Abstract
Magnetic nanofibres have attracted more and more attention recently due to their possible applications e.g., in spintronics and neuromorphic computing. This work presents the synthesis and physicochemical characterization of the electrospun nanofibres of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) doped by iron oxide nanoparticles with diameters of 5 nm. PCL is a semi-crystalline, hydrophilic polymer showing controllable biodegradation rates, biocompatibility, and flexible mechanical properties. In the composite material, two different concentrations of magnetic nanoparticles were used: 2 and 6 wt.%. PCL-based composites were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and thermogravimetry (TGA). Although in the literature one can find many studies on magnetic polymeric composites, the investigation of their magnetic properties is usually limited to measuring the magnetization curve. Detailed analysis of dynamic magnetic susceptibility is rather rare. In this report, special attention was paid to the detailed analysis of magnetic properties, where we followed the evolution of changes in the magnetic behavior of the material depending on the concentration of magnetic nanoparticles.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, there is a strong industrial demand for materials with a high level of multi-functionality. Access to multi-functionality at the nanoscale requires the development of hybrid nanostructures that combine materials of different natures. One of the examples of such nanocomposites is polymers doped with inorganic magnetic nanoparticles [1]. By combining magnetic and polymeric materials, composites with exceptional properties can be obtained. Thanks to this, they give a real chance for future applications in sensors, intelligent coatings, or in medicine, where they are considered as targeted drug delivery systems [2] as well as for cancer therapies [3].
The properties of magnetic nanoparticles are dramatically different from their bulk counterparts [4,5]. The reduction of the nanoparticles size up to a single domain limit (e.g., ∼15–20 nm for iron and iron oxide) brings about the occurrence of many novel properties like superparamagnetism or macroscopic quantum tunneling [6,7]. Since particles are usually dispersed in a non-magnetic matrix, one of the most important topics of investigation is the determination of the influence of the carrier matrix on magnetism [8]. In general, the non-magnetic matrix mediates particle agglomeration and magnetic interactions. The most important interactions occurring in the magnetic particle assemblies are exchange interactions and dipole-dipole interactions. In the systems, where the carrier matrix is metallic, the RKKY interaction between nanoparticles can be observed, while in the situation where a matrix is an insulator, superexchange interaction can occur. The most popular carrier matrices for nanoparticles are polymers. In the literature, one can find many examples of advanced polymer composites synthesized with a wide variety of admixtures like semiconductors [9], metals [10], carbon nanotubes [11] [12,13], and magnetic nanoparticles [14]. The combination of attractive properties of polymers like lightweight, biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and dielectric tunability along with novel magnetic properties of nanoparticles makes them multifunctional materials. The inclusion of ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic nanoparticles in polymers is especially important as magnetic nanoparticles have shown promise in various potential applications like spin-polarized devices, carriers for drug delivery, magnetic recording media, high-frequency applications, etc. [15,16,17,18].
One of the most powerful methods used in nanocomposites fabrication is electrospinning [19]. It is a simple method for generating fibres with diameters ranging from nano- to micrometers. The main advantage of this technique is low-cost, the ability to fabricate materials with large surface area-to-volume ratio, and its applicability to many types of materials. Moreover, electrospinning provides the possibility of the integration of magnetic nanoparticles into mats of electrospun fibres, where the magnetic functionality, as well as the mechanical properties are expected to be preserved.
The objective of this work is a detailed study of the magnetic properties of the electrospun nanofibres of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) doped by iron oxide nanoparticles with diameters of 5 nm. Special attention was paid to the influence of the nanoparticles concentration and nanoparticles aggregations on the dynamic properties of composite material.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Thermal Analysis
The thermal stability of the pristine PCL and PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites was investigated by TGA. As it is shown in Figure 1, sharp weight loss of pure PCL is observed at the temperature range 350–425 °C, which is related to the chains’ thermal degradation. The thermal degradation of Fe3O4-doped PCL occurs at much lower temperatures in comparison to pristine PCL. Similar phenomena were previously observed for PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites [20] as well as other composite materials e.g., Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO [21]. The admixture of nanoparticles in the polymer fibre brings about the random pyrolysis of polymer chains and finally their accelerated thermal decomposition. Moreover, the results of TGA measurements allow us to determine the weight residue of the PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites, which is equal to 2 and 6 wt. % of Fe3O4.
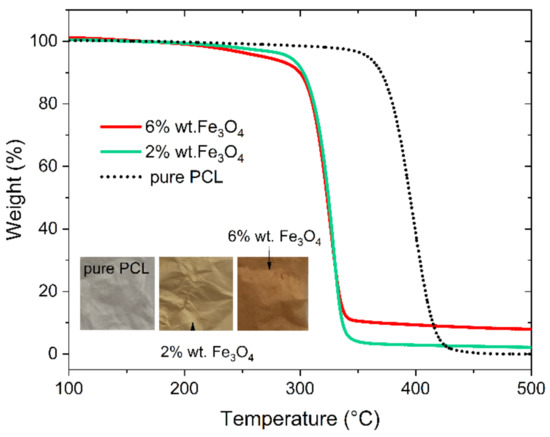
Figure 1.
TGA curves for the pure PCL and magnetic electrospun mats.
2.2. IRspectroscopy
The chemical structure of nanocoposites was analyzed using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Figure 2 presents the infrared spectra of plain PCL, PCL/Fe3O4 mats, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The characteristic absorption bands in PCL observed at 2942 cm−1 and 2864 cm−1 are related to asymmetric and symmetric stretching of CH2 groups, respectively. The carbonyl stretching vibrations in PCL appear at around 1720 cm−1; while bands that appeared at 1241 and 1186 cm−1 are related to stretching vibrations of C–C and C–O, respectively [22]. The addition of magnetite nanoparticles reveals a Fe–O peak at 590 cm−1. This peak is seen for PCL-Fe3O4 6 wt.% mats, while for PCL-Fe3O4 wt.2% it is not observed, which is probably due to low particle concentration.
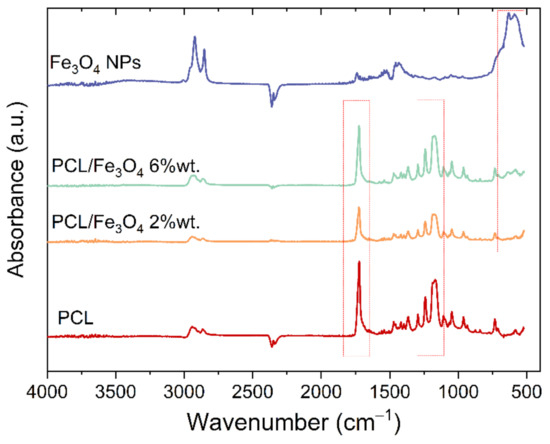
Figure 2.
ATR-IR spectra of plain PCL nanofibres, electrospun PCL/Fe3O4 NPs (2 and 6 wt.%) and Fe3O4 NPs.
2.3. Morphology of Electrospun PCL/Fe3O4 Mats
The macroscopic appearance of the electrospun PCL/Fe3O4 mats is presented in the inset of Figure 1. The pristine PCL mat is white, while the iron oxide nanoparticles-loaded PCL fibres are brown and the color intensity increases with the increase of Fe3O4 content. The morphology of magnetic mats is presented in Figure 3. The Fe3O4 NPs loading PCL mats are composed of continuous, intertwined, and crisscrossed fibres. The diameter of most fibres ranges from 220 nm to 2.1 µm with maximal abundances around 600 and 900 nm. Sporadically, single fibres of diameters exceeding 2.3 µm can be seen. The fraction of the fibres with diameters between 800 nm and 1.4 µm is higher for the samples containing NPs comparing to the plain ones, but there is no evident diameter-concentration dependence.
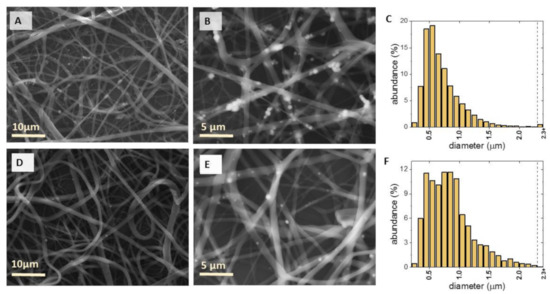
Figure 3.
SEM images and fiber diameter distribution of PCL nanofibres loaded with 6 wt.% (A–C) and 2 wt.% (D–F) magnetite nanoparticles respectively.
To clarify the effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on morphological changes, the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy has been carried out in the mode of elemental mapping of the electrospun PCL/Fe3O4 mats. As it is shown in Figure 4, two elements were detected in the prepared composite nanofibres, namely, carbon (C) and iron (Fe). EDX analysis provided evidence that Fe3O4 particles existed in PCL nanofibres. Moreover, for the sample with a higher concentration of iron oxide nanoparticles, the map presenting the distribution of Fe reveals the appearance of nanoparticle agglomerations. In comparison to PCL-6 wt.% Fe3O4 nanofibres, the agglomeration of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in PCL-2 wt.% Fe3O4 nanofibres is reduced.
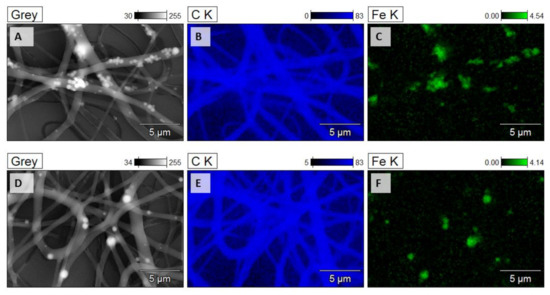
Figure 4.
Elemental mapping of PCL nanofibres loaded with 6 wt.% (A–C) and 2 wt.% (D–F) magnetite nanoparticles respectively by EDS.
2.4. Magnetic Properties
The magnetic hysteresis loops measured for PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites as well as Fe3O4 nanoparticles at two temperatures: 2 K and 300 K, are presented in Figure 5. For meaningful comparison of magnetic properties of the examined samples, the magnetization curves were normalized to the Fe3O4 content. The values of saturation magnetization measured for all samples are very similar and are close to 80 emu/g at 2 K and 63 emu/g at 300 K. The coercive field detected at 2 K is equal to 12 Oe, 14 Oe, and 15 Oe for pure Fe3O4 nanoparticles, PCL-2 wt.% Fe3O4, and PCL-6 wt.% Fe3O4, respectively.
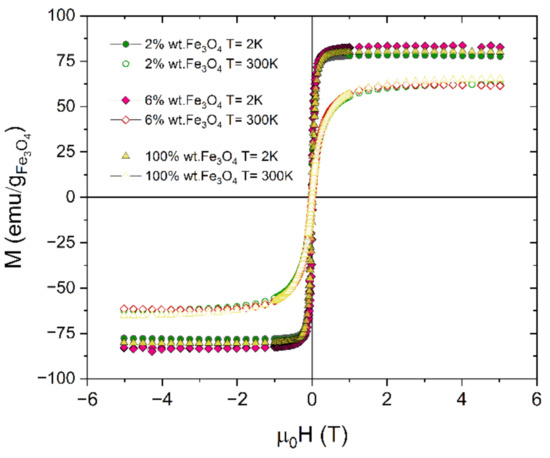
Figure 5.
Hysteresis loops obtained for Fe3O4 nanoparticles and PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2 wt.% and 6 wt.% measured at 2 K and 300 K.
The results of temperature-dependent zero-field-cooling and field cooling (ZFC-FC) magnetization reveal the significant differences in the behavior of nanocomposites with different magnetite content. During ZFC-FC measurements, first, the sample is cooled without the external magnetic field from 300 K to 2 K. Thereafter, 100 Oe magnetic field is applied and magnetic moment is recorded with increasing temperature to get the ZFC curve. The FC curve is obtained during the sample cooling from room temperature under the same 100 Oe field and magnetic moment is recorded with decreasing temperature. Figure 6 shows the temperature dependence of ZFC-FC magnetization curves for PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites with 2 wt.% and 6 wt.% particle content. The ZFC curves of both samples exhibit a maximum at 10 K for 2 wt.% Fe3O4 and at 16 K for 6 wt.% Fe3O4. For isolated, non-interacting nanoparticles, the maximum of the ZFC plot is related to the blocking temperature (TB)—the key parameter characterizing superparamagnetic materials. Blocking temperature is the temperature between the blocked and superparamagnetic states and can be defined as the temperature at which the average time for a magnetic nanoparticle moment to escape from an energy well is equal to the characteristic measurement time for the system. The lower value of TB observed for 2 wt.% Fe3O4 can be explained by the more homogeneous particle distribution within the PCL fibres and a reduced number of agglomerating particles in comparison to nanocomposites containing 6 wt.% Fe3O4. This feature is in agreement with the SEM/EDS results (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
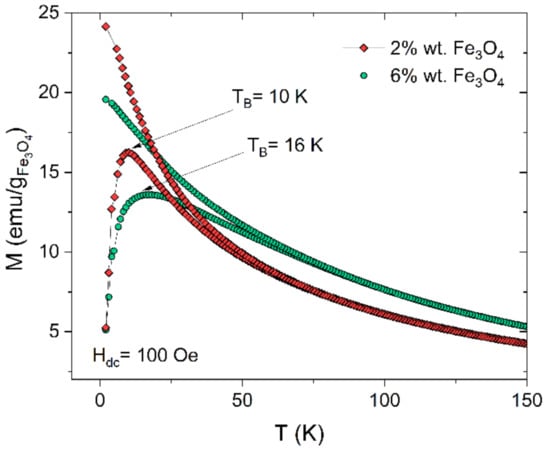
Figure 6.
ZFC and FC curves for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2% and 6% measured under an applied magnetic field of 100 Oe. The large hysteretic behaviour between ZFC and FC curves is characteristic for superparamagnets. For both composites, the ZFC curve reveals a maximum at temperature: T = 10 K (PCL-2 wt.% Fe3O4) and T = 16 K (PCL-6 wt.% Fe3O4), which is the average blocking temperature (TB) of magnetite nanoparticles.
To determine the role of particle agglomeration in PCL/Fe3O4 nanocomposites in magnetic properties, AC susceptibility measurements were performed in the 3.5 Oe oscillating field at seven different frequencies between 0.1 and 500 Hz. The in-phase and out of phase components of AC susceptibility measured for Fe3O4 nanoparticles are presented in Figure 7. For the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, with 5 nm in diameter, the clear frequency dependence of AC susceptibility is observed, which can be related to the blocking process of isolated, non-interacting, or weak-interacting nanoparticles. Moreover, for a higher frequency, a value of blocking temperature increases. To better understand the dynamic behavior of the blocking process, we have analyzed the χ”(T) data using the phenomenological relation:
where ΔTmax is the relative variance of Tmax per decade of frequency Δlog(f). According to literature, Φ < 0.03 is typical for a spin-glass system, Φ = 0.03–0.1 is characteristic for interacting nanoparticles, while Φ > 0.1 is reserved for non-integrating nanoparticles [23]. The value of Φ = 0.073 calculated for the studied Fe3O4 nanoparticles indicates the appearance of dipole-dipole interaction between particles.
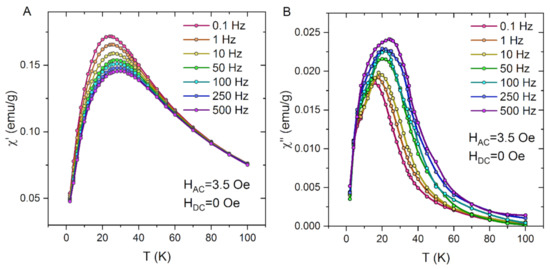
Figure 7.
Real (A) and imaginary (B) AC susceptibility data for Fe3O4 nanoparticles.
The AC susceptibility measured for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2 wt.% also exhibits significant frequency dependence (Figure 8). In comparison to pure iron oxide nanoparticles, the maxima of real and imaginary components of AC susceptibility are shifted to the lower temperature range. The frequency-sensitive parameter Φ calculated for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2 wt.% is equal to 0.094. These results suggest that the dilution of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in polymer fibres reduces the dipolar interaction and finally we observe the magnetic responses from noninteracting or only weakly interacting superparamagnetic particles.
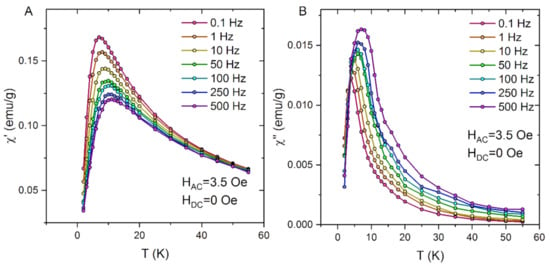
Figure 8.
Real (A) and imaginary (B) AC susceptibility data for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2%.
The dynamics of superparamagnets can be described by the Néel–Arrhenius law:
where τ is the time of particle magnetization flips in between two minimum energy states and τ0 is the relaxation time between two consecutive attempts. Ea/kB is the energy barrier required for the separation of metastable states. The linear fit corresponding to Equation (2) for Fe3O4 nanoparticles and PCL fibres with Fe3O4 contents of 2 wt.% is presented in Figure 9. The fitting parameters are found to be τ0 = 2.11 × 10−11 s, Ea/kB = 423.5 K for Fe3O4 NPs and τ0 = 6.42 × 10−8 s, Ea/kB= 72.6 K for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 2%. In both cases, the fitting parameters lie in the range expected for non-interacting superparamagnetic systems, which agrees well with the magnetic behavior interpreted using the value of Φ.
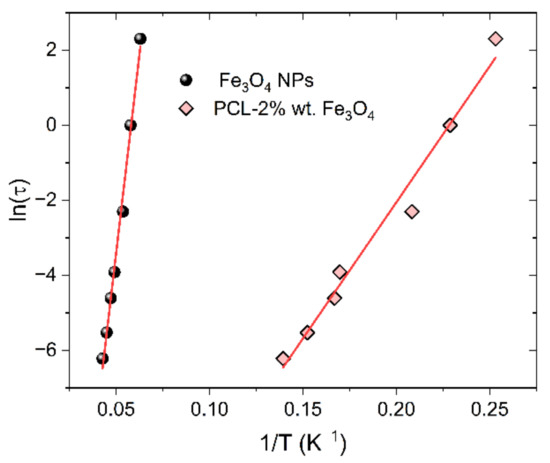
Figure 9.
Arrhenius plots for Fe3O4 nanoparticles and PCL fibres with Fe3O4 contents of 2%.
Figure 10 displays the AC susceptibility χ(T, f) plots for the PCL mat containing 6 wt.% Fe3O4 NPs. Similar to the previously described samples, the clear frequency dependence is observed. However, contrary to the PCL-2wt.% Fe3O4 sample, the AC susceptibility plots measured for PCL composites with Fe3O4 contents of 6 wt.% reveals an additional peak. The multiple peaks in χ(T) usually indicate the presence of several magnetic phases in a sample. In our opinion, the appearance of this anomaly is related to the presence of the NPs agglomerations. Therefore, according to the SEM results, in this sample, apart from non-interacting nanoparticles, one may expect particle clusters with pronounced dipole-dipole interactions.
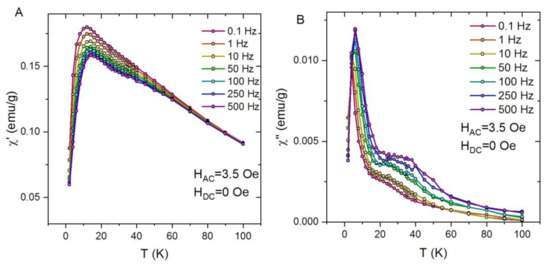
Figure 10.
Real (A) and imaginary (B) AC susceptibility data for PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 6%.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL, average MW = 80,000) and Fe3O4 nanoparticles (∼5 nm diameter) dispersed in chloroform at concentrations of 5 mg/mL were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. All the materials were used as received without further treatment.
3.2. Preparation of PCL and PCL-Fe3O4 Composite Fibres
Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and composite PCL-PCL-Fe3O4 fibres were obtained by electrospining method. The starting solution of 10 wt% PCL was composed of poly(ε-caprolactone) and a 3:1 mixture of chloroform (and/or chloroform dispersion of Fe3O4 nanoparticles) and methanol. The final concentration of nanoparticles in the fibres was determined by TGA measurements. The tip-to-ground distance was 11 cm and the applied voltage was set at 10 kV. The solution was dispensed at a constant flow rate of 1.5 mL/h. The fiber mats were collected on a metallic plate collector.
3.3. Characterization Techniques
TGA experiments were performed using a TA Instruments TGA 5500 high-resolution thermogravimetric analyzer using open platinum 100 μL pans. All samples were tested in a pure (5.0) nitrogen atmosphere from room temperature to 600 °C with s heating rate of 5 C/min.
Infrared spectra were recorded on EXCALIBUR FTS 3000 FT-IR spectrometer using a Veemax II Specular Reflectance Accessory.
Microstructure and composition analysis of electrospun mats was performed using a FEI ESEM XL30 and SCIOS 2 Dual Beam ultra-high-resolution, analytical Focused Ion Beam (FIB) scanning electron microscopes (SEM) equipped with an X-ray energy dispersive spectrometer EDAX GEMINI 4000.
Magnetic properties were measured by Quantum Design MPMS-XL magnetometer. AC susceptibility was measured with the frequency of 0.1–500 Hz and the oscillating field amplitude of 3.5 Oe. Magnetization curves in conditions of zero-field-cooled (ZFC) and field-cooled (FC) were measured in the temperature range of 2–300 K in the presence of an applied field of 100 Oe. The field-dependent magnetization curves were obtained at 2 K and 300 K in the magnetic field range of ±5 Tesla.
4. Conclusions
The application of magnetic nanofibres in any device needs homogenous distribution of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in the polymer matrix. In this report, we focused the attention on the role of particle agglomeration on dynamic magnetic properties.
In this study, PCL/Fe3O4 composite (2 and 6 wt.%) mats were successfully fabricated using electrospinning. The incorporation of iron oxide NPs into PCL nanofibres was confirmed by SEM/EDX, TGA, and FT-IR analyses. The value of blocking temperature determined based on the maximum of ZFC curves is equal to 10 K for PCL/2 wt.% Fe3O4 and 16 K for PCL/6 wt.% Fe3O4. At room temperature, the coercive field of the composites is equal to zero, while in the blocking state the hysteresis loops exhibit small coercivity (ca. 14 Oe). For both composite samples, the clear frequency dependence of χ′(T) and χ″(T) is observed. However, only for a PCL/2 wt.% Fe3O4 composite, the superparamagnetic properties of nearly isolated NPs were observed. For a higher NPs content, the agglomeration of nanoparticles cannot be avoided, which brings about the strong dipolar interaction between NPs. Finally, for the PCL fibres with magnetite contents of 6 wt.%, the dynamic susceptibility plots reveal two maxima related to the presence of non-interacting nanoparticles as well as the particle clusters with pronounced dipole-dipole interactions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.-D. and M.F.; methodology, W.S., M.J.-D. and M.F.; formal analysis, W.S., M.J.-D. and M.F.; investigation, W.S., M.J.-D., P.M.Z., P.C. and M.F.; writing—original draft preparation, W.S., M.J.-D.; writing—review and editing, P.C., P.M.Z. and M.F. supervision, M.F., M.J.-D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author: Magdalena.Fitta@ifj.edu.pl.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shifrina, Z.B.; Matveeva, V.G.; Bronstein, L.M. Role of Polymer Structures in Catalysis by Transition Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Composites. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1350–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, D.; Harlepp, S.; Goetz, J.; Bégin, D.; Schlatter, G.; Bégin-Colin, S.; Hébraud, A. Nanocomposite Polymer Scaffolds Responding under External Stimuli for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 1900143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, A.M.; Gonzalez, P.H. Hybrid Polymeric-Magnetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatments. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, M.; Podsiadły, M.; Bałanda, M. Magnetic Investigation of Carbon Coated Co-, Ni- and Fe-Nanoparticles. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2009, 115, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, V.; Sakthi Kumar, D.; Yoshida, Y.; Makarewicz, M.; Tabiś, W.; Anantharaman, M.R. Synthesis and properties of highly stable nickel/carbon core/shell nanostructures. Carbon NY 2010, 48, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieloch, A.A.; Kręcisz, M.; Rybka, J.D.; Strugała, A.; Krupiński, M.; Urbanowicz, A.; Kozak, M.; Skalski, B.; Figlerowicz, M.; Giersig, M. The influence of ligand charge and length on the assembly of Brome mosaic virus derived virus-like particles with magnetic core. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, N.; Guardia, P.; Roca, A.G.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J.; Iglesias, O.; Bartolomé, F.; García, L.M.; Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Surface anisotropy broadening of the energy barrier distribution in magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 475704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudakov, G.A.; Tsiberkin, K.B.; Ponomarev, R.S.; Henner, V.K.; Ziolkowska, D.A.; Jasinski, J.B.; Sumanasekera, G. Magnetic properties of transition metal nanoparticles enclosed in carbon nanocages. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 472, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deubel, F.; Steenackers, M.; Garrido, J.A.; Stutzmann, M.; Jordan, R. Semiconductor/Polymer Nanocomposites of Acrylates and Nanocrystalline Silicon by Laser-Induced Thermal Polymerization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Benny, L.; Cherian, A.R.; Narahari, S.Y.; Varghese, A.; Hegde, G. Electrochemical sensors using conducting polymer/noble metal nanoparticle nanocomposites for the detection of various analytes: A review. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2021, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Gao, X.; Xu, D. A review of the interfacial characteristics of polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28048–28085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, J. Polymer Nanocomposites for Biomedical and Biotechnology Applications. In Properties and Applications of Polymer Nanocomposites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S. Polymer/Carbon Nanotube Nano Composite Fibers—A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6069–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, M.C.; Zinoveva, S.; Miller, T.; Sabliov, C.M.; Monroe, W.T.; Kumar, C.S.S.R. Investigation of Magnetic Nanoparticle−Polymer Composites for Multiple-controlled Drug Delivery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11102–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, Y.; Khodadust, R.; Akkoc, Y.; Utkur, M.; Saritas, E.U.; Gozuacik, D.; Yagci Acar, H. Development of tailored SPION-PNIPAM nanoparticles by ATRP for dually responsive doxorubicin delivery and MR imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Wang, Y.-M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticulate system: Synthesis, targeting, drug delivery and therapy in cancer. Dalt. Trans. 2019, 48, 9490–9515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.-C.; Chang, C.-H.-T.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Su, W.-B.; Tsay, J.-S. A practical method for fabricating superparamagnetic films and the mechanism involved. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14096–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, M.; Crowgey, B.; Kempel, L.C.; Kofinas, P. Nanostructured flexible magneto-dielectrics for radio frequency applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Diverse Morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Leung, V.; Yuqin Wan, L.; Dutz, S.; Ko, F.K.; Häfeli, U.O. Electrospun magnetic nanofibre mats—A new bondable biomaterial using remotely activated magnetic heating. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Viswanathan, K.; Kasi, G.; Sadeghi, K.; Thanakkasaranee, S.; Seo, J. Poly(Lactic Acid)/ZnO Bionanocomposite Films with Positively Charged ZnO as Potential Antimicrobial Food Packaging Materials. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzein, T.; Nasser-Eddine, M.; Delaite, C.; Bistac, S.; Dumas, P. FTIR study of polycaprolactone chain organization at interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 273, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mydosh, J.A. Spin Glasses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781482295191. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
