Failure Mechanisms of Nickel/Metal Hydride Batteries with Cobalt-Substituted Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloy Anodes at 50 °C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
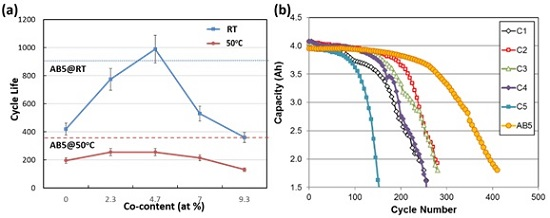
3.1. Cycle Life
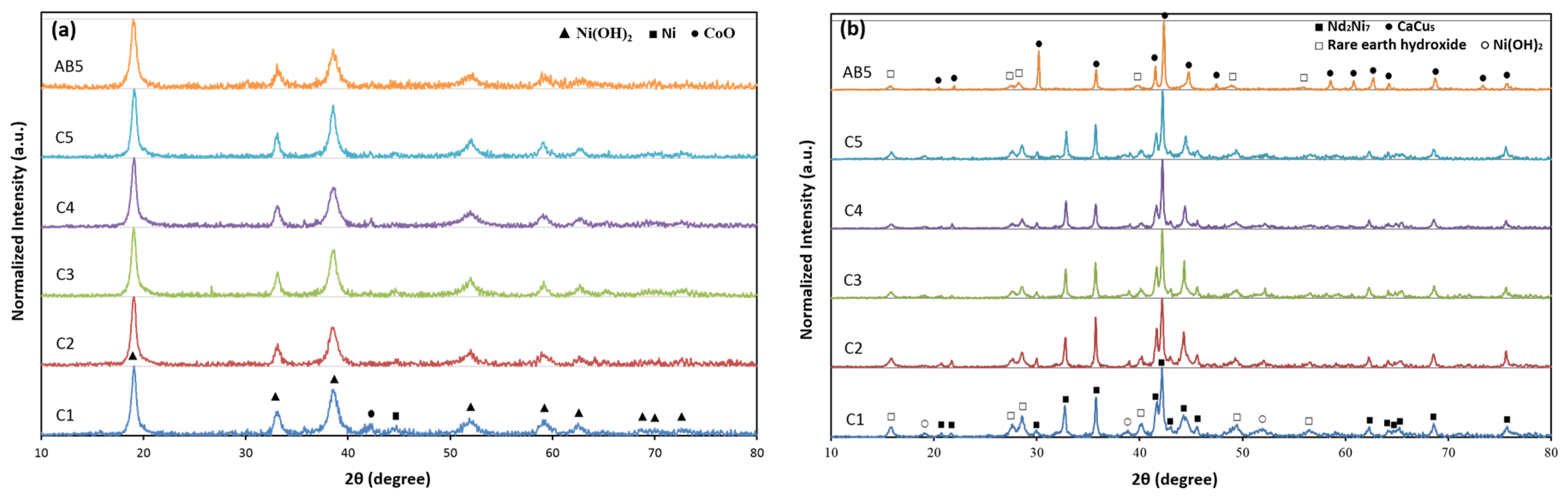
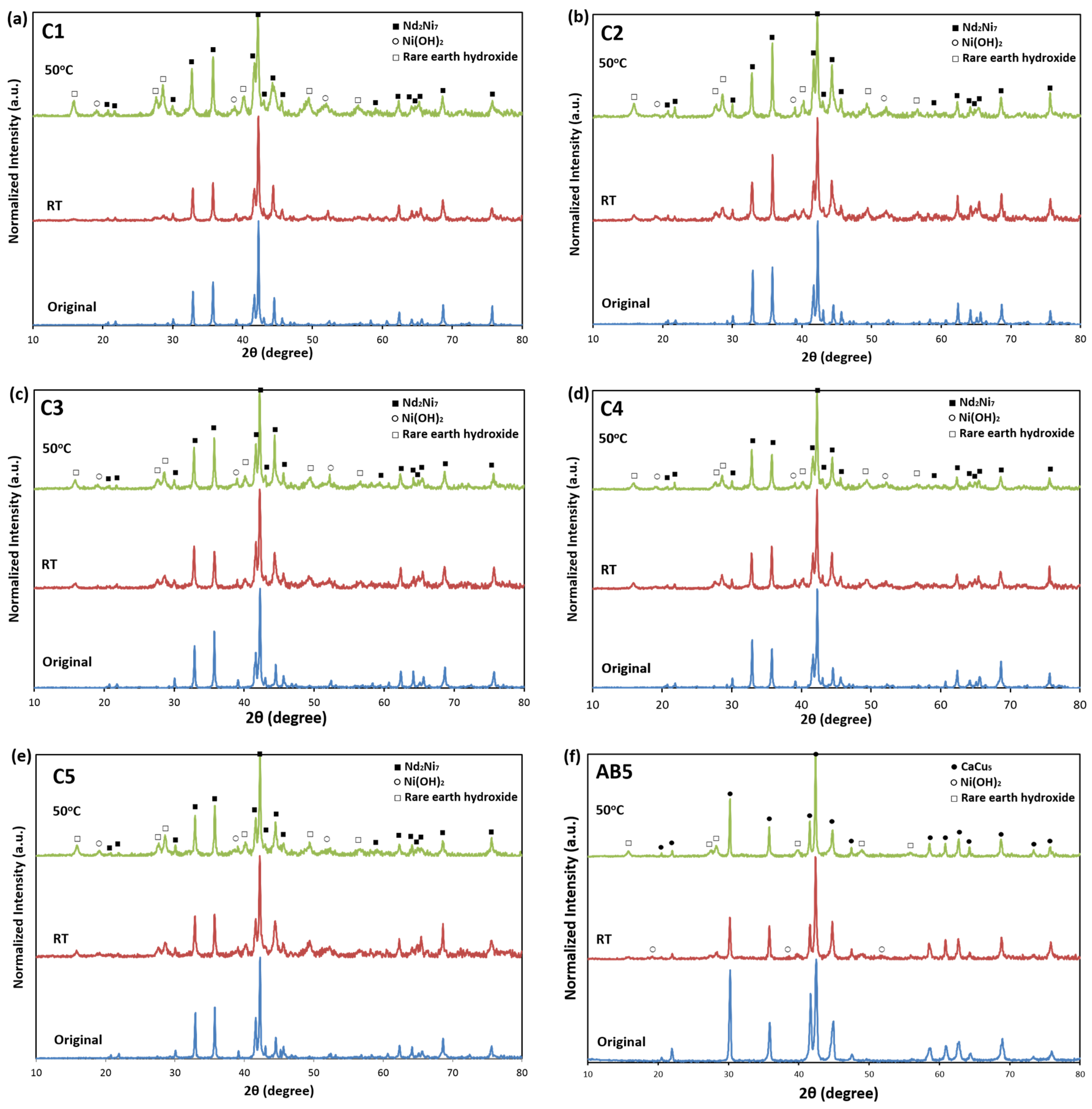
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction Structure Analysis
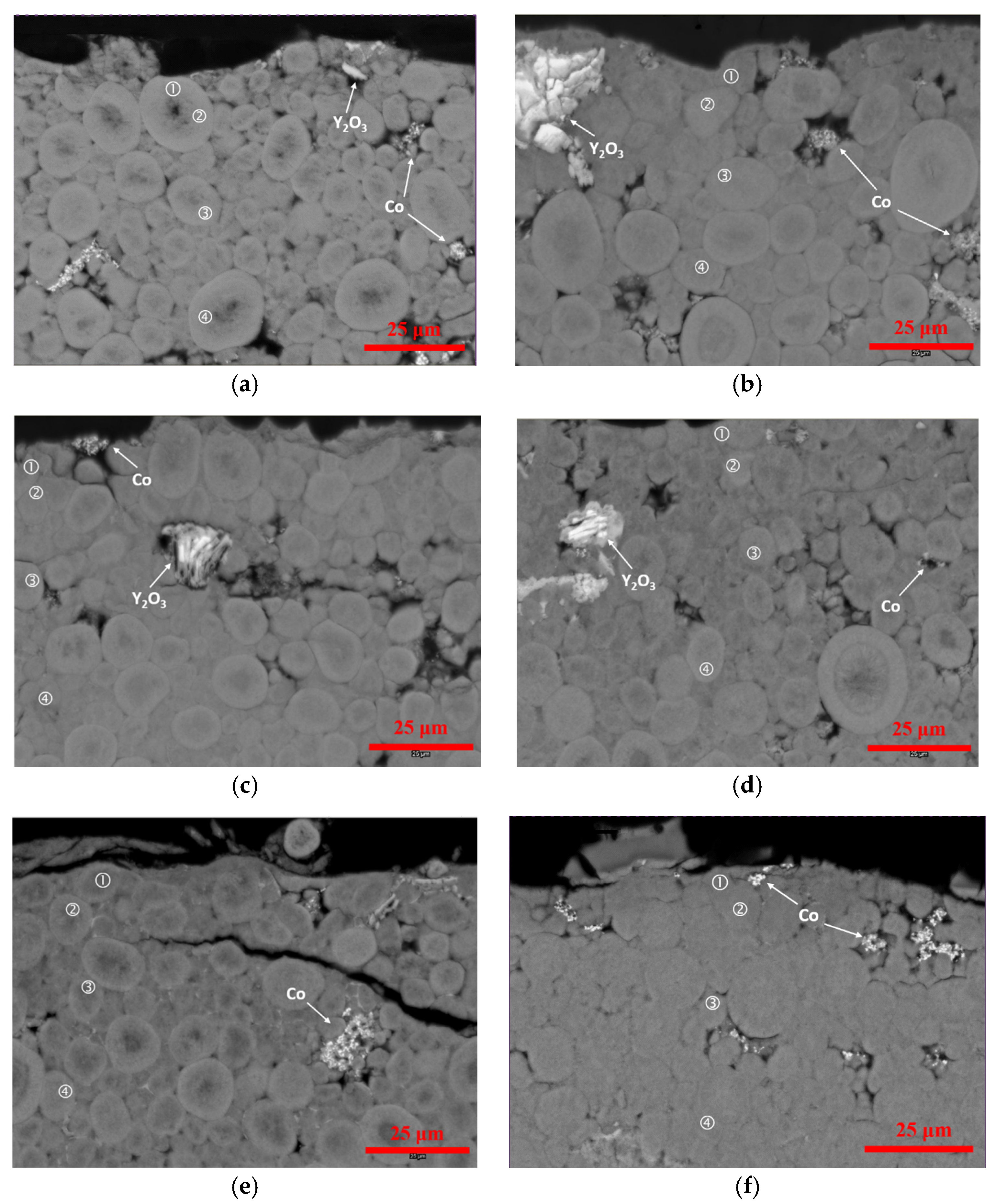
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HAA | Hydrogen absorbing alloy |
| Ni/MH | Nickel/metal hydride |
| MH | Metal hydride |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | Energy dispersive spectroscopy |
| ICP | Inductively coupled plasma |
| BEI | Backscattered electron image |
| O/M | Oxygen to metal ratio |
References
- Zelinsky, M.; Koch, J.; Fetcenko, M. Heat Tolerant NiMH Batteries for Stationary Power. Available online: www.battcon.com/PapersFinal2010/ZelinskyPaper2010Final_12.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Zelinsky, M.; Koch, J. Batteries and Heat—A Recipe for Success? Available online: www.battcon.com/PapersFinal2013/16-Mike%20Zelinsky%20-%20Batteries%20and%20Heat.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Young, K.; Ng, K.Y.S.; Bendersky, L. A Technical Report of the Robust Affordable Next Generation Energy Storage System-BASF Program. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VARTA Microbattery GmbH. Powerful High Temperature NiMH Batteries −20/+85 °C, 2008. Available online: http://www.varta-microbattery.com/applications/mb_data/documents/product_information/PI20081111_Electronica_Ni-MH_High_Temp_en.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Kai, T.; Ishida, J.; Yasuoka, S.; Takeno, K. The Effect of Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery’s Characteristics with Structure of the Alloy. In Proceedings of the 54th Battery Symposium in Japan, Osaka, Japan, 7–9 October 2013; p. 210.
- Li, W.; Campion, C.; Lucht, B.L.; Ravdel, B.; DiCarlo, J.; Abraham, K.M. Additives for stabilizing LiPF6-based electrolytes against thermal decomposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A1361–A1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Wan, C.C.; Wang, Y.Y. Thermal stability of the solid electrolyte interface on carbon electrodes of lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, A542–A547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bang, H.; Amine, K.; Prakash, J. Investigations of the exothermic reactions of natural graphite anode for Li-ion batteries during thermal runaway. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A73–A79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, A.; Raymond, N.; Armand, M. Lithium-ion batteries: Runaway risk of forming toxic compounds. Nature 2003, 424, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ping, P.; Zhao, X.; Chu, G.; Sun, J.; Chen, C. Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 208, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, C.; Zallen, A.; Koch, J.; Fetcenko, M.A. The influence of nickel-hydroxide composition and microstructure on the high-temperature performance of nickel metal hydride batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A492–A496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Yasuoka, S. Capacity degradation mechanisms in nickel/metal hydride batteries. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Chao, B.; Liu, Y.; Nei, J. Microstructures of the oxides on the activated AB2 and AB5 metal hydride alloys surface. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 616, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Huang, B.; Regmi, R.K.; Lawes, G.; Liu, Y. Comparisons of metallic clusters imbedded in the surface oxide of AB2, AB5, and A2B7 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wu, A.; Qiu, Z.; Tan, J.; Mays, W. Effects of H2O2 addition to the cell balance and self-discharge of Ni/MH batteries with AB5 and A2B7 alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 9882–9891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Young, K.; West, J.; Regalado, J.; Cherisol, K. Degradation mechanisms of high-energy bipolar nickel metal hydride battery with AB5 and A2B7 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 580, S373–S377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Wang, L.; Nei, J.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Mn in misch-metal based superlattice metal hydride alloy—Part 2 Ni/MH battery performance and failure mechanism. J. Power Sources 2015, 277, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Young, K.; Meng, T.; English, N.; Yasuoka, S. Partial substitution of cobalt for nickel in mixed rare earth metal based superlattice hydrogen absorbing alloy—Part 2 Battery performance and failure mechanism. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J. The current status of hydrogen storage alloy development for electrochemical applications. Materials 2013, 6, 4574–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X. Microstructures and electrochemical characteristics of the La0.75Mg0.25Ni2.5Mx (M = Ni, Co; x = 0–1.0) hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.J.; Adzic, G.D.; Johnson, J.R.; Vogt, T.; Mukerjee, S.; Mcbreen, J. The correlation between composition and electrochemical properties of metal hydride electrodes. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293–295, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; He, Y.; Shao, H. Comparative study of LaNi4.7M0.3 (M = Ni, Co, Mn, Al) by powder microelectrode technique. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Wong, D.F.; Wang, L.; Nei, J.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Mn in misch-metal based superlattice metal hydride alloy—Part 1 Structural, hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties. J. Power Sources 2015, 277, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Young, K.; Meng, T.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Partial substitution of cobalt for nickel in mixed rare earth metal based superlattice hydrogen absorbing alloy—Part 1 Structural, hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 660, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, J.; Young, K.; Rotarov, D. Studies on MgNi-based metal hydride electrode with aqueous electrolytes composed of various hydroxides. Batteries 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data®. Powder Diffraction File (PDF) No. 00-014-0117; JCPDS: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data®. Powder Diffraction File (PDF) No. 00-043-1004; JCPDS: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data®. Powder Diffraction File (PDF) No. 00-004-0850; JCPDS: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, X.Y.; Yuan, H.T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Song, D.Y.; Zhou, X.Y. Physical and electrochemical characteristics of aluminum-substituted nickel hydroxide. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1999, 29, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, T. Impedance of Al-substituted α-nickel hydroxide electrodes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, H.; Dehmelt, K.; Witte, J. Zur kenntnis der nickelhydroxidelektrode—I. Über das nickel (II)-hydroxidhydrat. Electrochim. Acta 1966, 11, 1079–1087. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, P.; Leonardi, J.; Laurent, J.F.; Delmas, C.; Braconnier, J.J.; Figlarz, M.; Fievet, F.; de Guibert, A. Review of the structure and the electrochemistry of nickel hydroxides and oxy-hydroxides. J. Power Sources 1982, 274, 8, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ven, A.; Morgan, D.; Meng, Y.S.; Ceder, G. Phase stability of nickel hydroxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A210–A215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, T. The relationship between structural stability and electrochemical performance of multi-element doped alpha nickel hydroxide. J. Power Sources 2015, 274, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, H. Fast determination of micro short circuit in sintered MH-Ni battery. Chin. J. Power Sources 2010, 34, 608–609. [Google Scholar]
- Shinyama, K.; Magari, Y.; Kumagae, K.; Nakamura, H.; Nohma, T.; Takee, M.; Ishiwa, K. Deterioration mechanism of nickel metal-hydride batteries for hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2005, 141, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.H.; Zhu, Y.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Self-discharge characteristics and performance degradation of Ni-MH batteries for storage applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 19789–19798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinyama, K.; Magari, Y.; Akita, H.; Kumagae, K.; Nakamura, H.; Matsuta, S.; Nohma, T.; Takee, M.; Ishiwa, K. Investigation into the deterioration in storage characteristics of nickel metal-hydride batteries during cycling. J. Power Sources 2005, 143, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.N.; Muralidharan, V.S.; Basha, C.A. Electrochemical investigations and characterization of a metal hydride alloy (MmNi3.6Al0.4Co0.7Mn0.3) for nickel metal hydride batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 467, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liang, F.; Sun, L.; Yin, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L. High temperature performance of La0.6Ce0.4Ni3.45Co0.75Mn0.7Al0.1 hydrogen storage alloy for nickel/metal hydride batteries. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 13231–13239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, C.; Boussami, S.; Tliha, M.; Azizi, S.; Fenineche, N.; El-kedim, O.; Mathlouthi, H.; Lamloumi, J. The effect of the temperature on the electrochemical properties of the hydrogen storage alloy for nickel-metal hydride accumulators. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 574, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zou, R.; Ni, C. Influence of temperature on self-discharge and high-rate discharge characteristics of La-rich AB5-based MH alloy electrode. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 654–656, 2835–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, J.; Chen, H.; Joiret, S.; Bourgon, J.; Latroche, M. Identification of a new pseudo-binary hydroxide during calendar corrosion of (La, Mg)2Ni7-type hydrogen storage alloys for nickel-metal hydride batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 266, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, E.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Dan, G.; Chang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H. Enhancement of the high-temperature performance of advanced nickel-metal hydride batteries with NaOH electrolyte containing NaBO2. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 10616–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, E.; Li, J.; Chang, Z.; Tang, H.; Li, B.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H. Sodium tungstate as electrolyte additive to improve high-temperature performance of nickel-metal hydride batteries. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 5153–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ma, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhu, D.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. The mechanism of suppressing capacity degradation of high-Al AB5-type hydrogen storage alloys at 60 °C. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, D.; Zhong, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y. Improvement in high-temperature performance of Co-free high-Fe AB5-type hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 12375–12383. [Google Scholar]
- Balogun, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Yao, Q.; Deng, J.; Zhou, H. Effect of high and low temperature on the electrochemical performance of LaNi4.4−xCo0.3Mn0.3Alx hydrogen storage alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 579, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rei, Y.; Han, F. Influence of small amount of addition elements on electrochemical and high temperature performance of La-riched RE-based hydrogen storage materials. Chin. J. Rare Metals 2002, 26, 47–50. [Google Scholar]

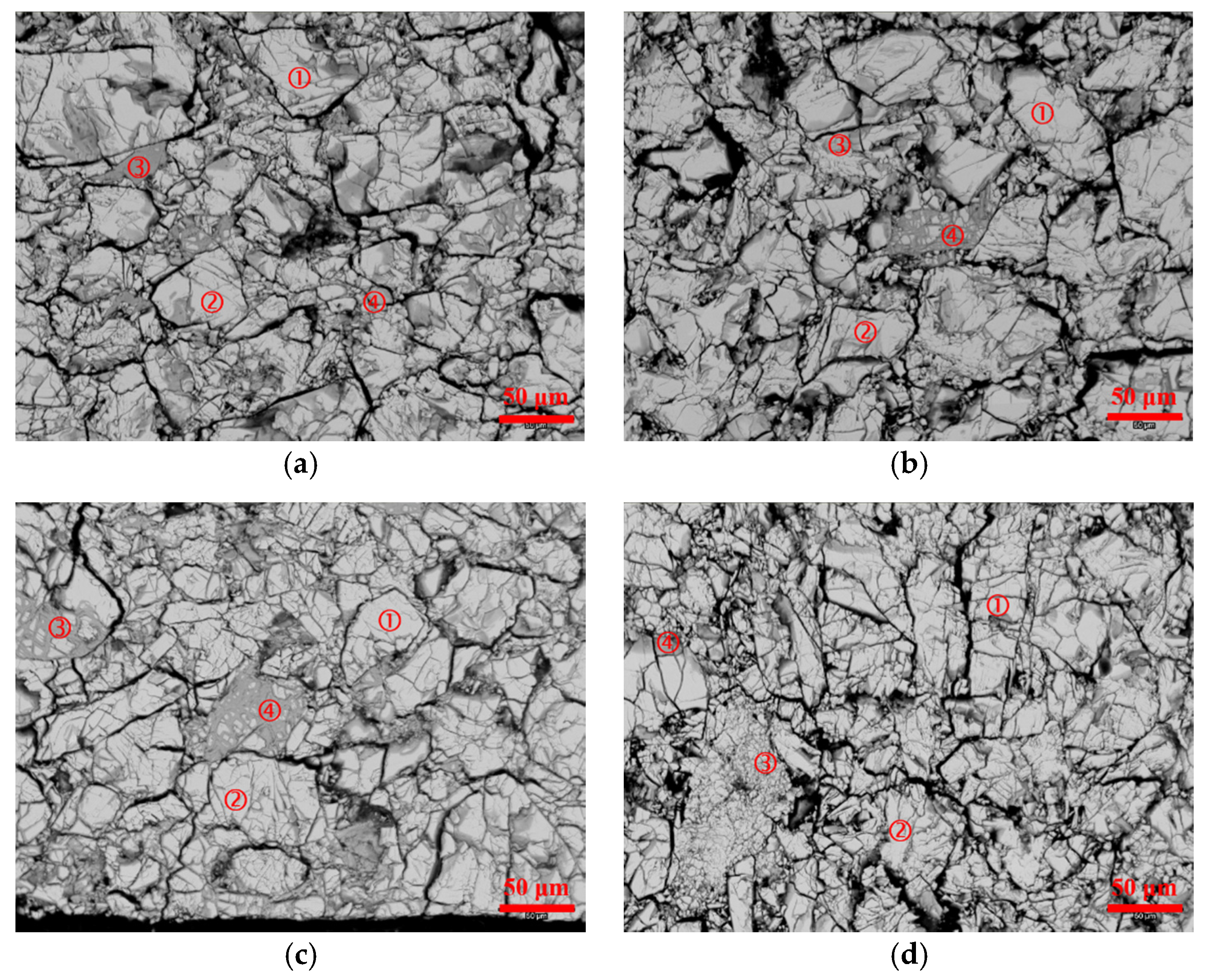
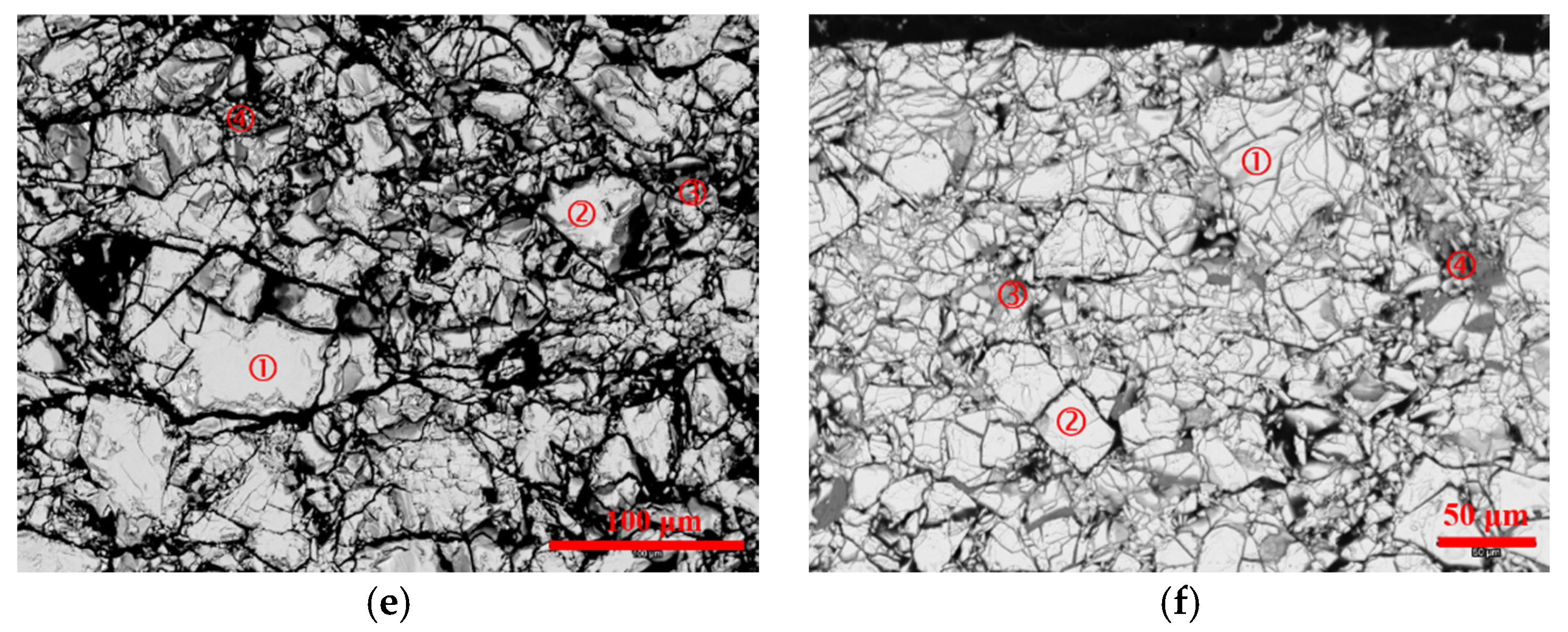
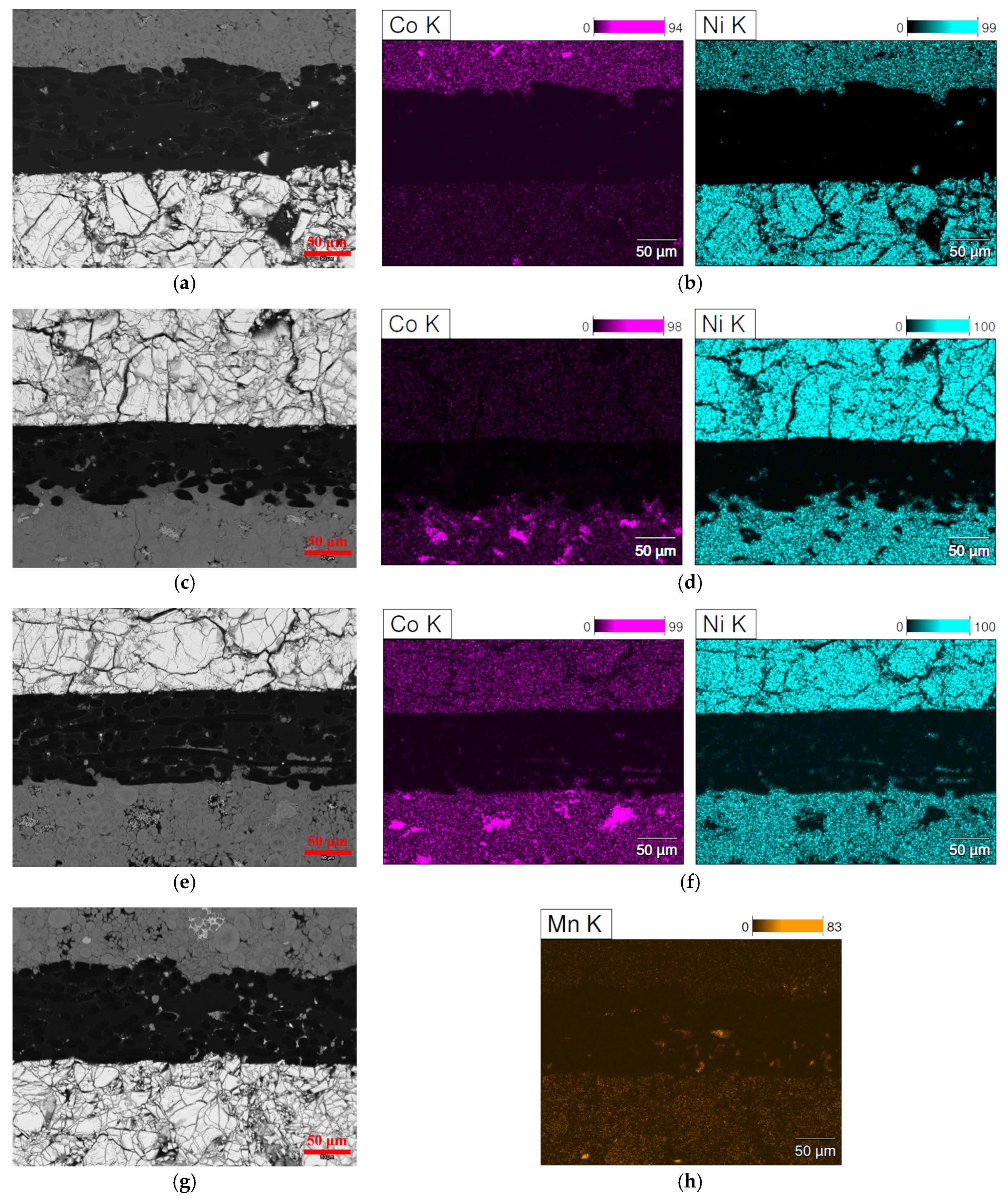
| Location | Ni | Co | Zn | Y | Al | Mg | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1-1 | 78.2 | 16 | 2.0 | ND | 2.5 | 1.3 | ND |
| C1-2 | 77.3 | 15.7 | 2.4 | ND | 3.4 | 1.2 | ND |
| C1-3 | 78.4 | 17.0 | 2.1 | ND | 2.5 | ND | ND |
| C1-4 | 77.5 | 18.0 | 1.9 | ND | 2.6 | ND | ND |
| C2-1 | 78.1 | 14.4 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 3.6 | 1.3 | ND |
| C2-2 | 78.0 | 16.6 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 2.7 | ND | ND |
| C2-3 | 78.2 | 16.8 | 2.3 | 0.2 | 2.4 | ND | ND |
| C2-4 | 78.8 | 16.1 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.4 | ND | ND |
| C3-1 | 75.1 | 17.3 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 2.6 | ND |
| C3-2 | 74.6 | 18.0 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 2.1 | ND |
| C3-3 | 76.4 | 18.4 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 2.5 | ND | ND |
| C3-4 | 76.8 | 18.2 | 2.4 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 0.1 | ND |
| C4-1 | 77.2 | 15.2 | 2.1 | 0.2 | 2.8 | 2.5 | ND |
| C4-2 | 78.1 | 15.0 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 2.2 | ND |
| C4-3 | 78.3 | 16.8 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 2.2 | ND | ND |
| C4-4 | 78.4 | 16.4 | 2.5 | 0.2 | 2.5 | ND | ND |
| C5-1 | 78.4 | 12.4 | 1.7 | ND | 4.1 | 3.4 | ND |
| C5-2 | 79.3 | 13.2 | 1.7 | ND | 3.2 | 2.6 | ND |
| C5-3 | 80.2 | 13.1 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 3.6 | 0.9 | ND |
| C5-4 | 81.5 | 13.7 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 2.8 | ND | ND |
| AB5-1 | 74.0 | 14.9 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 7.6 | ND | 1.6 |
| AB5-2 | 77.5 | 12.4 | 1.8 | ND | 7.7 | ND | 0.5 |
| AB5-3 | 75.9 | 15.0 | 2.2 | ND | 6.8 | ND | 0.2 |
| AB5-4 | 77.0 | 14.8 | 2.0 | 0.1 | 6.2 | ND | ND |
| Location | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Ni | Co | Al | Mg | Mn | O | B/A | O/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1-1 | 4.1 | ND | 7.9 | 7.8 | 73.1 | ND | 4.2 | 2.9 | ND | ND | 3.41 | ND |
| C1-2 | 3.9 | ND | 7.9 | 7.8 | 7.6 | ND | 4.0 | 2.9 | ND | ND | 3.45 | ND |
| C1-3 | 10.2 | ND | 0.3 | 2.0 | 64.0 | ND | 0.2 | ND | ND | 23.4 | 5.14 | 0.31 |
| C1-4 | 2.3 | ND | 3.5 | 3.5 | 64.1 | ND | 0.2 | 0.2 | ND | 26.2 | 6.77 | 0.36 |
| C2-1 | 3.6 | ND | 7.2 | 7.1 | 66.6 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 2.8 | ND | 7.1 | 3.49 | 0.08 |
| C2-2 | 3.4 | ND | 7.6 | 7.4 | 66.4 | 2.1 | 3.3 | 2.6 | ND | 7.2 | 3.42 | 0.08 |
| C2-3 | 2.0 | ND | 4.9 | 5.3 | 63.3 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 0.5 | ND | 20.9 | 5.23 | 0.26 |
| C2-4 | 2.2 | ND | 4.8 | 5.4 | 59.3 | 2.1 | ND | 0.3 | ND | 25.9 | 4.83 | 0.35 |
| C3-1 | 3.3 | ND | 7.5 | 7.5 | 62.9 | 4.4 | 3.0 | 3.0 | ND | 8.3 | 3.30 | 0.09 |
| C3-2 | 3.4 | ND | 7.3 | 7.2 | 62.8 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 2.8 | ND | 8.8 | 3.41 | 0.10 |
| C3-3 | 2.7 | ND | 6.3 | 6.1 | 52.5 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 1.1 | ND | 26.9 | 3.51 | 0.37 |
| C3-4 | 2.8 | ND | 5.6 | 5.8 | 51.3 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | ND | 29.2 | 3.79 | 0.41 |
| C4-1 | 3.4 | ND | 7.4 | 7.2 | 61.7 | 6.9 | 3.2 | 2.9 | ND | 7.2 | 3.44 | 0.08 |
| C4-2 | 3.7 | ND | 7.1 | 7.0 | 59.5 | 6.6 | 4.0 | 3.0 | ND | 9.1 | 3.37 | 0.10 |
| C4-3 | 3.3 | ND | 7.1 | 6.9 | 58.0 | 6.0 | 2.6 | 2.9 | ND | 13.2 | 3.30 | 0.15 |
| C4-4 | 2.2 | ND | 5.5 | 5.7 | 57.8 | 7.1 | 3.1 | 0.5 | ND | 18.1 | 4.89 | 0.22 |
| C5-1 | 3.2 | ND | 7.1 | 7.3 | 59.0 | 8.8 | 3.2 | 3.2 | ND | 8.1 | 3.41 | 0.09 |
| C5-2 | 4.5 | ND | 7.2 | 6.9 | 58.3 | 8.8 | 3.8 | 2.7 | ND | 7.8 | 3.33 | 0.08 |
| C5-3 | 2.7 | ND | 4.8 | 4.6 | 60.4 | 7.2 | 2.6 | 1.8 | ND | 15.8 | 5.05 | 0.19 |
| C5-4 | 7.5 | ND | 14.4 | 14.8 | 19.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 35.0 | ND | 36.5 | 0.58 | 0.58 |
| AB5-1 | 9.8 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 57.3 | 12.4 | 4.0 | ND | 6.5 | 3.6 | 5.24 | 0.04 |
| AB5-2 | 9.7 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 58.9 | 12.5 | 4.2 | ND | 5.1 | 3.3 | 5.34 | 0.03 |
| AB5-3 | 8.0 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 44.8 | 10.5 | 0.5 | ND | 0.7 | 30.5 | 4.83 | 0.44 |
| AB5-4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 | ND | 57.6 | 37.6 | 33.67 | 0.60 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, T.; Young, K.-h.; Koch, J.; Ouchi, T.; Yasuoka, S. Failure Mechanisms of Nickel/Metal Hydride Batteries with Cobalt-Substituted Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloy Anodes at 50 °C. Batteries 2016, 2, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030020
Meng T, Young K-h, Koch J, Ouchi T, Yasuoka S. Failure Mechanisms of Nickel/Metal Hydride Batteries with Cobalt-Substituted Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloy Anodes at 50 °C. Batteries. 2016; 2(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Tiejun, Kwo-hsiung Young, John Koch, Taihei Ouchi, and Shigekazu Yasuoka. 2016. "Failure Mechanisms of Nickel/Metal Hydride Batteries with Cobalt-Substituted Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloy Anodes at 50 °C" Batteries 2, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030020
APA StyleMeng, T., Young, K.-h., Koch, J., Ouchi, T., & Yasuoka, S. (2016). Failure Mechanisms of Nickel/Metal Hydride Batteries with Cobalt-Substituted Superlattice Hydrogen-Absorbing Alloy Anodes at 50 °C. Batteries, 2(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries2030020