A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues
Abstract
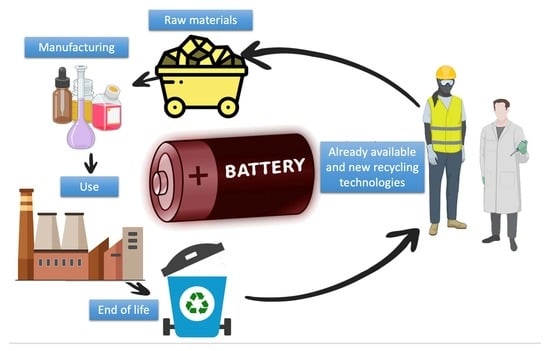
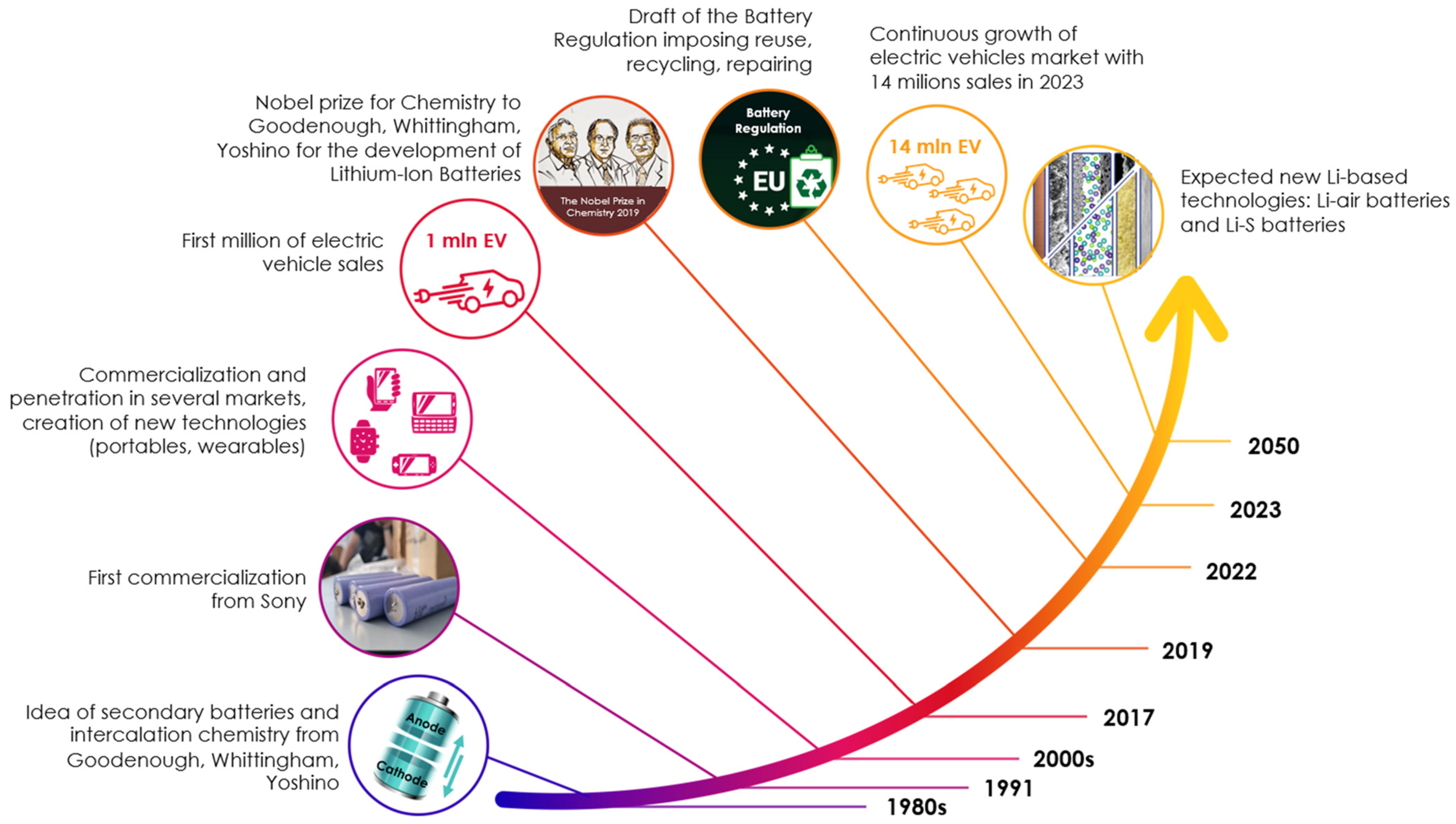
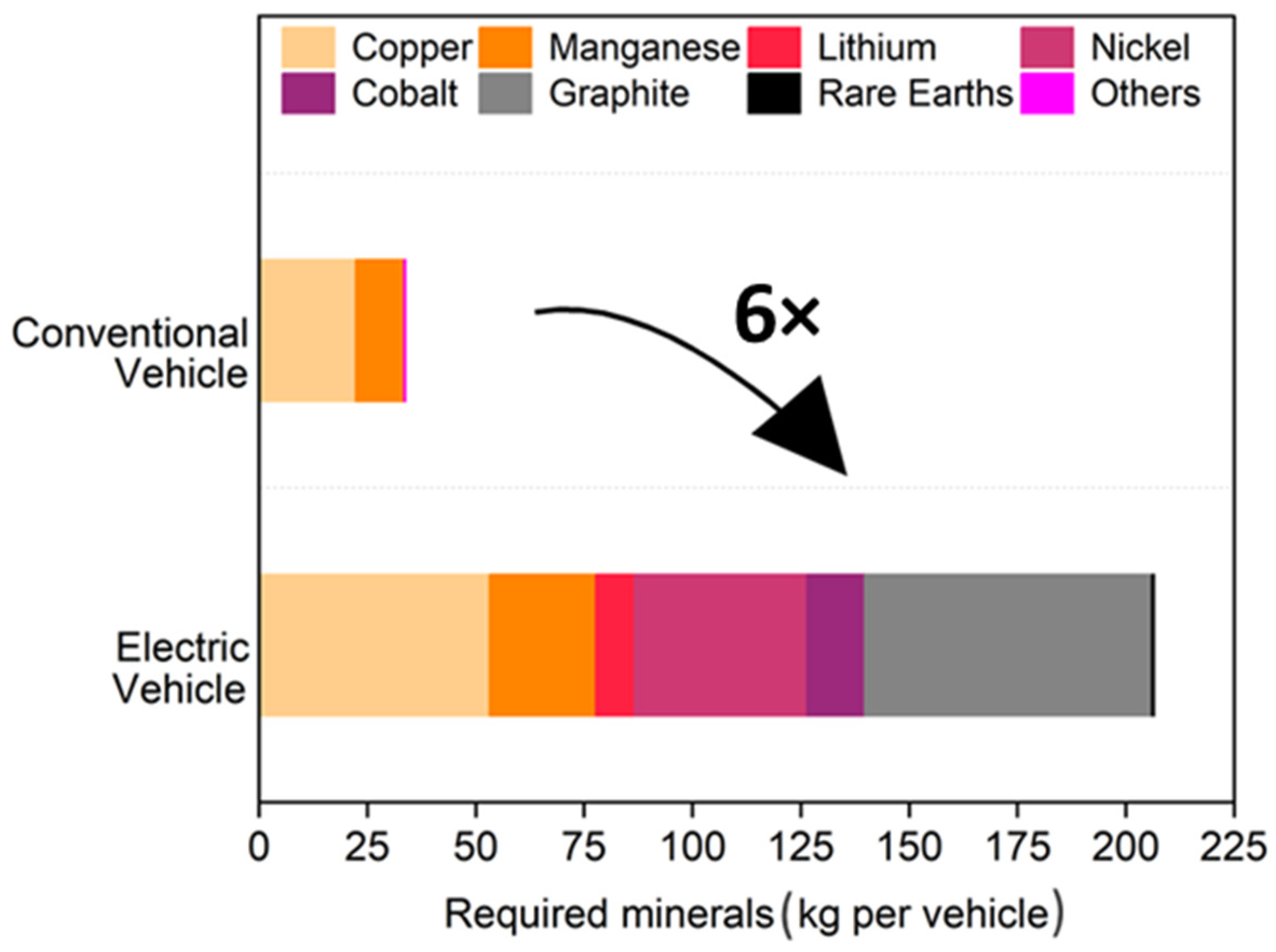
1. Introduction
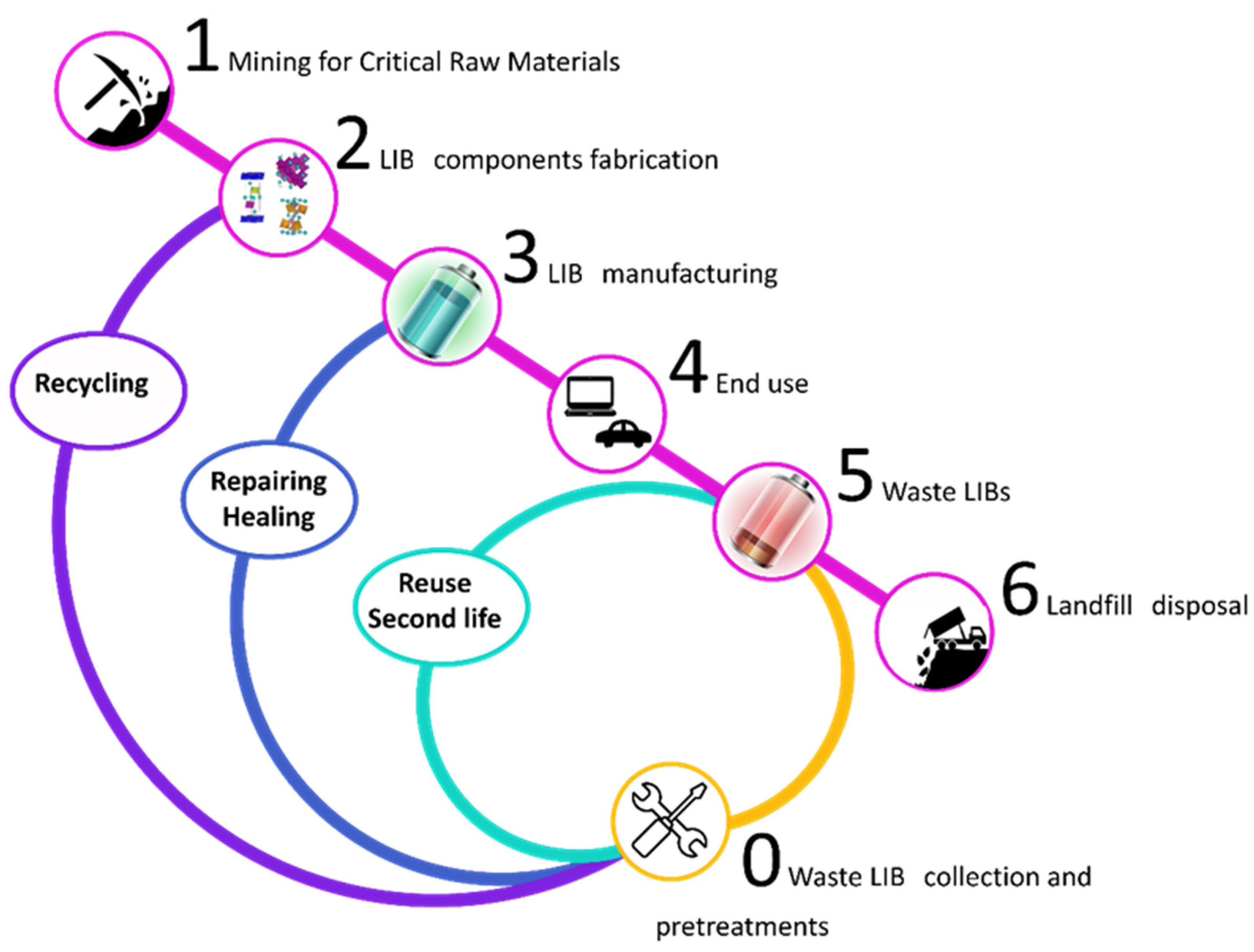
2. Recycling of Spent Li-Ion Batteries: Study Design
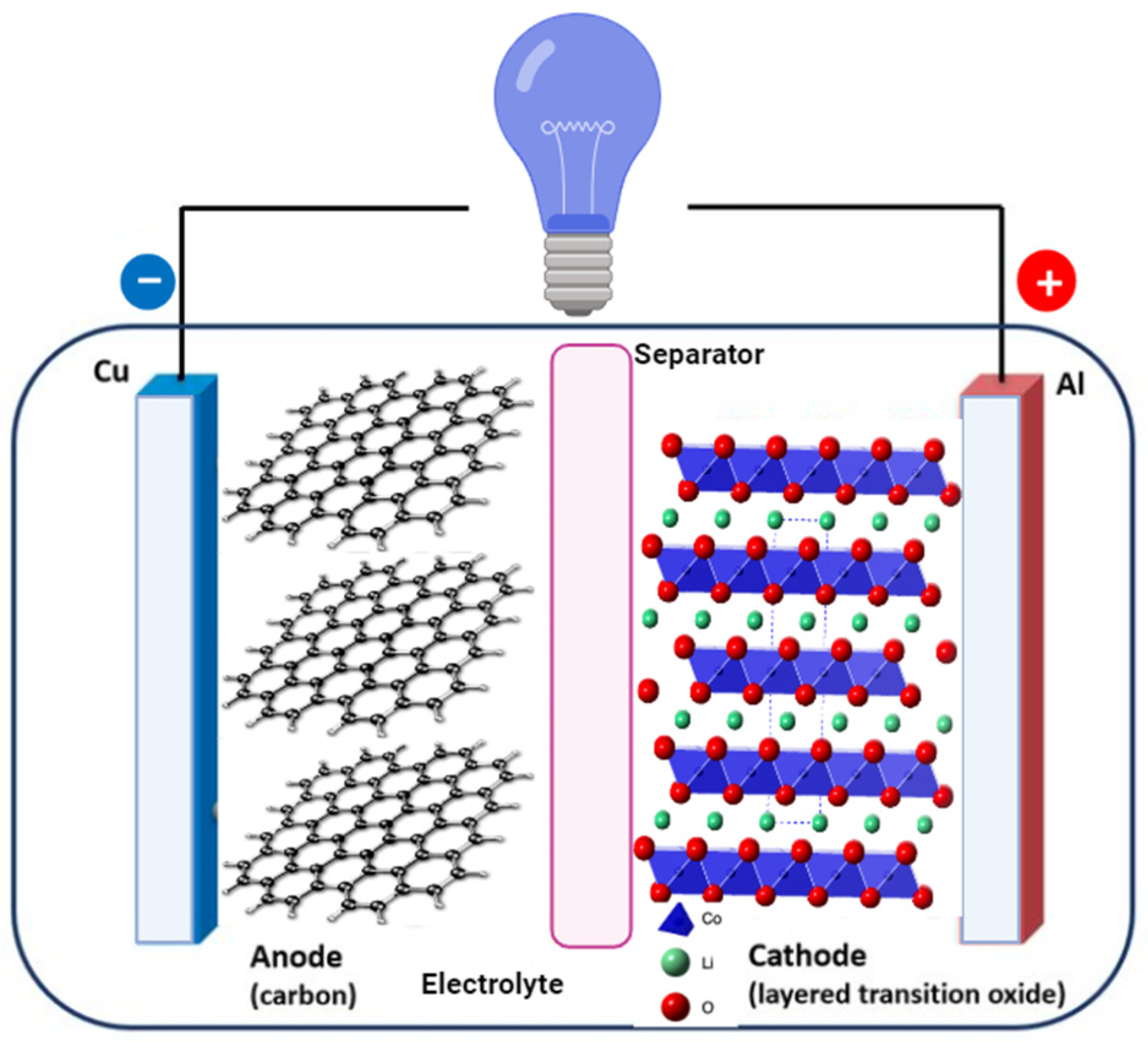
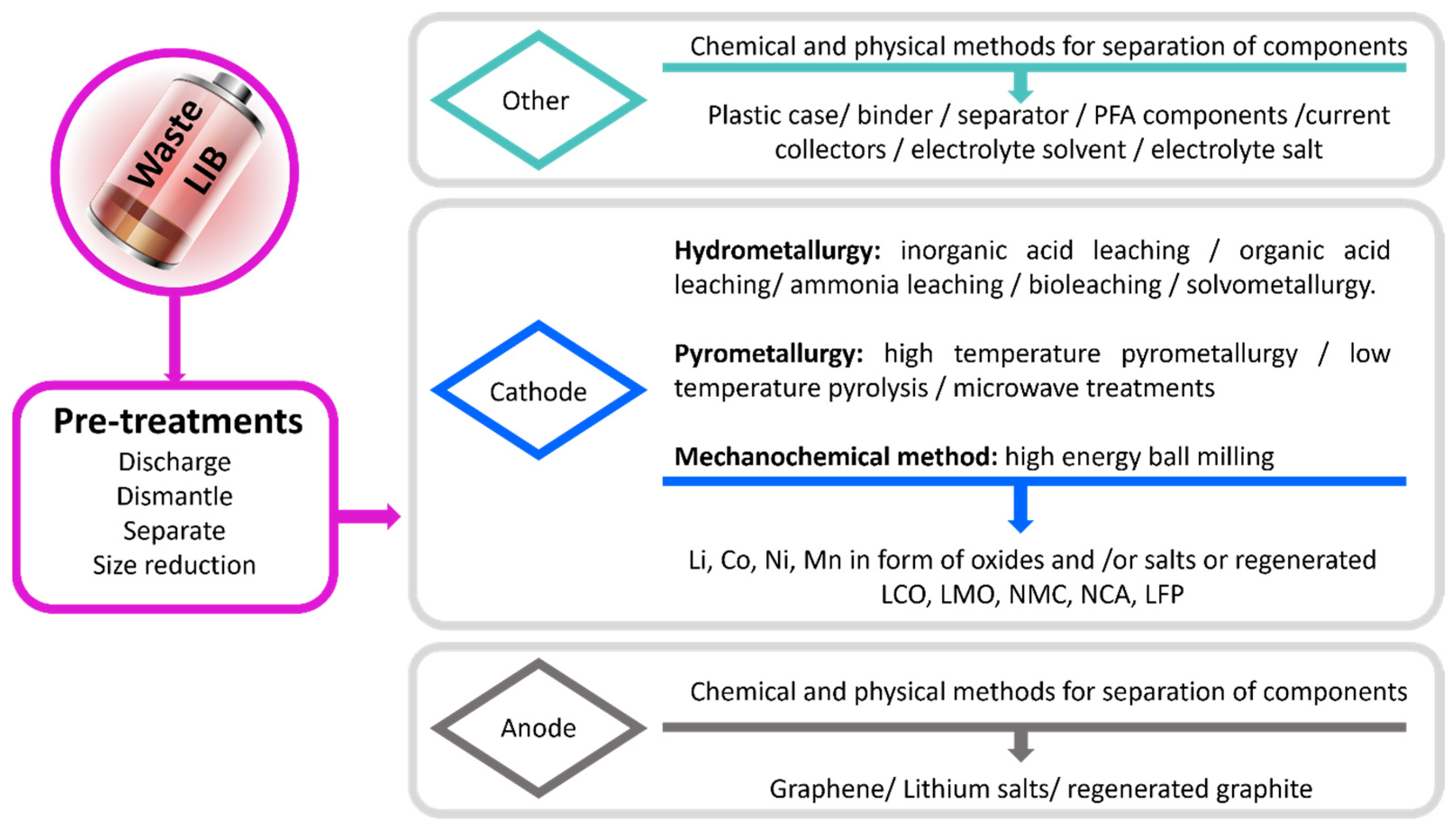
2.1. Materials Recycling
2.1.1. Pretreatments
2.1.2. Pyrometallurgy
2.1.3. Hydrometallurgy
2.1.4. Biometallurgy
2.1.5. Solvometallurgy
2.1.6. Direct Lithium Supplementation
2.1.7. Anode and Electrolyte Recovery
2.1.8. Current Collector Recycling
3. Sustainability
3.1. Environmental Aspects
3.2. Economic Aspects
3.3. Technologies Sustainability Evaluation
4. Open Issues
4.1. Batteries Collection
4.2. Battery Disassembly
4.3. Lack of Policies and Regulations
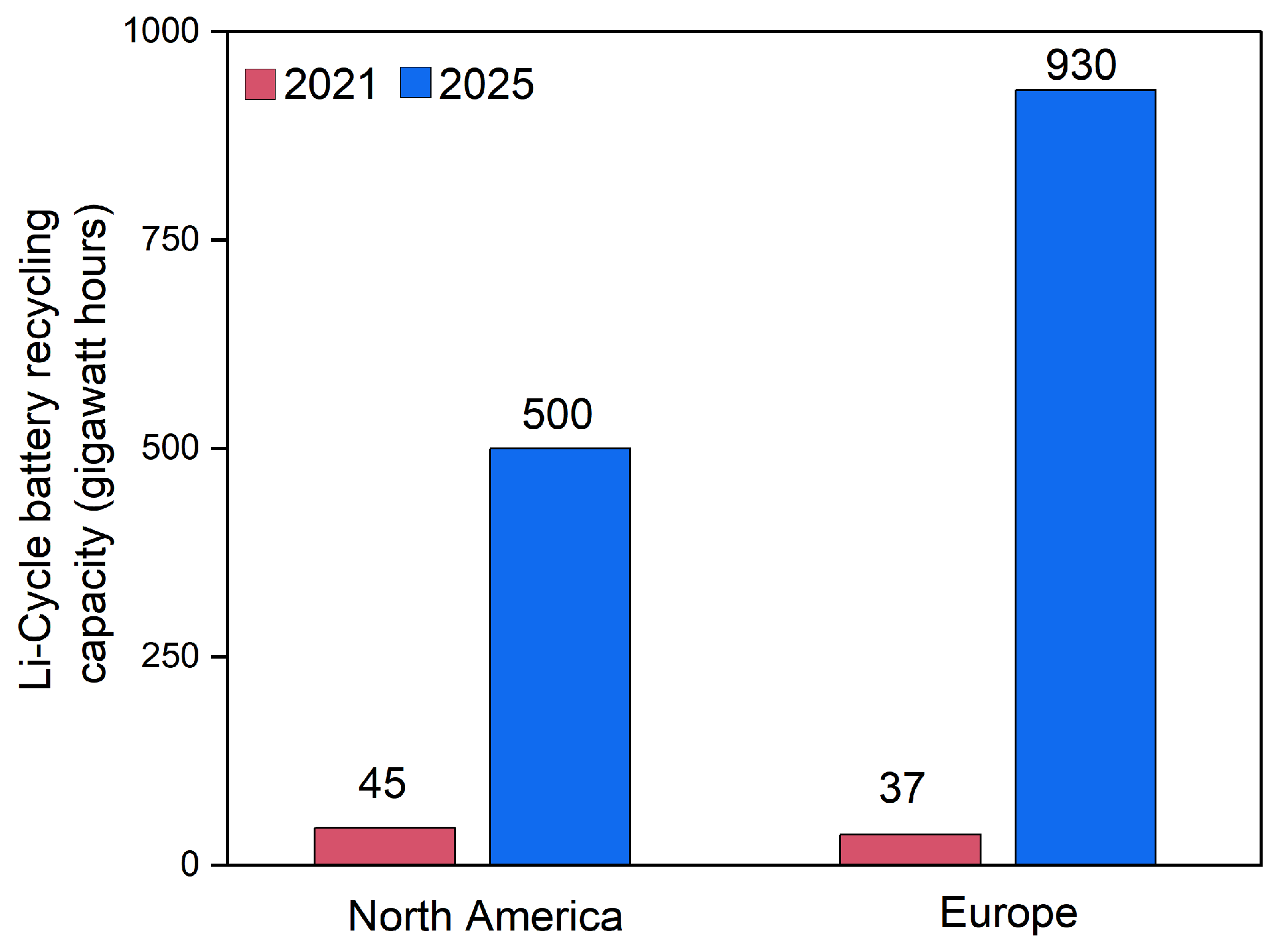
4.4. Scaling-Up and Industrialization
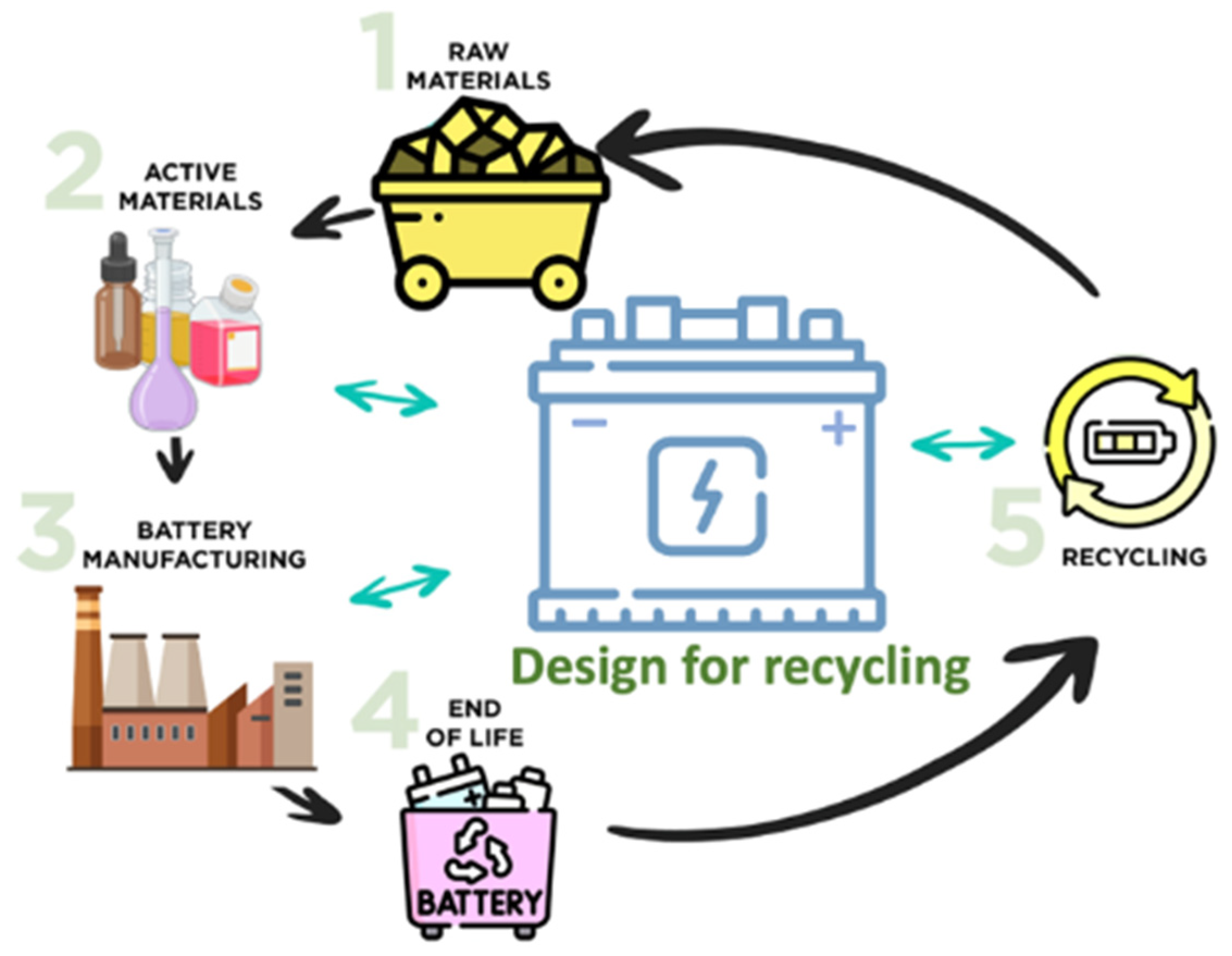
5. Design for Recycling
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Global EV Outlook 2020: Entering the Decade of Electric Drive? Global EV Outlook; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021; ISBN 9789264616226. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Q.; Li, J. An Overview of Global Power Lithium-Ion Batteries and Associated Critical Metal Recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insinna, T.; Bassey, E.N.; Märker, K.; Collauto, A.; Barra, A.L.; Grey, C.P. Graphite Anodes for Li-Ion Batteries: An Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Investigation. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5497–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaza, A.; Ferrari, S.; Wong, H.K.; Lyness, C.; Moore, A.; Weaving, J.; Blanco-Martin, M.; Dashwood, R.; Bhagat, R. Experimental Study of Internal and External Short Circuits of Commercial Automotive Pouch Lithium-Ion Cells. J. Energy Storage 2018, 16, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Park, K.S. The Li-Ion Rechargeable Battery: A Perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.; Sommerville, R.; Kendrick, E.; Driscoll, L.; Slater, P.; Stolkin, R.; Walton, A.; Christensen, P.; Heidrich, O.; Lambert, S.; et al. Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles. Nature 2019, 575, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Cano, Z.P.; Yu, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z. Automotive Li-Ion Batteries: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2019, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, C.; Ruffo, R.; Quartarone, E.; Mustarelli, P. Circular Economy and the Fate of Lithium Batteries: Second Life and Recycling. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Global EV Outlook 2021: Accelerating Ambitions Despite the Pandemic; Global EV Outlook; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020; ISBN 9789264723863. [Google Scholar]
- Greim, P.; Solomon, A.A.; Breyer, C. Assessment of Lithium Criticality in the Global Energy Transition and Addressing Policy Gaps in Transportation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinaro, M.; Bresser, D.; Beyer, E.; Faguy, P.; Hosoi, K.; Li, H.; Sakovica, J.; Amine, K.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Passerini, S.; et al. Bringing Forward the Development of Battery Cells for Automotive Applications: Perspective of R&D Activities in China, Japan, the EU and the USA. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 228073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Roadmap—Battery 2030+. 2020. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/archived-pages/batteries-europe/news-articles-and-publications/battery-2030-roadmap_en (accessed on 29 December 2023).
- Amnesty International. “This Is. What We Die for”: Human Rights Abuses in the Democratic Republic of the Congo Power the Global Trade in Cobalt; Amnesty International: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Scheele, F.; De Haan, E.; Kiezebrink, V. Cobalt Blues Environmental Pollution and Human Rights Violations in Katanga’s Copper and Cobalt Mines. 2016. Available online: https://www.somo.nl/nl/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2016/04/Cobalt-blues.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Sommer, P.; Rotter, V.S.; Ueberschaar, M. Battery Related Cobalt and REE Flows in WEEE Treatment. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.U. Modelling Global Extraction, Supply, Price and Depletion of the Extractable Geological Resources with the LITHIUM Model. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 114, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey & Company. The Race to Decarbonize Electric-Vehicle Batteries; McKinsey & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Tan, D.H.S.; Jiao, B.; Gao, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, Z. A Materials Perspective on Direct Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Principles, Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sheng, J.; Liang, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, H.-M. Direct and Green Repairing of Degraded LiCoO2 for Reuse in Lithium-Ion Batteries. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloop, S.E.; Crandon, L.; Allen, M.; Lerner, M.M.; Zhang, H.; Sirisaksoontorn, W.; Gaines, L.; Kim, J.; Lee, M. Cathode Healing Methods for Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 22, e00113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Lyu, J.; Bi, W.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Regeneration of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Materials. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwani, S.; Methekar, R.; Ramadesigan, V. Resynthesizing of Lithium Cobalt Oxide from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using an Environmentally Benign and Economically Viable Recycling Process. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, F.; Wu, F.; Liu, J. Preparation of LiCoO2 Films from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by a Combined Recycling Process. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, H.; Cao, H. An Overview on the Processes and Technologies for Recycling Cathodic Active Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2013, 15, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Cao, H.; Nawaz, F.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Process for Recycling and Resynthesizing LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 from the Cathode Scraps Intended for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Aravindan, V. Burgeoning Prospects of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries in Multifarious Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bang, J.; Yoo, J.; Shin, Y.; Bae, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, K.; Dong, P.; Kwon, K. A Comprehensive Review on the Pretreatment Process in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadmahmoudi, G.; Javdan Tabar, K.; Homayouni, A.H.; Chehreh Chelgani, S. Recycling Spent Lithium Batteries—An Overview of Pretreatment Flowsheet Development Based on Metallurgical Factors. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2023, 12, 2248559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, D.M.; Mütze, T.; Peuker, U.A. Influence of Cell Opening Methods on Organic Solvent Removal during Pretreatment in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; Mark, M.R.; Steenari, B.M.; Petranikova, M. Incineration of EV Lithium-Ion Batteries as a Pretreatment for Recycling—Determination of the Potential Formation of Hazardous by-Products and Effects on Metal Compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xie, W. Recent Advances in Pretreating Technology for Recycling Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Huang, Z.; Makuza, B.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q. Pretreatment Options for the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Comprehensive Review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 173, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Guo, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Comprehensive Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Fundamentals, Pretreatment, and Perspectives. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 54, 172–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lin, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries in View of Lithium Recovery: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, D.; Singh, P.; Zhang, W.; Nikoloski, A.N. Discharging of Spent Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Batteries in Sodium Hydroxide and Sodium Chloride for a Safe Recycling Process. JOM 2023, 75, 4946–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Yuan, G.; Aleksandrov, A.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Ivanov, M. Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Comprehensive Review for Identification of Main Challenges and Future Research Trends. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Kaden, N.; Dröder, K. A Systematic Review on Lithium-Ion Battery Disassembly Processes for Efficient Recycling. Batteries 2023, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Xu, G.; Peng, X.; Youcef-Toumi, K.; Li, J. Intelligent Disassembly of Electric-Vehicle Batteries: A Forward-Looking Overview. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 182, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Fan, E.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; Wu, F.; Li, L. Environmental and Economic Assessment of Structural Repair Technologies for Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Or, T.; Gourley, S.W.D.; Kaliyappan, K.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Recycling of Mixed Cathode Lithium-ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles: Current Status and Future Outlook. Carbon. Energy 2020, 2, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.C.-Y.; Sui, P.-C.; Zhang, J. A Review of Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials Using Hydrometallurgical Treatments. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Luo, D.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Enabling Future Closed-Loop Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Direct Cathode Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2203218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shi, X.; Esan, O.C.; An, L. Organic Electrolytes Recycling From Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 2200050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, X.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Xin, B. A Comprehensive Review of Full Recycling and Utilization of Cathode and Anode as Well as Electrolyte from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, L.; Rao, Z.; Shao, G.; Lei, Y. Recycling of Graphite Anode from Spent Lithium-ion Batteries: Advances and Perspectives. EcoMat 2023, 5, e12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Xiao, J.; Xu, Z. Advances and Challenges in Anode Graphite Recycling from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Li, L.; Amin, K.; Fan, E.; Manurkar, N.; Ahmad, A.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. A Comprehensive Review of the Advancement in Recycling the Anode and Electrolyte from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 13527–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, F.; Neef, C.; Marscheider-Weidemann, F.; Nissen, N.F. A Forecast on Future Raw Material Demand and Recycling Potential of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Pan, Z.; Su, X.; An, L. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Recent Advances and Perspectives. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latini, D.; Vaccari, M.; Lagnoni, M.; Orefice, M.; Mathieux, F.; Huisman, J.; Tognotti, L.; Bertei, A. A Comprehensive Review and Classification of Unit Operations with Assessment of Outputs Quality in Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling. J. Power Sources 2022, 546, 231979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Faraji, F.; Jong, B.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Banerjee, P.C. Current Challenges and Future Opportunities toward Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 159, 112202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, R.P.; Ranawat, N.S.; Chakraborty, A.; Mishra, R.P.; Khandelwal, M. The Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Process from a Circular Economy Perspective—A Review and Future Directions. Energies 2023, 16, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; An, N.; Wen, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Hou, F.; Yin, Y.; Liang, J. Recent Progress on the Recycling Technology of Li-Ion Batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 55, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista Value of Recycled EV Batteries by Battery Type. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1246828/value-of-recycled-ev-batteries-by-battery-type/ (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- van Halm, I.; Mullan, C. Booming EV Sales Challenge Critical Mineral Supply Chains. Available online: https://www.energymonitor.ai/sectors/transport/booming-ev-sales-challenge-mineral-supply-chains/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Widijatmoko, S.D.; Fu, G.; Wang, Z.; Hall, P. Recovering Lithium Cobalt Oxide, Aluminium, and Copper from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery via Attrition Scrubbing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widijatmoko, S.D.; Gu, F.; Wang, Z.; Hall, P. Selective Liberation in Dry Milled Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 23, e00134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossali, E.; Picone, N.; Gentilini, L.; Rodrìguez, O.; Pérez, J.M.; Colledani, M. Lithium-Ion Batteries towards Circular Economy: A Literature Review of Opportunities and Issues of Recycling Treatments. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, J.; Shang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S. Controlled Carbothermic Reduction for Enhanced Recovery of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 194, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuza, B.; Yu, D.; Huang, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, P. Synergetic Carbothermic Reduction and Selective Hydrochlorination of Spent Li-Ion Batteries Black Mass towards Enhanced Metal Recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Yang, R.; Jiao, J. Assessment of the Lifecycle Carbon Emission and Energy Consumption of Lithium-Ion Power Batteries Recycling: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Energy Storage 2023, 65, 107306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.; Fabritius, T.; Heikkinen, E.-P.; Vuolio, T.; Yu, Y.; Chen, G.; Kacar, Y. Microwave Catalyzed Carbothermic Reduction of Zinc Oxide and Zinc Ferrite: Effect of Microwave Energy on the Reaction Activation Energy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23959–23968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, A.; Alessandri, I.; Cornelio, A.; Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Mousa, E.; Ye, G.; Valentim, B.; Bontempi, E. A Microwave-Enhanced Method Able to Substitute Traditional Pyrometallurgy for the Future of Metals Supply from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 194, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Song, C.; Lu, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. Separation and Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries via Concentrated Sulfuric Acid Leaching and Regeneration of LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 863, 158775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Lin, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling-Reductive Ammonia Leaching of Metals from Cathode Scrap by Sodium Sulphite. Waste Manag. 2016, 60, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.; Jung, Y.; Jo, M.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, D.; Rhee, K.; An, E.-M.; Sohn, J.; Kwon, K. Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials by Ammoniacal Leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 313, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, W.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P. Recovery of Lithium, Nickel, and Cobalt from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Powders by Selective Ammonia Leaching and an Adsorption Separation System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11489–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaye, N.; Gueye, R.S.; Ledauphin, J.; Balde, M.; Seck, M.; Wele, A.; Diaw, M. Alkaline Leaching of Metals from Cathodic Materials of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2019, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Balasubramanian, R. Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Microbial Agents for Bioleaching: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1197081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnes, A.; Pospiech, B. A Brief Review on Hydrometallurgical Technologies for Recycling Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Jha, M.K.; Lee, J.; Singh, R.P. Clean Process for Recovery of Metals and Recycling of Acid from the Leach Liquor of PCBs. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4826–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, P.; Meng, Q.; Dong, P.; Duan, J.; Xu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Recycling of Cathode Material from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries Using an Ultrasound-Assisted DL-Malic Acid Leaching System. Waste Manag. 2020, 103, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Shen, B. Novel Approach to Recover Cobalt and Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Using Oxalic Acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R.; Chen, S.; Wu, B. Recovery of Cobalt and Lithium from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries Using Organic Citric Acid as Leachant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayaka, G.P.; Manjanna, J.; Pai, K.V.; Vadavi, R.; Keny, S.J.; Tripathi, V.S. Recovery of Valuable Metal Ions from the Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Using Aqueous Mixture of Mild Organic Acids as Alternative to Mineral Acids. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 151, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Yao, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, X.; Ji, H.; Mi, X.; Deng, C. Simultaneous Recycling of Critical Metals and Aluminum Foil from Waste LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Cathode via Ethylene Glycol–Citric Acid System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16133–16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzam, P.; Boroumand, Y.; Rabiei, P.; Baghbaderani, S.S.; Mokarian, P.; Mohagheghian, F.; Mohammed, L.J.; Razmjou, A. Lithium Bioleaching: An Emerging Approach for the Recovery of Li from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; He, W.; Li, G.; Huang, J. A Review on Management of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries and Strategy for Resource Recycling of All Components from Them. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2018, 36, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaloo-Horeh, N.; Mousavi, S.M. Enhanced Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries through Optimization of Organic Acids Produced by Aspergillus Niger. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Rastegar, S.O.; Beigzadeh, R.; Gu, T. Ultrasound-Assisted Leaching of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries by Natural Organic Acids and H2O2. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Shi, M.; Wu, C. Deep Eutectic Solvent for Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Comparison with Inorganic Acid Leaching. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 19029–19051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golmohammadzadeh, R.; Faraji, F.; Rashchi, F. Recovery of Lithium and Cobalt from Spent Lithium Ion Batteries (LIBs) Using Organic Acids as Leaching Reagents: A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Demarco, J.; Stefanello Cadore, J.; da Silveira de Oliveira, F.; Hiromitsu Tanabe, E.; Assumpção Bertuol, D. Recovery of Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Organic Acids. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 190, 105169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z. A Novel Method for Screening Deep Eutectic Solvent to Recycle the Cathode of Li-Ion Batteries. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4473–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Xu, Z.; Dutta, S.; Valix, M.; Alessi, D.S.; Huang, L.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Tsang, D.C.W. Selective Extraction of Critical Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3940–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyanarayanan, S.; Babu, M.P.; Murugan, R.; Muthuraj, D.; Ramanujam, K.; Nicholls, I.A. Highly Efficient Recovery and Recycling of Cobalt from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Using an N-Methylurea–Acetamide Nonionic Deep Eutectic Solvent. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6959–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.I.; García-Díaz, I.; López, F.A. Properties and Perspective of Using Deep Eutectic Solvents for Hydrometallurgy Metal Recovery. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wei, L.; Ren, P.; Mu, T. Efficient Dissolution of Lithium-Ion Batteries Cathode LiCoO2 by Polyethylene Glycol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents at Mild Temperature. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11713–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wen, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, H. Leaching NCM Cathode Materials of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries with Phosphate Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Waste Manag. 2023, 157, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Li, T.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; An, N.; Huang, W.; Guo, Q.; Ge, X. Ternary Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) with a Regulated Rate-Determining Step for Efficient Recycling of Lithium Cobalt Oxide. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11452–11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tan, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, J. A Low-Toxicity and High-Efficiency Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Separation of Aluminum Foil and Cathode Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Wang, K.; Li, X. Recovery of Cobalt from Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials by Using Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, C.; Pham, H.D.; Jadhav, S.; Do, T.T.; Nerkar, J.; Hoang, L.T.M.; Kumar Nanjundan, A.; Mundree, S.G.; Dubal, D.P. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Green Approach for Cathode Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, T.; Hu, T.; Ge, X. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) for Green Recycling of Wasted Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs): Progress on Pushing the Overall Efficiency. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 2149–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, T.; Shi, P.; Min, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. Efficient Recovery of Value Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Combining Deep Eutectic Solvents and Coextraction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, M.; Garg, S.; Wu, Y.; Nazmi Idros, M.; Hocking, R.; Duan, H.; Gao, S.; Yago, A.J.; Zhuang, L.; et al. Cobalt Electrochemical Recovery from Lithium Cobalt Oxides in Deep Eutectic Choline Chloride+Urea Solvents. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Rodrigues, M.-T.F.; Kato, K.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Cathode Recycling of Li-Ion Batteries. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. A Novel Deep-Eutectic Solvent with Strong Coordination Ability and Low Viscosity for Efficient Extraction of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Fan, M.; Gu, C.; He, W.; Meng, Q.; Wan, L.; Guo, Y. Selective Extraction of Transition Metals from Spent LiNixCoy Mn1−x−yO2 Cathode via Regulation of Coordination Environment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Svärd, M.; Forsberg, K. Recycling Cathode Material LiCo1/3Ni1/3Mn1/3O2 by Leaching with a Deep Eutectic Solvent and Metal Recovery with Antisolvent Crystallization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Gou, Q.; Li, M.; Xia, A.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q. Recovery and Regeneration of Anode Graphite from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries through Deep Eutectic Solvent Treatment: Structural Characteristics, Electrochemical Performance and Regeneration Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Z. Efficient Separation of Electrode Active Materials and Current Collector Metal Foils from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by a Green Deep Eutectic Solvent. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Wu, T.; Wang, G.; Huang, Q.; Su, Y.; Wu, F. Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Efficient Recovery of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode Materials. Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao/Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 42, 3151–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of the European Union; European Parliament. European Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/1542 of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning Batteries and Waste Batteries; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023; Volume 2023, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gulliani, S.; Volpe, M.; Messineo, A.; Volpe, R. Recovery of Metals and Valuable Chemicals from Waste Electric and Electronic Materials: A Critical Review of Existing Technologies. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 1085–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, K.; Liang, Z.; Ji, G.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Cheng, H.-M. Adaptable Eutectic Salt for the Direct Recycling of Highly Degraded Layer Cathodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20306–20314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.D.; Rupp, J.A.; Brungard, E. Lithium in the Green Energy Transition: The Quest for Both Sustainability and Security. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Tan, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. A Green, Efficient, Closed-Loop Direct Regeneration Technology for Reconstructing of the LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 Cathode Material from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Aravindan, V. An Urgent Call to Spent LIB Recycling: Whys and Wherefores for Graphite Recovery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhu, X. Application of Mechanical Crushing Combined with Pyrolysis-Enhanced Flotation Technology to Recover Graphite and LiCoO2 from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lei, S.; Wang, T.; Yi, C.; Sun, W.; Yang, Y. Lithium Recovery and Solvent Reuse from Electrolyte of Spent Lithium-Ion Battery. Waste Manag. 2023, 167, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Schuster, J.; Petranikova, M.; Ebin, B. Innovative Recycling of Organic Binders from Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 172, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Kwon, D.; Park, S.; Kwon, K.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kwon, E.E. Valorization of a Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Electrolyte through Syngas Formation Using CO2-Assisted Catalytic Thermolysis over a Battery Cathode Material. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 50, 101591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Akshay, M.; Aravindan, V. Recycling/Reuse of Current Collectors from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Benefits and Issues. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, W.; Han, J.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W.; Liu, T.; Zhao, C. Pyrolysis and Physical Separation for the Recovery of Spent LiFePO4 Batteries. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Bi, H.; He, P.; Gao, S. Recycling of Electrode Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Power Batteries via Thermal and Mechanical Treatments. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, X.; Han, W.; Wang, S. Recycling of LiFePO4 Cathode Materials from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries through Ultrasound-Assisted Fenton Reaction and Lithium Compensation. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Belharouak, I. Solvent-Based Electrode Recovery Toward Sustainable Direct Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2022, MA2022-02, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paone, E.; Miceli, M.; Malara, A.; Ye, G.; Mousa, E.; Bontempi, E.; Frontera, P.; Mauriello, F. Direct Reuse of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries as an Efficient Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Reductive Upgrading of Biomass-Derived Furfural. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducoli, S.; Fahimi, A.; Mousa, E.; Ye, G.; Federici, S.; Frontera, P.; Bontempi, E. ESCAPE Approach for the Sustainability Evaluation of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries Recovery: Dataset of 33 Available Technologies. Data Brief. 2022, 42, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, A.; Zanoletti, A.; Cornelio, A.; Mousa, E.; Ye, G.; Frontera, P.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Sustainability Analysis of Processes to Recycle Discharged Lithium-Ion Batteries, Based on the ESCAPE Approach. Materials 2022, 15, 8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempi, E. How to Perform a Material Recovery Sustainability Evaluation Preliminary to LCA? Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 9, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrmann, L.; Sann-Ferro, K.; Heininger, P.; Mähliß, J. Kompendium: Li-Ionen-Batterien; VDE Studie: Offenbach, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sandaka, B.P.; Kumar, J. Alternative Vehicular Fuels for Environmental Decarbonization: A Critical Review of Challenges in Using Electricity, Hydrogen, and Biofuels as a Sustainable Vehicular Fuel. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, E.; Hu, X.; Ånnhagen, L.; Ye, G.; Cornelio, A.; Fahimi, A.; Bontempi, E.; Frontera, P.; Badenhorst, C.; Santos, A.C.; et al. Characterization and Thermal Treatment of the Black Mass from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustainability 2022, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch-Kern, S.; Gerold, E.; Nigl, T.; Jandric, A.; Altendorfer, M.; Rutrecht, B.; Scherhaufer, S.; Raupenstrauch, H.; Pomberger, R.; Antrekowitsch, H.; et al. Recycling Chains for Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Critical Examination of Current Challenges, Opportunities and Process Dependencies. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.C.C.; Pontes, L.P.; Vasconcelos, A.S.M.; de Araujo Silva Junior, W.; Wu, K. Economic Aspects for Recycling of Used Lithium-Ion Batteries from Electric Vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Explore 2+ Mio. Startups & Scaleups: StartUs Insights Discovery Platform. Available online: https://www.startus-insights.com/startus-insights-platform/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Li-Cycle Holdings Corp. Annual Report; Li-Cycle Holdings Corp.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kallitsis, E.; Korre, A.; Kelsall, G.H. Life Cycle Assessment of Recycling Options for Automotive Li-Ion Battery Packs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 371, 133636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeau-Bettez, G.; Hawkins, T.R.; Strømman, A.H. Life Cycle Environmental Assessment of Lithium-Ion and Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries for Plug-In Hybrid and Battery Electric Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Wenz, R.; van Zuilichem, A.J.; Göllner-Völker, L.; Berberich, K.; Weidenkaff, A.; Schebek, L. Recycling Routes of Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Critical Review of the Development Status, the Process Performance, and Life-Cycle Environmental Impacts. MRS Energy Sustain. 2022, 10, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.F. Best Practices for Life Cycle Assessment of Batteries. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetti, B.; Toso, D.; Baldo, G.L.; Rollino, S. EcoAudit: A Renewed Simplified Procedure to Facilitate the Environmentally Informed Material Choice Orienting the Further Life Cycle Analysis for Ecodesigners. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, E. A New Approach for Evaluating the Sustainability of Raw Materials Substitution Based on Embodied Energy and the CO2 Footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, E. Raw Materials and Sustainability Indicators. In Raw Materials Substitution Sustainability; SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fahimi, A.; Ducoli, S.; Federici, S.; Ye, G.; Mousa, E.; Frontera, P.; Bontempi, E. Evaluation of the Sustainability of Technologies to Recycle Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries, Based on Embodied Energy and Carbon Footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Wang, Z.; Cao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z. A Critical Review and Analysis on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Arsenault, R.; Karlson, P.; Simon, N.; Wang, Y. Recycling End-of-Life Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries. Joule 2019, 3, 2622–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Petranikova, M.; Meeus, M.; Gamarra, J.D.; Younesi, R.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—Current State of the Art, Circular Economy, and Next Generation Recycling. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, H.A.; Pecht, M. Preprocessing of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries for Recycling: Need, Methods, and Trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, B. A Review on Dynamic Recycling of Electric Vehicle Battery: Disassembly and Echelon Utilization. Batteries 2023, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Gastol, D.; Sommerville, R.; Middleton, B.; Goodship, V.; Kendrick, E. Disassembly of Li Ion Cells—Characterization and Safety Considerations of a Recycling Scheme. Metals 2020, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Garg, A.; Zheng, J.; Gao, L.; Oh, K. Battery Pack Recycling Challenges for the Year 2030: Recommended Solutions Based on Intelligent Robotics for Safe and Efficient Disassembly, Residual Energy Detection, and Secondary Utilization. Energy Storage 2021, 3, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Algaba, M.; Ramirez, F.J. Techno-Economic and Environmental Disassembly Planning of Lithium-Ion Electric Vehicle Battery Packs for Remanufacturing. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Hyde, C.; Hartley, J.M.; Abbott, A.P.; Anderson, P.A.; Harper, G.D.J. To Shred or Not to Shred: A Comparative Techno-Economic Assessment of Lithium Ion Battery Hydrometallurgical Recycling Retaining Value and Improving Circularity in LIB Supply Chains. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, M.; Vaagsaether, K.; Lundberg, J.; Forseth, S.; Bjerketvedt, D. Explosion Characteristics for Li-Ion Battery Electrolytes at Elevated Temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, C.; Gu, H.; Han, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, M. Sorting, Regrouping, and Echelon Utilization of the Large-Scale Retired Lithium Batteries: A Critical Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kum, D. Development of Cell Selection Framework for Second-Life Cells with Homogeneous Properties. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 105, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Pan, A.; Liao, Q.; Yang, X. A Fast Classification Method of Retired Electric Vehicle Battery Modules and Their Energy Storage Application in Photovoltaic Generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.L.; Hartley, J.M.; Lambert, S.M.; Shiref, M.; Harper, G.D.J.; Kendrick, E.; Anderson, P.; Ryder, K.S.; Gaines, L.; Abbott, A.P. The Importance of Design in Lithium Ion Battery Recycling—A Critical Review. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 7585–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerville, R.; Shaw-Stewart, J.; Goodship, V.; Rowson, N.; Kendrick, E. A Review of Physical Processes Used in the Safe Recycling of Lithium Ion Batteries. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Grutzke, M.; Herrmann, C.; Kara, S.; Kwade, A. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries; Kwade, A., Diekmann, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 250–251. ISBN 978-3-319-70571-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ping, P.; Zhao, X.; Chu, G.; Sun, J.; Chen, C. Thermal Runaway Caused Fire and Explosion of Lithium Ion Battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 208, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.; Dunn, J.; Kendall, A. Transportation of Electric Vehicle Lithium-Ion Batteries at End-of-Life: A Literature Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudet, A.; Larouche, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Key Challenges and Opportunities for Recycling Electric Vehicle Battery Materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, W.; Gupta, V.; Gao, H.; Tran, D.; Sarwar, S.; Chen, Z. Current Challenges in Efficient Lithium-Ion Batteries’ Recycling: A Perspective. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 2200099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, V.; Baldè, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2020: Quantities, Flows and the Circular Economy Potential; United Nations University (UNU)/United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR)—Co-hosted SCYCLE Programme, International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Solid Waste Association (ISWA): Bonn, Germany; Geneva, Switzerland; Rotterdam, The Netherland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zubi, G.; Dufo-López, R.; Carvalho, M.; Pasaoglu, G. The Lithium-Ion Battery: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallo, H.; Benveniste, G.; Gestoso, I.; Amante, B. Economic Analysis of the Disassembling Activities to the Reuse of Electric Vehicles Li-Ion Batteries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 159, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamateros, G.; Abdoli, S. Automated Disassembly of Lithium Batteries; Methods, Challenges, and a Roadmap. Procedia CIRP 2023, 119, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, J. Evaluating the Electric Vehicle Popularization Trend in China after 2020 and Its Challenges in the Recycling Industry. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Research on Policies of Power Batteries Recycle in China from the Perspective of Life Cycle. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2021, 29, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosuè, C.; Marchese, D.; Cavalletti, M.; Isidori, R.; Conti, M.; Orcioni, S.; Ruello, M.L.; Stipa, P. An Exploratory Study of the Policies and Legislative Perspectives on the End-of-Life of Lithium-Ion Batteries from the Perspective of Producer Obligation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Tan, D.H.S.; Chen, Z. Emerging Trends in Sustainable Battery Chemistries. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo Diaz, L.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; Restuccia, F.; Marinescu, M.; Barreras, J.V.; Patel, Y.; Offer, G.; Rein, G. Review—Meta-Review of Fire Safety of Lithium-Ion Batteries: Industry Challenges and Research Contributions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 090559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Xue, D. Electronegativity Principles in Metal Oxides Based Supercapacitors. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, H.J. Synthesis of High-Performance Nickel Hydroxide Nanosheets/Gadolinium Doped-α-MnO2 Composite Nanorods as Cathode and Fe3O4/GO Nanospheres as Anode for an All-Solid-State Asymmetric Supercapacitor. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 64, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, H.J. Confinement of Zn-Mg-Al-Layered Double Hydroxide and α-Fe2O3 Nanorods on Hollow Porous Carbon Nanofibers: A Free-Standing Electrode for Solid-State Symmetric Supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde, P. Facilitating Circularity in the Lithium-Ion Battery Value Chain by Designing for Recycling. Master’s Thesis, Industrial Design Engineering, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Mu, D.; Lu, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tian, S.; Dai, C. A Comprehensive Review on the Recycling of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Urgent Status and Technology Advances. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, P. The Foreseeable Future of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries: Advanced Upcycling for Toxic Electrolyte, Cathode, and Anode from Environmental and Technological Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 13270–13291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LiMn2O4/LMO | LiCoO2/LCO | Li(Ni/Mn/Co)O2/NMC | LiFePO4/LFP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |  |  |  | 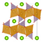 |
| Specific capacity/mAhg-1 | 148 | 275 | 275 | 170 |
| Practical specific capacity/mAhg-1 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 150 |
| Average discharge potential vs. graphite/V | 4.0 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.5 |
| Energy density/WhKg-1 | 480 | 564 | 608 | 525 |
| Application | Power tools, electric bikes | Portable devices | Portable devices, electric vehicles | Power tools, large electric vehicles |
| Market share | Small | Dumped | Dominant | Expanding |
| Global evaluation | Medium safety, low cost, low lifetime, medium energy density | Low safety, high cost, medium performance | Medium safety, medium cost, high energy density | High safety, medium cost, medium energy density, high thermal stability |
 |  |  |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrometallurgy | Hydrometallurgy | Biometallurgy | Solvometallurgy (Ionic Liquid) | Solvometallurgy (DES) | |
| Advantages | Short process flow, low equipment requirements, strong operability | Low energy consumption, great versatility, high product purity, high recovery efficiency | Complete metal recovery, simplicity, cost-effectiveness, low energy consumption, mild conditions | Nonflammable, low volatility, tunable | Nonflammable, low recovery cost, green process, cheap and easy preparation, low toxicity |
| Disadvantages | High energy consumption, poor metal purity, difficulty in lithium recovery | Need to dispose of large amount of acid and toxic wastewater, long recovery process | Long processes and low kinetics, vulnerability to pollution | Expensive | Difficulty to scale-up, low cathode/DES ratio |
| Applied at industrial level | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Main source of pollution | Emission of polluting gases and production of slags | Release of toxic gases (e.g. NOx, SOx, Cl2) | - | - | - |
| Output Material | Definition | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Active material | Lithium-ion batteries consist of both cathode and anode materials, with graphite being the predominant material used for the anode. The active material in the battery is a combination of these two components. | The output material represents a complete process for physical recycling directly. |
| Cathode material | Common cathode materials are LiCoO2 (LCO), LiaNixCoyMnzO2 (NMC), LiMn2O4 (LMO), LiNixCoyAlzO2 (NCA), and LiFePO4 (LFP). | The direct physical route yields a purified output material. |
| Alloy and Slag | Typically, a pyrometallurgical process results in the production of metal alloys as the main product, with slag being a secondary byproduct of the process. | A final product that represents the entire process of pyrometallurgical recycling. |
| Salt of transition metals | Precipitation product in a hydrometallurgical process. | A final product obtained from a complete hydrometallurgical recycling process. |
| LIBs | Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that comprise an anode and cathode, with an ion-conducting electrolyte present between them for the migration of lithium ions. | The highest level of refinement achievable in a recycling process is the production of a new LIB. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanoletti, A.; Carena, E.; Ferrara, C.; Bontempi, E. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues. Batteries 2024, 10, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10010038
Zanoletti A, Carena E, Ferrara C, Bontempi E. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues. Batteries. 2024; 10(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanoletti, Alessandra, Eleonora Carena, Chiara Ferrara, and Elza Bontempi. 2024. "A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues" Batteries 10, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10010038
APA StyleZanoletti, A., Carena, E., Ferrara, C., & Bontempi, E. (2024). A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling: Technologies, Sustainability, and Open Issues. Batteries, 10(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries10010038