Application Progress of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
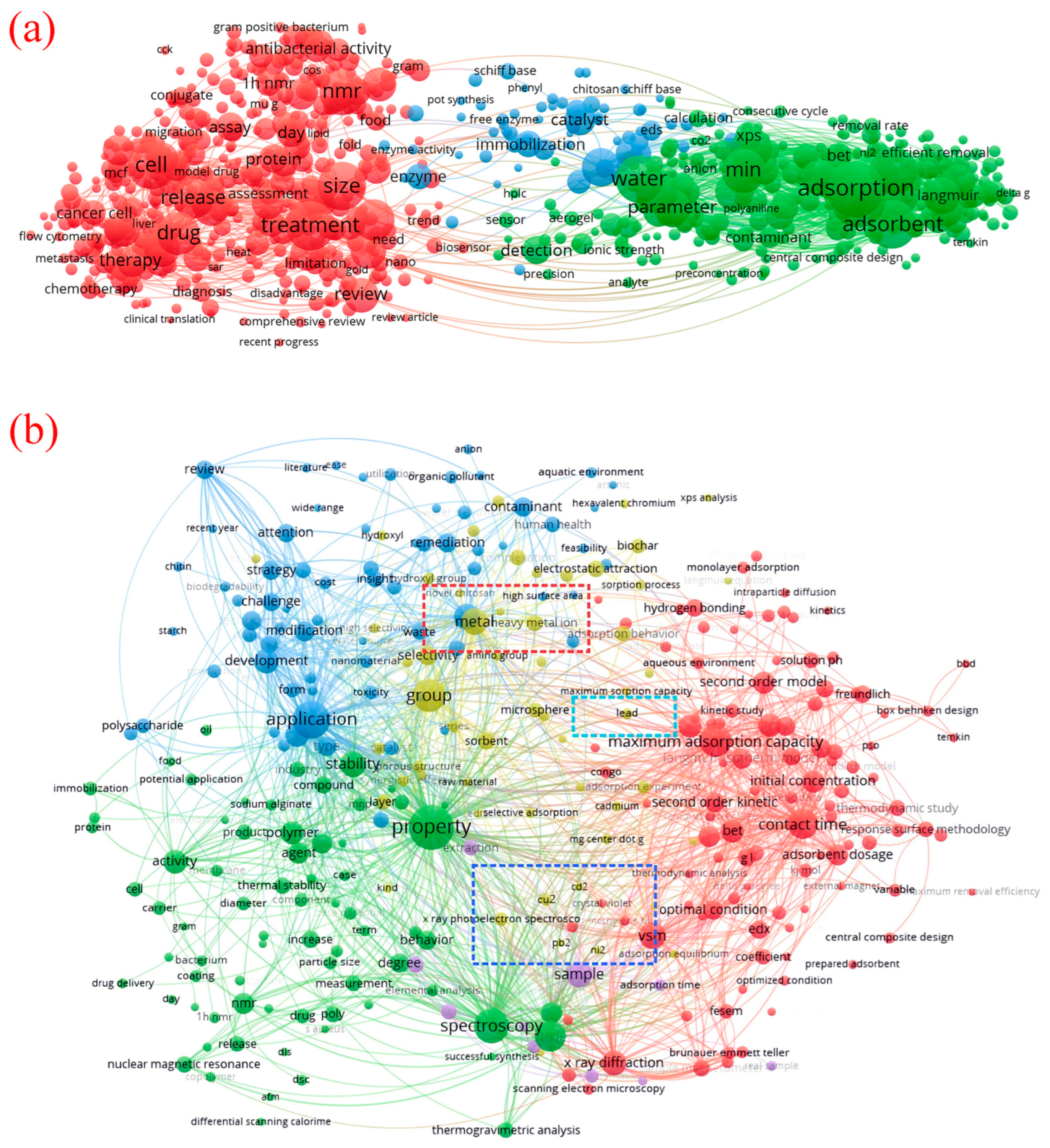
1. Introduction
2. Toxic Effects of Heavy Metals
2.1. Toxic Effects of Lead (Pb)
2.2. Toxic Effects of Mercury (Hg)
2.3. Toxic Effects of Chromium (Cr)
2.4. Toxic Effects of Other Heavy Metals
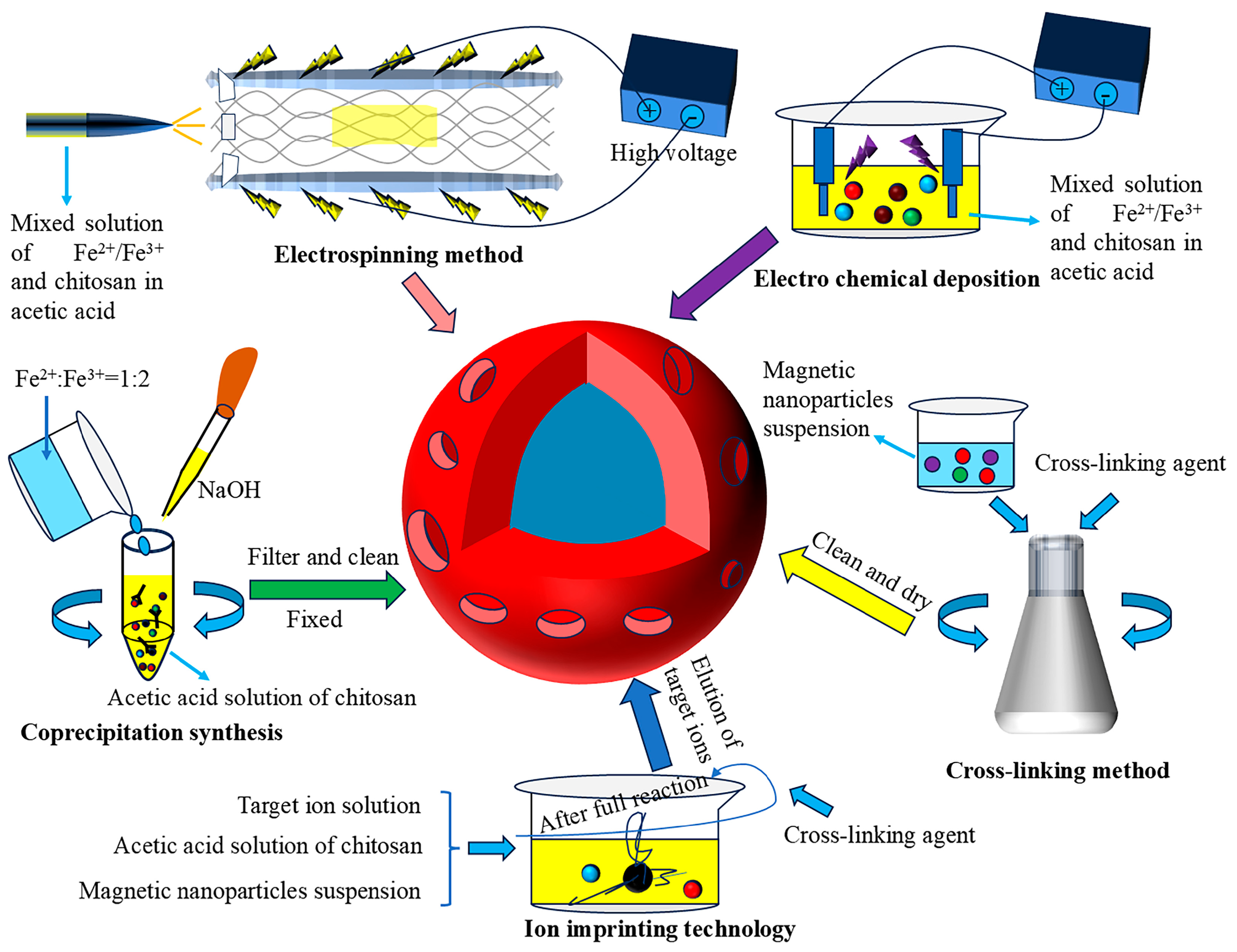
3. Preparation and Modification Technology of Magnetic Chitosan
3.1. Coprecipitation Method
3.2. Crosslinking Method
3.3. Other Preparation Modification Methods
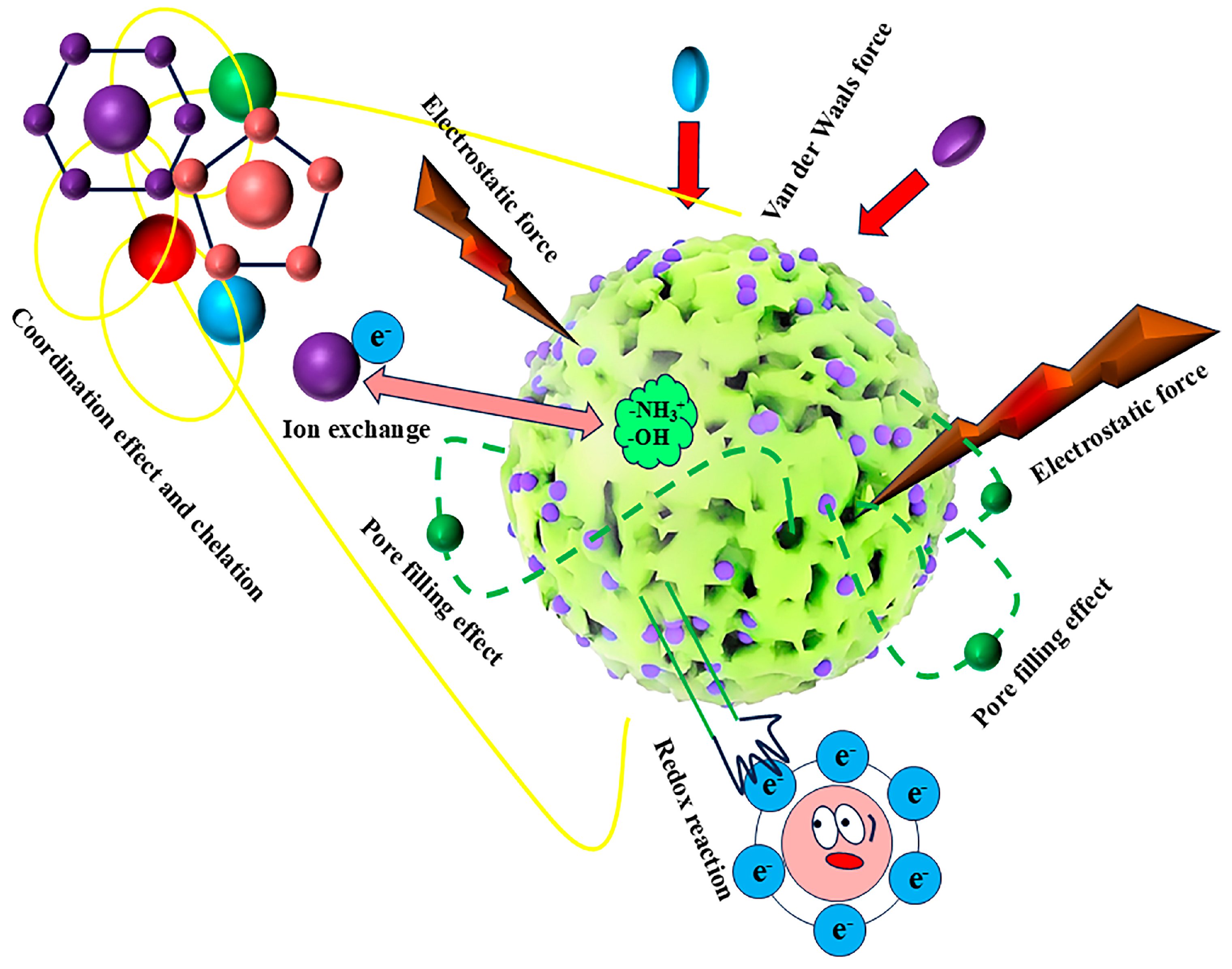
4. Adsorption Mechanism of Magnetic Chitosan
4.1. Physical Adsorption
4.2. Chemical Action
4.3. Mechanism Model and Equation
5. Study on the Application of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment
5.1. Study on the Adsorption Properties of Single Heavy Metal Ions
5.1.1. Lead (Pb2+)
5.1.2. Cadmium (Cd2+)
5.1.3. Chromium (Cr3+ and Cr6+)
5.1.4. Mercury (Hg2+)
5.1.5. Copper (Cu2+), Nickel (Ni2+) and Other Metals
5.2. Multi-Metal Ion Coexistence System
5.3. Actual Industrial Wastewater
6. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, D. Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: A review. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, V.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood-Ur-Rahman; Iqbal, M.; Ramzani, P.M.A.; Fatima, M. Promoting the productivity and quality of brinjal aligned with heavy metals immobilization in a wastewater irrigated heavy metal polluted soil with biochar and chitosan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, N.; Wu, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Xia, Y.F.; Lu, D.B.; Zhu, L.F.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Bioaccumulation of potentially toxic elements by submerged plants and biofilms: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.E.; Ali, M.H.H.; El-Sayed, S.M. Heavy metals contents in Nasser Lake and the Nile River, Egypt: An overview. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Show, P.L.; Lau, B.F.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C. New Prospects for Modified Algae in Heavy Metal Adsorption. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.M.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of heavy metals from water sources in the developing world using low-cost materials: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nompumelelo, K.S.M.; Edward, N.N.; Muthumuni, M.; Moloko, M.; Makwena, M.J. Fabrication, Modification, and Mechanism of Nanofiltration Membranes for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202300741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reta, Y.D.; Desissa, T.D.; Desalegn, Y.M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A critical review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 315, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, A.; Jayasinghe, N.; Thiviya, P.; Wasana, M.L.D.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T.; Koduru, J.R. Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katibi, K.K.; Shitu, I.G.; Othman, S.H.b.; Yunos, K.F.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Aqmar, N.A.b.N.K.; Ilias, H.M.B. Development of eco-friendly microwaved chitosan-based nanocomposite membrane for efficient capturing of cationic dyes from aqueous solution: Permeability and fouling studies. Emergent Mater. 2024, 7, 999–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Paramasivan, M. Chitosan derivatives act as a bio-stimulants in plants: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, M.; Zamani, A.; Liu, B. A review on the use of chitosan and chitosan derivatives as the bio-adsorbents for the water treatment: Removal of nitrogen-containing pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, M.W.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.J.; Han, X.G.; Fan, Z.H.; Su, G.Y.; Pan, D.; Li, Z.Y. Research progress of adsorption and removal of heavy metals by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hu, Z.Y.; Lei, X.; Wang, Y.L.; Guo, X. Fluorescent magnetic chitosan-based hydrogel incorporating Amino-Functionalized Fe3O4 and cellulose nanofibers modified with carbon dots for adsorption and detection of Cr (VI). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 658, 130673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.W.; Wu, J.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Sun, P.L.; Xiao, Z.B.; Zhao, D. Recent advances of magnetic chitosan hydrogel: Preparation, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, F.B.; Xu, K.X.; Che, Y.J.; Qi, M.Y.; Song, C. Modified magnetic chitosan materials for heavy metal adsorption: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 6713–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.C.; Zhang, G.H.; Zhu, J.F.; Wu, Z. Adsorption of heavy metal ions in water by surface functionalized magnetic composites: A review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogundade, I.; Hefnawy, M.; Ofudje, E.A.; El Gamal, A.; Emran, T.B. Pb2+ and Cd2+ removal from aqueous solutions onto calcium-phosphate hydroxyl surface: Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic investigations. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2025, 19, 2504745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.G.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; et al. Bioaccumulation of lead (Pb) and its effects on human: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.N.; Brown, D.J.; Hubbart, J.A.; Anderson, J.T. Environmental factors influencing bioaccumulation of xenobiotic metals in freshwater turtles. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2025, 37, 2474007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.F.; Yang, X.C.; Tang, Q.L.; Duan, R.; Yang, H.L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.B.; Yan, S.; Xu, R. Co-immobilization of organic and inorganic pollutants via functional magnetic hydrochar derived from potato straw: Mechanisms insight and practicality assessment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 377, 134444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.S.; Gou, C.L.; Wang, C.L.; Xue, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.S.; Liu, W.Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, J. Visible Light Accelerates Cr(III) Release and Oxidation in Cr-Fe Chromite Residues: An Overlooked Risk of Cr(VI) Reoccurrence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17674–17683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Y.; Li, K.Q.; Liao, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, H.B. Machine learning insight into the synergistic effect and influencing mechanism of iron-supporting and nitrogen-doping on Cr(VI) removal by engineered biochar. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 373, 133494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradhi, K.K.; Dasari, B.M.; Banothu, D.; Manavalan, S. Spatial distribution, sources and health risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil around oil and natural gas drilling sites, Andhra Pradesh, India. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Gutiérrez, M. Geogenic arsenic in groundwater: Challenges, gaps, and future directions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 27, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houmia, I.; Fardioui, M.; El Amri, A.; Houmia, B.; Kaibous, N.; Bazhar, K.; Hammani, O.; Arhoutane, M.R.; Guedira, T. Structural characterization and ecological evaluation of natural clay mixtures for the removal of heavy metals (Cu(II), Co(II), and Zn(II)) from aqueous solutions: Experimental study combined with RSM process optimization. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1344, 142917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.; Elanchezhiyan, S.S.D.; Saravanakumar, K.; Jagan, G.; Njaramba, L.K.; Jang, M.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.M. Synthesis of sulfur and bromine co-doped bentonite-chitosan composite hydrogels for selective adsorption of cobalt and strontium radionuclides. J. Nucl. Mater. 2025, 614, 155917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanagria, C.C.; Haddou, B.; Debab, A.; Ameri, I.; Ansar, S.; Sharma, K.; Benettayeb, A. Synthesis and Characterization of a New Clay Based Magnetic Composite Muscovite/Fe2O3/FTS for Efficient Removal of Toxic Metal Ions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025, 236, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowojuni, O.A.; Amulejoye, F.D.; Ikuesan, B.B.; Maulu, S.; Bwalya, H.; Hasimuna, O.J. Water quality, heavy metal contamination, and ecological risk assessment in Asejire reservoir, Nigeria. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2025, 40, 2516505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghipour, E.; Pakshir, M. Process optimization and modeling of Pb(II) ions adsorption on chitosan-conjugated magnetite nano-biocomposite using response surface methodology. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Garg, U.; Khan, K.U.; Azim, Y. Removal of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants Using CSFe3O4@CeO2 Nanocatalyst via Adsorption-Reduction Catalysis: A Focused Analysis on Methylene Blue. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4435–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, H.B.; Gao, Z.; Xu, L.L.; Xu, C.; Yu, D.H.; Xiang, X.R.; Huang, H.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of functional ionic liquid modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for porcine pancreatic lipase immobilization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkara, S.G.; Meena, J. Synthesis and applications of biopolymer/FeO nanocomposites: A review. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2022, 25, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Bibi, S.; Haleem, R.; Waqar, K.; Mir, S.; Maalik, A.; Sabahat, S.; Hassan, S.; Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A.; et al. Functional potential of chitosan-metal nanostructures: Recent developments and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.X.; Wang, M.H. In Situ, synthesis of chitosan fabricated tellurium nanoparticles for improved antimicrobial and anticancer applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.F.; Ao, Z.F.; Niu, X.R.; Dong, J.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Wu, H. Facile one-step synthesis of 3D honeycomb-like porous chitosan bead inlaid with Mn-Fe bimetallic oxide nanoparticles for enhanced degradation of dye pollutant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.X.; Foley, S.R.; Wilson, L.D. Cross-linked chitosan as biomacromolecular adsorbents for adsorption of precious metal-chloride complexes from aqueous media. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 138962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Shen, T.T.; Zhu, H.Y.; Fu, Y.Q.; Jiang, S.T.; Li, J.B.; Wang, J.L. Magnetic Fe3O4 embedded chitosan-crosslinked-polyacrylamide composites with enhanced removal of food dye: Characterization, adsorption and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.H.; Mandavinia, G.R.; Massoumi, B.; Baghban, A.; Saraei, M. Ionically crosslinked magnetic chitosan/κ-carrageenan bioadsorbents for removal of anionic eriochrome black-T. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Yao, C. Highly Efficient Removal of Uranium(VI) From Aqueous Solution Using the Polyethyleneimine Modified Magnetic Chitosan. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, R.; Xing, Y.J. Preparation and adsorption properties of citrate-crosslinked chitosan salt microspheres by microwave assisted method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandavinia, G.R.; Mosallanezhad, A. Facile and green rout to prepare magnetic and chitosan-crosslinked κ-carrageenan bionanocomposites for removal of methylene blue. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 10, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghioua, A.; Barkat, D.; Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Khan, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A. Magnetic Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde/Zinc Oxide/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite: Optimization and Adsorptive Mechanism of Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dye Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3932–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Fu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, R.; Fu, K.; Wu, G.Y.; Jia, B.T.; Li, S.; Li, J.C. Removal of emulsified oil from water by using recyclable chitosan based covalently bonded composite magnetic flocculant: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, D.; Tang, X.; Abdulhasanb, M.J.; Zaidi, M.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Jasem, H.; Altimari, U.S.; Chem, C. Epichlorohydrin Crosslinked 2,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde Schiff Base Chitosan@SrFe12O19 (EP-DBSB-CS@SrFe12O19) Magnetic Nanocomposite for Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from Aqueous Solution. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 4201–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Fan, L.Y.; An, Y.A.; Guan, R.G. Combination of Micelle Collapse and CuNi Surface Dissolution for Electrodeposition of Magnetic Freestanding Chitosan Film. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippou, K.; Christou, C.N.; Socoliuc, V.; Vekas, L.; Tanasa, E.; Miclau, M.; Pashalidis, I.; Krasia-Christoforou, T. Superparamagnetic polyvinylpyrrolidone/chitosan/Fe3O4 electrospun nanofibers as effective U(VI) adsorbents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabaso, N.B.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Nyaba, L. Recent Advances in Synthesising and Applying Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymers to Detect, Pre-Concentrate, and Remove Heavy Metals in Various Matrices. Processes 2024, 12, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, A.K.; Jamoussi, B.; Albalawi, A.E.; Alhawiti, O.H.N.; Alsharif, A.A. Designing of modified ion-imprinted chitosan particles for selective removal of mercury (II) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, S.; Somasundaram, A.; Ramasamy, P. A comprehensive review on nanochitosan and its diverse applications in various industries. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirozzi, D.; Latte, A.; Yousuf, A.; De Mastro, F.; Brunetti, G.; El Hassanin, A.; Sannino, F. Magnetic Chitosan for the Removal of Sulfamethoxazole from Tertiary Wastewaters. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Bulin, C.; Li, C.; Xin, G.; Bao, J.; Song, J. Experimental and statistical physics illumination of Pb(II) adsorption on magnetic chitosan-graphene oxide surface. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Lu, W.D. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using inorganic clays modified magnetic chitosan adsorbent: Kinetic and thermodynamic study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulin, C. Adsorption mechanism and removal efficiency of magnetic graphene oxide-chitosan hybrid on aqueous Zn(II). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulin, C.; Zheng, R.X.; Song, J.L.; Bao, J.X.; Xin, G.X.; Zhang, B.W. Magnetic graphene oxide-chitosan nanohybrid for efficient removal of aqueous Hg(II) and the interaction mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, R.T.; Sun, D.J.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.J. Fabrication of chitosan/magnetite-graphene oxide composites as a novel bioadsorbent for adsorption and detoxification of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Hashem, O.A.; Abdel-Hamid, H.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Ayoup, M.S. Synthesis of a new magnetic Sulfacetamide-Ethylacetoacetate hydrazone-chitosan Schiff-base for Cr(VI) removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Deng, J.L.; Qin, Z.; Huang, R.H.; Wang, Y.; Tong, S.S. Construction of MoS2 nanoarrays and MoO3 nanobelts: Two efficient adsorbents for removal of Pb(II), Au(III) and Methylene Blue. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridi, H.; Talebi, M.; Jafarnezhad, B.; Mousavi, S.E.; Abbasizadeh, S. The role of chitosan grafted copolymer/zeolite schiff base nanofiber in adsorption of copper and zinc cations from aqueous media. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, S.R.; Abuessawy, A.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.H.; El-Hema, H.S.; Eisa, M.N.; Hawata, M.A. New functionalized magnetite chitosan-heterocyclic nanocomposites excelling in Cd2+ removal from aqueous solution with biological activity. Appl. Water Sci. 2025, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Tunali Akar, S.T.; Akar, T.; Celik, S.; Gedikbey, T. Chitosan immobilization and Fe3O4 functionalization of olive pomace: An eco–friendly and recyclable Pb2+ biosorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmin, R.; Sarkar, B.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Tsuzuki, T.; Liu, Y.J.; Naidu, R. Facile one pot preparation of magnetic chitosan-palygorskite nanocomposite for efficient removal of lead from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; He, Y.Y.; Lu, S.Y.; Wang, S.L.; Yi, J.C.; He, Y.F.; Zhang, J.W.; Xiang, S.; Ding, P.; Kai, T.H.; et al. A regenerable ion-imprinted magnetic biocomposite for selective adsorption and detection of Pb2+ in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.B.; Cui, W.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, S.R. Removing copper and cadmium from water and sediment by magnetic microspheres-MnFe2O4/chitosan prepared by waste shrimp shells. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi, R.; Lelifajri, L.; Iqbal, M.; Fathurrahmi, F.; Jalaluddin, J.; Sembiring, R.; Farida, M.; Iqhrammullah, M. Preparation, Characterization and Adsorption Study of PEDGE-Cross-linked Magnetic Chitosan (PEDGFE-MCh) Microspheres for Cd2+ Removal. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi; Iqhrammullah, M.; Audina, U.; Husin, H.; Fathana, H. Adsorptive removal of Cd(II) using oil palm empty fruit bunch-based charcoal/chitosan-EDTA film composite. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmi; Julinawati; Nina, M.; Fathana, H.; Iqhrammullah, M. Preparation and characterization of new magnetic chitosan-glycine-PEDGE (Fe3O4/Ch-G-P) beads for aqueous Cd(II) removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Cui, E.T.; Gu, N.P.; Ma, W.X.; Guo, Q.Y.; Li, X.; Jin, J.X.; Wang, Q.; Ding, C. Unveiling the biointerfaces characteristics and removal pathways of Cr(VI) in Bacillus cereus FNXJ1-2-3 for the Cr(VI)-to-Cr(0) conversion. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, H.Y.; Xiao, C.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, W.F.; Bai, R.; Ding, R.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhao, F. Proteomic analysis of the reduction and resistance mechanisms of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 under long-term hexavalent chromium stress. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.X.; Li, M.G.; Lin, H.Y.; Feng, Q.G.; Hu, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.X.; Lv, J.T.; Lin, J.; Li, L.H.; Wu, X.H. A Novel Magnetic and Amino Grafted Chitosan-Based Composite for Efficient Adsorption and Reduction of Cr(VI): Performance and Removal Mechanism. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 6375–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Liao, Q.; Hou, B.C.; He, C.S.; Liu, J.M.; Li, B.R.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.C.; Lai, B.; Yang, B. Synchronous reduction and removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater by modified magnetic chitosan beads. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, H.F. Thymine chitosan nanomagnets for specific preconcentration of mercury(II) prior to analysis using SELDI-MS. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.T.; Jiang, J.W.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, J.S. New network polymer functionalized magnetic-mesoporous nanoparticle for rapid adsorption of Hg(II) and sequential efficient reutilization as a catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Gharibi, H.; Kakavandi, B.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Javid, A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Sharafi, K.; Khosravia, T. Magnetic adsorption separation process: An alternative method of mercury extracting from aqueous solution using modified chitosan coated Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.C.; Zheng, Q. Selective adsorption behavior of ion-imprinted magnetic chitosan beads for removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.F.; Ragab, A.H.; Hosny, R.; Ahmed, I.A.; Ahmed, H.A.; El-Bahy, S.M.; El Shahawy, A. Enhanced Performance of Chitosan via a Novel Quaternary Magnetic Nanocomposite Chitosan/Grafted Halloysitenanotubes@ZnγFe3O4 for Uptake of Cr(III), Fe(III), and Mn(II) from Wastewater. Polymers 2021, 13, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.A.; Fawzy, M.E.; Ahmed, H.M.; Alshammari, S.O.; El-Khateeb, M.A. Treatment of heavy metal ions from simulated water using adsorption process via modified iron magnetic nanocomposite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuryono, N.; Miswanda, D.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Rusdiarso, B.; Krisbiantoro, P.A.; Utami, N.; Otomo, R.; Kamiya, Y. Chitosan-functionalized natural magnetic particle@silica modified with (3-chloropropyl)trimethoxysilane as a highly stable magnetic adsorbent for gold(III) ion. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 255, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Cui, J.; He, L.S.; Wang, J.Z.; Yan, C.L.; Kou, Y.Y.; Li, J.Q. Facile fabrication of magnetic phosphorylated chitosan for the removal of Co(II) in water treatment: Separation properties and adsorption mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.G.; Peng, J.B. Highly selective removal and recovery of Ni(II) from aqueous solution using magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilki, S.; Celikbicak, O.; Acikgoz-Erkaya, I.; Arica, M.Y.; Bayramoglu, G. Preparation of fibrous polymer grafted magnetic chitosan beads and modified with hydrazone and imidazole groups: Isolation of U(VI) ions from seawater. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2025, 334, 3319–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Zeng, H.P.; Wang, Q.H.; Sun, X.; Zeng, Y.W.; Li, D.; Zhang, J. Utilization of waste iron sludge to achieve bifunctional magnetic and adsorptive cores for synthesizing magnetic chitosan microspheres: Arsenic decontamination and its mechanism. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 199, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.P.; Xu, H.; Zeng, Y.W.; Sun, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Facile Preparation of Magnetic Chitosan Carbon Based on Recycling of Iron Sludge for Sb(III) Removal. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dim, P.E.; Mustapha, L.S.; Termtanun, M.; Okafor, J.O. Adsorption of chromium (VI) and iron (III) ions onto acid-modified kaolinite: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Arabian J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.X.; Zhuo, Y.T.; Hu, L.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, Y.H.; He, Z.G. Research on the Adsorption Behavior of Heavy Metal Ions by Porous Material Prepared with Silicate Tailings. Minerals 2019, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Ouyang, L.K.; Yuan, S.J. Single-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Biochar from H3PO4-Activated Lettuce Waste for Efficient Adsorption of Cd(II) in Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2022, 27, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.F.; Zhou, H.; Tan, W.T.; Huang, J.G.; Zeng, P.; Gu, J.F.; Liao, B.H. Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanisms of Fe-Mn Oxide Modified Biochar for Pb(II) in Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahandeh, A.; Parvareh, A.; Moraveji, M.K. Synthesis and characterization of γ-MnO2/chitosan/Fe3O4 cross-linked with EDTA and the study of its efficiency for the elimination of zinc(II) and lead(II) from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9235–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.C.; Yang, C.; Qu, G.F.; Cui, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Ren, Y.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, F. Chitosan-modified magnetic carbon nanomaterials with high efficiency, controlled motility, and reusability-for removal of chromium ions from real wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 51271–51287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.A.; Khan, A.M.; Manea, Y.K.; Singh, M. Facile synthesis of layered superparamagnetic Fe3O4-MoS2 nanosheets on chitosan for efficient removal of chromium and ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Y.; Wang, G.S.; Chen, F.; Hu, J.S. Novel magnetic covalent organic framework loaded ligand for rapid removal and selective detection of mercury(II) from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 341, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaghani, A.S.; Manafi, M.; Hojjati, M. Pb2+ recovery from real water samples by adsorption onto nano Fe3O4/chitosan-acrylamide hydrogel ions in real water samples. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 17, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Li, Q.; Tao, Y.; Gong, J.; Shi, J.; Yan, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Efficient removal of copper and silver ions in electroplating wastewater by magnetic-MOF-based hydrogel and a reuse case for photocatalytic application. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.H.; Liang, W.; Huang, H.; Jiang, S.C.; Guo, D.; Li, M.L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Ali, A.; Wang, J.J. Removal of cadmium(II) cations from an aqueous solution with aminothiourea chitosan strengthened magnetic biochar. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidinasab, M.; Rahbar, N.; Ahmadi, M.; Kakavandi, B.; Ghanbari, F.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Martinez, S.S.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Removal of vanadium and palladium ions by adsorption onto magnetic chitosan nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34262–34276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Chauhan, P.; Kaur, C.; Arora, P.K.; Garg, S.K.; Singh, V.P.; Singh, K.P.; Srivastava, A. Comprehensive heavy metal remediation mechanisms with insights into CRISPR-Cas9 and biochar innovations. Biodegradation 2025, 36, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.F.; Heng, Z.W.; Teoh, H.C.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L. Recent development of magnetic biochar crosslinked chitosan on heavy metal removal from wastewater-Modification, application and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, P.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Shao, Q.Q. Efficient adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in water by functionalized lignin-rich ragweed biochar: Combining experiments, DFT calculation, and projected density of states. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 318, 145138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Crosslinking Type | Crosslinker | Name of Magnetic Chitosan Adsorbent | Adsorption Object | Adsorbability | Isolation and Regeneration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical crosslinking | Polyphosphates | MCS-PEI | U(VI) | Q = 181.8 | n = 4, r = 89.8 | [43] |
| Physical crosslinking | Citric acid | CSC | Cr(VI) | Q = 172 | / | [44] |
| Physical crosslinking | Kappa-carrageenan | Magnetic bionanocomposite adsorbent based on kappa-carrageenan | MB | Q = 123.1 | n = 5, r > 90 | [45] |
| Chemical crosslinking | Glutaraldehyde | CHT-GLA/ZnO/Fe3O4 | RBBR dye | Q = 176.6 | / | [46] |
| Chemical crosslinking | Silane coupling agent | FS-MC | Emulsified oil | Under the optimal dosage, R = 92.98–94.47; under the optimal pH, R = 69.97–96.3 | n = 5, r = 69.97–81.31 | [47] |
| Chemical crosslinking | Epichlorohydrin | EP-DBSB-CS@SrFe12O19 | Pb(II), Cd(II) | QPb(II) = 103.5, QCd(II) = 73.5 | / | [48] |
| Method | Dominance | Defects | Application Potential | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coprecipitation method | The process is simple, easy to modify, controllable porous structure, compatible with multi-functional components. | Stepwise mixing is easy to cause uneven dispersion of particles. | High—process mature, mild conditions. | Low |
| Crosslinking method | It has stable structure, high mechanical strength and long-term cycle use resistance. | There are many steps, high requirements for crosslinking conditions, and toxic residues may be introduced. | Moderate—there are many steps in the middle-reaction, and batch production is feasible. | More than middle |
| Electro chemical deposition | The film layer is uniform and controllable. | High equipment requirements, small output. | Low—limited by production and equipment size. | Moderate |
| Electrospinning method | It has large specific surface area, rich pore structure and easy functionalization. | Precise control of solution and spinning conditions is required. | Moderate—it can be scaled but requires professional equipment. | More than middle |
| Ion imprinting technology | High selectivity, strong anti-interference | Template removal is complex and site stability is limited. | Low—template cost and regeneration limitations. | More than middle |
| Name of Magnetic Chitosan Adsorbent | Adsorption Object | Adsorption Condition | Adsorbability | Isolation and Regeneration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IIMCD | Cu(II) | pH = 5, T = 25 °C, t = 2 h, C = 800–900 | Q = 78.1 | n = 10, q decreased 8% | [78] |
| Ch/g-hnts@ZnγM | Mn(II) | pH = 9, T = 30 °C, t = 60 min, C = 40 | R = 87.1 | / | [79] |
| C-Fe2O3 NPs | Zn(II) | pH = 6, T = 25 °C, t = 60 min, C = 3 | R = 99.8 | n = 3, r = 65.1 | [80] |
| MP@[Chi-CPTMS(1/4)-SiO2] | Au(III) | pH = 5, D = 20 mg, t = 2 h. | Q = 112 | n = 5, A = 39.2 | [81] |
| P-MCS | Co(II) | T = 298 K, t = 25 min, D = 1 g/L, C = 100 | Q = 46.1 | n = 5, i = 85.26 | [82] |
| MIIPs | Ni(II) | pH = 7, t = 1 h, T = 298 K, D = 0.05 g | Q = 18.5 | n = 15, q decreased about 10% | [83] |
| Fe3O4@CHT@p(GMA) | U(VI) | pH = 6, t = 120 min, T = 25 °C, C = 1–400 | Q = 328.4–434.7 | n = 5, q > 87% of the initial adsorption capacity | [84] |
| MCMB | As(V) | pH = 7, T = 298 K, D = 1 g/L | Q = 21.63 | n = 5, i > 76 | [85] |
| MCC | Sb(III) | pH = 3–10, T = 25 °C, D = 0.4 g/L | Q = 38.234 | n = 3, i > 75.54 | [86] |
| Name of Magnetic Chitosan Adsorbent | Adsorption Object | Adsorption Condition | Adsorbability | Isolation and Regeneration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC@CS | Cr(VI) | pH = 3, D = 60 or 70, C0 = 55.67 mg/L | D = 60 mg: C < 0.01, D = 70 mg: R = 100 | In the actual wastewater experiment: n = 10, q = 68 | [92] |
| Fe3O4-MoS2@CS | Cr(VI) | pH = 4, D = 1 g/L, C0 = 10 ppm | R = 97 | n = 3, r = 89 | [93] |
| MCM | Hg(II) | C0 = 21.65 mmol/L | C < 0.05 | n = 3, q = 96.89% of the initial adsorption capacity | [94] |
| Nano-Fe3O4/chitosan-acrylamide hydrogel | Pb(II) | pH = 5, t = 8 min, D = 0.02 g, C0 = 0–15 μg/L | A > 97 | n = 3, i > 90 | [95] |
| Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2/CTS-PEI | Cu(II), Ag(I) | pH = 4.93, C0(Cu) = 23.83 mg/L, C0(Ag) = 37.82 mg/L | C(Cu) = 0.64, R(Cu) = 97.32; C(Ag) = 0.82 mg/L, R(Ag) = 97.7 | n = 5, r(Cu) = 82, r(Ag) = 79 | [96] |
| TMBC | Cd(II) | pH = 3.86, D = 0.25 g, t = 6 h, C0 = 4.9 mg/L | R ≈ 100 | n = 5, i = 84.83 | [97] |
| Fe3O4-CSN | V(V), Pd(II) | pH = 5(V), pH = 6(Pd), C0 = 10 mg/L, D = 1.5 g/L, t = 10 min, T = 20 ± 1 °C | R(V) = 99.99, R(Pd) = 92.3 | / | [98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Shah, K.J.; Sun, Y. Application Progress of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment. Magnetochemistry 2025, 11, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090071
Wang X, Zhuang Y, Shah KJ, Sun Y. Application Progress of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment. Magnetochemistry. 2025; 11(9):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaotian, Yan Zhuang, Kinjal J. Shah, and Yongjun Sun. 2025. "Application Progress of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment" Magnetochemistry 11, no. 9: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090071
APA StyleWang, X., Zhuang, Y., Shah, K. J., & Sun, Y. (2025). Application Progress of Magnetic Chitosan in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment. Magnetochemistry, 11(9), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry11090071








