Novel Approaches for Solving the Capacity Fade Problem during Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
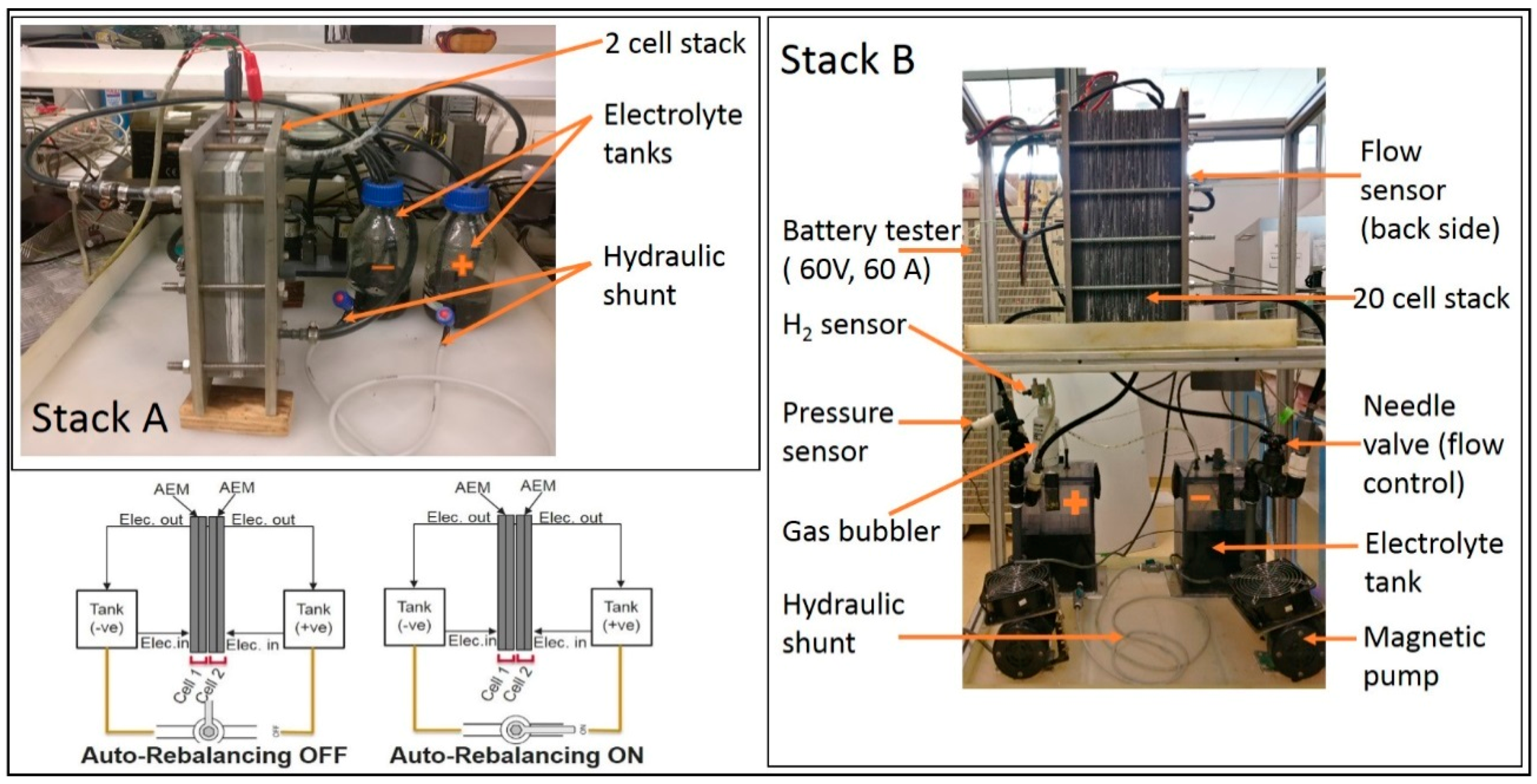
2.1. Hydraulic Shunt Test
2.2. Stack with a Combination of AEM and CEM
3. Results and Discussion
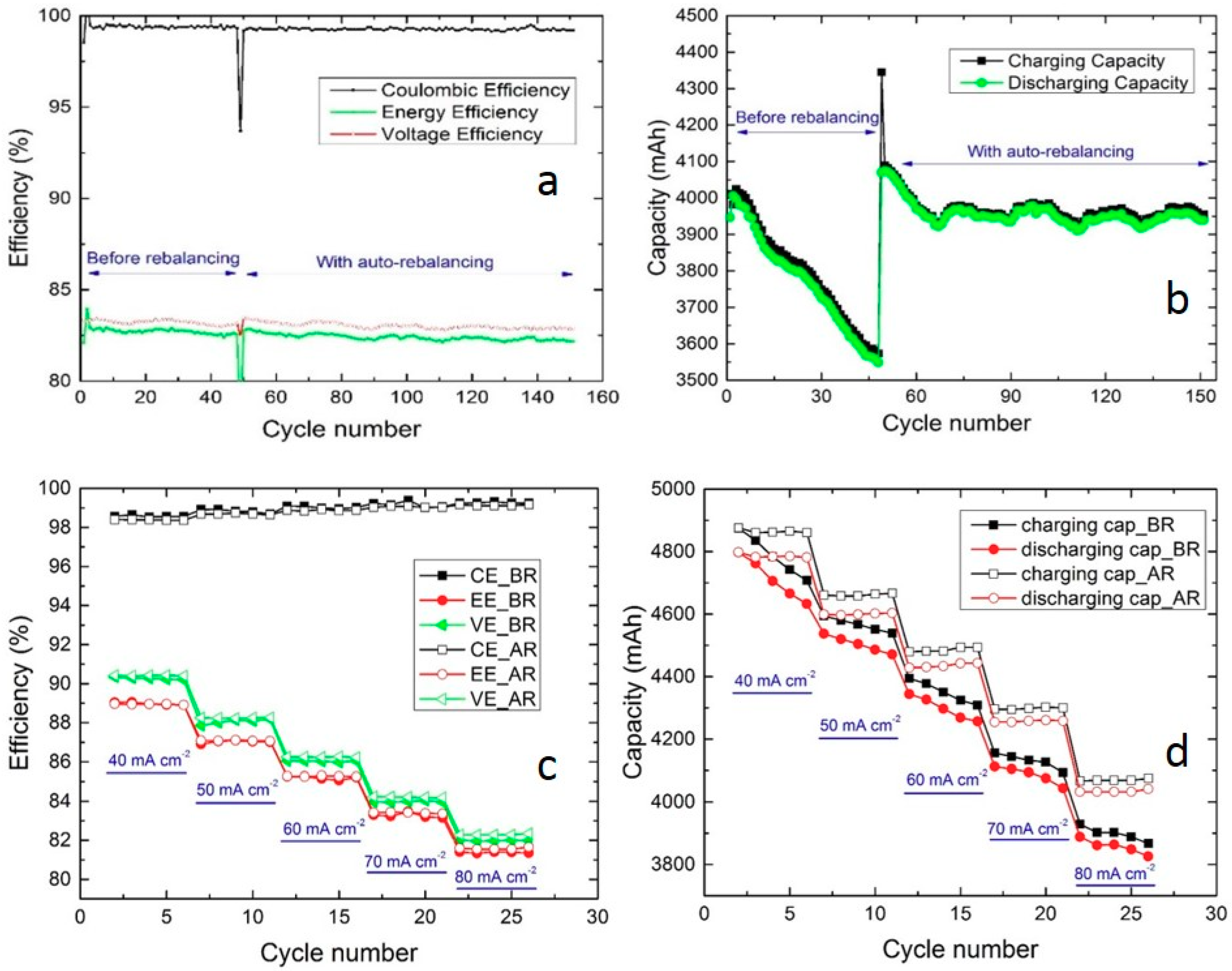
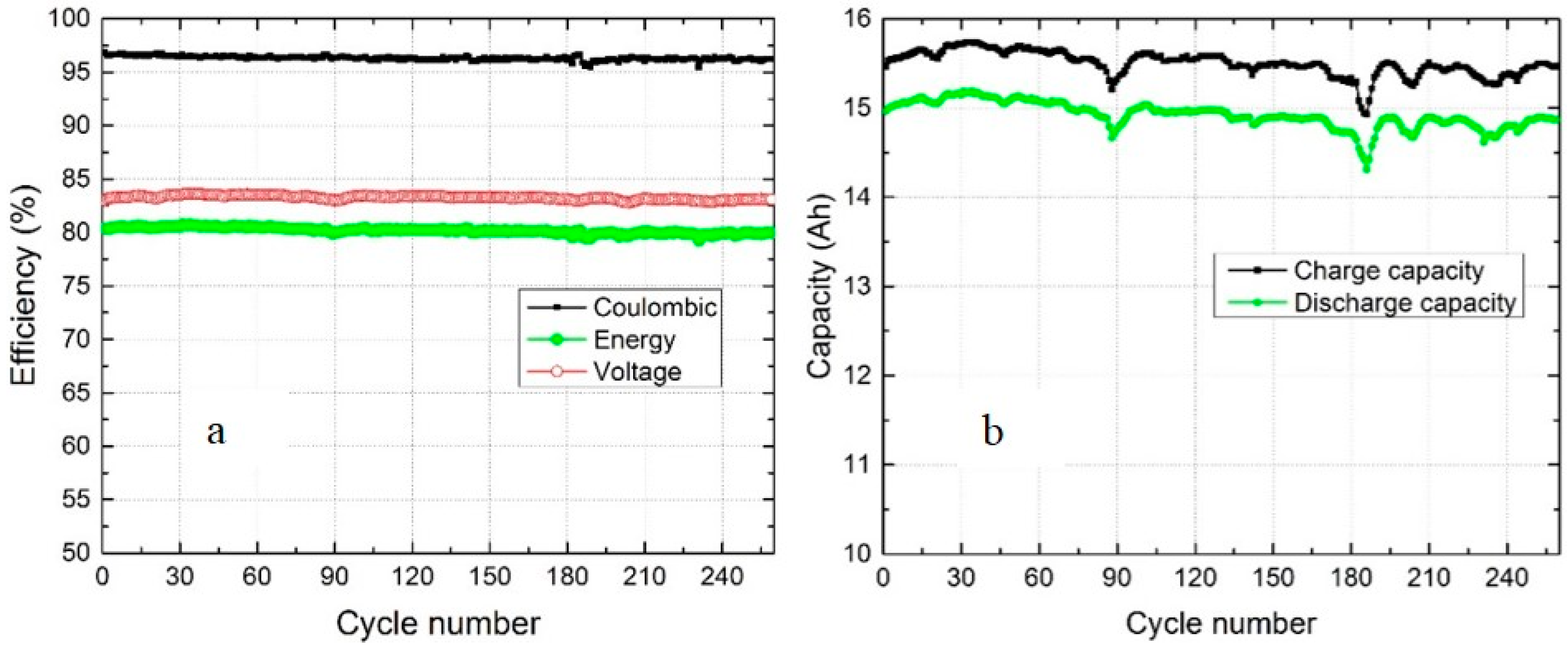
3.1. Hydraulic Shunt of Electrolyte Tanks
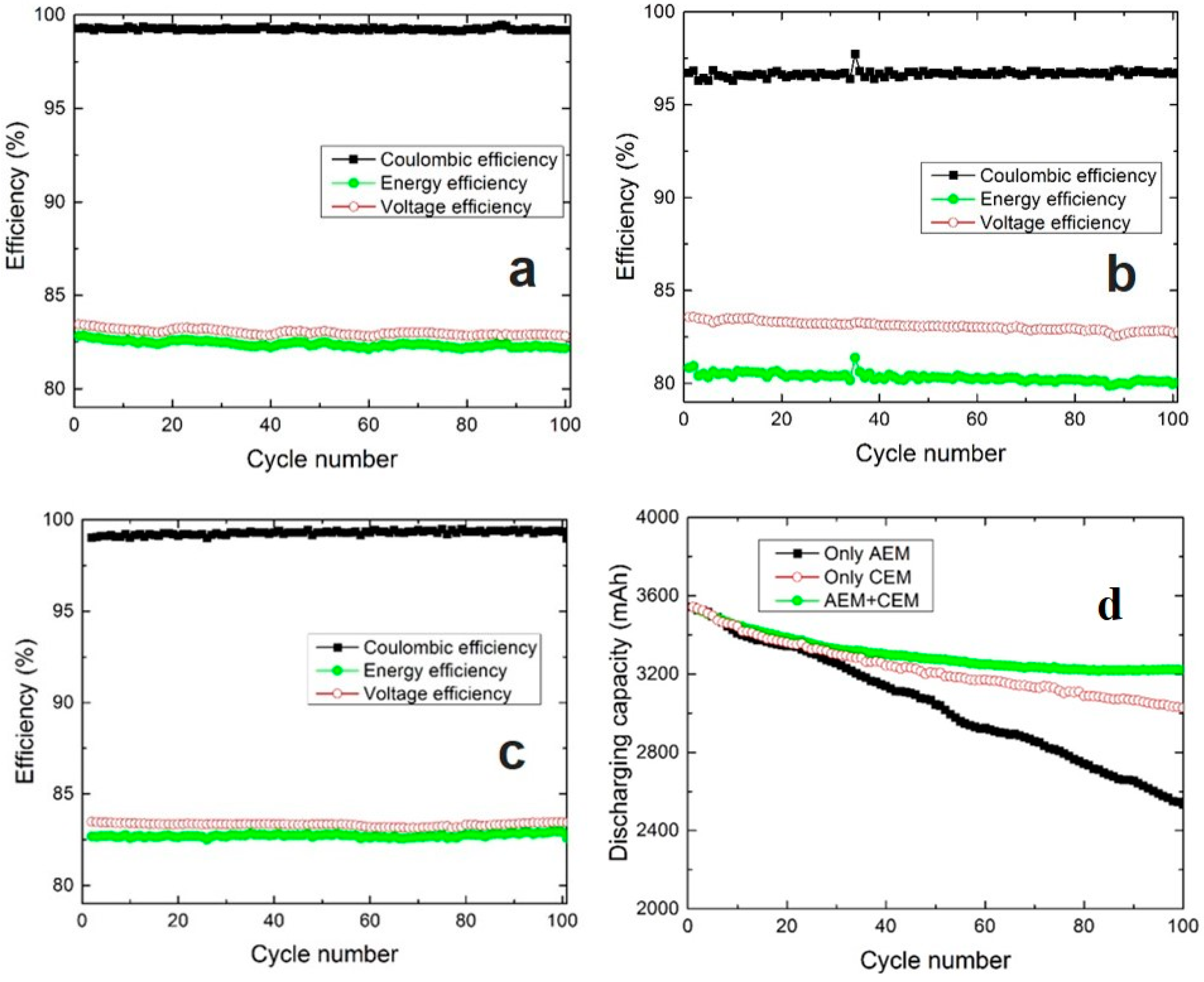
3.2. Use of a Combination of AEM and CEM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acronym | Definition |
| VRFB | Vanadium redox flow battery |
| CEM | Cation exchange membrane |
| AEM | Anion exchange membrane |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| CE | Coulombic efficiency |
| EE | Energy efficiency |
| VE | Voltage efficiency |
| SOC | State of charge |
References
- Poullikkas, A. A comparative overview of large-scale battery systems for electricity storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotto, P.; Guarnieri, M.; Moro, F. Redox flow batteries for the storage of renewable energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Lim, T.M.; Menictas, C.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Review of material research and development for vanadium redox flow battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 101, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Kronander, A.; Tang, A.; Wang, D.-W.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Membrane Permeability Rates of Vanadium Ions and Their Effects on Temperature Variation in Vanadium Redox Batteries. Energies 2016, 9, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Luo, Q. Investigations on transfer of water and vanadium ions across Nafion membrane in an operating vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, L.; Nie, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, X.; Li, B.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z. In-situ investigation of vanadium ion transport in redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Chieng, S.; Kazacos, M.S. Water transport study across commercial ion exchange membranes in the vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 133, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.; Wei, X.; Li, B.; Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Sprenkle, V. Capacity decay and remediation of Nafion-based all-vanadium redox flow batteries. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieng, S.C. Membrane Processes and Membrane Modification for Redox Flow Battery Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Gu, S.; Gong, K. Multiple-Membrane Multiple-Electrolyte Redox Flow Battery Design. U.S. Patent 9,640,826, 14 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, T.; Kazacos, M.S. Modification of anion-exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Power Sources 1996, 63, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Modification of membranes using polyelectrolytes to improve water transfer properties in the vanadium redox battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.; Zhai, M.; Li, J.; Wei, G. Amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by radiation-induced graft copolymerization of styrene and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate into PVDF film for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, F.J.; Schmidt, T.J.; Gubler, L. Tackling capacity fading in vanadium flow batteries with amphoteric membranes. J. Power Sources 2017, 368, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, M. A novel amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by radiation-induced grafting α-methylstyrene and N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407–408, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, T. Bipolar membrane technology and its applications. Membr. Technol. 2000, 2000, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibel, O.; Schmidt, T.J.; Gubler, L. Bifunctional ion-conducting polymer electrolyte for the vanadium redox flow battery with high selectivity. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, S.; Furusato, K.; Miyabayashi, M.; Satou, K.; Tanimoto, T.; Naitou, S. Redox Flow Battery. U.S. Patent 6,764,789, 27 September 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Xi, J.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, X. Reduction of capacity decay in vanadium flow batteries by an electrolyte-reflow method. J. Power Sources 2017, 338, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Menictas, C. The vanadium redox battery for emergency back-up applications. In Proceedings of the Telecommunications Energy Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 2–5 April 1997; pp. 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafner, K.; Becker, M.; Turek, T. Capacity balancing for vanadium redox flow batteries through electrolyte overflow. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, E.; Benjamin, A.; Dennison, C.R.; Chen, D.; Hickner, M.A.; Kumbur, E.C. Reducing capacity fade in vanadium redox flow batteries by altering charging and discharging currents. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegri, A.; Broman, B.M. Redox Flow Battery System and Cell Stack. U.S. Patent 6475661B1, 28 January 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Huang, M.; Andy, C.; Mclennan, H.M.A. Redox Flow Battery and Method for Enabling Battery to Operate Continuously for Long Time. Patent CN102055000, 14 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Genders, J.D.; Hennessy, T.D.J.; Symons, P.G. Vanadium Redox Battery cell Stack. WO Patent 2,007,040,545, 23 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, A.; Wai, N.; Schweiss, R.; Whitehead, A.; Lim, T.M.; Hng, H.H. Advanced porous electrodes with flow channels for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2017, 341, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Shin, H.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Oh, S.-G.; Lee, J.Y.; Hong, Y.T. Crosslinked anion exchange membranes with primary diamine-based crosslinkers for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, S.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. State-of-charge monitoring and electrolyte rebalancing methods for the vanadium redox flow battery. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2012, 1, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhattarai, A.; Ghimire, P.C.; Whitehead, A.; Schweiss, R.; Scherer, G.G.; Wai, N.; Hng, H.H. Novel Approaches for Solving the Capacity Fade Problem during Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. Batteries 2018, 4, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4040048
Bhattarai A, Ghimire PC, Whitehead A, Schweiss R, Scherer GG, Wai N, Hng HH. Novel Approaches for Solving the Capacity Fade Problem during Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. Batteries. 2018; 4(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhattarai, Arjun, Purna C. Ghimire, Adam Whitehead, Rüdiger Schweiss, Günther G. Scherer, Nyunt Wai, and Huey Hoon Hng. 2018. "Novel Approaches for Solving the Capacity Fade Problem during Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery" Batteries 4, no. 4: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4040048
APA StyleBhattarai, A., Ghimire, P. C., Whitehead, A., Schweiss, R., Scherer, G. G., Wai, N., & Hng, H. H. (2018). Novel Approaches for Solving the Capacity Fade Problem during Operation of a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery. Batteries, 4(4), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4040048





