Critical Analysis of Simulation of Misalignment in Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
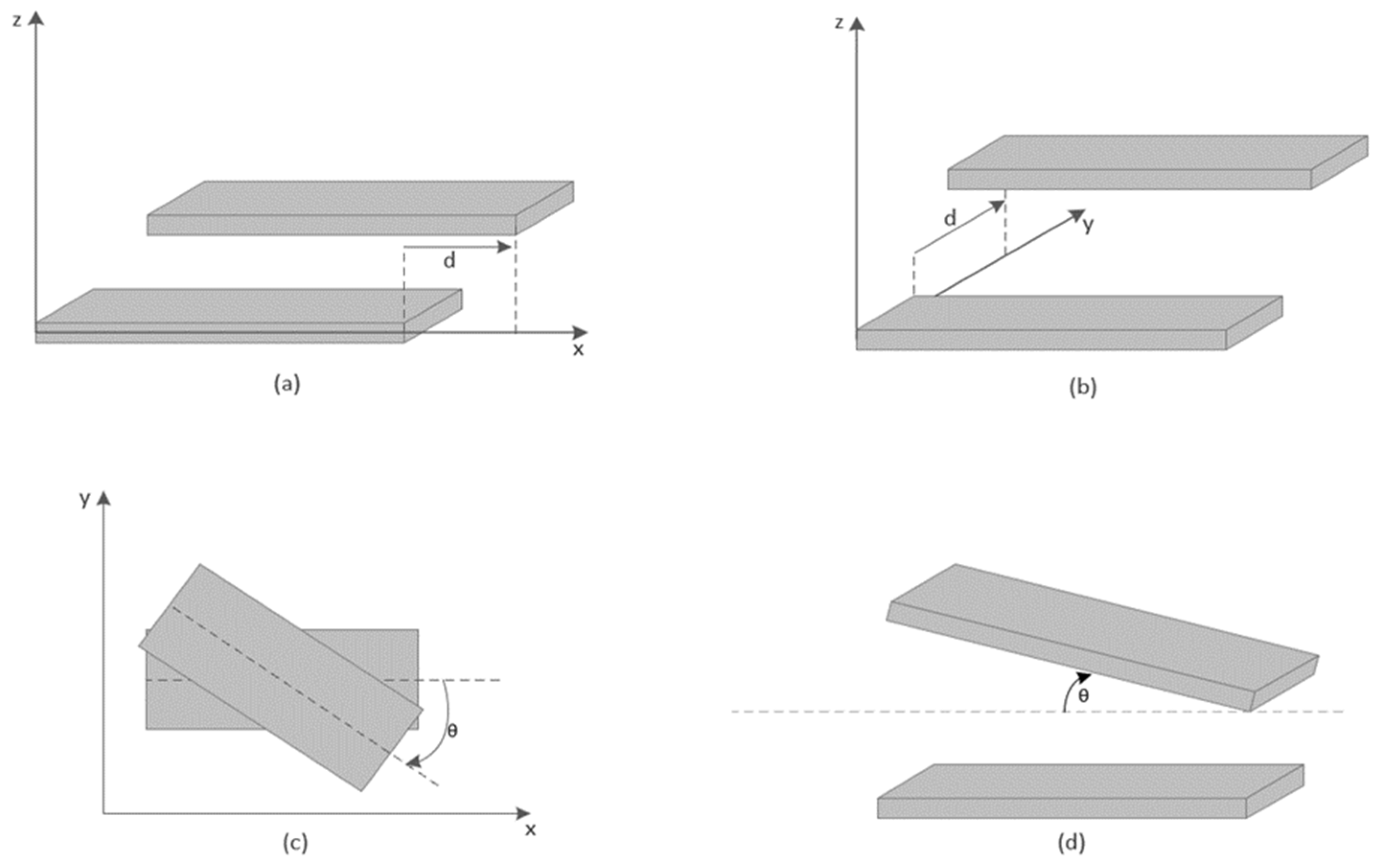
2. Classification of Different Types of Misalignments
- (1)
- Translational misalignment;
- (2)
- Angular and rotational misalignment.
3. The Effect of Coupler Structure on the Efficiency of a WPT System
3.1. Circular Coils
3.2. Rectangular Coils
3.3. Comparative Analysis
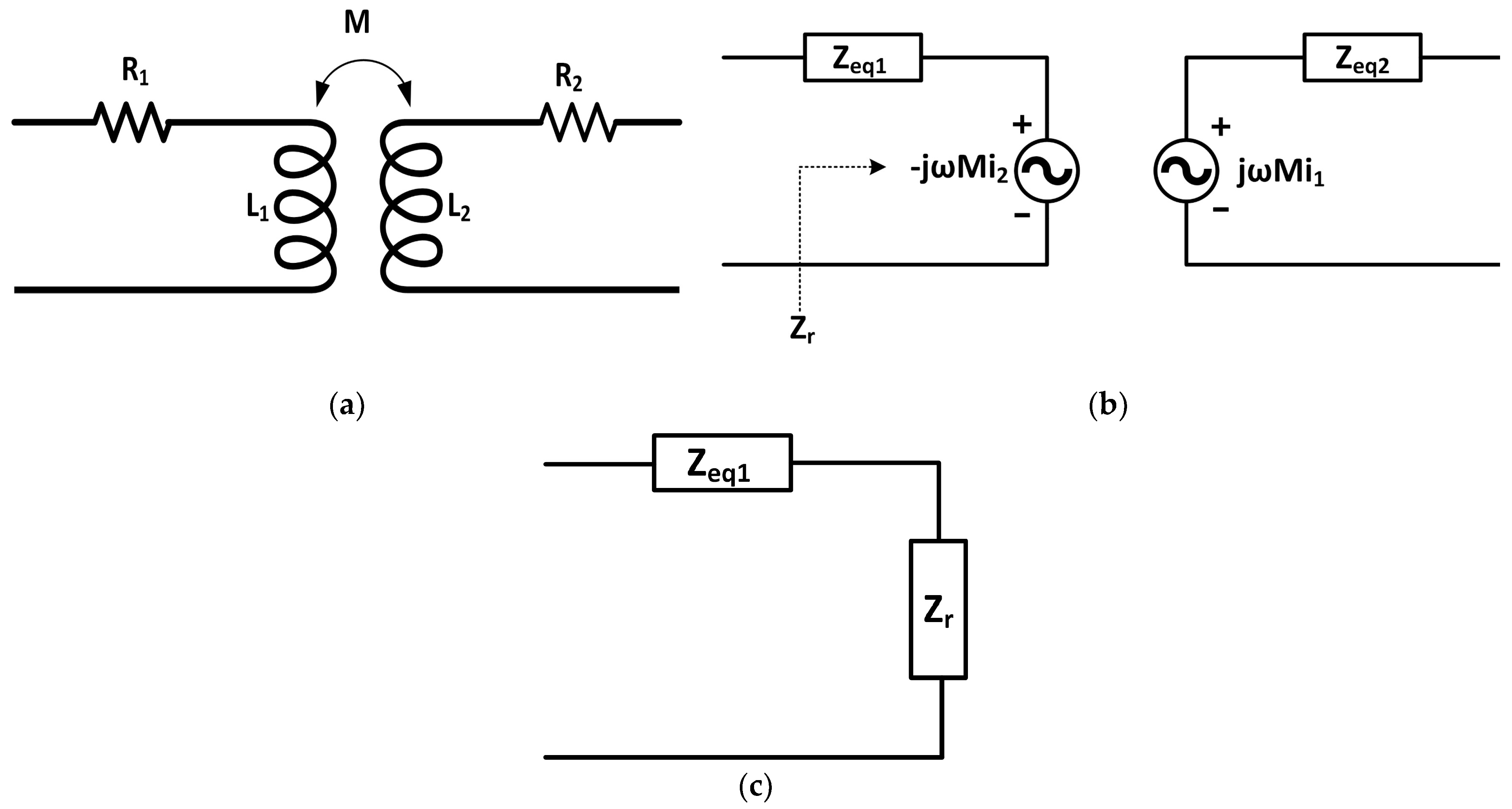
4. Impact of Compensation Topology on System Performance
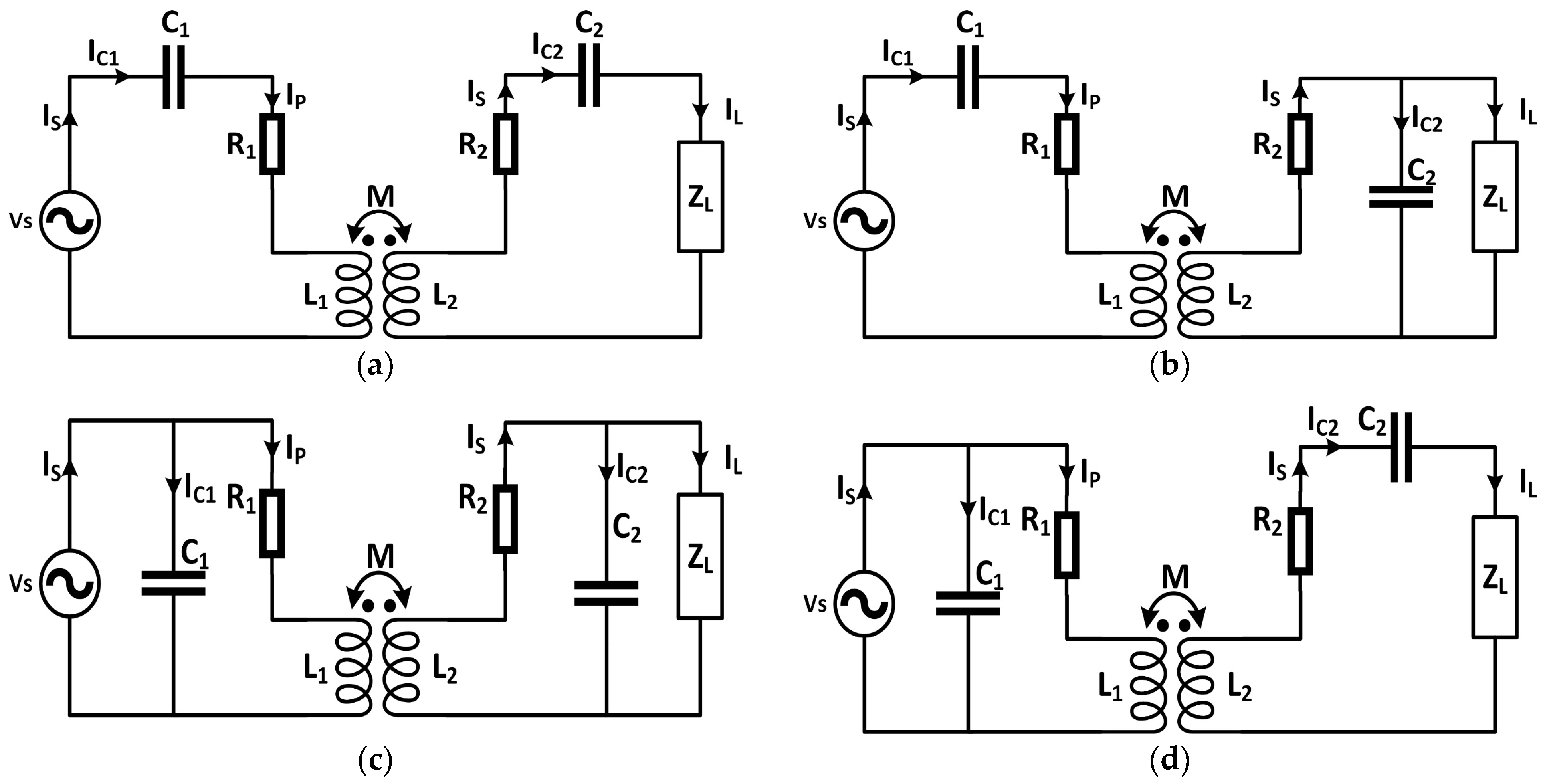
4.1. S–S (Series–Series)
4.2. S–P (Series–Parallel)
4.3. P–P (Parallel–Parallel)
4.4. P–S (Parallel–Series)
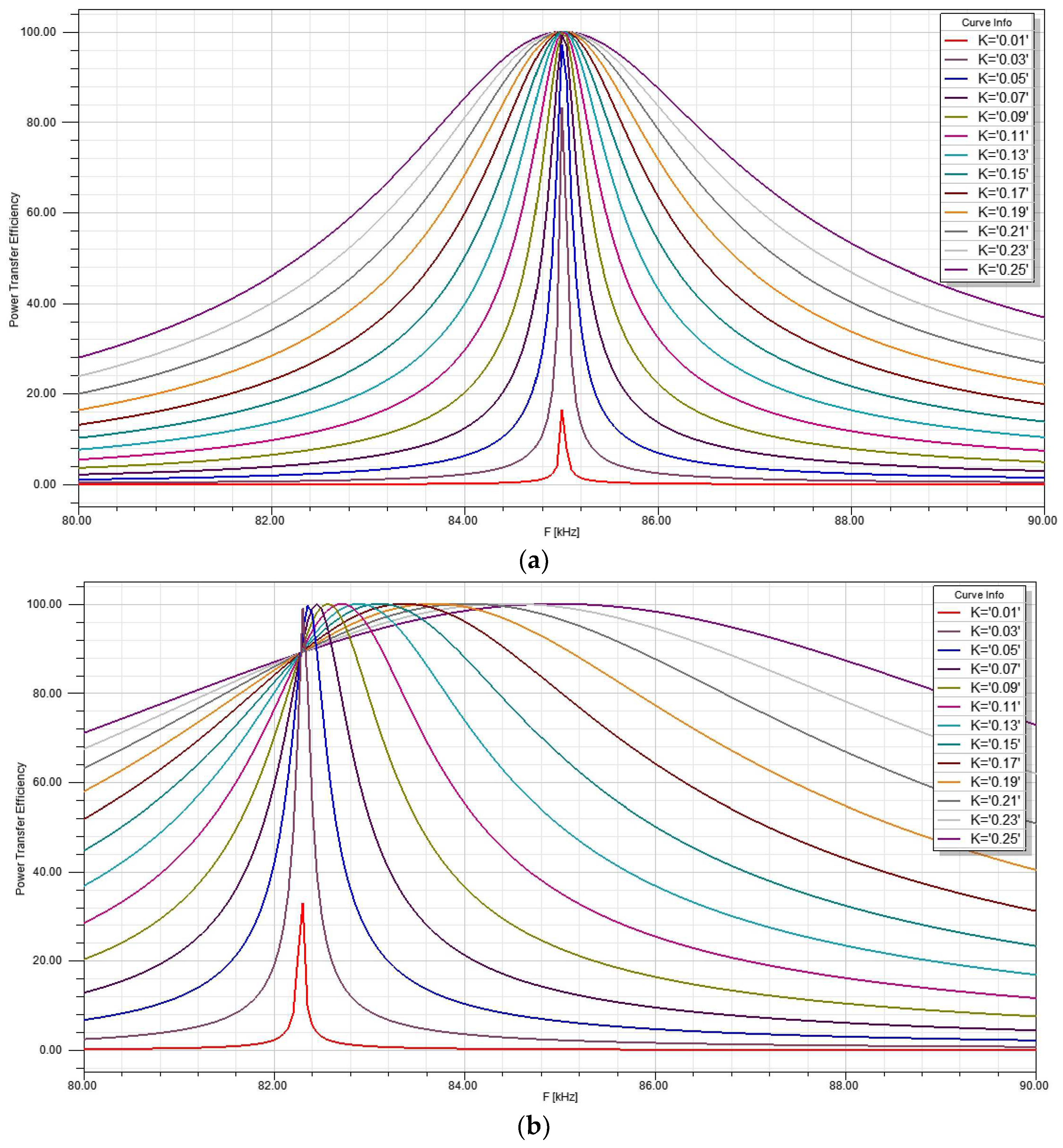
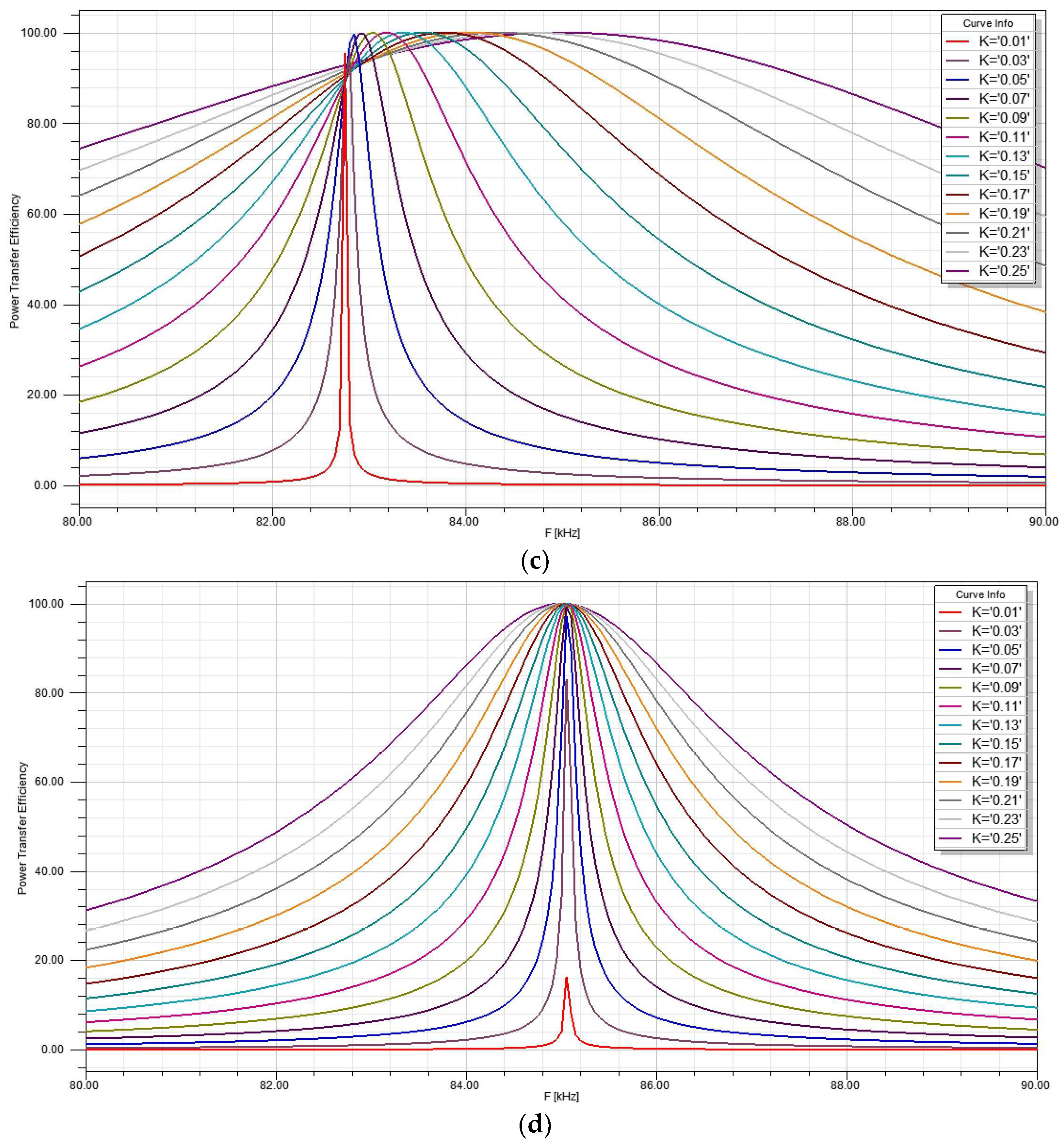
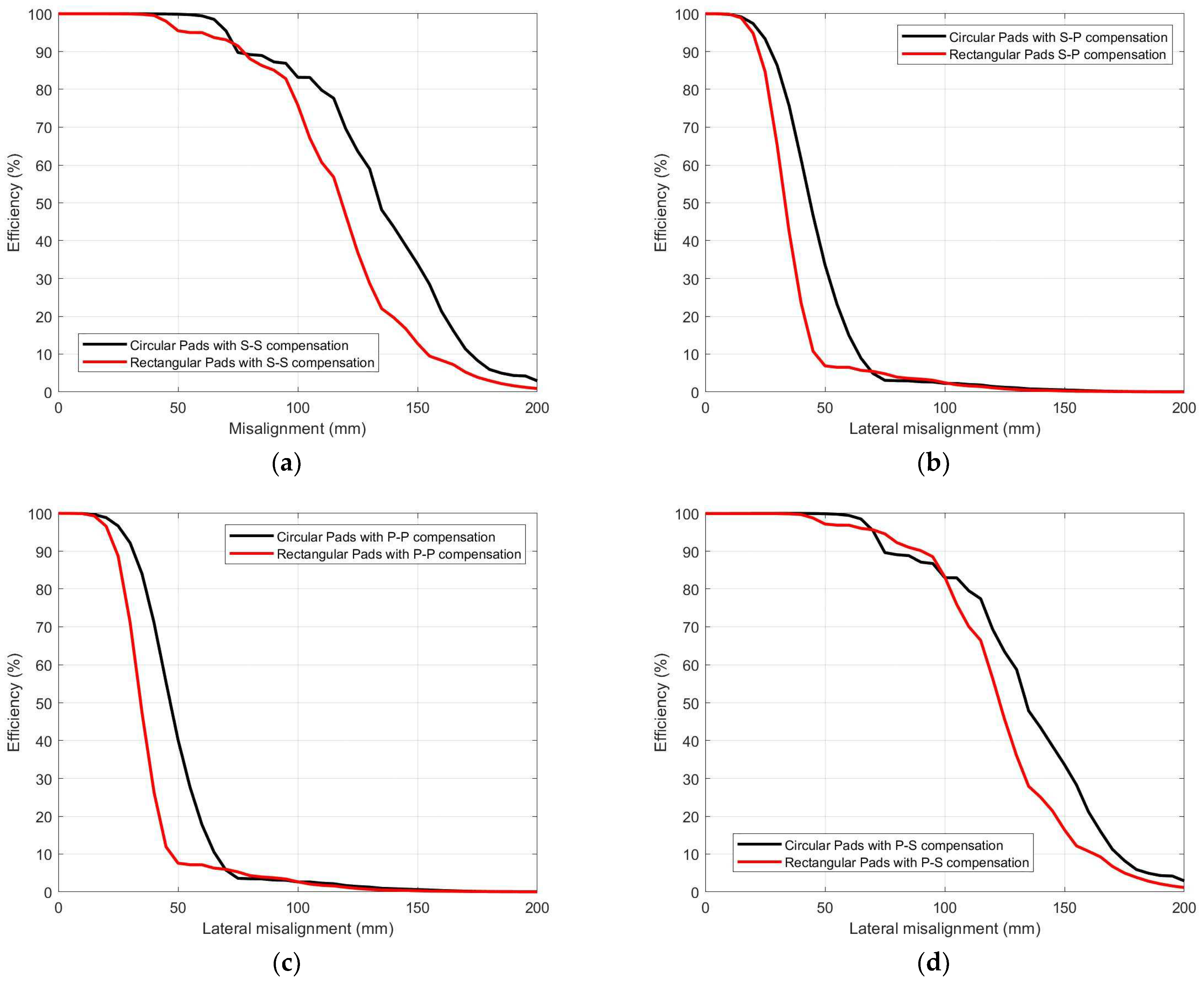
4.5. Comparative Analysis
5. Limitations and Future Trends
- A reconfigurable arrangement of coil design that can switch different arrangements of coils to offer high coupling coefficients between EVs and chargers for each misalignment condition;
- Instead of using communication between the EV and the charging circuit, a new control using system parameters whose changes reflect misalignment between the charging coils, e.g., mutual inductance deviations, should be a candidate for future research;
- Current studies on the thermal failure of the ferrite core employed in coil construction are inadequate, making it difficult to draw any firm conclusions;
- Although dynamic wireless charging is a promising solution to the challenges of EVs, there are limited studies considering misalignment with this type of EV charging.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fachrizal, R.; Shepero, M.; van der Meer, D.; Munkhammar, J.; Widén, J. Smart charging of electric vehicles considering photovoltaic power production and electricity consumption: A review. eTransportation 2020, 4, 100056. [Google Scholar]
- Madani, S.S.; Soghrati, R.; Ziebert, C. A Regression-Based Technique for Capacity Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2022, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovet, S.; Farley, B.; Perry, J.; Kirsche, K.; Jerue, M.; Tse, Z.T.H. Introduction of electric vehicle charging stations to university campuses: A case study for the university of Georgia from 2014 to 2017. Batteries 2018, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.S.H.; Mamun, A.A.; Ansari, S.; Miah, M.S.; Hasan, K.; Meraj, S.T.; Abdolrasol, M.G.; Rahman, T.; Maruf, M.H.; Sarker, M.R. Battery Management, Key Technologies, Methods, Issues, and Future Trends of Electric Vehicles: A Pathway toward Achieving Sustainable Development Goals. Batteries 2022, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandoman, F.H.; El-Shahat, A.; Alaas, Z.M.; Ali, Z.M.; Berecibar, M.; Abdel Aleem, S.H. Understanding Voltage Behavior of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles Applications. Batteries 2022, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Alam, M.S.; Rafat, Y.; Shariff, S. Designing and demonstration of misalignment reduction for wireless charging of autonomous electric vehicle. eTransportation 2020, 4, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, S.; Vaez-Zadeh, S.; Isfahani, A.H. Optimization of a contactless power transfer system for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3566–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Deng, J.; Kan, T.; Mi, C.C. Integrated LCC compensation topology for wireless charger in electric and plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K.; Hu, A.P.; Mi, C.C. A misalignment-tolerant series-hybrid wireless EV charging system with integrated magnetics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Mcdonough, M.K.; Miller, J.M.; Fahimi, B.; Balsara, P.T. Wireless power transfer for vehicular applications: Overview and challenges. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 4, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Harada, K.; Washimiya, S.; Takehara, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Nakao, F. Large air-gap coupler for inductive charger [for electric vehicles]. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 3526–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.G.; Egan, M.G.; Murphy, J.M.; Schulz, S.E.; Hall, J.T. Wide-load-range resonant converter supplying the SAE J-1773 electric vehicle inductive charging interface. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1999, 35, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severns, R.; Yeow, E.; Woody, G.; Hall, J.; Hayes, J. An Ultra-Compact Transformer for a 100 W to 120 kW Inductive Coupler for Electric Vehicle Battery Charging. In Proceedings of the Applied Power Electronics Conference, APEC’96, San Jose, CA, USA, 3–7 March 1996; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Klontz, K.W.; Divan, D.M.; Novotny, D.W. An actively cooled 120 kW coaxial winding transformer for fast charging electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klontz, K.; Esser, A.; Bacon, R.; Divan, D.; Novotny, D.; Lorenz, R. An electric vehicle charging system with’universal’inductive interface. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Power Conversion Conference-Yokohama 1993, Yokohama, Japan, 19–21 April 1993; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Modern trends in inductive power transfer for transportation applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proceedings of the IECON ‘97: 23rd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control, and Instrumentation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 1997; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA.
- Kushwaha, B.K.; Rituraj, G.; Kumar, P. 3-D analytical model for computation of mutual inductance for different misalignments with shielding in wireless power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwar, K.A.; Aamir, M.; Mekhilef, S. A design method for developing a high misalignment tolerant wireless charging system for electric vehicles. Measurement 2018, 118, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Huh, J.; Lee, W.Y.; Rim, C.T. Asymmetric coil sets for wireless stationary EV chargers with large lateral tolerance by dominant field analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 6406–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadakuduti, J.; Douglas, M.; Lu, L.; Christ, A.; Guckian, P.; Kuster, N. Compliance testing methodology for wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6264–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Ma, H.; Lai, J.-S.; Zhang, L. Design considerations to reduce gap variation and misalignment effects for the inductive power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6108–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Saeedifard, M.; Cai, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Lin, H. A Misalignment Tolerant Design for a Dual-Coupled LCC-S-Compensated WPT System with Load-Independent CC Output. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 7480–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K. Hybrid bidirectional wireless EV charging system tolerant to pad misalignment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7079–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.Y.; Cui, X.; Avestruz, A.-T. Accurate transfer-power measurement for wireless charging of electric vehicles under misalignment. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (Wow), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–7 June 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani, A.; Narimani, M. Optimized electric vehicle wireless chargers with reduced output voltage sensitivity to misalignment. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 8, 3569–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, R.; Shabanian, T.; Dede, E.M.; Chou, C.; Pantic, Z. EV Misalignment Estimation in DWPT Systems Utilizing the Roadside Charging Pads. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, C.; Stegen, S.; Lu, J. Review of static and dynamic wireless electric vehicle charging system. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 922–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pang, H.; Georgiadis, A.; Cecati, C. Wireless power transfer—An overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.L.; Sallan, J.; Osorio, J.F.S.; Llombart, A. High-misalignment tolerant compensation topology for ICPT systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, K.; Flynn, B.W. Wireless power transfer in loosely coupled links: Coil misalignment model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 47, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ginart, A.; Farley, K.B.; Tse, Z.T.H. Misalignment effect on efficiency of wireless power transfer for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3526–3528. [Google Scholar]
- Joy, E.R.; Dalal, A.; Kumar, P. Accurate computation of mutual inductance of two air core square coils with lateral and angular misalignments in a flat planar surface. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Carlson, R.B.; Smart, J.G.; Dufek, E.J.; Liaw, B. Challenges of future high power wireless power transfer for light-duty electric vehicles----technology and risk management. eTransportation 2019, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, N.N.; Yusoff, S.H.; Toha, S.F.; Hasbullah, N.F.; Roszaidie, A.S. A brief review: Basic coil designs for inductive power transfer. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci 2020, 20, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Mosammam, B.M.; Rasekh, N.; Mirsalim, M.; Moghani, J.S. Comparative analysis of the conventional magnetic structure pads for the wireless power transfer applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Power Electronics, Drive Systems and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Shiraz, Iran, 12–14 February 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, M.; Choi, S.; Islam, Z.; Kwak, S.; Baek, J. Core design and optimization for better misalignment tolerance and higher range of wireless charging of PHEV. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Yoshitomi, K.; Pokharel, R.K. Design approach for efficient wireless power transfer systems during lateral misalignment. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 4170–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastri, F.; Costanzo, A.; Mongiardo, M. Coupling-independent wireless power transfer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Wong, S.-C.; Chi, K.T. A model for coupling under coil misalignment for DD pads and circular pads of WPT system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Wireless power transfer for electric vehicle applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 3, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Li, W.; Nguyen, T.D.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Compact and efficient bipolar coupler for wireless power chargers: Design and analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6130–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, F.L.; de Sousa, F.R. Achieving optimal efficiency in energy transfer to a CMOS fully integrated wireless power receiver. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 3703–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Moon, G.-W. Wireless power transfer system with an asymmetric four-coil resonator for electric vehicle battery chargers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 6844–6854. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C.; He, Y. Comparative analysis of two-coil and three-coil structures for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, A.P.; Meyer, D.T.; Smith, J.R. Analysis, experimental results, and range adaptation of magnetically coupled resonators for wireless power transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 58, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, V.; Husev, O.; Strzelecki, R.; Pakhaliuk, B.; Poliakov, N.; Strzelecka, N. Compensation topologies in IPT systems: Standards, requirements, classification, analysis, comparison and application. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120559–120580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, G.A.; Raabe, S.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Multiphase pickups for large lateral tolerance contactless power-transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhia, M.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Design and optimization of circular magnetic structures for lumped inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W.; Mühlethaler, J.; Stevanović, I.; Wunsch, B.; Canales, F. Modeling and η-α-Pareto Optimization of Inductive Power Transfer Coils for Electric Vehicles. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 3, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallán, J.; Villa, J.L.; Llombart, A.; Sanz, J.F. Optimal design of ICPT systems applied to electric vehicle battery charge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Alam, M.S.; Chabaan, R. A comprehensive review of wireless charging technologies for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 4, 38–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Daga, A. Elements of wireless power transfer essential to high power charging of heavy duty vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Dong, J.; Qin, Z.; Bauer, P. Comparison of Optimized Chargepads for Wireless EV Charging Application. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019-ECCE Asia), Busan, Republic of Korea, 27–30 May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Shu, Y. A new analytical calculation of the mutual inductance of the coaxial spiral rectangular coils. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.; Sun, M. Analytical design study of a novel witricity charger with lateral and angular misalignments for efficient wireless energy transmission. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2616–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Iyer, A.; Bharatiraja, C.; Vaghasia, I.; Rajesh, V. Design optimisation for an efficient wireless power transfer system for electric vehicles. Energy Procedia 2017, 117, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, S.D.; Reza, A.W.; Kumar, N.; Karim, M.E.; Munir, A.B. Wireless powering by magnetic resonant coupling: Recent trends in wireless power transfer system and its applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1525–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwar, K.A.; Aamir, M.; Mekhilef, S. Inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) for electric vehicle charging—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H. An overview of resonant circuits for wireless power transfer. Energies 2017, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.H.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lim, G.C.; Cho, G.-H.; Rim, C.T. General unified analyses of two-capacitor inductive power transfer systems: Equivalence of current-source SS and SP compensations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6030–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wei, X. Analysis of square and circular planar spiral coils in wireless power transfer system for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Mi, C.C. Compensation topologies of high-power wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 65, 4768–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Covic, G.A.; Stielau, O.H. Power transfer capability and bifurcation phenomena of loosely coupled inductive power transfer systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaligh, A.; Dusmez, S. Comprehensive topological analysis of conductive and inductive charging solutions for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3475–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElGhanam, E.; Hassan, M.; Osman, A.; Kabalan, H. Design and performance analysis of misalignment tolerant charging coils for wireless electric vehicle charging systems. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-S.; Stielau, O.H.; Covic, G.A. Design considerations for a contactless electric vehicle battery charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinthavali, M.; Wang, Z.J. Sensitivity analysis of a wireless power transfer (WPT) system for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Spanik, P.; Frivaldsky, M.; Drgona, P.; Jaros, V. Analysis of proper configuration of wireless power transfer system for electric vehicle charging. In Proceedings of the 2016 ELEKTRO, Strbske Pleso, Slovakia, 16–18 May 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Kalwar, K.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Horan, B. Coil design for high misalignment tolerant inductive power transfer system for EV charging. Energies 2016, 9, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.; Ko, K.; Tung, H.; Tung, H.; Tsang, K.; Lai, L. ZigBee electric vehicle charging system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 507–508. [Google Scholar]
- Aditya, K.; Williamson, S.S. Design considerations for loosely coupled inductive power transfer (IPT) system for electric vehicle battery charging-A comprehensive review. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 15–18 June 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saadi, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Al-Omari, A.; Al-Gizi, A.; Craciunescu, A. Analysis and comparison of resonance topologies in 6.6 kW inductive wireless charging for electric vehicles batteries. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 32, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Kou, Z.; He, Z.; Cao, G.; Mai, R. Hybrid and reconfigurable IPT systems with high-misalignment tolerance for constant-current and constant-voltage battery charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8259–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


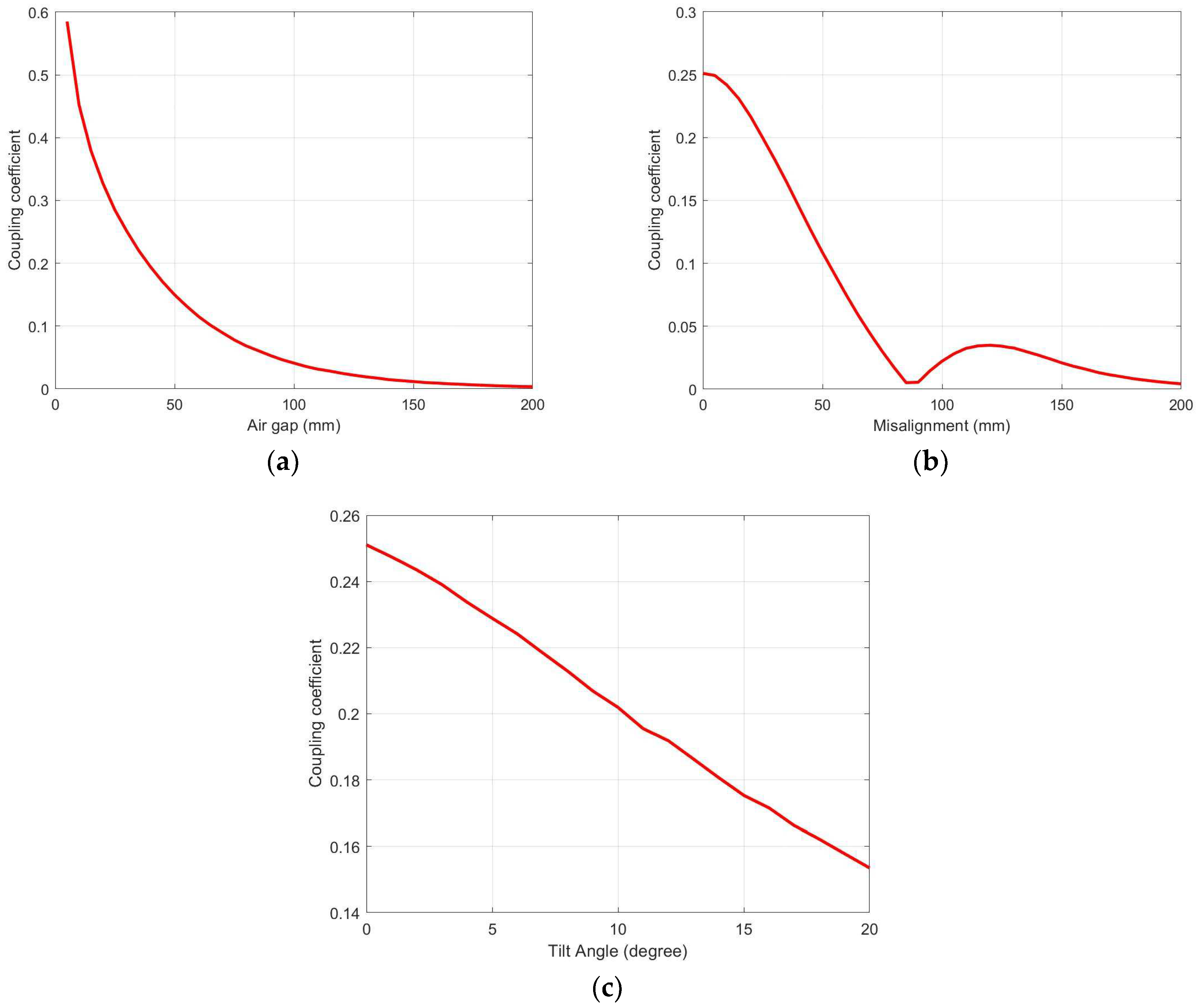
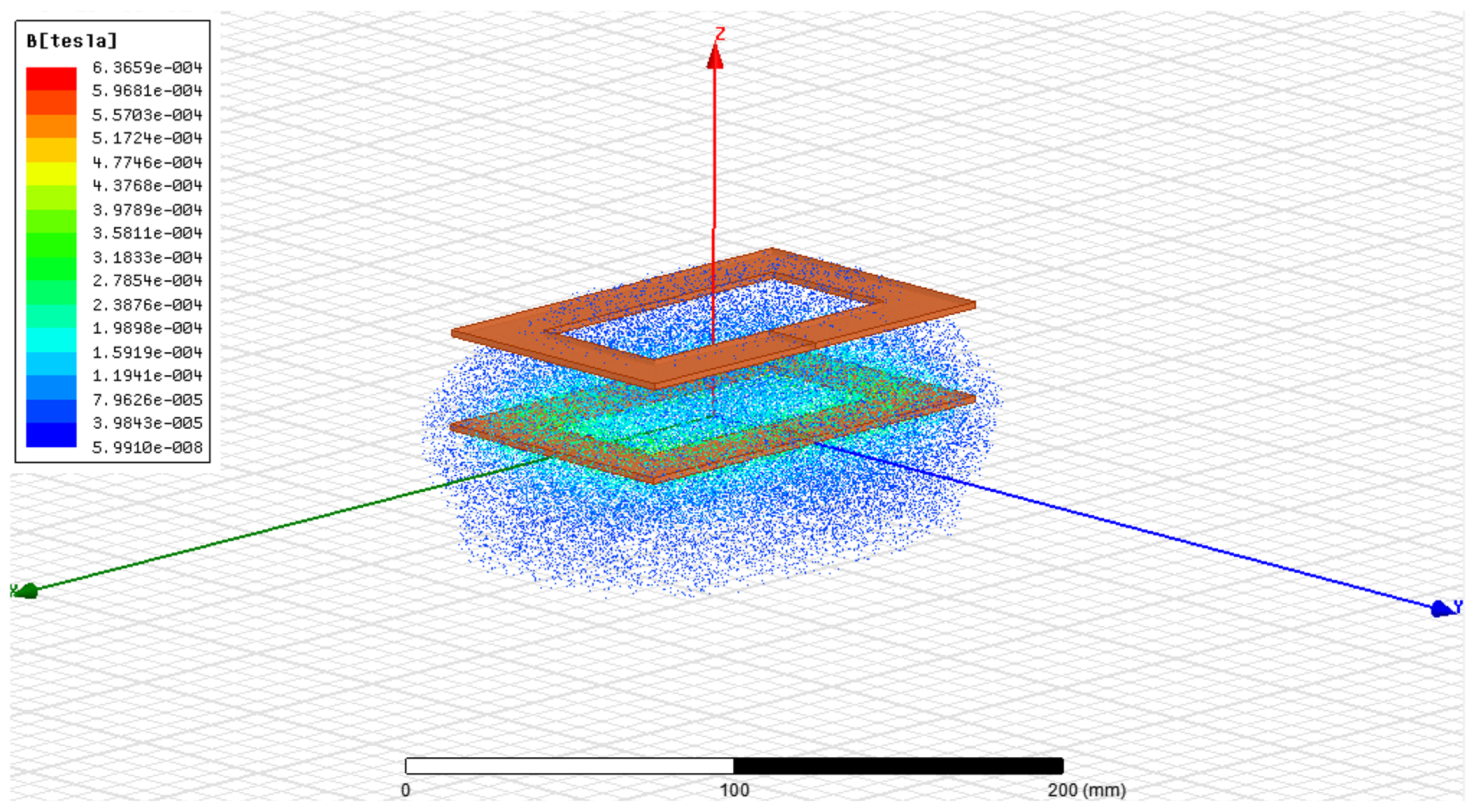
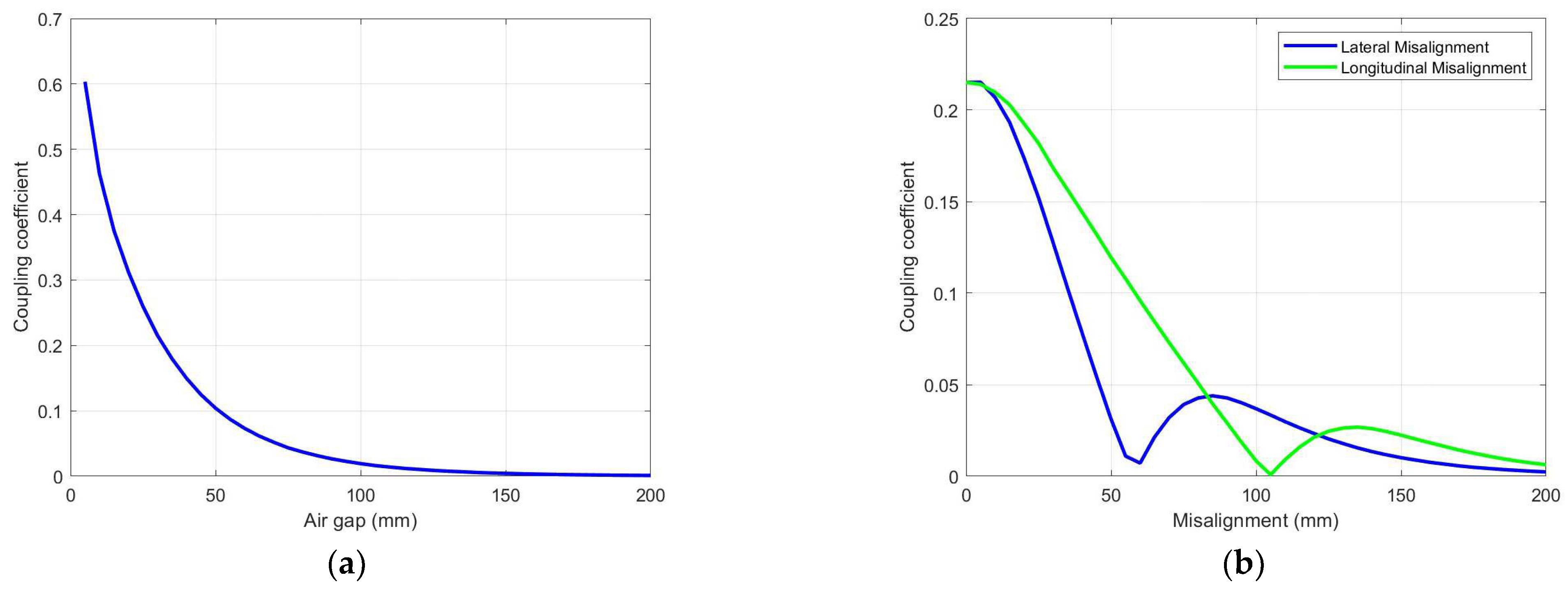
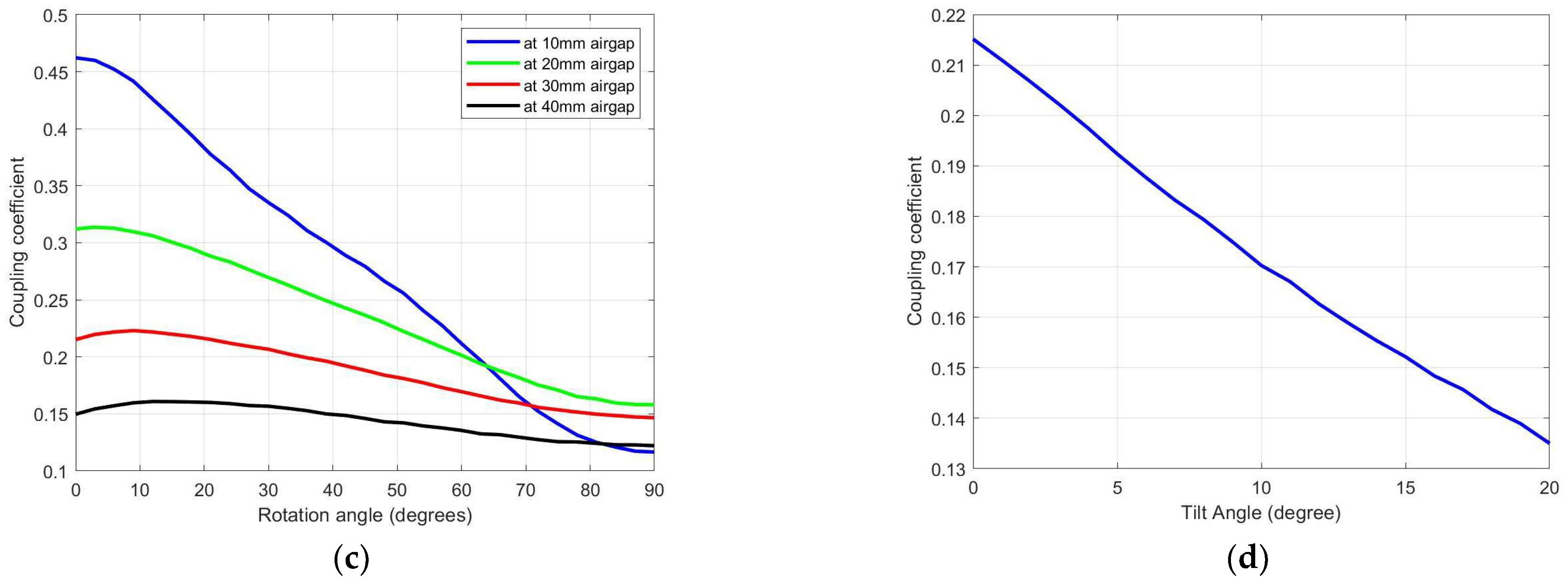
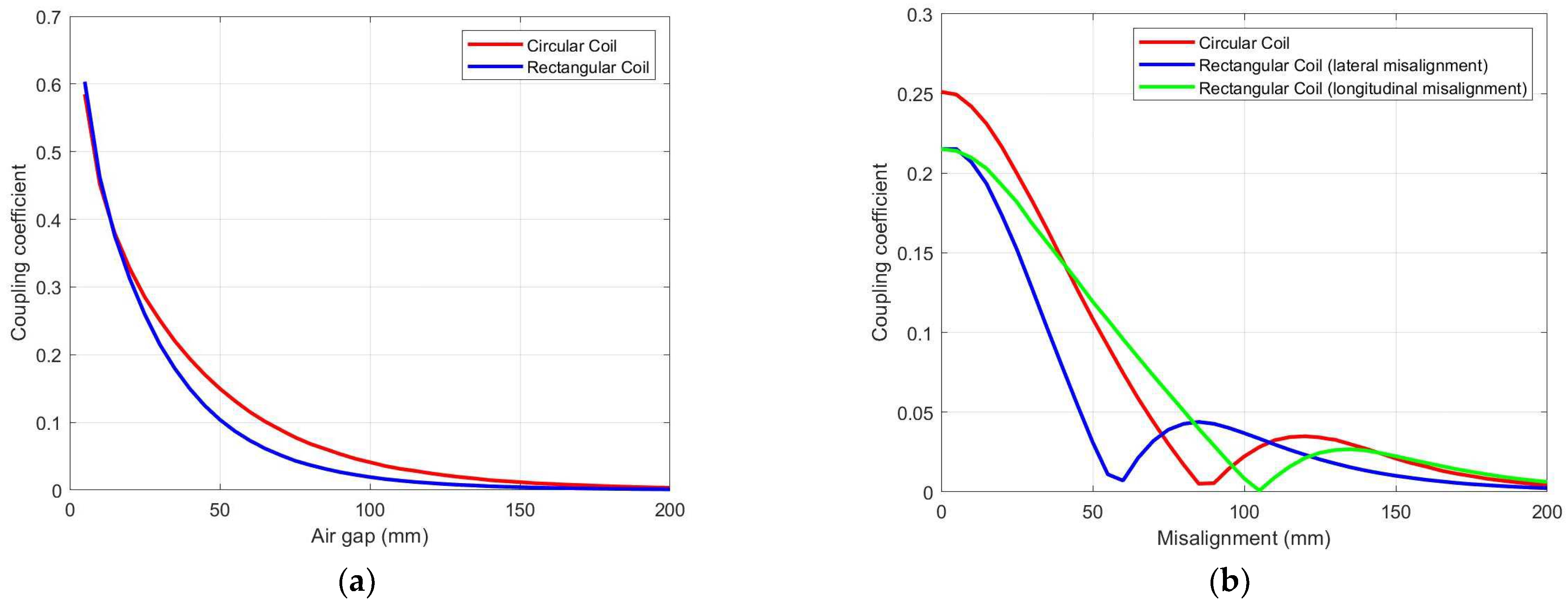
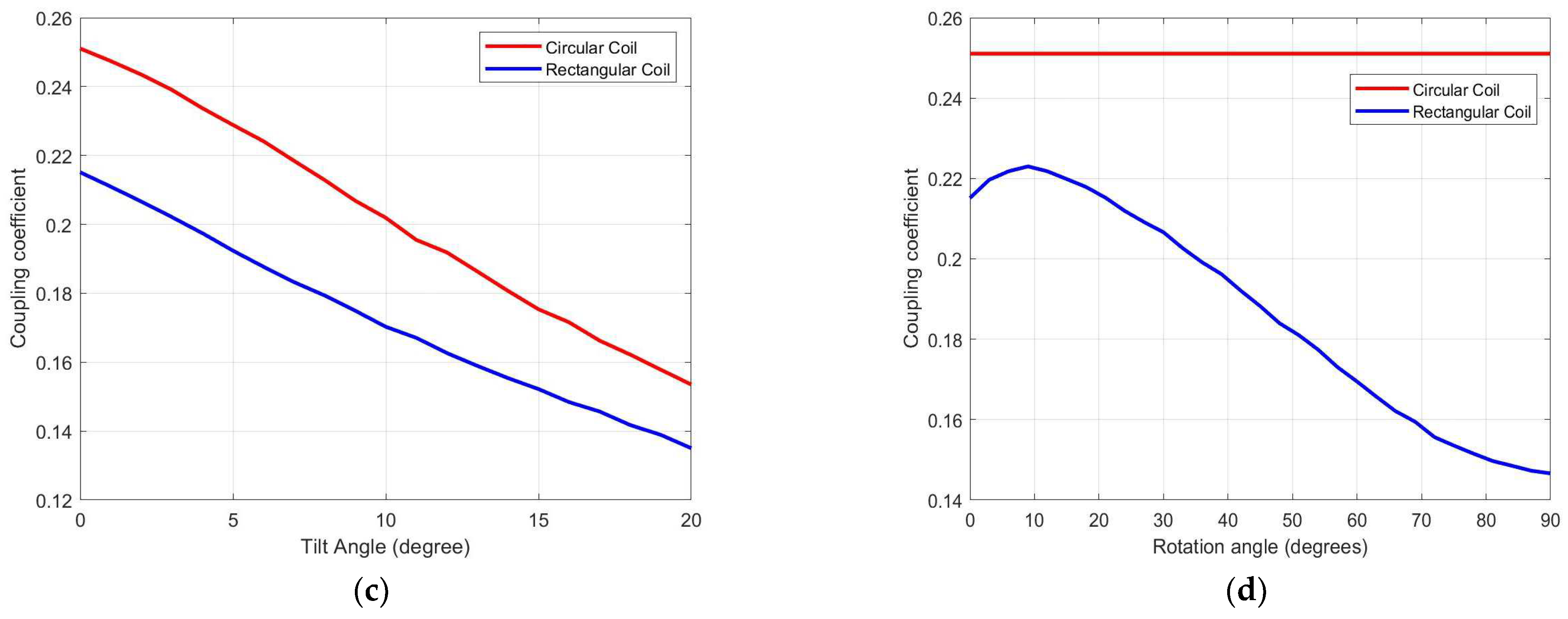

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Current in Rx | 10 A |
| Coil inner radius (Tx and Rx) | 50 mm |
| Coil outer radius (Tx and Rx) | 70 mm |
| Vertical distance between coils | 30 mm |
| Tx turns | 20 |
| Rx turns | 20 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Current in Rx | 10 A |
| Coil length (Tx and Rx) | 140 mm |
| Coil width (Tx and Rx) | 88 mm |
| Vertical distance between coils | 30 mm |
| Tx turns | 20 |
| Rx turns | 20 |
| Compensation Topology | Reflected Impedance |
|---|---|
| S–S | |
| S–P | |
| P–P | |
| P–S |
| Compensation Topology | Primary Capacitance |
|---|---|
| S–S | |
| S–P | |
| P–P | |
| P–S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghazizadeh, S.; Ahmed, K.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Chandran, J.; Stojcevski, A. Critical Analysis of Simulation of Misalignment in Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles Batteries. Batteries 2023, 9, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020106
Ghazizadeh S, Ahmed K, Seyedmahmoudian M, Mekhilef S, Chandran J, Stojcevski A. Critical Analysis of Simulation of Misalignment in Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles Batteries. Batteries. 2023; 9(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhazizadeh, Saeid, Kafeel Ahmed, Mehdi Seyedmahmoudian, Saad Mekhilef, Jaideep Chandran, and Alex Stojcevski. 2023. "Critical Analysis of Simulation of Misalignment in Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles Batteries" Batteries 9, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020106
APA StyleGhazizadeh, S., Ahmed, K., Seyedmahmoudian, M., Mekhilef, S., Chandran, J., & Stojcevski, A. (2023). Critical Analysis of Simulation of Misalignment in Wireless Charging of Electric Vehicles Batteries. Batteries, 9(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries9020106










