Electrospun PCL/PVA Coaxial Nanofibers with Embedded Titanium Dioxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Stabilization and Controlled Release of Dithranol for Therapy of Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
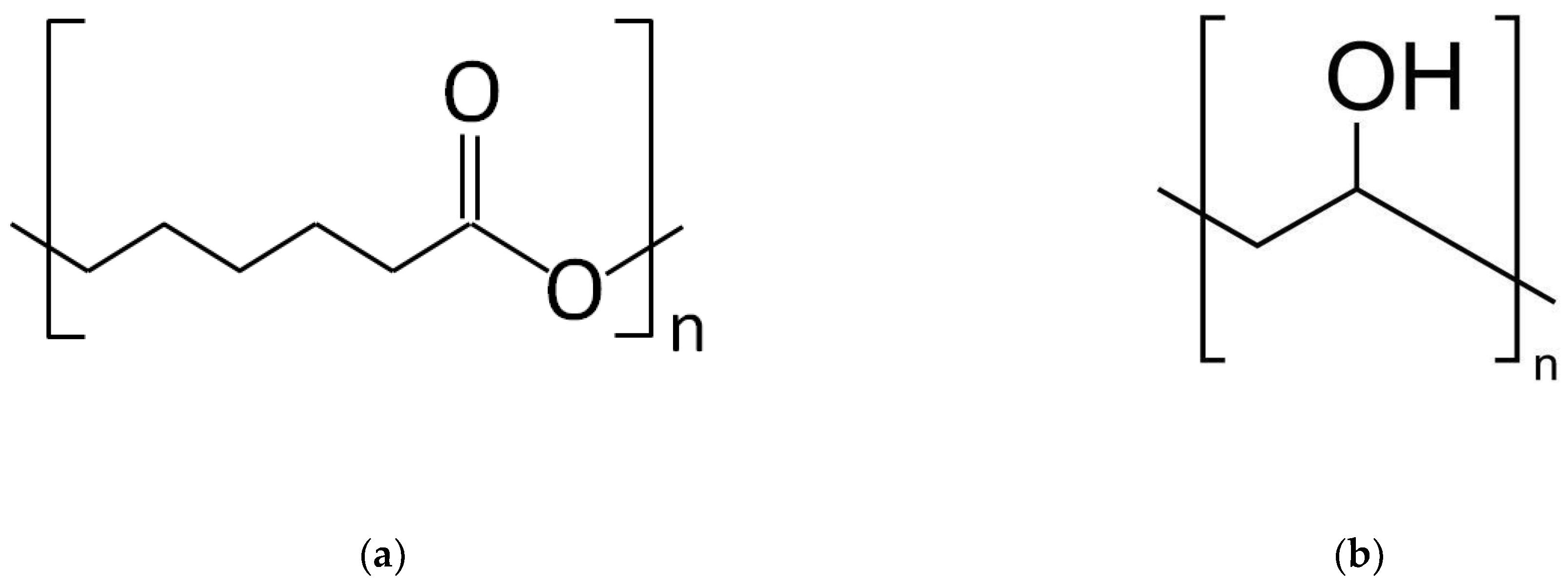
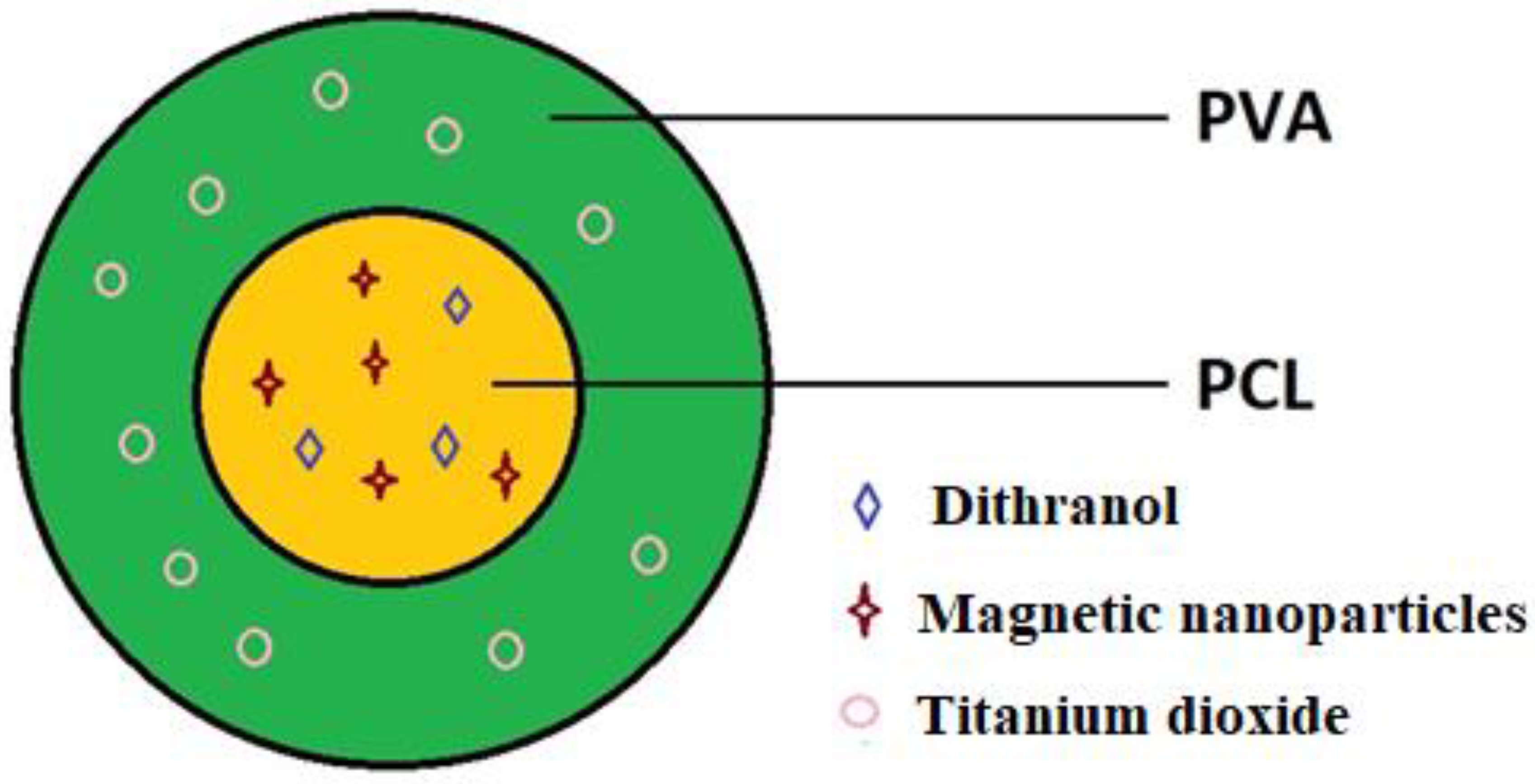
2.2. Coaxial Electrospinning Process
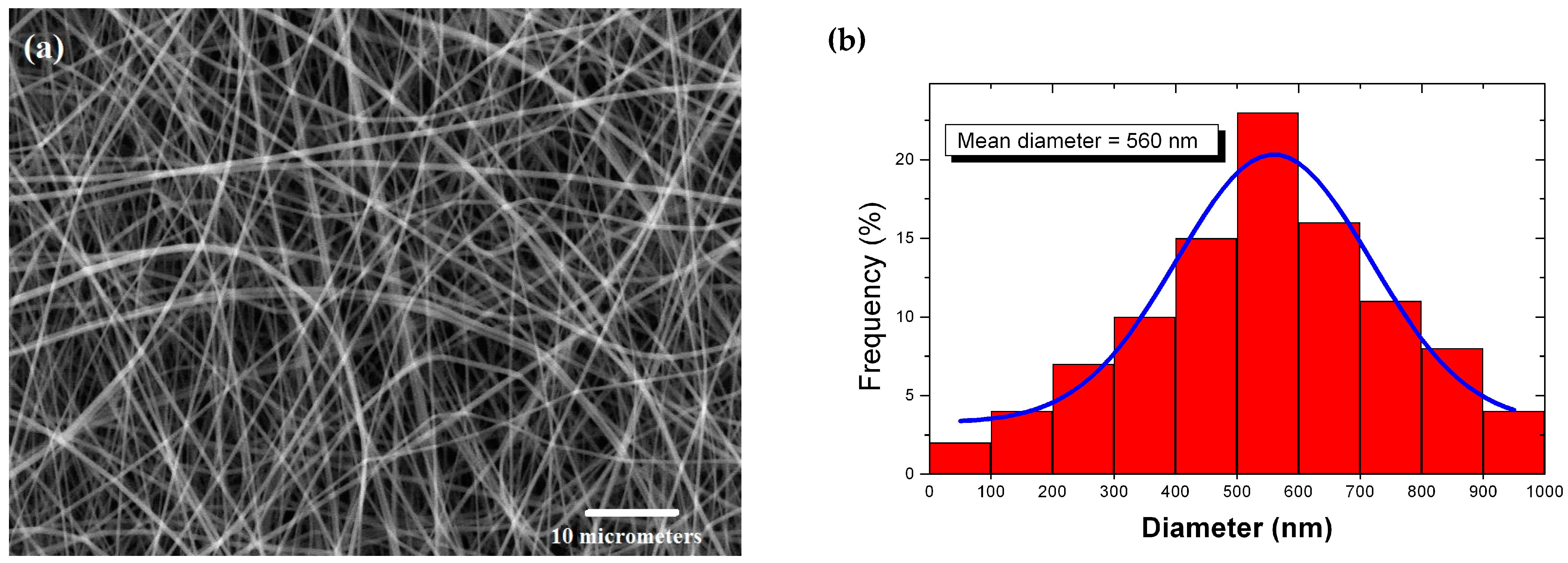
2.3. Study of the Morphology and Structure of the Nanofibers
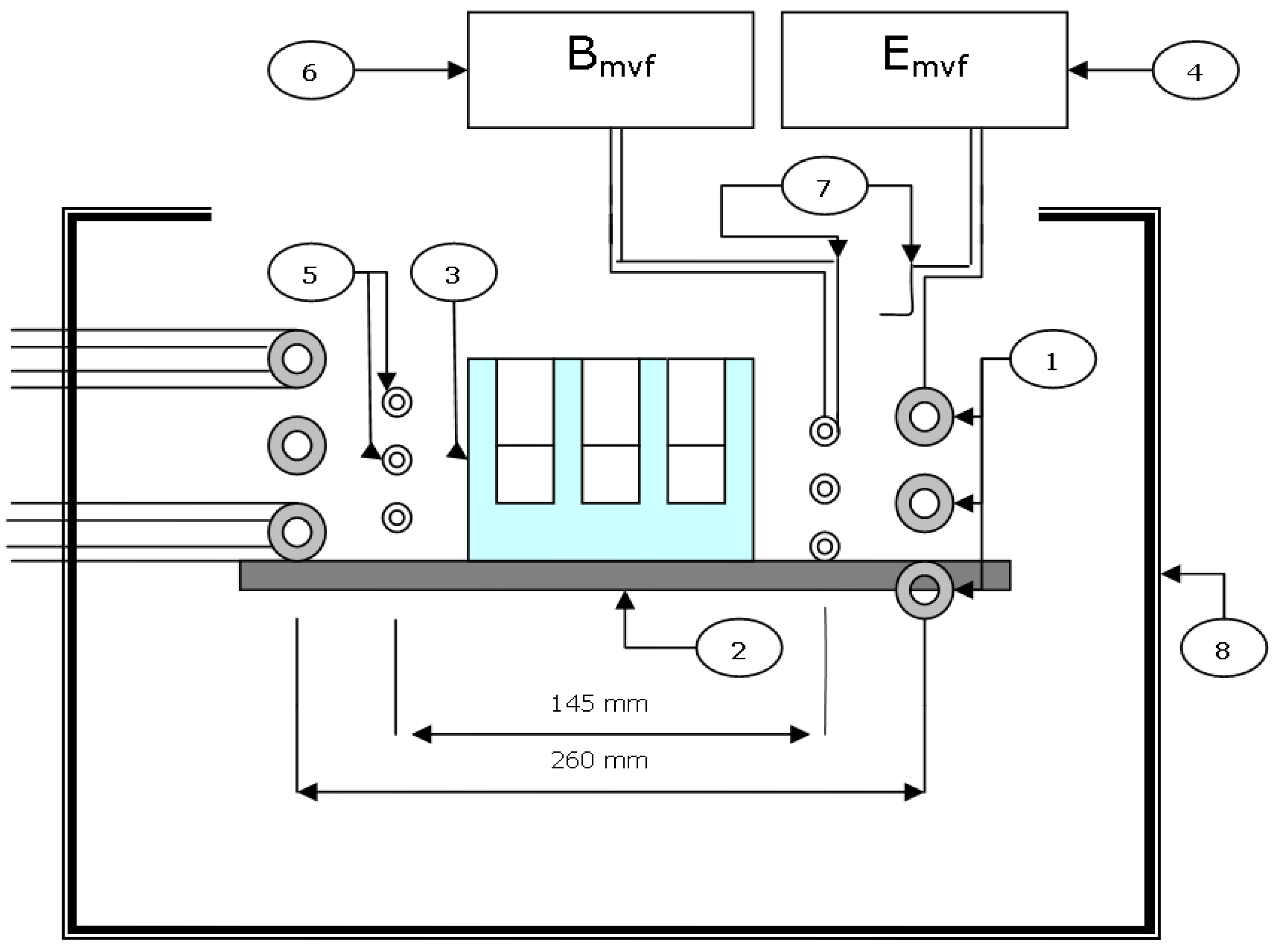
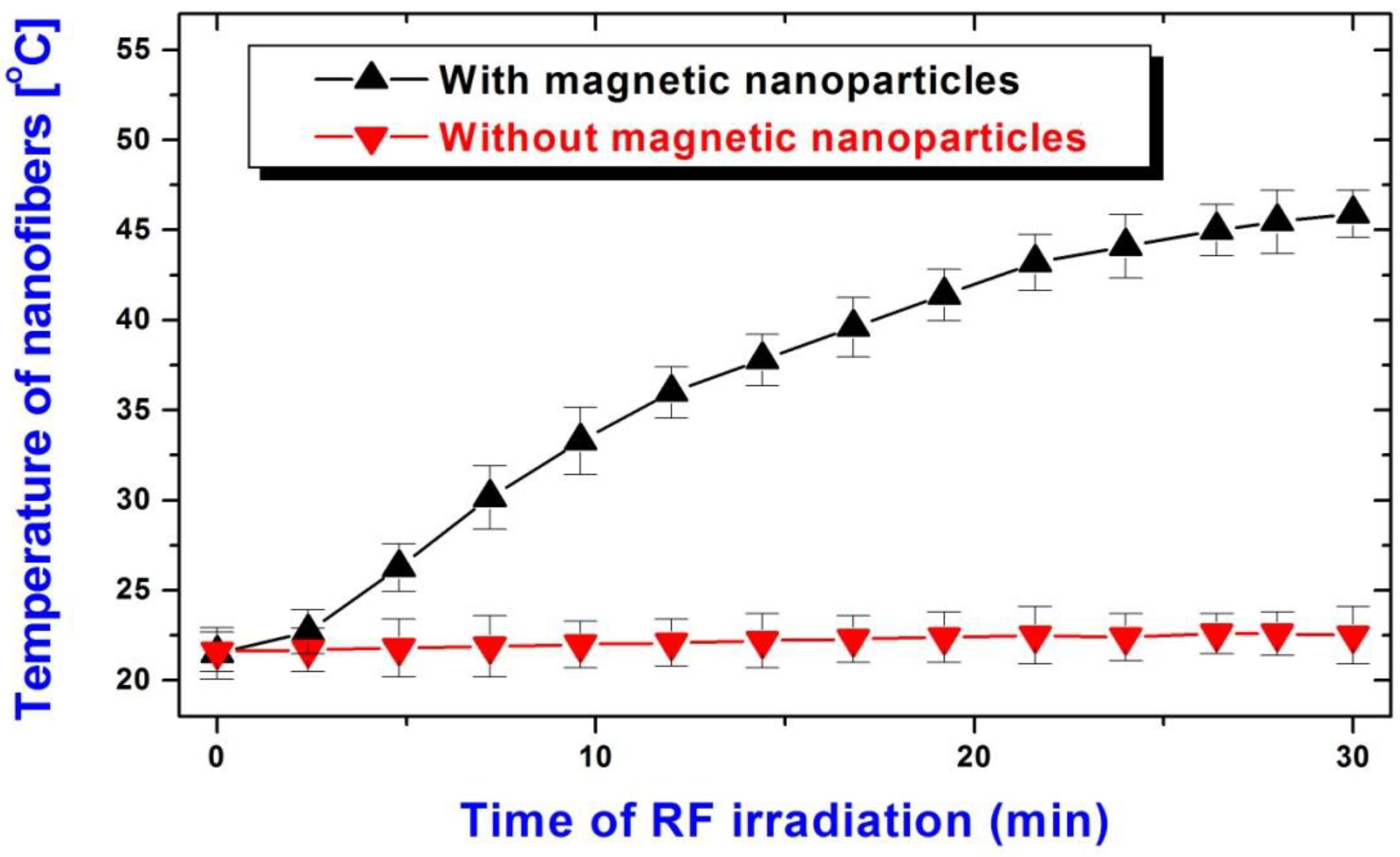
2.4. Application of the Radio-Frequency Field (RF) for Nanofiber Heating
- maximum voltage on the resonance coil Umvf = 4.5 KV;
- maximum power Pmvf = 6 kW (Pmvf and Umvf can be regulated);
- maximum input Pmax = 10 kVA;
- magnetic induction B = 1.13 mT.
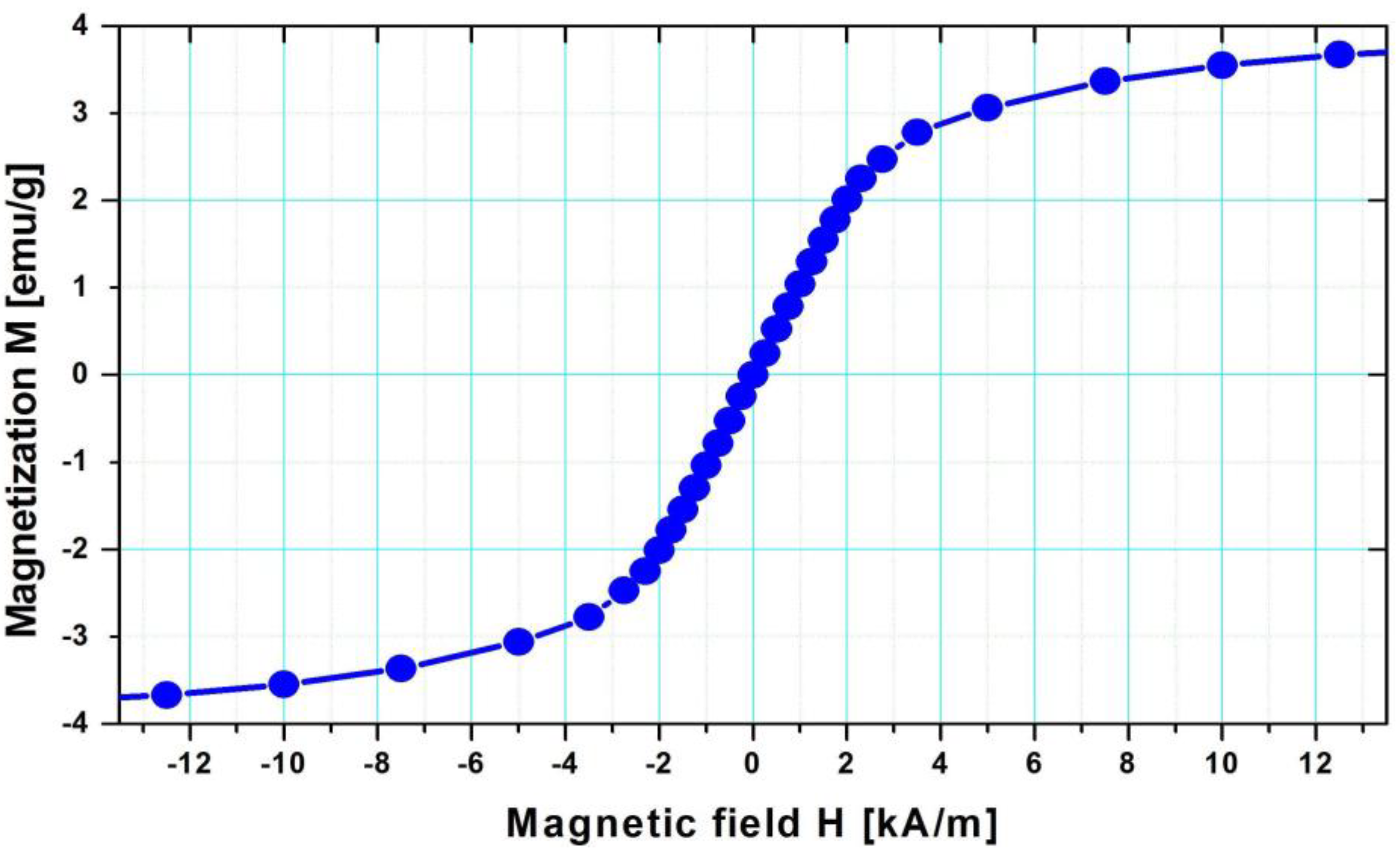
2.5. Determination of Magnetic Properties
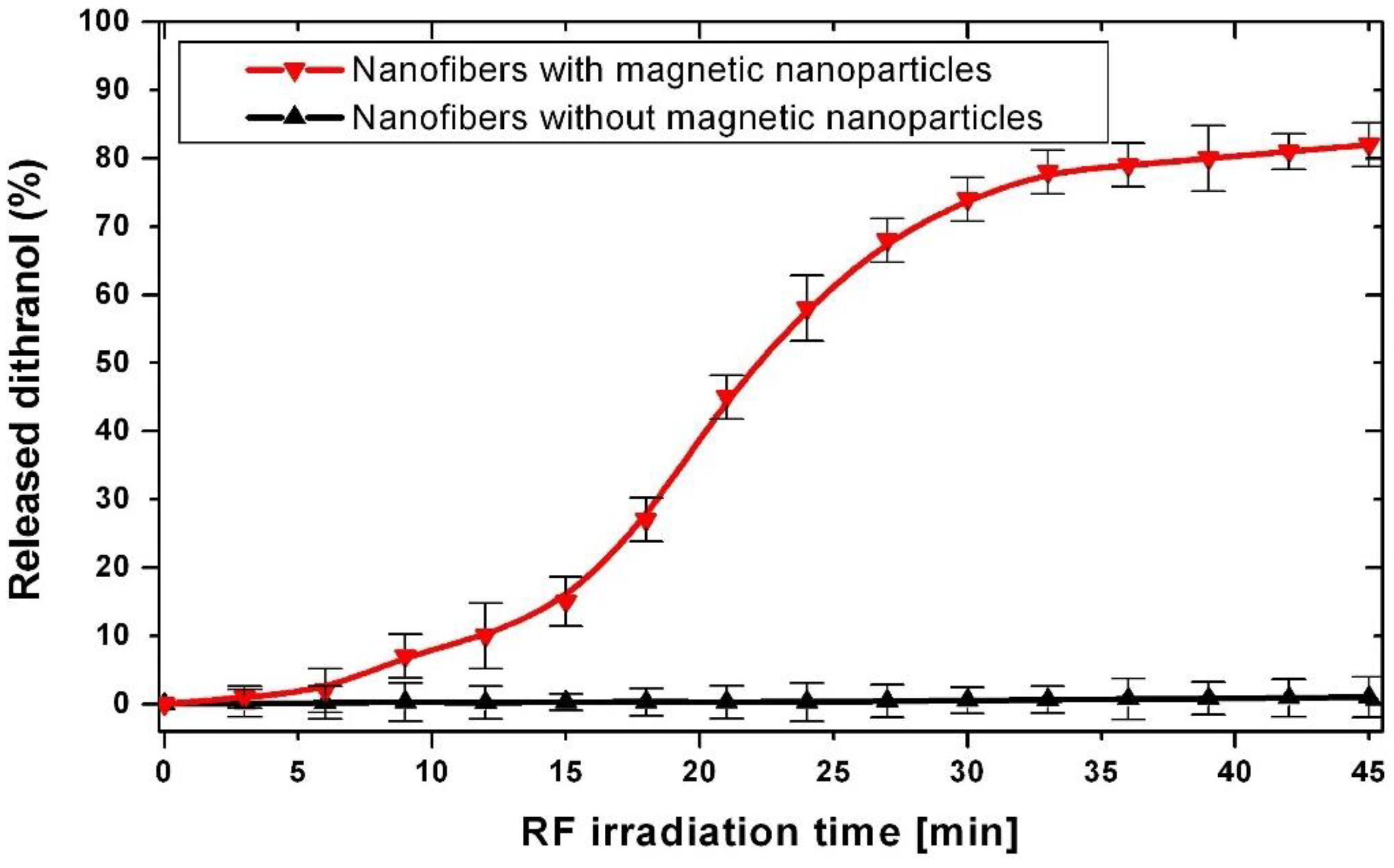
2.6. Dithranol Controlled Release
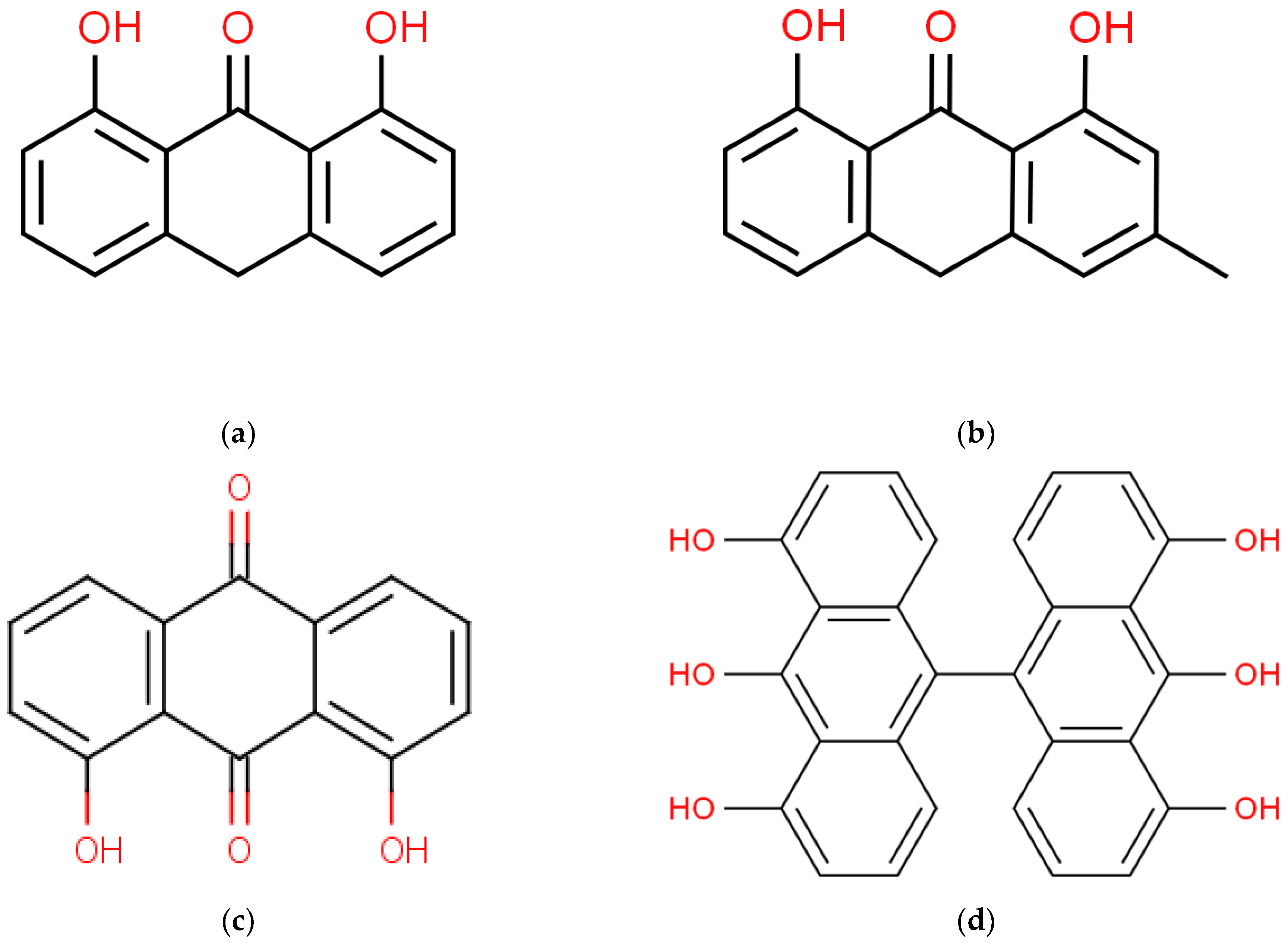
2.7. Quantification of Dithranol Photodegradation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
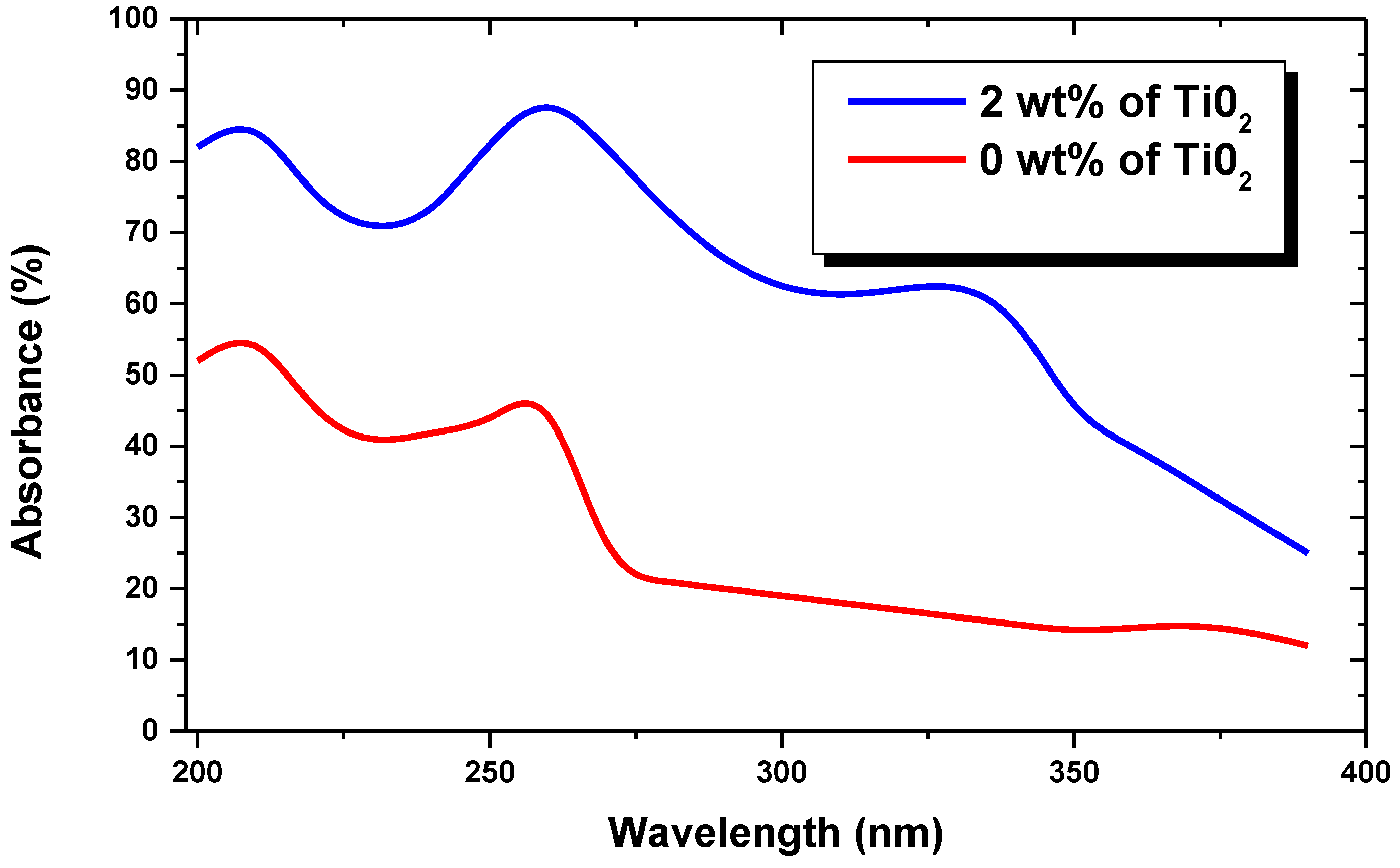
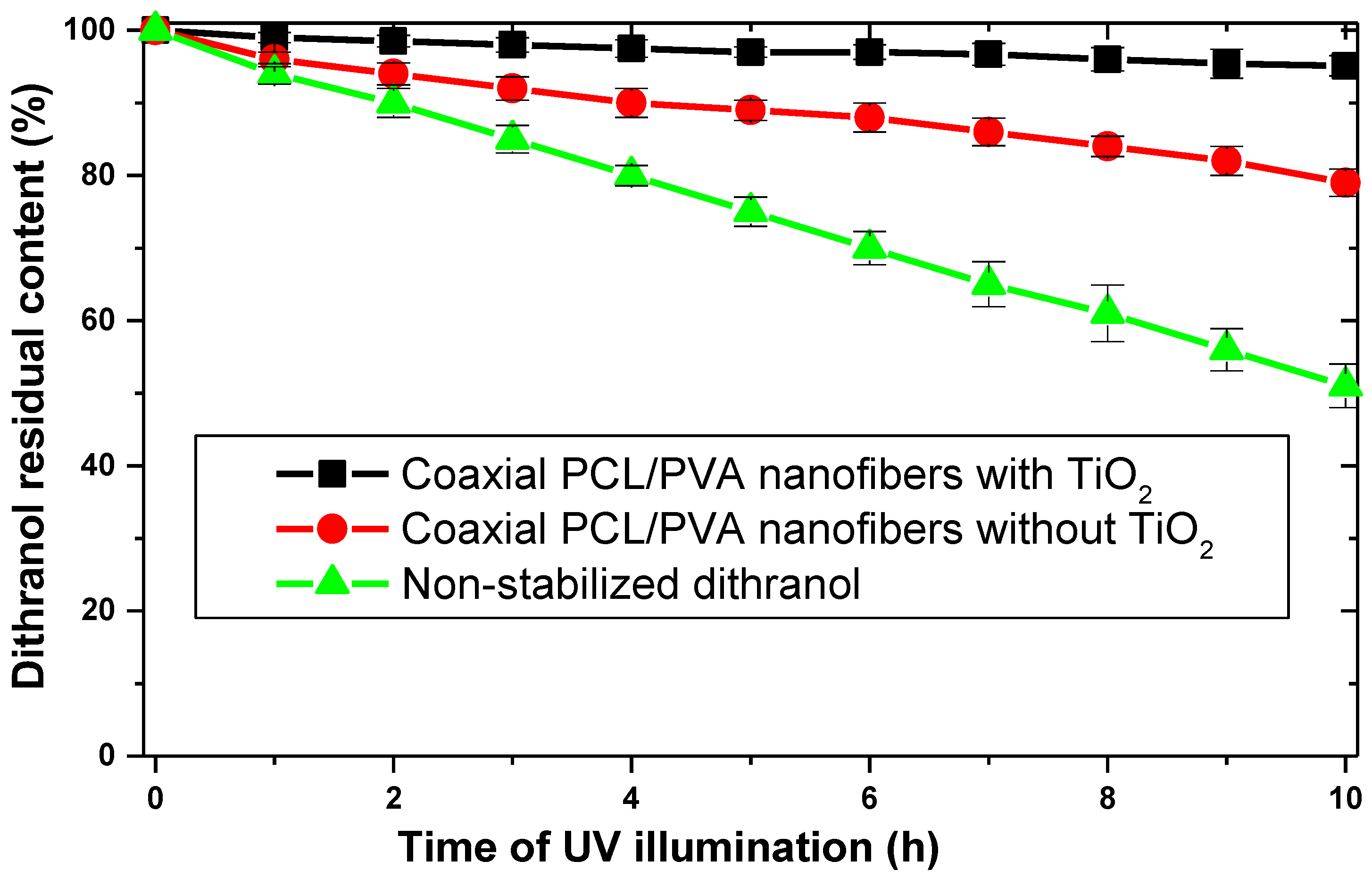
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kocaaga, A.; Kocaaga, M. Psoriasis: An Immunogenetic Perspective. Glob. Med. Genet. 2022, 9, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simaljaková, M.; Buchvald, D. Dermatovenereology; Comenius University Press: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buc, M. Autoimunita a Autoimunitné Choroby; VEDA: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaljaková, M. Psoriasis—Etiopathogenesis, clinical picture and current therapy options. Dermatol. Prax 2008, 2, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lidaj, J.; Hegyi, V.; Danilla, T.; Masarovičová, A. PASI—Teória a prax. In Péč J a kol. Chronická Ložisková Psoriáza, Komplexný Pohľad na Problematiku a Biologická liečba; Dali-BB, s.r.o.: Banská Bystrica, Slovakia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Z.; Zibert, J.R.; Dahiya, P.; Johansen, C.B.; Holm, J.G.; Jørgensen, A.-H.R.; Manole, I.; Suru, A.; Egeberg, A.; Thomsen, S.F.; et al. Mild-to-moderate severity of psoriasis may be assessed remotely based on photographs and self-reported extent of skin involvement. JAAD Int. 2023, 11, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Falco, O.; Plewig, G.; Helmut, H.W. Dermatology and Venereology; Vydavatel’stvo Osveta: Martin, Slovakia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, F.; Neha, K.; Sharma, K.; Khasimbi, S.; Chauhan, G. Nanotechnology-based medicinal products and patents: A promising way to treat psoriasis. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jin, H. Research progress of metabolomics in psoriasis. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 2023, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Carvalho, A.; Gonçalves, M.B.S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Veiga, F. Nanocarriers for the topical treatment of psoriasis—Pathophysiology, conventional treatments, nanotechnology, regulatory and toxicology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 176, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, G.S.; Frank, L.A.; Contri, R.V.; Longhi, M.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Nanotechnology-based alternatives for the topical delivery of immunosuppressive agents in psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, R.G.; Cano, A.; Ortiz, A.; Espina, M.; Prat, J.; Muñoz, M.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; García, M.L.; Pujol, M.; et al. Psoriasis: From Pathogenesis to Pharmacological and Nano-Technological-Based Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Alexander, A.; Singh, M.R.; Singh, D.; Saraf, S.; Saraf, S. Ajazuddin Understanding the prospective of nano-formulations towards the treatment of psoriasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Liu, R.; Tan, S.; Xu, X.; Fang, J. Advances in pathogenesis and nanoparticles (NPs)-mediated treatment of psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1089262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereig, S.A.; El-Zaafarany, G.M.; Arafa, M.G.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A. Tackling the various classes of nano-therapeutics employed in topical therapy of psoriasis. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unna, P.G. Cignolin als Heilmittel der Psoriasis. Derm. Wochenschr. 1916, 7, 150–163. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, V.N.; Verma, P.; Khurana, A. Anthralin/dithranol in dermatology. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e449–e460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, R.E.; Andre, P.; Lowe, N.J.; Whitefield, M. Anthralin: Historical and current perspectives. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1983, 9, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seville, R. Advances in the use of anthralin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1981, 5, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezeder, T.; Gehad, A.; Patra, V.; Clark, R.; Wolf, P. Induction of IL-1β and antimicrobial peptides as a potential mechanism for topical dithranol. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, E.; Roohaninasab, M.; Sadeghzadeh-Bazargan, A.; Nobari, N.N.; Ghassemi, M.; Seirafianpour, F.; Goodarzi, A.; Dodangeh, M.; Md-Mph, M.D. A systematic review on the treatment of pediatric severe alopecia areata by topical immunotherapy or Anthralin (contact sensitization) or low-level light/laser therapy (LLLT): Focus on efficacy, safety, treatment duration, recurrence, and follow-up based on clinical studies. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 2727–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painsi, C.; Patscheider, M.; Inzinger, M.; Huegel, R.; Lange-Asschenfeldt, B.; Quehenberger, F.; Wolf, P. Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 75 rate of classical inpatient dithranol therapy under daily life conditions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, V.; Kumar, S.; Saini, K.; Kakkar, V.; Rao, R. Dithranol: An Insight into its Novel Delivery Cargos for Psoriasis Management. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2021, 12, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussini, J.; Charalambous, A.; Sachsenweger, F.; Steinert, M. Successful removal of anthralin staining from facial skin. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, e21–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, U.; Mehra, N.K.; Gupta, U.; Jain, N.K. Hyperbranched dendritic nano-carriers for topical delivery of dithranol. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, K.; Katare, O.P.; Setia, A.; Bhatia, A.; Singh, B. Improved therapeutic performance of dithranol against psoriasis employing systematically optimized nanoemulsomes. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, P.; Saka, R.; Kommineni, N.; Raza, K.; Khan, W. Dithranol-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier-based gel ameliorate psoriasis in imiquimod-induced mice psoriatic plaque model. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2019, 45, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, U.U.M.; Ahmad, N.; Salim, N.; Yusof, N.S.M. Lipid-based nanoparticles for psoriasis treatment: A review on conventional treatments, recent works, and future prospects. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29080–29101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazari, S.A.; Kaur, H.; Karwasra, R.; Abourehab, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Kesharwani, P. An overview of topical lipid-based and polymer-based nanocarriers for treatment of psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 638, 122938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Katare, O.; Vyas, S. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of liposomal/niosomal delivery systems for antipsoriatic drug dithranol. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 228, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Mohammed, A.A.; Algahtani, M.S.; Mishra, A.; Ahmad, J. Nanoscale Topical Pharmacotherapy in Management of Psoriasis: Contemporary Research and Scope. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mare, S.; Calis, N.; Hartog, G.D.; van Erp, P.; van de Kerkhof, P. The Relevance of Salicylic Acid in the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis with Dithranol Creams. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1988, 1, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, C.; Diffey, B.; Lawlor, F.; Downey, A. Dithranol-UV-A phototherapy (DUVA) for psoriasis: A treatment without dressings. Br. J. Dermatol. 1983, 108, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Kerkhof, P.; Van Der Valk, P.; Swinkels, O.; Kucharekova, M.; De Rie, M.; De Vries, H.; Damstra, R.; Oranje, A.; Spek, F.D.W.-V.d.; Van Neer, P.; et al. A comparison of twice-daily calcipotriol ointment with once-daily short-contact dithranol cream therapy: A randomized controlled trial of supervised treatment of psoriasis vulgaris in a day-care setting. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathalla, D.; Youssef, E.M.K.; Soliman, G.M. Liposomal and Ethosomal Gels for the Topical Delivery of Anthralin: Preparation, Comparative Evaluation and Clinical Assessment in Psoriatic Patients. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuyama, M.; Mabuchi, T. New Treatment Addressing the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Qin, Y.; Dai, D.; Wang, P.; Shi, M.; Gao, J.; Yang, J.; Xiao, W.; Song, P.; Xu, R. Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Compounds with Nanotechnological Approaches in Psoriasis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 804415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ortega, L.; Mira, A.; Fernandez-Carvajal, A.; Mateo, C.R.; Mallavia, R.; Falco, A. Development of A New Delivery System Based on Drug-Loadable Electrospun Nanofibers for Psoriasis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, Y.; Pandit, N.; Priya, S.; Singhvi, G. Evolving Trends in Nanofibers for Topical Delivery of Therapeutics in Skin Disorders. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 18340–18357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Anjum, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Kumar, A.; Deepak, P.; Anand, S.; Singh, S.; Rajinikanth, P.S. Novel Synergistic Approach: Tazarotene-Calcipotriol-Loaded-PVA/PVP-Nanofibers Incorporated in Hydrogel Film for Management and Treatment of Psoriasis. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrýsková, N.; Sourivong, P.; Babincová, M.; Šimaljaková, M. Controlled Release of Tazarotene from Magnetically Responsive Nanofiber Patch: Towards More Efficient Topical Therapy of Psoriasis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babinec, P.; Jirsák, O. Microwave absorbing nonwoven textile from electrospun magnetically responsive nano-fibers. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 2008, 2, 474–477. [Google Scholar]
- Babincová, N.; Jirsák, O.; Babincová, M.; Babinec, P.; Šimaljaková, M. Remote magnetically controlled drug release from electrospun composite nanofibers: Design of a smart platform for therapy of psoriasis. Z. Naturforsch. 2020, 75, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbakht, S.; Asghari-Sana, F.; Fathi-Azarbayjani, A.; Sharifi, Y. Fabrication and characterization of tretinoin-loaded nanofiber for topical skin delivery. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, B.; Park, M.; Park, S.-J. Drug Delivery Applications of Core-Sheath Nanofibers Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyaderani, A.K.; Lama-Odría, M.d.C.D.; del Valle, L.J.; Puiggalí, J. Multifunctional Scaffolds Based on Emulsion and Coaxial Electrospinning Incorporation of Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, A.; Gupta, A.; Hasan, N.; Fauziya; Ahmad, S.; Kesharwani, P.; Ahmad, F.J. Recent update on electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Current trends and their applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 23808–23828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Shen, J.; Tang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Engineered Shellac Beads-on-the-String Fibers Using Triaxial Electrospinning for Improved Colon-Targeted Drug Delivery. Polymers 2023, 15, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Nagamatsu, A.; Nenoi, M.; Fujimori, A.; Kakinuma, S.; Katsube, T.; Wang, B.; Tsuruoka, C.; Shirai, T.; Nakamura, A.J.; et al. Space Radiation Biology for “Living in Space”. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4703286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, G.H.; Bais, A.F.; Aucamp, P.J.; Klekociuk, A.R.; Liley, J.B.; McKenzie, R.L. Stratospheric ozone, UV radiation, and climate interactions. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2023, 22, 937–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Maytorena-Verdugo, C.I.; González-Silva, N.; Romero-Toledo, R.; Aguilera-Aguirre, S.; Pérez-Larios, A.; Montalvo-González, E. Chitosan-TiO2: A Versatile Hybrid Composite. Materials 2020, 13, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.L.; Lim, H.W. A review of inorganic UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiśniewski, M.; Roszek, K. Underestimated Properties of Nanosized Amorphous Titanium Dioxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Dong, K.; An, J.; Liang, F.; Yi, J.; Peng, X.; Ning, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, Z.L. UV-Protective, Self-Cleaning, and Antibacterial Nanofiber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Human Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11205–11214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koozekonan, A.G.; Esmaeilpour, M.R.M.; Kalantary, S.; Karimi, A.; Azam, K.; Golbabaei, F. Fabrication and characterization of TiO2 and MWCNT coated electrospinning nanofibers for UV protection properties. Methodsx 2021, 8, 101354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayatnasab, Z.; Dabbagh, A.; Abnisa, F.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Polycaprolactone-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide na-noparticles for in vitro magnetic hyperthermia therapy of cancer. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://imagetool.software.informer.com/3.0/ (accessed on 19 March 2017).
- Thoma, K.; Holzmann, C. Photostability of dithranol. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 46, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savian, A.L.; Rodrigues, D.; Weber, J.; Ribeiro, R.F.; Motta, M.H.; Schaffazick, S.R.; Adams, A.I.; de Andrade, D.F.; Beck, R.C.; da Silva, C.B. Dithranol-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules improve the photostability and reduce the in vitro irritation potential of this drug. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.S.E.; Dubertret, L.; Prognon, P.; Gond, A.; Mahuzier, G.; Santus, R. Physicochemical Properties and Stability of Anthralin in Model Systems and Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrle, G.; Bonnekoh, B.; Ghyczy, M.; Wiegrebe, W. Stability of anthralin in liposomal phospholipids. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1991, 283, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.; Remon, J.; De Bersaques, J. Influence of storage conditions on the stability of anthralin in the presence of coal tar and salicylic acid in a white soft paraffin base. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1988, 18, 750–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babincová, M. Microwave induced likage of magnetoliposomes. Possible clinical implications. Bioelectrochemistry Bioenerg. 1993, 32, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babincová, M.; Vrbovská, H.; Sourivong, P.; Babinec, P.; Durdík, Š. Application of Albumin-embedded Magnetic Nanoheaters for Release of Etoposide in Integrated Chemotherapy and Hyperthermia of U87-MG Glioma Cells. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caizer, C. Optimization Study on Specific Loss Power in Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia with Magnetite Nanoparticles for High Efficiency in Alternative Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn, D.; Landers, J.; Buchwald, J.; Diegel, M.; Salamon, S.; Müller, R.; Köhler, M.; Ecke, G.; Wende, H.; Dutz, S. Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic nanoparticle heating and heat transfer on a microscale: Basic principles, realities and physical limitations of hyperthermia for tumour therapy. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2013, 29, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babincová, N.; Sourivong, P.; Babinec, P.; Bergemann, C.; Babincová, M.; Durdík, Š. Applications of magnetoliposomes with encapsulated doxorubicin for integrated chemotherapy and hyperthermia of rat C6 glioma. Z. Naturforsch. C 2018, 73, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niiyama, E.; Uto, K.; Lee, C.M.; Sakura, K.; Ebara, M. Alternating Magnetic Field-Triggered Switchable Nanofiber Mesh for Cancer Thermo-Chemotherapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boraei, S.B.A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Bakhshandeh, B.; Dehghan, M.M.; Gholami, H.; Gonzalez, Z.; Sanchez-Herencia, A.J.; Ferrari, B. Capability of core-sheath polyvinyl alcohol–polycaprolactone emulsion electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds in releasing strontium ranelate for bone regeneration. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 25009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ni, S.; Xia, T.; Yao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Su, W. Anti-Neoplastic Cytotoxicity of SN-38-Loaded PCL/Gelatin Electrospun Composite Nanofiber Scaffolds against Human Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4345–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.R.; Sousa, A.; Augusto, A.; Bártolo, P.J.; Granja, P.L. Electrospun Polycaprolactone (PCL) Degradation: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, C.N.C.; Pamfil, D.; Vasile, C.; Bibire, N.; Lupuşoru, R.-V.; Zamfir, C.-L.; Lupușoru, C.E. Toxicity, Biocompatibility, pH-Responsiveness and Methotrexate Release from PVA/Hyaluronic Acid Cryogels for Psoriasis Therapy. Polymers 2017, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malašauskiene, J.; Milašius, R.; Kuchanauskaitė, E. Possibilities for the Estimation of Electrospun Nanofibre Diameter Distribution by Normal (Gaussian) Distribution. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 24, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylova, M.; Kim, D.K.; Bobrysheva, N.; Osmolowsky, M.; Semenov, V.; Tsakalakos, T.; Muhammed, M. Superparamagnetism of Magnetite Nanoparticles: Dependence on Surface Modification. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boreham, D.R.; Gasmann, H.C.; Mitchel, R.E.J. Water bath hyperthermia is a simple therapy for psoriasis and also stimulates skin tanning in response to sunlight. Int. J. Hyperth. 1995, 11, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrýsková, N.; Sourivong, P.; Babincová, M.; Babinec, P.; Šimaljaková, M. Electrospun PCL/PVA Coaxial Nanofibers with Embedded Titanium Dioxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Stabilization and Controlled Release of Dithranol for Therapy of Psoriasis. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070187
Andrýsková N, Sourivong P, Babincová M, Babinec P, Šimaljaková M. Electrospun PCL/PVA Coaxial Nanofibers with Embedded Titanium Dioxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Stabilization and Controlled Release of Dithranol for Therapy of Psoriasis. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(7):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070187
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrýsková, Natália, Paul Sourivong, Melánia Babincová, Peter Babinec, and Mária Šimaljaková. 2023. "Electrospun PCL/PVA Coaxial Nanofibers with Embedded Titanium Dioxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Stabilization and Controlled Release of Dithranol for Therapy of Psoriasis" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 7: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070187
APA StyleAndrýsková, N., Sourivong, P., Babincová, M., Babinec, P., & Šimaljaková, M. (2023). Electrospun PCL/PVA Coaxial Nanofibers with Embedded Titanium Dioxide and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Stabilization and Controlled Release of Dithranol for Therapy of Psoriasis. Magnetochemistry, 9(7), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9070187





