Abstract
The aim of this paper was to propose and test a continuous cobalt recovery process from waste mobile phone batteries. The procedure started with dismantling, crushing, and classifying the materials. A study on leaching with sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide was carried out with subsequent selective separation of cobalt by means of liquid–liquid extraction. The best extraction conditions were determined based on a sequence of experiments that consisted of selecting the best extractant for cobalt, then assessing the impact of extractant concentration, pH, and contact time on the extraction yield. With these conditions, an extraction isotherm was obtained and correlated with a mathematical model to define the number of extraction stages for a countercurrent process using the McCabe–Thiele method. Then, a similar study was done for stripping conditions and, as a last step, cobalt electroplating was performed. The proposed process offers a solution for the treatment of these batteries, avoiding potential problems of contamination and risk for living beings, as well as offering an opportunity to recover valuable metal.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, the use of lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) in a large number of portable devices, such as mobile phones, laptops, tablets, toys, medical equipment, and tools, has increased. This consumption has generated a large number of spent batteries. The Global E-waste Monitor [1] classifies this e-waste within the category “small IT and telecommunication equipment”, with an estimated generation of 3.9 million metric tons in 2016 [1]. In a mobile phone, the battery represents 21.12% of the total weight, together with other materials such as plastics (25.75 wt%), printed circuit boards (PCBs) (17.67 wt%), metals (17.30 wt%), and displays (8.37 wt%) [2]. Worldwide, there are around 780,000 metric tons of spent LiBs, and for China alone, there is an estimated increase to 500,000 metric tons for 2020 [3].
There are two main reasons to recycle batteries: to recover valuable materials, especially if their supply is limited, and to comply with any government regulations on the disposal of this type of spent battery [4]. LiBs are composed of an anode, a cathode, a separator, and an electrolyte. The average composition of the materials in LiBs is presented in Table 1 [5].

Table 1.
Material percentage %(w/w) in lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) [5].
In more than half of these batteries, the cathode contains any of the following compounds: LiCoO2 and LiNi0.33Co0.33Mn0.33O2 [6]. As previously mentioned, cobalt accounts for around 20 wt% of spent LiBs. These residues also contain lithium, nickel, copper, and aluminum; however, there is a higher composition of cobalt than the other metals, which is why it is important to recover [5,7]. Due to the complicated assembly of the batteries and the composition of the electrodes, recycling LiBs requires physical and chemical processes. Physical processes include pretreatments, such as dismantling, crushing, screening, magnetic separation, washing, and thermal pretreatment. Chemical processes include acid leaching, bioleaching, ultrasonic-assisted separation, solvent extraction, chemical precipitation, and electrochemical processes [6,8,9].
Many articles have focused on the stage of leaching with minerals acid [4,7,10,11], bioleaching [5], and organics acids [12,13,14,15]. Other proposed processes include precipitation [16,17], thermal treatment [18], reduction roasting [19], and mechanical separation [20].
While solvent extraction has industrial applications in the recovery and purification of metals from lixiviation liquors and residues of materials [21], few works have proposed solvent extraction to recover cobalt [22,23], copper [24], and other metals of spent batteries [25]. This work focused on the recovery of cobalt by solvent extraction, measuring the effect of parameters such as time, pH, and concentration of the extractant. Liquid–liquid extraction was used because of its flexibility, high selectivity, and lower energy requirements in comparison with pyrometallurgic methods [26]. The number of extraction and stripping stages required to perform the separation in a continuous scheme was estimated using the McCabe–Thiele method. After stripping, it was possible to achieve the electrodeposition of cobalt in sulfate medium [27], and it may be possible even with the presence of organic impurities [28]. With this last stage, the process of cobalt recovery was complete and could be used at the industrial level. The electrodeposition of cobalt was also studied in this work.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The first step of this research was to gather mobile phone batteries from collection centers, mobile phone repair shops, and friends and relatives. To dissolve the spent battery material, sulfuric acid (Karal) and hydrogen peroxide (Karal) were used. For the recovery of cobalt, the selected extractant was Cyanex 272 (bis-(2,4,4-tri-methyl-pentyl) phosphinic acid), which was supplied by Cytec Solvay and used without further purification. The organic phase was prepared by diluting the extractant in kerosene (Reasol, technical grade). All other chemical products were of analytical reagent grade.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
The experimental procedure is illustrated in Figure 1, and it indicates the components that were removed at each stage.
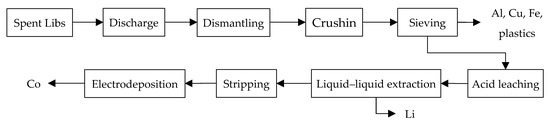
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure for recovery of cobalt.
Each step is described below.
Collection. After collecting about 40 batteries of different brands, they were classified into two groups by weight: batteries of 20–30 g and those of 30–40 g.
Discharge. To discharge the residual energy, each battery was connected to a lamp until its energy was minimal. This was measured with a multimeter model MP9600-MITZU.
Dismantling and crushing. Each battery was cut into three or four parts with the help of metal-cutting scissors, which were then crushed with a 500-W blender.
Sieving and classification. After crushing, a sieve was applied for 1 min, which consisted of four meshes corresponding to mesh 18, 35, 60, and 140 with openings of 1 mm, 0.50 mm, 0.25 mm, and 0.105 mm, respectively. Then, each mesh was taken apart to weigh its contents.
Leaching. The leaching process was carried out using a sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide solution to dissolve the components of the batteries containing cobalt and lithium, using a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10, with controlled temperature and time. Cobalt concentration in solution was detected by stoichiometry. Corresponding dilutions were prepared and defined by AAS using a Perkin Elmer AAnalyst 200.
Liquid–liquid extraction. In order to define the extraction operation conditions, batch experimentation was performed in a 30-mL beaker using an aqueous-to-organic-phase ratio of 10:10 mL. The phases were in contact with constant stirring at 700 rpm for 30 min, which was sufficient time to reach equilibrium. Once the extraction time was over, the phases were separated and the concentration of metal in the aqueous phase ([Co]aq) was determined by AAS, and in the organic phase, ([Co]org) was determined by mass balance. Every point of the pH range between 2 and 7 was evaluated with unitary steps, adjusting the pH by using concentrated alkaline or acid solutions. A Hanna Digital pH meter model HI2209 with a combined glass electrode was used to measure the pH of the aqueous solutions. Every point of the proposed extractant concentration range was evaluated between 0.1 mol/L and 0.5 mol/L, with steps of 0.1 mol/L. A contact time test was performed, monitoring the extraction yield for each time interval. All of these experiments were performed at 22 ± 1 °C. The cobalt extraction rate was:
Cobalt Extraction % = 100 [Co]org/([Co]org + [Co]aq)
Isotherms of extraction and continuous process. To obtain the isotherms, the parameters found by the experimental procedures were used at different rates of the aqueous phase in relation to the organic phase (A/O). The concentration of cobalt in the organic phase was calculated as follows:
where [Co]aq initial is the initial cobalt concentration before extraction, [Co]aq is the final silver concentration after extraction, while A and O are the volumes of aqueous and organic phases, respectively. Aiming for industrial application, the number of stages required for a continuous process was computed by using the McCabe–Thiele method [21]. Figure 2 shows the experimental mixer-settler with a size of 3.8 × 23.3 × 6.5 cm and a stirring section of 3.8 × 3.8 × 6.5 cm. Stirring was performed with a magnetic stirrer, and to control flows, pumps and valves were used.
[Co]org = A/O ([Co]aq initial − [Co]aq)

Figure 2.
Mixer-settler for continuous process.
Electrodeposition. The stripping solution of cobalt was treated in a system with a lead anode and a stainless-steel cathode, both with an area of 0.00499 m2. The electrodes were cleaned and polished and the temperature was controlled. The system for electrodeposition is shown in the Figure 3 with a regulated DC power supply. The effect of the current over the cobalt deposition was studied by testing five values for current (0.25 A, 0.5 A, 0.75 A, 1 A, and 1.5 A). The current efficiency was computed as:
Current efficiency = (deposited mass/theoretical deposition mass) ∗ 100
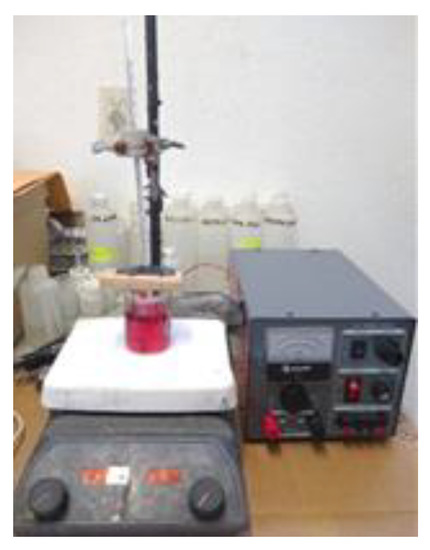

Figure 3.
System for electrodeposition of cobalt.
3. Results
3.1. Collection, Discharge, Dismantling, Drushing, and Sieving
Commercial LiBs of different brands were collected from numerous sources such as markets and stores. For safe handling, they were discharged, and the remaining voltage was less than 0.2 V. The batteries were discharged at a controlled rate to avoid overdischarge-related phenomena, such as those reported by Ouyang et al. [29]. In the first step of dismantling, the plastic or metallic cases were removed, and the batteries were crushed with a blender at 500 W for 5 min. The batteries collected were classified into two groups: batteries between 15 g and 30 g, and those between 30 g and 40 g. Table 2 presents the fractions obtained from the batteries after the classification.

Table 2.
Material percentage % (w/w) present in LiBs.
Figure 4 shows the fractions obtained in this study. Figure 4c shows the copper and aluminum fractions with a particle size greater than 0.25 mm, while Figure 4d presents the cobalt–lithium powder with a particle size smaller than 0.105 mm.

Figure 4.
Fractions obtained from the crushing and sieving of batteries.
3.2. Leaching
Leaching was performed in sulfuric acid (2 mol/L) and hydrogen peroxide (6 vol%) at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1/10 and a temperature of 75 °C for 90 min; the system is shown in Figure 5. Operating conditions were taken from a preliminary work, which reported that such leaching conditions allow for obtaining the highest efficiency [30].

Figure 5.
Experimental setup for acid leaching.
It has been reported that the addition of hydrogen peroxide helps to dissolve cobalt and lithium oxides [10]. After the leaching step, the product solution was filtered, and the cobalt concentration was analyzed by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) using a Perkin Elmer AAnalyst 200. With this process, an average concentration of 10–12 g/L for cobalt was obtained. The Co–Li powder before leaching and residue after leaching were characterized using a D8 Bruker X-ray diffractometer, and the results are shown in Figure 6. Figure 6a shows the presence of different cobalt–lithium oxides and aluminum, copper, and graphite. Figure 6b confirms that the decrease of these metal oxide peaks was observed only in the presence of carbon peaks in the residue. The graphite peaks reported to appear in the 2θ range were at 25–28°, 43–46°, and 54–56° [7,10].
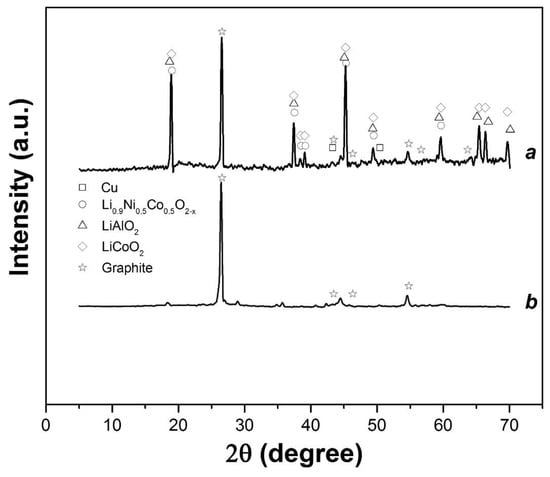
Figure 6.
Spectra of X-ray diffraction analysis before (a) and after (b) leaching. Al2O3 PDF Card #00-010-0173, Cu PDF Card #00-004-0836, C (graphite) PDF Card #00-026-1079, Li0.9Ni0.5Co0.5O2−x PDF Card #00-050-0509, LiAlO2 PDF Card #00-044-0224, and LiCoO2 PDF Card #00-050-0653. PDF = Powder Diffraction File.
3.3. Effect of pH on Extraction
Based on preliminary tests, an evaluation pH range between 2 and 7 was used, with steps of 1 unit. After sulfur acid leaching, the aqueous phase obtained a pH near 0. Then, in order to control pH, a sodium hydroxide concentrated solution was added. Figure 7 shows that the extraction percentage increased as pH increased. For cobalt extraction, pH was a key factor. Within the evaluation range for pH values, there were low extraction percentages, starting from 7% to 12% for a pH range from 2 to 3, up to yield values as high as 92% or 93% with pH values of 6 and 7.
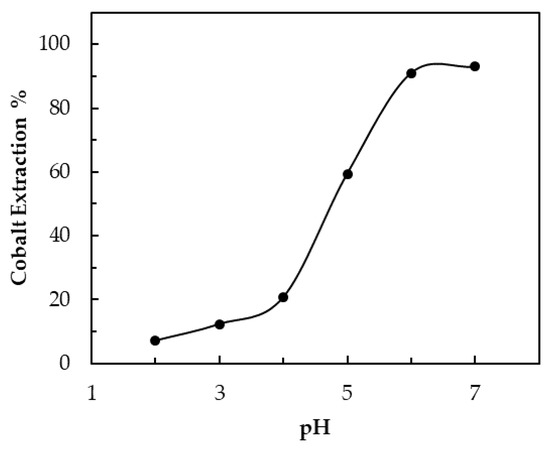
Figure 7.
Effect of pH on extraction: aqueous-to-organic-phase ratio (A/O) = 1, initial concentration of aqueous phase (Xi) = 12 g/L, [Cyanex 272] = 0.4 mol/L, time = 12 min, and temperature = 22 ± 1 °C.
The effect of pH on extraction can be explained in terms of the extraction mechanism, which occurs by ionic exchange, as follows [31]:
where RH is the acid extractant Cyanex 272 molecule, and 2(RH)2 org is the organic complex formed in the organic phase.
Co2+aq + 2(RH)2 org ↔ Co(R2H)2 org + 2H+aq
3.4. Effect of Extractant Concentration
Cobalt was extracted using the extractant Cyanex 272 diluted in kerosene. The extractant concentration was evaluated in the range between 0.1 mol/L and 0.5 mol/L, with 0.1-mol/L steps. Figure 8 shows that the extraction yield increased as the extractant concentration increased. Within the evaluation range for concentration values, slightly low values around 27% were observed for a 0.1-mol/L extractant concentration; on the other hand, values as high as 97% or 99% were obtained for concentration values between 0.4 mol/L and 0.5 mol/L.
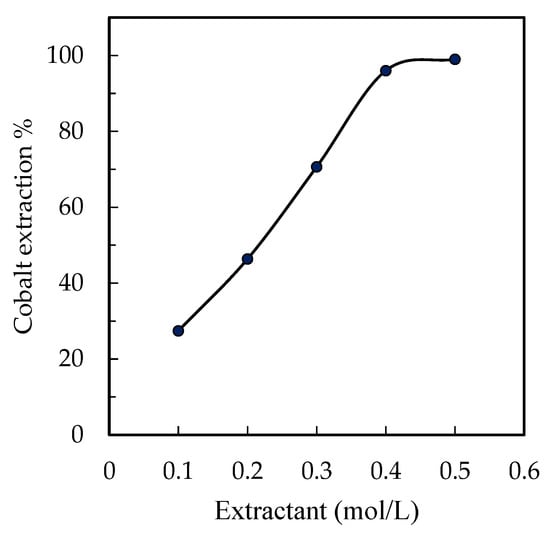
Figure 8.
Effect of extractant concentration: extraction at A/O = 1, Xi = 11 g/L, pH = 6, time = 12 min, and temperature = 22 ± 1 °C.
3.5. Extraction Kinetics
Contact time is a key parameter for defining an extraction process. Based on preliminary tests, an evaluation range for contact time between 2 min and 30 min was used. Figure 9 shows that extraction percentage increased as the contact time increased. Within the evaluation range, there were relatively high values in the extraction percentage that varied from 57% for a contact time of 2 min, up to recovery values as high as 98% from 10 min of operation.
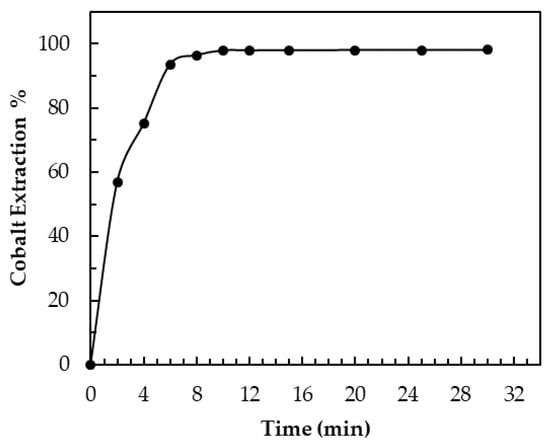
Figure 9.
Extraction at A/O = 1, Xi = 10.2 g/L, [Cyanex 272] = 0.4 mol/L, pH = 6, and temperature = 22 ± 1 °C.
3.6. Extraction Isotherm and Stages
The concentration experimental data was obtained for each phase and is represented in graphical form, with the aqueous phase in the horizontal axis and the organic phase in the vertical axis. The correlation between the concentration of cobalt in the organic phase ([Co]org) and the aqueous phase ([Co]aq) was defined by Equation (4), with: a = 0.005634419 and b = 10198.184. Figure 10 shows the isotherm from experimental data for cobalt extraction.
[Co]org = b (1 − e−a[Co]aq).
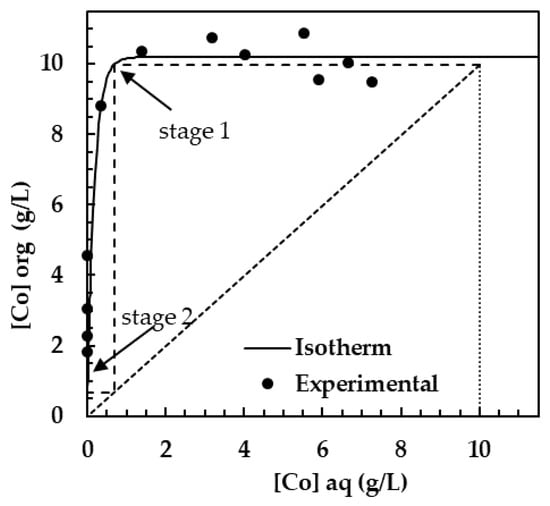
Figure 10.
Extraction stages at A/O = 1, Xi = 10 g/L, Xf = 12.18 mg/L, [Cyanex 272] = 0.4 mol/L, pH = 6, time = 10 min, and temperature = 22 ± 1 °C.
Calculation of Theoretical Stages
Based on the proposed isotherm model and the McCabe–Thiele method using iterative software, the extraction steps were calculated by performing parameter variations, such as the aqueous-to-organic-phase ratio (A/O) and the initial concentration of aqueous phase (Xi). This method allowed for obtaining the concentration profiles through steps and a proper extraction process. For an initial concentration of 10 g/L of cobalt in sulfate medium in the aqueous phase, two theoretical extraction stages were obtained. With a rate of A/O = 1.0 and a final concentration of cobalt (Xf) of 12.18 mg/L, the calculation of these steps is shown in Figure 10.
In the extraction study in the continuous mixer-settler, a flow of 5.5 mL/min was used for the organic phase and a flow of 5.5 mL/min was used for the aqueous phase (A/O = 1), obtaining yield of global extraction of 99%, which allowed for validation of the results obtained by the McCabe–Thiele method. The equipment is shown in the Figure 11.

Figure 11.
Extraction of cobalt in the continuous mixer-settler.
In order to regenerate the extractant and obtain a cobalt electrolyte solution for subsequent electrodeposition, the correlation between the concentration of cobalt in the aqueous phase ([Co]aq) and the organic phase ([Co]org) was defined by Equation (6):
[Co]aq = 23.1338 [Co]org.
For an initial concentration of 9.630 g/L of cobalt in the organic phase, two theoretical extraction stages were obtained, with a rate of O/A = 1.5 and a final concentration of cobalt of 37.87 mg/L. The calculation of these steps is shown in Figure 12.
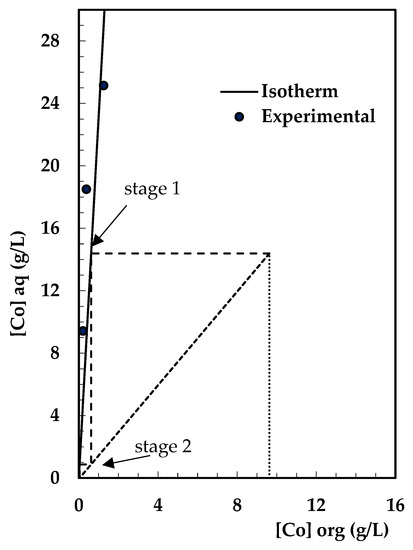
Figure 12.
Stripping stages at O/A = 1.5, Xi = 9630 mg/L, Xf = 37.87 mg/L, [H2SO4] = 1 mol/L, time = 4 min, and temperature = 22 ± 1 °C.
In the stripping operation in the continuous mixer-settler, a flow of 11.0 mL/min was used for the aqueous phase and that of 16.5 mL/min for the organic phase (O/A = 1.5), obtaining a yield of global extraction of 97% using a single extraction stage after 40 min of operation, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 13 shows the UV–VIS spectra obtained in the organic phase, which shows that the organic solution could be regenerated.
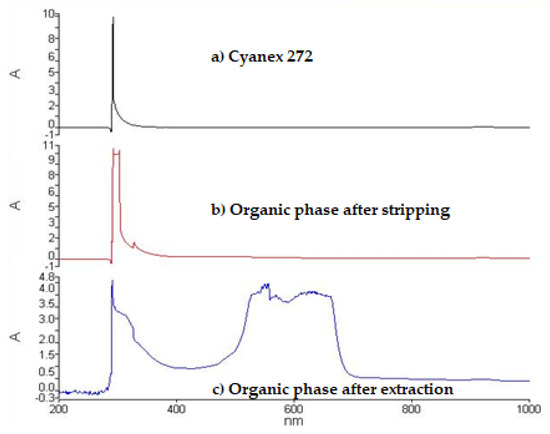
Figure 13.
UV-VIS spectra: (a) Cyanex 272 in kerosene, (b) organic phase after stripping, and (c) organic phase complex cobalt–Cyanex 272 after extraction.
3.7. Electroplating
Cobalt was recovered from a cobalt solution with a concentration of 9 g/L using a lead anode and a stainless-steel cathode. In Table 3, the results of the current efficiency are shown. As the current was increased, the current efficiency was higher. This implies that high values of current allow for obtaining cobalt deposition closer to the theoretical deposition mass.

Table 3.
Results of the electrodeposition of cobalt.
The Figure 14 shows the cobalt layer deposited on the stainless-steel cathode after removing it from the electrolytic cell.
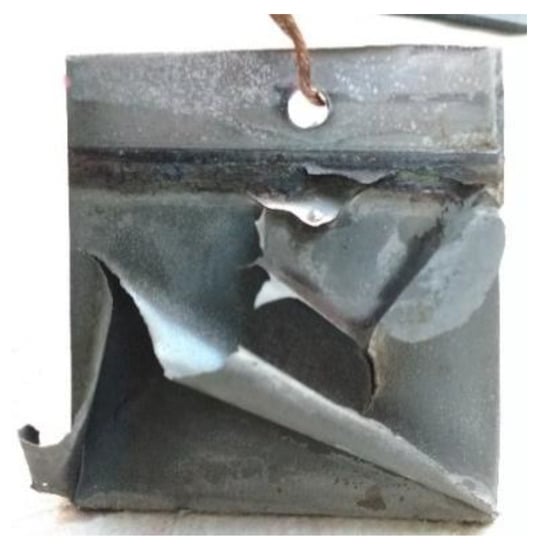

Figure 14.
Cobalt deposited in the cathode.
4. Conclusions
A process for the recovery of cobalt from spent lithium-ion mobile phone batteries has been proposed and analyzed. The process involved mechanical conditioning of the batteries, leaching, liquid–liquid extraction, and electrodeposition. The best conditions for the selective separation of cobalt from the leaching-based treatment step, using the commercial extractant Cyanex 272 dissolved in kerosene, were defined. It has been determined that the extraction yields were higher, in the range 97–99%, for pH between 6 and 7 and concentration of extractant between 0.4 mol/L and 0.5 mol/L. It is important to mention that the temperature was ambient; thus, no external energy input was required in this stage.
A mathematical model to define the number of extraction and stripping steps for cobalt recovery was established, and its reliability was tested in a continuous process in an experimental mixer-settler system. The best conditions were established for the electrodeposition of cobalt. It has been determined that increasing the current also increases the current efficiency.
The proposed process has proved to be efficient for the recovery of cobalt from spent lithium-ion mobile phone batteries and has the potential to be scaled to an industrial level, allowing the second use of waste materials and the recovery of high-value metal.
Author Contributions
All the authors made significant contributions to the development of the experimental tests, the analysis of results, and the writing of this manuscript.
Funding
The authors wish to thank to Direccción de Apoyo a la Investigación y Posgrado of Universidad de Guanajuato for the financial support given to this project, 1078/2016.
Acknowledgments
To Enrique Villegas of Cytec Solvay for supplying the extractants. We thank Dra Marina Vega of the Institute of Geology of the UNAM and M.I.Q. Paloma Eloisa Ramírez of the Universidad de Guanajuato for their assistance in DRX analysis. Daniel Quintero Almanza thanks the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT, Mexico) for the scholarship granted for his Master degree studies.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; nor in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2017; United Nations University (UNU), International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Bonn, Germany; Geneva, Switzerland; Viena, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Tan, Q.; Dong, Q. Potential recycling availability and capacity assessment on typical metals in waste mobile phones: A current research study in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Ren, Y. Prediction of various discarded lithium batteries in China. IEEE Int. Symp. Sustain. Syst. Technol. 2012, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnes, A.; Pospiech, B. A brief review on hydrometallurgical technologies for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horeh, N.B.; Mousavi, S.M.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Bioleaching of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion mobile phone batteries using Aspergillus Niger. J. Power Sources 2016, 320, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Su, X.; An, L. Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaltonen, M.; Peng, C.; Wilson, B.; Lundström, M. Leaching of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Recycling 2017, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, J.; Gago, E.J.; Girard, A. Processes and technologies for the recycling and recovery of spent lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Cao, H.; Sun, Z. A Mini-Review on Metal Recycling from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Engineering 2018, 4, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Sohn, J.S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Development of a metal recovery process from Li-ion battery wastes. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 79, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R. Hydrometallurgical processing of spent lithium ion batteries (LIBs) in the presence of a reducing agent with emphasis on kinetics of leaching. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, G.P.; Manjanna, J.; Pai, K.V.; Vadavi, R.; Keny, S.J.; Tripathi, V.S. Recovery of valuable metal ions from the spent lithium-ion battery using aqueous mixture of mild organic acids as alternative to mineral acids. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, G.P.; Pai, K.V.; Santhosh, G.; Manjanna, J. Dissolution of cathode active material of spent Li-ion batteries using tartaric acid and ascorbic acid mixture to recover Co. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 161, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, G.P.; Pai, K.V.; Manjanna, J.; Keny, S.J. Use of mild organic acid reagents to recover the Co and Li from spent Li-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dunn, J.B.; Zhang, X.X.; Gaines, L.; Chen, R.J.; Wu, F.; Amine, K. Recovery of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries with organic acids as leaching reagents and environmental assessment. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, G.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, L.; Kong, F.; Qiu, J. Study on Separation of Cobalt and Lithium Salts from Waste Mobile-phone Batteries. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; He, Y. Lithium recycling and cathode material regeneration from acid leach liquor of spent lithium-ion battery via facile co-extraction and co-precipitation processes. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, G.; Xu, S.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Thermal treatment process for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Efficient and economical recovery of lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese from cathode scrap of spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nadi, Y.A. Solvent Extraction and Its Applications on Ore Processing and Recovery of Metals: Classical Approach. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2017, 46, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Senanayake, G.; Sohn, J.; Shin, S.M. Recovery of cobalt sulfate from spent lithium ion batteries by reductive leaching and solvent extraction with Cyanex 272. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 100, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; He, F.; Zhao, J.; Sui, N.; Xu, L.; Liu, H. Extraction and separation of cobalt(II), copper(II) and manganese(II) by Cyanex272, PC-88A and their mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 93, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Han, D.; Zuo, X. Recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion batteries with chemical deposition and solvent extraction. J. Power Sources 2005, 152, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Han, D.; Yang, M.; Cui, M.; Hou, X. Recovery of metal values from a mixture of spent lithium-ion batteries and nickel-metal hydride batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 84, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanong, K.; Tran, L.-H.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.-F. Recovery of Zn (II), Mn (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) from the unsorted spent batteries using solvent extraction, electrodeposition and precipitation methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, I.G.; Alex, P.; Bidaye, A.C.; Suri, A.K. Electrowinning of cobalt from sulphate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 80, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.G.; Singh, P.; Muir, D.M. Electrowinning of cobalt from sulphate solutions contaminated with organic impurities. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 65, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Wei, R.; Weng, J.; Wang, J. Investigation of a commercial lithium-ion battery under overcharge/over-discharge failure conditions. RSC Adv. 2018, 58, 33414–33424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Godinez, M.A. Estudio de lixiviación para la recuperación de cobalto, litio, cobre, aluminio y niquel de las baterias de teléfonos móviles (Spanish). Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Guanajuato, Guanajuato, Mexico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, H.A.; Bahri, P.A.; Rumball, J.A.; Barnard, K.R. Modelling cobalt extraction with Cyanex 272. In Proceedings of the International Solvent Extraction Conference 2008—Volume I, Tucson, AZ, USA, 15–19 September 2008; pp. 459–465. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).