Effect of Topology Parameters on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Magnetic PLA 3D-Printed Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Methods
3. Results
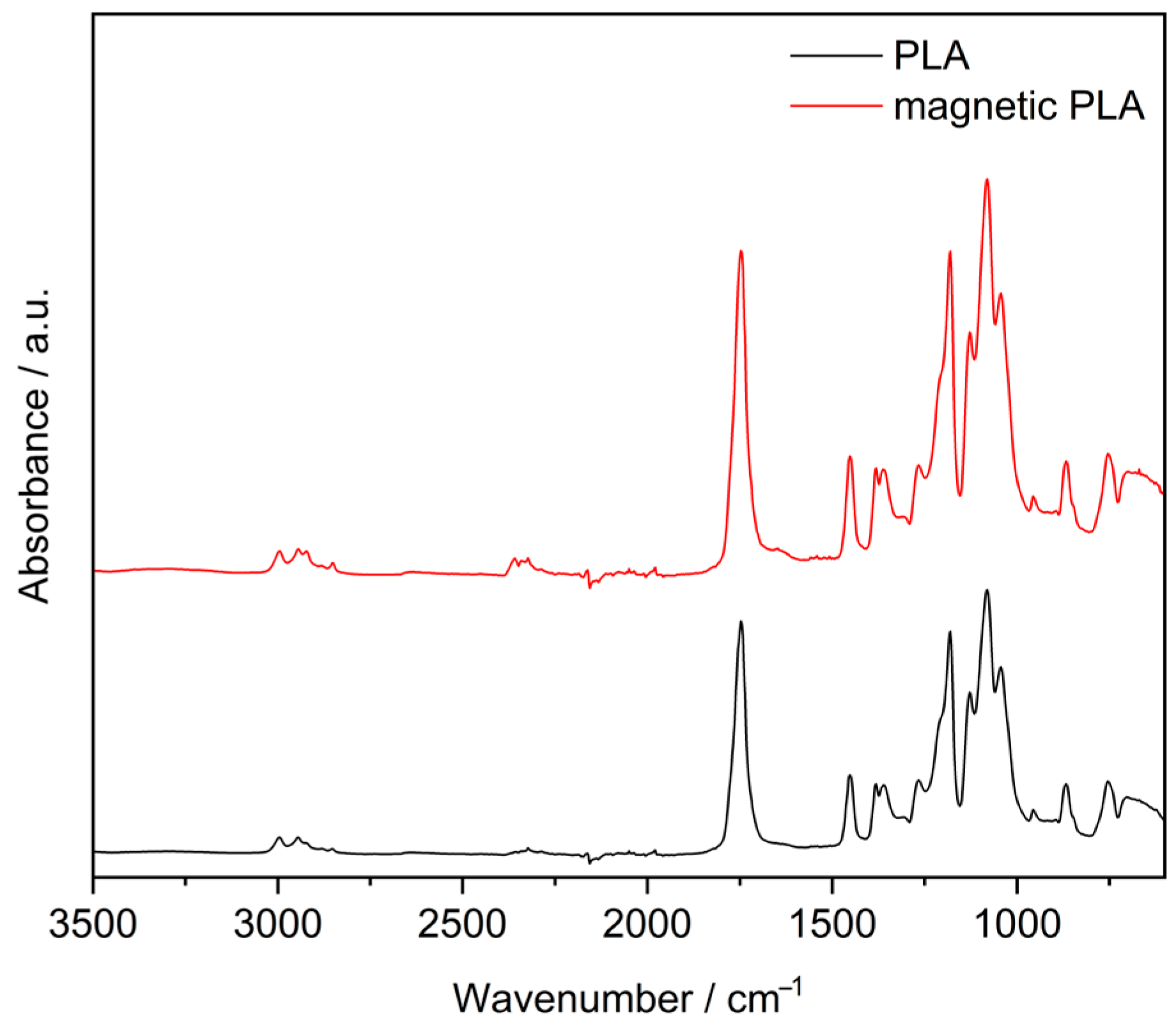
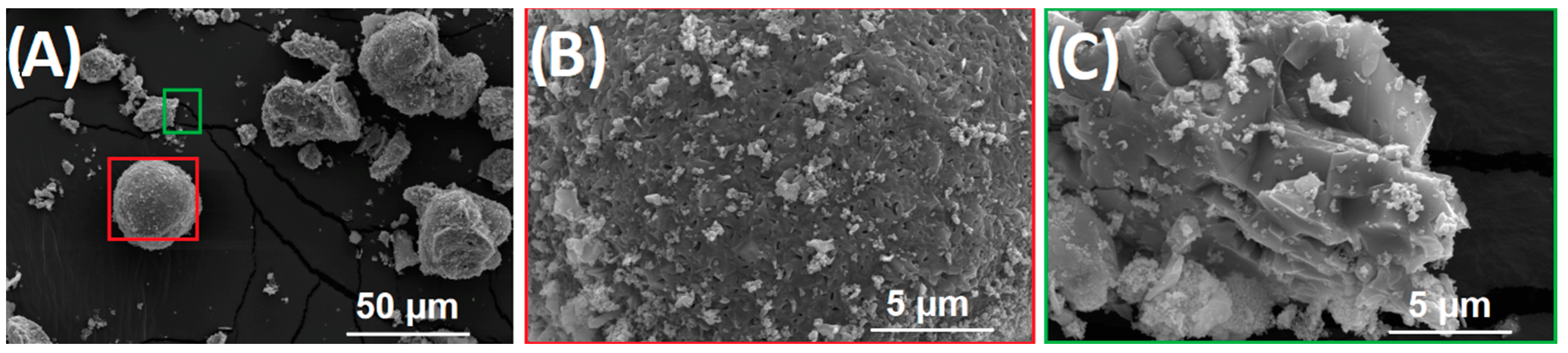
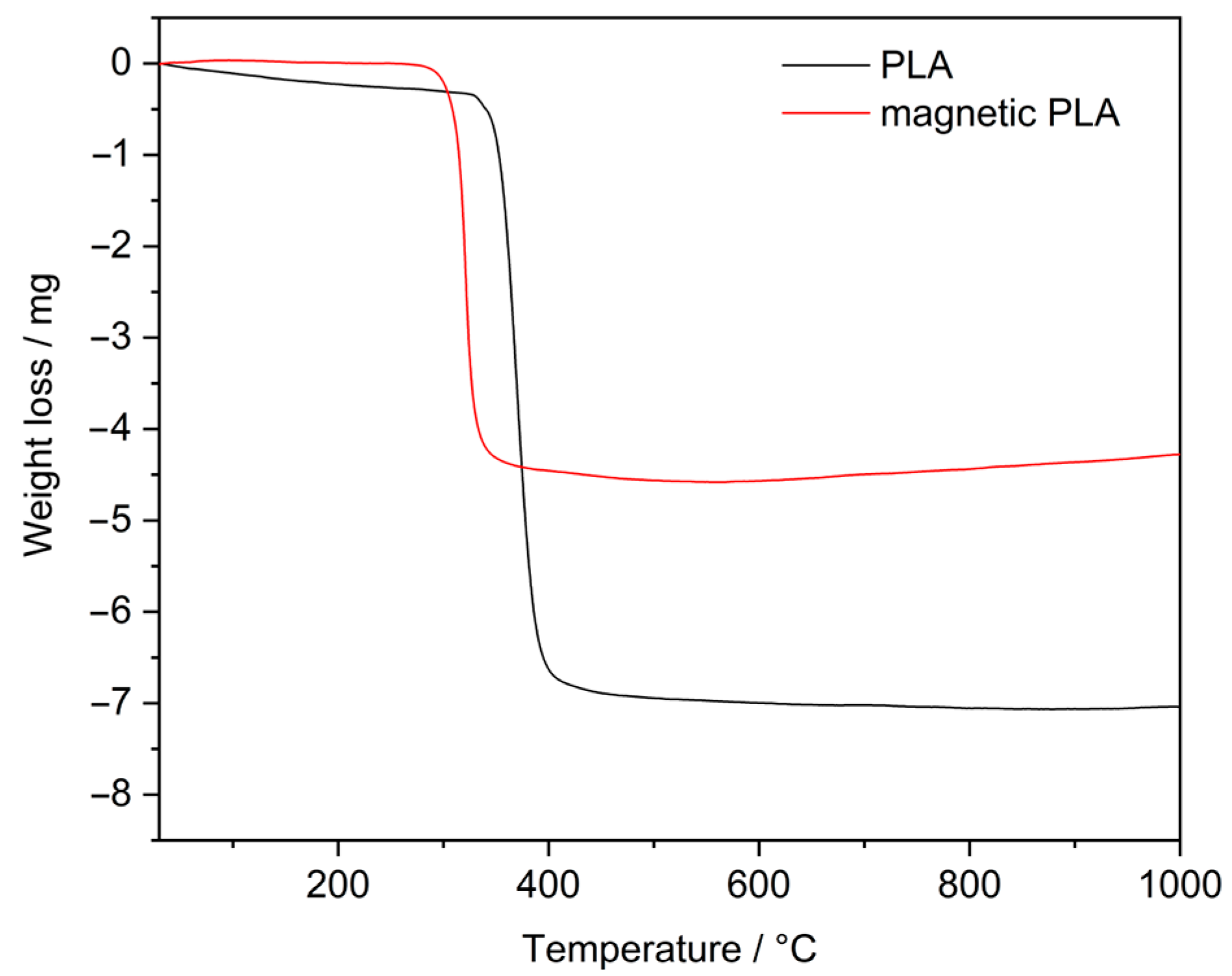
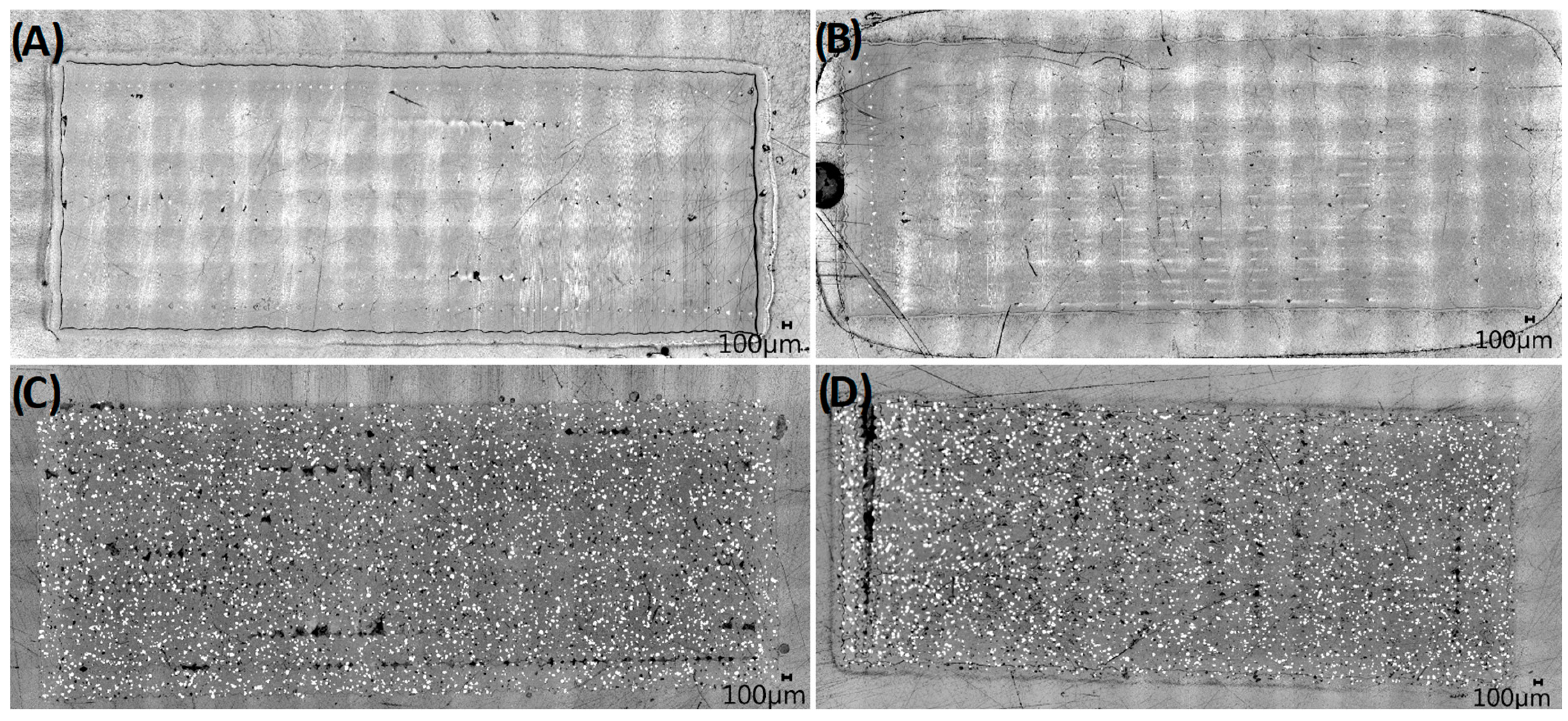
3.1. Characterization of Material
3.2. Magnetic Properties Results
3.3. Mechanical Properties Results
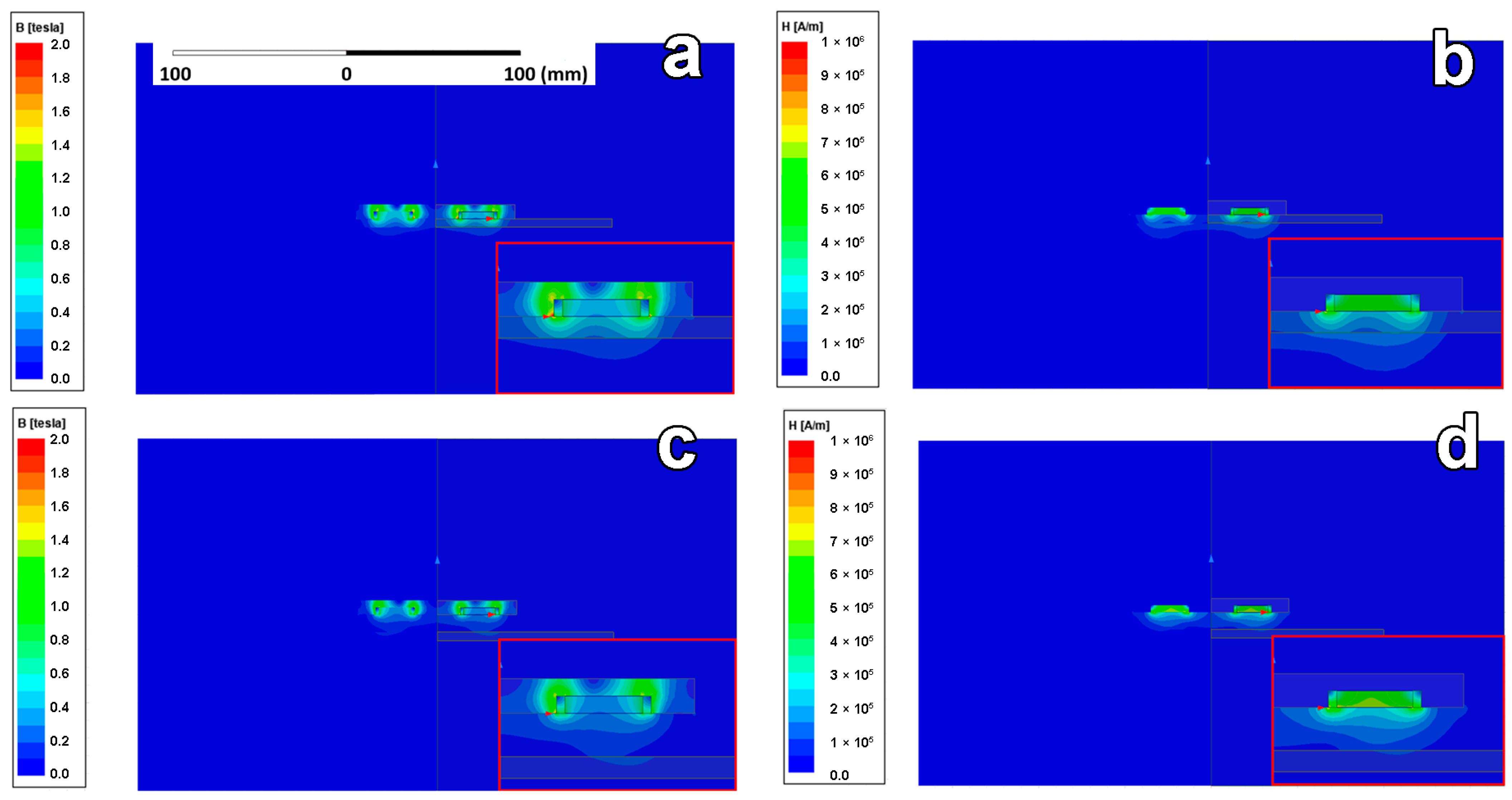
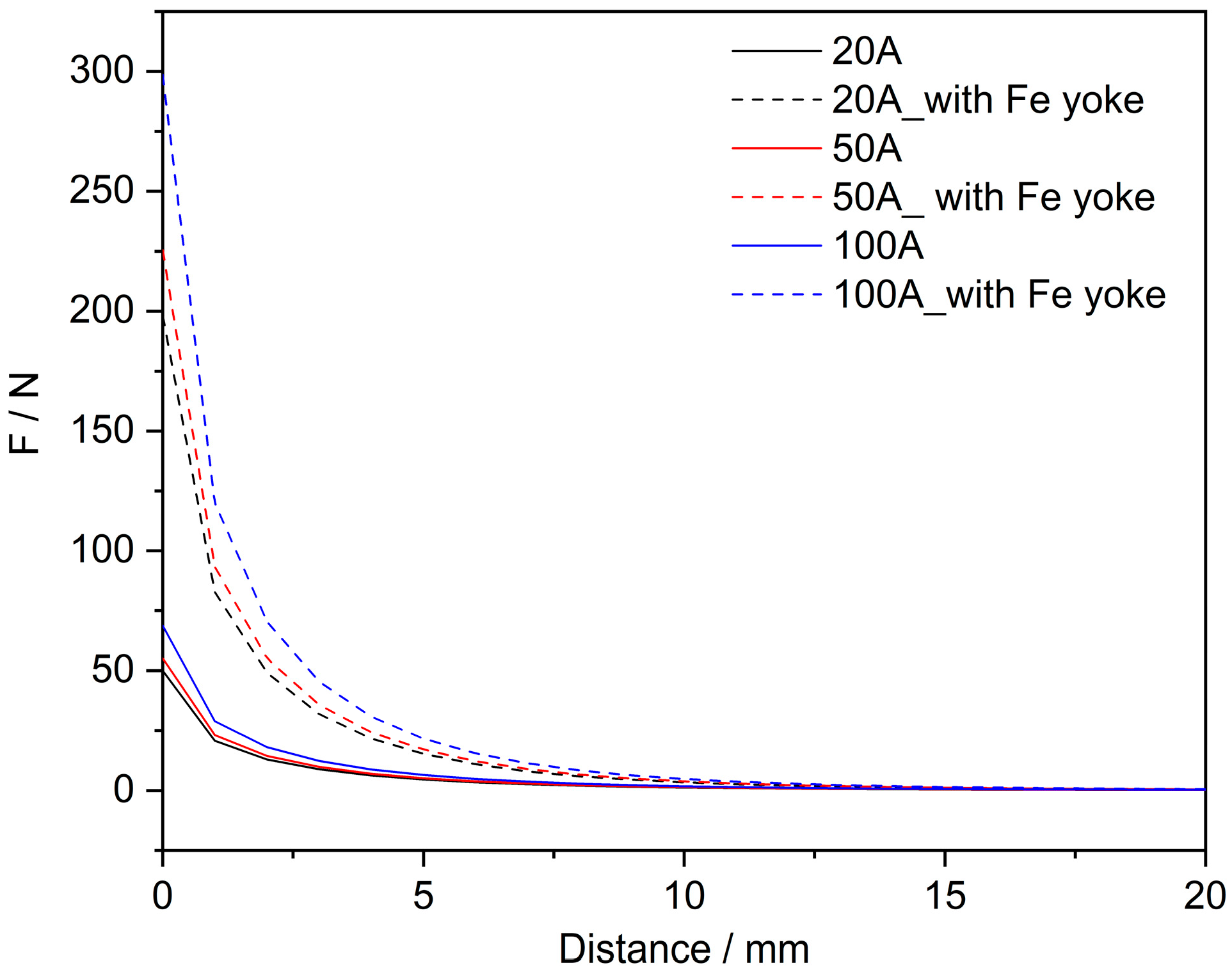
3.4. Magnetic Field Simulation and Calculation of Force Effects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Culmone, C.; Smit, G.; Breedveld, P. Additive manufacturing of medical instruments: A state-of-the-art review. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.; Hickel, R.; Reymus, M. 3D printing in dentistry—State of the art. Oper. Dent. 2020, 45, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, T.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.A.; Planell, J.A.; Navarro, M. 3D printed PLA-based scaffolds: A versatile tool in regenerative medicine. Organogenesis 2013, 9, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böckin, D.; Tillman, A.-M. Environmental assessment of additive manufacturing in the automotive industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C. Streamlining automotive production with additive manufacturing. Quality 2018, 57, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhakeyev, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Shu, W.; Wang, H.; Xuan, J. Additive manufacturing: Unlocking the evolution of energy materials. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambach, M.; Rutzen, M.; Volkmer, D. Properties of 3D-printed fiber-reinforced Portland cement paste. In 3D Concrete Printing Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 73–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lille, M.; Nurmela, A.; Nordlund, E.; Metsä-Kortelainen, S.; Sozer, N. Applicability of protein and fiber-rich food materials in extrusion-based 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B.; Khorasani, M. Materials for additive manufacturing. In Additive Manufacturing Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 379–428. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, L.D.; Williams, L. Additive manufacturing or 3d scanning and printing. In Manufacturing Engineering Handbook; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Shukla, V.R.; Varadarajan, K.M.; Kumar, S. Microarchitected 3D printed polylactic acid (PLA) nanocomposite scaffolds for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureto, J.; Tomasi, J.; King, J.A.; Pearce, J.M. Thermal properties of 3-D printed polylactic acid-metal composites. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 2, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, M.; Han, W.; Li, P. Waste office paper filled polylactic acid composite filaments for 3D printing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 221, 108998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, I.; Vale, D.; Machado, M.; Lino, J. Additive manufacturing of polyethylene terephthalate glycol/carbon fiber composites: An experimental study from filament to printed parts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2019, 233, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolzyk, G.; Jung, S. Tensile and fatigue analysis of 3D-printed polyethylene terephthalate glycol. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2019, 19, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Tsongas, K.; Tzetzis, D.; Antoniadis, A. Mechanical and dynamic behavior of fused filament fabrication 3D printed polyethylene terephthalate glycol reinforced with carbon fibers. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Maniadi, A.; Koudoumas, E.; Liebscher, M.; Tzounis, L. Mechanical properties of 3D-printed acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene TiO2 and ATO nanocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farcas, M.T.; Stefaniak, A.B.; Knepp, A.K.; Bowers, L.; Mandler, W.K.; Kashon, M.; Jackson, S.R.; Stueckle, T.A.; Sisler, J.D.; Friend, S.A. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate (PC) filaments three-dimensional (3-D) printer emissions-induced cell toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 317, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Maniadi, A.; Koudoumas, E.; Vairis, A.; Kechagias, J. Sustainable additive manufacturing: Mechanical response of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene over multiple recycling processes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León, A.S.; Domínguez-Calvo, A.; Molina, S.I. Materials with enhanced adhesive properties based on acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS)/thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) blends for fused filament fabrication (FFF). Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.J.; Woern, A.L.; Tanikella, N.G.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical properties and applications of recycled polycarbonate particle material extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Materials 2019, 12, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Yan, Y.; Agarwal, O.; Seppala, J.E.; Hemker, K.J.; Kang, S.H. Processing-structure-property relationships of bisphenol-A-polycarbonate samples prepared by fused filament fabrication. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, A.; Bao, X.; Ni, T.; Ling, J. A review on geopolymer in potential coating application: Materials, preparation and basic properties. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Tzounis, L.; Maniadi, A.; Velidakis, E.; Mountakis, N.; Papageorgiou, D.; Liebscher, M.; Mechtcherine, V. Sustainable additive manufacturing: Mechanical response of polypropylene over multiple recycling processes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhar, N.; Gudadhe, A.; Kumar, A.; Andrade, P.; Kumaraswamy, G. 3D printing of semicrystalline polypropylene: Towards eliminating warpage of printed objects. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafel, I.; Aguirresarobe, R.H.; Peñas, M.I.; Santamaria, A.; Tierno, M.; Conde, J.I.; Pascual, B. Searching for rheological conditions for FFF 3D printing with PVC based flexible compounds. Materials 2020, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Lambeth, R.H. Recycled polyethylene terephthalate as a new FFF feedstock material. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrete, I.A.; Quiñonez, P.A.; Bermudez, D.; Roberson, D.A. Incorporating textile-derived cellulose fibers for the strengthening of recycled polyethylene terephthalate for 3D printing feedstock materials. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, E.; Shen, J.; Watling, J. Direct 3D printing of polymers onto textiles: Experimental studies and applications. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollig, L.M.; Hilpisch, P.J.; Mowry, G.S.; Nelson-Cheeseman, B.B. 3D printed magnetic polymer composite transformers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 442, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, M.V.; Ryan, P.; Calascione, T.; Fischer, N.; Morgenstern, A.; Stenger, N.; Nelson-Cheeseman, B.B. Manipulating magnetic anisotropy in fused filament fabricated parts via macroscopic shape, mesoscopic infill orientation, and infill percentage. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Abert, C.; Bruckner, F.; Groenefeld, M.; Muthsam, O.; Schuschnigg, S.; Sirak, K.; Thanhoffer, R.; Teliban, I.; Vogler, C. 3D print of polymer bonded rare-earth magnets, and 3D magnetic field scanning with an end-user 3D printer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 162401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.L. Hindered amine light stabilizers: Recent developments. Plast. Addit. 1998, 1, 360–371. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, G. Plastics Additives: An AZ Reference; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 1, ISBN 9401158622. [Google Scholar]
- Gangopadhyay, S.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Dale, B.; Sorensen, C.M.; Klabunde, K.J.; Papaefthymiou, V.; Kostikas, A. Magnetic properties of ultrafine iron particles. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bødker, F.; Hansen, M.F.; Koch, C.B.; Lefmann, K.; Mørup, S. Magnetic properties of hematite nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanda, L.C.; Jafelicci, M., Jr.; Goya, G.F. Magnetic properties of spindle-type iron fine particles obtained from hematite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 226, 1933–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, M.; Čitaković, N.; Panjan, M.; Stojanović, Z.; Marković, D.; Spasojević, V. Synthesis, morphology, microstructure and magnetic properties of hematite submicron particles. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 7639–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.G.; Williams, W.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; McVitie, S.; Chapman, J.N. Magnetic properties of magnetite arrays produced by the method of electron beam lithography. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 23, 2847–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Noqta, O.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Katsikini, M.; Pinakidou, F.; Paloura, E.C. Influence of capping agents on fraction of Fe atoms occupying octahedral site and magnetic property of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by one-pot co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 938, 168558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridis, A.; Okkalidis, N.; Trygoniaris, D.; Kazeli, K.; Angelakeris, M. Composite magnetic 3D-printing filament fabrication protocol opens new perspectives in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 285002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazin, I.; Rossegger, E.; Roppolo, I.; Sangermano, M.; Granitzer, P.; Rumpf, K.; Schlögl, S. Digital light processing 3D printing of dynamic magneto-responsive thiol-acrylate composites. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17536–17544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, J.M.; Thatcher, H.G.; Calascione, T.M.; Lu, J.; Fischer, N.A.; Ziemann, S.J.; Höft, T.; Nelson-Cheeseman, B.B. Effects of infill orientation and percentage on the magnetoactive properties of 3D printed magnetic elastomer structures. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 2023, 4, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubutin, I.S.; Baskakov, A.O.; Starchikov, S.S.; Shih, K.-Y.; Lin, C.-R.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Yang, S.-S.; Han, Z.-Y.; Ogarkova, Y.L.; Nikolaichik, V.I. Synthesis and characterization of graphene modified by iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patkowski, J.; Myśliwiec, D.; Chibowski, S. Adsorption of polyethyleneimine (PEI) on hematite. Influence of magnetic field on adsorption of PEI on hematite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 144, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvallo, C.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Dunlop, D.J. First-order reversal curve (FORC) diagrams of magnetic mixtures: Micromagnetic models and measurements. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 2006, 154, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 664. [Google Scholar]
- Kono, M. Geomagnetism. Treatise on Geophysics, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Marcial, J.; McCloy, J. Crystallization of iron-containing sodium aluminosilicate glasses in the NaAlSiO4-NaFeSiO4 join. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2017, 122, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caizer, C. Nanoparticle size effect on some magnetic properties. In Handbook of Nanoparticles; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 475–519. [Google Scholar]
- Kechagias, J.; Chaidas, D.; Vidakis, N.; Salonitis, K.; Vaxevanidis, N.M. Key parameters controlling surface quality and dimensional accuracy: A critical review of FFF process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 963–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopasta Technical Data Sheet Rev. 1; PLA, Magnetic Iron. Available online: https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0717/9095/files/TDS__Iron_PLA_1.0.1.pdf?1771 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Innofil Technical Data Sheet; Innofil3D PLA. Available online: https://asset.conrad.com/media10/add/160267/c1/-/en/001417248DS01/list-technickych-udaju-1417248-basf-ultrafuse-pla-0001a075-pla-natural-vlakno-pro-3d-tiskarny-pla-plast-175-mm-750-g-prirodni-1-ks.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Tumanski, S. Handbook of Magnetic Measurements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 1439829527. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorillo, F. Characterization and Measurement of Magnetic Materials; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; ISBN 0080528929. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D. Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Hilzinger, R.; Rodewald, W. Magnetic Materials; Vacuumschmeltze GmbH Co KG: Hanau, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, K.M. Fundamentals and Applications of Magnetic Materials; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; ISBN 0199570442. [Google Scholar]
- ČSN EN ISO 3451-1:2019; Plasty—Stanovení Popela—Část 1: Obecné Metody. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.technicke-normy-csn.cz/csn-en-iso-3451-1-640219-211726.html (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Marek, M. Numerical computation of magnetic field and inductivity of power reactor with respect of real magnetic properties of iron core. In Scientific Computing in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-M. The Finite Element Method in Electromagnetics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 1118842022. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, J.P.A.; Sadowski, N. Electromagnetic Modeling by Finite Element Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 0203911172. [Google Scholar]
- ČSN EN ISO 527-1:2019; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/75824.html (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- ČSN EN ISO 178:2019; Plastics—Determination of Bending Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/70513.html (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- ČSN EN ISO 604:2002; Plastics—Determination of Compressive Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/31261.html (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Edith, D.; Six, J.-L. Surface characteristics of PLA and PLGA films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2758–2764. [Google Scholar]
- Stoia, M.; Istratie, R.; Păcurariu, C. Investigation of magnetite nanoparticles stability in air by thermal analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.S.; Hayman, D. An overview of mechanical properties and material modeling of polylactide (PLA) for medical applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerk, M.; Gonzalez-Gutierrez, J.; Sapkota, J.; Schuschnigg, S.; Holzer, C. Effect of the printing bed temperature on the adhesion of parts produced by fused filament fabrication. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2018, 47, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steingroever, E.; Ross, G. Magnetic Measuring Techniques; Magnet-Physic: Köln, Germany, 1997; Volume 1, p. 997. [Google Scholar]
- Zárybnická, L.; Marek, M.; Ševčík, R.; Stolín, R.; Pokorný, J.; Šál, J. Effect of Infill Density of the Printed PET-G Structures Containing Iron Oxides on Magnetic Properties. Magnetochemistry 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, B. 3D magnetic printing of bio-inspired composites with tunable mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14274–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, B.; Behravesh, A.H. Effect of filling pattern on the tensile and flexural mechanical properties of FDM 3D printed products. Exp. Mech. 2019, 59, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.; Thakur, D.G.; Chandel, S. An insight into the effect of printing orientation on tensile strength of multi-infill pattern 3D printed specimen: Experimental study. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 7391–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Osgouei, M.; Li, Y.; Vahid, A.; Ataee, A.; Wen, C. High strength porous PLA gyroid scaffolds manufactured via fused deposition modeling for tissue-engineering applications. Smart Mater. Med. 2021, 2, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, J.R. Magnetic Actuators and Sensors; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 0471777706. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, A.M. Sensors and Actuators in Mechatronics: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 1420008315. [Google Scholar]


| Material/Filament | Magnetic/Clear PLA | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer thickness/mm | 0.15 | ||
| Type of infill | gyroid | solid | |
| Infill density/% | 20 | 50 | 100 |
| Tensile test, print orientation xy | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 42 | 58 | 51 |
| Tensile test, print orientation z | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 51 | 74 | 88 |
| Bending test, print orientation xy | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 16 | 20 | 20 |
| Bending test, print orientation z | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 20 | 23 | 27 |
| Compressive test, print orientation xy | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 83 | 181 | 132 |
| Magnetic properties test, print orientation xy | |||
| Print time for 1 sample/min | 84 | 144 | 125 |
| Sample | Inductance/H | Relative Permeability/- |
|---|---|---|
| 20R | 1.600 × 10−5 ± 7.395 × 10−8 | 1.083 ± 0.005 |
| 50R | 1.650 × 10−5 ± 9.899 × 10−8 | 1.097 ± 0.007 |
| 100R | 1.640 × 10−5 ± 1.118 × 10−7 | 1.107 ± 0.008 |
| 20A | 2.050 × 10−5 ± 7.395 × 10−8 | 1.510 ± 0.005 |
| 50A | 2.330 × 10−5 ± 1.515 × 10−7 | 1.583 ± 0.010 |
| 100A | 2.510 × 10−5 ± 9.354 × 10−8 | 1.780 ± 0.006 |
| Sample | Modulus of Elasticity/MPa | Tensile Strength/MPa | Tensile Strain/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20R_xy | 1960 ± 4 | 30 ± 0.1 | 4.1 ± 0.5 |
| 20R_z | 2014 ± 22 | 29 ± 0.9 | 3.3 ± 0.2 |
| 50R_xy | 2268 ± 13 | 34 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.3 |
| 50R_z | 2428 ± 46 | 37 ± 0.5 | 3.9 ± 0.5 |
| 100R_xy | 3306 ± 93 | 51 ± 1.2 | 3.1 ± 0.2 |
| 100R_z | 3409 ± 17 | 50 ± 0.4 | 2.8 ± 0.2 |
| 20A_xy | 2187 ± 39 | 19 ± 0.8 | 2.5 ± 0.1 |
| 20A_z | 2302 ± 17 | 21 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| 50A_xy | 2271 ± 74 | 21 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 0.2 |
| 50A_z | 2834 ± 25 | 25 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 0.3 |
| 100A_xy | 3582 ± 56 | 32 ± 1.0 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| 100A_z | 3922 ± 61 | 33 ± 0.8 | 2.4 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | Modulus of Elasticity/MPa | Bending Strength/MPa | Elongation/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20R_xy | 2605 ± 43 | 71 ± 4.7 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| 20R_z | 2616 ± 27 | 68 ± 0.6 | 2.5 ± 0.1 |
| 50R_xy | 2872 ± 36 | 76 ± 4.2 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| 50R_z | 2994 ± 31 | 82 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.4 |
| 100R_xy | 3198 ± 75 | 95 ± 8.9 | 3.4 ± 0.5 |
| 100R_z | 3221 ± 110 | 89 ± 7.5 | 2.9 ± 0.1 |
| 20A_xy | 2712 ± 95 | 45 ± 1.9 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| 20A_z | 2932 ± 121 | 54 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
| 50A_xy | 2868 ± 119 | 49 ± 2.7 | 1.9 ± 0.1 |
| 50A_z | 3420 ± 40 | 64 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 0.1 |
| 100A_xy | 3378 ± 107 | 65 ± 2.5 | 2.5 ± 0.1 |
| 100A_z | 3811 ± 77 | 75 ± 2.1 | 2.3 ± 0.1 |
| Sample | Modulus of Elasticity/MPa | Compressive Strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|
| 20R_xy | 462 ± 22 | 12.0 ± 0.4 |
| 50R_xy | 800 ± 6 | 22.2 ± 0.1 |
| 100R_xy | 1767 ± 30 | 68.7 ± 1.6 |
| 20A_xy | 440 ± 9 | 8.9 ± 0.2 |
| 50A_xy | 757 ± 7 | 17.3 ± 0.1 |
| 100A_xy | 1677 ± 15 | 51.3 ± 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zárybnická, L.; Pagáč, M.; Ševčík, R.; Pokorný, J.; Marek, M. Effect of Topology Parameters on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Magnetic PLA 3D-Printed Structures. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9120232
Zárybnická L, Pagáč M, Ševčík R, Pokorný J, Marek M. Effect of Topology Parameters on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Magnetic PLA 3D-Printed Structures. Magnetochemistry. 2023; 9(12):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9120232
Chicago/Turabian StyleZárybnická, Lucie, Marek Pagáč, Radek Ševčík, Jaroslav Pokorný, and Martin Marek. 2023. "Effect of Topology Parameters on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Magnetic PLA 3D-Printed Structures" Magnetochemistry 9, no. 12: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9120232
APA StyleZárybnická, L., Pagáč, M., Ševčík, R., Pokorný, J., & Marek, M. (2023). Effect of Topology Parameters on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Magnetic PLA 3D-Printed Structures. Magnetochemistry, 9(12), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9120232








