Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the magnetic properties of mixed nanocrystalline Zn/manganese oxide compounds synthesized by a hydrothermal method. These compounds are designed as (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n, where index n ranges from 0.05 to 0.60. The results of magnetic measurements, including AC magnetic susceptibility as a function of temperature (up to 160 K) and frequency (from 7 Hz up to 9970 Hz), as well as DC magnetization in magnetic fields up to 9 T and temperature up to 50 K, are reported. We observed various types of magnetic behavior depending on the nominal weight content of MnO. Samples with a low nominal content (up to n = 0.10) of MnO exhibited Curie–Weiss behavior at higher temperatures. For samples with high nominal weight contribution (from n = 0.30 to 0.60), spin-glass-like or/and weak ferromagnetic behavior is observed.
1. Introduction
Inorganic magnetic nanomaterials are crucial materials used in various fields, for example, biotechnology, medical diagnostics, targeted drug delivery, cancer treatment, high-density data storage, and magnetic sensors [1,2,3,4]. Moreover, magnetic nanoparticles offer significant potential benefits in environmental protection, such as wastewater remediation [5].
Manganese oxide nanomaterials possess unique magnetic properties that make them highly useful in technological applications, such as catalysis, magnetic information storage, and biomedical applications [6,7,8,9,10,11]. The magnetic properties of magnetic oxides depend significantly on their aggregate size and shape, chemical composition, degree of agglomeration, structural features, and surface effects. As a result, there has been a surge in the study of nanosized manganese oxides in recent years. Additionally, magnetic nanoparticles in real systems interact with each other, leading to modifications of the magnetic properties of the nanoparticle system. Long-range dipole interactions are present, which can lead to frustration effects similar to spin glasses and the appearance of spin-glass-type behavior [12,13]. Moreover, when magnetic nanoparticles are in direct contact with each other at high concentrations, short-range exchange couplings occur, further modifying the properties of the nanoparticle system [14].
The magnetic properties of nanoscopic magnetic materials are strongly influenced by the type of chemical synthesis and the conditions under which it is performed [5,13,15]. The synthesis process establishes the basic properties of magnetic nanoparticles, including particle size, size distribution, morphology, stability, and surface properties. Hydrothermal synthesis, in particular, is characterized by low preparation temperatures, low synthesis costs, the ability to obtain relatively large amounts of products, and a relatively low dispersion of nanocrystalline sizes. Furthermore, the hydrothermal method enables the control of nanocrystallite shapes [4,16]. Our previous studies of mixed systems of Zn/transition metal oxides demonstrated that the hydrothermal method results in a much lower degree of agglomeration than the calcination method. Consequently, it reduces the impact of short-range interactions between magnetic nanoparticles [13,17].
ZnO has gained significant attention recently due to its unique properties and versatile applications. Its high electron mobility, transparency, wide band-gap, piezoelectricity, photocatalytic activity, effective photocatalytic activity, and high chemical sensitivity to various absorbed gases make it an attractive material for various/many electronic, optoelectronic and environmental applications [18,19,20,21]. To broaden the practical use of ZnO nanoparticles, they are often doped with transition metals (TM), and/or hybrid Zn/transition metal oxides are obtained [3,13,15,17,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. The combination of magnetic particles with semiconductor oxide nanoparticles enables the material to be separated from its aqueous medium after a given process [26]. These hybrid nanocomposites exhibit enhanced catalytic properties compared to their isolated semiconducting counterparts [3]. Previous studies have shown that combining ZnO with transition metal oxides can significantly enhance photocatalytic activity [31]. The sensitivity and selectivity of ZnO-based gas sensors can also be improved by incorporating transition metal oxides into the system [32,33]. ZnO and α-Fe2O3 composites show promise as photoelectrochemical water-splitting materials for environmentally friendly hydrogen production [34]. Additionally, incorporation of transition metal oxides into ZnO-based electrodes significantly improves the ability to achieve large specific capacities and long cycle life in lithium-ion batteries [35].
Compared to these cases, the magnetic behavior of Zn/Mn oxides has been only scarcely investigated. However, understanding the magnetic properties of these nanocomposites is essential to unlocking their full potential in scientific and technological applications. For instance, mixed systems of ZnO and transition metal oxides play a crucial role in various applications such as catalysis, gas sensing, and energy storage. Additionally, these nanocomposites can exhibit new and improved properties not present in either ZnO or transition metal oxides individually.
In our previous work, we investigated nanocomposites of Zn/Mn oxides synthesized using the wet chemical method followed by calcination [36,37]. We observed two different types of magnetic behavior: superparamagnetism, which we attributed to the presence of ZnMnO3 nanoparticles, and ferrimagnetism, which was driven by the presence of Mn3O4 nanocrystals. Structural characterization enabled us to unambiguously assign the observed magnetic features to the appropriate magnetic phase in a multiphase magnetic system. Additionally, micro-Raman spectroscopy measurements allowed us to detect nanophases that were undetectable by the X-ray diffraction technique.
This study aims to investigate the magnetic properties of Zn/Mn oxides synthesized via the hydrothermal method and compare them with the properties of calcined samples. Our previous research on nanocomposites consisting zinc oxide and iron oxide/cobalt oxide demonstrated that the magnetic properties can be manipulating by altering the synthesis method [7,11].
2. Samples and Experimental Methods
The samples were prepared using a microwave-assisted hydrothermal process, which provided even heat distribution and improved product quality. Zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2*6H2O A.C.S. Chempur) and manganese nitrate (Mn(NO3)2*4H2O A.C.S. Chempur) were used as precursors. Firstly, the zinc nitrate and manganese nitrate were dissolved in distilled water. Next, a 2 M solution of KOH was added to the mixture with continuous stirring in ambient conditions to adjust the pH to 11. After stirring for 0.5 h, the solution was transferred to a hydrothermal microwave reactor, where the process was carried out for 15 min at a pressure of 3.8 MPa. The resulting material was washed with distilled water and dried at 100 °C for 48 h. The mixed nanocrystalline compounds obtained were labeled as (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n, with the nominal MnO weight composition index n of MnO ranging from 0.05 to 0.60. This notation was consistently used throughout the study to refer to the samples of ZnO mixed with MnO prepared by hydrothermal and calcination methods [36,37,38].
The morphology of the samples was examined using a LEO 1530 scanning electron microscope (SEM).
The magnetic properties of the samples were studied using AC/DC Lake Shore 7229 magnetometer. The real, Re(χ), as well as imaginary, Im(χ) parts of magnetic susceptibility were collected using a mutual inductance method in an AC magnetic field with frequencies (f) ranging from 7 to 9970 Hz and amplitude (HAC) not exceeding 20 Oe. The susceptibility measurements were performed in the temperature range of 4.5 K to 160 K. Magnetization was measured up to a magnetic field of 9 T using the extraction technique.
3. Results
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterization
The samples used in this study were the same as those used in our previous work [38]. In that earlier study, only structural and morphological characterization was conducted [38]. A summary of the results is presented below: XRD measurements indicated the presence of two crystalline phases, hexagonal ZnO and spinel ZnMn2O4. The average size of the ZnMn2O4 nanocrystallites was between 16 nm and 26 nm, while the mean crystalline size of ZnO nanocrystals was found to be in the range of 42 nm to 99 nm.
The utilization of micro-Raman spectroscopy measurements provided a deeper understanding of the crystalline phase composition of the samples. Unlike XRD, Raman spectroscopy is capable of detecting impurities and traces of nano-inclusions, making it a highly sensitive analytical tool [39]. The Raman analysis confirmed the presence of two phases registered by XRD ZnO and ZnMn2O4, in all the studied samples. Additionally, other magnetic oxide phases were detected. It is worth noting that the locally formed phases are not detectable by XRD. For samples with n = 0.05, 0.20, the presence of the MnO phase was additionally confirmed. The formation of MnO, Mn3O4, and ZnMnO3 phases, apart from ZnO and ZnMn2O4, was demonstrated for samples with higher n index. The concentration of all manganese oxide phases was found to increase with an increase in the nominal MnO weight contribution, as revealed by Raman spectroscopy measurements.
SEM images for three samples of (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with n = 0.10, 0.30, 0.50 are presented in Figure 1a–c. SEM measurements of samples with n = 0.05, 0.40, and 0.60 were previously reported [38]. The images show small oval and larger non-oval agglomerates. For samples with a higher n index, only oval agglomerates are present. These images suggest that the degree of agglomeration increases with the increase in nominal MnO weight contribution, which is the opposite of what was observed in samples containing Fe and Co [7,11].
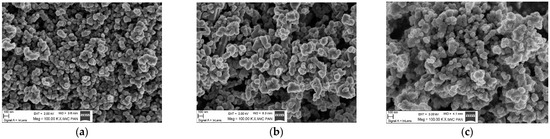
Figure 1.
SEM images for samples of (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with (a) n = 0.10, (b) n = 0.30, (c) n = 0.50.
3.2. Magnetic Studies
Figure 2 shows the temperature dependence of the inverse magnetic susceptibility for samples with n = 0.05 and 0.10. The inset displays the susceptibility versus temperature curve for n = 0.05. We did not include the curve for n = 0.10 in the inset as it would reduce the clarity of the graph. Nevertheless, we observed a similar paramagnetic dependence for both samples. The imaginary part of the AC magnetic susceptibility was temperature-independent and close to zero for these two samples. At high-temperatures, the inverse low-field susceptibility exhibited nearly linear behavior, and the samples followed Curie–Weiss law. To obtain the susceptibility data, we subtracted the diamagnetic AC susceptibility of ZnO (−0.33 ×·10−6 emu/g [40]) from the collected susceptibility. We fitted the χ versus T data at high temperatures to the Curie–Weiss law χ = C/(T − θ) with C = N μ2/3kB, μ2 = g2J(J + 1)μB2, and θ—the Curie–Weiss temperature. The determined parameter values are shown in Table 1. Negative values of the Curie–Weiss temperature indicate that antiferromagnetic interactions prevail in the studied samples.
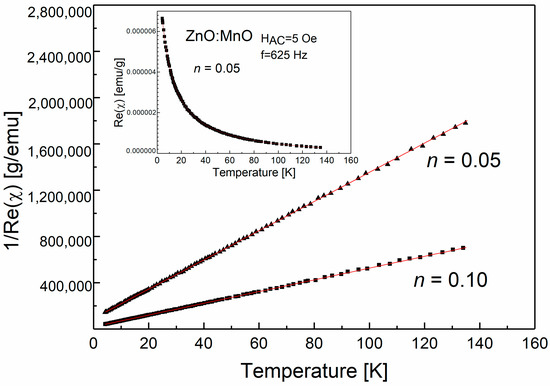
Figure 2.
The inverse magnetic susceptibility for nanosized (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n samples prepared by hydrothermal method. The inset shows the AC susceptibility measurement result as a function of temperature. The solid line represents the Curie–Weiss law fitted to the experimental data.

Table 1.
The values of parameters C and Θ determined from fits to Curie–Weiss law.
The prevailing magnetic phase for samples of (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with n = 0.05 and 0.10 is the spinel ZnMn2O4. The observed Curie–Weiss-type paramagnetic behavior can be explained by the presence of an additional nanosized spinel phase. Our previous studies of nanocomposites based on ZnO and cobalt oxide [11] also found a similar paramagnetic behavior attributed to nanoscopic spinel phases, namely Co3O4 and ZnCo2O4.
It has been established that the spinel ZnMn2O4 exhibits antiferromagnetic properties [41,42,43,44,45], with a reported Néel TN temperature of around 250 K for bulk samples [41]. However, for nanocrystalline samples, TN has been observed in the temperature range of 15 K to 150 K [42,44,45]. Furthermore, it has been reported that the low-temperature ferromagnetic behavior of ZnO(Mn) samples can be attributed to nanosized ZnMn2O4 [46]. Experimental evidence has shown that even antiferromagnetic bulk materials can exhibit ferromagnetic properties when they are in nanosized oxide form. This difference in magnetic properties between nanoparticles and bulk materials is often attributed to surface or/and size effects [47,48,49]. In our study, we observed a significant decrease in the absolute values of the Curie–Weiss temperature as the n index increased, indicating the breakdown of the predominant antiferromagnetic interactions. Structural measurements revealed an increase in the content of ZnMn2O4 with increasing n index. A similar trend was observed for nanocomposites containing Co synthesized via the hydrothermal method [11], where the absolute values of the Curie–Weiss temperature decreased with the increase in the n index, corresponding to an increase in the content of the magnetic ZnCo2O4 phase. This provides a means to manipulate the value of the magnetic parameter θ, making it technologically significant.
As previously mentioned, the nanosized spinel phase of ZnMn2O4 is present in all the studied samples and is the dominant magnetic phase. The magnetic response in samples with the lowest nominal MnO content is attributed to ZnMn2O4, and this contribution to the paramagnetic response is also evident in the remaining samples.
In Figure 3, the temperature dependence of the real part of AC magnetic susceptibility is presented for a sample with a nominal n index of 0.30. Figure 3 illustrates the temperature dependence of the real part of AC magnetic susceptibility for a sample with a nominal n index equal to 0.30. Once again, a clear paramagnetic contribution is observed, which can be attributed to the ZnMn2O4 phase. Moreover, a broad maximum at of 34.4 K is clearly evident. Further measurements of the AC magnetic susceptibility conducted as a function of frequency f indicate that the positions of the observed maxima do not change remain unchanged with the driving frequency, as shown in the inset of Figure 3.
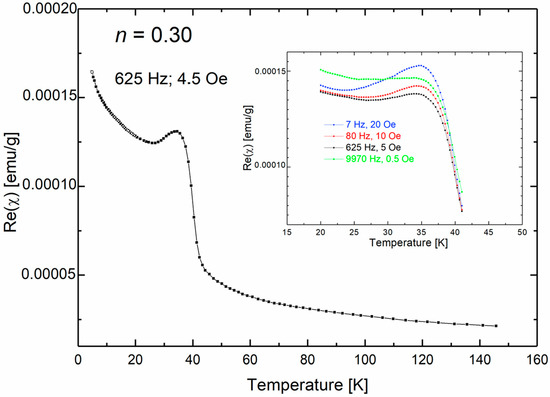
Figure 3.
Temperature dependence of the real part of magnetic susceptibility of the nanocrystalline sample of (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with n = 0.30.
In addition to the predominant ZnMn2O4 phase, micro-Raman spectroscopy identified the existence of other magnetic oxides, such as MnO, Mn3O4, and ZnMnO3. This finding presents a challenge in assigning the AC magnetic susceptibility peak to a specific phase, given the presence of multiple magnetic oxide phases.
The results of AC magnetic susceptibility for samples with nominal n index 0.50 and 0.60 are shown in Figure 4, indicating a clear multiphase behavior with two broad maxima. In addition, a paramagnetic contribution was observed in both samples. The peak at approximately 35 K is similar to the sample with n = 0.30, while the low-temperature peak, observed around 14 K, is evident only in samples with n = 0.50 and 0.60. The inset in Figure 4 displays the frequency dependence of the low-temperature maximum for a sample with n = 0.50. The real and imaginary parts of the magnetic susceptibility were measured by warming up the sample after cooling it down in a zero magnetic field. The position of the maxima (Tf) shifts towards higher values of the driving frequency, indicating the presence of superparamagnetic or spin-glass-like systems.
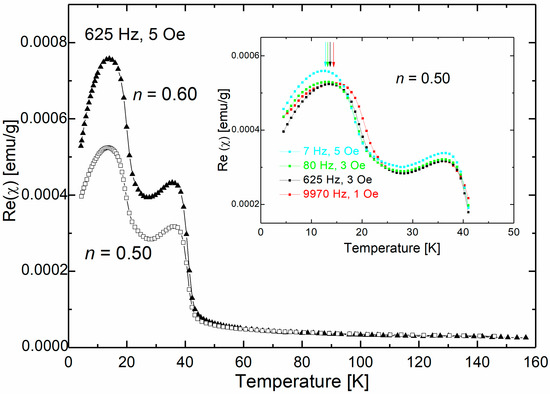
Figure 4.
Temperature dependence of the real part of magnetic susceptibility of nanocrystalline (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with n = 0.50 and 0.60.
To classify the observed freezing/blocking process, we utilized a helpful criterion: R = ΔTf/(Tf Δlog10(f)), where ΔTf is the difference between Tf measured in the Δlog10(f) frequency interval. The empirical parameter R represents the relative shift of the temperature Tf per decade of frequency f [50]. For interacting nanoparticles, experimental studies have shown that R values between 0.05 and 0.10 indicate superparamagnetic systems, while R < 0.05 indicates spin-glass systems [7,51]. In our case, the value of the R value parameter was 0.045 for both studied samples, indicating the presence of spin-glass-like behavior.
The presence of multiple magnetic oxide phases in the samples makes it challenging to attribute a specific phase to the observed magnetic behavior. We observed the superparamagnetic behavior in (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n samples obtained by calcination and associated it with the presence of ZnMnO3 nanocrystals [36]. The blocking temperatures determined for these samples were in the low-temperature range between 6.3 K and 10.5 K. It is important to note that spin-glass-like behavior can arise from agglomeration, interparticle interactions, and surface effects.
To expand our analysis and establish a connection between the observed features in AC susceptibility and the magnetic oxide phases present in the sample, we conducted magnetization measurements.
The DC magnetization data for the sample with n = 0.30 collected at 4.5 K and 40 K is presented in Figure 5. The results of the DC magnetization measurements indicated the presence of a hysteresis loop at low temperatures, with a coercive field of approximately 0.2 T at 4.5 K.
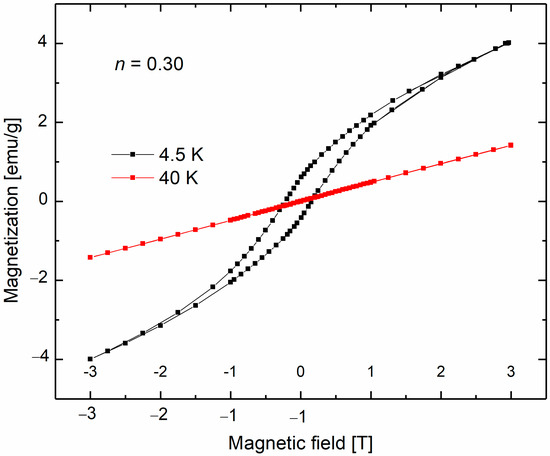
Figure 5.
DC magnetization curves of the nanocrystalline sample with n = 0.30.
The literature indicates that Mn3O4 exhibits much higher values of coercivity fields. Previous studies have experimentally established that bulk Mn3O4 behaves as a ferrimagnet with TC at 20 K [52]. However, different Curie temperature values were observed for nanocrystalline Mn3O4 [53,54], and superparamagnetic behavior has also been reported [55].
Various methods of Mn3O4 preparation lead to a specific range of high-coercivity field values observed at low temperatures. For instance, coercivity from 0.7 T up to 1.1 T was reported for nanosized Mn3O4 [35,36,56] at around 5 K. In addition, in our earlier research on ZnO(MnO) nanocrystals synthesized via calcination, we associated high values of the coercivity field HC (0.7 T) with the presence of the ferrimagnetic Mn3O4 nanosized phase.
On the other hand, previous studies have reported superparamagnetic, ferrimagnetic, and spin-glass behavior of ZnMnO3 nanoparticles [57,58,59]. We attributed the observed magnetic behavior of the calcined ZnO(MnO) samples to the presence of ZnMnO3 nanocrystals, exhibiting superparamagnetic behavior above a blocking temperature (TB below 10 K) [36]. Below the blocking temperature, we observed very narrow hysteresis loops in DC magnetization with very low coercivity values (HC~0.04 T at 4.5 K) for the calcined ZnMnO3 phase [58]. In contrast, the DC magnetization measurements in this work showed much higher coercivity field values, as seen in Figure 5. The Raman spectroscopy measurements revealed the existence of the MnO phase in all the studied samples, even in those with the lowest n index. The content of this phase increases with the increase in n, as demonstrated by Raman spectroscopy measurements. Although bulk MnO is an antiferromagnet with a Néel temperature of 122 K, weak ferromagnetic, superparamagnetic, or spin-glass-like behavior has been reported for MnO nanocrystals at low temperatures [60,61,62]. The reported ferromagnetic behavior of MnO nanoparticles may be attributed to size or spin surface effects. A similar coercivity field value of 0.18 T, as reported for MnO nanoparticles at low temperatures [60,61,62], was observed for a sample with n = 0.30 at 4.5 K. The peak observed at 34.4 K in the AC magnetic susceptibility could be associated with the MnO phase.
The measured magnetic response depends on the size and the distribution of the size of nanocrystals, their shape, degree of agglomeration, exchange interactions, and dipolar interactions. With the increase in the n index, the nonmagnetic ZnO content decreases, and the amount of four different magnetic phases increases along with the degree of agglomeration.
Figure 6 shows DC magnetization curves collected for (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n samples with n = 0.50 and 0.60 at 4.5 K. The observed coercivity field values (0.2 T at 4.5 K) and high remanence are much higher than those reported for samples with lower nominal MnO weight content. The complex shape of the hysteresis is due to the magnetically multiphase system obtained for these samples. The magnetic response of hydrothermal samples is more complex when compared to samples prepared via the calcination method.
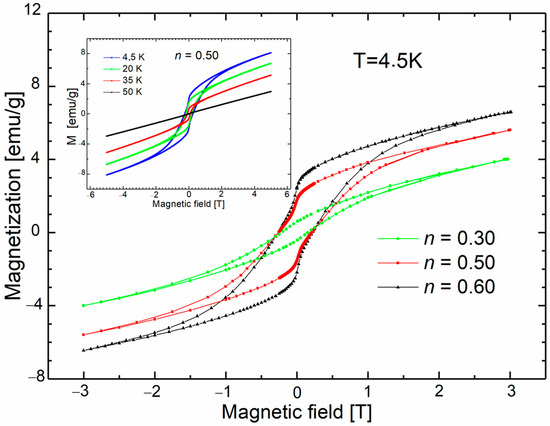
Figure 6.
DC magnetization curves of nanocrystalline samples with n = 0.50 and 0.60 at 4.5 K. The magnetization curve measured for the sample with n = 0.30 was added for comparison. The inset shows the magnetization collected for the sample with n = 0.60.
4. Summary and Conclusions
We present a study on the magnetic properties of composite samples of Zn/manganese oxides prepared via hydrothermal synthesis.
At higher temperatures, samples of (ZnO)1−n(MnO)n with a low n index exhibited Curie–Weiss paramagnetic behavior, with ZnMn2O4 being the major magnetic phase in this region. Negative values of the Curie–Weiss temperature (θ) were also observed, indicating the predominance of antiferromagnetic interactions. However, as the nominal MnO weight contribution increased, a breakdown of the predominance of antiferromagnetic coupling was observed. We conclude that the observed paramagnetic behavior is related to the presence of the ZnMn2O4 phase, which dominates as the magnetic phase for all samples studied, including those with a high n index. In comparison to the magnetic results obtained for calcined samples, we observed superparamagnetic blocking for calcined samples with a low n index. This occurrence was associated with the forming of single-domain ZnMnO3 nanocrystallites [36].
We attribute the observed feature in the AC magnetic susceptibility of sample with n = 0.30 to the presence of the MnO phase. For samples with a higher n index, the complex with two broad maxima responses in AC magnetic susceptibility was observed. The weak ferromagnetic behavior observed up to TC ≈ 35 K can be attributed to the MnO phase. Additionally, spin-glass-like behavior with a freezing temperature of ~14 K was visible. In these two samples, we expected much more significant effects associated with many of the magnetic phases, agglomeration, and the interaction between magnetic particles. In this range of a high n index, a comparison of the results obtained with those from the calcination method reveals a stark contrast in the observed magnetic behavior [36]. In contrast to the hydrothermal method, the calcination method produced a completely different magnetic behavior, where we observed ferrimagnetism associated with the Mn3O4 phase. Despite many magnetic phases in the calcined samples, other magnetic phases did not disturb this magnetic response. In conclusion, the hydrothermal method produced a more complex magnetic response for Mn-based nanocomposites than the calcination method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.K.-K. and W.D.; magnetic investigations, I.K.-K. and M.A.; Raman measurements, B.H., N.R. and M.R.; data analysis, I.K.-K. and B.H.; synthesis, SEM, measurements, D.S. and U.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research in Serbia was supported by the Science Fund of the Republic of Serbia, Grant No. 7504386, Nano object in own matrix—Self composite—NOOM-SeC.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mittal, A.; Roy, I.; Gandhi, S. Magnetic Nanoparticles: An Overview for Biomedical Applications. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Nunes, W.C.; Socolovsky, L.M.; De Biasi, E.; Vargas, J.M.; Denardin, J.C. Superparamagnetism and other magnetic features in granular materials: A review on ideal and real systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong Nguyen, T.; Thanh Vu, M.; Son Nguyen, N. Hybrid Magnetic-Semiconductor Oxides Nanomaterial: Green Synthesis and Environmental Catalytic. In Photocatalysts—New Perspectives; Awwad, N.S., Alarfaji, S.S., Alomary, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022; Volume 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.-H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schüth, F. Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Protection, Functionalization, and Application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khan, R.; Daverey, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles, and their applications in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, D.; Testa, A.M.; Tronc, E.; Lucari, F.; D’Orazio, F.; Nogués, M. Magnetic properties adjustment of ZrO2:Mn nanocrystals by changing hydrothermal synthesis conditions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 226, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Hadžić, B.; Sibera, D.; Romčević, M.; Romčević, N.; Narkiewicz, U.; Dobrowolski, W. Dynamic magnetic properties of ZnO nanocrystals incorporating Fe. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 3756–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, J.L.; Fiorani, D.; Tronc, E. Magnetic relaxation in fine-particle systems. Adv. Chem. Phys. 1997, 98, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerdj, I.; Jagličić, Z.; Arčon, D.; Niederberger, M. Co-Doped ZnO nanoparticles: Minireview. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zafar, H.; Zia, M.; ul Haq, I.; Phull, A.R.; Ali, J.S.; Hussain, A. Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Hadžić, B.; Sibera, D.; Romčević, M.; Romčević, N.; Narkiewicz, U.; Łojkowski, W.; Arciszewska, M.; Dobrowolski, W. Magnetic properties of ZnO(Co) nanocrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 561, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. ZnO nanostructured materials and their potential applications: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.K.; Shukla, S.; Sharma, K.K.; Kumar, V. A review on ZnO: Fundamental properties and applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 49, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, D.; Özgür, Ü.; Morkoç, H. ZnO devices and applications: A review of current status and future prospects. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Weng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Chu, P.K. Biomedical applications of functionalized ZnO nanomaterials: From biosensors to bioimaging. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 3, 1500494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, F.d.S.; Melo, A.L.M.d.S.; Ferro, A.d.B.; Zanta, C.L.d.P.e.S.; Duarte, J.L.d.S.; Oliveira, R.M.P.B. Magnetic Zinc Oxide/Manganese Ferrite Composite for Photodegradation of the Antibiotic Rifampicin. Materials 2022, 15, 8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayani, Z.N.; Anjum, M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S.; Zeeshan, T. Role of Mn in biological, optical, and magnetic properties ZnO nano-particles. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 125, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, T.; Matei, C.O.; Vlaicu, I.D.; Kuncser, A.C.; Stefan, M.; Ghica, D.; Miclea, L.C.; Savapol, T.; Culira, D.C.; Moisescu, M.G. Influence of surfactant-tailored Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles on ROS production and DNA damage induced in murine fibroblast cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.I. Seed-mediated synthesis and characterization of ZnO@γ-Fe2O3 nanospheres: Building up the core-shell model. J. Crys. Growth 2021, 572, 126279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, B.; Bhatti, M.A.; Shah, A.A.; Tahira, A.; Shah, A.K.; Usto, A.; Aftab, U.; Bukhari, S.I.; Alshehri, S.; Shah Bukhari, S.N.U.; et al. Mn3O4@ZnO Hybrid Material: An Excellent Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Synthetic Dyes including Methylene Blue, Methyl Orange and Malachite Green. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.E.; Montero-Muñoz, M.; López, L.L.; Ramos-Ibarra, J.E.; Coaquira, J.A.H.; Heinrichs, B.; Páez, C.A. Significantly enhancement of sunlight photocatalytic performance of ZnO by doping with transition metal oxides. Sci. Rep. 2021, 1, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Narayanan, M.; Gautam, R.; Gopalan, R.; Swaminathan, P. Effect of processing route on the structural and functional properties of manganese doped zinc oxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 261, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathidevi, K.; Nanjan, V.; Tamilselvi, D. Structural, morphological and optical performance of synthesized Co, Mn/ZnO nanocomposities. J. Ovonic. 2020, 16, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.T.; Saikia, K.; Raveesh, S.; Paily, R. Hydrogen sensing of heterostructured magnetic nanospheres with different Fe to Zn Molar Ratio. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2021, 20, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichhandran, K.; Karthika, K.; Baneto, M.; Shanthakumari, K.; Lalithanbika, K.C. Inducing superparamagnetic behavior and enhancing antibacterial efficiency of ZnO nanopowders through Mn + F doping. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yan, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, D.A. Selective NH3 gas sensor based on Fe2O 3-ZnO nanocomposites at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, W.; Meng, X.; Ruan, A.; Su, P.; Yang, H. Synthesis and enhanced gas sensing properties of flower-like ZnO/α-Fe2O3 core-shell nanorods. Ceramics Int. 2017, 43, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, L.; Lushaj, E.; Compare, L.D.; Moretti, E.; Vomiero, A. Nanoscale ZnO/α-Fe2O3 Heterostructures: Toward Efficient and Low-Cost Photoanodes for Water Splitting. Small Sci. 2022, 2, 2100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A. Porous Fe2O3/ZnO composite derived from MOFs as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Ceramics Int. 2016, 42, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Zou, B.S.; Wu, X.C.; Lin, J.G.; Guo, L.; Li, Q.S. Magnetic properties of nanostructured Mn oxide particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawazeer, T.M.; Alsoufi, M.S.; Badria, M.S.; Al-Shehri, M.; Hamdy, M.S. Excellent improvement in photocatalytic nature of ZnO nanoparticles via Fe doping content. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, M.M. Manganese Oxides for Lithium Batteries. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1997, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.G.; Scrosati, B.; Tarascon, J.M. Nanomaterials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milivojević, D.; Babić-Stojić, B.; Jokanović, V.; Jagličić, Z.; Makovec, D. Magnetic Properties of Mn-Oxide Nanoparticles Dispersed in an Amorphous SiO2 Matrix. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigiani, L.; Hassan, M.; Peddis, D.; Maccato, C.; Varvaro, G.; Sada, C.; Bontempi, E.; Martí-Sánchez, S.; Arbiol, J.; Barreca, D. High Magnetic Coercivity in Nanostructured Mn3O4 Thin Films Obtained by Chemical Vapor Deposition. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Arciszewska, M.; Romčević, N.; Romčević, M.; Hadžić, B.; Sibera, D.; Narkiewicz, U. Superparamagnetic and ferrimagnetic behavior of nanocrystalline ZnO(MnO). Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. 2018, 98, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžić, B.; Romčević, N.; Romčević, M.; Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Wróbel, R.; Narkiewicz, U.; Sibera, D. Raman study of surface optical phonons in ZnO(Mn) nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadžić, B.; Romčević, N.; Romčević, M.; Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Dobrowolski, W.; Narkiewicz, U.; Sibera, D. Raman study of surface optical phonons in hydrothermally obtained ZnO(Mn) nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2016, 58, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; MacManus-Drisoll, J.L. Impurity control in Co-doped ZnO films through modifying cooling atmosphere. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 022503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRC. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 80th ed.; CRC Press LLC.: Boca Raton, NY, USA; Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 4–136. [Google Scholar]
- Aiyama, Y. Magnetic Structures in Spinel B-Site Lattices; A Proposal of Linear Antiferromagnetism in ZnMn2O4. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 21, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbrink, S.; Waskowska, A.; Gerward, L.; Olsen, J.S.; Talik, E. High-pressure phase transition and properties of spinel ZnMn2O4. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhor, H.; Bocquet, J.F.; Pommier, C. Heat capacity and thermodynamic behavior of Mn3O4 and ZnMn2O4 at low temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1986, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, M.M.; Lofland, S.E.; Ramanujachary, K.V.; Ganguli, A.K. Magnetic and photocatalytic properties of nanocrystalline ZnMn2O4. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2009, 32, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, B.; Wang, W.J.; Chen, X.L. Facile synthesis, thermal, magnetic, Raman characterizations of spinel structure ZnMn2O4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.; Bartolome, F.; Garcia, L.M.; Garcia, J. Extrinsic origin of ferromagnetism in doped ZnO. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.N.; Ollivier, G. Hydrothermal preparation and low temperature magnetic properties of Mn(OH)2. Solid State Commun. 1972, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K.; Jena, P. Equilibrium geometry, stability, and magnetic properties of small MnO clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.H.; Makhlouf, S.A.; Berkowitz, A.E. Finite size effects in antiferromagnetic NiO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydosh, A. Spin-Glasses: An Experimental Introduction; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Mamiya, H. Dynamical properties of a crystalline rare-earth boron cluster spin-glass system. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 2144221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwight, K.; Menyuk, N. Magnetic properties of Mn3O4 and the canted spin problem. Phys. Rev. 1960, 119, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ramanujachary, K.V.; Lofland, S.E.; Ganguli, A.K. Nanorods of manganese oxalate: A single source precursor to different manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO, Mn2O3, Mn3O4). J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.; Zysler, R.D.; Fiorani, D. Surface and magnetic interaction effects in Mn3O4 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 174406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackett, R.J.; Parson, J.G.; Machado, B.I.; Gaytan, S.M.; Murr, L.E.; Botez, C.E. Evidence of low-temperature superparamagnetism in Mn3O4 nanoparticle ensembles. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 365703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.T.; Si, P.Z.; Choi, C.J.; Ge, H.L. Large coercivity and exchange bias in Mn3O4 nanoparticles prepared by laser ablation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 489, 165481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćimović, J.; Micković, Z.; Gaál, R.; Smajda, R.; Vâju, C.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Forró, L.; Magrez, A. Synthesis, electrical resistivity, thermo-electric power and magnetization of cubic ZnMnO3. Solid State Commun. 2011, 151, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhande, L.V.; Dhas, V.V.; Kolekar, Y.D.; Ghosh, K.; Date, S.K.; Patil, S.I. Role of defects in enhancing room temperature ferromagnetism of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi B 2013, 250, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnik, S.; Dabrowski, B.; Mais, J. Origin of spin-glass behavior of Zn1—xMnxO. J. Supercond. Nov. Mag. 2002, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Huh, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, S.H.; Ri, H.-C. Anomalous Magnetic Properties of MnO Nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Pakhomov, A.B. Size-driven magnetic tra62nsitions in monodisperse MnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09E124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Yang, H.D.; Pal, A.K.; Majumdar, S. Magnetic properties of MnO nanocrystals dispersed in a silica matrix. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).