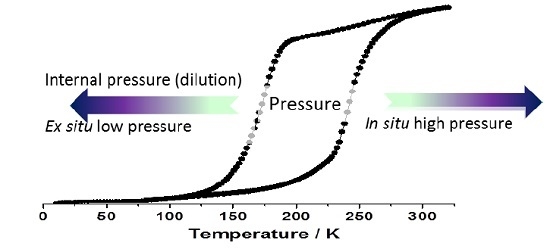
Effects of Internal and External Pressure on the [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2] Spin-Crossover Compound (with PM-PEA = N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. External Pressure on [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2]
2.1.1. SCO at High-Pressure
2.1.2. Ex situ Pressure Effects
2.2. Internal Pressure
2.2.1. Synthesis
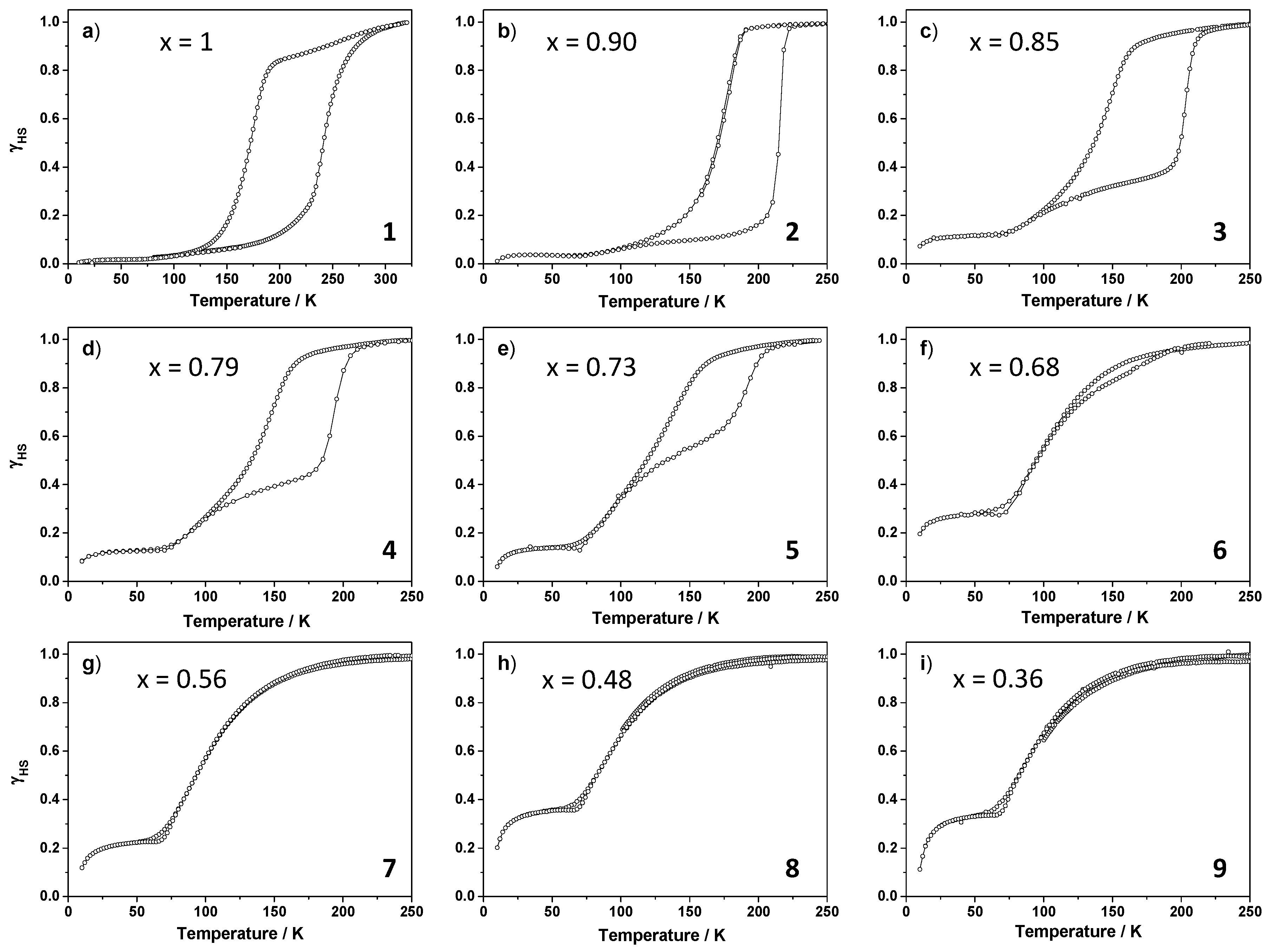
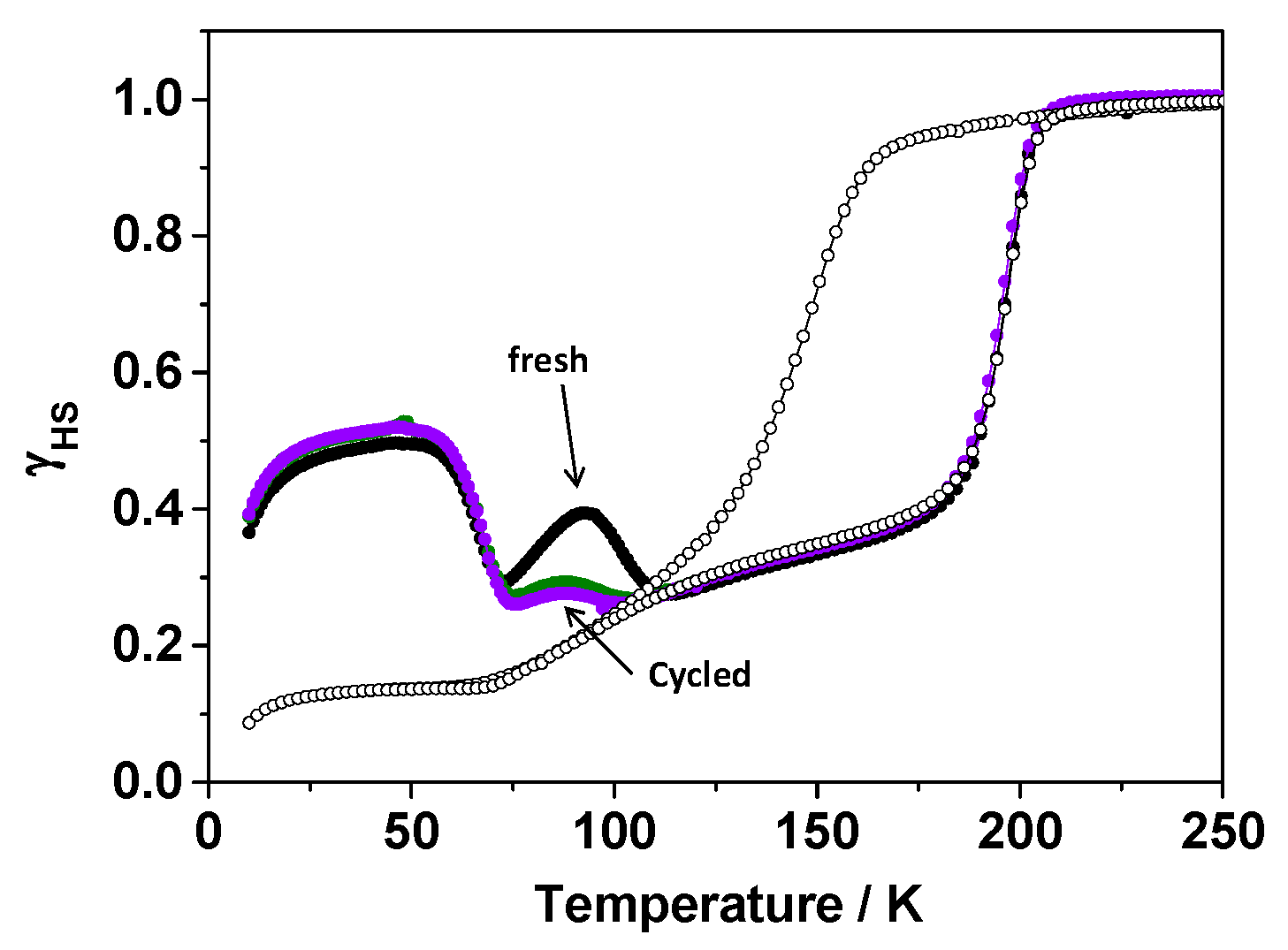
2.2.2. Magnetic Properties
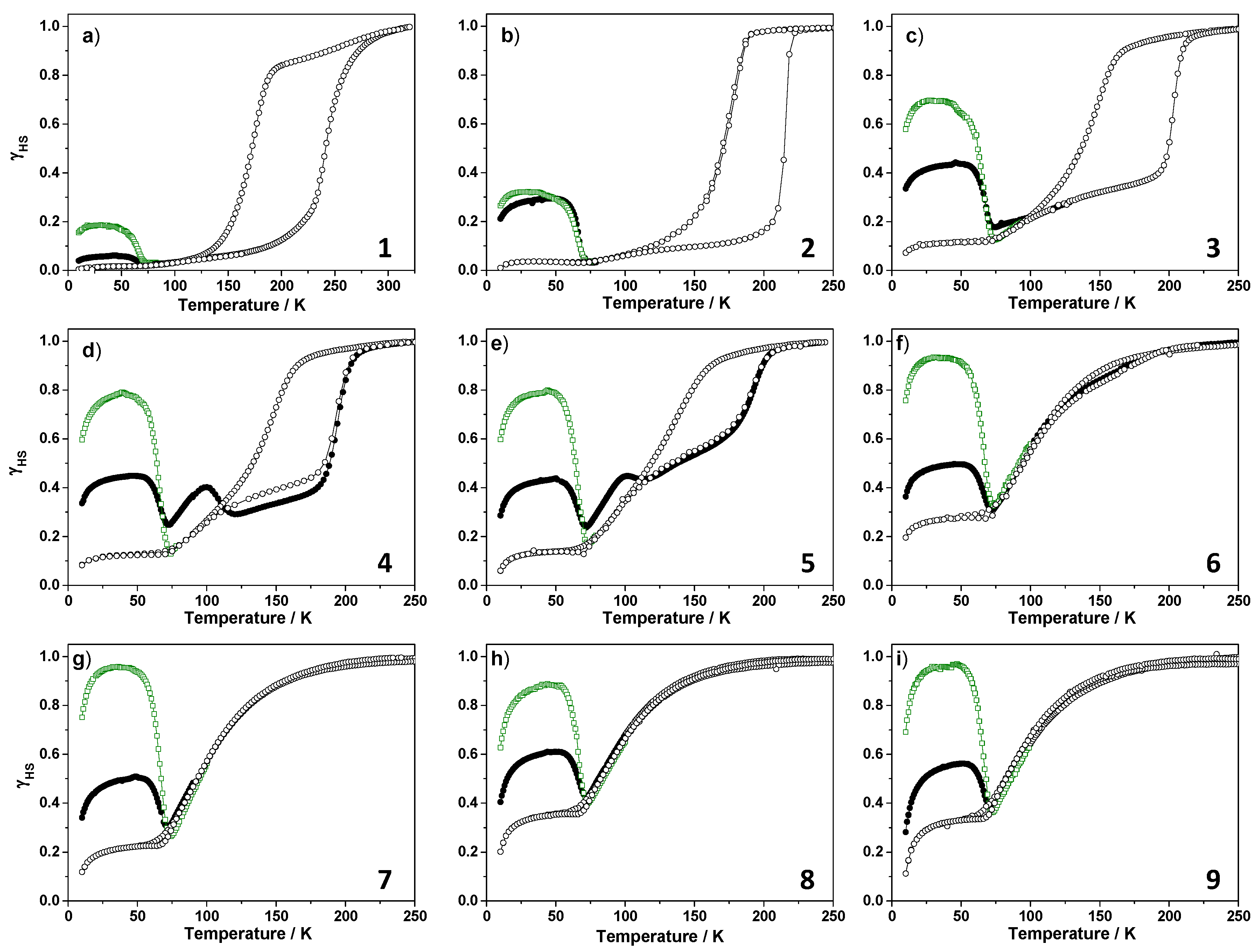
2.2.3. T(LIESST) and T(TIESST) versus Internal Pressure
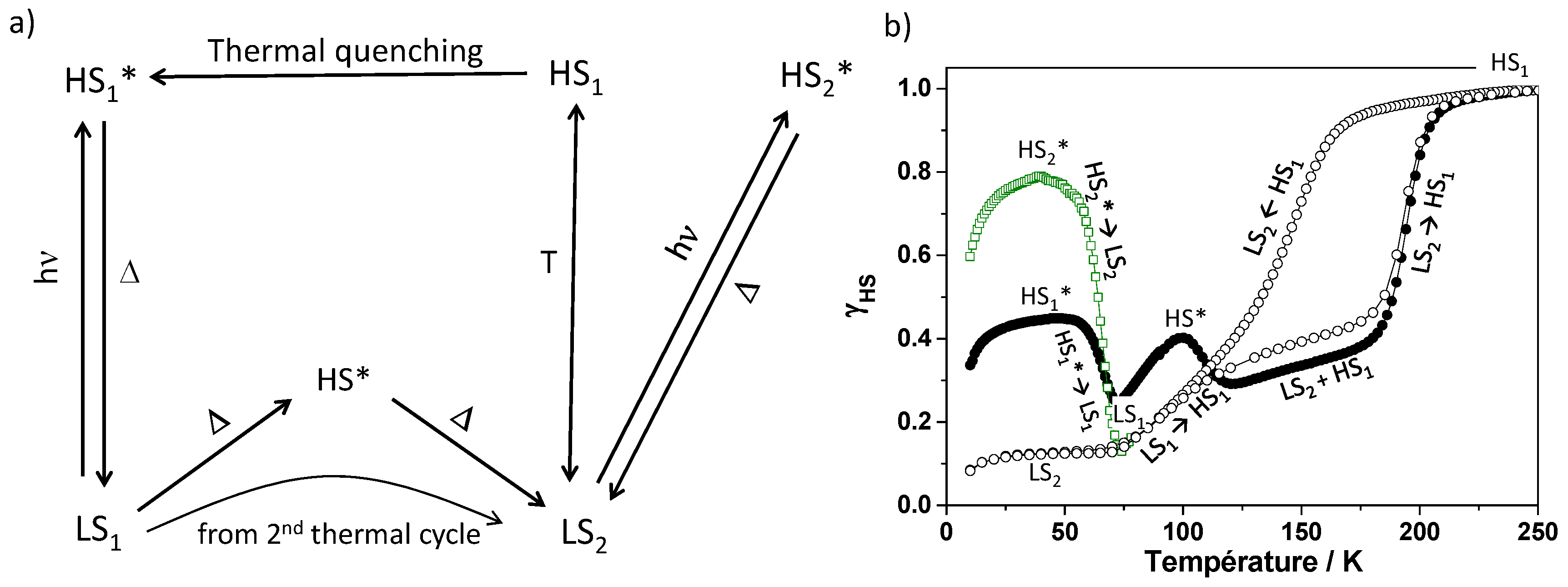
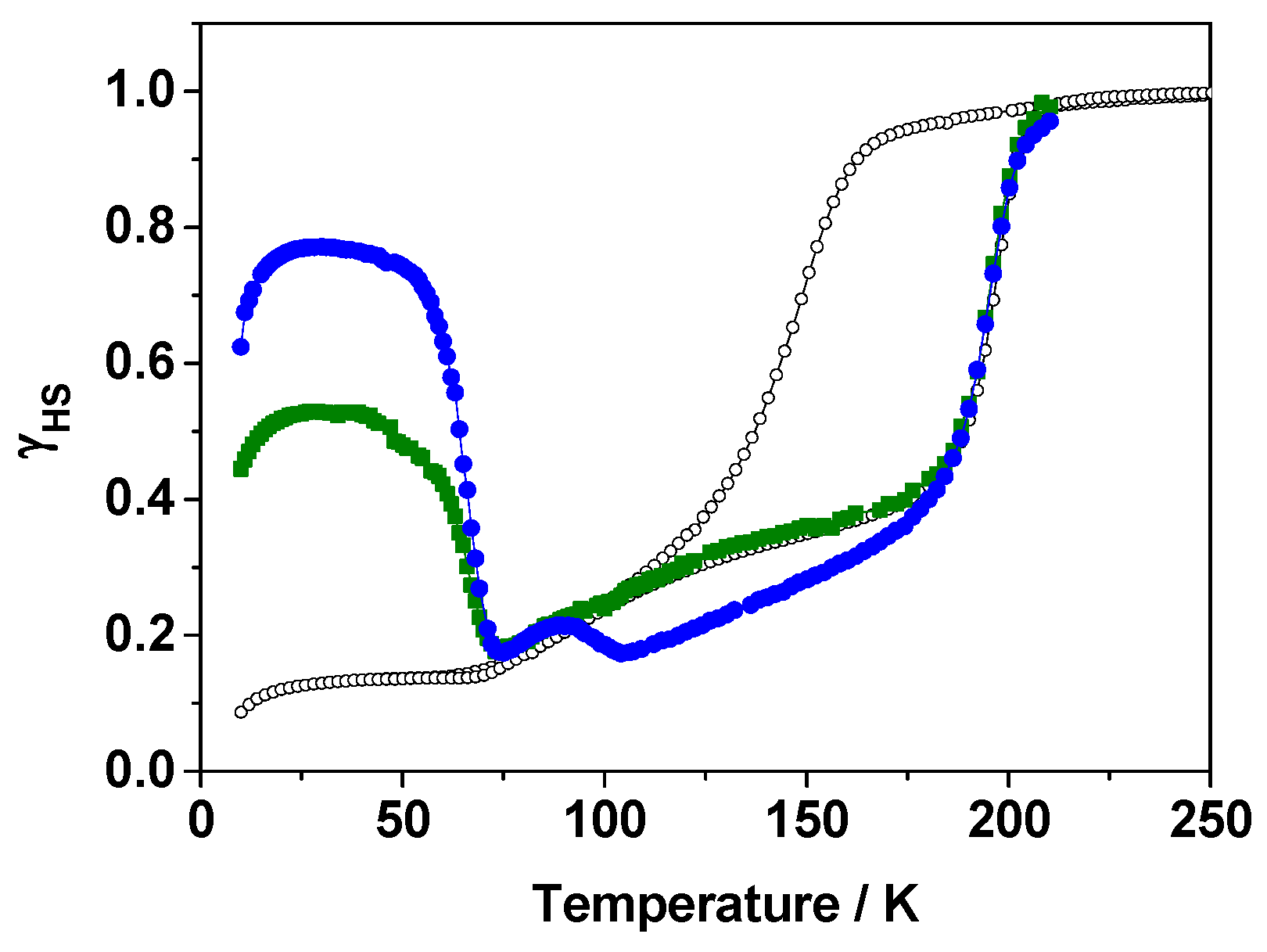
2.2.4. Focus on the Thermally-Quenched Metastable-State
3. Experimental Section
4. Physical Measurements
5. External Pressure Investigated by Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tidey, J.; Wong, L.S.; Schröder, M.; Blake, A. Structural chemistry of metal coordination complexes at high pressure. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 227–278, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perutz, M.F.; Kilmartin, J.V.; Nagai, K.; Szabo, A.; Simon, S.R. Influence of globin structures on the state of the heme: Ferrous low spin derivatives. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, G.; Drickamer, H.G. The effect of high pressure upon proteins and other biomolecules. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1983, 16, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Primo, C.; Deprez, E.; Hoa, G.H.B.; Douzou, P. Antagonistic effects of hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure on cytochrome P-450cam spin transition. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 2056–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGammon, C.; Kantor, I.; Narygina, O.; Rouquette, J.; Ponkratz, U.; Sergueev, I.; Mezouar, M.; Prakapenka, V.; Dubrovinsky, L. Stable intermediate-spin ferrous iron in lower-mantle perovskite. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 684–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, S. A theory of the pressure-induced high-spin—Low-spin transition of transition-metal oxides. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 1978, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksenofontov, V.; Gaspar, A.B.; Gütlich, P. Pressure effect studies on spin crossover and valence tautomeric systems. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds III; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H.A., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 235, pp. 23–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gütlich, P.; Gaspar, A.B.; Ksenofontov, V.; Garcia, Y. Pressure effect studies in molecular magnetism. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, S1087–S1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhommeau, S.; Molnár, G.; Goiran, M.; Boukheddaden, K.; Bousseksou, A. Theoretical study of the effect of an intense and pulsed magnetic field and a pressure pulse on the spin crossover complex Fe(phen)2(NCS)2. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 064424/1–064424/8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, C.; Zarembowitch, J.; Itié, J.P.; Polian, A.; Verdaguer, M. Pressure-induced spin-state crossovers in six-coordinate FeIILnL′m(NCS)2 complexes with L = L′ and L ≠ L′: A XANES investigation. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Goux-Capes, L. Towards spin crossover applications. In Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds III; Gütlich, P., Goodwin, H.A., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 235, pp. 221–249. [Google Scholar]
- Slichter, C.P.; Drickamer, H.G. Pressure-induced electronic changes in compounds of iron. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 2142–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoleriu, L.; Chakraborty, P.; Hauser, A.; Stancu, A.; Enachescu, C. Thermal hysteresis in spin-crossover compounds studied within the mechanoelastic model and its potential application to nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 134102/1–134102/9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P.; Collet, E. Piezo- and Photo-Crystallography Applied to Spin-Crossover Materials. In Spin-Crossover Materials: Properties and Applications; Halcrow, M.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 508–526. [Google Scholar]
- König, E.; Ritter, G.; Waigel, J.; Goodwin, H.A. The effect of pressure on the thermal hysteresis of the first-order spin transition in bis(1,10-phenanthroline-2-carbaldehyde phenylhydrazone) iron(II) complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilágyi, P.A.; Dorbes, S.; Molnár, G.; Real, J.A.; Homonnay, Z.; Faulmann, C.; Bousseksou, A. Temperature and pressure effects on the spin state of ferric ions in the [Fe(sal2-trien)][Ni(dmit)2] spin crossover complex. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2008, 69, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksenofontov, V.; Levchenko, G.; Spiering, H.; Gütlich, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Bouhedja, Y.; Kahn, O. Spin crossover behavior under pressure of Fe(PM-L)2(NCS)2 compounds with substituted 2′-pyridylmethylene 4-anilino ligands. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 294, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargeron, C.B.; Drickamer, H.G. Effect of pressure on the electronic structure of complexes of ferrous iron with substituted phenanthrolines. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 7, 3471–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Hutchinson, B.B. Spin equilibrium in iron(II) poly(1-pyrazolyl)borate complexes: Low-temperature and high-pressure Mössbauer spectral studies. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, Y.; Ksenofontov, V.; Levchenko, G.; Schmitt, G.; Gütlich, P. Pressure-induced high spin state in [Fe(btr)2(NCS)2]·H2O (btr = 4,4′-bis-1,2,4-triazole). J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 5045–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, P.; Gütlich, P.; Müller, E.W. Effect of metal dilution on the spin-crossover behavior in [FexM1−x(phen)2(NCS)2] (M = Mn, Co, Ni, Zn). Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 3429–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.S.; Federer, W.D.; Lynch, M.W.; Hendrickson, D.N. An explanation of unusual properties of spin-crossover ferric complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.S.; Federer, W.D.; Lynch, M.W.; Hendrickson, D.N. Spin-crossover ferric complexes: Unusual effects of grinding and doping solids. Inorg. Chem. 1981, 20, 131–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, V.; Fernàndes, J.R. An infrared spectroscopy study of the low-spin-high-spin transition in [FexM1−x(phen)2(NCS)2]. A composition-induced change in the order of the spin-state transition. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 167, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.-P.; Zarembowitch, J.; Dworkin, A.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Varret, F. Solid-state effects in spin transitions: Influence of iron(II) dilution on the magnetic and calorimetric properties of the series [FexNi1−x(4,4′-bis(1,2,4-triazole))2(NCS)2].cntdot.H2O. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 2617–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.-P.; Zarembowitch, J.; Bousseksou, A.; Dworkin, A.; Haasnoot, J.G.; Varret, F. Solid state effects on spin transitions: Magnetic, calorimetric, and Mossbauer-effect properties of [FexCo1−x(4,4′-bis(1,2,4-triazole))2(NCS)2].cntdot.H2O mixed-crystal compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 6325–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.; Desplanches, C.; Gütlich, P.; Freysz, E.; Létard, J.-F. Effect of the metal dilution on the thermal and light-induced spin transition in [FexMn1−x(bpp)2](NCSe)2: When T(LIESST) reaches T1/2. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2008, 361, 3529–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.; Desplanches, C.; Nguyen, O.; Létard, J.-F. Complete temperature study of the relaxation from HS to LS state in mixed [FexZn1−x(phen)2(NCS)2] systems (with x = 1, 0.73, 0.5, 0.32, 0.19, 0.04). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 148, 012026/1–012026/9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Light-induced spin-crossover and the high spin → low spin relaxation. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 234, 155–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, A.; Enachescu, C.; Daku, M.L.; Vargas, A.; Amstutz, N. Low-temperature lifetimes of metastable high-spin states in spin-crossover and in low-spin iron(II) compounds: The rule and exceptions to the rule. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Intersystem crossing in Fe(II) coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1991, 111, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descurtins, S.; Gütlich, P.; Köhler, C.P.; Spiering, H.; Hauser, A. Light-induced excited spin state trapping in a transition-metal complex: The hexa-1-propyltetrazole-iron(II) tetrafluoroborate spin-crossover system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 105, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Rabardel, L.; Howard, J.A.K.; Goeta, A.E.; Chasseau, D.; Kahn, O. Structural, magnetic and photomagnetic studies of a mononuclear iron(II) derivative exhibiting an exceptionally abrupt spin transition. Light induced thermal hysteresis phenomenon. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 4432–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Létard, J.-F.; Capes, L.; Chastanet, G.; Moliner, N.; Létard, S.; Real, J.A.; Kahn, O. Critical temperature of the LIESST effect in iron(II) spin-crossover compounds. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 313, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Chastanet, G.; Guionneau, P.; Desplanches, C. Optimising the stability of trapped metastable spin states. In Spin-Crossover Materials—Properties and Applications; Halcrow, M.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 475–506. [Google Scholar]
- Baldé, C.; Desplanches, C.; Wattiaux, A.; Guionneau, P.; Gütlich, P.; Létard, J.-F. Effect of metal dilution on the light-induced spin transition in [FexZn1−x(phen)2(NCS)2] (phen = 1,10-phenanthhroline). Dalton Trans. 2008, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldé, C.; Desplanches, C.; Grunert, M.; Wei, Y.; Gütlich, P.; Létard, J.-F. Influence of metal dilution on the light-induced spin transition in two 1D chain compounds: [FexZn1−x(btzp)3](BF4)2 and [FexZn1−x(endi)3](BF4)2 {btzp = 1,2-bis(tetrazol-1-yl)propane and endi = 1,2-Bis(tetrazol-1-yl)ethane}. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 5382–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, N.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.-F. When stable and metastable HS states meet in spin-crossover compounds. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 3618–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, N.; Chastanet, G.; Varret, F.; Létard, J.-F. Metal dilution of cooperative spin-crossover compounds: When stable and metastable high-spin states meet. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, N.; Chastanet, G.; Palamarciuc, T.; Rosa, P.; Varret, F.; Boukheddaden, K.; Létard, J.-F. Detailed investigation of the interplay between the thermal decay of the low temperature metastable HS state and the thermal hysteresis of spin-crossover solids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 20039–20050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P.; Codjovi, E.; Lavastre, O.; Bravic, G.; Chasseau, D.; Kahn, O. Wide thermal hysteresis for mononuclear spin-crossover compound cis-bis(thiocyanato)bis[N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline] iron(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10861–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P.; Le Gac, F.; Lakhoufi, S.; Kaiba, A.; Chasseau, D.; Létard, J.-F.; Négrier, P.; Mondieg, D.; Howard, J.A.K.; Léger, J.-M. X-ray diffraction investigation of a spin-crossover hysteresis loop. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 326211/1–326211/11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P. Crystallography and spin-crossover. A view of breathing materials. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gac, F.; Guionneau, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Rosa, P. The Zn polymorphic analogues of the [Fe(PM–PEA)2(NCS)2] spin-transition compound. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2008, 361, 3519–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, V.; Pechev, S.; Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P. Synergy between polymorphism, pressure, spin-crossover and temperature in [Fe(PM-BiA)2(NCS)2]: A neutron powder diffraction investigation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13872–13880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbeuf, A.; Matar, S.F.; Négrier, P.; Kabalan, L.; Létard, J.-F.; Guionneau, P. Molecular dynamics of spin crossover: The (P, T) phase diagram of [Fe(PM-BIA)2(NCS)2]. Chem. Phys. 2013, 420, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftic, J.; Menéndez, N.; Wack, A.; Codjovi, E.; Linarès, J.; Goujon, A.; Hamel, G.; Klotz, S.; Syfosse, G.; Varret, F. Helium gas pressure apparatus with optical reflectivity detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchivie, M.; Guionneau, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Chasseau, D. Towards direct correlations between spin-crossover and structural features in iron(II) complexes. Acta Cryst. B 2003, 59, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Létard, J.-F.; Kollmansberger, M.; Carbonera, C.; Marchivie, M.; Guionneau, P. Structural, magnetic and photomagnetic study of the [Fe(PM-NEA)2(NCS)2] spin crossover complex. C. R. Chim. 2008, 11, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow, M.A. Structure: Function relationships in molecular spin-crossover complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4119–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatruk, M.; Phan, H.; Chrisostomo, B.A.; Suleimenova, A. Symmetry-breaking structural phase transitions in spin crossover complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289–290, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bail, A. Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: A retrospection. Powder Diffr. 2005, 20, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 1976, 35, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchivie, M.; Guionneau, P.; Letard, J.-F.; Chasseau, D.; Howard, J.A.K. Thermal trapped iron(II) high spin state investigated by X-ray diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2004, 65, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelleteret, D.; Clérac, R.; Mathonière, C.; Harté, E.; Schmitt, W.; Kruger, P.E. Asymmetric spin crossover behaviour and evidence of light-induced excited spin state trapping in a dinuclear iron(II) helicate. Chem. Commun. 2009, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yufit, D.S.; Howard, J.A.K. Simple pressure cell for single-crystal X-ray crystallography. J. Appl. Cryst. 2005, 38, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guionneau, P.; Lepevelen, D.; Marchivie, M.; Pechev, S.; Gaultier, J.; Barrans, Y.; Chasseau, D. Laboratory high-pressure single-crystal X-ray diffraction—Recent improvements and examples of studies. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2004, 16, 1129–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
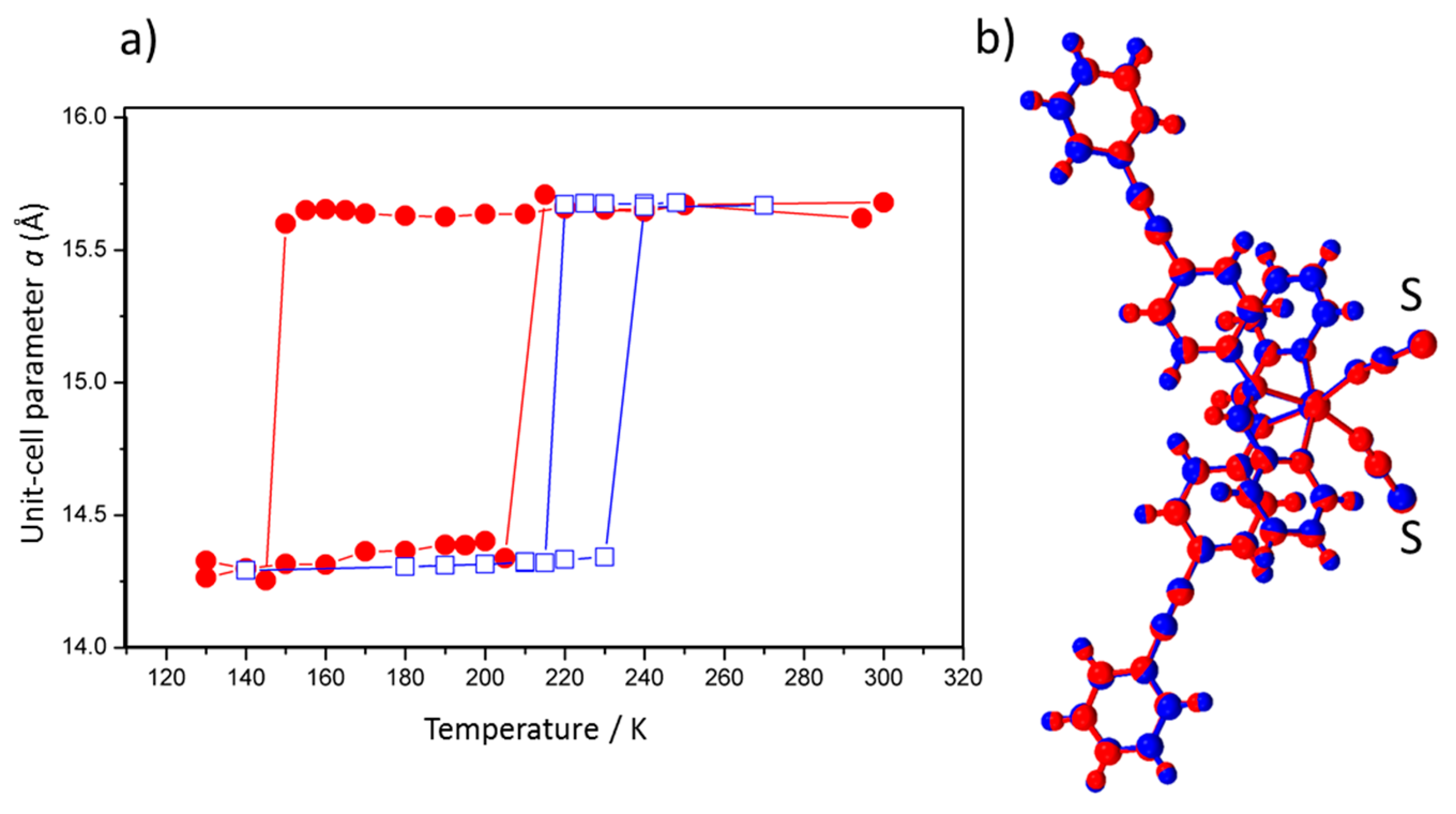
| In situ Pressure (MPa) | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | β | V (Å3) | Crystal System |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 15.659 | 14.482 | 16.844 | 93.00 | 3814 | monoclinic |
| 150 | 15.624 | 14.315 | 16.746 | 92.97 | 3740 | monoclinic |
| 248 | 15.621 | 14.116 | 16.716 | 92.94 | 3681 | monoclinic |
| 365 | 15.605 | 13.968 | 16.622 | 92.81 | 3619 | monoclinic |
| 465 | 14.356 | 13.850 | 17.415 | 90 | 3462 | orthorhombic |
| 658 | 14.147 | 14.147 | 17.119 | 90 | 3426 | orthorhombic |
| 1135 | 14.099 | 13.687 | 17.032 | 90 | 3287 | orthorhombic |
| Pressure (MPa) | 55 in situ | 20 ex situ | 80 ex situ | 110 ex situ | 200 ex situ | 0.001 ex situ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | 15.652(5) | 15.653(1) | 15.668(1) | 15.688(5) | 15.6600(6) | 15.645(1) |
| b (Å) | 14.434(4) | 14.523(1) | 14.571(1) | 14.521(5) | 14.5380(8) | 14.555(1) |
| c (Å) | 16.785(3) | 16.825(1) | 16.869(1) | 16.841(5) | 16.8252(9) | 16.863(1) |
| β (°) | 93.053(7) | 93.011(4) | 93.114(5) | 93.163(5) | 93.066(3) | 93.161(5) |
| V (Å3) | 3786(2) | 3819.9(5) | 3845.6(4) | 3831(2) | 3825.0(3) | 3834.3(6) |
| Refl. coll. | 11749 | 25950 | 15716 | 10769 | 25950 | 21614 |
| Refl. obs. (I > 2σ) | 2441 | 3286 | 3214 | 2411 | 3286 | 4457 |
| Rint | 0.081 | 0.138 | 0.071 | 0.063 | 0.139 | 0.058 |
| Robs (all) | 0.058(0.192) | 0.058(0.111) | 0.043(0.086) | 0.052(0.101) | 0.075(0.223) | 0.054(0.115) |
| wR2obs (all) | 0.103(0.136) | 0.162(0.226) | 0.095(0.111) | 0.089(0.111) | 0.162(0.226) | 0.112(0.143) |
| RMSD | 0.0353 | 0.0299 | 0.0320 | 0.0337 | 0.0318 | 0.0312 |
| Ex situ Pressure (MPa) | 0.1 (Ambient) | 20 | 80 | 110 | 200 | 0.001 (Vacuum) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2↓ (K) | 216 | 150 | 163 | 165 | 161 | 175 |
| T1/2↑ (K) | 235 | 213 | 215 | 225 | 213 | 218 |
| ΔT (K) | 19 | 63 | 52 | 60 | 52 | 43 |
| Compound | x | T1/2↑ (K) | T1/2↓ (K) | ∆T (K) | T(LIESST) (K) | T(TIESST) (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 245 | 170 | 75 | 65 | 66 |
| 2 | 0.90 | 218 | 160 | 58 | 65 | 67 |
| 3 | 0.85 | 202 | 141 | 61 | 66 | 67 |
| 4 | 0.79 | 191 | 137 | 54 | 65 | 66 |
| 5 | 0.73 | 190 | 134 | 56 | 65 | 66 |
| 6 | 0.68 | 108 | 108 | - | 67 | 66 |
| 7 | 0.56 | 105 | 105 | - | 67 | 67 |
| 8 | 0.48 | 100 | 100 | - | 67 | 67 |
| 9 | 0.36 | 98 | 98 | - | 67 | 66 |
| 10 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paradis, N.; Le Gac, F.; Guionneau, P.; Largeteau, A.; Yufit, D.S.; Rosa, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Chastanet, G. Effects of Internal and External Pressure on the [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2] Spin-Crossover Compound (with PM-PEA = N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline). Magnetochemistry 2016, 2, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010015
Paradis N, Le Gac F, Guionneau P, Largeteau A, Yufit DS, Rosa P, Létard J-F, Chastanet G. Effects of Internal and External Pressure on the [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2] Spin-Crossover Compound (with PM-PEA = N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline). Magnetochemistry. 2016; 2(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleParadis, Nicolas, Frédéric Le Gac, Philippe Guionneau, Alain Largeteau, Dmitry S. Yufit, Patrick Rosa, Jean-François Létard, and Guillaume Chastanet. 2016. "Effects of Internal and External Pressure on the [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2] Spin-Crossover Compound (with PM-PEA = N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline)" Magnetochemistry 2, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010015
APA StyleParadis, N., Le Gac, F., Guionneau, P., Largeteau, A., Yufit, D. S., Rosa, P., Létard, J.-F., & Chastanet, G. (2016). Effects of Internal and External Pressure on the [Fe(PM-PEA)2(NCS)2] Spin-Crossover Compound (with PM-PEA = N-(2′-pyridylmethylene)-4-(phenylethynyl)aniline). Magnetochemistry, 2(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010015