Surface-Bulk 2D Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles within Ising-like Model Solved by Using Entropic Sampling Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ising like Model and Principles of Calculations
3. Monte Carlo Entropic Sampling
4. Numerical Results and Analysis
4.1. The Case = 0
4.2. The Case ≠ 0
4.3. Size Effects under Temperature
4.4. The Case Jbs = 0
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gütlich, P.; Goodwin, H.A. Spin Crossover–An Overall Perspective. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds II; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H., Eds.; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 233, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Hauser, A.; Spiering, H. Thermal and optical switching of Iron(II) Complexes. Angew. Chem. 1994, 33, 2024–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Galan-Mascaros, J.R.; Monrabal-Capilla, M.; Garcia-Martinez, J.; Parbo-Ibanez, P. Bistable Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles Showing Magnetic thermal Hysteresis near Room Temperature. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Spin-Crossover Materials. Properties and Applications. Edited by Malcolm A. Halcrow. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.; Belmouri, N.E.I.; Linares, J.; Boukheddaden, K. Elastic Origin of the Unsymmetrical Thermal Hysteresis in Spin Crossover Materials: Evidence of Symmetry Breaking. Symmetry 2021, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Gütlich, P. Thermal Spin crossover in Mn(II), Mn(III), Cr(II) and Co(III) Coordination compounds. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds II; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 234, pp. 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukheddaden, K.; Linares, J.; Tanasa, R.; Chong, C. Theoretical investigations on an axial next nearest neighour Ising-like model for spin crossover solids: One- and two-step spin transitions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2007, 19, 106201–106212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, A.; Linares, J.; Varret, F.; Codjovi, E.; Slimani, A.; Tanasa, R.; Enachescu, C.; Stancu, A.; Haasnoot, J. Pressure effect investigated with first-order reversal-curve method on the spin-transition compounds [FexZn1−x(btr)2(NCS)2]·H2O (x = 0.6,1). Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 224107–224114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, A.; Dîrtu, M.; Enachescu, C.; Tanasa, R.; Linares, J.; Stancu, A.; Garcia, Y. Calorimetric measurements of diluted spin crossover complexes [FexM1−x(btr)2(NCS)2]•H2O with M = Zn and Ni. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Jureschi, C.M.; Boukheddaden, K. Surface effects leading to unusual size dependence of the thermal hysteresis behavior in spin-crossover nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2016, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constant-Machado, H.; Stancu, A.; Linares, J.; Varret, F. Thermal hysteresis loops in spin-crossover compounds analyzed in terms of classical Preisach model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1998, 34, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krober, J.; Audière, J.P.; Claude, R.; Codjovi, E.; Kahn, O.; Hassnoot, J.; Grolière, F.; Jay, C.; Bousseksou, A.; Linares, J.; et al. Spin Transitions and Thermal Hysteresis in the Molecular-Based Materials [Fe(Htrz)2(trz)](BF4) and [Fe(Htrz)3](BF4)2.cntdot.H2O (Htrz = 1,2,4-4H-triazole; trz = 1,2,4-triazolato). Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Codjovi, E.; Garcia, Y. Pressure and Temperature Spin Crossover Sensors with Optical Detection. Sensors 2012, 12, 4479–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukheddaden, K.; Ritti, M.H.; Bouchez, G.; Sy, M.; Dîrtu, M.M.; Parlier, M.; Linares, J.; Garcia, Y. Quantitative contact pressure sensor based on spin crossover mechanism for civil security applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 7597–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Martinez, C.J. Spin-Transition Polymers: From Molecular Materials Toward Memory Devices. Science 1998, 279, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallone, S.P.; Tantillo, A.N.; dos Santos, A.M.; Molaison, J.J.; Kulmaczewski, R.; Chapoy, A.; Ahmadi, P.; Halcrow, M.A.; Sandeman, K.G. Giant barocaloric effect at the spin crossover transition of a molecular crystal. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Ranke, P.J. A microscopic refrigeration process triggered through spin-crossover mechanism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 181909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaicha, B.; Van Do, K.; Yangui, A.; Pittala, N.; Lusson, A.; Sy, M.; Bouchez, G.; Fourati, H.; Gomez-Garcia, C.J.; Triki, S.; et al. Interplay between spin-crossover and luminescence in a multifunctional single crystal iron(II) complex: Towards a new generation of molecular sensors. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukheddaden, K.; Fourati, H.; Singh, Y.; Chastanet, G. Evidence of photo-thermal effects on the first-order thermo-induced spin transition of [{Fe(NCSe)(py)2}2(m-bpypz)] spin-crossover material. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastanet, G.; Gaspar, A.B.; Real, J.A.; Létard, J.F. Photo-switching spin pairs synergy between liesst effect and magnetic interaction in an iron(II) binuclear spin-crossover compound. Chem. Commun. 2001, 9, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Hauser, A. Thermal and light-induced spin crossover in iron(II) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1990, 97, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.; Boukheddaden, K. Pressure-induced multi-step and self-organized spin states in an electro-elastic model for spin-crossover solids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 12870–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousseksou, A.; Negre, N.; Goiran, M.; Salmon, L.; Tuchagues, J.P.; Boillot, M.L.; Boukheddaden, K.; Varret, F. Dynamic triggering of a spin-transition by a pulsed magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. B 2000, 13, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerroudj, S.; Caballero, R.; de Zela, F.; Jureschi, C.; Linares, J.; Boukheddaden, K. Monte Carlo–Metropolis investigations of shape and matrix effects in 2d and 3d spin-crossover nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 738, 012068–012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, A.; Boukheddaden, K.; Linares, J.; Varret, F. Two-dimensional Ising-like model with specific edge effects for spin-crossover nanoparticles: A monte Carlo study. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 054119–054125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Cazelles, C.; Dahoo, P.R.; Sohier, D.; Dufaud, T.; Boukheddaden, K. Shape, size, pressure and matrix effects on 2D spin crossover nanomaterials studied using density of states obtained by dynamic programming. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2021, 187, 110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Oubouchou, H.; Nishino, M.; Miyashita, S.; Boukheddaden, K. Elastic-frustration-driven unusual magnetoelastic properties in a switchable core-shell spin-crossover nanostructure. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 101, 054105–054119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, G.; Mikolasek, M.; Molnár, G.; Nicolazzi, W.; Bousseksou, A. Tuning the spin crossover in nano-objects: From hollow to core–shell particles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 607, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, A.; Khemakhem, H.; Boukheddaden, K. Structural synergy in a core-shell spin crossover nanoparticle investigated by an electroelastic model. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 174104–174114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubouchou, H.; Singh, Y.; Boukheddaden, K. Magnetoelastic modeling of core-shell spin-crossover nanocomposites. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 014106–014119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enachescu, C.; Stoleriu, L.; Nishino, M.; Miyashita, S.; Stancu, A.; Lorenc, M.; Bertoni, R.; Cailleau, H.; Collet, E. Theoretical approach for elastically driven cooperative switching of spin-crossover compounds impacted by an ultrashort laser pulse. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 224107–224115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourati, H.; Ndiaye, M.; Sy, M.; Triki, S.; Chastanet, G.; Pillet, S.; Boukheddaden, K. Light-induced thermal hysteresis and high-spin low-spin domain formation evidenced by optical microscopy in a spin-crossover single crystal. Phys. Rev. B 2022, 105, 174436–174451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, M.; Murakami, K.; Fujinami, T.; Nishi, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Sunatsuki, Y. Syntheses, three types of hydrogen-bonded assembly structures, and magnetic properties of [FeIII (Him)2(hapen)]y.solvent (Him=imidazole, hapen=N,N′-bis(2-hydroxyacetophenylidene)ethylenediamine, Y=BPh4, CF3SO3, PF6, ClO4, and BF4). Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 399, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajnflasz, J.; Pick, R. Transitions “low spin”-“high spin” dans les complexes de Fe2+. J. Phys. Colloq. 1971, 32, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Spiering, H.; Varret, F. Analytical solution of 1d Ising-like systems modified by weak long-range interaction—application to spin crossover compounds. Eur. Phys. J. B 1999, 10, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Cazelles, C.; Dahoo, P.R.; Boukheddaden, K. A first-order phase transition studied by an Ising-like model solved by entropic Sampling Monte Carlo Method. Symmetry 2021, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiruta, D.; Jureschi, C.M.; Linares, J.; Dahoo, P.R.; Garcia, Y.; Rotaru, A. On the origin of multi-step spin transition behaviour in 1d nanoparticles. Eur. Phys. J. B 2015, 88, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteto, I.; Linares, J.; Varret, F. Monte Carlo entropic sampling for the study of metastable states and relaxation paths. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 5128–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.; Enachescu, C.; Boukheddaden, K.; Varret, F. Monte Carlo entropic sampling applied to spin crossover solids: The squareness of the thermal hysteresis loop. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 2453–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
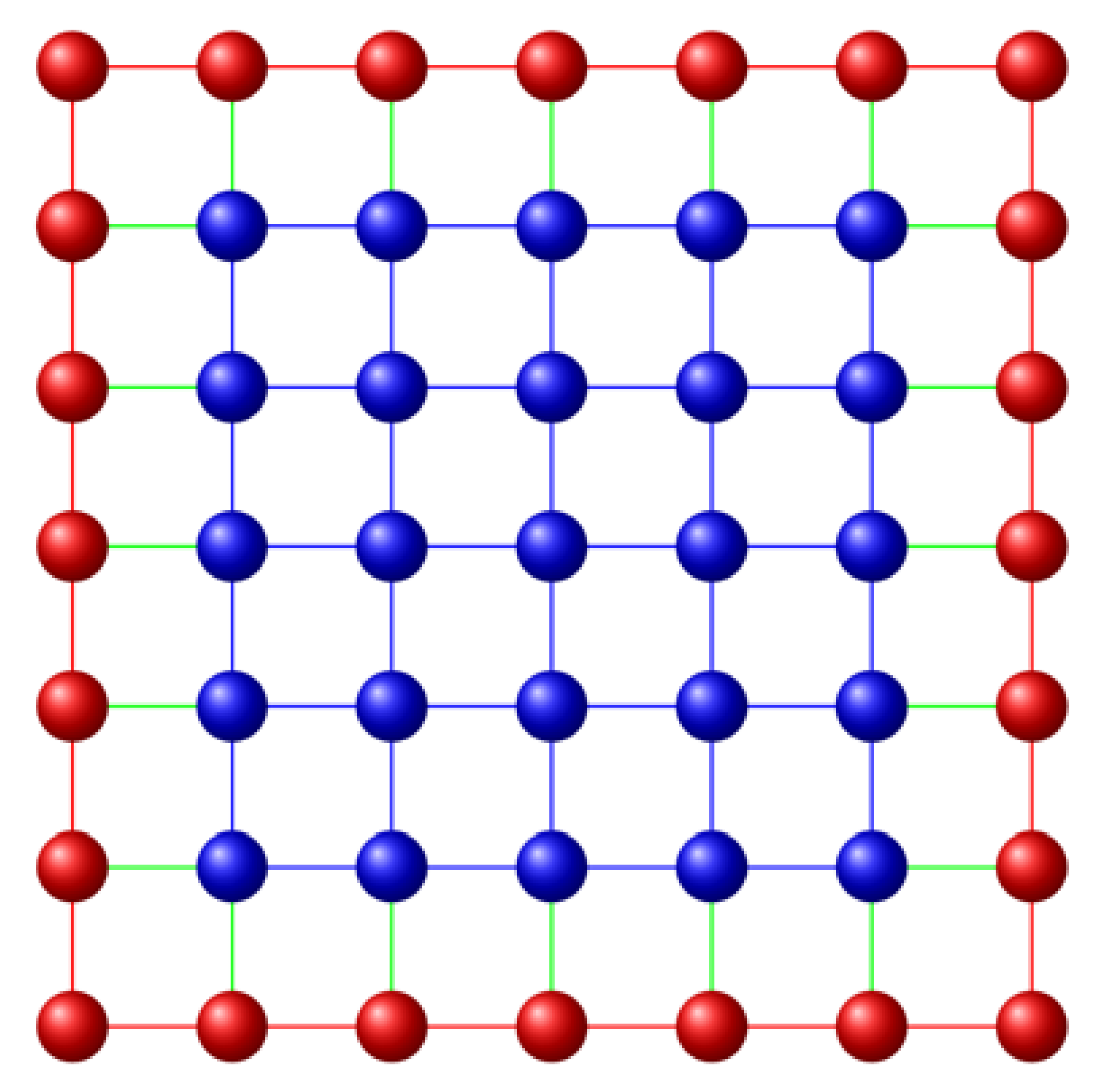
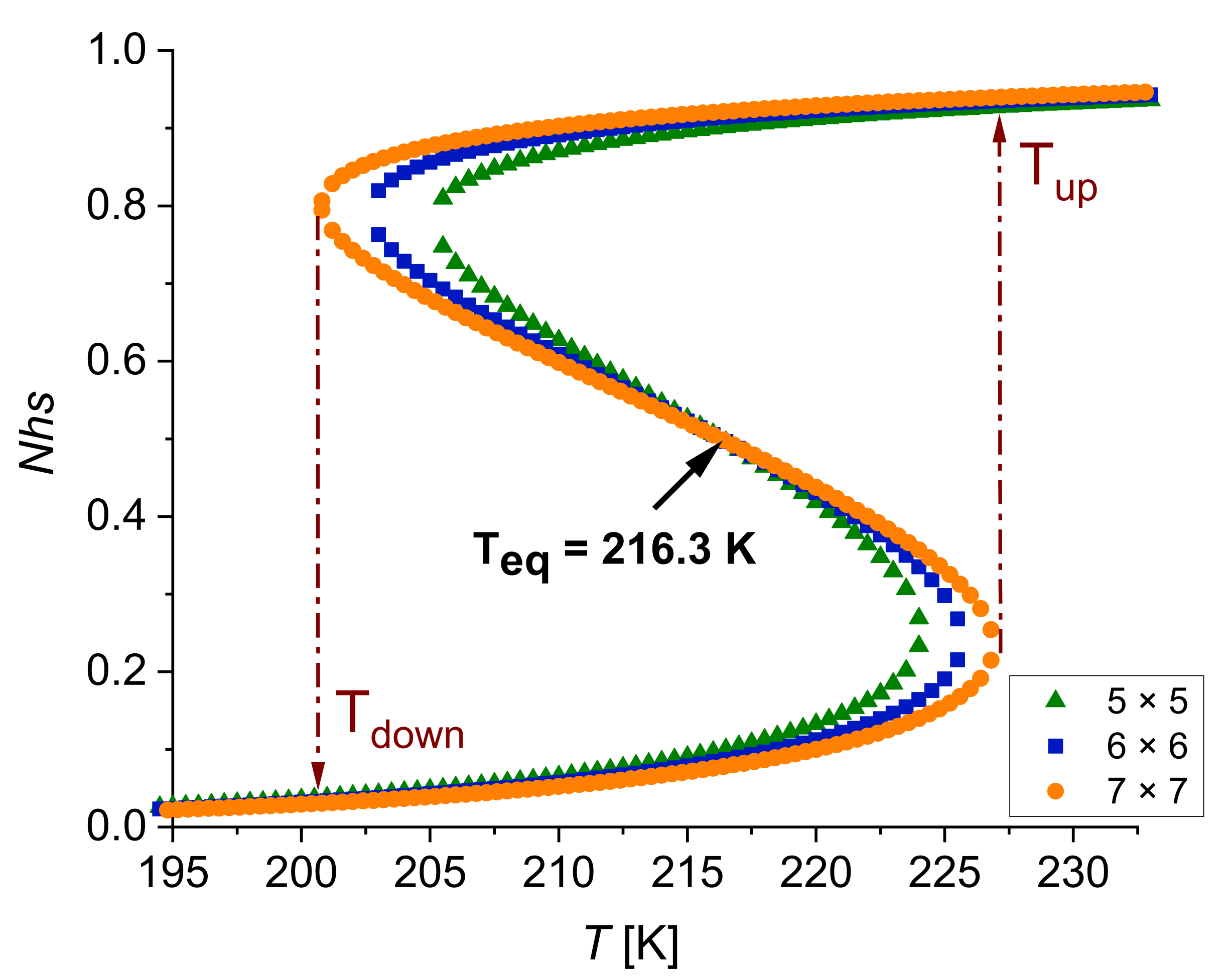

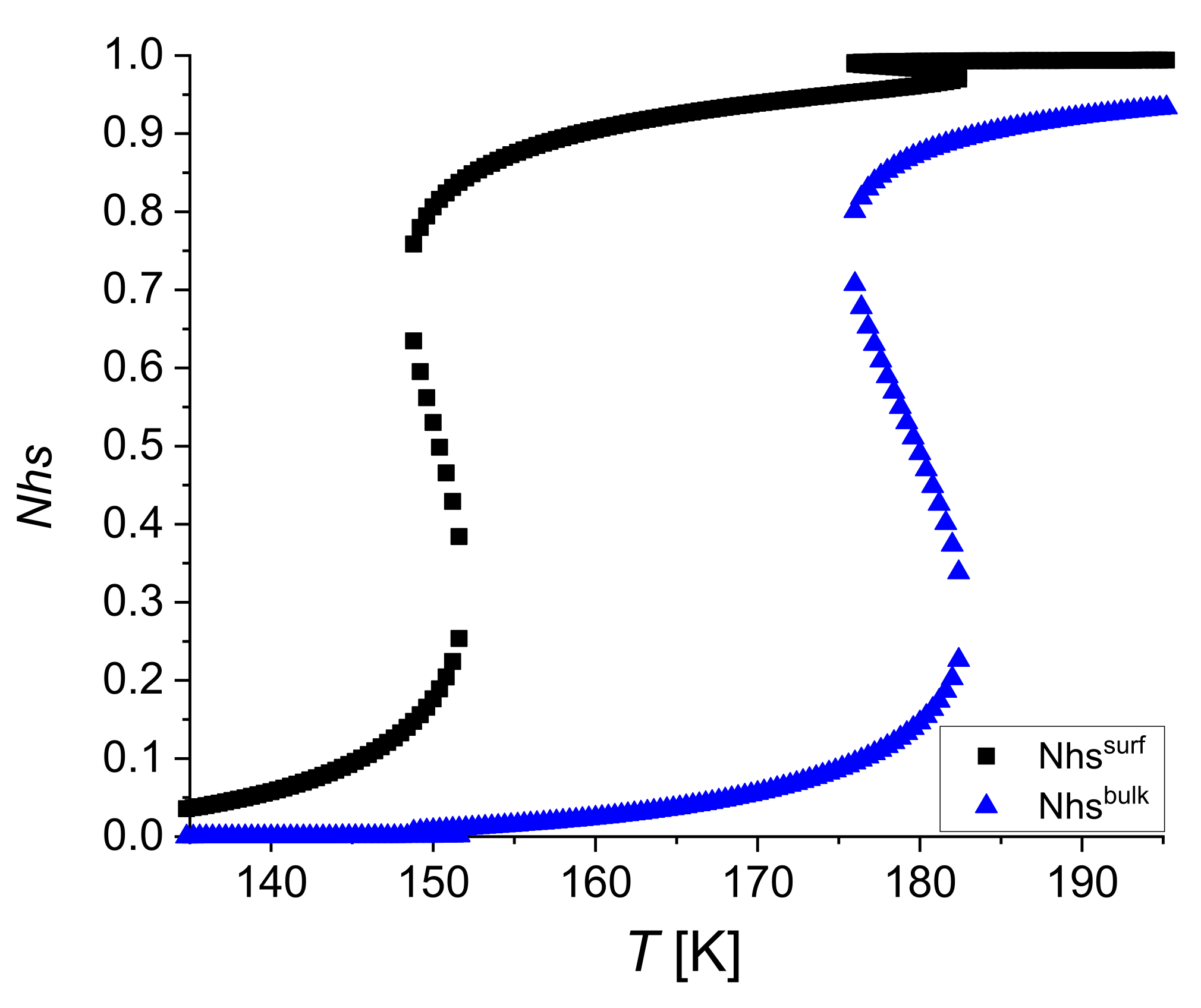
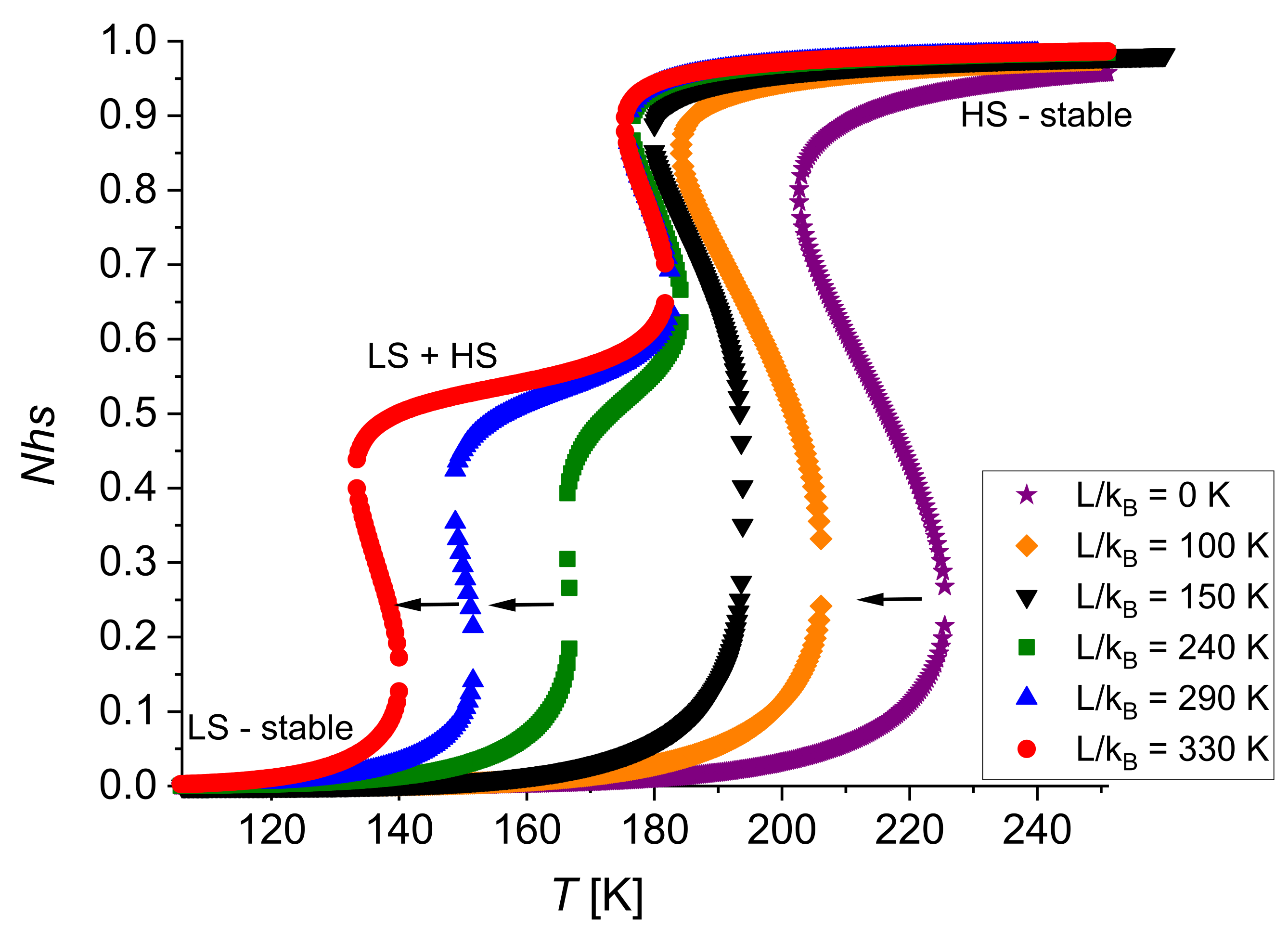
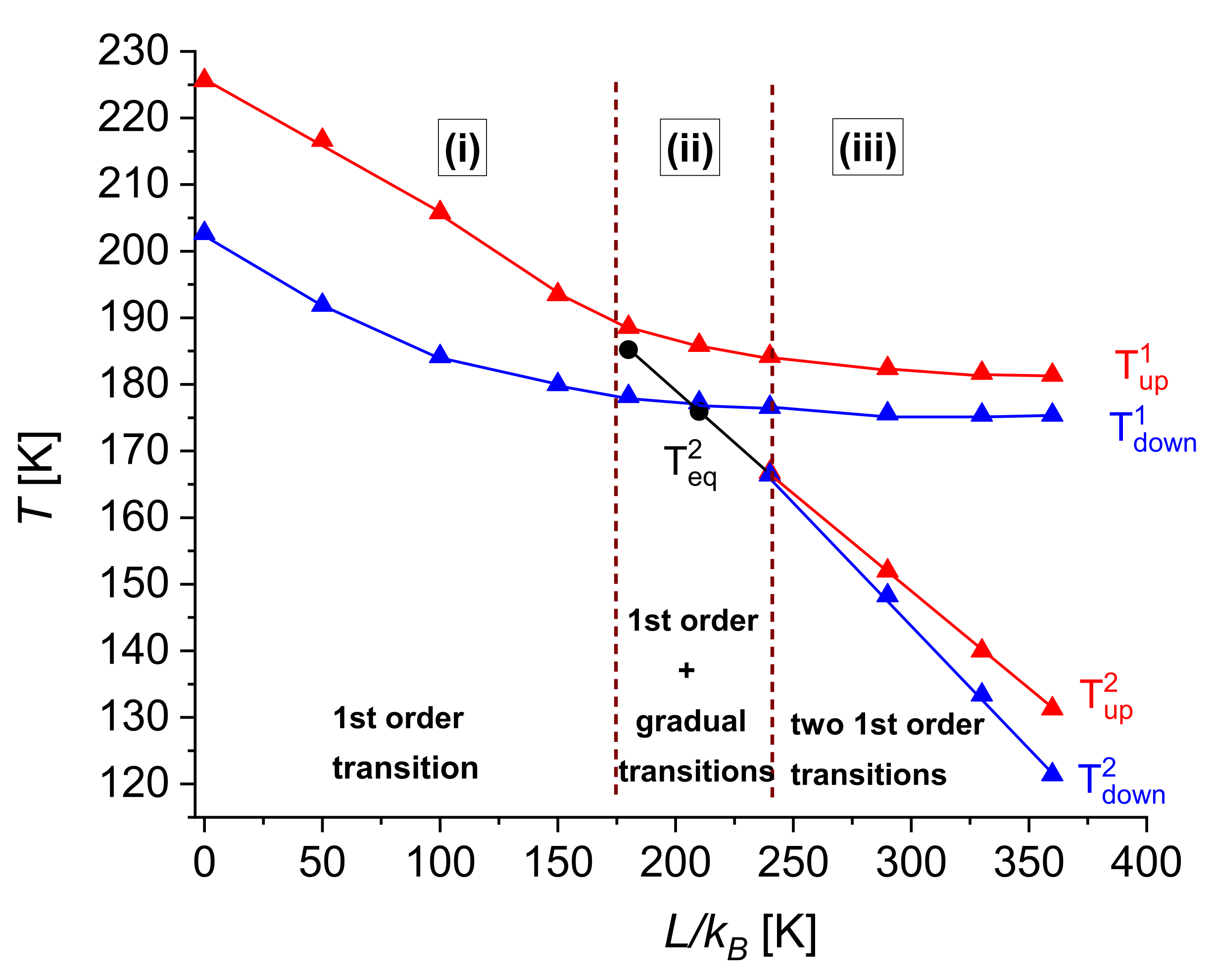

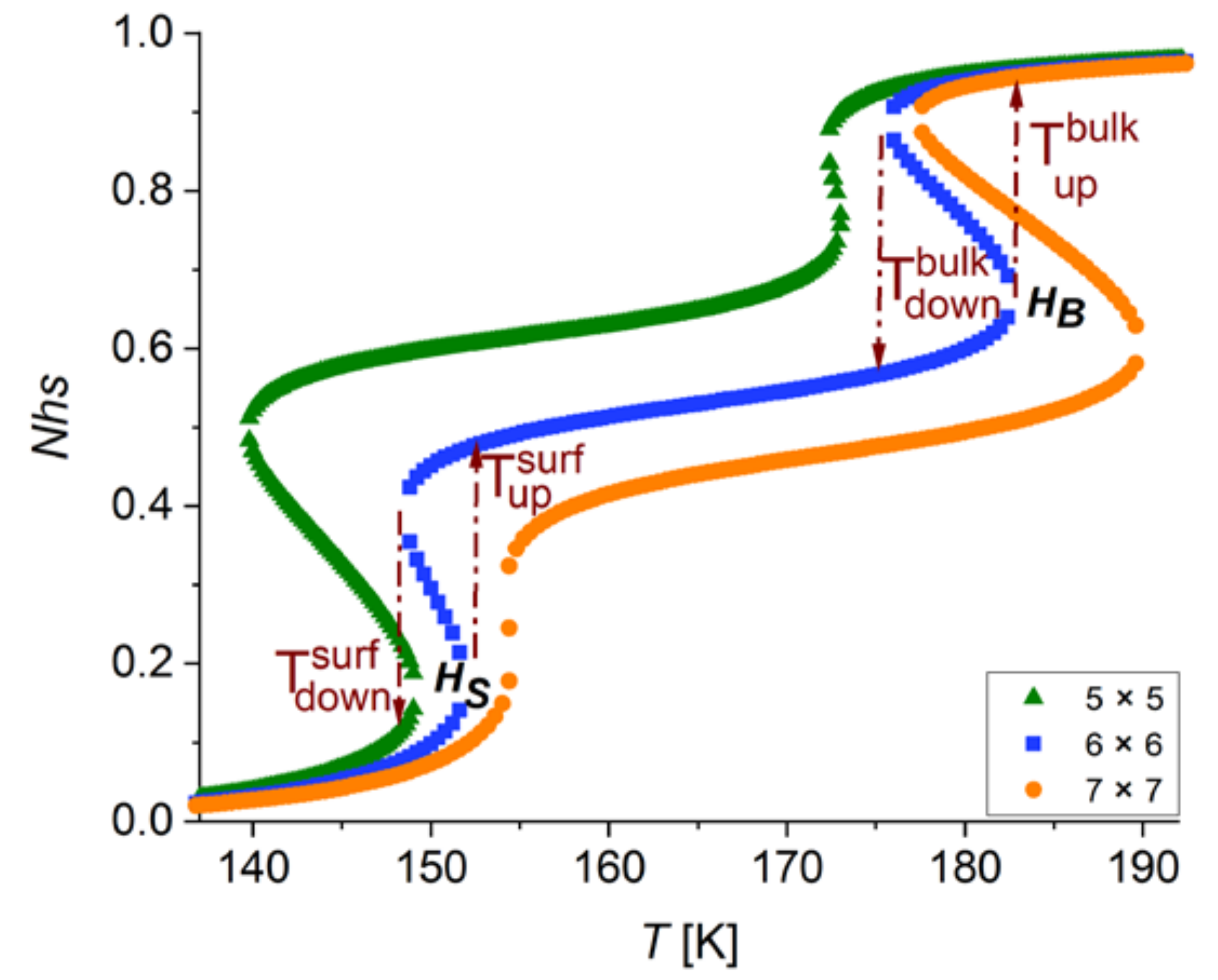
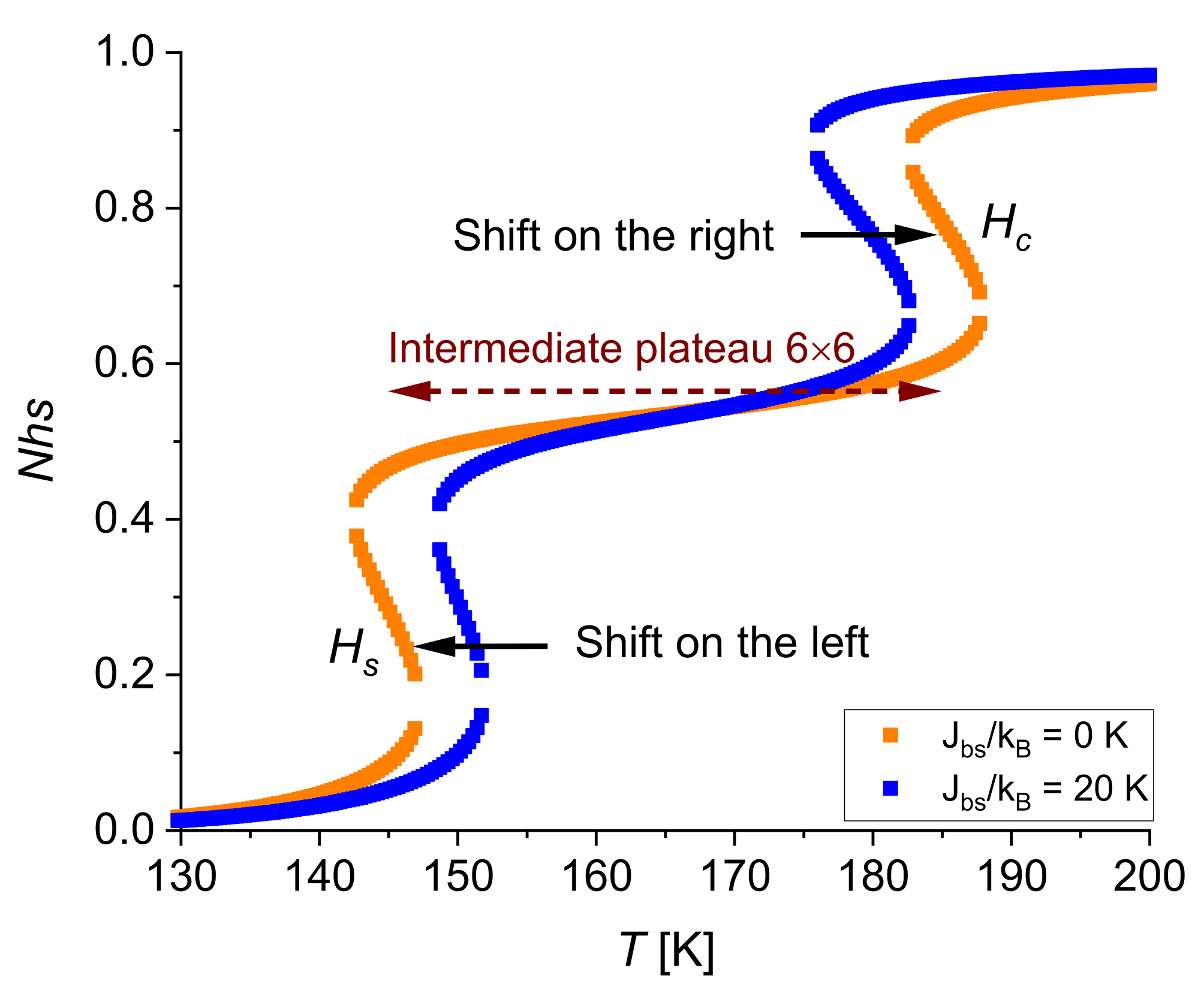
| Size of the System | 5 × 5 | 6 × 6 | 7 × 7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TO.D. (K) | 296 | 308 | 316 |
| (K) | 19 | 22.6 | 26 |
| System’s Size | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 × 5 | 25 | 9 | 16 | 0.64 |
| 6 × 6 | 36 | 16 | 20 | 0.55 |
| 7 × 7 | 49 | 25 | 24 | 0.48 |
| System’s Size | (K) | (K) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 × 5 | 10.0 | 1.0 |
| 6 × 6 | 4.4 | 7.3 |
| 7 × 7 | 0.0 | 12.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cazelles, C.; Ndiaye, M.; Dahoo, P.; Linares, J.; Boukheddaden, K. Surface-Bulk 2D Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles within Ising-like Model Solved by Using Entropic Sampling Technique. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030061
Cazelles C, Ndiaye M, Dahoo P, Linares J, Boukheddaden K. Surface-Bulk 2D Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles within Ising-like Model Solved by Using Entropic Sampling Technique. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030061
Chicago/Turabian StyleCazelles, Catherine, Mamadou Ndiaye, Pierre Dahoo, Jorge Linares, and Kamel Boukheddaden. 2023. "Surface-Bulk 2D Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles within Ising-like Model Solved by Using Entropic Sampling Technique" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030061
APA StyleCazelles, C., Ndiaye, M., Dahoo, P., Linares, J., & Boukheddaden, K. (2023). Surface-Bulk 2D Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles within Ising-like Model Solved by Using Entropic Sampling Technique. Magnetochemistry, 9(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9030061







