Do Silicon-Based Li-Ion Batteries Require a Time-Consuming Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation Process?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
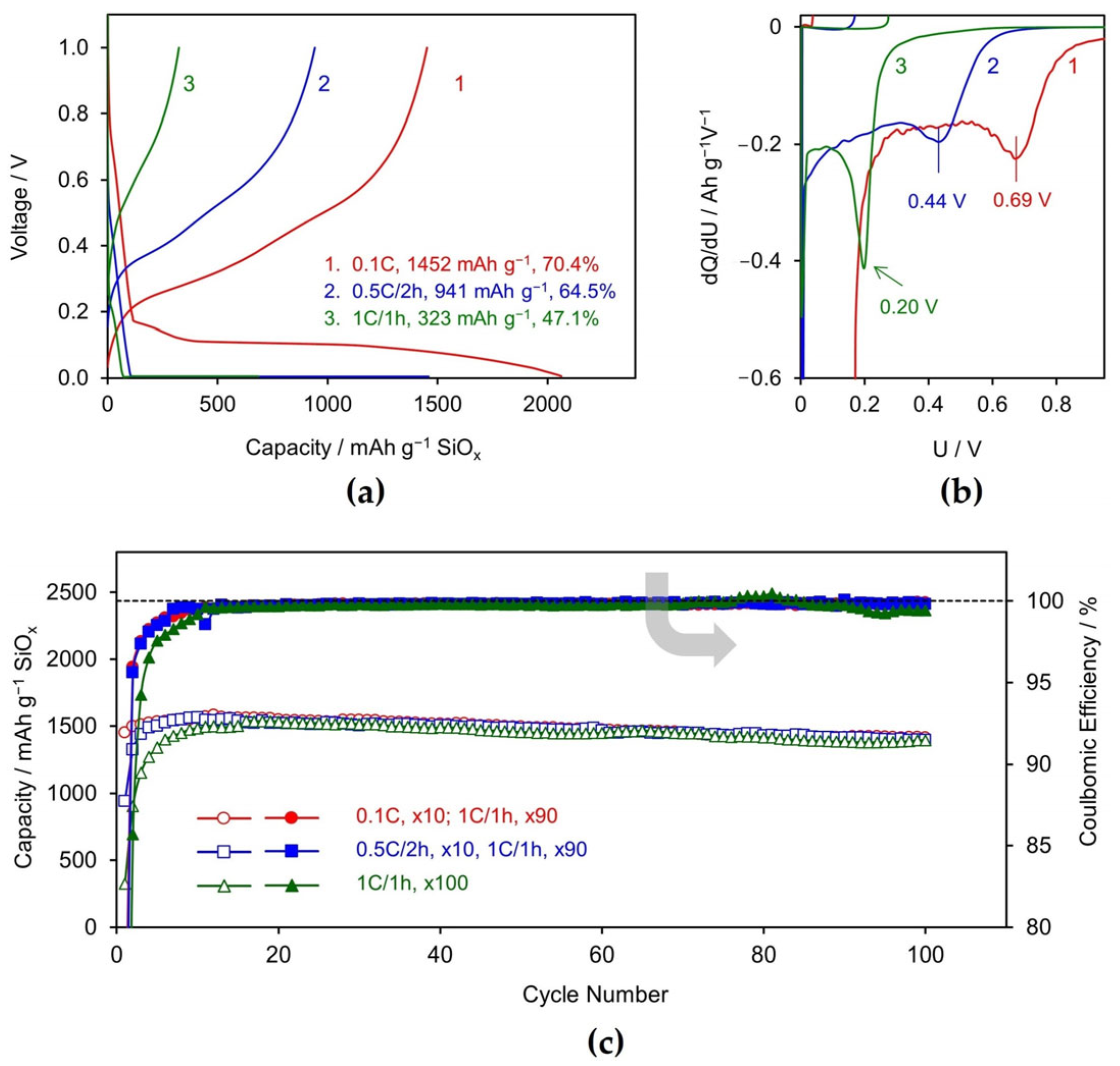
3.1. Li/SiOx Half-Cell
3.2. SiOx/NCM811 Full Cells
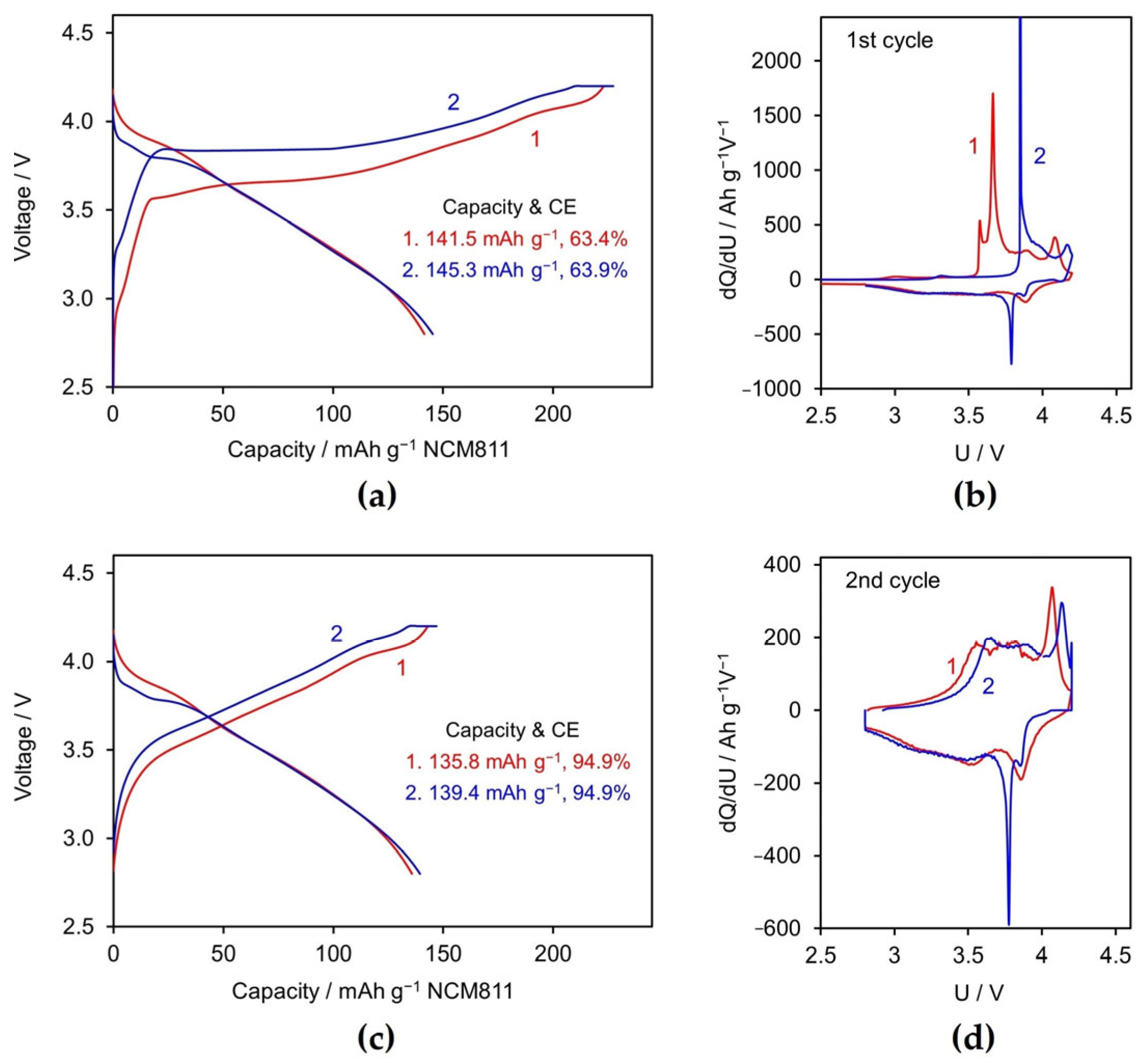
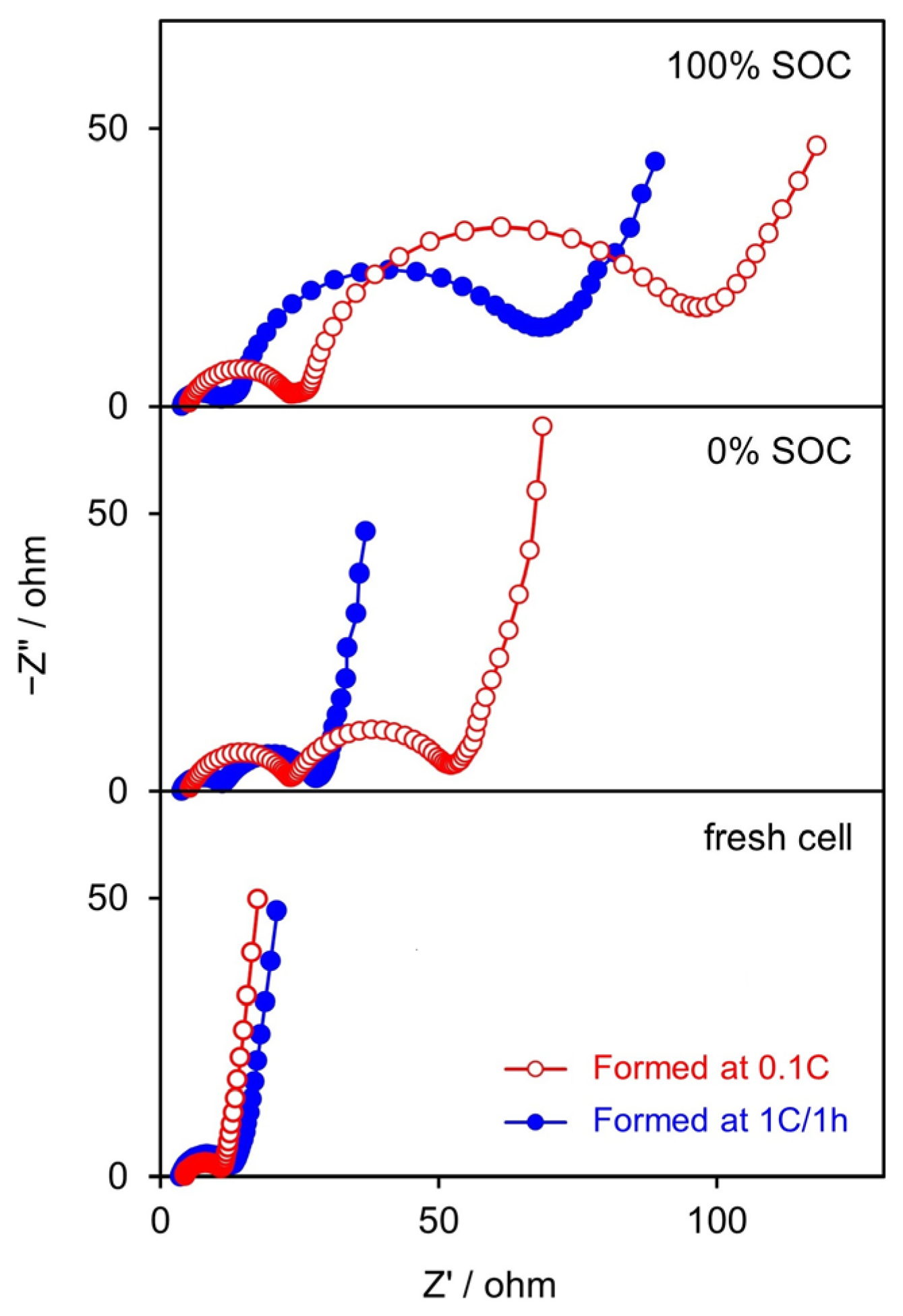
3.2.1. Formation Cycle
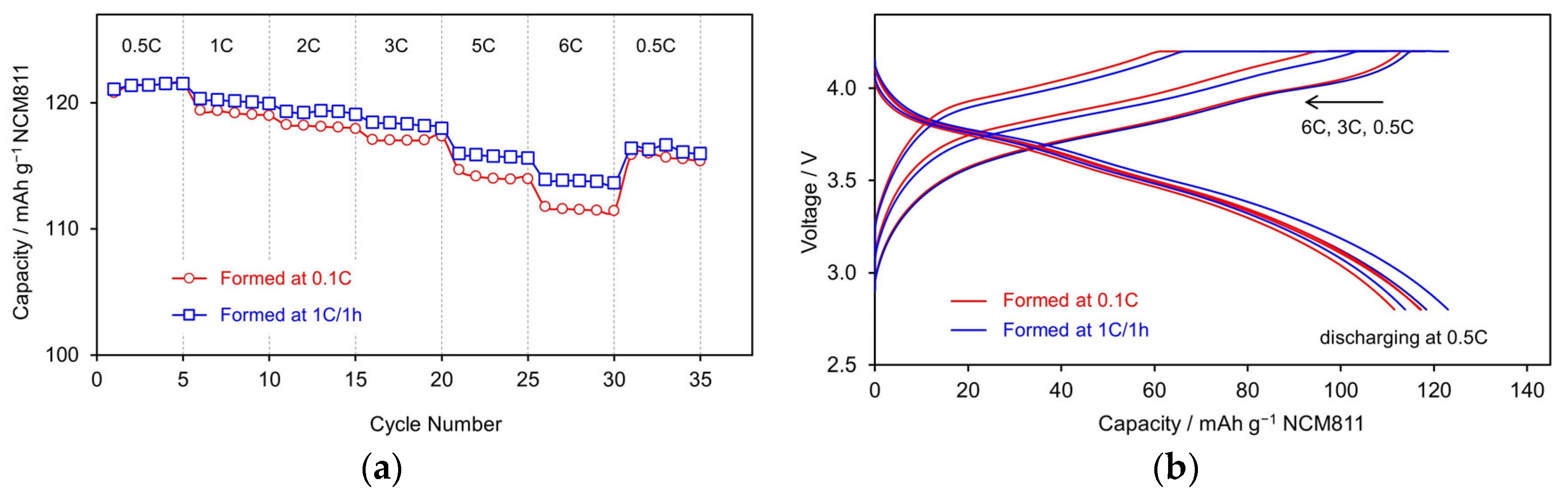
3.2.2. Rate Capability
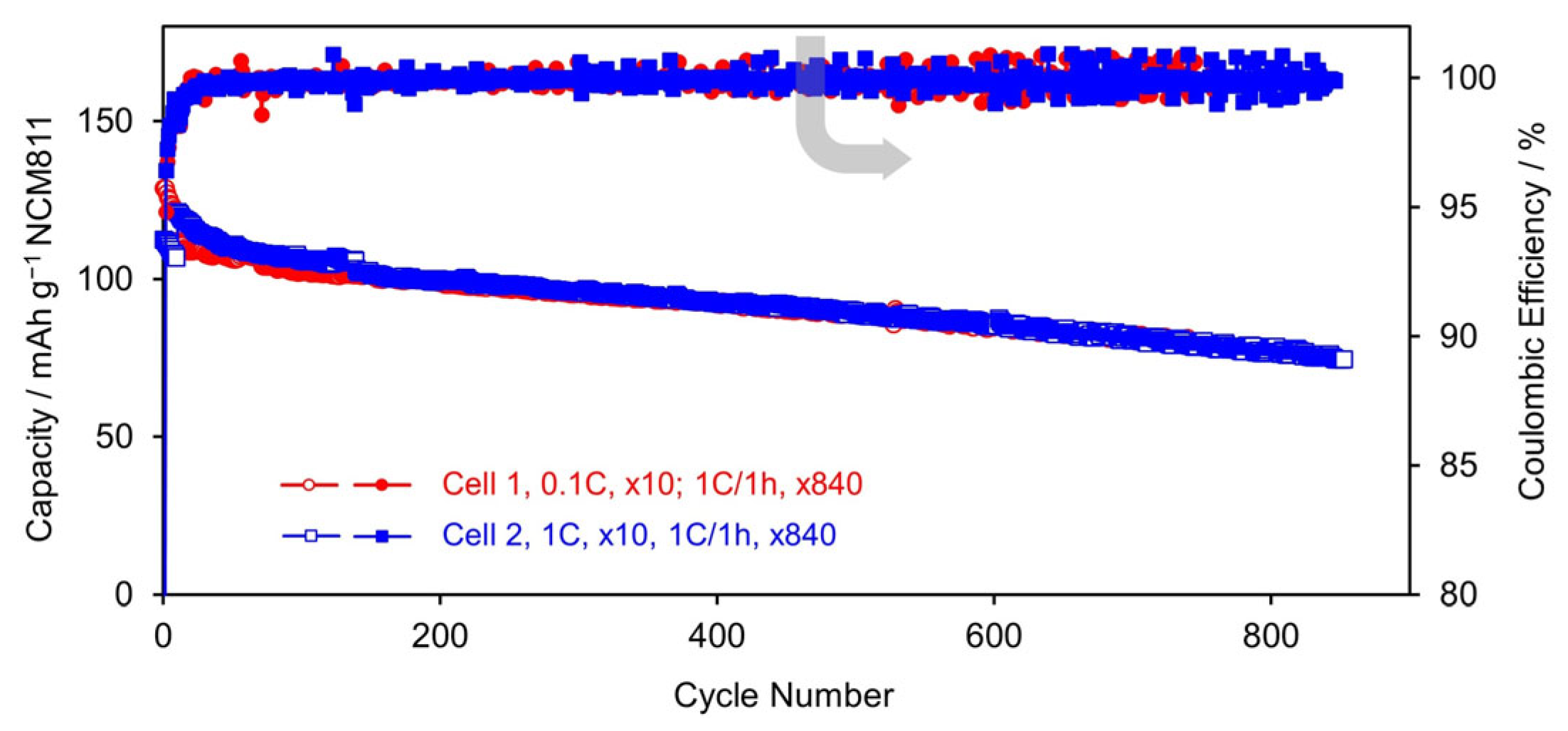
3.2.3. Cycling Stability
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood, D.L.; Li, J.; An, S.J. Formation Challenges of Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing. Joule 2019, 3, 2884–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, F.; Heidrich, B.; Wennemar, S.; Drees, R.; Roth, T.; Kurrat, M.; Heimes, H.; Jossen, A.; Winter, M.; Cheong, J.Y.; et al. Lithium-ion battery cell formation: Status and future directions towards a knowledge-based process design. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 2686–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.M.; Song, J.; Lee, S.; Jang, I.-C. Effect of current rate on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase layer at the graphite anode in lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 397, 139269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xu, K.; Jow, T.R. Optimization of the forming conditions of the solid-state interface in the Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2004, 130, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; He, X. Thermodynamic Understanding of Formation and Evolution of Solid Electrolyte Interface in Li-Ion Batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2024, 7, e202400059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, B.K.; Stock, C.; Maglia, F.; Hoster, H.E. Solid electrolyte interphase: Can faster formation at lower potentials yield better performance? Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Xu, K.; Jow, T.R. EIS study on the formation of solid electrolyte interface in Li-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, P.-C.J.; Wu, M.-S.; Lin, J.-C. A Novel Dual-Current Formation Process for Advanced Lithium-Ion Batteries. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2005, 8, A423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, T.S.; Rashid, M.; Walker, M.; Widanage, W.D.; Kendrick, E. Active formation of Li-ion batteries and its effect on cycle life. J. Phys. Energy 2019, 1, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Pedersen, K.; Gurevich, L.; Stroe, D.-I. Investigation of multi-step fast charging protocol and aging mechanism for commercial NMC/graphite lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 80, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.D.; Allen, J.P.; Hill, I.G.; Dahn, J.R. High-Precision Coulometry Studies of the Impact of Temperature and Time on SEI Formation in Li-Ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.; Sharova, V.; Carvalho, D.V.; Boulineau, A.; Porcher, W.; de Meatza, I.; Passerini, S. A Comparison of Formation Methods for Graphite//LiFePO4 Cells. Batter. Supercaps 2019, 2, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yao, Y.-X.; Cai, W.-L.; Xu, L.; Kaskel, S.; Park, H.S.; Huang, J.-Q. The influence of formation temperature on the solid electrolyte interphase of graphite in lithium ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 49, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Wan, C.-C.; Yang, M.-H.; Wu, H.-C.; Shieh, D.-T. A fast formation process for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.J.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Daniel, C.; Wood, D.L. Fast formation cycling for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 342, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-M.; Wang, H.-Y.; Yu, M.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Tsai, Y. Differential pulse effects of solid electrolyte interface formation for improving performance on high-power lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10395–10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-M.; Wang, J.-C.; Rick, J. Forward and reverse differential-pulse effects applied in the formation of a solid electrolyte interface to enhance the performance of lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 147, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreaga-Salas, D.E.; Sra, A.K.; Roodenko, K.; Chabal, Y.J.; Hinkle, C.L. Progression of Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation on Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9072–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, Y.; Ben-Barak, I.; Schneier, D.; Goor-Dar, M.; Kasnatscheew, J.; Meister, P.; Grünebaum, M.; Wiemhöfer, H.-D.; Winter, M.; Golodnitsky, D.; et al. Study of the Formation of a Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) on a Silicon Nanowire Anode in Liquid Disiloxane Electrolyte with Nitrile End Groups for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2019, 2, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chae, O.B.; Lucht, B.L. Perspective—Structure and Stability of the Solid Electrolyte Interphase on Silicon Anodes of Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 030521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Frisco, S.; Tao, R.; Philip, N.; Bennett, T.H.; Stetson, C.; Zhang, J.-G.; Han, S.-D.; Teeter, G.; Harvey, S.P.; et al. Robust Solid/Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) Formation on Si Anodes Using Glyme-Based Electrolytes. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, D.; Chai, S.; Chang, Z.; Pan, A. Enhanced Silicon Anodes with Robust SEI Formation Enabled by Functional Conductive Binder. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S. Is Li/Graphite Half-Cell Suitable for Evaluating Lithiation Rate Capability of Graphite Electrode? J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.S. Do Silicon-Based Li-Ion Batteries Require a Time-Consuming Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation Process? Batteries 2025, 11, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11040122
Zhang SS. Do Silicon-Based Li-Ion Batteries Require a Time-Consuming Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation Process? Batteries. 2025; 11(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sheng S. 2025. "Do Silicon-Based Li-Ion Batteries Require a Time-Consuming Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation Process?" Batteries 11, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11040122
APA StyleZhang, S. S. (2025). Do Silicon-Based Li-Ion Batteries Require a Time-Consuming Solid Electrolyte Interphase Formation Process? Batteries, 11(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11040122






