Magnetic Field-Induced Deformation of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Measurement Methods
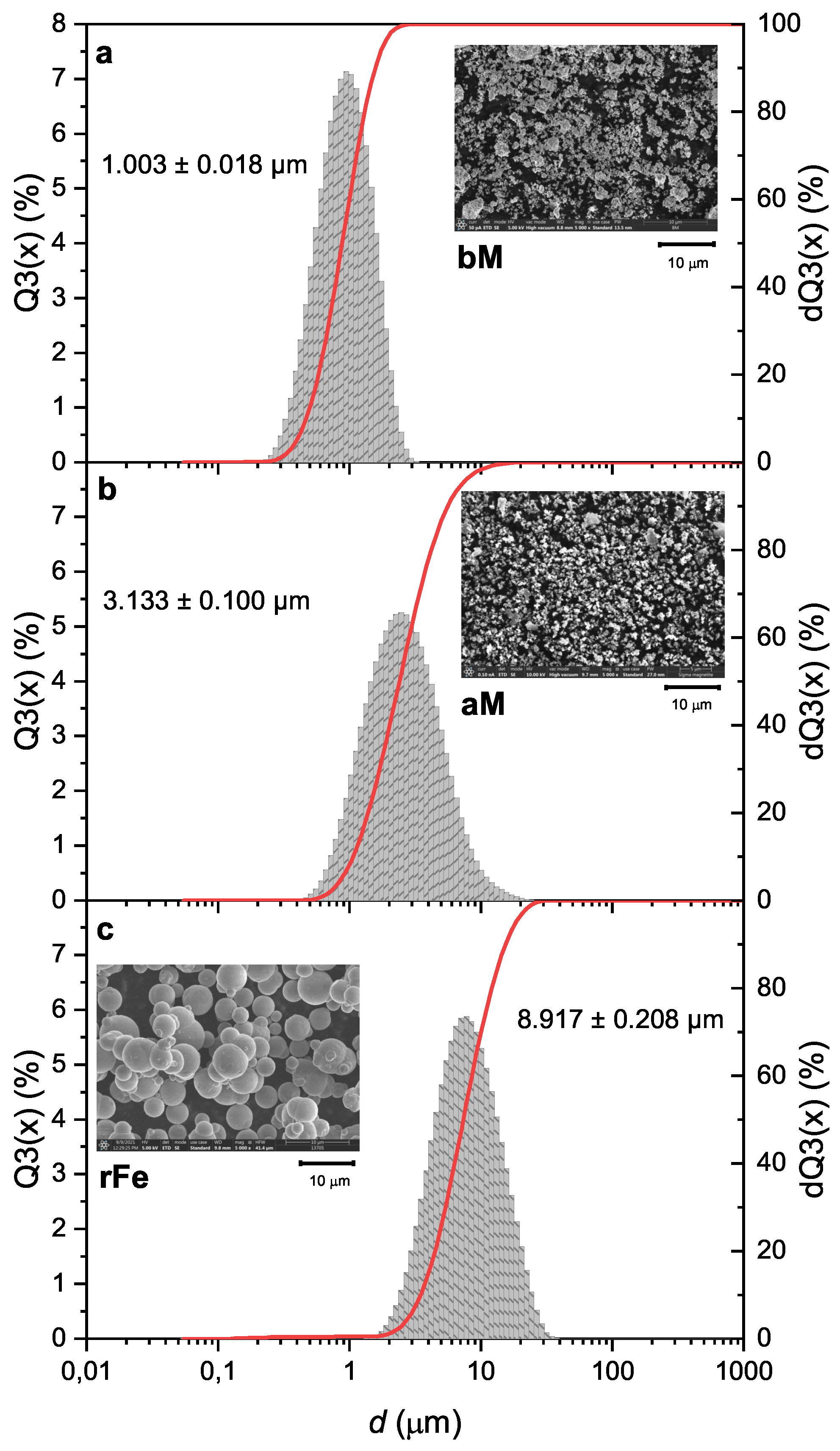
2.1.1. Filler Characterization
2.1.2. Mechanical Testing
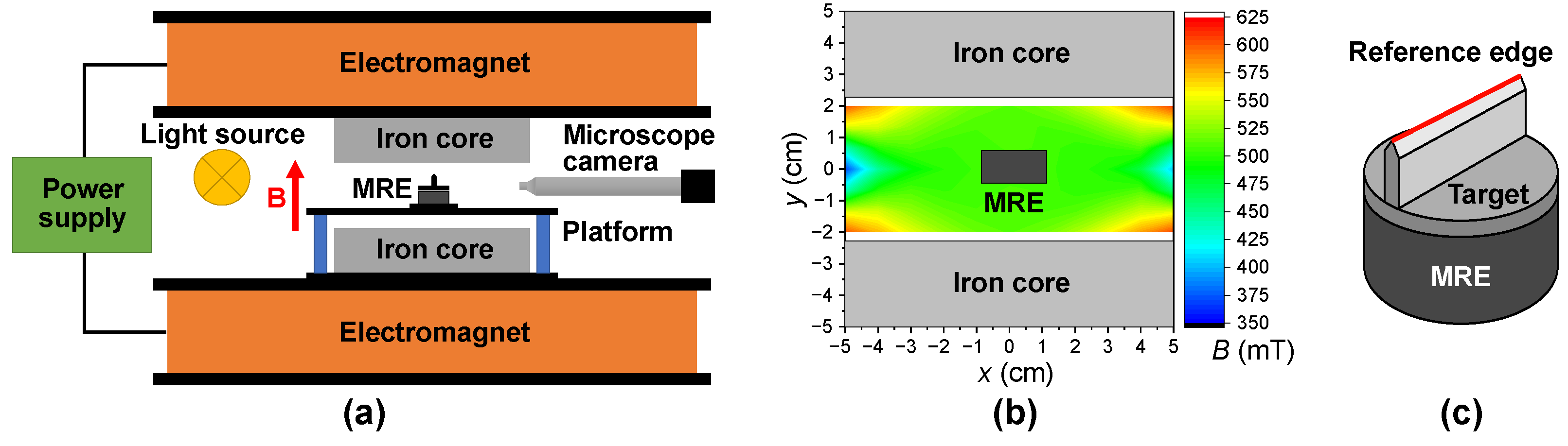
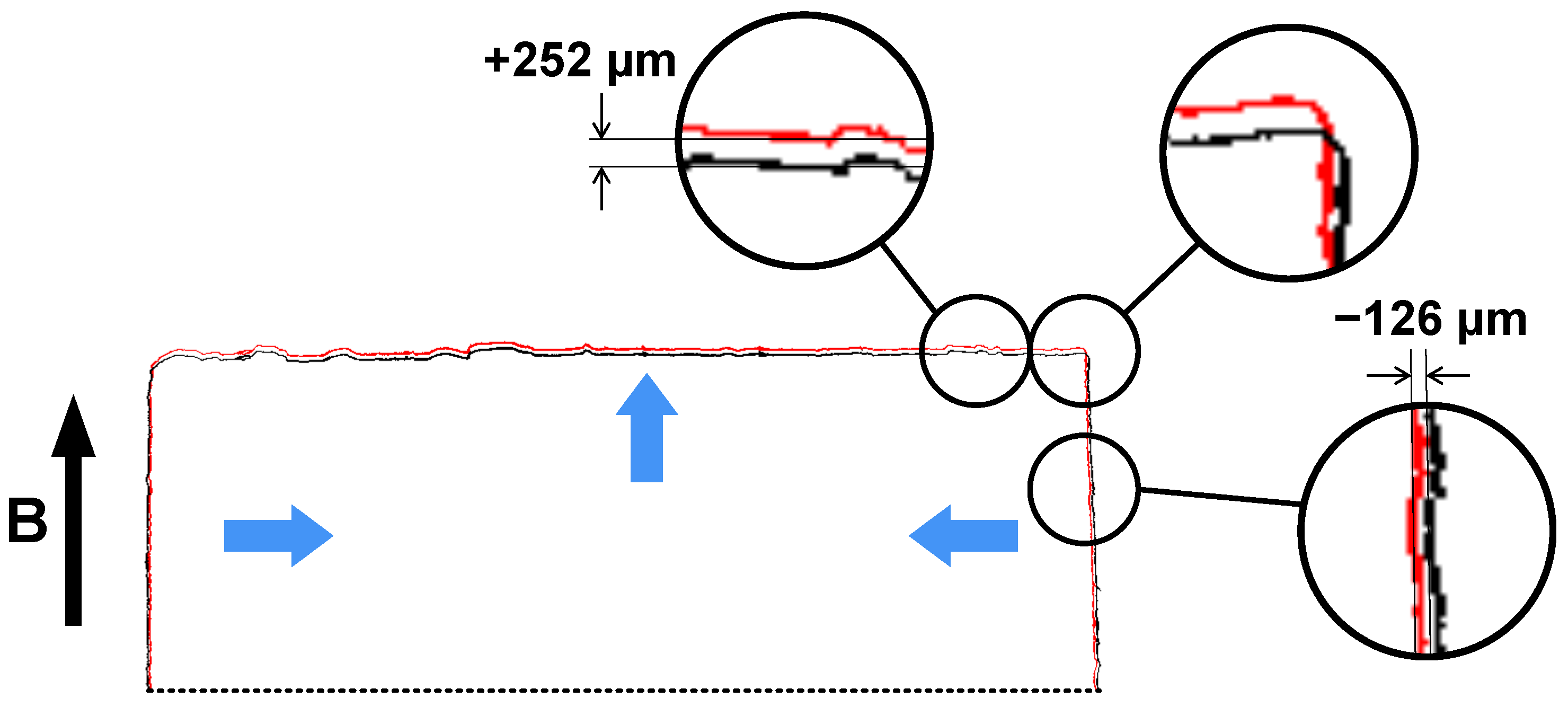
2.1.3. Deformation under Magnetic Field
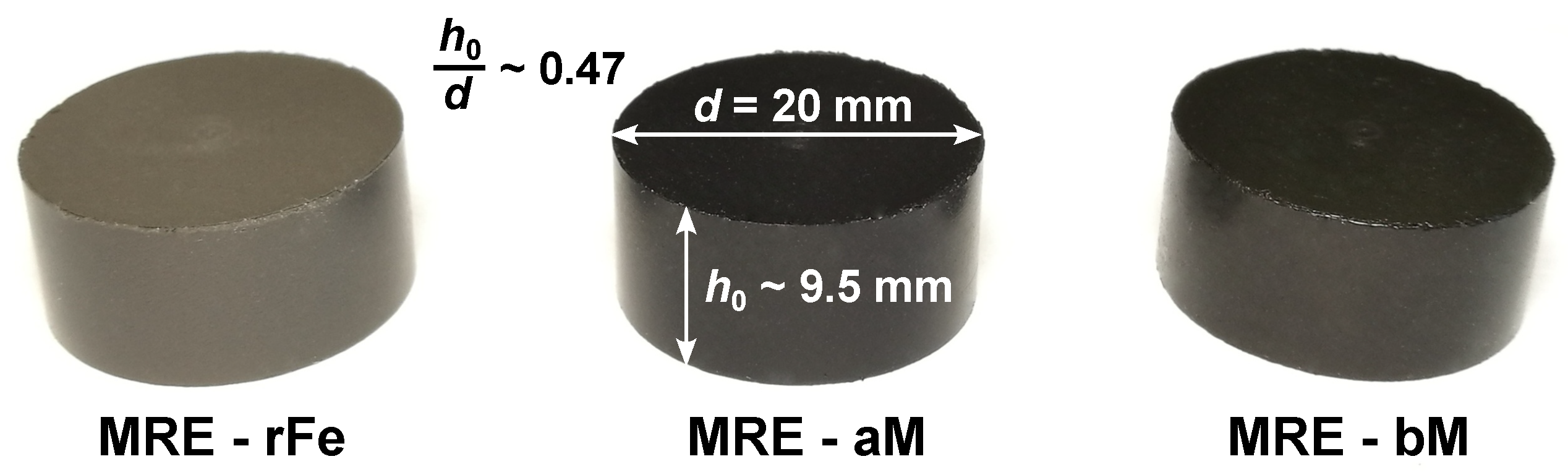
2.2. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
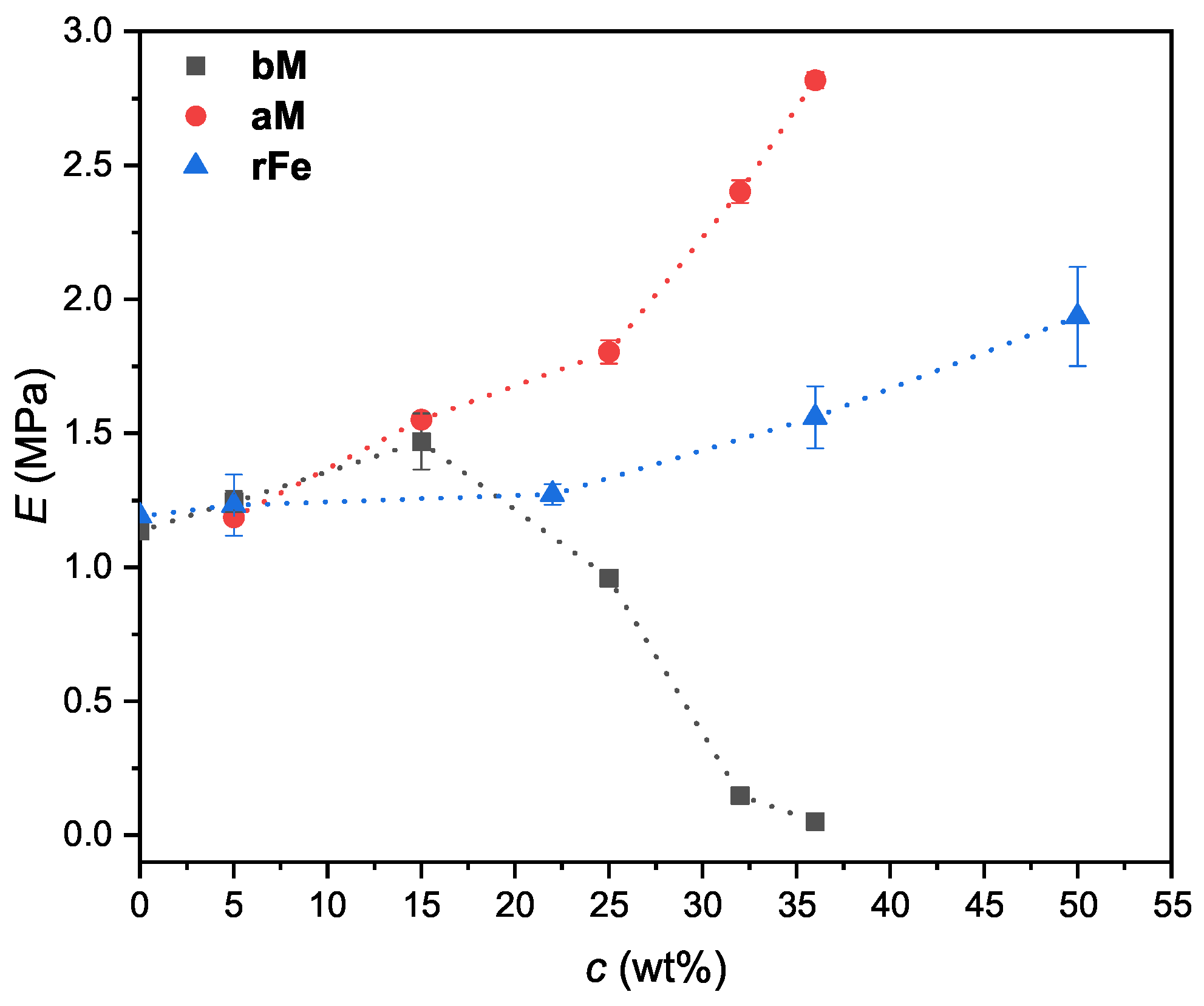
3.1. Elastic Modulus
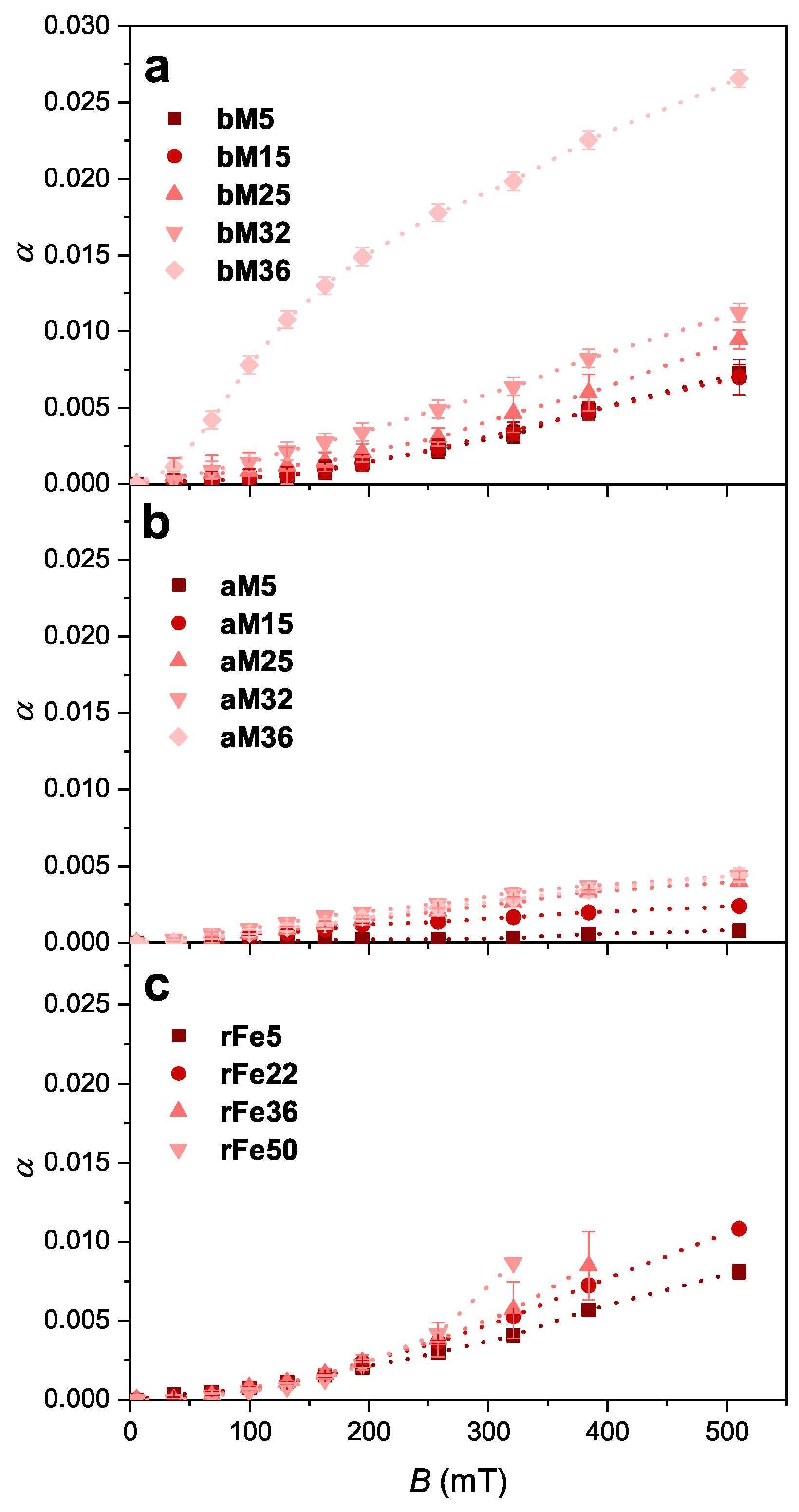
3.2. Field-Induced Deformation
Effect of Magnetic Field
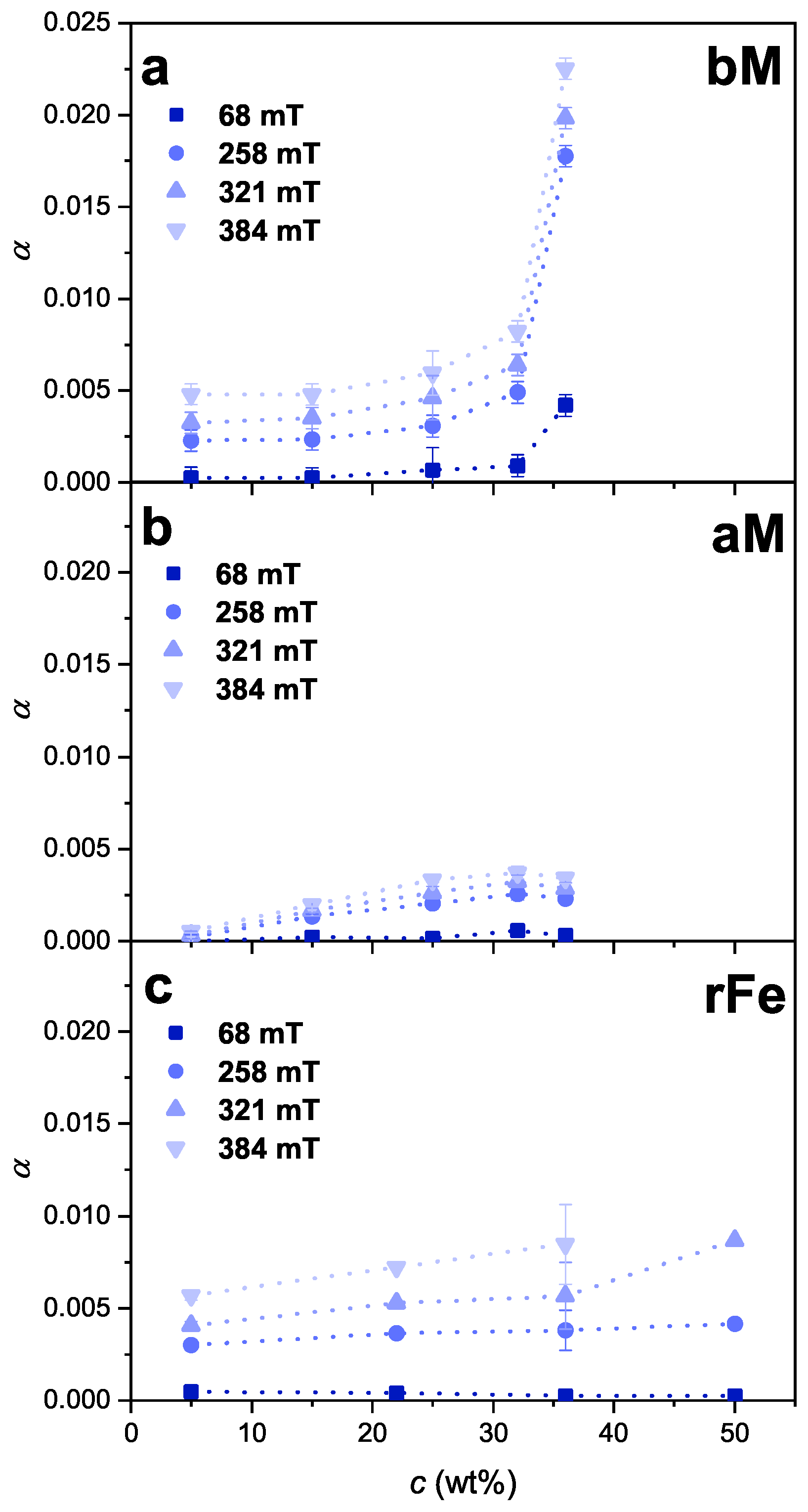
Effect of the Particle Concentration
4. Conclusions
- In all our cases, the sign of the deformation was positive; thus dilatation was observed in the direction of the field, which is consistent with the aspect ratio of the samples. The estimated change in volume of the MRE discs remained under 0.1%; thus, the overall volume was conserved during the field-induced deformation.
- With increasing field strength, the dilatation of the MREs became larger in cases of all three filler materials, but the exact trend depended on the type and concentration of the filler.
- The aM-filled MREs displayed a near linear concentration dependence, while the dilatation of the bM MREs at high particle concentration was considerably enhanced, which was attributed to the incomplete polymerization, and thus to the reduced modulus of the matrix. This inhibitor effect of the bM particles could be caused by the residual materials detected by elemental analysis.
- By comparing the aM- and rFe-filled MREs—in which no inhibitor effect was observed, and thus the elastic matrix had the same modulus—the dilatation of the samples was increasing near linearly with the concentration of the particles.
- The resulting Young’s modulus of the MREs was increasing with the particle loading. The exception was the bM magnetite filler where the abovementioned inhibited cross-linking of the matrix was responsible for the observed softening of the MREs at high particle concentration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorokin, V.V.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Kramarenko, E.Y. Hysteresis of the Viscoelastic Properties and the Normal Force in Magnetically and Mechanically Soft Magnetoactive Elastomers: Effects of Filler Composition, Strain Amplitude and Magnetic Field. Polymer 2015, 76, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winger, J.; Schümann, M.; Kupka, A.; Odenbach, S. Influence of the Particle Size on the Magnetorheological Effect of Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 481, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, H.; Röder, R. Magnetorheological Elastomers with High Variability of Their Mechanical Properties. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Borin, D.; Odenbach, S. Magnetorheological Effect of Magneto-Active Elastomers Containing Large Particles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, P.Q. Fabrication and Characterization of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, J.M.; Clark, S.M.; Schlotter, W.F.; Nichols, M.E. Magnetostrictive phenomena in magnetorheological elastomers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2002, 16, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hu, W.; Ze, Q.; Sitti, M.; Zhao, R. Multifunctional Magnetic Soft Composites: A Review. Multifunct. Mater. 2020, 3, 042003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanala, S.V.; Triantafyllidis, N. On Finitely Strained Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 2869–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Read, D.; Gulley, G. Magnetostriction of Field-Structured Magnetoelastomers. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 051507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaneyko, D.; Toshchevikov, V.; Saphiannikova, M.; Heinrich, G. Effects of Particle Distribution on Mechanical Properties of Magneto-Sensitive Elastomers in a Homogeneous Magnetic Field. Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 15, 33601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diguet, G.; Beaugnon, E.; Cavaillé, J.Y. From Dipolar Interactions of a Random Distribution of Ferromagnetic Particles to Magnetostriction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coquelle, E.; Bossis, G. Magnetostriction and Piezoresistivity in Elastomers Filled with Magnetic Particles. J. Adv. Sci. 2005, 17, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, K.; Shliomis, M.; Yamaguchi, H. Magnetic Deformation of Ferrogel Bodies: Procrustes Effect. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 040801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Jiang, Z.Y. Deformation in Magnetorheological Elastomer and Elastomer–Ferromagnet Composite Driven by a Magnetic Field. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, K.A.; Metsch, P.; Brummund, J.; Kästner, M. A Macroscopic Model for Magnetorheological Elastomers Based on Microscopic Simulations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2020, 193–194, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobroserdova, A.; Schümann, M.; Borin, D.; Novak, E.; Odenbach, S.; Kantorovich, S. Magneto-Elastic Coupling as a Key to Microstructural Response of Magnetic Elastomers with Flake-like Particles. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Dong, X.; Ou, J. Magnetostrictive Effect of Magnetorheological Elastomer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A.; Gouveia, C.; Dinis, G.; Pinto, A.M.; Pereira, A.M. Giant Magnetostriction in Low-Concentration Magnetorheological Elastomers. Compos. B. Eng. 2022, 243, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, H.; Gerlach, T.; Ehrlich, J. Magnetorheological Elastomers—An Underestimated Class of Soft Actuator Materials. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2021, 32, 1550–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liao, G.; Xuan, S. Full-Field Deformation of Magnetorheological Elastomer under Uniform Magnetic Field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 211909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbáth, T.; Günther, S.; Borin, D.; Gundermann, T.; Odenbach, S. XμCT Analysis of Magnetic Field-Induced Phase Transitions in Magnetorheological Elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundermann, T.; Günther, S.; Borin, D.; Odenbach, S. Detection of the Surface Deformation of Magneto-Active Composites Using X-Ray μ-Tomography. Magnetohydrodynamics 2013, 49, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, D.; Günther, D.; Hintze, C.; Heinrich, G.; Odenbach, S. The Level of Cross-Linking and the Structure of Anisotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 3452–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, R.Y.; Kuchkaev, A.M.; Sukhov, A.V.; Bekmukhamedov, G.E.; Yakhvarov, D.G. Platinum-Catalyzed Hydrosilylation in Polymer Chemistry. Polymers 2020, 12, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, B.; Decsi, P.; Szalai, I. Measurement of the Response Time of Magnetorheological Fluids and Ferrofluids Based on the Magnetic Susceptibility Response. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2022, 33, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gong, X.; Fan, Y.; Xia, H. Improving the Magnetorheological Properties of Polyurethane Magnetorheological Elastomer through Plasticization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairi, M.H.A.; Noor, E.E.M.; Ubaidillah, U.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Tarmizi, S.M.A.; Nordin, N.A. Enhancement of Magneto-Induced Modulus by the Combination of Filler and Plasticizer Additives-Based Magnetorheological Elastomer. Materials 2022, 15, 6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, H. Viscoelastic properties of silicone-based magnetorheological elastomers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2007, 21, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Filler Type | Filler Concentration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (wt%) | (vol%) | ||
| bM5 | 5.0 | 1.0 | |
| bM15 | 15.0 | 3.2 | |
| bM25 | 25.0 | 5.9 | |
| bM32 | 32.0 | 8.1 | |
| bM36 | 36.0 | 9.5 | |
| aM5 | 5.0 | 1.0 | |
| aM15 | 15.0 | 3.2 | |
| aM25 | 25.0 | 5.9 | |
| aM32 | 32.0 | 8.1 | |
| aM36 | 36.0 | 9.5 | |
| rFe5 | 5.1 | 0.7 | |
| rFe22 | 21.6 | 3.3 | |
| rFe36 | 36.4 | 6.6 | |
| rFe50 | 50.0 | 11.0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balogh, D.; Guba, S.; Horváth, B.; Szalai, I. Magnetic Field-Induced Deformation of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110146
Balogh D, Guba S, Horváth B, Szalai I. Magnetic Field-Induced Deformation of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers. Magnetochemistry. 2022; 8(11):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalogh, Diána, Sándor Guba, Barnabás Horváth, and István Szalai. 2022. "Magnetic Field-Induced Deformation of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers" Magnetochemistry 8, no. 11: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110146
APA StyleBalogh, D., Guba, S., Horváth, B., & Szalai, I. (2022). Magnetic Field-Induced Deformation of Isotropic Magnetorheological Elastomers. Magnetochemistry, 8(11), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8110146







