Magnetic Functionalization of Scanning Probes by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction to FEBID and MFM
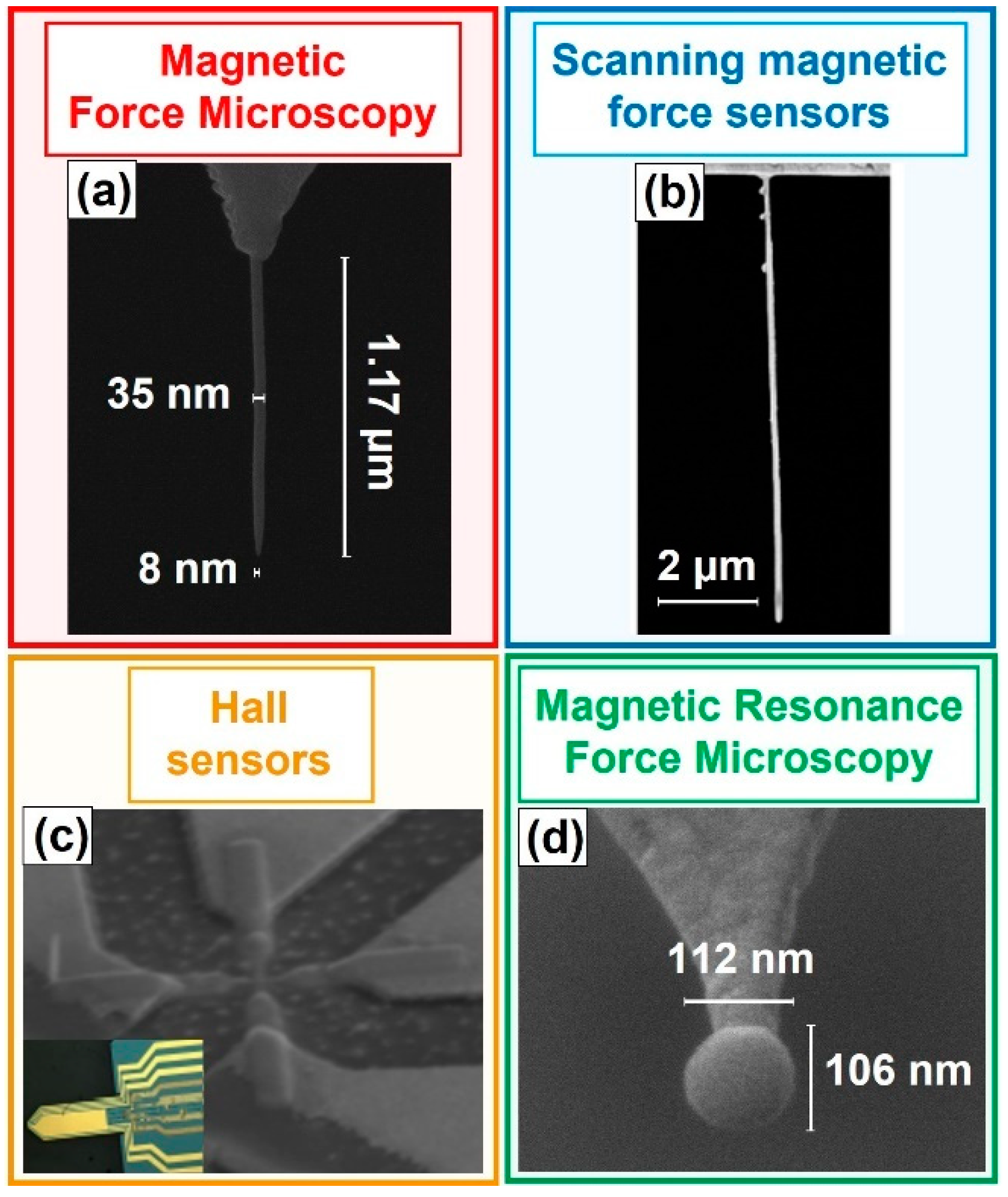
2. Magnetic Force Microscopy Using Tips Grown by FEBID
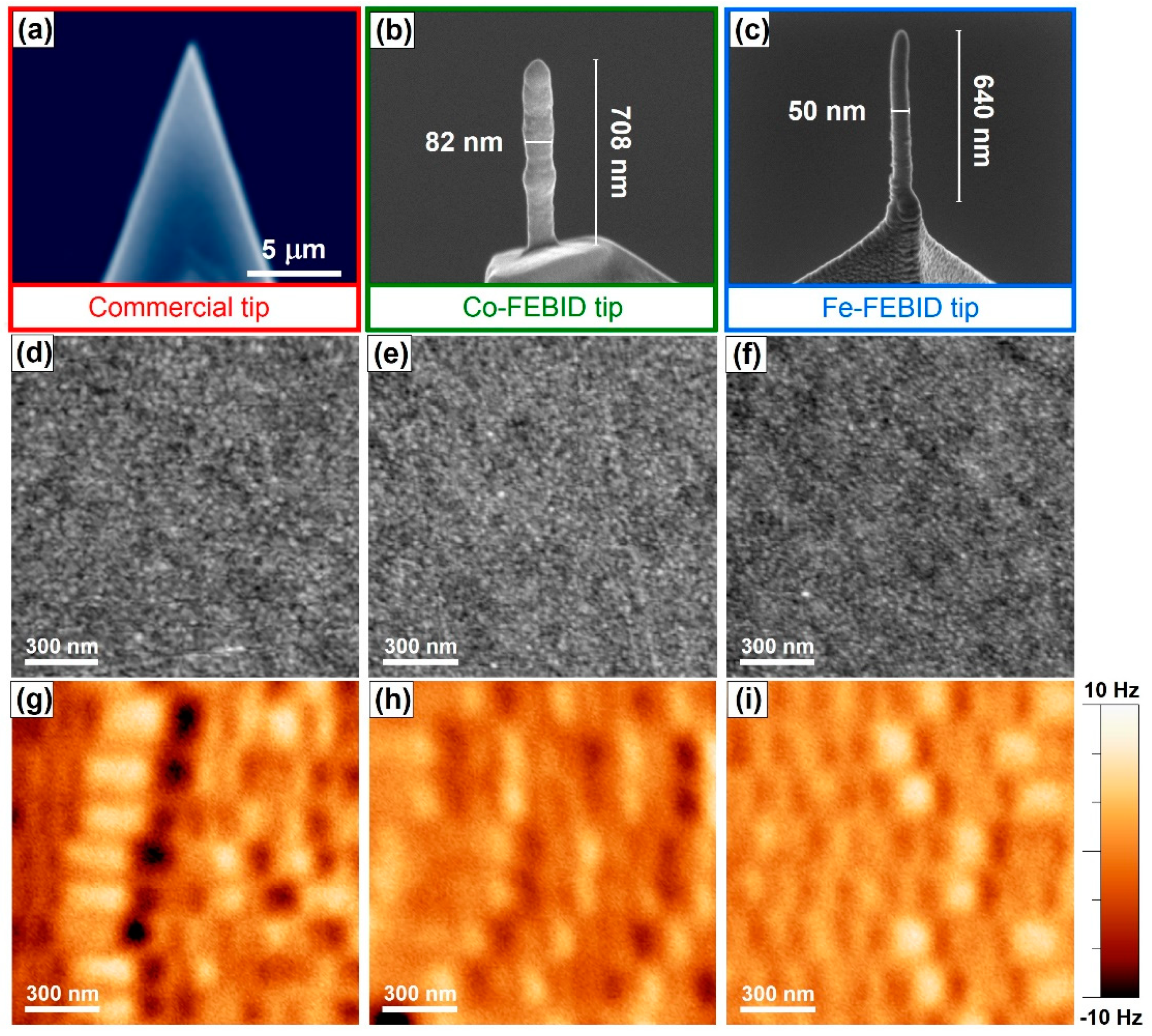
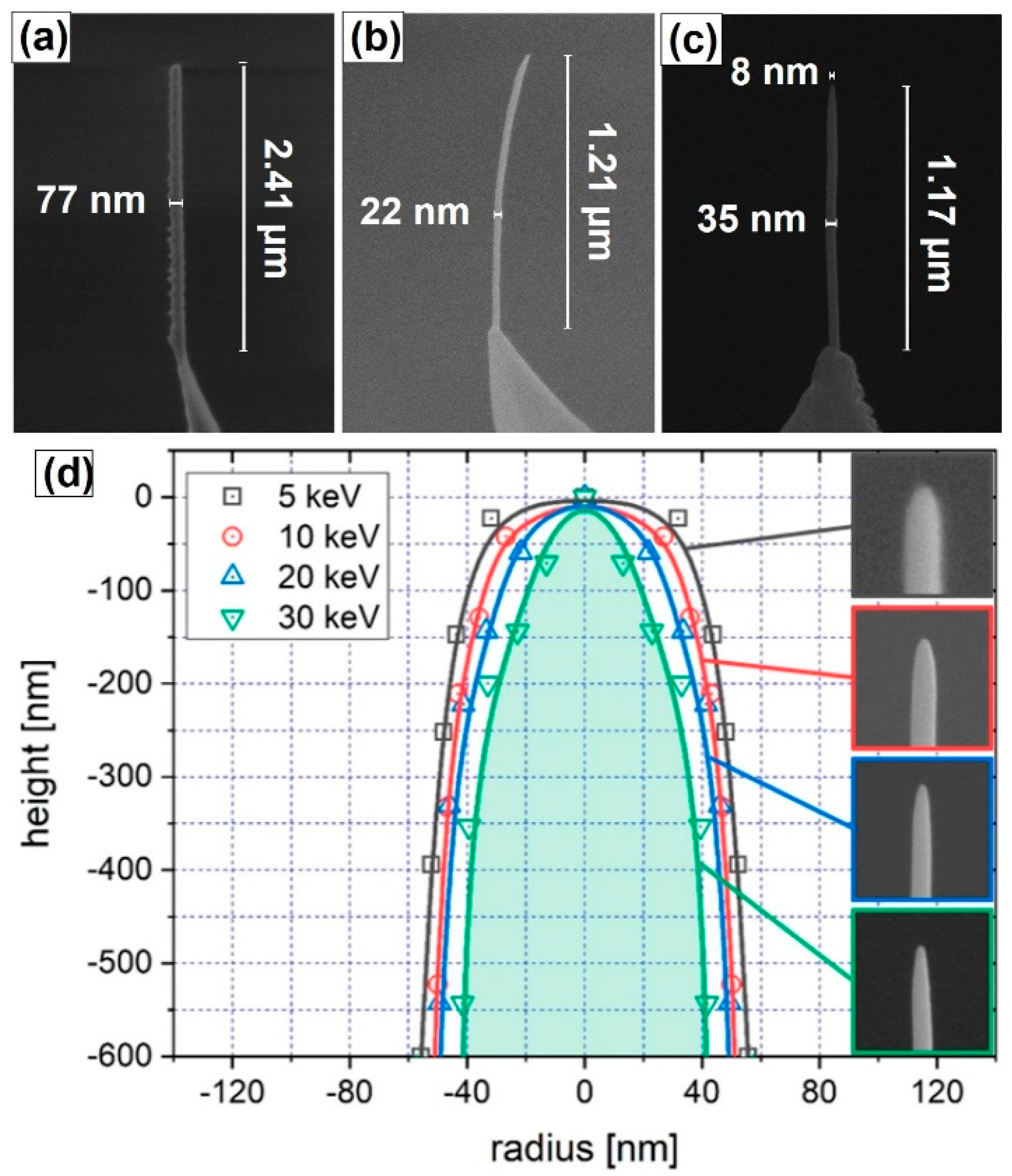
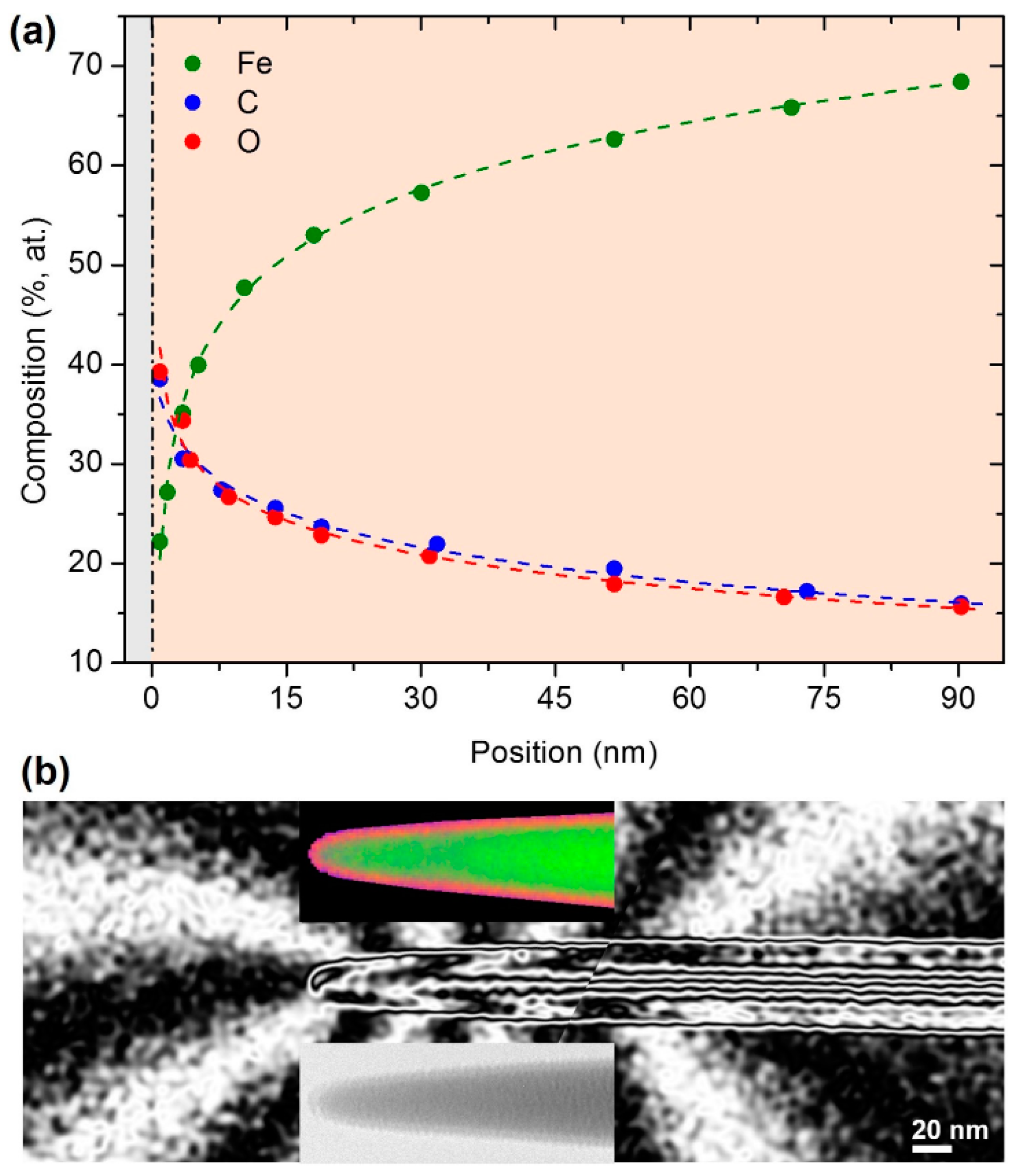
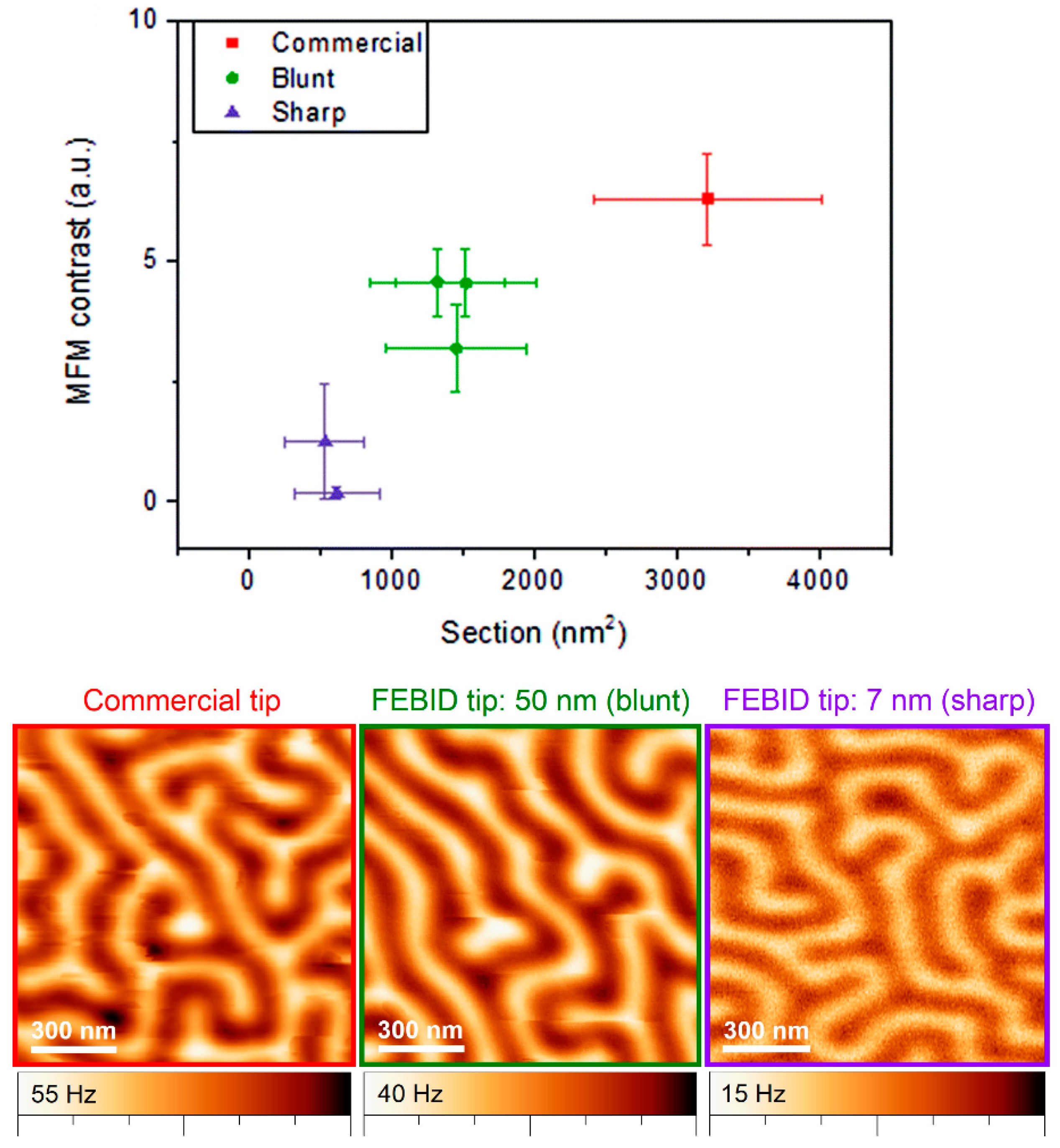
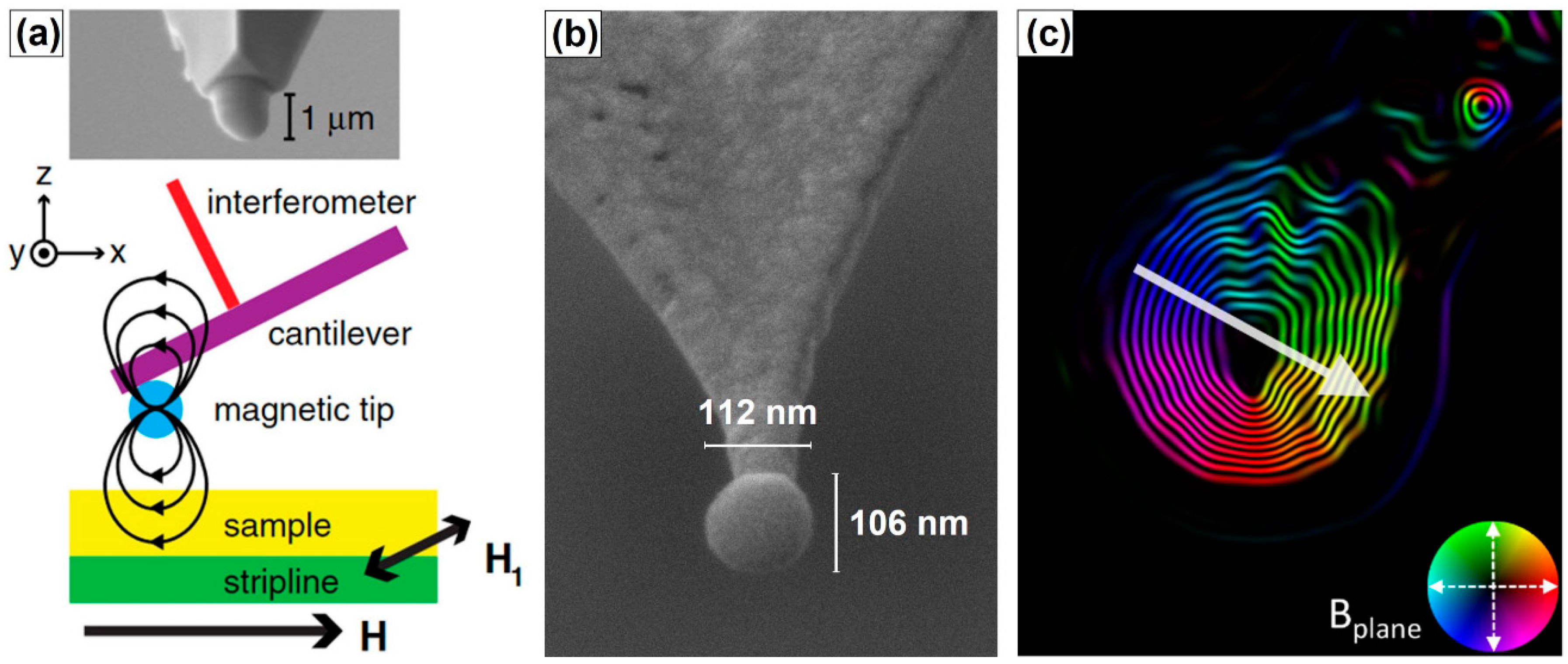
2.1. Growth and Properties of MFM Tips Grown by FEBID
2.2. Detection of Soft Magnetic Textures
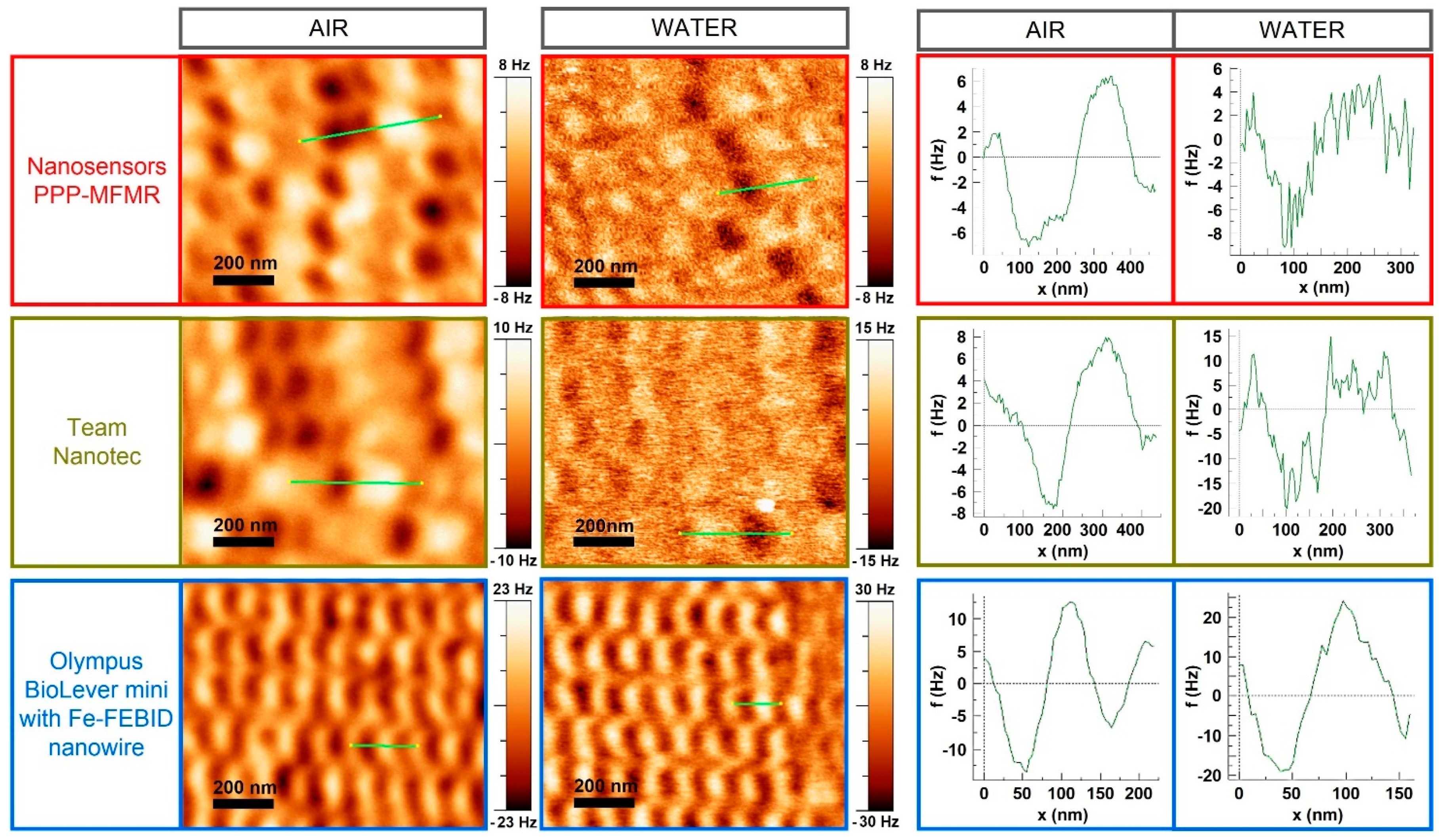
2.3. Applications in Liquid Media
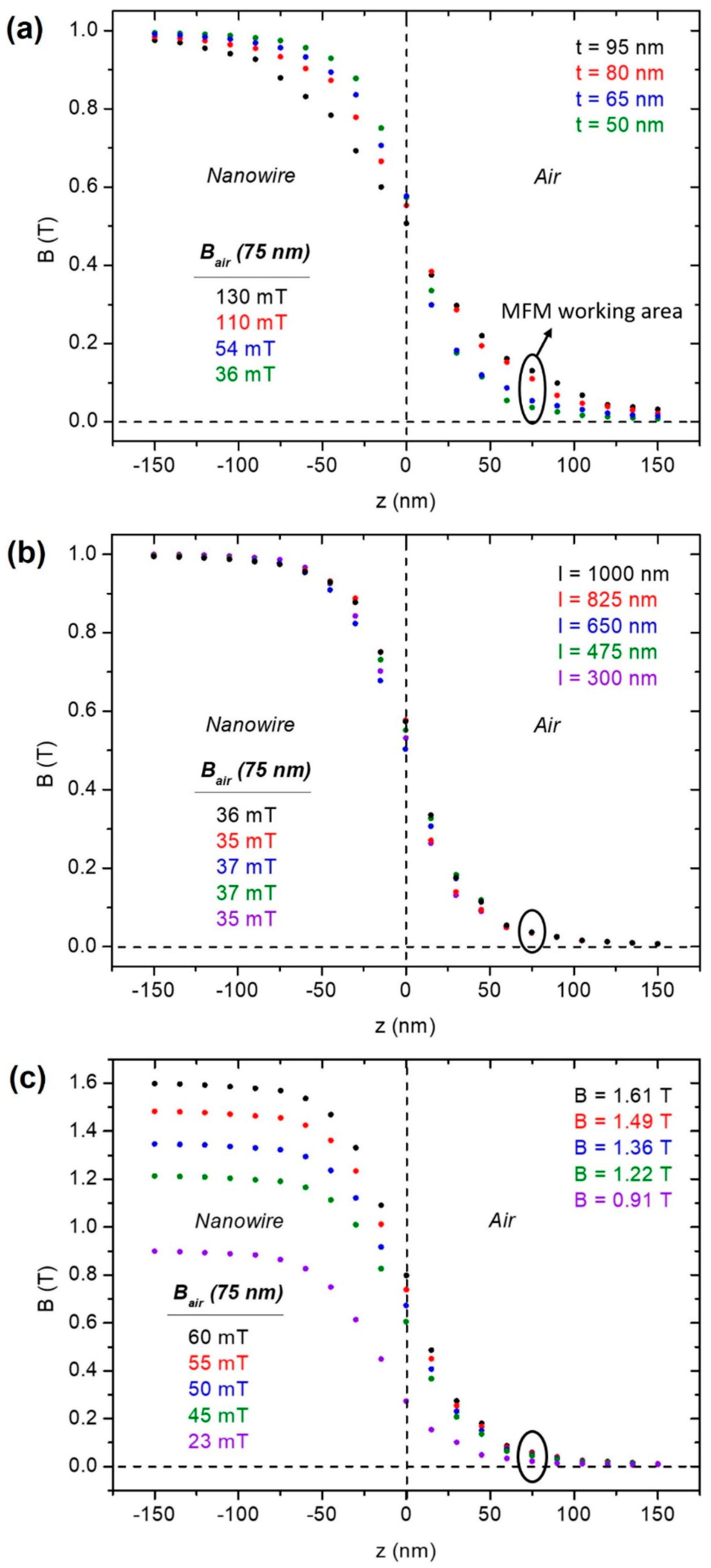
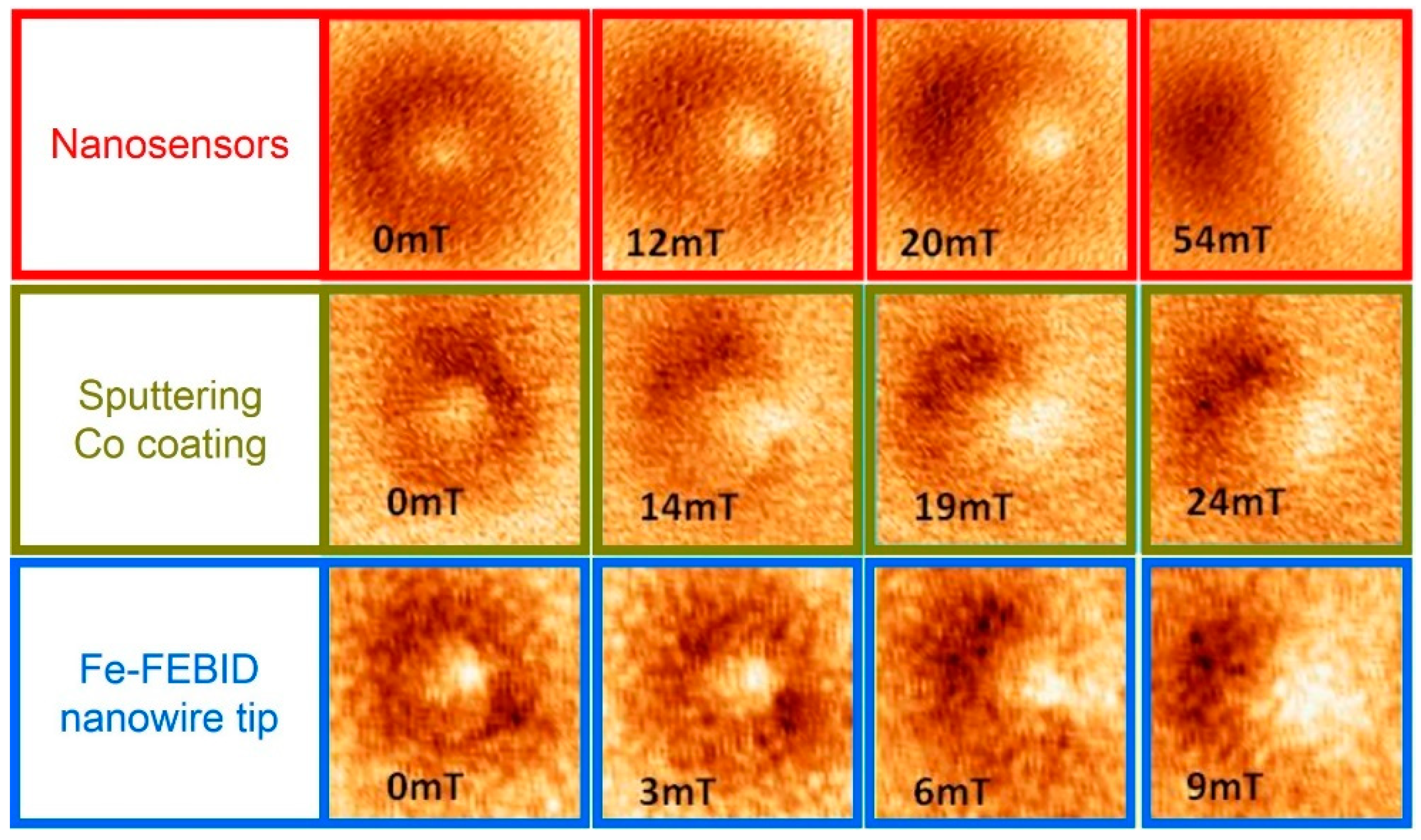
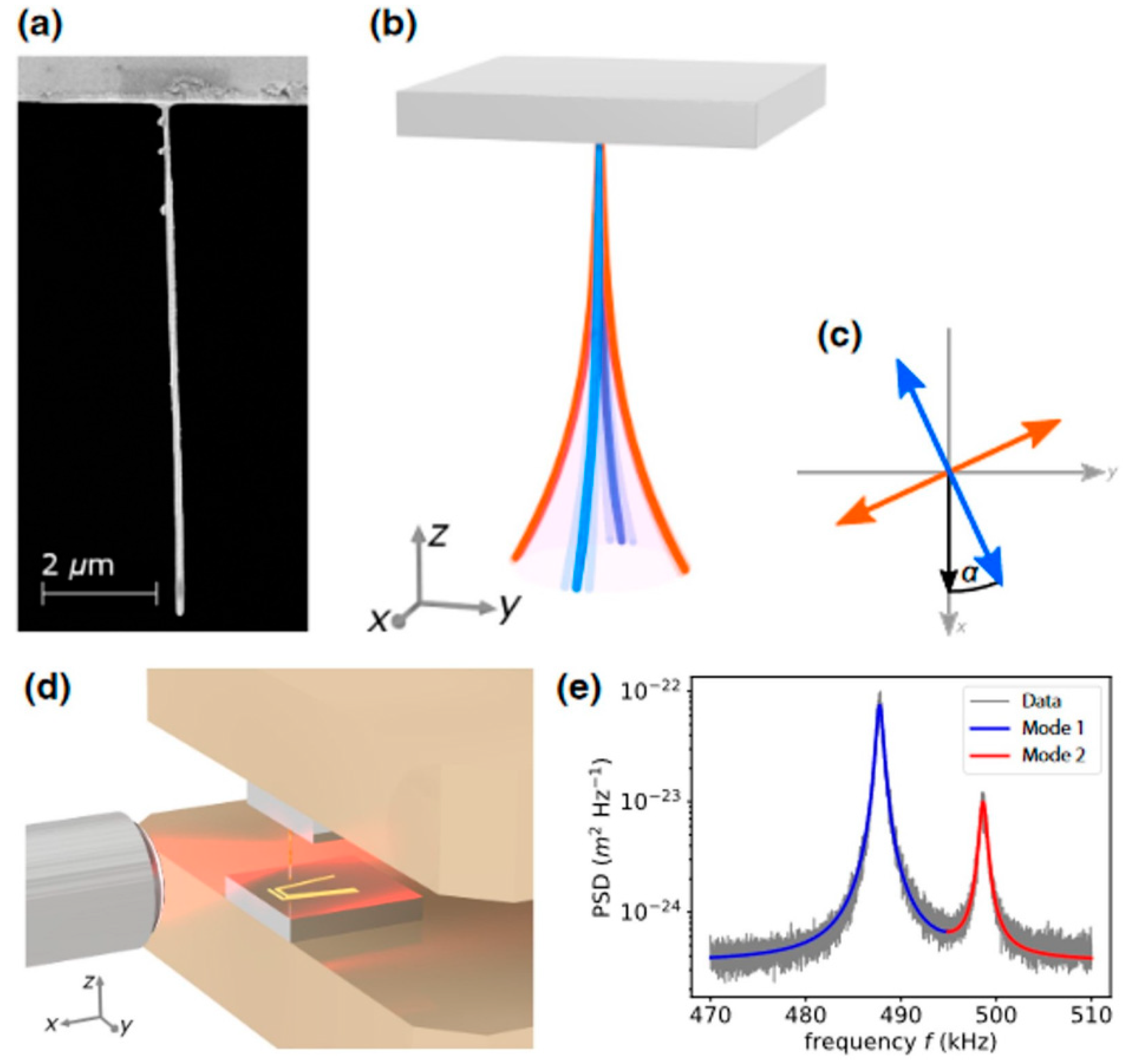
3. Nanowire Magnetic Force Sensors
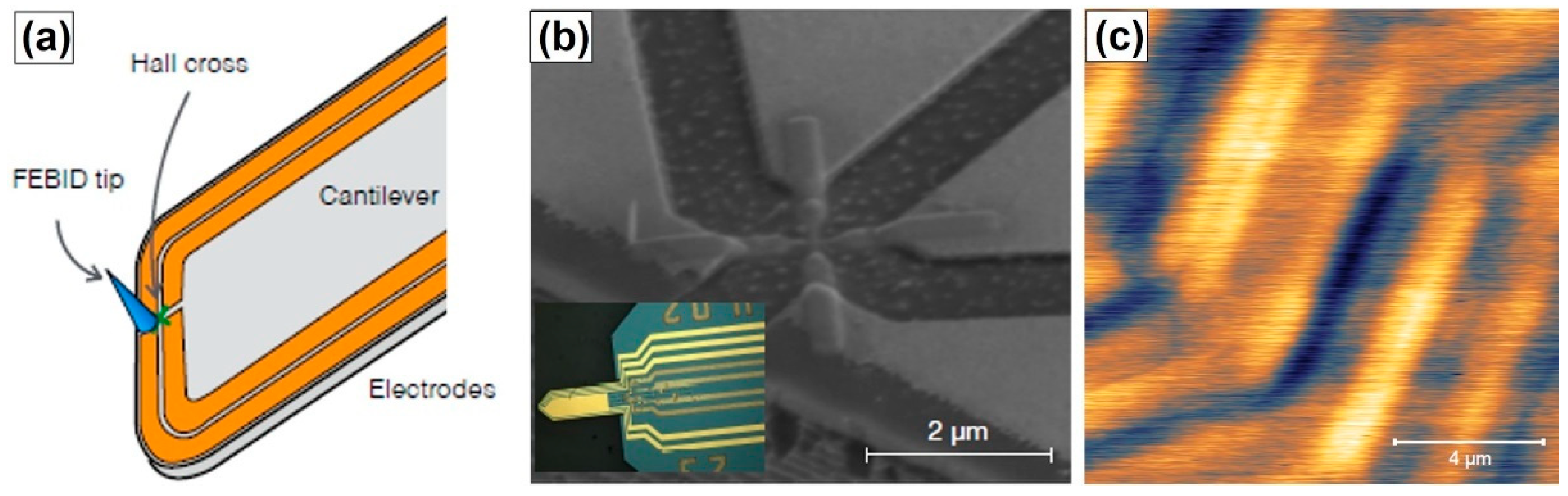
4. Scanning Ferromagnetic Hall Sensors
5. Magnetic Resonance Force Microscopy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsui, S.; Mori, K. New Selective Deposition Technology by Electron Beam Induced Surface Reaction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 23, L706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, M.; Porrati, F.; Schwalb, C.; Winhold, M.; Sachser, R.; Dukic, M.; Adams, J.; Fantner, G. Focused electron beam induced deposition: A perspective. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randolph, S.J.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Rack, P.D. Focused, Nanoscale Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition and Etching. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2006, 31, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dorp, W.F.; Hagen, C.W. A critical literature review of focused electron beam induced deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 081301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utke, I.; Hoffmann, P.; Melngailis, J. Gas-assisted focused electron beam and ion beam processing and fabrication. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2008, 26, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, H.; Smith, D.A.; Haber, T.; Rack, P.D.; Hofer, F. Fundamental Proximity Effects in Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, R.; Szkudlarek, A.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Rack, P.D.; Utke, I.; Plank, H. Toward Ultraflat Surface Morphologies During Focused Electron Beam Induced Nanosynthesis: Disruption Origins and Compensation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3289–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höflich, K.; Yanh, R.B.; Berger, A.; Leuchs, G.; Christiansen, S. The Direct Writing of Plasmonic Gold Nanostructures by Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2657–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuishi, K.; Shimojo, M.; Tanaka, M.; Takeguchi, M.; Furuya, K. Resolution in New Nanofabrication Technique Combining Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition and Low-Energy Ion Milling. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, A.G.; Kim, S.; Henry, M.; Kulkarni, D.; Tsukruk, V.V. Focused-electron-beam-induced processing (FEBIP) for emerging applications in carbon nanoelectronics. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Ramón, L.; Córdoba, R.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Magén, C.; Snoeck, E.; Gatel, C.; Serrano, I.; Ibarra, M.R.; de Teresa, J.M. Ultrasmall functional ferromagnetic nanostructures grown by focused electron-beam-induced deposition. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7781–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Teresa, J.M.; Córdoba, R. Arrays of Densely Packed Isolated Nanowires by Focused Beam Induced Deposition Plus Ar+ Milling. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3788–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boero, G.; Utke, I.; Bret, T.; Quack, N.; Todorova, M.; Mouaziz, S.; Kejik, P.; Brugger, J.; Popovic, R.S.; Hoffmann, P. Submicrometer Hall devices fabricated by focused electron-beam-induced deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 042503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Serrano-Ramón, L.; Michalik, J.M.; Ibarra, M.R.; de Teresa, J.M.; O’Brien, L.; Petit, D.; Lee, J.; Cowburn, R.P. Three dimensional magnetic nanowires grown by focused electron-beam induced deposition. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kouwen, L.; Botman, A.; Hagen, C.W. Focused Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition of 3 nm Dots in a Scanning Electron Microscope. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2149–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavagnin, M.; Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Belić, D.; Bertagnolli, E. Synthesis of Individually Tuned Nanomagnets for Nanomagnet Logic by Direct Write Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoric, L.; Sanz-Hernández, D.; Meng, F.; Donnelly, C.; Merino-Aceituno, S.; Fernández-Pacheco, A. Layer-by-Layer Growth of Complex-Shaped Three-Dimensional Nanostructures with Focused Electron Beams. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, R.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Rack, P.D.; Kothleitner, G.; Plank, H. Shape evolution and growth mechanisms of 3D-printed nanowires. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102076. [Google Scholar]
- Riazanova, A.V.; Costanzi, B.N.; Aristov, A.; Rikers, Y.G.M.; Ström, V.; Mulders, J.J.L.; Kabashin, A.V.; Dahlberg, E.D.; Belova, L.M. Gas-assisted electron-beam-induced nanopatterning of high-quality Si-based insulator. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 155301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Li, C.; Baumier, C.; Kasumov, A.; Guéron, S.; Bouchiat, H.; Fortuna, F. Superconducting nanowires by electron-beam-induced deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 042601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utke, I.; Hoffmann, P.; Berger, R.; Scandella, L. High-resolution magnetic Co supertips grown by a focused electron beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabureac, M.; Bernau, L.; Utke, I.; Boero, G. Granular Co-C nano-Hall sensors by focused-beam-induced deposition. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Graells, S.; Aćimović, S.; Volpe, G.; Quidant, R. Direct Growth of Optical Antennas Using E-Beam-Induced Gold Deposition. Plasmonics 2010, 5, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; de Teresa, J.M.; Córdoba, R.; Ibarra, M.R. Magnetotransport properties of high-quality cobalt nanowires grown by focused-electron-beam-induced deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeguchi, M.; Shimojo, M.; Furuya, K. Fabrication of magnetic nanostructures using electron beam induced chemical vapour deposition. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrijsen, R.; Córdoba, R.; Schoenaker, F.J.; Ellis, T.H.; Barcones, B.; Kohlhepp, J.T.; Swagten, H.J.M.; Koopmans, B.; de Teresa, J.M.; Magén, C.; et al. Fe:O:C grown by focused-electron-beam-induced deposition: Magnetic and electric properties. Nanotechnology 2010, 22, 025302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parentes, A.; Sinicco, G.; Boero, G.; Dwir, B.; Hoffmann, P. Focused electron beam induced deposition of nickel. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2007, 25, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, R.; Barcones, B.; Roelfsema, E.; Verheijen, M.A.; Mulders, J.J.L.; Trompenaars, P.H.F.; Koopmans, B. Functional nickel-based deposits synthesized by focused beam induced processing. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 065303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikulina, E.; Idigoras, O.; Porro, J.M.; Vavassori, P.; Chuvilin, A.; Berger, A. Origin and control of magnetic exchange coupling in between focused electron beam deposited cobalt nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 123112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Belic, D.; Shawrav, M.M.; Persson, A.; Gunnarsson, K.; Svedlindh, P.; Bertagnolli, E. Magnetic force microscopy study of shape engineered FEBID iron nanostructures. Phys. Status Solidi A 2014, 211, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; de Teresa, J.M. Present and future applications of magnetic nanostructures grown by FEBID. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar]
- De Teresa, J.M.; Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Córdoba, R.; Serrano-Ramón, L.; Sangiao, S.; Ibarra, M.R. Review of magnetic nanostructures grown by focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 243003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Skoric, L.; de Teresa, J.M.; Pablo-Navarro, J.; Huth, M.; Dobrovolskiy, O.V. Writing 3D Nanomagnets Using Focused Electron Beams. Materials 2020, 13, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Donnelly, C.; Skoric, L.; Hierro-Rodriguez, A.; Liao, J.-W.; Fernández-Pacheco, A. Fabrication of a 3D Nanomagnetic Circuit with Multi-Layered Materials for Applications in Spintronics. Micromachines 2021, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magén, C.; Pablo-Navarro, J.; de Teresa, J.M. Focused-Electron-Beam Engineering of 3D Magnetic Nanowires. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavagnin, M.; Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Wachter, S.; Shawrav, M.M.; Persson, A.; Gunnarsson, K.; Svedlindh, P.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Bertagnolli, E. Free-Standing Magnetic Nanopillars for 3D Nanomagnet Logic. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20254–20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Belova, L.M.; McMichael, R.D. Spectroscopy and Imaging of Edge Modes in Permalloy Nanodisks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 017601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; van Mourik, R.A.; Yin, Y.; Koopmans, B.; Parkin, S.S.P. Focused-electron-beam-induced-deposited cobalt nanopillars for nanomagnetic logic. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 165301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskiy, O.V.; Begun, E.; Huth, M.; Shklovskij, V.A.; Tsindlekht, M.I. Vortex lattice matching effects in a washboard pinning potential induced by Co nanostripe arrays. Phys. C Supercond. Appl. 2011, 471, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavassori, P.; Pancaldi, M.; Perez-Roldan, M.J.; Chuvilin, A.; Berger, A. Remote Magnetomechanical Nanoactuation. Small 2016, 12, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafar, M.; Pablo-Navarro, J.; Berganza, E.; Ares, P.; Magén, C.; Masseboeuf, A.; Gatel, C.; Snoeck, E.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; de Teresa, J.M.; et al. Customized MFM probes based on magnetic nanorods. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 10090–10097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berganza, E.; Jaafar, M.; Fernandez-Roldan, J.A.; Goiriena-Goikoetxea, M.; Pablo-Navarro, J.; García-Arribas, A.; Guslienko, K.; Magén, C.; de Teresa, J.M.; Chubykalo-Fesenko, O.; et al. Half-hedgehog spin textures in sub-100 nm soft magnetic nanodots. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 18646–18653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiat, H.; Rossi, N.; Gross, B.; Pablo-Navarro, J.; Magén, C.; Badea, R.; Berezovsky, J.; de Teresa, J.M.; Poggio, M. Nanowire Magnetic Force Sensors Fabricated by Focused-Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 13, 044043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, N.; Gross, B.; Dirnberger, F.; Bougeard, D.; Poggio, M. Magnetic Force Sensing Using a Self-Assembled Nanowire. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidles, J.A.; Garbini, J.L.; Bruland, K.J.; Rugar, D.; Züger, O.; Hoen, S.; Yannoni, C.S. Magnetic resonance force microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1995, 67, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakova, O.; Puttock, R.; Barton, C.; Corte-León, H.; Jaafar, M.; Neu, V.; Asenjo, A. Frontiers of magnetic force microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 060901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ares, P.; Jaafar, M.; Gil, A.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Asenjo, A. Magnetic Force Microscopy in Liquids. Small 2015, 11, 4731–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belova, L.M.; Hellwig, O.; Dobisz, E.; Dahlberg, E.D. Rapid preparation of electron beam induced deposition Co magnetic force microscopy tips with 10 nm spatial resolution. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 093711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koblischka, M.R.; Hartmann, U.; Sulzbach, T. Improving the lateral resolution of the MFM technique to the 10 nm range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272–276, 2138–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Freire, Ó.; Jaafar, M.; Berganza, E.; Asenjo, A. Customized MFM probes with high lateral resolution. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román García, E.L.; Martínez-Orellana, L.; Díaz Lagos, M.; Huttel, Y. Modification of Atomic Force Microscopy Tips by Deposition of Nanoparticles with an Aggregate Source. Patent WO/2011/141602, 4 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Amos, N.; Ikkawi, R.; Haddon, R.; Litvinov, D.; Khizroev, S. Controlling multidomain states to enable sub-10-nm magnetic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 203116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, H.; Uzumaki, T.; Yasutake, M.; Tanaka, A.; Akinaga, H.; Yokoyama, H. A magnetic force microscope using CoFe-coated carbon nanotube probes. Nanotechnology 2004, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tang, J.; Kato, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L.C.; Woodson, M.; Liu, J.; Kim, J.W.; Littlehei, P.T.; Park, C.; et al. Magnetic nanowire based high resolution magnetic force microscope probes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, H.; Jaafar, M.; Llobet, J.; Esteve, J.; Vázquez, M.; Asenjo, A.; del Real, R.P.; Plaza, J.A. Nanomagnets with high shape anisotropy and strong crystalline anisotropy: Perspectives on magnetic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 505301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.M.; Chee, P.C.; Thong, J.T.L.; Ng, V. Properties and applications of cobalt-based material produced by electron-beam-induced deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2002, 20, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alotaibi, S.; Samba, J.; Pokharel, S.; Lan, Y.; Uradu, K.; Afolabi, A.; Unlu, I.; Basnet, G.; Aslan, K.; Flanders, B.N.; et al. Individually grown cobalt nanowires as magnetic force microscopy probes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 092401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiller, M.; Barzola-Quiquia, J.; Esquinazi, P.D.; Sangiao, S.; de Teresa, J.M.; Meijer, J.; Abel, B. Functionalized Akiyama tips for magnetic force microscopy measurements. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 125401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, H.; Winkler, R.; Schwalb, C.H.; Hütner, J.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Rack, P.D.; Utke, I.; Huth, M. Focused Electron Beam-Based 3D Nanoprinting for Scanning Probe Microscopy: A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, M.; Lobo, C.; Friedli, V.; Szkudlarek, A.; Utke, I. Continuum models of focused electron beam induced processing. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1518–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pablo-Navarro, J. Development and Optimization of 3D Advanced Functional Magnetic Nanostructures Grown by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pablo-Navarro, J.; Magén, C.; de Teresa, J.M. Three-dimensional core-shell ferromagnetic nanowires grown by focused electron beam induced deposition. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 285302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Navarro, J.; Sanz-Hernández, D.; Magén, C.; Fernández-Pacheco, A.; de Teresa, J.M. Tuning shape, composition and magnetization of 3D cobalt nanowires grown by focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 18LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, R.; Sesé, J.; de Teresa, J.M.; Ibarra, M.R. High-purity cobalt nanostructures grown by focused-electron-beam-induced deposition at low current. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernau, L.; Gabureac, M.; Erni, R.; Utke, I. Tunable Nanosynthesis of Composite Materials by Electron-Impact Reaction. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9064–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Navarro, J.; Winkler, R.; Haberfehlner, G.; Magén, C.; Plank, H.; de Teresa, J.M. In situ real-time annealing of ultrathin vertical Fe nanowires grown by focused electron beam induced deposition. Acta Mater. 2019, 174, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, M.; Takeguchi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Mitsuishi, K.; Furuya, K. Electron beam-induced deposition using iron carbonyl and the effects of heat treatment on nanostructure. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 1869–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P.; Neu, V.; Havlíček, M.; Puttock, R.; Kazakova, O.; Hu, X.; Zajíčková, L. Determination of tip transfer function for quantitative MFM using frequency domain filtering and least squares method. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rack, P.D.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Randolph, S.J. In situ probing of the growth and morphology in electron-beam-induced deposited nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 465602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AsdWolf, D.; Rodriguez, L.A.; Béché, A.; Javon, E.; Serrano, L.; Magen, C.; Gatel, C.; Lubk, A.; Lichte, H.; Bals, S.; et al. 3D Magnetic Induction Maps of Nanoscale Materials Revealed by Electron Holographic Tomography. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6771–6778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Manipulating and trapping skyrmions by magnetic field gradients. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 083008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pérez, R. Dynamic atomic force microscopy methods. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 197–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachser, R.; Hütner, J.; Schwalb, C.H.; Huth, M. Granular Hall Sensors for Scanning Probe Microscopy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hammel, P.C.; Wigen, P.E. Observation of ferromagnetic resonance in a microscopic sample using magnetic resonance force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O.; de Loubens, G.; Naletov, V.V.; Boust, F.; Guillet, T.; Hurdequint, H.; Leksikov, A.; Slavin, A.N.; Tiberkevich, V.S.; Vukadinovic, N. Ferromagnetic resonance force spectroscopy of individual submicron-size samples. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 144410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, H.-J.; Guo, F.; Belova, L.M.; McMichael, R.D. Nanoscale Spin Wave Localization Using Ferromagnetic Resonance Force Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 087206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangiao, S.; Magén, C.; Mofakhami, D.; de Loubens, G.; de Teresa, J.M. Magnetic properties of optimized cobalt nanospheres grown by focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID) on cantilever tips. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pablo-Navarro, J.; Sangiao, S.; Magén, C.; de Teresa, J.M. Magnetic Functionalization of Scanning Probes by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition Technology. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7100140
Pablo-Navarro J, Sangiao S, Magén C, de Teresa JM. Magnetic Functionalization of Scanning Probes by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition Technology. Magnetochemistry. 2021; 7(10):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7100140
Chicago/Turabian StylePablo-Navarro, Javier, Soraya Sangiao, César Magén, and José María de Teresa. 2021. "Magnetic Functionalization of Scanning Probes by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition Technology" Magnetochemistry 7, no. 10: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7100140
APA StylePablo-Navarro, J., Sangiao, S., Magén, C., & de Teresa, J. M. (2021). Magnetic Functionalization of Scanning Probes by Focused Electron Beam Induced Deposition Technology. Magnetochemistry, 7(10), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry7100140