Effects of Alkaline Pre-Etching to Metal Hydride Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Set-Up
- (1)
- Charge at 0.1 C and discharge at 0.1 C (to ‒0.7 V vs. Hg/HgO). Record discharge capacity;
- (2)
- Charge at 0.1 C, discharge 0.1 C to 80% state-of-charge (SOC);
- (3)
- Conduct internal resistance test at 80% SOC (1st internal resistance test):
- Put in open circuit for 10 min;
- Discharge at 0.5 C for 10 s;
- Charge at 0.5 C for 10 s;
- Put in open circuit for 10 min;
- Discharge at 2 C for 10 s;
- Charge at 2 C for 10 s;
- Put in open circuit for 10 min;
- Calculate internal resistance.
- (4)
- Charge at 0.1 C back from 80% SOC to 100% SOC;
- (5)
- Conduct 4 more capacity tests at 0.2 C charge rate and 0.1 C discharge rate. Record discharge capacities;
- (6)
- Repeat step 3 (2nd internal resistance test);
- (7)
- Repeat step 4;
- (8)
- Conduct rate test:
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 0.1 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 0.2 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 0.5 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 1 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 2 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 3 C;
- Charge at 0.2 C, discharge at 5 C.
- (9)
- Repeat step 3 (3rd internal resistance test).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Alloys Selection
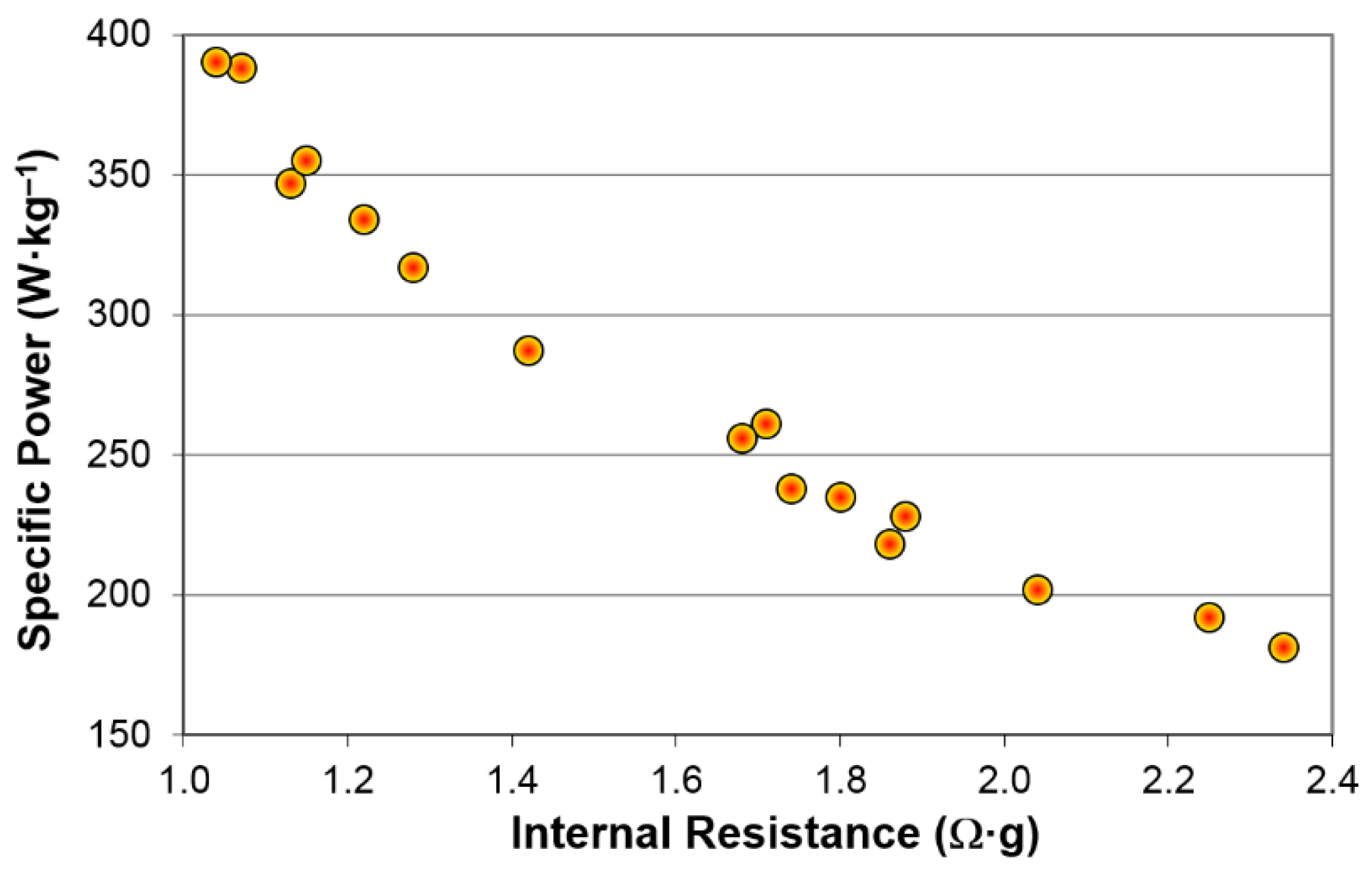
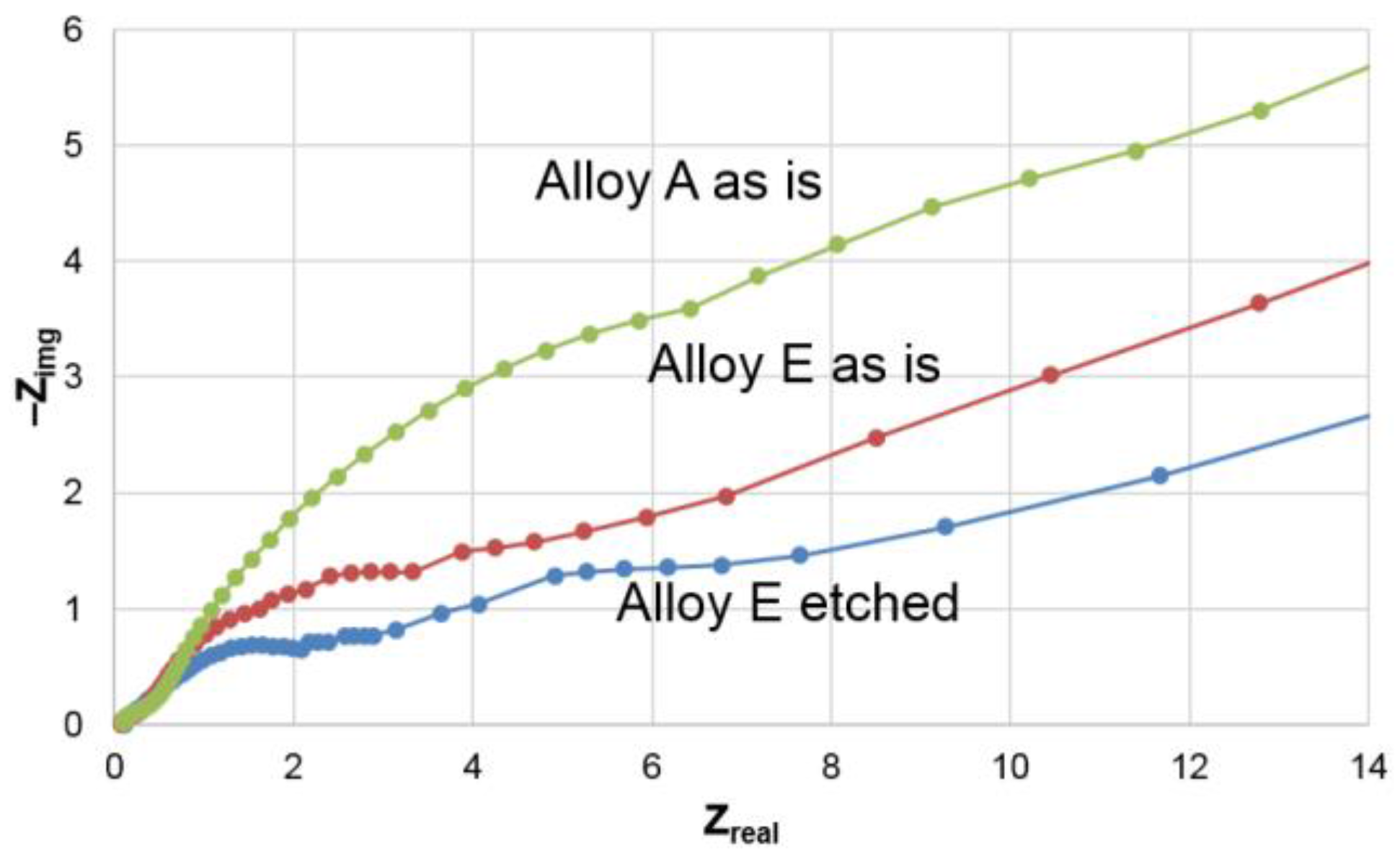
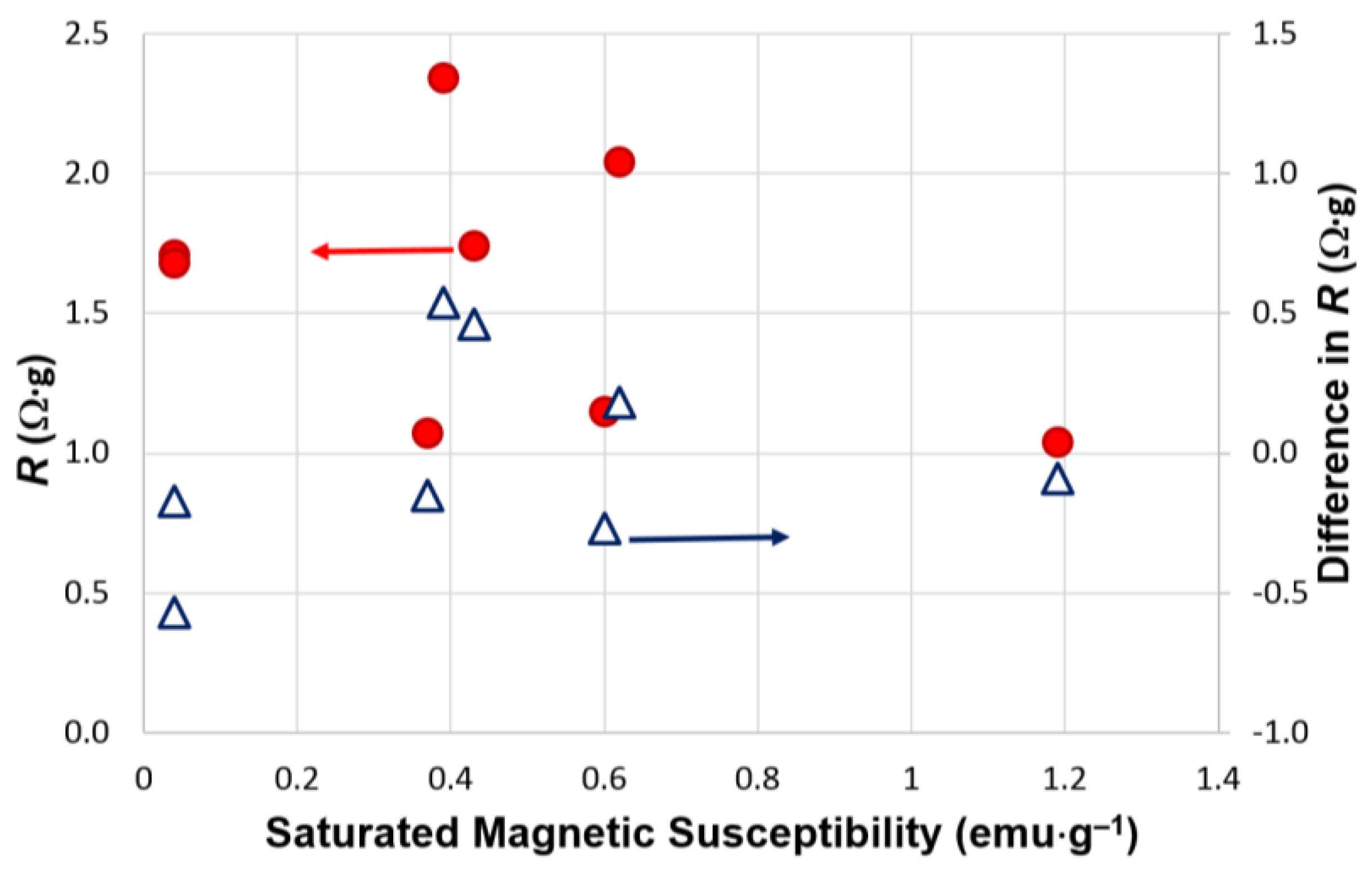
3.2. Electrochemical Results
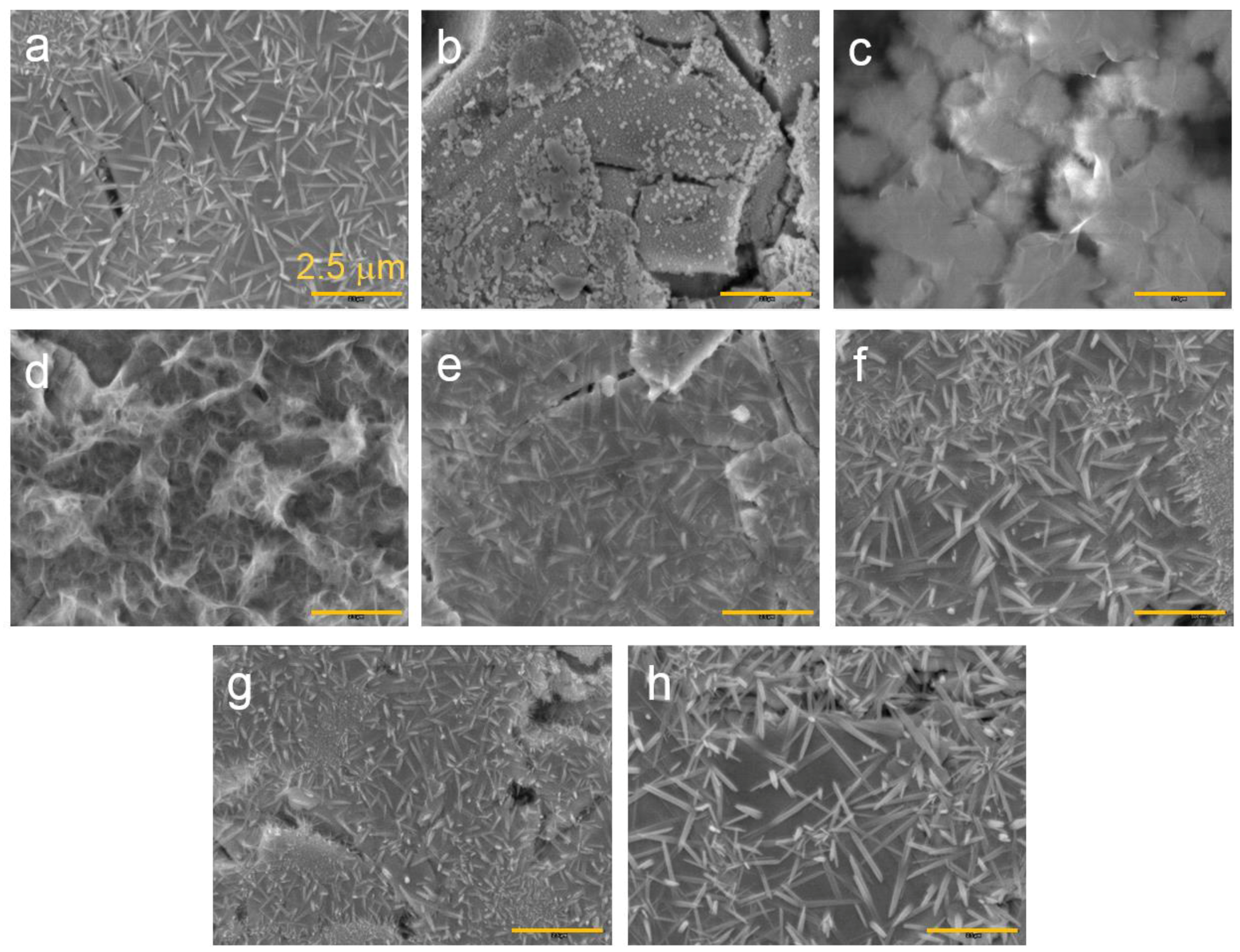
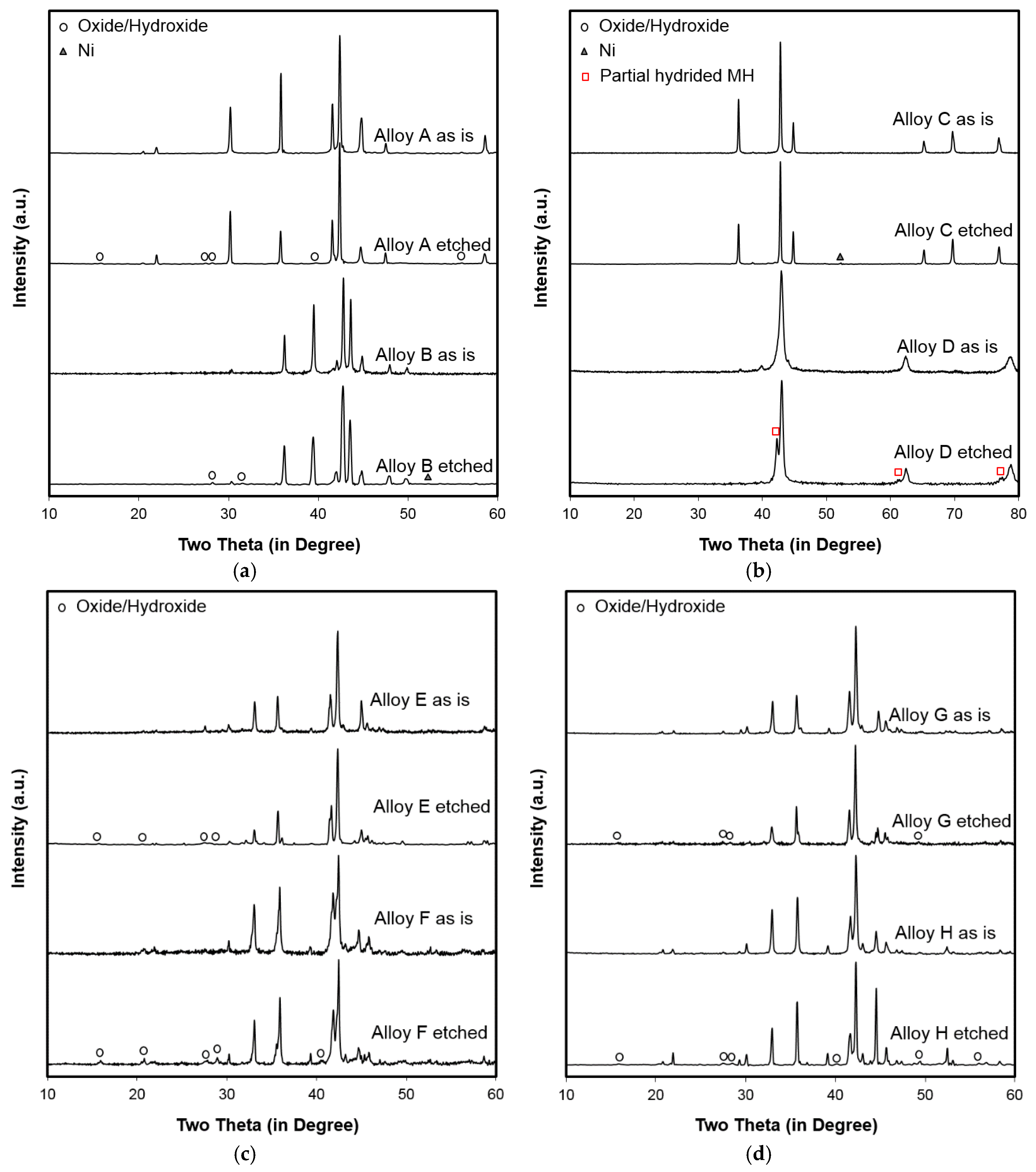
3.3. Microsnalysis of the Activated Surface
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MH | Metal hydride |
| IMC | Intermetallic compound |
| Ni/MH | Nickel/metal hydride |
| BCC | Body-centered-cubic |
| TM | Transition metal |
| RE | Rare earth |
| HRD | High-rate dischargeability |
| VIM | Vacuum induction melting |
| AM | Arc melting |
| PCT | Pressure–concentration–temperature |
| ICP-OES | Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer |
| XRD | X-ray diffractometer |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SOC | State of charge |
| MS | Saturated magnetic susceptibility |
| AC | Alternative current |
| R | Internal resistance |
| P | Specific power |
| Voc | Open-circuit voltage |
References
- Young, K. Metal Hydride. In Elsevier Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Reedijk, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goo, N.H.; Woo, J.H.; Lee, K.S. Mechanism of Rapid Degradation of Nanostructured Mg2Ni Hydrogen Storage Alloy Electrode Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and the Effect of Mechanically Coating with Nickel. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 288, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.A.; Lei, Y.Q.; Wang, C.S.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, Q.D. Structure of the Secondary Phase and Its Effects on Hydrogen-storage Properties in a Ti0.7Zr0.2V0.1Ni Alloy. J. Power Sour. 1998, 75, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, J.; Young, K. Gaseous Phase and Electrochemical Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti50Zr1Ni44X5 (X = Ni, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, or Cu) for Nickel Metal hydride Battery Applications. Batteries 2016, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züttel, A.; Meli, F.; Schlapbach, L. Electrochemical and Surface Properties of Zr(VxNi1‒x)2 Alloys as Hydrogen-absorbing Electrodes in Alkaline Electrolyte. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 203, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Lei, Y.Q.; Chen, L.X.; Lu, G.L.; Pan, H.G.; Wang, Q.D. A Study on the Structure and Electrochemical Properties of La2Mg(Ni0.95M0.05)9 (M = Co, Mn, Fe, Al, Cu, Sn) Hydrogen Storage Electrode Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 376, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, S.; Magari, Y.; Murata, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ishida, J.; Nakamura, H.; Nohma, T.; Kihara, M.; Baba, Y.; Teraoka, H. Development of High-capacity Nickel-metal Hydride Batteries Using Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloys. J. Power Sour. 2006, 156, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Cao, J.; Jia, Z.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Han, S. Comparative Study on the Capacity Degradation Behavior of Pr5 Co19-type Single-phase Pr4MgNi19 and La4MgNi19 Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, J.J.G.; Buschow, K.H.J. From Permanent Magnets to Rechargeable Hydride Electrodes. J. Less Common Met. 1987, 129, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Nei, J. Structure, Hydrogen Storage, and Electrochemical Properties of Body-centered-cubic Ti40V30 Cr15Mn13X2 alloys (X = B, Si, Mn, Ni, Zr, Nb, Mo, and La). Batteries 2015, 1, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Wong, D.F.; Wang, L. Structural, Hydrogen Storage, and Electrochemical Properties of Laves Phase-related Body-centered-cubic Solid Solution Metal Hydride Alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 21489–21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Bendersky, L.A. A Technical Report of the Robust Affordable Next Generation Energy Storage System-BASF program. Batteries 2016, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Chao, B.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Bendersky, L.A.; Wang, K.; Chiu, C. The Correlation of C14/C15 Phase Abundance and Electrochemical Properties in the AB2 Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J. The Current Status of Hydrogen Storage Alloy Development for Electrochemical Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 4574–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.; Chang, S.; Lin, X. C14 Laves Phase Metal Hydride Alloys for Ni/MH Batteries Applications. Batteries 2017, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Seiler, A.; Siegmann, H.C.; Waldkirch, T.V.; Zücher, P.; Brundle, C.R. Self Restoring of the Active Surface in LaNi5. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 1979, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetcenko, M.A.; Young, K.; Ovshinsky, S.R.; Reichman, B.; Koch, J.; Mays, W. Modified Electrochemical Hydrogen Storage Alloy Having Increased Capacity, Rate Capability and Catalytic Activity. US Patent 6,740,448, 25 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Meli, F.; Schlapbach, L. Surface Analysis of AB5-type electrodes. J. Less Common Met. 1991, 172, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broom, D.P.; Kemali, M.; Ross, D.K. Magnetic Properties of Commercial Metal Hydride Battery Materials. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 255, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, L.; Wen, M.F.; Tong, M.; Chen, D.M.; Tian, Y.W.; Zhai, Y.C. Surface Modification of AB2 and AB5 Hydrogen Storage Alloy Electrodes by the Hot-charging Treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2001, 17, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Peng, F.; Kontos, S.; Noréus, D. Improved NiMH Performance by a Surface Treatment that Creates Magnetic Ni-clusters. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 9933–9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Shen, Y.; Şahin, E.Q.; Noréus, D.; Öztürk, T. Activation Behavior of an AB2 Type Metal Hydride Alloy for NiMH Batteries. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 9948–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Noréus, D. Metal hydride electrodes: The Importance of Surface Area. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chao, B.; Liu, Y.; Nei, J. Microstructures of the Oxides on the Activated AB2 and AB5 Metal Hydride Alloys Surface. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 606, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Meng, T.; Nei, J.; Wu, X. Studies on Incorporation of Mg in Zr-based AB2 Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries 2016, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Nei, J. Effects of Vanadium/nickel Contents in Laves Phase-related Body-centered-cubic Solid Solution Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries 2015, 1, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraoka, H. Development of Low Self-Discharge Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery. Available online: http://www.scribd.com/doc/9704685/Teraoka-Article-En (accessed on 9 April 2016).
- Kai, T.; Ishida, J.; Yasuoka, S.; Takeno, K. The Effect of Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery’s Characteristics with Structure of the Alloy. In Proceedings of the 54th Battery Symposium in Japan, Osaka, Japan, 7–9 October 2013; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.J.; Kitayama, K.; Suda, S. La and Ce-incorporation Effects on the Surface Properties of the Fluorinated (Ti,Xr)(Mn,Cr,Ci)2 Hydriding Alloys. Vacuum 1996, 47, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J. Activation behaviour of ZrCrNiM0.05 metal hydride electrode (M = La, Mm (misch metal), Nd). J. Alloys Compd. 1992, 185, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Chang, I.; Cho, W.I.; Cho, B.W.; Jang, H.; Lee, S.R.; Yun, K.S. Electrode Characteristics of the Cr and La Doped AB2-type Hydrogen Storage Alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2001, 26, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.J.; Sandrock, G.; Suda, S. Surface and Metallographic Microstructure of the La-added AB2 Compound (Ti, Zr)(Mn, Cr, Ni)2. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 231, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Latroche, M.; Percheron-Guégan, A. Effects of Lanthanum or Cerium on the Equilibrium of ZrNi1.2Mn0.6V0.2 Cr0.1 and Its Related Hydrogenation Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 248, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.G.; Lei, Y.Q.; Shu, K.Y.; Lin, G.F.; Zhang, Q.A.; Zhang, W.K.; Zhang, X.B.; Lu, G.L.; Wang, Q.D. Contribution of Rare-earths to Activation Property of Zr-based Hydride Electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.C.; Li, S.; Ji, S.J. The Effects of the Substitution of Ti and La for Zr in ZrMn0.7V0.2 Co0.1Ni1.2 Hydrogen Storage Alloys on the Phase Structure and Electrochemical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446, 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.X. Effects of Addition of Rare-earth Element on Electrochemical Characteristics of ZrNi1.1Mn0.5V0.3 Cr0.1 Hydrogen Storage Alloy Electrodes. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 319, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Huang, B.; Reichman, B.; Fetcenko, M.A. Effect of Molybdenum Content on Structural, Gaseous Storage, and Electrochemical Properties of C14-predominant AB2 Metal Hydride Alloys. J. Power Sour. 2011, 196, 8815–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Wan, C.; Denys, R.V.; Yartys, V.A. Comparison of C14- and C15-predominated AB2 Metal Hydride Alloys for Electrochemical Applications. Batteries 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Meng, T.; Wong, D.F. Studies on the Synergetic Effects in Multi-phase Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries 2016, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Ouchi, T.; Nei, J.; Koch, J.M.; Lien, Y. Comparison among constituent phases in superlattice metal hydride alloys for battery applications. Batteries 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, J.M.; Young, K.; Nei, J.; Hu, C.; Reichman, B. Performance comparison between AB5 and superlattice metal hydride alloys in sealed cells. Batteries 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Young, K.; Meng, T.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Partial Substitution of Cobalt for Nickel in Mixed Rare Earth Metal Based Superlattice Hydrogen Absorbing Alloy—Part 1 Structural, Hydrogen Storage and Electrochemical Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Yasuoka, S. Past, present, and future of metal hydride alloys in nickel-metal hydride batteries. In Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Metal-Hydrogen Systems, Manchester, UK, 21–25 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Young, K.; West, J.; Regalado, J.; Cherisol, K. Degradation Mechanisms of High-energy Bipolar Nickel Metal Hydride Battery with AB5 and A2B7 Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 580, S373–S377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, F.; Schlapbach, L. Magnetic Properties of LaNi5, FeTi, Mg2Ni and Their Hydrides. J. Less Common Met. 1980, 74, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Stucki, F.; Seiler, A.; Siegmann, H.C. Magnetism and Hydrogen Storage in LaNi5, FeTi and Mg2Ni. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1980, 15–18, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chao, B.; Nei, J. Microstructures of the Activated Si-containing AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy Surface by Transmission Electron Microscope. Batteries 2016, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chao, B.; Pawlik, D.; Shen, H.T. Transmission Electron Microscope Studies in the Surface Oxide on the La-containing AB2 Metal Hydride Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 672, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.H.; Fetcenko, M.A.; Ovshinsky, S.R.; Ouchi, T.; Reichman, B.; Mays, W.C. Improved Surface Catalysis of Zr-based Laves Phase Alloys for NiMH Batteries. In Hydrogen at Surface and Interfaces; Jerkiewicz, G., Feliu, J.M., Popov, B.N., Eds.; Electrochemical Society: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Chourashiya, M.G.; Park, C.; Park, C. Hydrogen Storage and Electrochemical Properties of the Ti0.32 Cr0.43−x−yV0.25FexMny (x = 0–0.055, y = 0–0.080) Alloys and Their Composites with MmNi3.99Al0.29Mn0.3 Co0.6 Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 566, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Arai, S.; Iwakura, C. Crystallographic and Electrochemical Characterization of TiV4−xNix Alloys for Nickel-metal Hydride Batteries. Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Wu, Z.; Xia, B.J.; Xu, N.X. A Ti-V-based bcc Phase Alloy for Use as Metal Hydride Electrode with High Discharge Capacity. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
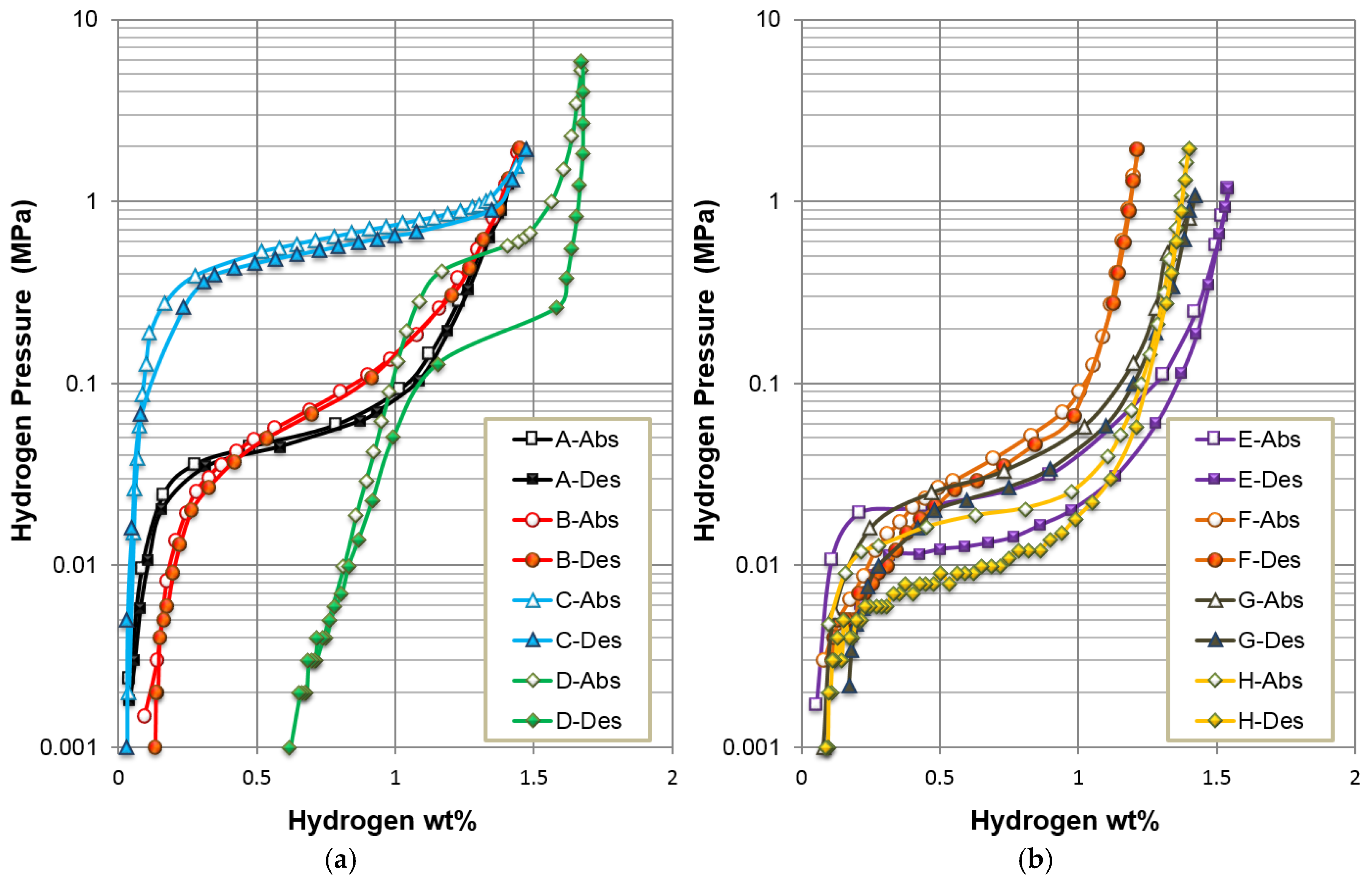
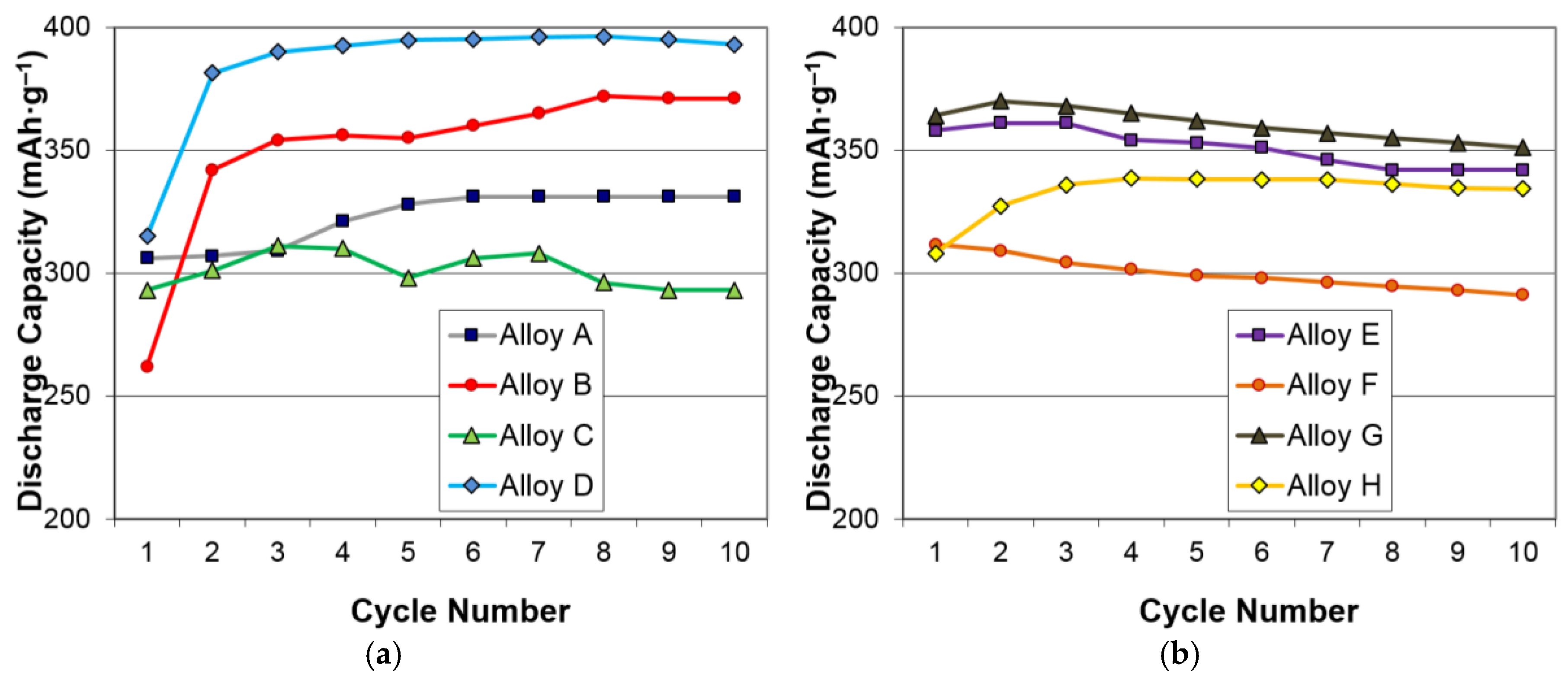
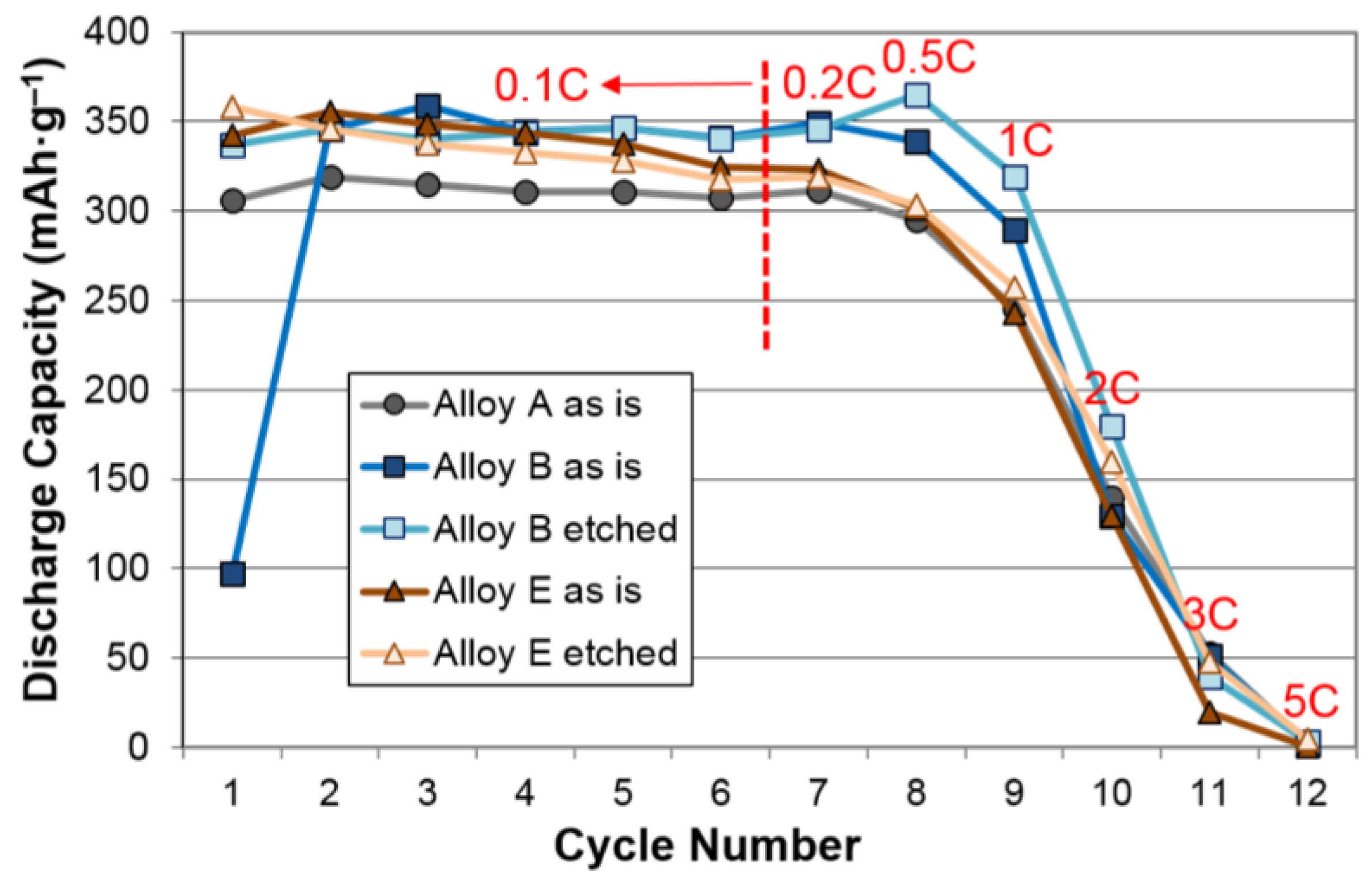
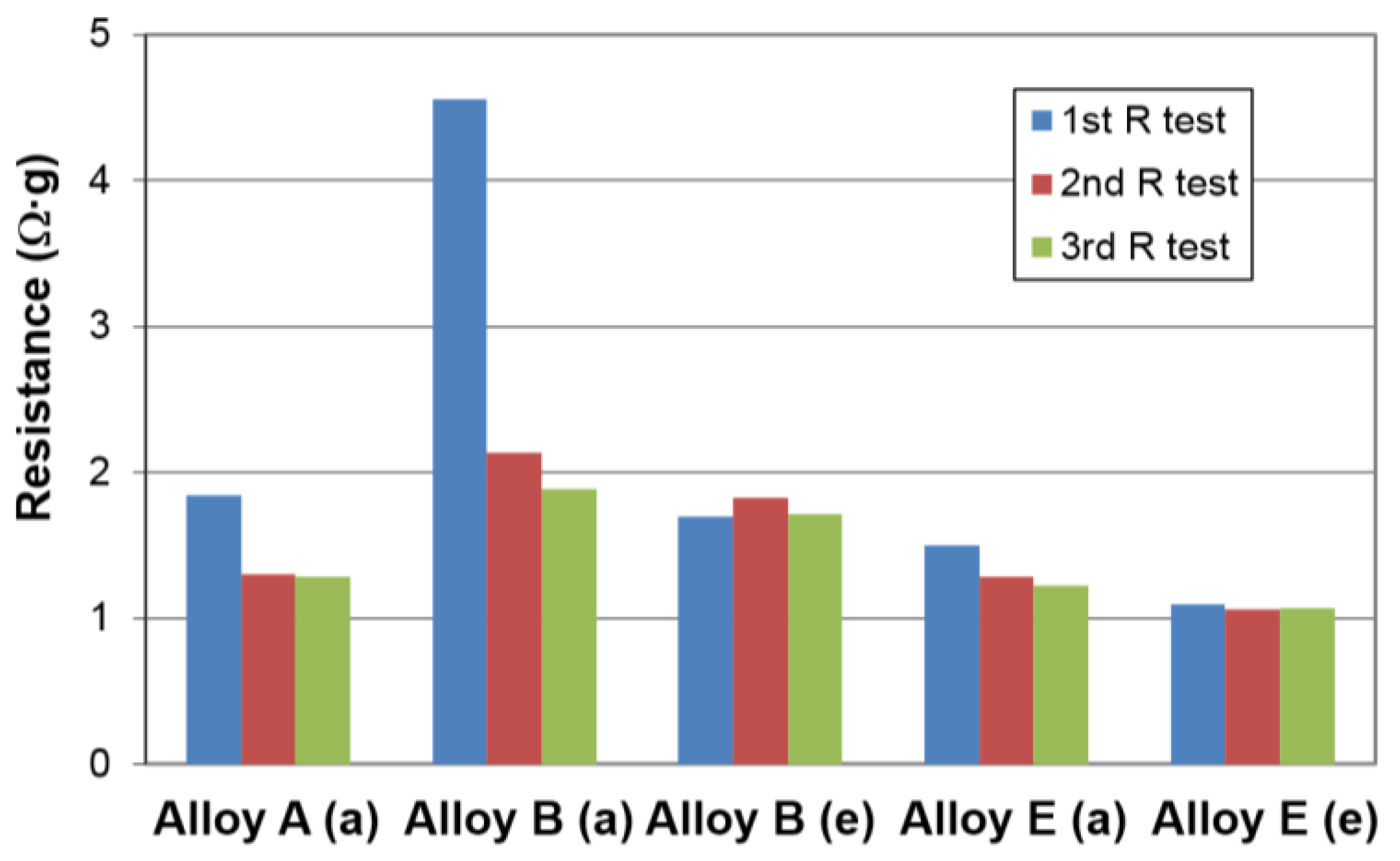
| Alloys | System | Composition | Melting | Annealing | Capacity | HRD | MS | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | AB5 | La10.5 Ce4.3Pr0.5Nd1.4Ni60 Co12.7Mn5.9Al4.7 | VIM | In vacuum | 331 | 0.99 | 0.43 | A in [13] |
| B | AB2-C14 | Zr21.5Ti12V310 Cr7.5Mn8.1 Co8Ni32.2Sn0.3Al0.4 | VIM | None | 354 | 0.90 | 0.04 | Mo0 in [37] |
| C | AB2-C15 | Zr25Ti6.5V3.9Mn22.2Fe3.8Ni38Sn0.3La0.3 | AM | None | 307 | 0.99 | 0.04 | C15 in [38] |
| D | BCC-C14 | Zr2.1Ti15.6V44 Cr11.2Mn6.9 Co1.4Ni18.5Al0.3 | VIM | None | 397 | 0.95 | 0.39 | P17 in [39] |
| E | A2B7 | La16.3Mg7Ni65.1 Co11.6 | VIM | In Ar | 361 | 0.98 | 0.37 | C in [13] |
| F | A2B7 | La6Sm13.8Mg3Ni73.8Al3.4 | VIM | In Ar | 320 | 0.99 | 0.60 | A3 in [40] |
| G | A2B7 | La11.3Pr1.7Nd5.1Mg4.5Ni63.6 Co13.6Zr0.2 | VIM | In Ar | 370 | 0.98 | 1.19 | B in [41] |
| H | A2B7 | La3.9Pr7.7Nd7.7Mg3.9Ni68.1 Co4.7Al4 | VIM | In Ar | 354 | 0.94 | 0.62 | C3 in [42] |
| Alloys | Treatment | Capacity (mAh·g‒1) | Resistance (Ω·g) | Specific Power (W·kg‒1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | None | 321 | 1.28 | 317 |
| KOH-etch | 321 | 1.74 | 238 | |
| B | None | 360 | 1.88* | 228* |
| KOH-etch | 352 | 1.71* | 261* | |
| C | None | 290 | 2.25* | 192* |
| KOH-etch | 291 | 1.68* | 256* | |
| D | None | 390 | 1.80 | 235 |
| KOH-etch | 349 | 2.34 | 181 | |
| E | None | 356 | 1.22* | 334* |
| KOH-etch | 358 | 1.07* | 388* | |
| F | None | 300 | 1.42* | 287* |
| KOH-etch | 304 | 1.15* | 355* | |
| G | None | 353 | 1.13* | 347* |
| KOH-etch | 353 | 1.04* | 390* | |
| H | None | 345 | 1.86 | 218 |
| KOH-etch | 320 | 2.04 | 202 |
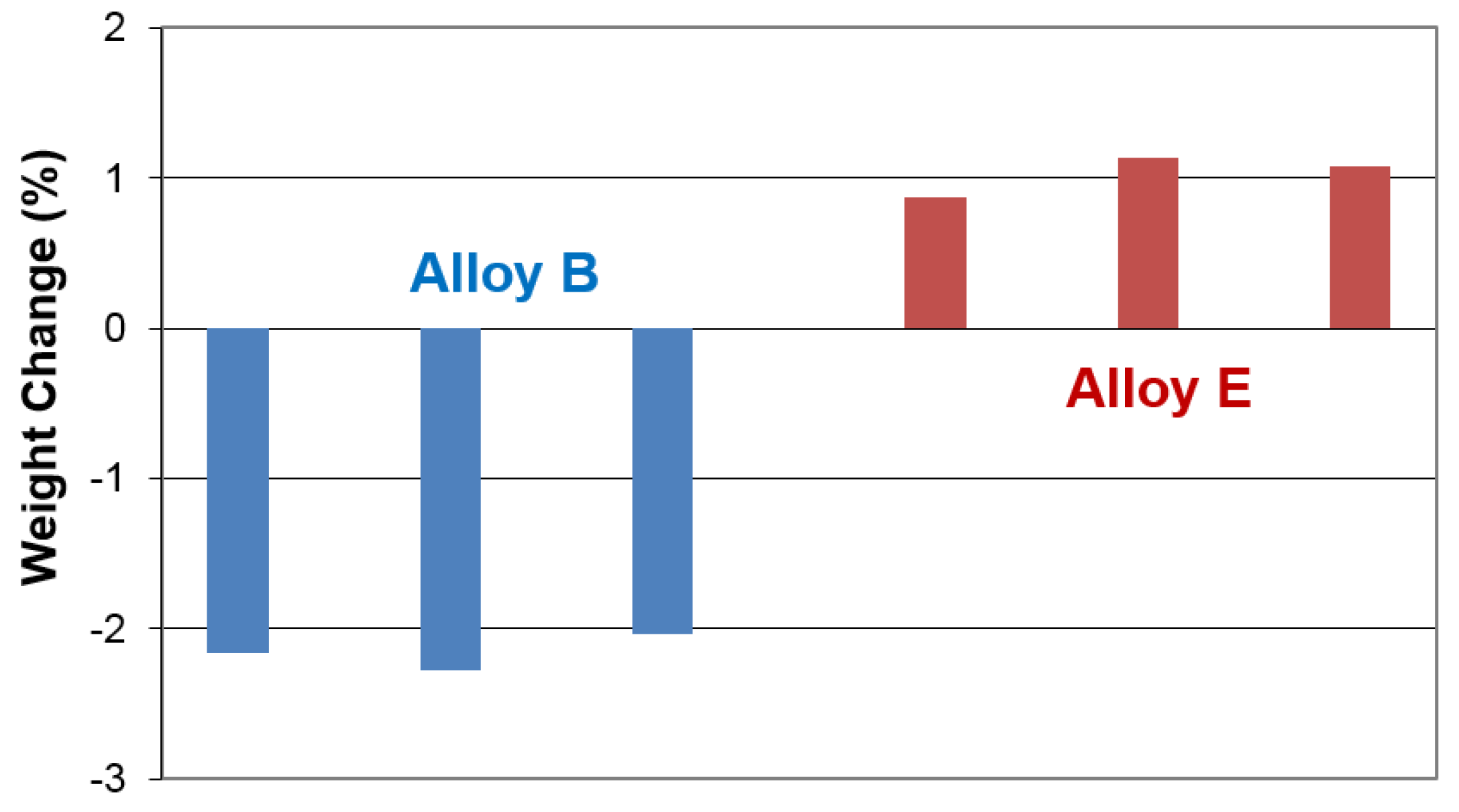
| Sample # | Substrate Weight | Electrode Wright Before | Electrode Weight After | Weight Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B 1 | 192.8 | 262.3 | 260.8 | −1.5 |
| B 2 | 182.7 | 257.4 | 255.7 | −1.7 |
| B 3 | 178.4 | 252.0 | 250.5 | −1.5 |
| E 1 | 199.5 | 279.6 | 280.3 | 0.7 |
| E 2 | 181.3 | 278.7 | 279.8 | 1.1 |
| E 3 | 186.4 | 289.0 | 290.1 | 1.1 |
| Alloy | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | LLD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 58 | 1.6 | N.D. | 29 | N.D. | 78 | N.D. | 20 | 0.012 |
| Co | N.D. | 0.1 | N.D. | 1.0 | N.D. | N.D. | 1.2 | N.D. | 0.004 |
| Cr | N.D. | 4.3 | N.D. | 48 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.054 |
| Fe | N.D. | N.D. | 1.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.002 |
| Mg | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.5 | N.D. | 0.001 |
| Mn | N.D. | 2.0 | 0.1 | 8.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.001 |
| Ni | N.D. | 6.0 | 0.3 | 5.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.001 |
| Ti | N.D. | 150 | 7 | 416 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.004 |
| V | N.D. | 125 | 92 | 988 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.013 |
| Zr | N.D. | 495 | 518 | 309 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.002 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, T.; Young, K.-H.; Hu, C.; Reichman, B. Effects of Alkaline Pre-Etching to Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries 2017, 3, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040030
Meng T, Young K-H, Hu C, Reichman B. Effects of Alkaline Pre-Etching to Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries. 2017; 3(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Tiejun, Kwo-Hsiung Young, Chaolan Hu, and Benjamin Reichman. 2017. "Effects of Alkaline Pre-Etching to Metal Hydride Alloys" Batteries 3, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040030
APA StyleMeng, T., Young, K.-H., Hu, C., & Reichman, B. (2017). Effects of Alkaline Pre-Etching to Metal Hydride Alloys. Batteries, 3(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries3040030






