generation of miniature wireless sensor networks (WSN).
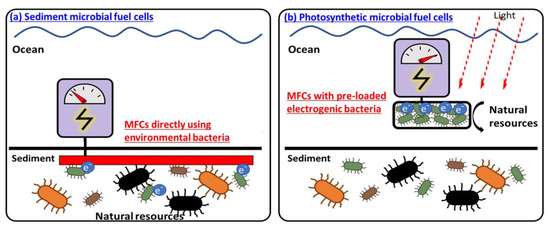
Figure 5.
Sediment MFCs and photosynthetic MFCs.
Instead of using intact natural microorganisms in real-time, selecting special exoelectrogens and pre-inoculating them in MFC can allow for device miniaturization with excellent control of the microenvironment (Figure 5b). Especially, photosynthetic microorganisms have emerged as a self-sustainable biocatalyst in MFC to perform photosynthesis and respiration by exploiting light and water, the most renewable and abundant energy resources [129]. Those photosynthetic MFCs have successfully been demonstrated as a miniaturized power supply for a relatively long time without replenishment of any organic fuel [60]. Recently, it has been reported that an engineered microbial consortium with the photosynthetic microorganism can revolutionize the power and lifetime of MFC through their syntrophic relationship [20,130,131]. Ideally, the consortium can be designed so a photosynthetic microorganism produces an organic matter that another species needs for its exoelectrogenic activity. During electrogenesis, that species will produce gases that preserve the viability of the photosynthetic microorganism, consequently exhibiting self-sustainable capabilities in a closed, miniaturized device platform and generating longer and greater power for real-world WSN applications [20,130].
MFCs for self-powered biosensing: While EFCs can be very selective biosensors because each enzyme exhibits specificity towards a particular substrate-type biomarker, the microorganisms in MFCs typically lack specificity [29]. However, MFCs have been successfully demonstrated as a general biosensor to monitor water quality. Although MFCs cannot specifically detect particular substances, they can sensitively measure the number of organic compounds (BOD; biological oxygen demand) or toxic contaminants in water as the microbial metabolic activity and their electrical output are sensitive to those compounds and contaminants (Figure 4d) [132,133]. In the early days, mid-scale MFCs were used for long-term, on-line monitoring of water quality, demonstrating their practical efficiency [133,134]. Recently, to improve their controllability and maintenance, the MFCs have been miniaturized, targeting practical applications for continuous or single-use disposable operation [135,136,137,138,139]. In addition to the water quality monitoring, MFCs can be readily applicable for antibiotic susceptibility testing because the bacterial extracellular electron transfer (EET) is inversely proportional to the concentration of antibiotics [140,141,142].
4. Challenges
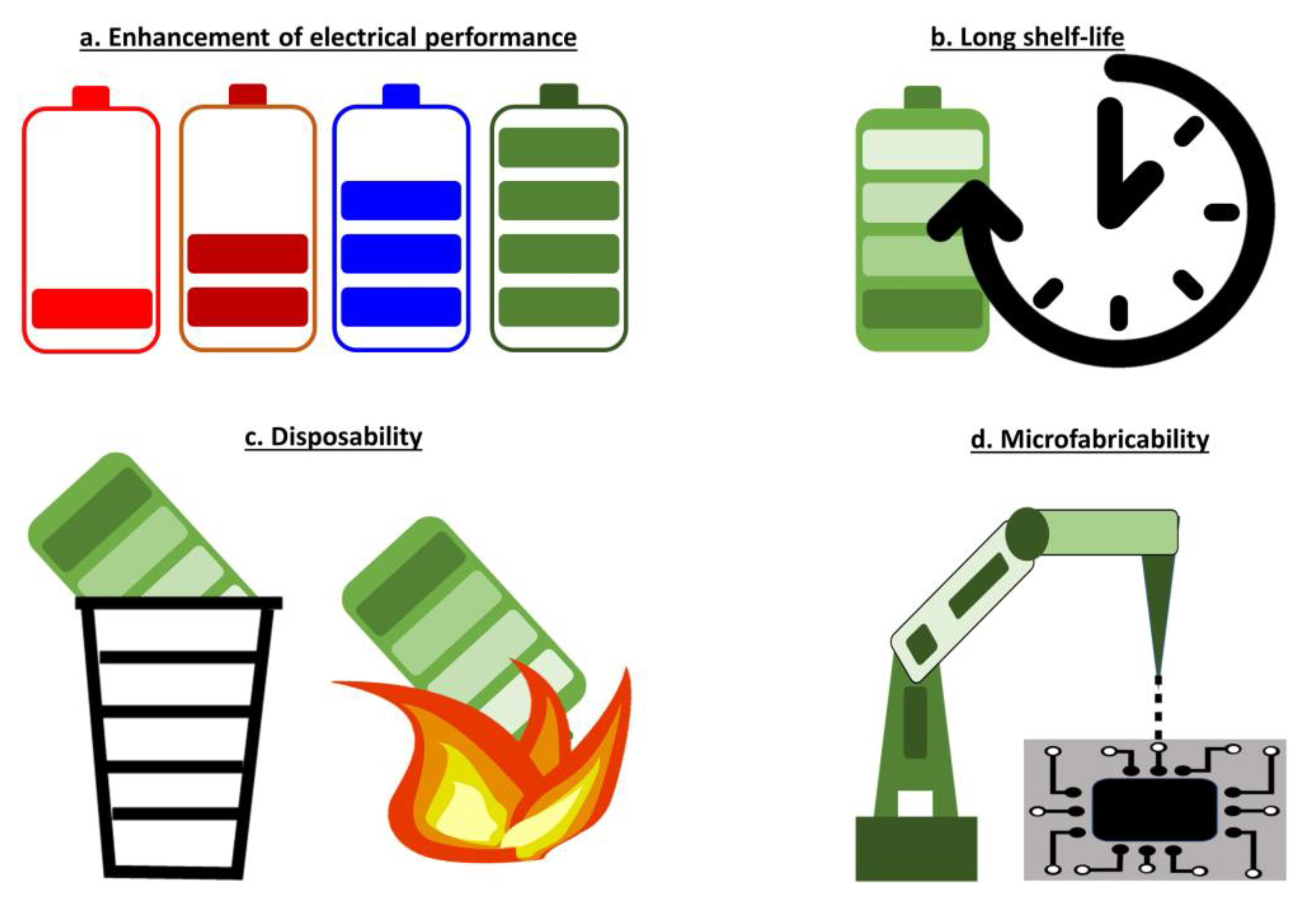
Even for the applications discussed above, several challenges need to be addressed for immediate use and commercial viability of biofuel cells (Figure 6).
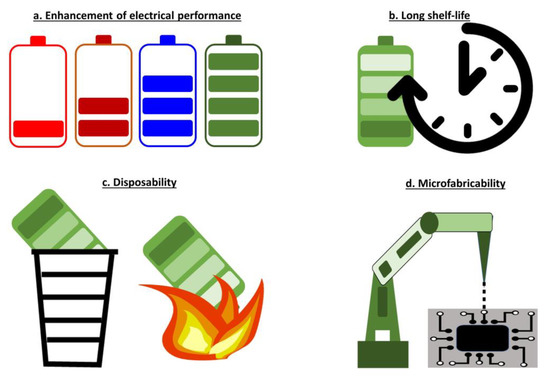
Figure 6.
Challenges for biobattery development.
4.1. Enhancement of Electrical Performance
All biofuel cell applications now face sub-optimal power, current, output-voltage, open-circuit-potential, and other electrical performance issues. When biobatteries are designed as the power source for long-term or short-term operation, sub-optimal performance can be a major problem that restricts potential use from power-demanding devices. Even if biobatteries are used in self-powered biosensors, the electrical performance can be an important factor for determining the sensitivity of the biosensors. The main reason for this low electrical performance is the inefficient electron transfer from the biocatalysts to the electrode [29]. For EFCs, the redox electroactive site of the enzymes is buried deeply in the enzyme matrix, leading to a significant performance reduction [30]. For MFCs, the EET through the cell membrane requires activation energy, which reduces the output performance of the MFC [108]. Multiple solutions to improve the performance of EFCs and MFCs have been proposed and will be briefly discussed.
Improving intrinsic activities of biocatalysts: Typically, naturally occurring enzymes and microorganisms do not possess sufficient electron transfer efficiencies that are required for biofuel cells. To overcome the electron transfer constraints and improve the electrochemical performance, we have entered a new phase of development with a biotechnique in synthetic biology that genetically engineers the enzymes and the microorganisms [143,144]. For example, modified enzymes can increase affinity toward substrates, provide oriented immobilization, and shorten the distance between the active site of the enzyme to the electrode, while engineered microorganisms can regulate microbial metabolic pathways and improve their electrogenic potential.
Improving biotic-abiotic interfaces: Seamless and low-impedance biotic–abiotic interfacing is critical for high-performing and -stable biobatteries [145]. Recent advances in micro-/nano-technologies and material science/engineering have provided opportunities for realizing the interfaces between biological systems and external electrodes [145,146]. These strategies include adding nanomaterials to facilitate electron transfer at the biotic–abiotic interfaces, applying various immobilization techniques to improve biotic stability and activity, and modifying electrode architectures to offer a large surface area and reduce a too-high impedance at the interface.
Creating supercapacitive electrodes: Recently, extensive research has improved the electrical performance of biofuel cells by creating an anode with two desirable features: bio-electrocatalysis and charge storage [147,148]. The capacitive anode can store charges generated from biocatalytic activities, which will be delivered with high and short discharge pulses, leading to high-power output generation. Multiple demonstrations of these hybrid devices have combined supercapacitors and biofuel cells, exhibiting that even low-performance biobatteries can become a practical power supply for actual applications [147,148,149,150].
Serial and parallel connection along with a power management system: The typical sustainable voltage and power outputs from a single biobattery are about 0.1~0.6 V and 10~100 µW, respectively. Most conventional electronic and biosensing applications require voltage and power > 1.5V and >1mW when a wireless signal transmission is required. Serial and parallel assembly of the biobatteries will amplify the electrical performance [30]. In addition, the performance of the biobatteries can be boosted by a power management circuit through a charge pump or a booster converter [30]. However, the design and construction of the battery interconnection need to be very carefully manipulated because the overall performance will be limited by the weakest unit in the stack. Moreover, the net voltage and power outputs need to be well evaluated because some of the generated electricity from the biobatteries will be consumed by the power management system in exchange for the voltage boost.
4.2. Long Shelf-Life
To achieve effective implementation of the biobatteries in practical settings, a critical challenge is that the biocatalysts (i.e., enzymes and microorganisms) must be stably stored within the device for use at the desired time. In particular, EFCs suffer from very low operational and shelf-life stability because the enzymes tend to become denatured and deactivated over time [151]. Although we can minimize the most critical issue of EFC, the low operational stability, by limiting its applications to single-use operation for a short time, achieving long-term, stable storage of the enzymes remains challenging. While emerging immobilization techniques have demonstrated prolonged enzymatic activity and stability during EFC operation, the storage conditions of the enzymes can determine the shelf-life [152]. Generally, the enzymes stored in frozen or freeze-dried forms exhibit longer shelf-life stability than the enzymes in solutions [153]. Therefore, EFCs need to be stored in dry or frozen form with an optimized storage condition.
For MFCs, the operational stability can be a less critical issue because biocatalytic enzymes are continuously regenerated from microbial metabolism. However, long-term storage of viable microorganisms has been extremely challenging for miniature MFC applications. Recently, a lyophilization technique has been applied for MFC operation, enabling long-term storage of biocatalytic cells without degradation and denaturation [118,154]. Although the effects of cryoprotectants and storage conditions on microbial shelf-life stability must be further examined, this storage approach will establish an innovative strategy to revolutionize MFC applications for portable on-demand power generation. As an alternative approach, spore-forming microbial species can be used as the MFC biocatalyst [119,123,124,125,126]. Their endospores are extremely stable and storable for quite a long period and can become vegetative cells during germination when environmental conditions become favorable. The spore-forming MFCs can offer long-term shelf-life stability and on-demand power generation with nutrient introduction.
4.3. Disposability
Generally, biobatteries are disposable because the catalysts are biodegradable. However, the other components must be disposable and biodegradable. Many paper-based biobatteries have been proposed as a low-cost, eco-friendly, and disposable power source for immediate single-use applications [32,119]. In particular, MFCs must be disposed of after use to prevent potential carry-over contamination and infection originating from the microorganisms.
4.4. Microfabricability
Next-generation self-powered electronics and sensors are expected to have closely integrated biobatteries as on-board energy harvesters for WSN applications. Those stand-alone systems will require a direct integration of miniaturized biobatteries through microfabrication. Although microfabricated EFCs and MFCs have previously been demonstrated [137,155], their aquatic components need to be replaced with solid-phase counterparts to make them more suitable for miniaturization, integration, and operation with solid-state electronics and sensors [156,157].
5. Conclusions
Since the first demonstration of conceptual MFCs in 1911 and EFCs in 1964, biofuel cells have received much research interest as an innovative energy-producing technique, and their miniaturized formats as biobatteries have been revolutionized as an energy harvesting technique self-sustainably working with the human body and our environment. Despite successful innovations and creative application proposals, biofuel cells and biobatteries have been limited to the status of laboratory curiosity without any commercial success. The main reason is that, traditionally, research has been done by individuals and research groups, and this fragmented approach supports an unbalanced and misleading view of biofuel cells, which lends itself more to science fiction than immediate solutions. In this report, the blind alleys that have long prevented their practical development have been identified and corrected. Although several technological obstacles need to be overcome, we can revisit the most practical and potential applications of biofuel cells that can be realized in the near future. There will be potential applications for EFCs ranging from wearable and portable EFCs, especially for single-use and disposable operation, to self-powered EFC-based biosensors for point-of-care testing. MFCs will find more practical applications in their miniaturized format with pre-inoculated, selected microorganisms. Self-powered MFC-based biosensors for water quality monitoring and antibiotic susceptibility testing will also have real potential.
Funding
This work was supported by the Office of Naval Research (#N00014-21-1-2412), and the National Science Foundation (CBET #2100757, ECCS #2020486, and ECCS #1920979).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Orji, N.G.; Badaroglu, M.; Barnes, B.M.; Beitia, C.; Bunday, B.D.; Celano, U.; Kline, R.J.; Neisser, M.; Obeng, Y.; Vladar, A.E. Me-trology for the next generation of semiconductor devices. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 532–547. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, S.; Karahan, H.E.; Wang, C.; Pei, Z.; Wei, L.; Chen, Y. 1D Supercapacitors for Emerging Electronics: Current Status and Future Directions. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, e1902387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, P.R.; Davis, J.J. Charge transport and energy storage at the molecular scale: From nanoelectronics to electrochemical sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7505–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Hu, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, W.; Huang, Y. The Evolution of Flexible Electronics: From Nature, Beyond Nature, and To Nature. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001116. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Ren, P.; Song, R.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Dong, J.; O’Connor, B.T.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-Enabled Flexible and Stretchable Sensing Systems: Processing, Integration, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Kong, M.; Jeong, U. Interface Design for Stretchable Electronic Devices. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, K. Electronic skin: From flexibility to a sense of touch. Nature 2021, 591, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. Skin Electronics: Next-Generation Device Platform for Virtual and Augmented Reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuslem, A.S.; Shaikh, S.F.; Hussain, M.M. Flexible and Stretchable Electronics for Harsh-Environmental Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pharr, M.; Salvatore, G.A. Lab-on-Skin: A Review of Flexible and Stretchable Electronics for Wearable Health Moni-toring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9614–9635. [Google Scholar]
- Gummeson, J. A body area power network. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.L.; Fukuda, K.; Someya, T. Flexible self-charging power sources. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 870–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Entropy theory of distributed energy for internet of things. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Self-charging power system for distributed energy: Beyond the energy storage unit. Chem. Sci. 2020, 12, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Kim, K.N.; Trifonov, A.; Podhajny, T.; Wang, J. Designing wearable microgrids: Towards autonomous sustainable on-body energy management. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 15, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xuan, J.; Leung, D.Y. Powering future body sensor network systems: A review of power sources. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Choi, J.; Ko, S.H. Energy Harvesting Untethered Soft Electronic Devices. Adv. Health Mater. 2021, 10, e2002286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, X.; Lian, S.W.M.; Ying, Y.; Ho, J.S.; Ping, J. Wireless Technologies for Energy Harvesting and Transmission for Ambient Self-Powered Systems. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9328–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallem, V.; Sargolzaeiaval, Y.; Ozturk, M.; Lai, Y.; Dickey, M.D. Energy Harvesting and Storage with Soft and Stretchable Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadad, A.; Liu, L.; Choi, S. Plug-and-play modular biobatteries with microbial consortia. J. Power Sources 2022, 535, 231487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xia, X.; Mai, W.; Tu, J.; Fan, H.J. Integration of Energy Harvesting and Electrochemical Storage Devices. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeerapan, I.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Wang, J. On-Body Bioelectronics: Wearable Biofuel Cells for Bioenergy Harvesting and Self-Powered Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1906243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kjøniksen, A.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. Wearable Biofuel Cells: Advances from Fabrication to Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-E.; Gai, P.; Song, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.-J. Nanostructured material-based biofuel cells: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sencadas, V.; You, S.S.; Jia, N.Z.; Srinivasan, S.S.; Huang, H.; Ahmed, A.E.; Liang, J.Y.; Traverso, G. Powering Im-plantable and Ingestible Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009289. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S. Electrogenic Bacteria Promise New Opportunities for Powering, Sensing, and Synthesizing. Small 2022, 18, 2107902. [Google Scholar]
- Catania, C.; Karbelkar, A.A.; Furst, A.L. Engineering the interface between electroactive bacteria and electrodes. Joule 2021, 5, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Rossi, R.; Ragab, A.; Saikaly, P.E. Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 17, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Simoska, O.; Lim, K.; Grattieri, M.; Yuan, M.; Dong, F.; Lee, Y.S.; Beaver, K.; Weliwatte, S.; Gaffney, E.M.; et al. Fundamentals, Applications, and Future Directions of Bioelectrocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 12903–12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xia, H.-Q.; Wu, R.; Bai, L.; Yan, L.; Magner, E.; Cosnier, S.; Lojou, E.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, A. Tackling the Challenges of Enzymatic (Bio)Fuel Cells. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9509–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Brodd, R.J. What Are Batteries, Fuel Cells, and Supercapacitors? Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4245–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Mohammadifar, M.; Choi, S. From microbial fuel cells to Biobatteries: Moving toward on-demand micro-power gen-eration for Small-scale Single-Use Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1970039. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, S.; Mizuno, T.; Kusama, S.; Sato, K.; Raut, B.; Nishizawa, M. Series-Connected Flexible Biobatteries for Higher Voltage Electrical Skin Patches. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 2, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahidhara, G.; Chintalapati, V.R. Eco-physiological and interdisciplinary approaches for empowering biobatteries. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 66, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiem, V.N.; Minteer, S.D. Investigating DNA hydrogels as a new biomaterial for enzyme immobilization in biobatteries. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13071–13073. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.-H.P. Coenzyme Engineering of a Hyperthermophilic 6-Phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase from NADP+ to NAD+ with Its Application to Biobatteries. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehlenbrock, M.J.; Minteer, S.D. Extended lifetime biofuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; Bollella, P. Fuel Cells and Biofuel Cells: From Past to Perspectives. Isr. J. Chem. 2020, 61, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.J.; Holzinger, M.; Cosnier, S. Buckypaper bioelectrodes: Emerging materials for implantable and wearable biofuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1670–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halámková, L.; Halámek, J.; Bocharova, V.; Szczupak, A.; Alfonta, L.; Katz, E. Implanted Biofuel Cell Operating in a Living Snail. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5040–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, E.; MacVittie, K. Implanted biofuel cells operating in vivo—Methods, applications and perspectives—Feature article. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2791. [Google Scholar]
- Mano, N.; Mao, F.; Heller, A. Characteristics of a miniature compartment-less Glucose−O2 biofuel cell and its operation in a living plant. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6588–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacVittie, K.; Halámek, J.; Halámková, L.; Southcott, M.; Jemison, W.D.; Lobel, R.; Katz, E. From “cyborg” lobsters to a pace-maker powered by implantable biofuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mano, N.; Mao, F.; Heller, A. A Miniature Biofuel Cell Operating in A Physiological Buffer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12962–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazar, F.M.; Martinez, J.G.; Tyagi, M.; Alijanianzadeh, M.; Turner, A.P.F.; Jager, E.W.H. Artificial Muscles Powered by Glucose. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1901677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; You, S.; Gong, X.; Qi, D.; Chandran, B.K.; Bi, L.; Cui, F.; Chen, X. Bioinspired Nanosucker Array for Enhancing Bioe-lectricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Ma, M.; Wang, W.; Qi, D.; Chen, X.; Qu, J.; Ren, N. 3D Macroporous Nitrogen-Enriched Graphitic Carbon Scaffold for Efficient Bioelectricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 7, 1601364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, L.; Shiu, H.-Y.; Ding, M.; Song, F.; Guan, X.; Lee, C.K.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.; et al. Silver nanoparticles boost charge-extraction efficiency in Shewanella microbial fuel cells. Science 2021, 373, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.U.; Duteanu, N.; Ciocan, S.; Nasar, A. Inamuddin A review: Evolution of enzymatic biofuel cells. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yu, C.; Liu, H. A microbial fuel cell as power supply for implantable medical devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2156–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Jia, B.; Yu, C.; Dong, W.; Du, F.; Liu, H. Microbial fuel cell as power supply for implantable medical devices: A novel configuration design for simulating colonic environment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wen, D.; Bai, L.; Lou, B.; Dong, S. Small-size biofuel cell on paper. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, C.; Nedellec, Y.; Gross, A.J.; Ondel, O.; Buret, F.; Le Goff, A.; Holzinger, M.; Cosnier, S. Assembly and Stacking of Flow-through Enzymatic Bioelectrodes for High Power Glucose Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23836–23842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraiwan, A.; Kwan, L.; Choi, S. A disposable power source in resource-limited environments: A paper-based biobattery generating electricity from wastewater. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraiwan, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sundermier, S.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, S. A paper-based microbial fuel cell: Instant battery for disposable diagnostic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattieri, M.; Minteer, S.D. Self-powered biosensors. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, R.C.; Mahbub, I. Wearable self-powered biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, J.; Dong, S. Recent development of biofuel cell based self-powered biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.; Ay, S.U.; Karim, M.N.; Beyenal, H. Alternative power sources for remote sensors: A review. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Choi, S. Miniature microbial solar cells to power wireless sensor networks. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.J.; Bombelli, P. Electricity Production by Photosynthetic Microorganisms. Joule 2020, 4, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, U. Discover the possibilities: Microbial bioelectrochemical systems and the revival of a 100-year–old discovery. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.B.A.; Verstrete, W. 100 years of microbial electricity production: Three concepts for the future. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosnier, S.; Gross, A.J.; Giroud, F.; Holzinger, M. Beyond the hype surrounding biofuel cells: What’s the future of enzymatic fuel cells. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 12, 148–155. [Google Scholar]
- Gamella, M.; Koushanpour, A.; Katz, E. Biofuel cells—Activation of micro- and macro-electronic devices. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 119, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, A.; Perveen, R. Applications of enzymatic biofuel cells in bioelectronic devices—A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 15287–15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechederra, R.; Minteer, S.D. Organelle-based biofuel cells: Immobilized mitochondria on carbon paper electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6698–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerster, D.; Reichert, J.; Bi, H.; Barth, J.; Kaniber, S.M.; Holleitner, A.W.; Visoly-Fisher, I.; Sergani, S.; Carmeli, I. Photocurrent of a single photosynthetic protein. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehezkeli, O.; Tel-Vered, R.; Wasserman, J.; Trifonov, A.; Michaeli, D.; Nechushtai, R.; Willner, I. Integrated photosystem II-based photo-bioelectrochemical cells. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.; Abdellaoui, S.; Minteer, S.D. Enzymatic biofuel cells: 30 years of critical advancements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S. Microorganisms in sediment microbial fuel cells: Ecological niche, microbial response, and environmental function. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144145. [Google Scholar]
- Kluger, J. (Ed.) The 50 Best Inventions of 2009. Available online: http://content.time.com/time/specials/packages/article/0,28804,1934027_1934003_1933965,00.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Logan, B.E. Scaling up microbial fuel cells and other bioelectrochemical systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borole, A.P.; Reguera, G.; Ringeisen, B.; Wang, Z.-W.; Feng, Y.; Kim, B.H. Electroactive biofilms: Current status and future research needs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4813–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Simões, M.; Melo, L.; Pinto, A. Overview on the developments of microbial fuel cells. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 73, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Harnisch, F. Is there a Specific Ecological Niche for Electroactive Microorganisms? Chemelectrochem 2016, 3, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahernia, M.; Mohammadifar, M.; Gao, Y.; Panmanee, W.; Hassett, D.J.; Choi, S. A 96-well high-throughput, rapid-screening platform of extracellular electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 162, 112259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.E.; Marsili, E. Weak electricigens: A new avenue for bioelectrochemical research. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahernia, M.; Plotkin-Kaye, E.; Mohammadifar, M.; Gao, Y.; Oefelein, M.R.; Cook, L.C.; Choi, S. Characterization of Electrogenic Gut Bacteria. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 29439–29446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, S.H.; Su, L.; Rivera-Lugo, R.; Cornejo, J.A.; Louie, A.; Iavarone, A.T.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M.; Portnoy, D.A. A flavin-based extracellular electron transfer mechanism in diverse Gram-positive bacteria. Nature 2018, 562, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.U.; Yasir, M.; Cosnier, S. Recent advancements in the field of flexible/wearable enzyme fuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 214, 114545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Lee, I.; Blaauw, D.; Katz, E. A Microelectronic Sensor Device Powered by a Small Implantable Biofuel Cell. ChemPhysChem 2019, 21, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebda, A.; Alcaraz, J.-P.; Vadgama, P.; Shleev, S.; Minteer, S.D.; Boucher, F.; Cinquin, P.; Martin, D.K. Challenges for successful implantation of biofuel cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 124, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, S.C.; Gallaway, J.; Atanassov, P. Enzymatic Biofuel Cells for Implantable and Microscale Devices. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4867–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.H.; Scott, K. Enzymatic fuel cells—Fabrication of enzyme electrodes. Energies 2010, 3, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J. Review-Wearable biofuel cells: Past, present, and future. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, H3007. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Wang, X.; Imani, S.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Ramírez, J.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Wearable textile biofuel cells for powering electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18184–18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; You, J.-M.; Kim, N.-H.; Gu, Y.; Kumar, R.; Mohan, A.M.V.; Kurniawan, J.; Imani, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Parish, B.; et al. Soft, stretchable, high power density electronic skin-based biofuel cells for scavenging energy from human sweat. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Tehrani, F.; Yin, L.; Silva-Lopez, C.A.; Jang, J.-H.; Joshuia, D.; Shah, R.; Liang, Y.; Xie, L.; et al. Sweat-based wearable energy harvesting-storage hybrid textile devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kim, J.; Walter, J.R.; Ghaffari, R.; Rogers, J.A. Translational gaps and opportunities for medical wearables in digital health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Yin, L.; Nathan, A.; Wang, J.; Dahiya, R. Energy Autonomous Sweat-Based Wearable Systems. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonner, Z.; Wilder, E.; Gaillard, T.; Kasting, G.; Heikenfeld, J. Integrated sudomotor axon reflex sweat stimulation for continuous sweat analyte analysis with individuals at rest. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Ghaffari, R.; Baker, L.B.; Rogers, J.A. Skin-interfaced systems for sweat collection and analysis. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar3921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Killard, A.J. Disposable sensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Fernandez-Abedul, M.T.; Merkoci, A.; Manz, A.; Urban, G.A.; Guder, F. Disposable sensors in diagnostics, food, and environmental monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ReportLiner. Disposable Medical Device Sensor Market Research Report: Global Forecast to 2025. January 2021. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2021/01/22/2162900/0/en/Disposable-Medical-Device-Sensor-Market-Research-Report-by-Placement-of-Sensors-by-Product-by-Application-Global-Forecast-to-2025-Cumulative-Impact-of-COVID-19.html (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Thakur, A.; Devi, P. Paper-based flexible devices for energy harvesting, conversion and storage applications: A review. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106927. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Fraiwan, A.; Choi, S. Paper-based batteries: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.; Goswami, S.; Marques, A.; Gaspar, D.; Grey, P.; Cunha, I.; Nunes, D.; Pimentel, A.; Igreja, R.; Barquinha, P.; et al. Cellulose: A Contribution for the Zero e-Waste Challenge. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Advances in paper-based point-of-care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Su, B.S.Q.; Song, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. Enzymatic Biofuel Cell: Opportunities and Intrinsic Challenges in Fu-turistic Applications. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2100031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Huang, K.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X.M. Enzyme-based biofuel cells for biosensors and in vivo power supply. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Gai, P.; Li, F. Construction of biofuel cells-based self-powered biosensors via design of nanocatalytic system. Nano Energy 2021, 93, 106806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; De Wael, K. Wearable Self-Powered Electrochemical Devices for Continuous Health Management. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Fraiwan, A.; Choi, S. A 3D paper-based enzymatic fuel cell for self-powered, low-cost glucose monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; McGourty, K.D.; Magner, E. Enzymatic biofuel cells for self-powered, controlled drug release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11602–11609. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Shao, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.-R.; Song, R.-B.; Zhu, J.-J. A glucose/O2 fuel cell-based self-powered biosensor for probing a drug delivery model with self-diagnosis and self-evaluation. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8482–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovely, D.R. Electromicrobiology. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 391–409. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, F.; Morse, D.E. Miniaturizing microbial fuel cells. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S. Microscale microbial fuel cells: Advances and challenges. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Baum, M.; Gu, Q.; Morse, D.E. A 1.5 uL microbial fuel cell for on-chip bioelectricity generation. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3076–3081. [Google Scholar]
- Han, A.; Hou, H.; Li, L.; Kim, H.S.; de Figueiredo, P. Microfabricated Devices in Microbial Bioenergy. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Lee, H.-S.; Yang, Y.; Parameswaran, P.; Torres, C.I.; Rittmann, B.E.; Chae, J. A μL-scale Micromachined Microbial Fuel Cell Having High Power Density. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabey, D.; Peeling, R.W.; Ustianowski, A.; Perkins, M.D. Diagnostics for the developing world. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, S. An origami paper-based bacteria-powered battery. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, K.J.; Boeras, D.I.; Chen, X.; Ramsay, A.R.; Peeling, R.W. REASSURED diagnostics to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems and improve patient outcomes. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraiwan, A.; Choi, S. Bacteria-Powered Battery on Paper. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 26288–26293. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Choi, S. A Papertronics, On-demand and Disposable Biobattery: Saliva-activated Electricity Generation from Lyophilized Exoelectrogens pre-inoculated on Paper. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, M.; Choi, S. Small-scale, storable paper biobatteries activated via human bodily fluids. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.H.; Shah, A.A.; Walsh, F.C. Recent progress and continuing challenges in bio-fuel cells. Part I: Enzymatic cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3087–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, M.H.; Shah, A.A.; Walsh, F.C. Recent progress and continuing challenges in bio-fuel cells. Part II: Microbial cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Tahernia, M.; Yang, J.H.; Koh, A.; Choi, S. Biopower-on-Skin: Electricity generation from sweat-eating bacteria for self-powered E-Skins. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Choi, S. Bioelectricity production from sweat-activated germination of bacterial endospores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Landers, M.; Choi, S. A sweat-activated, wearable microbial fuel cell for long-term, on-demand power generation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 205, 114128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaie, M.; Rafiee, Z.; Choi, S. A Biobattery Capsule for Ingestible Electronics in the Small Intestine: Biopower Production from Intestinal Fluids Activated Germination of Exoelectrogenic Bacterial Endospores. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 13, 2202581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Rezaie, M.; Choi, S. A Wearable, Disposable Paper-based Self-Charging Power System Integrating Sweat-driven Mi-crobial Energy Harvesting and Energy Storage Devices. Nano Energy 2022, 104, 107923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Lin, L.; Snyder, R.L.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered System with Wireless Data Transmission. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Rüdiger, C.; Yuce, M.R. Real-Time Performance of a Self-Powered Environmental IoT Sensor Network System. Sensors 2017, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.J.; Bombelli, P.; Bradley, R.W.; Thorne, R.; Wenzel, T.; Howe, C.J. Biophotovoltaics: Oxygenic photosynthetic organisms in the world of bioelectrochemical systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1092–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Mohammadifar, M.; Elhadad, A.; Tahernia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Choi, S. Spatial Engineering of Microbial Consor-tium for Long-lasting, Self-sustaining, and High-power Generation in a Bacteria-powered Biobattery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100713. [Google Scholar]
- Elhadad, A.; Choi, S. Biofabrication and characterization of multispecies electroactive biofilms in stratified paper-based scaffolds. Analyst 2022, 147, 4082–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, J.; Ezugwu, C.I.; Ghosh, P.C. Microbial Fuel Cell-Based Biological Oxygen Demand Sensors for Monitoring Wastewater: State-of-the-Art and Practical Applications. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2297–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.; Naik, S.; Jujjavarappu, S.E. A critical review on early-warning electrochemical system on microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for on-site water quality monitoring. Chemosphere 2021, 291, 133098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olias, L.G.; Di Lorenzo, M. Microbial fuel cells for in-field water quality monitoring. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16307–16317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Ryu, J.; Choi, S. A portable, disposable, paper-based microbial fuel cell sensor utilizing freeze-dried bacteria for in-situ water quality monitoring. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13940–13947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chouler, J.; Cruz-Izquierdo, Á.; Rengaraj, S.; Scott, J.L.; Di Lorenzo, M. A screen-printed paper microbial fuel cell biosensor for detection of toxic compounds in water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila, D.; Esquivel, J.; Sabaté, N.; Mas, J. Silicon-based microfabricated microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Choi, S. A Portable, Single-Use, Paper-Based Microbial Fuel Cell Sensor for Rapid, On-Site Water Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2019, 19, 5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Xuejian, W.; Choi, S. A Dual-channel, Interface-free, Bacteria-based Biosensor for Highly-Sensitive Water Quality Monitoring. IEEE Sens. 2016, 16, 8672–8677. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Ryu, J.; Liu, L.; Choi, S. A simple, inexpensive, and rapid method to assess antibiotic effectiveness against exoelectro-genic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168, 112518. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee, Z.; Rezaie, M.; Choi, S. Accelerated antibiotic susceptibility testing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by monitoring extra-cellular electron transfer on a 3-D paper-based cell culture platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 216, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbits, G.; Mohamed, A.; Call, D.R.; Beyenal, H. Rapid differentiation of antibiotic-susceptible and -resistant bacteria through mediated extracellular electron transfer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 197, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, P.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, X. Enzymatic biofuel cells based on protein engineering: Recent advances and future prospects. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5230–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TerAvest, M.A.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Transforming exoelectrogens for biotechnology using synthetic biology. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 113, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, D.T.; Gabrielsson, E.O.; Tybrandt, K.; Berggren, M. Organic Bioelectronics: Bridging the Signaling Gap between Biology and Technology. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 13009–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prominski, A.; Tian, B. Bridging the gap—Biomimetic design of bioelectronic interfaces. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 72, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankratova, G.; Bollella, P.; Pankratov, D.; Gorton, L. Gorton. Supercapacitive biofuel cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Choi, S. A self-charging cyanobacterial supercapacitor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 140, 111354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnès, C.; Holzinger, M.; Le Goff, A.; Reuillard, B.; Elouarzaki, K.; Tingry, S.; Cosnier, S. Supercapacitor/biofuel cell hybrids based on wired enzymes on carbon nanotube matrices: Autonomous reloading after high power pulses in neutral buffered glucose solutions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1884–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Choi, S. PEDOT:PSS/MnO2/CNT Ternary Nanocomposite Anodes for Supercapacitive Energy Storage in Cyanobac-terial Biophotovoltaics. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaufils, C.; Man, H.-M.; de Poulpiquet, A.; Mazurenko, I.; Lojou, E. From Enzyme Stability to Enzymatic Bioelectrode Stabilization Processes. Catalysts 2021, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchitta, G.; Spanu, A.; Babudieri, S.; Latte, G.; Madeddu, G.; Galleri, G.; Nuvoli, S.; Bagella, P.; Demartis, M.I.; Fiore, V.; et al. Enzyme Biosensors for Biomedical Applications: Strategies for Safeguarding Analytical Performances in Biological Fluids. Sensors 2016, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, V.; Atanassov, P. Enzymatic Fuel Cell Design, Operation, and Application. Chapter 16 in Enzymatic Fuel Cells; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Choi, S. Merging Electric Bacteria with Paper. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, A.G.; Suraniti, E.; Roche, J.; Richter, H.; Kuhn, A.; Mano, N.; Fischer, P. On-chip enzymatic microbiofuel cell-powered integrated circuits. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Choi, S. A Solid Phase Bacteria-Powered Biobattery for Low-Power, Low-Cost, Internet of Disposable Things. J. Power Sources 2019, 429, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Tahernia, M.; Choi, S. A miniaturized, self-sustaining, and integrable bio-solar power system. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).