Abstract
Blended electrodes are becoming increasingly more popular in lithium-ion batteries, yet most modeling approaches are still lacking the ability to separate the blend components. This is problematic because the different components are unlikely to degrade at the same pace. This work investigated a new approach towards the simulation of blended electrodes by replicating the complex current distributions within the electrodes using a paralleling model rather than the traditional constant-current method. In addition, a blending model was used to generate three publicly available datasets with more than 260,000 unique degradations for three exemplary blended cells. These datasets allowed us to showcase the necessity of considering all active components of the blend separately for diagnosis and prognosis.
1. Introduction
Since their commercialization in the early 1990s, lithium-ion batteries have used different electrode materials both at the positive and negative electrodes (PE and NE, respectively) with the material choice dictated by cost, availability, performance, and safety. A concept that has gained considerable interest in the industry is the use of blended electrodes, which involve a physical mixture of two or more different materials. Performance-wise, blending was shown to take advantage of the best features of each material and several commercial cells started to adopt this concept [1,2,3]. One typical PE blend is to mix either lithium nickel aluminum oxide (NCA) or lithium nickel manganese oxide (NMC) with lithium manganese oxide (LMO) to take advantage of the high energy of layered oxides and of the rate capability of the spinel structure [2,4]. Other configurations are possible, and blends of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) with a layered oxide such as lithium nickel manganese oxide have been developed to provide additional capacity at high voltage [1]. On the NE side, most state-of-the-art cells now use a blend of graphite with high-capacity silicon [5,6].
On the experimental side, studies on blended electrodes were pioneered by Ma et al. and Numata et al. [7,8] among others [4,9,10,11], in the late 1990s and 2000s with work on LMO with different layered oxides. Work on blends with LMO and NCA or NMC continued in the 2010s with several works by us [12,13], Smith et al. [14], Schmidt et al. [15], and others [16,17,18,19,20,21]. In addition, other types of PE blends were investigated with lithium manganese iron phosphate and nickel cobalt manganese aluminum oxide [22] or LMO [23], NMC 622 and 111 [24], NMC and LCO [25,26,27], LCO and NCA [28], or NMC and LFP [29]. On the negative side, Wang et al. investigated graphite and lithium titanate blends [30] and Chen et al. investigated graphite and hard carbon [31], but the most significant work came with the introduction of a blended NE containing silicon [5,6,32,33,34]. Most notably, Anseán et al. were the first to showcase the different impact of the loss of graphite or silicon upon aging on the voltage response of the full cell [32].
On the modeling side, Newman’s group started modeling blends’ electrochemical responses in the late 2000s [35] using physics-based models, while we and Schmidt et al. started investigating the aging of blends using the mechanistic degradation mode modeling approach [15,36] in the early 2010s. Most of the following work used physics-based models [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] with some exceptions using the degradation mode approach [25,47,48,49,50,51,52]. Overall, while physics-based models offer better insights into the processes occurring within the cells, their parameterization is always complex, especially when considering aging. Degradation mode models, on the other hand, are much simpler to parameterize, are much less calculation-intensive, and offer a higher fidelity in replicating the voltage response upon aging. However, despite the increased availability and popularity of cells using blended electrodes, the literature on their modeling upon aging is still scarce, with few studies attempting to investigate how degradation could impact the different components of the blends [6,12,27,28,46,48,49,50,51]. Even at the experimental level, most aging studies do not separate components when investigating the loss of active material (LAM), whereas it was shown that different components might not age at the same pace [47].
Early versions of the degradation mode modeling approach offered to simulate blends by adding up and then integrating the incremental capacity (IC) signature of each component [14,15,36]. While this seems to work well without being computationally expensive, recent work by Heubner et al. [1,53,54,55] showcased that this constant-current approach is not realistic and that the current distribution within the electrode should probably be considered for accurate modeling. In response to their studies, we proposed the use of a paralleling model to simulate the current distribution in each component of the blend instead of the IC method [56]. This could be achieved by simulating a wide array of different rates for each state of health to enable the use of a paralleling model adapted from the literature [57,58]. Preliminary results showcased that the complex, experimentally observed current distributions [1,53,54,55] could be reproduced [56], but that the calculation cost was increased by close to two orders of magnitude, as many simulations at different rates needed to be performed to limit the noise in the simulations. While this is not a problem for punctual simulations, this could prove to be a limiting factor for the generation of large synthetic datasets [49,59,60,61,62] that will likely be necessary to train algorithms for the accurate diagnosis of blended electrodes.
This work aimed to compare both approaches to decipher whether the increase in calculation cost is mandatory to generate data that is truly representative of real cells. Three case studies were investigated to cover the main behavior of electrodes with blends composed of materials with a completely separated electrochemical response (LFP and LMO), a mostly overlapping response (NMC and NCA), and an only partially overlapping response (NMC and LMO). In addition, we will seize this opportunity to discuss the impact of the composition of the LAM on the electrochemical response of the cells. In blended electrodes, since the total electrode LAM is the sum of the LAM on both components, there exists different voltage curves for the same electrode-level LAM, which can significantly complicate diagnosis. Finally, we will also provide the community with three synthetic datasets for the three exemplary cells mentioned above, each containing more than 260,000 unique degradations [63]. These datasets could be used to develop different diagnosis methods for blended electrodes, enabling the separation of the degradation by component.
2. Materials and Methods
All simulations were conducted with the ‘alawa toolbox version 2.2.2 [36,64] using stock electrode materials. The degradation mode model behind the toolbox [36,56] uses experimental data to link the electrochemical response for both electrodes to the full cell by adjusting six parameters, the loading ratio between the electrodes, their offset, their relative rates (PE and NE), and their relative resistances (PE and NE). The impact of different degradation modes was simulated by adjusting these parameters with the loss of lithium inventory (LLI) impacting the offset, the LAM impacting the loading and offset, and kinetic limitations impacting the rates and resistances. For the sake of simplicity, all cells were simulated with the same blending ratio (50:50), graphite electrode, initial matching parameters (loading ratio = 1.1, offset = 4, all kinetic parameters set to 1), and cutoffs (3 V and 4.2 V). The lower cutoff voltage of 3 V was chosen to avoid over-discharging issues with LMO [13].
The simulated rate and regime for the results in the main body of this publication was a C/25 charge. Additional experiments were also performed under discharge and at higher rates to ensure the generalization of the results. Results from some of these extra simulations are provided in Appendix A.
The challenge in simulating blended electrodes is to allow each electrode to pass the required capacity at each individual voltage step before proceeding to the next one. If a constant current is assumed, the overall capacity to pass for each voltage step can be calculated by adding each component increment of capacity (dQ) for each increment of voltage (dV), which corresponds to summing IC (dQ/dV = f(V)) curves. If the current is not constant, a paralleling model is needed to determine how much current is going into each component based on the SOC, rate, and polarization to determine the dQ for each dV. Figure 1 presents a schematic representation of both approaches with (a–f) the original constant-current one and (g–j) the one using the paralleling model.
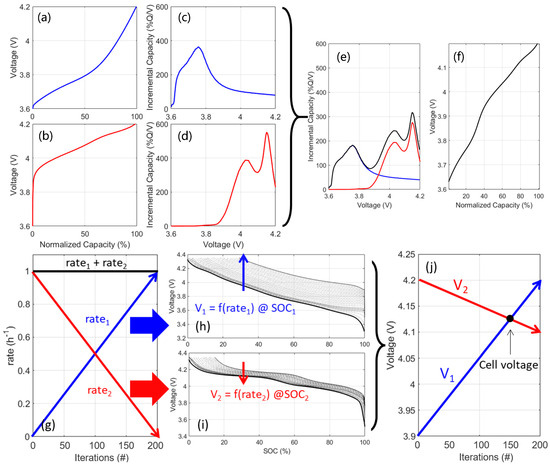
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of both approaches for blended electrode simulations with (a–f) the constant-current approach and (g–j) the paralleling approach (adapted from [56]). For the constant-current approach, (a,b) display the voltage vs. capacity response for both components of the blend and (c,d) their associated IC signature; (e) showcases both IC signatures together with their sum with (f) being the integration of the latter. For the paralleling approach, (g) presents the link between the rates in both components for all iterations, (h,i) the impact of rate on each component, and (j) the relationship between rate and voltage in both components at the current SOC.
In the traditional approach [14,15,36], the constant-current response of each component of the blend is calculated at the requested rate (Figure 1a,b) before being derived to obtain the IC response (Figure 1c,d). The IC responses are then weighted with the blend ratio (50:50 here), summed (Figure 1e), and finally integrated to obtain the blended electrode voltage response (Figure 1f). Typical simulations using this approach were performed in around 30 ms each on a laptop with a 12th Gen Intel® CoreTM i7-1280P 1.80 GHz processor and 32 GB of RAM. It should to be noted that, as proposed in [56], this approach could be easily improved by enabling to simulate the electrode response at a weighted rate to emulate the current density only affecting one component at the time.
The principles of the calculation for the paralleling approach [56,57,58] are presented in Figure 1g–j. With the requested rate known and at every given state of charge (SOC), the rates on both components are linked, since their sum must equal the requested rate (Figure 1g). By simulating a wide array of rates for each component (between 0 and the maximum current defined as the requested rate divided by blend percentage (Figure 1h,i)), the voltage vs. rate response for each component can then be calculated and related (Figure 1j). Their intersection represents the only rate combination at which the voltages are equal, with the sum of rates also being equal to the requested one. These steps must be repeated for all SOCs until the cutoff is reached. From Figure 1h,i, it is easy to understand where the additional calculation cost is coming from; the more rates simulated, the lesser the noise but the higher the calculation cost. An optimal balance was found by using between 100 and 200 rates with simulations typically requiring in average of 2.5 s using the configuration mentioned above and the Matlab© paralleling toolbox with 12 workers. Alternative approaches for paralleling, such as the one recently proposed [65,66,67], might allow us to reduce the calculation cost, and this will be investigated at a later time.
In this work, three publicly available synthetic datasets [63], each containing more than 260,000 unique degradations for the three exemplary blended cells, were generated using the method we proposed in [61], which is summarized in Figure 2. A set of 5450 different degradation paths was defined by combining every combination of LLI and LAMs on NE as well as both components of the PE in 1/30th increments. These paths can be visualized as red dots on an LLI/LAMNE/LAMPE ternary diagram representing all their possible combinations at the selected resolution. For each dot, 31 combinations of LAMPE1/LAMPE2 must be considered to account for loss on either component of the PE. Finally, 49 simulations at different levels of degradation (from 0 to 50% with a periodically increasing time step, right of Figure 2) were then performed for each path for a total of 267,050 simulations.
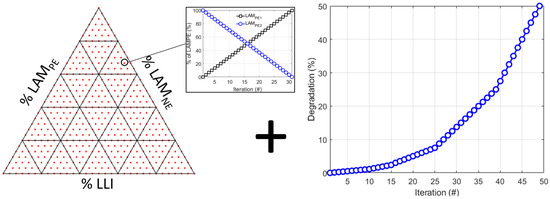
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of synthetic data generation process with the different LLI/LAMPE/LAMNE studied triplets as red dots in a ternary diagram (left). Each dot is associated with 31 different LAMPE compositions (insert). All compositions were tested for 49 different levels of degradation between 0 and 50% with incremental spacing (right).
For each dataset, calculations were performed using the constant-current approach and took around 90 s each on an Intel® CoreTM i9-10900F 2.80 GHz GPU computer with 64 GB of RAM. A similar generation paralleling approach took approximately 9000 s.
3. Results
Figure 3a–c present more details on the materials used in this work with the IC response of all individual components for a constant-current C/25 charge. The first cell contains a 50:50 LFP and LMO blend. This configuration was chosen to represent cells with completely separate voltage responses. The second cell contains a 50:50 NMC and NCA blend to account for electrodes with overlapping voltage responses. Finally, the last cell contains 50:50 NMC and LMO to investigate cells with partially overlapping voltage response. More details on the significance of the IC peaks are outside the scope of this work and can be found in [68].
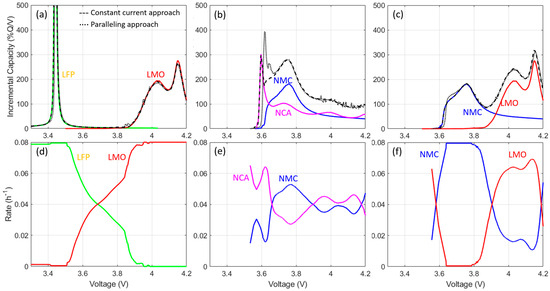
Figure 3.
IC response of the blended electrodes and individual components for the three exemplary cells studied in this work with (a) LFP and LMO, (b) NMC and NCA, and (c) NMC and LMO with (d–f) the associated current distributions when paralleled. Dashed lines correspond to a blend calculated from constant current and the dotted line from the paralleling approach.
Figure 3d–f showcase the associated current distribution once parallelized. For the cell with separate electrochemical responses, the current is either on one material or the other. Therefore, for a 50:50 blend, the local current density on both components is doubled compared to the requested rate (i.e. a rate of C/12.5 for a requested C/25 at the electrode level). For the cell with overlapping responses, the current was first mostly on NCA, because its response started at a slightly lower voltage, and then fluctuated around C/25 until the end of charge. For cells with only partially overlapping responses, the current distribution is more complex and has some parts with the current solely on one electrode at low voltage before the current splits, when both phases become active. In our example, and despite the 50:50 blend, the split is not 50:50 because LMO has a greater capacity than NMC in the considered potential window.
The black curves in Figure 3a–c showcase the calculated electrode response for both the constant-current (dashed curves) and paralleling (dotted curves) approaches. The simulations were very similar for the LFP/LMO blend, which was expected, since the responses are separated and since they are both high-power materials with a limited impact of polarization between C/25 and C/12.5. For the NMC/NCA blend, there were clear differences at low voltages; the first NCA peak seemed delayed and more pronounced for the paralleling approach, because the NCA phase received most of the current and thus had a higher local current density than the constant-current one. For the NMC/LMO blend, some minor differences were also visible at low voltages when NMC received all the current.
Figure 3 showcases that, at the electrode level and without any degradation, the signature of the blends was, overall, really similar for both approaches. Figure 4 provides a comparison of the voltage responses for the full cell and upon aging. Each row corresponds to four specific subsets from the synthetic datasets, where there was up to 50% of LAMPE on the first component of the blend only in the first column (no LLI, no LAMPE2, no LAMNE), LAMPE1 and LLI in the second column (no LAMPE2, no LAMNE), LAMPE2 in the third column (no LLI, no LAMPE1, no LAMNE), and LAMPE1 and LLI in the fourth column (LAMPE1, no LAMNE). For the initial state (thick curves), the difference between the two approaches is less evident than on the electrode alone. This is because of the slippage between the PE and NE that prevents the PE from being fully delithiated [36], and, as such, the electrode portion where the most variations were observed was not utilized in the pristine full cell. Not surprisingly, the difference is much more visible for the NMC/NCA blend when delithiated LAMPE occurs (columns 1 and 3) because this increases the range of utilization of the PE and thus enables access to the states of charge where the PE simulations were different. For opposite reasons, and when lithium was lost along the PE (columns 2 and 4), the slippage increased and the simulation from both approaches became nearly indistinguishable.
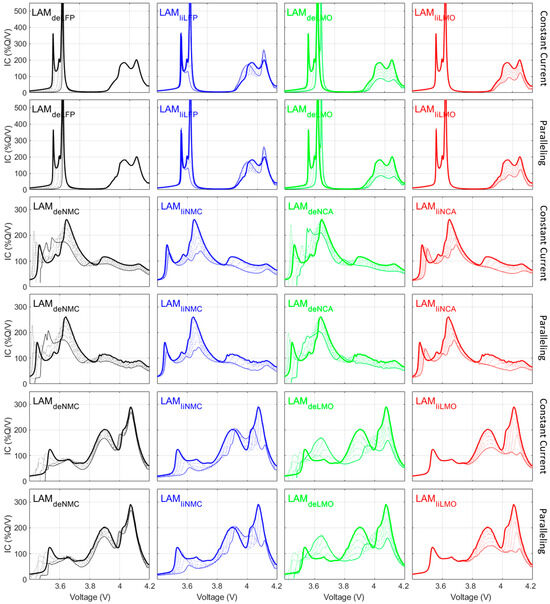
Figure 4.
Simulation of up to 50% LAMPE on both components of the blend with or without lithium for the three exemplary cells: rows 1 and 2 for LFP/LMO, rows 3 and 4 for NMC/NCA, and rows 5 and 6 for NMC/LMO. Rows 1, 3, and 5 were simulated using the constant-current approach and rows 2, 4, and 6 with the paralleling one. Thick lines represent the initial state and thin lines the final ones, with the dotted lines representing the progression in between.
4. Discussion
At the full-cell level and for low-rate simulations, and because of the slippage between the PE and NE, the observed differences between the constant-current and paralleling approaches were slim. While the differences increase with high delithiated LAMPEs, this is not a big issue for prognosis, as the signature of a limiting PE at end of discharge is unique and easily identifiable either way. Therefore, the calculation cost increase induced by using the paralleling approach, on top of the noisier data, might not be justifiable for generating large datasets. Looking at faster rates (0.2 C) (Figure A1 and Figure A2), the differences are more visible because the rate has more impact. For the LFP/LMO blend (Figure A1), the impact of polarization on the LFP results in a misevaluation of the potential of the main peak at 3.4 V using the constant-current approach (Figure A1, second column). However, this could be solved without paralleling by weighting the rates (i.e., summing the IC response at C/2.5, C/5 ÷ 2 for a 50:50 blend, Figure A1, third column). For the NMC/NCA blend (Figure A2, columns 1 and 2), the signatures of LAMPE and LLI are still really similar, whereas the one with LAMPE alone might be different enough to justify the use of the paralleling approach. However, this scenario is unlikely as the inevitable growth of the SEI layer in graphite-based cells usually consumes Li ions at a steady pace, thereby increasing the slippage which, as mentioned above, limits the utilization of the PE in a range where both approaches provide similar results.
In addition to allowing us to study the impact of the calculation approach, the synthetic datasets also cover all possible combinations of LAMs and LLI, and thus, a subset covering all different compositions of LAMPE could be extracted and investigated. An example is presented in Figure 5 with the different voltage responses associated with 10% LAMPE for all three exemplary chemistries. For this example, paths with neither LLI nor LAMNE were selected. This filtering led to 21 unique paths with LAMPE on each component of the blend varying from 0 to 20 in 1% increments, with their sum always equal to 20 (20% loss on one component equals 10% loss at the electrode level for a 50:50 blend). The black curve corresponds to the impact of LAMPE if the composition of the electrode is not considered because the loss is similar on both components of the blend (10% each). For the LFP/LMO blend, the composition of the LAMPE was especially visible when looking at the capacity at which the LFP intercalation was completed, which could vary by more than ±5% around the 10% line between 20% LAMLFP and 20% LAMLMO, respectively. More variations are visible on the IC curves, with the area and intensities of all peaks varying up and down the 10% line depending on the LAMPE composition. No significant variations are observable for the NMC/NCA blend, which implies that it will be impossible to determine the true origin of the LAMPE in this particular blend. Finally, with the NMC/LMO blend, the voltage vs. capacity response did not showcase changes as clearly as for the LFP/LMO blend, but the IC curves showcased a lot of up-and-down peak variations around the 10% line.
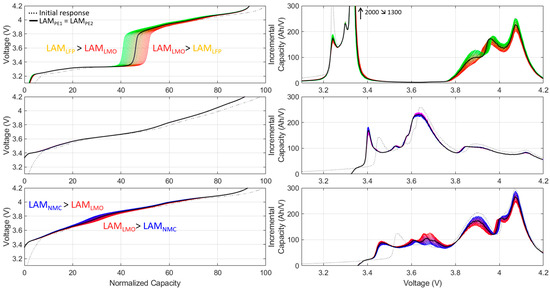
Figure 5.
Voltage vs. capacity (column 1) and IC signatures (column 2) for simulations of 10% LAMPE from 20% LAMPE1 and 0% LAMPE2 to 0% LAMPE1 and 20% LAMPE2 in 1% increments for the three exemplary cells: LFP/LMO (row 1), NMC/NCA (row 2), and NMC/LMO (row 3). Unless black, the color indicates which LAMPE is preponderant following the color code from Figure 3 (green: LFP, red: LMO, blue: NMC, magenta: NCA). The arrow on the top right figure indicates that the peak was cropped. The numbers indicate the initial and final intensity of the peak.
The discrepancies induced by the composition of the LAMPE will need to be considered to reach an accurate diagnosis of the degradation, because the observed variation might interfere with the signature of the other degradation modes, both thermodynamic (LLI and LAMNE) and kinetic (rate degradation factors (RDFs)) [36]. Figure 6 presents the voltage variations associated with the non-LAMPE degradation modes for the LFP/LMO and NMC/LMO cells. For both cells, the thermodynamic degradation modes also significantly impacted the high-voltage response of the cell. For the kinetic modes, the RDF on the NE seemed to impact the shape of the high-voltage peaks the most before plating started to occur. Therefore, misdiagnosing the peak variations could have serious safety implications, which highlights the necessity to separate the LAMPE quantification.
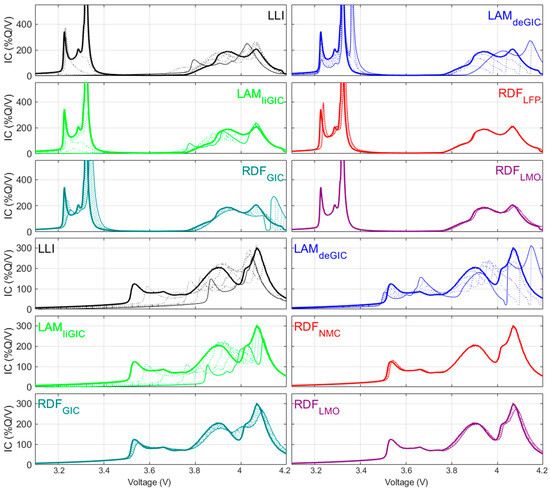
Figure 6.
Simulation of up to 50% LLI, LAMdeNE, and LAMliNE as well as up to x5 kinetic variations on both PE components and the NE using the constant-current approach for the LFP/LMO cell (row 1–3) and the NMC/LMO cell (row 4–6). Thick lines represent the initial state and thin lines the final ones, with the dotted lines representing the progression in between.
5. Conclusions
This work first investigated the impact of using a paralleling model within the mechanistic degradation mode modeling approach to replicate the current distribution more accurately within blended electrodes. Using three exemplary chemistries with electrochemical responses that cover all possible scenarios (separated, overlapping, or only partially overlapping), we demonstrated that although the paralleling approach enhances accuracy and better replicates experimentally observed current distributions, the actual effect on the voltage response of the full cell, whether pristine or aged, was close to negligible at low rates, while the computational cost was increased by two orders of magnitude and resulted in noisier results. While it might be better to use the paralleling model for simulation at higher rates or when the loss of active material on the PE is significant, the computational limitations could hinder the application of the paralleling approach in scenarios where simulation speed is crucial because of the two-order-of-magnitude increase.
Recognizing that the constant-current approach is accurate enough to provide data representative of the behavior of the individual components within a blend, three publicly available synthetic datasets covering more than 260,000 different degradations were generated to enable the development of new diagnosis techniques for blended electrodes. Such techniques must enable component-specific diagnosis, since we showcased a significant impact of the composition of the LAMPE on the cell electrochemical response. Because these variations could be confused with the one induced by other degradation modes, overlooking them could lead to false diagnosis, potentially compromising the safety of deployed systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.; methodology, M.D.; software, M.D.; validation, D.B. and M.D.; formal analysis, D.B. and M.D.; investigation, D.B. and M.D.; resources, M.D.; data curation, M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.; writing—review and editing, D.B. and M.D.; visualization, M.D.; supervision, M.D.; project administration, M.D.; funding acquisition, M.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ONR, grant number #N00014-20-1-2270, and by Element Energy.
Data Availability Statement
The data used for this work are publicly available in Mendeley Data (doi:10.17632/w48j7rn4x3.1t) [63].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
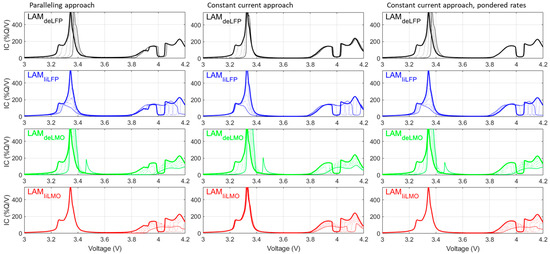
Figure A1.
C/5 simulations of up to 50% LAMPE on both components of the blend with or without lithium for the LFP/LMO blend using the paralleling approach (column 1), the constant-current approach (column 2), and the constant-current approach with weighted rates. Thick lines represent the initial state and thin lines the final ones, with the dotted lines representing the progression in between.
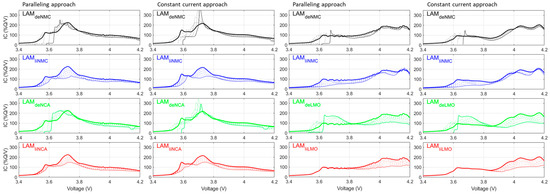
Figure A2.
C/5 simulations of up to 50% LAMPE on both components of the blend with or without lithium for the NMC/NCA (column 1 and 2) and NMC/LMO (column 3 and 4) blends using the paralleling approach (column 1 and 3), the constant-current approach (column 2 and 3), and the constant-current approach with weighted rates. Thick lines represent the initial state and thin lines the final ones, with the dotted lines representing the progression in between.
References
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Recent insights into the electrochemical behavior of blended lithium insertion cathodes: A review. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotal, M.; Jakhar, S.; Roy, S.; Sharma, H.K. Cathode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries: Recent progress and future prospects. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuch, R.; Wagner, R.; Hörpel, G.; Placke, T.; Winter, M. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergus, J.W. Recent developments in cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, C.; Biesold, G.M.; Sewell, C.D.; Hao, S.M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Lai, Y.; Lin, Z. Recent Advances in Silicon-Based Electrodes: From Fundamental Research toward Practical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2004577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, J.; Schindler, M.; Jossen, A. Change in the half-cell open-circuit potential curves of silicon–graphite and nickel-rich lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide during cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2021, 506, 230240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.F.; Yang, X.Q.; Liao, X.Z.; Sun, X.; McBreen, J. Electrochemical evaluation of composite cathodes base on blends of LiMn2O4 and LiNi0.8Co0.2O2. Electrochem. Commun. 2001, 3, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Amemiya, C.; Kumeuchi, T.; Shirakata, M.; Yonezawa, M. Advantages of blending LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 into Li1+xMn2−xO4 cathodes. J. Power Sources 2001, 97–98, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikkannanavar, S.B.; Bernardi, D.M.; Liu, L. A review of blended cathode materials for use in Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.-W.; Yoon, W.-S.; Shin, H.; Chung, K.Y.; Choi, S.; Yang, X.-Q. In situ X-ray diffraction studies of mixed LiMn2O4–LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 composite cathode in Li-ion cells during charge–discharge cycling. J. Power Sources 2009, 192, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.K.; Shin, J.S.; Nahm, K.S.; Kumar, T.P.; Stephan, A.M. Electrochemical studies on cathode blends of LiMn2O4 and Li[Li1/15Ni1/5Co2/5Mn1/3O2]. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Liaw, B.Y.; Gering, K.; Sazhin, S.; Jamison, D.; Michelbacher, C. Evaluation of commercial lithium-ion cells based on composite positive electrode for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle applications. Part II. Degradation mechanism under 2C cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10336–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Devie, A.; Liaw, B.Y.; Gering, K.; Sazhin, S.; Jamison, D.; Michelbacher, C. Evaluation of Commercial Lithium-Ion Cells Based on Composite Positive Electrode for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A1787–A1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Smith, S.R.; Byrne, T.; Burns, J.C.; Dahn, J.R. Synergies in Blended LiMn2O4 and Li[Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3]O2 Positive Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A1696–A1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.P.; Tran, H.Y.; Richter, J.; Ivers-Tiffée, E.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Analysis and prediction of the open circuit potential of lithium-ion cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.Y.; Täubert, C.; Fleischhammer, M.; Axmann, P.; Küppers, L.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. LiMn2O4 Spinel/LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Blends as Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, A556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.-S.; Nam, K.-W.; Jang, D.; Chung, K.Y.; Cho, Y.-H.; Choi, S.; Hanson, J.C.; Yang, X.-Q. The kinetic effect on structural behavior of mixed LiMn2O4–LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode materials studied by in situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction technique. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 15, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Wiegart, Y.-c.K.; Liu, Z.; Faber, K.T.; Barnett, S.A.; Wang, J. 3D analysis of a LiCoO2–Li(Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2 Li-ion battery positive electrode using X-ray nano-tomography. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 28, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiaszny, B.; Ziegler, J.C.; Krauß, E.E.; Schmidt, J.P.; Ivers-Tiffée, E. Electrochemical characterization and post-mortem analysis of aged LiMn2O4–Li(Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2)O2/graphite lithium ion batteries. Part I: Cycle aging. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Wilka, M.; Kasper, M.; Fleischhammer, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Temperature dependent ageing mechanisms in Lithium-ion batteries—A Post-Mortem study. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H. Lithium migration between blended cathodes of a lithium-ion battery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 8653–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Kong, D.; Wu, M.; Liu, H. Interaction between LMFP and NCMA and Its Effect on Blending Cathode-Based Cells. Energies 2024, 17, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Axmann, P.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Origin of the Synergetic Effects of LiFe0.3Mn0.7PO4–Spinel Blends via Dynamic In Situ X-ray Diffraction Measurements. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A1936–A1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, J.; Schmid, A.U.; Rau, L.; Gesterkamp, A.; Storch, M.; Spier, B.; Birke, K.P.; Sauer, D.U. Fast-charging capability of lithium-ion cells: Influence of electrode aging and electrolyte consumption. Appl. Energy 2022, 305, 117747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baure, G.; Dubarry, M. Battery durability and reliability under electric utility grid operations: 20-year forecast under different grid applications. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Lee, P.-H. Storage fading of a commercial 18650 cell comprised with NMC/LMO cathode and graphite anode. J. Power Sources 2017, 349, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baure, G.; Devie, A.; Dubarry, M. Battery Durability and Reliability under Electric Utility Grid Operations: Path Dependence of Battery Degradation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A1991–A2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Keil, P.; Schuster, S.F.; Jossen, A. Impact of Temperature and Discharge Rate on the Aging of a LiCoO2/LiNi 0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Lithium-Ion Pouch Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A1438–A1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnard, N.; Etiemble, A.; Douillard, T.; Dubrunfaut, O.; Tran-Van, P.; Gautier, L.; Franger, S.; Badot, J.-C.; Maire, E.; Lestriez, B. Multiscale Morphological and Electrical Characterization of Charge Transport Limitations to the Power Performance of Positive Electrode Blends for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Verbrugge, M.W.; Liu, P. Composite Titanate–Graphite Negative Electrode for Improved State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Goel, V.; Namkoong, M.J.; Wied, M.; Müller, S.; Wood, V.; Sakamoto, J.; Thornton, K.; Dasgupta, N.P. Enabling 6C Fast Charging of Li-Ion Batteries with Graphite/Hard Carbon Hybrid Anodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 11, 2003336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anseán, D.; Baure, G.; González, M.; Cameán, I.; García, A.B.; Dubarry, M. Mechanistic investigation of silicon-graphite/LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 commercial cells for non-intrusive diagnosis and prognosis. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 227882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.-T.F. Capacity and Coulombic Efficiency Measurements Underestimate the Rate of SEI Growth in Silicon Anodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 080524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Schindler, M.; Oberbauer, A.; Jossen, A. Determination of degradation modes of lithium-ion batteries considering aging-induced changes in the half-cell open-circuit potential curve of silicon–graphite. J. Power Sources 2022, 532, 231296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertus, P.; Christensen, J.; Newman, J. Experiments on and modeling of positive electrodes with multiple active materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A606–A618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Truchot, C.; Liaw, B.Y. Synthesize battery degradation modes via a diagnostic and prognostic model. J. Power Sources 2012, 219, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S. Mathematical model of lithium-ion batteries with blended-electrode system. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Choe, S.-Y.; Joe, W.T. A reduced order electrochemical and thermal model for a pouch type lithium ion polymer battery with LiNixMnyCo1−x−yO2/LiFePO4 blended cathode. J. Power Sources 2015, 294, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, W.A.; Park, J.; Van Khue, L.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Ryou, M.-H.; Lee, Y.M. Comparative study on experiments and simulation of blended cathode active materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yan, L.; Xie, J. Degradation Analysis of a Lithium-Ion Battery with a Blended Electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, A295–A303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Farkhondeh, M.; Pritzker, M.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Charge/Discharge Asymmetry in Blended Lithium-Ion Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, A39–A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Farkhondeh, M.; Pritzker, M.; Fowler, M.; Chen, Z. Dynamics of a Blended Lithium-Ion Battery Electrode During Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Plett, G.L. Controls-oriented models of lithium-ion cells having blend electrodes. Part 2: Physics-based reduced-order models. J. Energy Storage 2017, 11, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, K.P.; Budarapu, P.R. Design and analysis of Lithium-ion pouch cell with LMO-NMC blended cathode using coupled thermo-electro-chemical model. J. Energy Storage 2024, 78, 109958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tredenick, E.C.; Wheeler, S.; Drummond, R.; Sun, Y.; Duncan, S.R.; Grant, P.S. A multilayer Doyle-Fuller-Newman model to optimise the rate performance of bilayer cathodes in Li ion batteries. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, S.; Quarti, M.; Yagci, M.C.; Bessler, W.G. Modeling and Experimental Validation of a High-Power Lithium-Ion Pouch Cell with LCO/NCA Blend Cathode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2990–A3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kawasaki, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shono, K.; Mita, Y.; Miyashiro, H. A method of separating the capacities of layer and spinel compounds in blended cathode. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahbaz, A.; Meishner, F.; Li, W.; Ünlübayirl, C.; Uwe Sauer, D. Non-Invasive Identification of Calendar and Cyclic Ageing Mechanisms for Lithium-Titanate-Oxide Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 42, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Kirkaldy, N.; Offer, G.J.; Wu, B. Diagnosing health in composite battery electrodes with explainable deep learning and partial charging data. Energy AI 2024, 16, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Svens, P.; Varini, M.; Lindbergh, G.; Lindström, R.W. Expanded in situ aging indicators for lithium-ion batteries with a blended NMC-LMO electrode cycled at sub-ambient temperature. J. Electochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W. Capacity Decay Mechanism of the LCO + NMC532/Graphite Cells Combined with Post-Mortem Technique. Energies 2017, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.; Matsuda, T.; Imamura, D. Degradation diagnosis of lithium-ion batteries with a LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 and LiMn2O4 blended cathode using dV/dQ curve analysis. J. Power Sources 2018, 390, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Deconvolution of Cyclic Voltammograms for Blended Lithium Insertion Compounds by using a Model-like Blend Electrode. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heubner, C.; Liebmann, T.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Internal dynamics of blended Li-insertion electrodes. J. Energy Storage 2018, 20, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, T.; Heubner, C.; Lämmel, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Investigations on the Effective Electric Loads in Blended Insertion Electrodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 5728–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Perspective on Mechanistic Modeling of Li-Ion Batteries. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Baure, G.; Pastor-Fernández, C.; Yu, T.F.; Widanage, W.D.; Marco, J. Battery energy storage system modeling: A combined comprehensive approach. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Devie, A.; Liaw, B.Y. Cell-balancing currents in parallel strings of a battery system. J. Power Sources 2016, 321, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Berecibar, M.; Devie, A.; Anseán, D.; Omar, N.; Villarreal, I. State of health battery estimator enabling degradation diagnosis: Model and algorithm description. J. Power Sources 2017, 360, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Analysis of Synthetic Voltage vs. Capacity Datasets for Big Data Li-ion Diagnosis and Prognosis. Energies 2021, 14, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Beck, D. Big data training data for artificial intelligence-based Li-ion diagnosis and prognosis. J. Power Sources 2020, 479, 228806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yi, Z.; Chen, B.-R.; Tanim, T.R.; Dufek, E.J. Rapid failure mode classification and quantification in batteries: A deep learning modeling framework. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 45, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.; Dubarry, M. Synthetic data for LFP/LMO, NMC/LMO, and NCM/NCA blended electrodes vs. Graphite. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- HNEI. Alawa Central. Available online: https://www.hnei.hawaii.edu/alawa (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Weng, A.; Movahedi, H.; Wong, C.; Siegel, J.B.; Stefanopoulou, A. Current Imbalance in Dissimilar Parallel-Connected Batteries and the Fate of Degradation Convergence. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2024, 146, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Yang, X. Influence of connection impedance on the performance of parallel-connected lithium-ion batall tery modules. J. Power Sources 2024, 593, 233949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor Marlow, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, B. Degradation in parallel-connected lithium-ion battery packs under thermal gradients. Commun. Eng. 2024, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubarry, M.; Anseán, D. Best practices for incremental capacity analysis. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1023555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).