Copper Chloro-Complexes Concentrated Solutions: An Electrochemical Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Solutions with Calcium Chloride
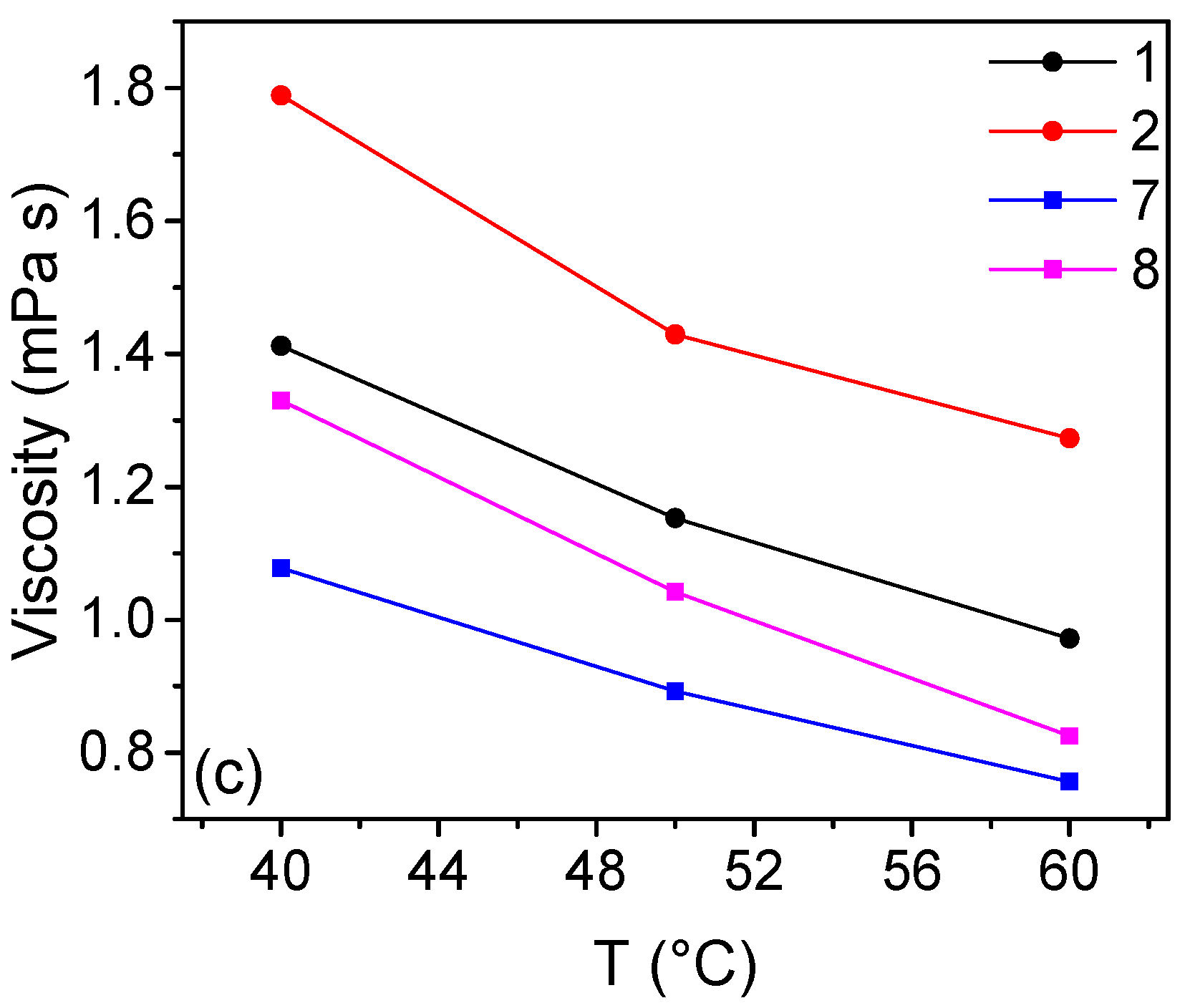
2.2. Solutions Containing NH4Cl as Chloride Source
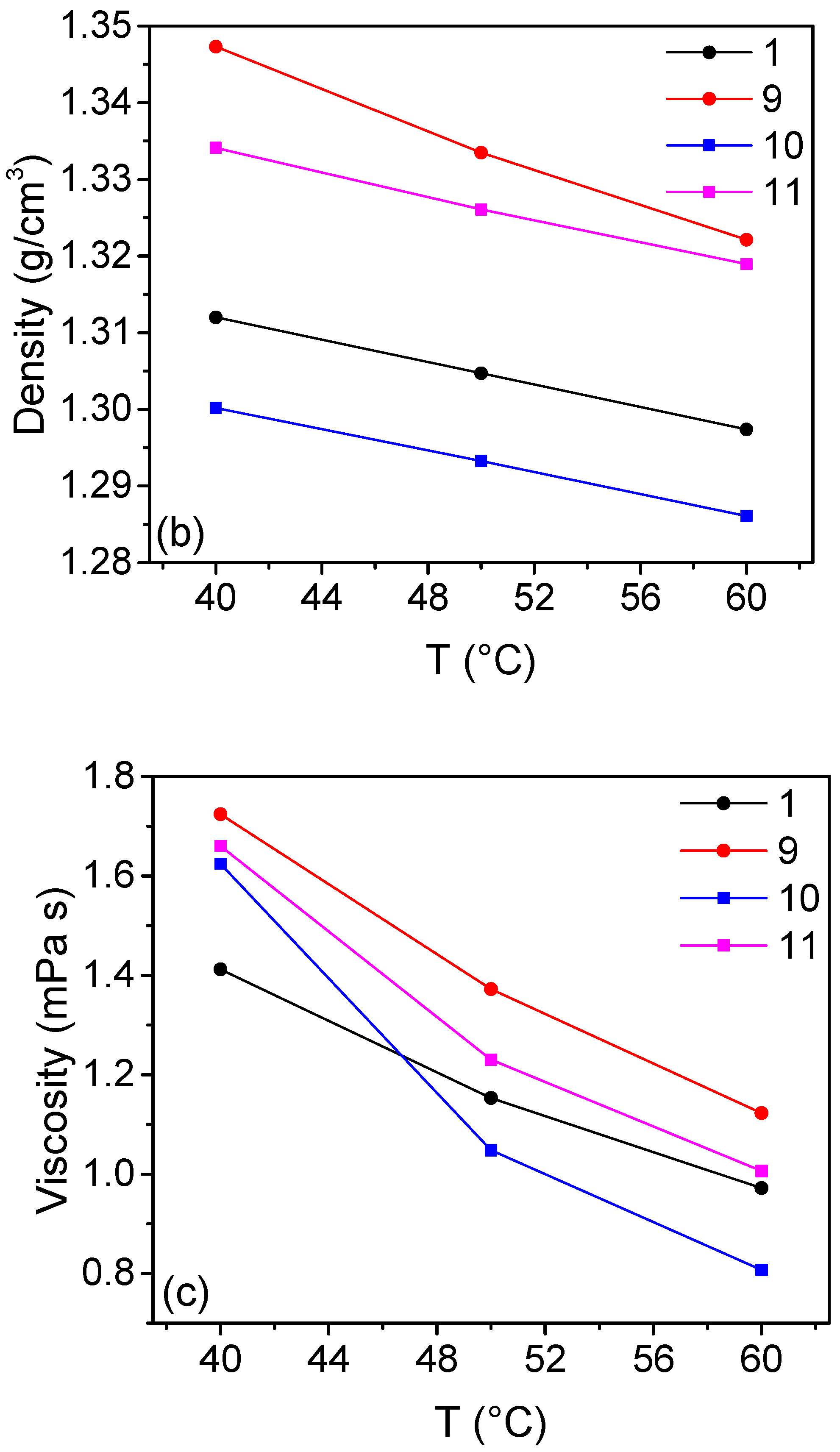
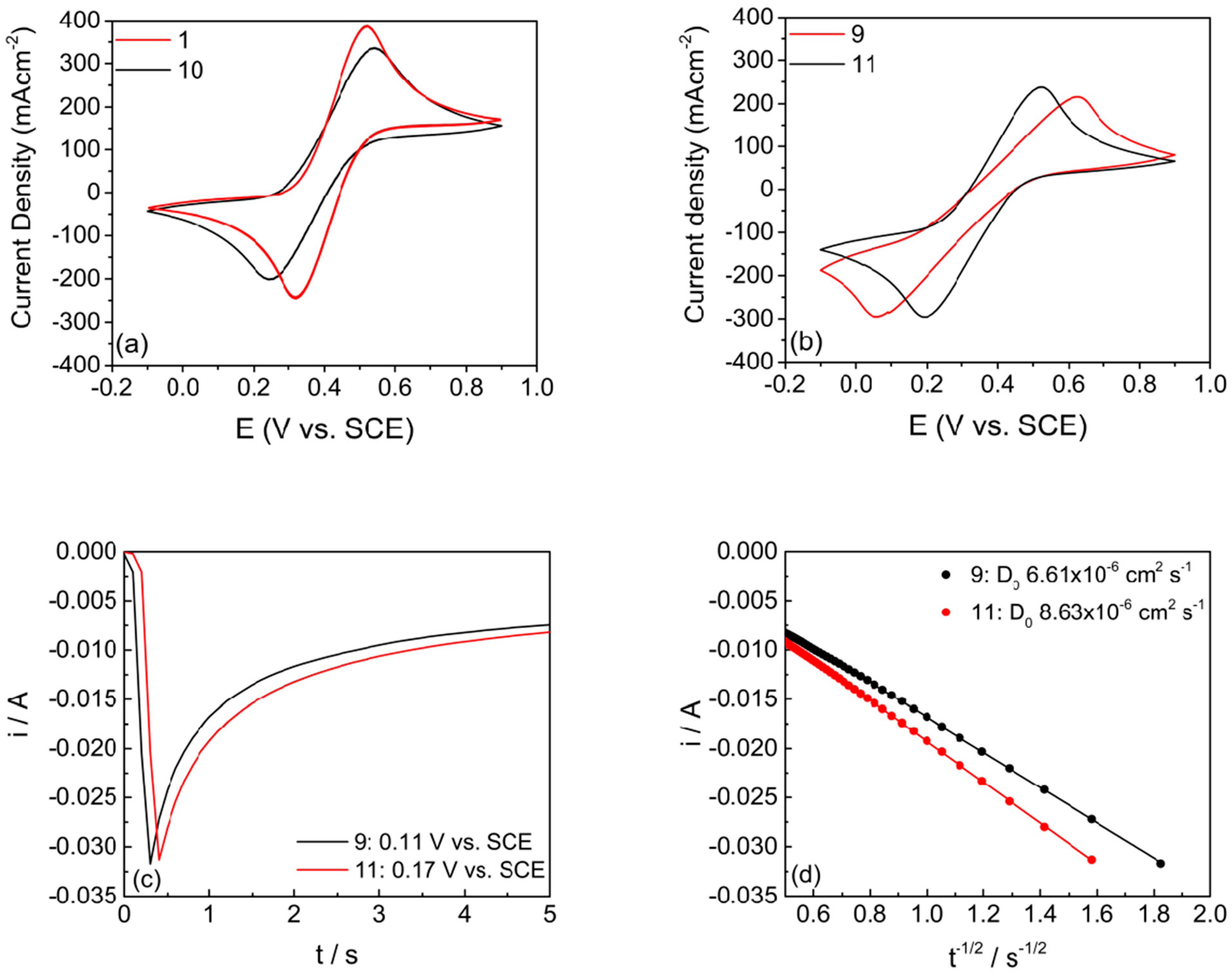
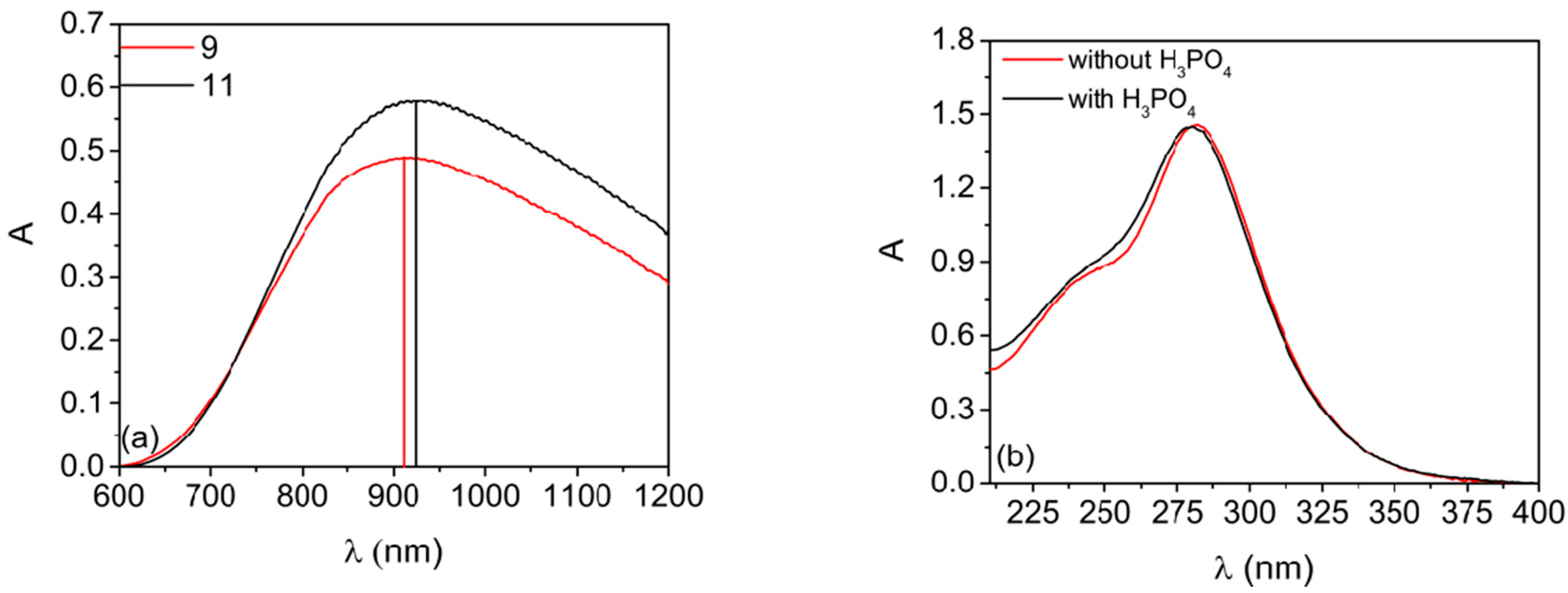
2.3. Solutions Containing H3PO4 as Additive
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mussler, R.E.; Campbell, T.T.; Olsen, R.S. Electrowinning of Copper from Chloride Solutions U.S. Dept. of Interior, Bureau of Mines, Report of Investigation 8076, Washington: 1975. Available online: http://books.google.com (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Sugasaka, K.; Fujii, A. A Spectrophotometric Study of Copper(I) Chloro-Complexes in Aqueous 5M Na(Cl,ClO4) Solutions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1976, 42, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.J. Chloride Complexes of CuCI in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 84, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, J.; McPhail, D.C.; Black, J.; Spiccia, L. Complexation of metal ions in brines: Application of electronic spectroscopy in the study of the Cu(II)-LiCl-H2O system between 25 and 90 °C. Geoch. Cosmoch. Acta 2001, 65, 2691–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, O.; Hämäläinen, M.; Lamberg, P.; Liipo, J. Recovering Gold from Copper Concentrate via the HydroCopperTM Process. JOM 2004, 56, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, M.; Aromaa, J.; Forsén, O.; Hyvärinen, O.; Barker, M.H. Cathodic reactions of Cu2+ in cupric chloride solution. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 85, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naterer, G.; Suppiah, S.; Lewis, M.; Gabriel, K.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M. Recent Canadian advances in nuclear-based hydrogen production and the thermochemical Cu–Cl cycle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 2901–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevani, L.; Ehlerova, J.; Sedlbauer, J.; Tremaine, P.R. Complexation in the Cu(II)–LiCl–H2O system at temperatures to 423 K by UV-Visible spectroscopy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 4893–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Electrochemical analysis of a HCl(aq)/CuCl(aq) electrolyzer: Equilibrium thermodynamics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 19, 7835–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, A.; Zamfirescu, C.; Dincer, I.; Naterer, G.F. Electrochemical Transport in CuCl/HCl(aq) Electrolyzer Cells and Stack of the Cu–Cl Cycle. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 044515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, R.; Cross, N.R.; Lvov, S.N.; Logan, B.E.; Gorski, C.A.; Hall, D.M. An All-Aqueous Thermally Regenerative Ammonia Battery Chemistry Using Cu(I, II) Redox Reactions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 070523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvil, B.; Betty, K.R. A Secondary Battery Based on the Copper(II)-(I) and (I)-(0) Couples in Acetonitrile. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1974, 121, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porterfield, W.W.; Yoke, J.T. Inorganic Compounds with Unusual Properties; King, R.B., Ed.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1976; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Peljo, P.; Lloyd, D.; Doan, N.; Majaneva, M.; Kontturi, K. Towards a thermally regenerative all-copper redox flow battery. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, D.; Vainikka, T.; Kontturi, K. The development of an all copper hybrid redox flow battery using deep eutectic solvents. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 100, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Palma, J.; García-Quismondo, E.; Anderson, M. The effect of chloride ion complexation on reversibility and redox potential of the Cu(II)/Cu(I) couple for use in redox flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 224, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.; Palma, J.; Garcia-Quismondo, E.; Sanz, L.; Mohamed, M.R.; Anderson, M. Evaluation of electrode materials for all-copper hybrid flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 310, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, E.A.; Krueger, K.W.; Savinell, R.F.; Wainright, J.S. Investigating a Bromide Supported Electrolyte for an All-Copper Flow Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A1797–A1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolozzi, M. Development of redox flow batteries. A historical bibliography. J. Power Sources 1989, 27, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Lim, T.M.; Menictas, C.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Review of material research and development for vanadium redox flow battery application. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 101, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Díez, E.; Ventosa, E.; Guarnieri, M.; Trovò, A.; Flox, C.; Marcilla, R.; Soavi, F.; Mazur, P.; Aranzabe, E.; Ferret, R. Redox flow batteries: Status and perspective towards sustainable stationary energy storage. J. Power Sources 2021, 481, 228804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Millero, F.J. Equilibrium Constants for the Formation of Cu(I) Halide Complexes. J. Solut. Chem. 1990, 19, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zeng, D.; Voigt, W. Thermodynamic modeling of salt-water systems up to saturation concentrations based on solute speciation: CuCl2–MCln–H2O at 298 K (M = Li, Mg, Ca). Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 322, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applegarth, L.M.; Corbeil, C.R.; Mercer, D.J.W.; Pye, C.C.; Tremaine, P.R. Raman and ab Initio Investigation of Aqueous Cu(I) Chloride Complexes from 25 to 80 °C. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Bard, A.J. Measurement of Temperature-Dependent Stability Constants of Cu(I) and Cu(II) Chloride Complexes by Voltammetry at a Pt Ultramicroelectrode. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 3498–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, E.A.; Adler, Z.; Wainright, J.S.; Savinell, R.F. Diffusion Coefficients of Cuprous and Cupric Ions in Electrolytes with High Concentration of Bromide Ions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Kinetic and electrochemical analyses of a CuCI/HCl electrolyzer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 6890–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Akinfiev, N.N.; LaRow, E.G.; Schatz, R.S.; Lvov, S.N. Thermodynamics and Efficiency of a CuCl(aq)/HCl(aq) Electrolyzer. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 143, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balashov, N.; Schatz, R.S.; Chalkova, E.; Akinfiev, N.N.; Fedkin, M.V.; Lvov, S.N. CuCl Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production in the Cu–Cl Thermochemical Cycle. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, B266–B275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, L.; Lloyd, D.; Magdalena, E.; Palma, J.; Anderson, M.; Kontturi, K. Study and characterization of positive electrolytes for application in the aqueous all-copper redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-C.; Awakura, Y.; Ando, S.; Majima, H. Determination of the Diffusion Coefficients of CuCl2, FeCl3, CuSO4, and Fe2(SO4)3 in Aqueous Solutions. Mater. Trans. JIM 1990, 31, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Chang, J.; Boika, A.; Bard, A.J. Electrochemistry of High Concentration Copper Chloride Complexes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7696–7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveant, J.-M. Elements of Molecular and Biomolecular Electrochemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q.; Xu, J.J.; Li, H.J.; Yi, H.B. Ion association characteristics in MgCl2 and CaCl2 aqueous solutions: A density functional theory and molecular dynamics investigation. Mol. Phys. 2015, 113, 3545–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, H. Molecular dynamics simulation study on distinctive hydration characteristics of highly coordinated calcium chloride complexes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 274, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmanov, S.A.; Silkin, S.A.; Belkin, P.N. Effect of Plasma-Electrolytic Polishing on the Corrosion Resistance of Structural Steels after Their Anodic Saturation with Nitrogen, Boron, and Carbon. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2020, 56, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamchuea, K.; Eloul, S.; Tschulik, K.; Compton, R.G. Planar diffusion to macro disc electrodes—What electrode size is required for the Cottrell and Randles-Sevcik equations to apply quantitatively? J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 3251–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, M.V.; Vasylenko, K.V.; Myrhorodska, V.D.; Kostyniuk, A.; Likozar, B. Synthesis of Calcium Orthophosphates by Chemical Precipitation in Aqueous Solutions: The Effect of the Acidity, Ca/P Molar Ratio, and Temperature on the Phase Composition and Solubility of Precipitates. Processes 2020, 8, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, X.; Zeng, D. Trace Amounts of Aqueous Copper(II) Chloride Complexes in Hypersaline Solutions: Spectrophotometric and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Solut. Chem. 2014, 43, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liang, M.; Zeng, D.; Hefter, G. A spectroscopic study of solvent effects on the formation of Cu(II)–chloride complexes in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan, S.E.; Iwamoto, R.T. Chloro Complexes of Copper(II) and Copper(I) in Acetonitrile. Inorg. Chem. 1965, 4, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miessler, G.; Tarr, D. Inorganic Chemistry. In Pearson Educational International, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall, 2011; pp. 367–369. Available online: https://hostnezt.com/cssfiles/chemistry/Inorganic%20Chemistry%20By%20GARY%20L.%20MIESSLER.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Mereshchenko, A.; Olshin, P.K.; Myasnikova, O.S.; Panov, M.; Kochemirovsky, V.; Skripkin, M.; Moroz, P.; Zamkov, M.; Tarnovsky, A. Ultrafast Photochemistry of Copper(II) Monochlorocomplexes in Methanol and Acetonitrile by Broadband Deep-UV-to-Near-IR Femtosecond Transient Absorption Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
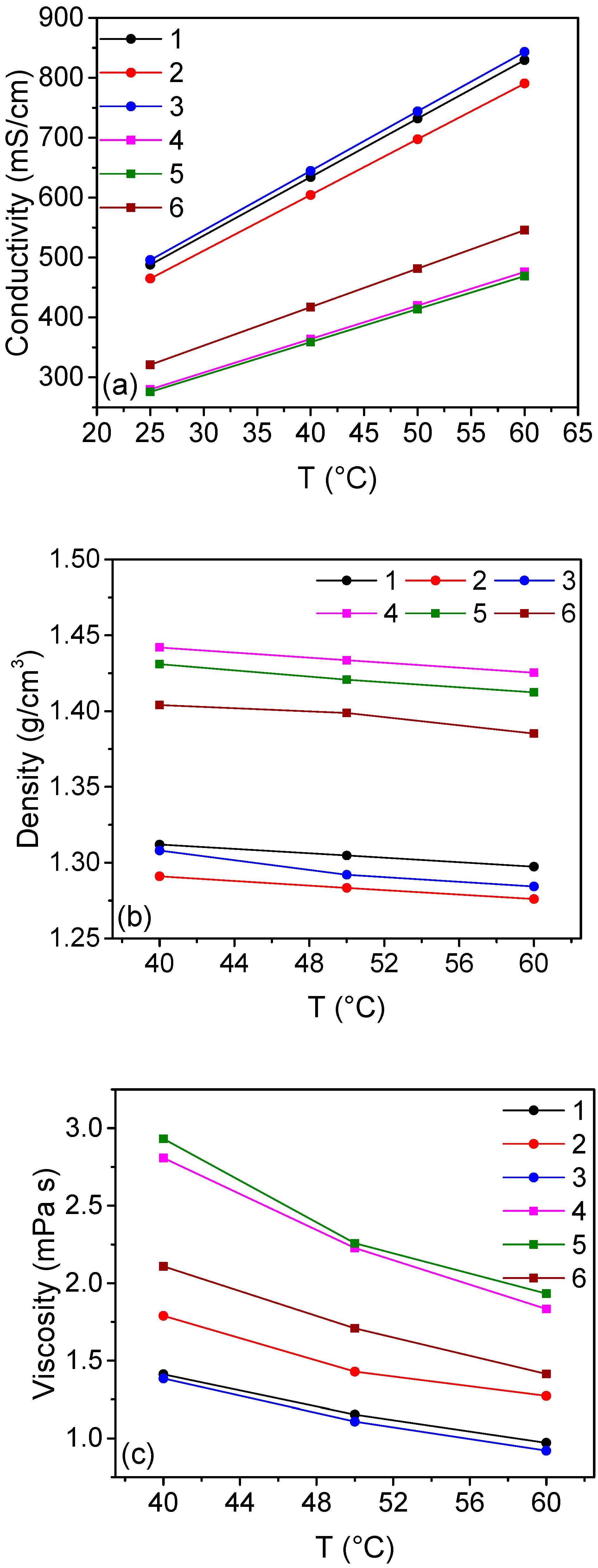





| n | CuCl2 M | CuCl M | CaCl2 M | HCl M | Cu:Cl | σ mS cm−1 | η mPa s | ρ kg m−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | / | 2 | 1 | 6 | 1:5 | 634 | 1.41 | 1312 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 6 | 1:5 | 605 | 1.78 | 1291 |
| 3 | 2 | / | / | 6 | 1:5 | 645 | 1.38 | 1308 |
| 4 | / | 2 | 3 | 6 | 1:7 | 364 | 2.80 | 1442 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 2.5 | 6 | 1:7 | 359 | 2.93 | 1431 |
| 6 | 2 | / | 2 | 6 | 1:7 | 417 | 2.10 | 1404 |
| n | OCP V vs. SCE | E+ V vs. SCE | E− V vs. SCE | ΔE V | (E+ + E−)/2 V | ipa mA cm−2 | ipc mA cm−2 | ipa/ipc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.309 | 0.483 | 0.347 | 0.136 | 0.415 | 149 | −171 | 0.87 |
| 2 | 0.409 | 0.469 | 0.340 | 0.129 | 0.405 | 162 | −163 | 0.99 |
| 3 | 0.622 | 0.419 | 0.299 | 0.120 | 0.359 | 151 | −151 | 1 |
| 4 | 0.302 | 0.447 | 0.296 | 0.151 | 0.372 | 112 | −107 | 1.05 |
| 5 | 0.417 | 0.481 | 0.340 | 0.141 | 0.411 | 117 | −118 | 0.99 |
| 6 | 0.525 | 0.430 | 0.293 | 0.137 | 0.362 | 107 | −113 | 0.95 |
| n | T °C | CuCl2 M | CuCl M | CaCl2 M | HCl M | NH4Cl M | Cu:Cl | σ mS cm−1 | η mPa s | ρ kg m−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | 40 | / | 2 | / | 6 | 2 | 1:5 | 812 | 1.08 | 1296 |
| 7b | 60 | / | 2 | / | 6 | 2 | 1:5 | 1003 | 0.76 | 1283 |
| 8a | 40 | 1 | 1 | / | 6 | 1 | 1:5 | 819 | 1.33 | 1250 |
| 8b | 60 | 1 | 1 | / | 6 | 1 | 1:5 | 1012 | 0.83 | 1236 |
| n | T °C | OCP V vs. SCE | E+ V vs. SCE | E− V vs. SCE | ΔE V | (E+ + E−)/2 V | ipa mA/cm−2 | ipc mAcm−2 | ipa/ipc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7a | 40 | 0.324 | 0.548 | 0.283 | 0.265 | 0.416 | 150 | −126 | 1.19 |
| 7b | 60 | 0.324 | 0.550 | 0.309 | 0.241 | 0.430 | 211 | −216 | 0.98 |
| 8a | 40 | 0.375 | 0.528 | 0.270 | 0.258 | 0.399 | 125 | −143 | 0.87 |
| 8b | 60 | 0.380 | 0.484 | 0.326 | 0.158 | 0.405 | 146 | −170 | 0.86 |
| n | CuCl2 M | CuCl M | CaCl2 M | HCl M | H3PO4 M | Cu:Cl | σ mS cm−1 | η mPa s | ρ kg m−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | / | 2 | 1 | 6 | / | 1:5 | 634 | 1.41 | 1312 |
| 9 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 1 | 6 | / | 1:5.9 | 569 | 1.73 | 1347 |
| 10 | / | 2 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1:5 | 714 | 1.62 | 1300 |
| 11 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1:5.9 | 508 | 1.66 | 1334 |
| n | OCP V vs. SCE | E+ V vs. SCE | E− V vs. SCE | ΔE V | (E+ + E−)/2 V | ipa mA cm−2 | ipc mA cm−2 | ipa/ipc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.309 | 0.483 | 0.347 | 0.136 | 0.415 | 149 | −171 | 0.87 |
| 9 | 0.490 | 0.477 | 0.209 | 0.268 | 0.343 | 127 | −120 | 1.06 |
| 10 | 0.297 | 0.473 | 0.309 | 0.164 | 0.391 | 142 | −154 | 0.92 |
| 11 | 0.427 | 0.444 | 0.277 | 0.167 | 0.361 | 125 | −120 | 1.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacarbonara, G.; Faggiano, L.; Porcu, S.; Ricci, P.C.; Rapino, S.; Casey, D.P.; Rohan, J.F.; Arbizzani, C. Copper Chloro-Complexes Concentrated Solutions: An Electrochemical Study. Batteries 2021, 7, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7040083
Lacarbonara G, Faggiano L, Porcu S, Ricci PC, Rapino S, Casey DP, Rohan JF, Arbizzani C. Copper Chloro-Complexes Concentrated Solutions: An Electrochemical Study. Batteries. 2021; 7(4):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7040083
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacarbonara, Giampaolo, Luigi Faggiano, Stefania Porcu, Pier Carlo Ricci, Stefania Rapino, Declan P. Casey, James F. Rohan, and Catia Arbizzani. 2021. "Copper Chloro-Complexes Concentrated Solutions: An Electrochemical Study" Batteries 7, no. 4: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7040083
APA StyleLacarbonara, G., Faggiano, L., Porcu, S., Ricci, P. C., Rapino, S., Casey, D. P., Rohan, J. F., & Arbizzani, C. (2021). Copper Chloro-Complexes Concentrated Solutions: An Electrochemical Study. Batteries, 7(4), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries7040083








