Evaluating a Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder as a Novel Negative Electrode Material for Applications in Ni-MH Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrochemical Techniques
2.2. Characterization Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Fe-Based MG and LaNi5 Powders
3.2. Electrochemical Results
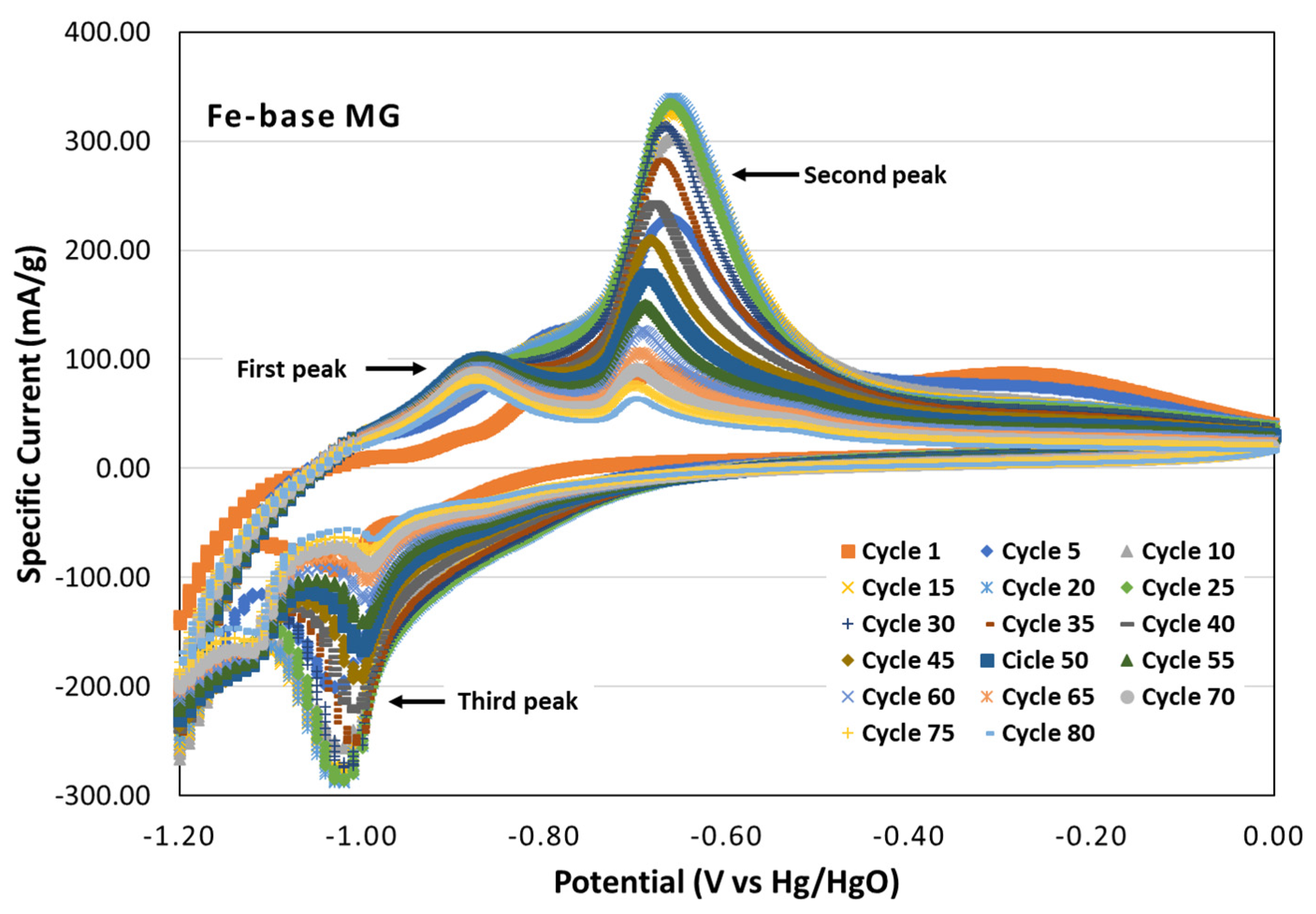
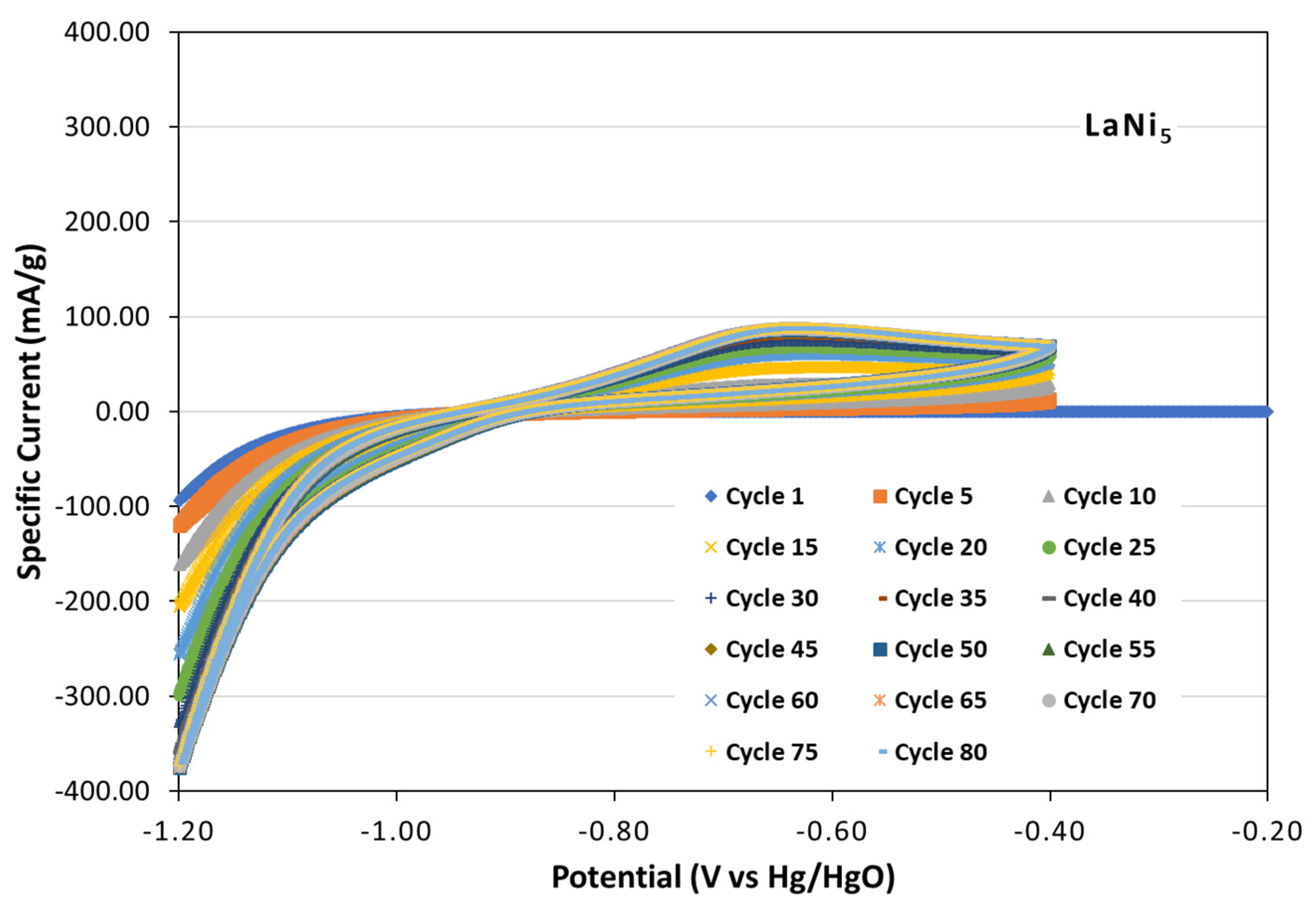
3.2.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
3.2.2. Galvanostatic Charge/Discharge Tests
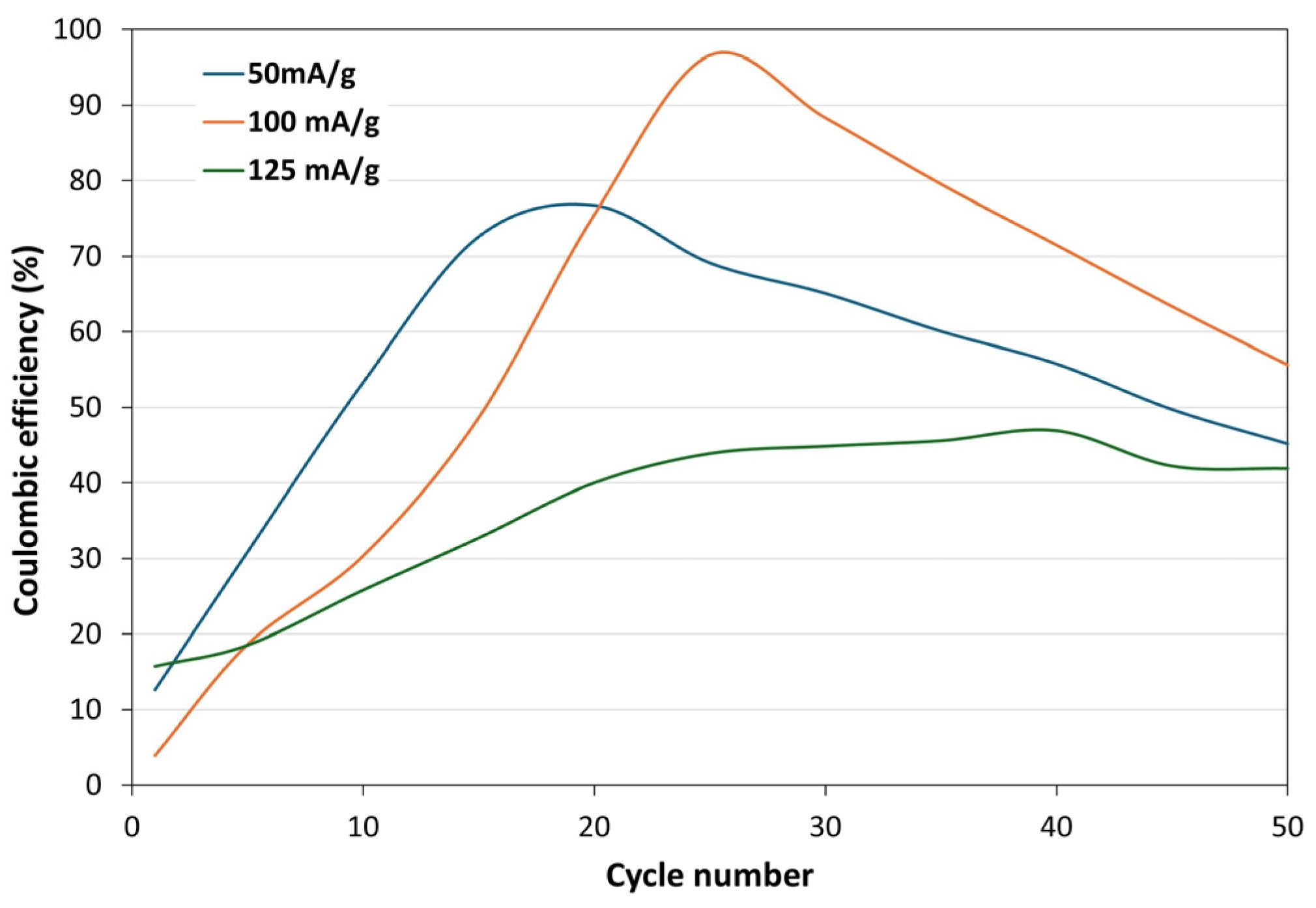
3.2.3. Coulombic Efficiency
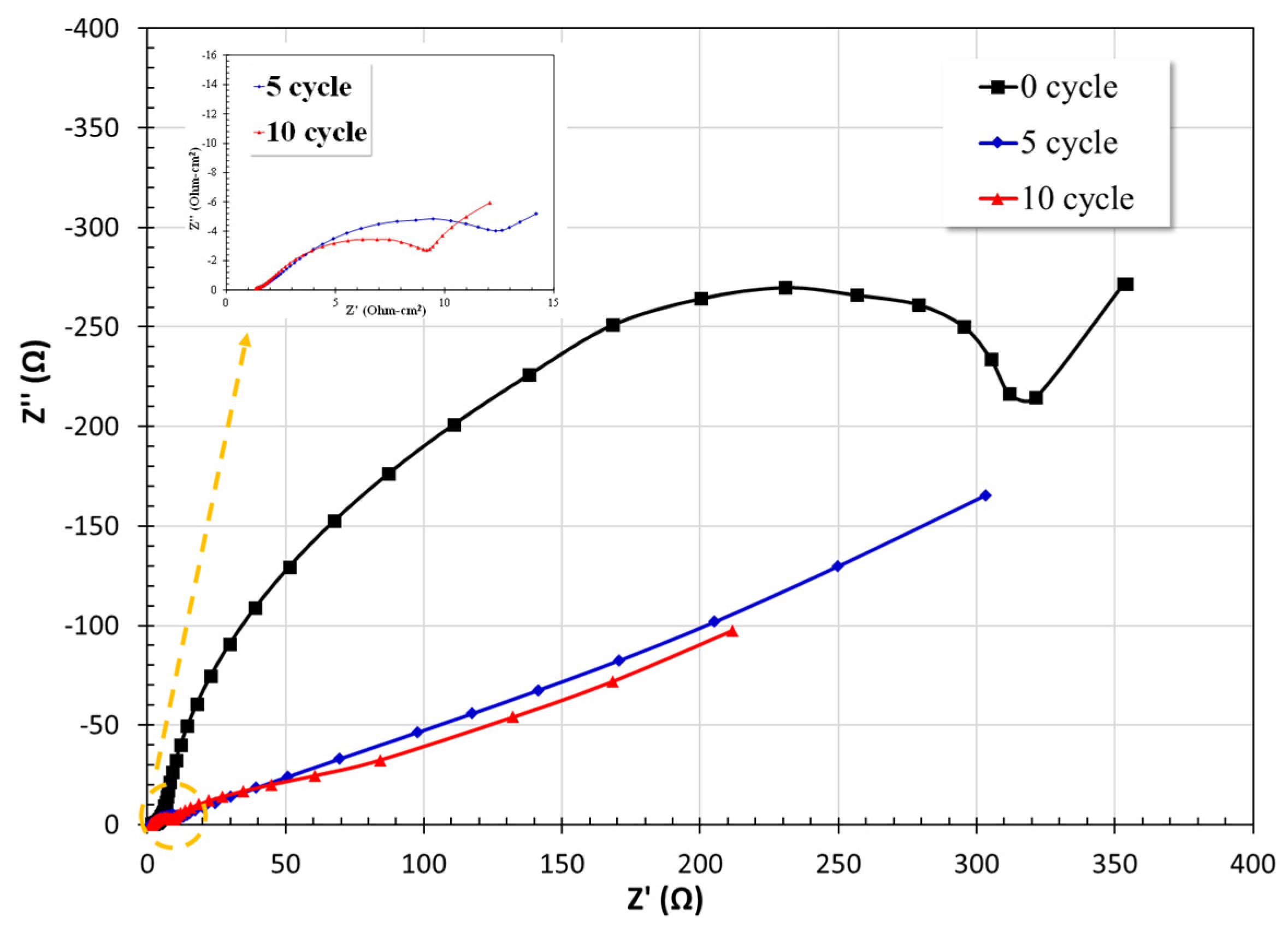
3.2.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3.3. XRD Analysis after Cyclic Voltammetry Test
3.4. Raman Analysis
3.5. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. Environmental Impact Assessment and End-of-Life Treatment Policy Analysis for Li-Ion Batteries and Ni-MH Batteries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3185–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistoia, G. Battery Categories and Types. In Battery Operated Devices and Systems: From Portable Electronics to Industrial Products, 1st ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 17–73. [Google Scholar]
- Vishnumurthy, K.A.; Girish, K.H. A comprehensive review of battery technology for E-mobility. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetcenko, M.A.; Ovshinsky, S.R.; Reichman, B.; Young, K.; Fierro, C.; Koch, J.; Zallen, A.; Mays, W.; Ouchi, T. Recent advances in NiMH battery technology. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, T.K.; Gao, X.P.; Hu, W.-K.; Wu, F.; Noréus, D. Studies on rechargeable NiMH batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Young, K.; Nei, J.; Pawlik, D.; Ng, K.Y.S. Hydrogenation of AB5 and AB2 metal hydride alloys studied by in situ X-ray diffraction. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 616, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Nemati, A.; Rahman, Z.U.; Shah, U.H.; Asgar, H.; Haider, W. Recent Advancements in Bulk Metallic Glasses and Their Applications: A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 43, 233–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Ivanov, Y.P.; Kvaratskheliya, A.; Ketov, S.; Karazehir, T.; Gumrukcu, S.; Berdonosova, E.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Micusik, M.; et al. Surface-Governed electrochemical hydrogenation in FeNi-Based metallic glass. J. Power Sources 2020, 475, 228700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J. Bulk Metallic Glasses. Phys. Today 2013, 66, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Yi, L.; Arroyo, E.M.; Ceder, G. Amorphous Metallic Glass as New High Power and Energy Density Anodes For Lithium Ion Rechargeable Batteries. Adv. Mater. Micro Nano-Syst. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jabed, A.; Bhuiyan, M.N.; Haider, W.; Shabib, I. Distinctive Features and Fabrication Routes of Metallic-Glass Systems Designed for Different Engineering Applications: A Review. Coatings 2023, 13, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartys, V.A.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Akiba, E.; Albert, R.; Antonov, V.E.; Ares, J.R.; Baricco, M.; Bourgeois, N.; Buckley, C.E.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.M.; et al. Magnesium based materials for hydrogen based energy storage: Past, present and future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7809–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G. Hydrogen absorption/desorption behavior of Mg50La20Ni30 bulk metallic glass. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 4670–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Da, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cui, X.; Han, X.; Ke, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Hu, W. Progress and Perspective of Metallic Glasses for Energy Conversion and Storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Xu, W.; Huo, J.; Li, R.W.; Qiu, H.; Chen, M. Flexible supercapacitor electrodes fabricated by dealloying nanocrystallized Al-Ni-Co-Y-Cu metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 772, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.Y.; Liu, S.N.; Ge, J.C.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, Y.R.; Duan, Y.; Qin, S.; Dong, W.; Yu, X.; et al. Nickel–Molybdenum–Niobium metallic glass for efficient hydrogen oxidation in hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, N.; Qaseem, A.; Johnston, R.L. A silver–copper metallic glass electrocatalyst with high activity and stability comparable to Pt/C for zinc–air batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3527–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, A.K.; Emran, K.M. Effect of immersion time on electrochemical and morphology of new Fe-Co metal-metal glassy alloys in acid rain. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Bulk glassy alloys: Historical development and current research. Engineering 2015, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, J.; Concustell, A.; Cano, I.G.; Cinca, N.; Dosta, S.; Guilemany, J.M. Influence of Cold Gas Spray process conditions on the microstructure of Fe-Based amorphous coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 622, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblano-Salas, C.A.; Sotelo-Mazon, O.; Henao, J.; Corona-Castuera, J.; Martinez, G.; Casales-Diaz, M.; Porcayo-Calderon, J.; Tathagata, K.; Navarro, M.; Kumar-Kesarla, M. Flame Sprayed LaNi5-Based Mischmetal Alloy: Building-up Negative Electrodes for Potential Application in Ni-Based Batteries. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 1940–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Posada, J.O.; Hall, P.J. Controlling hydrogen evolution on iron electrodes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 20807–20817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Posada, J.O.; Hall, P.J. Towards the development of safe and commercially viable nickel–iron batteries: Improvements to Coulombic efficiency at high iron sulphide electrode formulations. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.K.; Malkhandi, S.; Yang, B.; Yang, C.; Prakash, G.K.S.; Narayanan, S.R. A High-Performance Rechargeable Iron Electrode for Large-Scale Battery-Based Energy Storage. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaldi, C.; Mathlouthi, H.; Lamloumi, J. A comparative study, of 1 M and 8 M KOH electrolyte concentrations, used in Ni–MH batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 469, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Nishizawa, M.; Uchida, I. Single particle electrochemistry for hydrogen storage alloys, MmNi3.55Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.3. Electrochim. Acta 1999, 45, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamedi, M.; Sato, T.; Itoh, T.; Umeda, M.; Uchida, I. Cyclic Voltammetry and AC Impedance of MmNi3.55Co0.75Mn0.4Al0.3 Alloy Single-Particle Electrode for Rechargeable Ni/MH Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixiang, C. Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance of MmNi3.6Co0.7Mn0.4Al0.3 alloy electrode before and after treatment with a hot alkaline solution containing reducing agent. J. Power Sources 2000, 90, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Feng, F.; Gamboa, S.A.; Sebastian, P.J.; Matchett, A.J.; Northwood, D.O. Electrocatalytic characteristics of the metal hydride electrode for advanced Ni/MH batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 96, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Iwakura, C.; Tamura, H. Comparative study of LaNi5,-type alloy electrodes with and without Pd-Plated layer by means of cyclic voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 1982, 27, 1729–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q. Advanced hydrogen storage alloys for Ni/MH rechargeable batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4743–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, H.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J. Effects of substitution of other elements for nickel in mechanically alloyed Mg50Ni50 amorphous alloys used for nickel-metal hydride batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 1997, 261, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourashiya, M.G.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, C.N.; Park, C.J. Hydrogenation and microstructural properties of hydriding combustion synthesized Mg-Ni-C composite ball-milled with NbF5 catalyst. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Northwood, D.O. Development of advanced rechargeable Ni/MH and Ni/Zn batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2003, 28, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Uhlemann, M.; Gebert, A.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L. The electrochemical hydrogen sorption behaviour of Zr–Cu–Al–Ni metallic glasses. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, L.J.; Lin, H.J.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.Z.; Zhu, M. Amorphous alloys for hydrogen storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 941, 168945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Eliezer, D. Hydrogen Effects on an Amorphous Fe-Si-B Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Han, J.; Feng, F.; Northwood, D.O. Characteristics of the high-rate discharge capability of a nickel/metal hydride battery electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 3591–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Noreus, D.; Starborg, S. Increasing NiMH battery cycle life with oxygen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18626–18631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Pan, H.G.; Gao, M.X.; Ma, J.X.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, Q.D. The effect of Zr substitution for Ti on the microstructures and electrochemical properties of electrode alloys Ti1−xZrxV1.6Mn0.32Cr0.48Ni0.6. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2002, 27, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Miao, J.; Shen, W.; Su, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. High temperature electrochemical discharge performance of LaFeO3 coated with C/Ni as anode material for NiMH batteries. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2002, 32, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fernandez, C.; Chunmei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wen, C.; Stroe, D.I.; Chen, Z. Battery System Modeling, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Bengaluru, India, 2021; pp. 1–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Sridhar, M.P.; Srinivasane, S. AC Impedance Studies on Metal Hydrid Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Leng, Y.; Yuan, A.; Cao, C. Study of early cycling deterioration of a Ni/MH battery by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Power Sources 1998, 74, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Cao, C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of Ni/MH batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 1999, 293, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.F.; Tsai, C.J. Hydrothermal phase transformation of hematite to magnetite. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucherit, N.; Goff, H.L.A.; Joiret, S. Raman studies of corrosion films grown on Fe and Fe-6Mo in pitting conditions. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman study of magnetite (Fe3O4): Laser-Induced thermal effects and oxidation. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatarah, I.S.M.; Imiela, A.; Surmacki, J.; Olbrycht, R.; Wittchen, W.; Borecki, M.; Abramczyk, H.; Wiecek, B. FeO content estimation in steel slag using Raman spectroscopy in NIR range. In Proceedings of the 14th Quantitative InfraRed Thermographic Conference, Berlin, Germani, 25–29 June 2018; Available online: https://www.ndt.net/article/qirt2018/papers/p31.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- McCarty, K.F. Inelastic light scattering in α-Fe2O3: Phonon vs magnon scattering. Solid State Commun. 1988, 68, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Devine, T.M. A SERS investigation of the passive of the passive films formed on iron in mildly alkaline solution of carbonate/bicarbonate and nitrate. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, J.; Shen, L.; Ford, M.E.; Gao, J.; Xu, J.; Wachs, I.E.; Han, Y.F. Probing the surface of promoted CuO-Cr2O3-Fe2O3 catalysts during CO2 activation. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 271, 118943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T. Raman spectroscopy of clay minerals. In Book Developments in Clay Science; Gates, W.P., Kloprogge, J.T., Madejová, J., Bergaya, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 150–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crousier, J.; Crousier, J.P.; Bellucci, F. Electrochemical and electrocatalytic behaviour of iron-base amorphous alloys in 1M KOH at 25 °C. Electrochim. Acta 1993, 38, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, M.L.; Huot, J.Y.; Schulz, R. The crystallization of amorphous Fe60Co20Si10B10 and its effect on the electrocatalytic activity for H2 evolution. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Lu, Z.C.; Wang, S.L.; Wua, Y.; Lu, Z.P. Fe-Based bulk metallic glasses: Glass formation, fabrication, properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 235–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xiong, F.; Tan, S.; Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; An, Q. Iron metal anode for aqueous rechargeable batteries. Mater. Today Adv. 2021, 11, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Ravikumar, M.K.; Balasubramanian, T.S. Nickel/iron batteries. J. Power Sources 1995, 51, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Current (mA/g) | Cycle Number | Maximum Discharge Capacity (mAh/g) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 20 | 135.86 |
| 100 | 25 | 173.88 |
| 125 | 45 | 83.79 |
| % Discharge Capacity | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycles | 50 mA/g | 100 mA/g | 125 mA/g |
| 1 | 16.74 | 4 | 33.84 |
| 10 | 70.62 | 31.38 | 55.46 |
| 20 | 100 | 78.13 | 85.92 |
| 30 | 86.27 | 91.44 | 96.34 |
| 40 | 73.92 | 74.02 | 99.23 |
| 50 | 59.87 | 57.57 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotelo, O.; Henao, J.; Poblano, C.; Campillo, B.; Castañeda, E.; Flores, N.; Molina, A.; Martínez, H. Evaluating a Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder as a Novel Negative Electrode Material for Applications in Ni-MH Batteries. Batteries 2024, 10, 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10090312
Sotelo O, Henao J, Poblano C, Campillo B, Castañeda E, Flores N, Molina A, Martínez H. Evaluating a Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder as a Novel Negative Electrode Material for Applications in Ni-MH Batteries. Batteries. 2024; 10(9):312. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10090312
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotelo, Oscar, John Henao, Carlos Poblano, Bernardo Campillo, Erick Castañeda, Néstor Flores, Arturo Molina, and Horacio Martínez. 2024. "Evaluating a Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder as a Novel Negative Electrode Material for Applications in Ni-MH Batteries" Batteries 10, no. 9: 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10090312
APA StyleSotelo, O., Henao, J., Poblano, C., Campillo, B., Castañeda, E., Flores, N., Molina, A., & Martínez, H. (2024). Evaluating a Fe-Based Metallic Glass Powder as a Novel Negative Electrode Material for Applications in Ni-MH Batteries. Batteries, 10(9), 312. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10090312







