Reentrant Spin Glass and Magnetic Skyrmions in the Co7Zn7Mn6−xFex β-Mn-Type Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
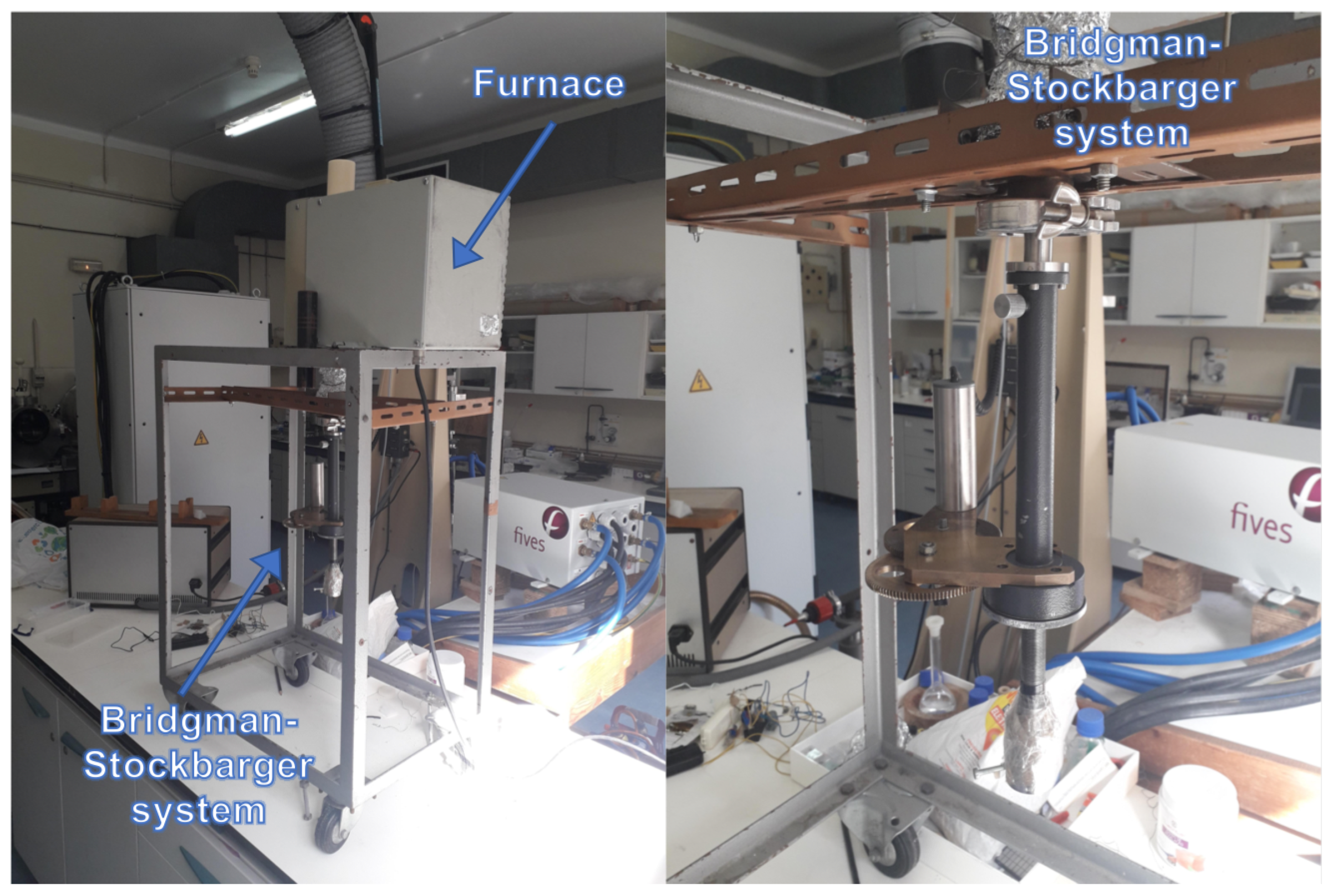
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sample Characterisation
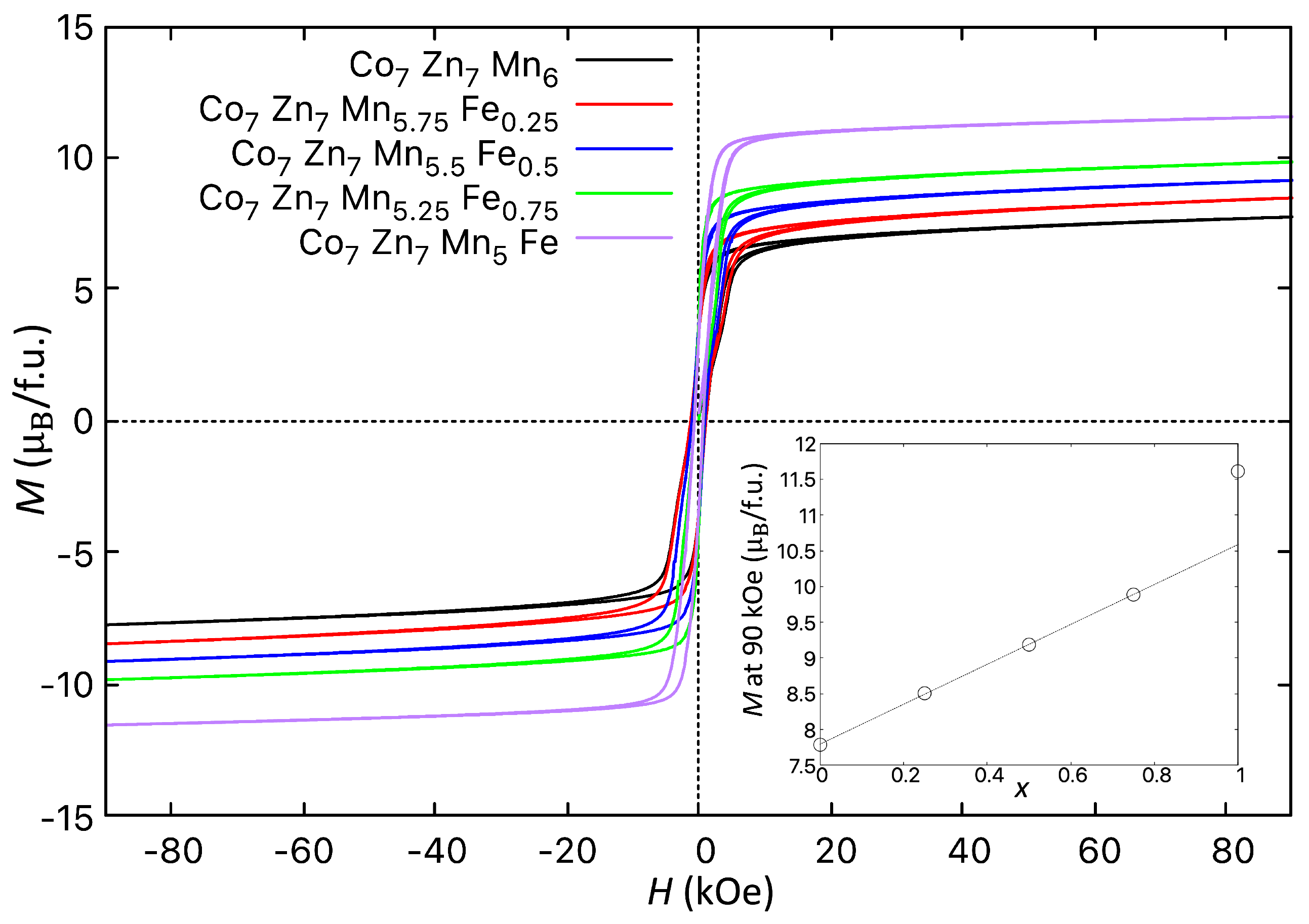
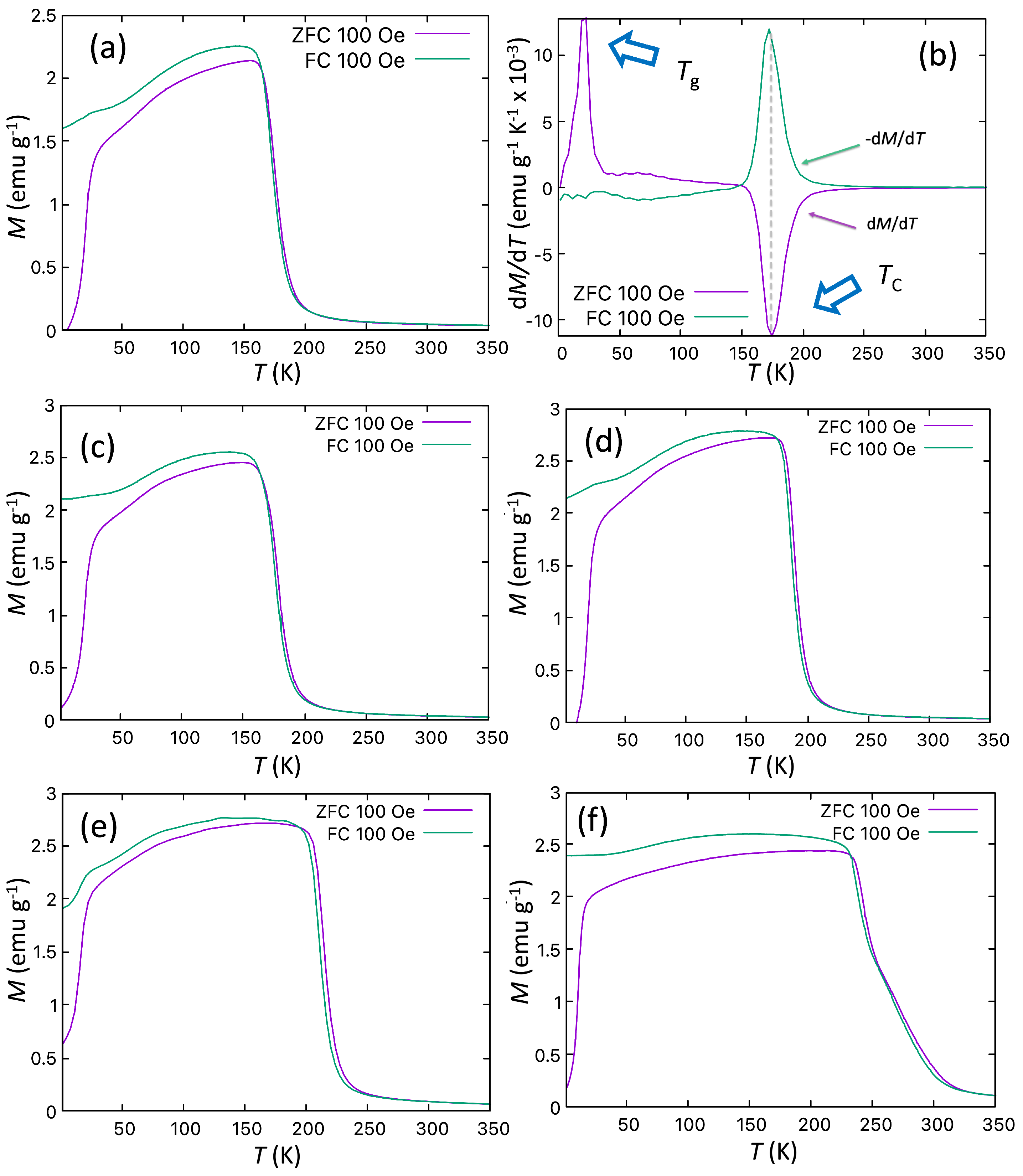
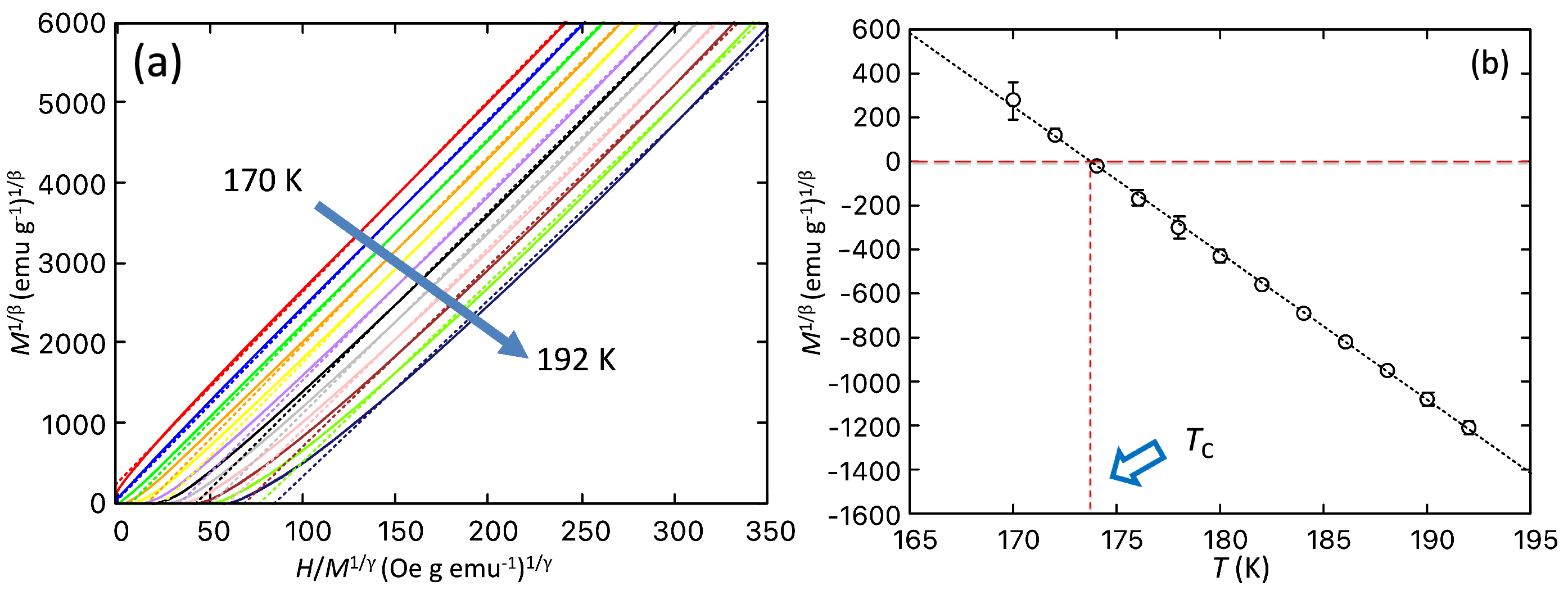
3.2. Magnetisation Studies
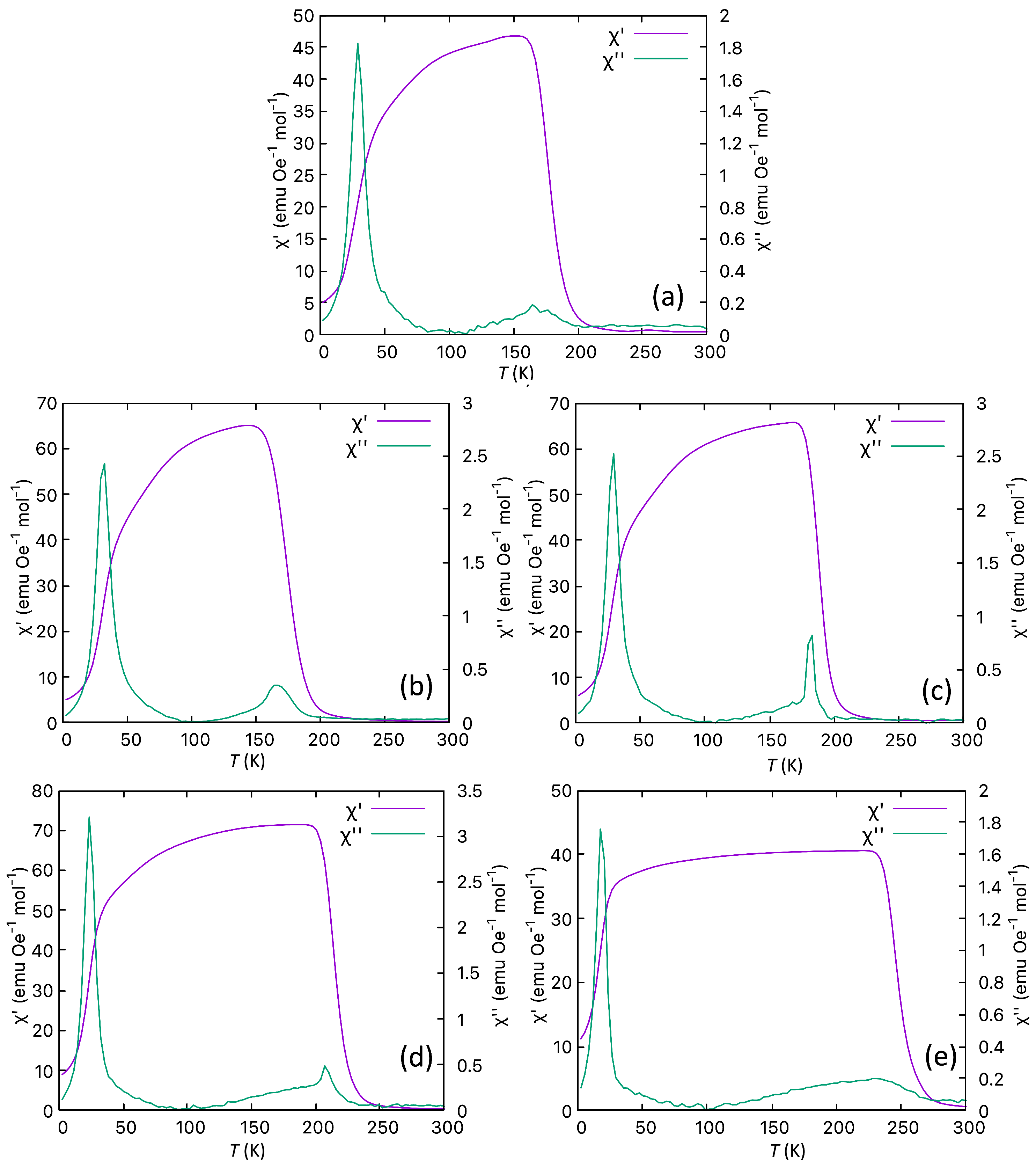
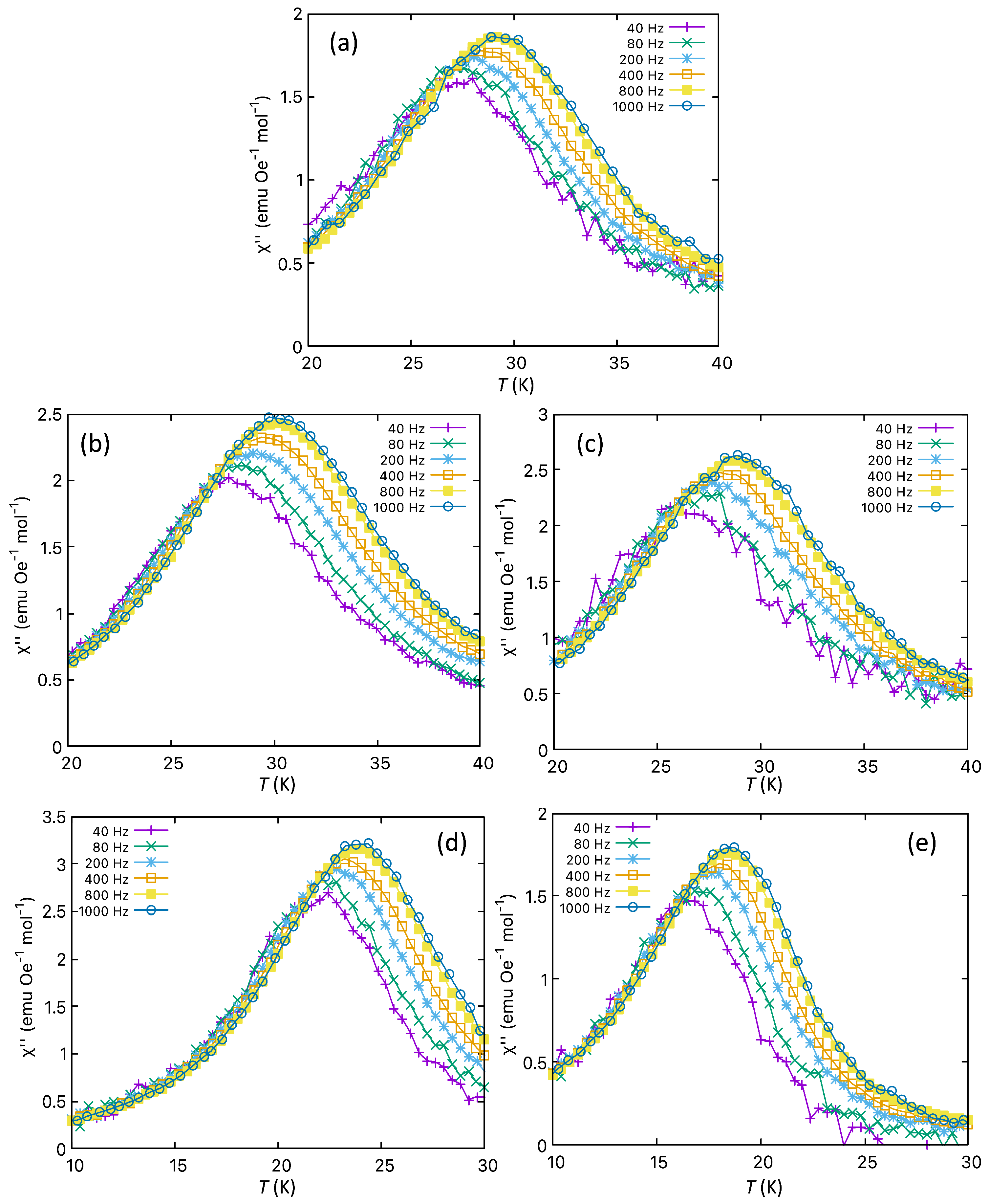
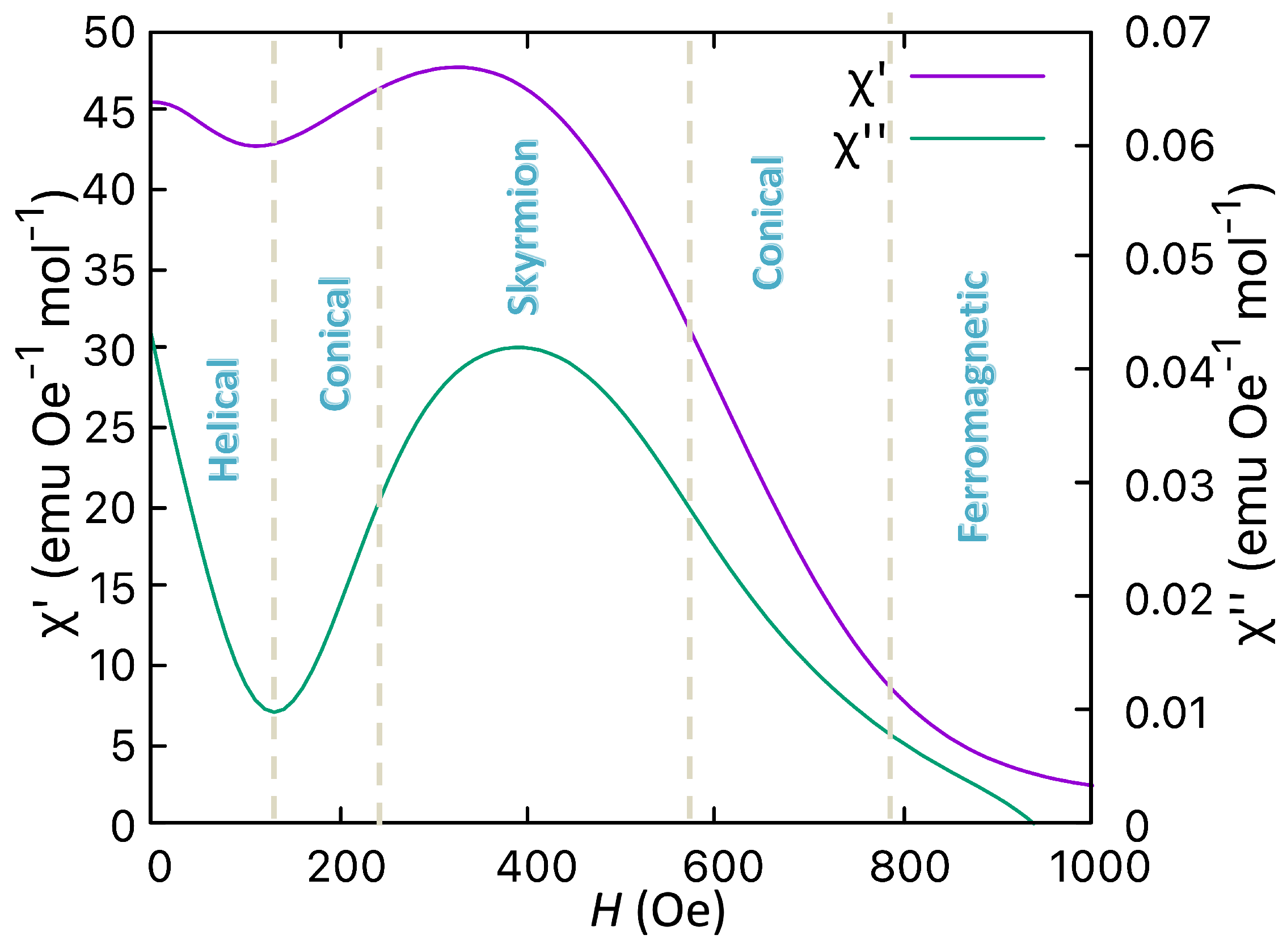
3.3. AC Susceptibility Measurements
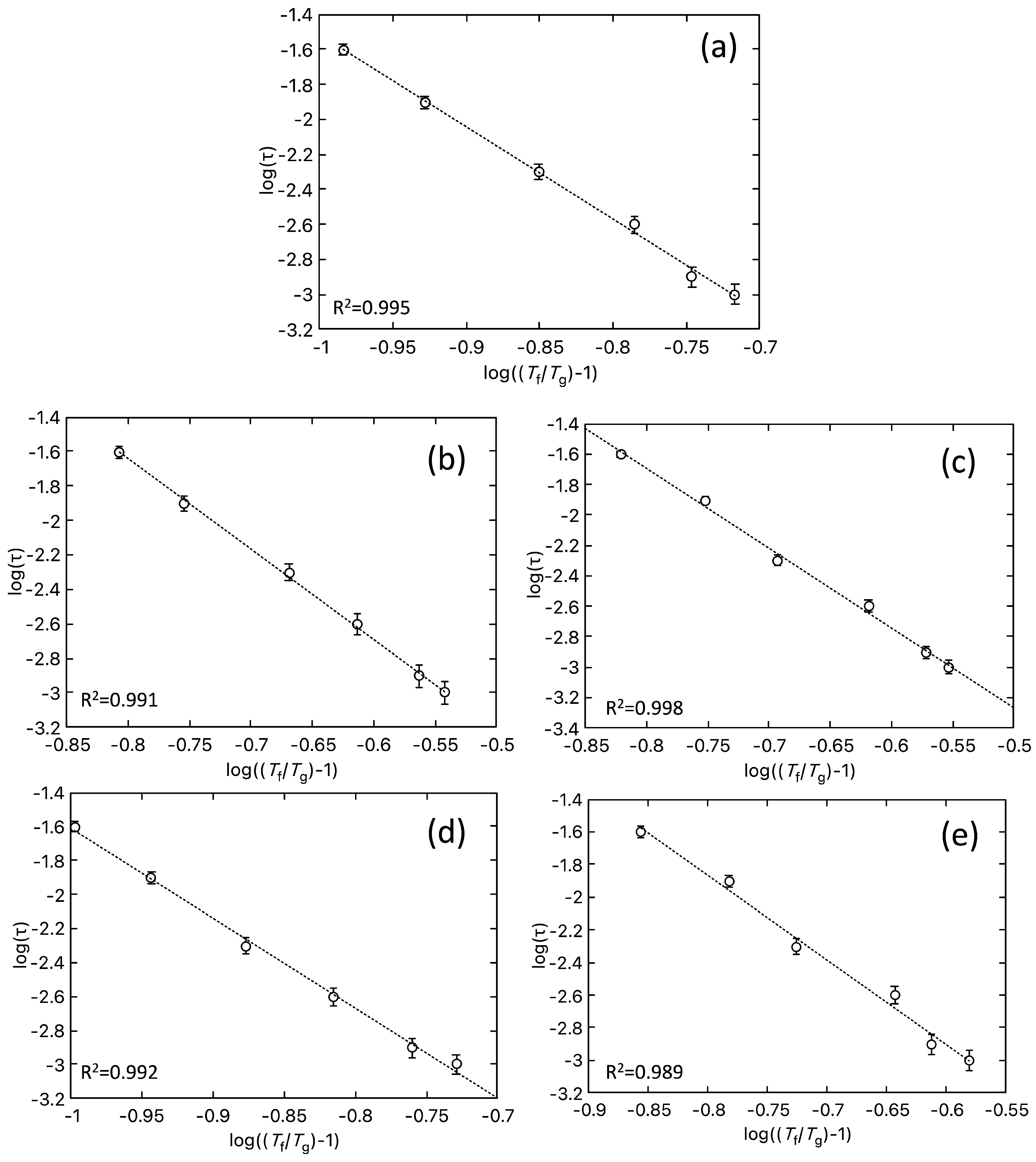
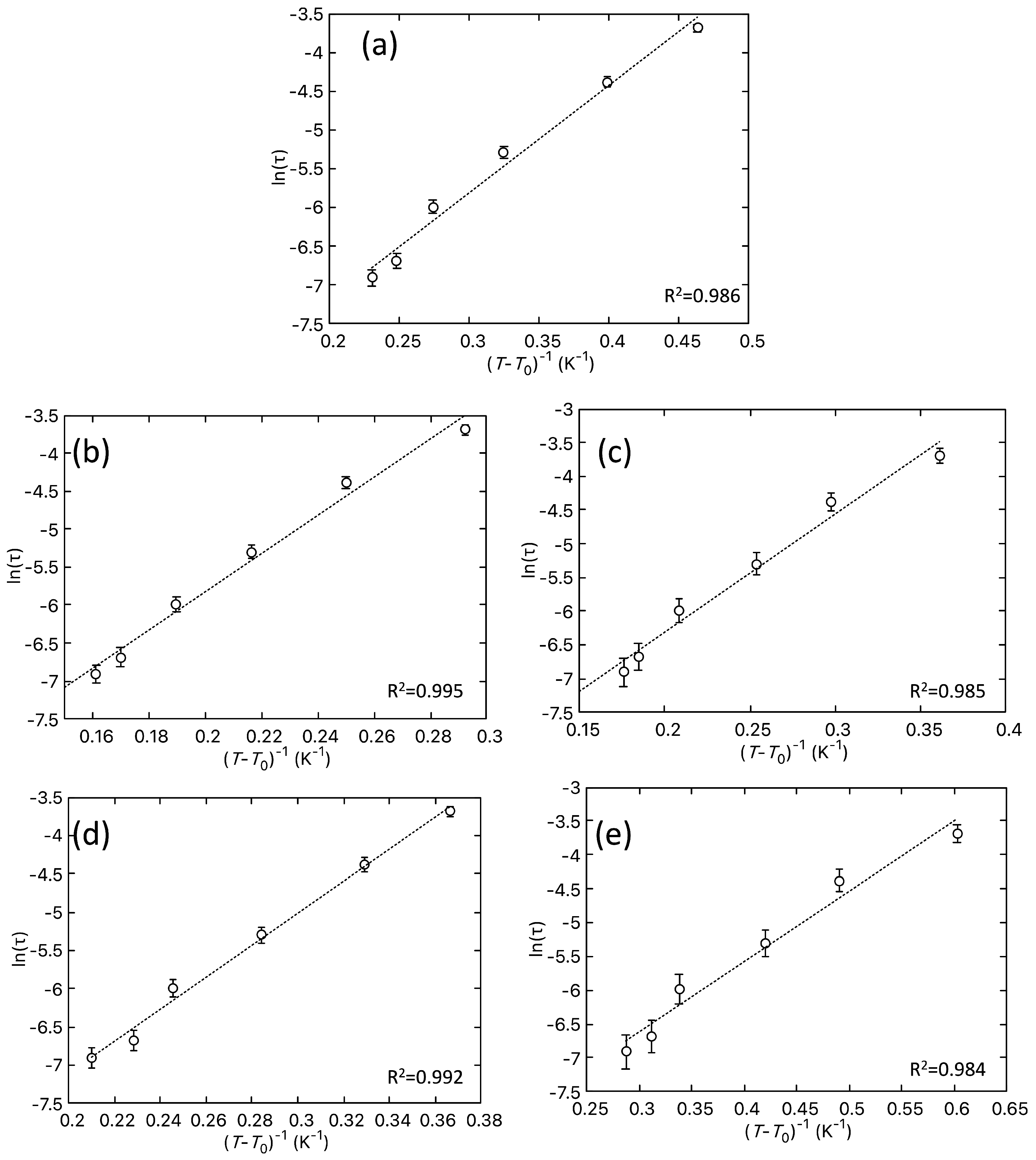
3.3.1. Evidence for a Reentrant Spin Glass Phase
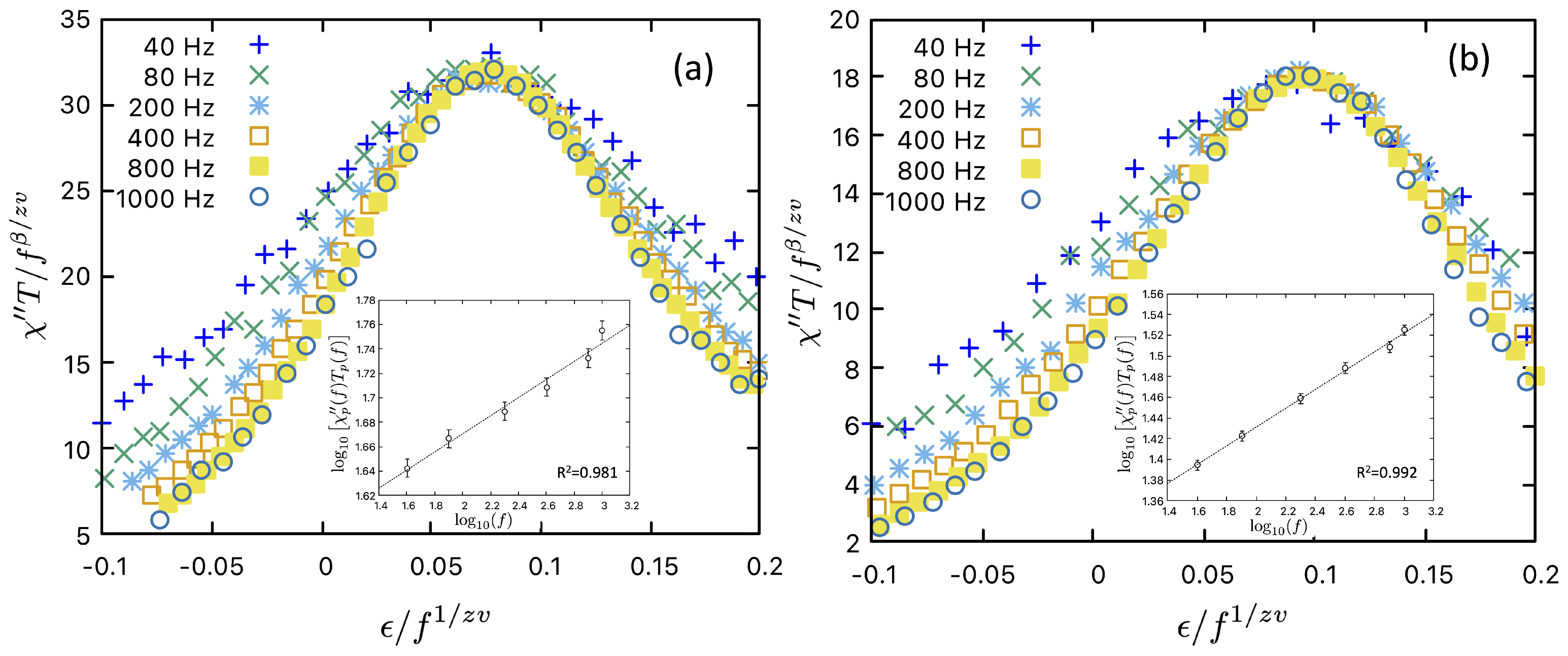
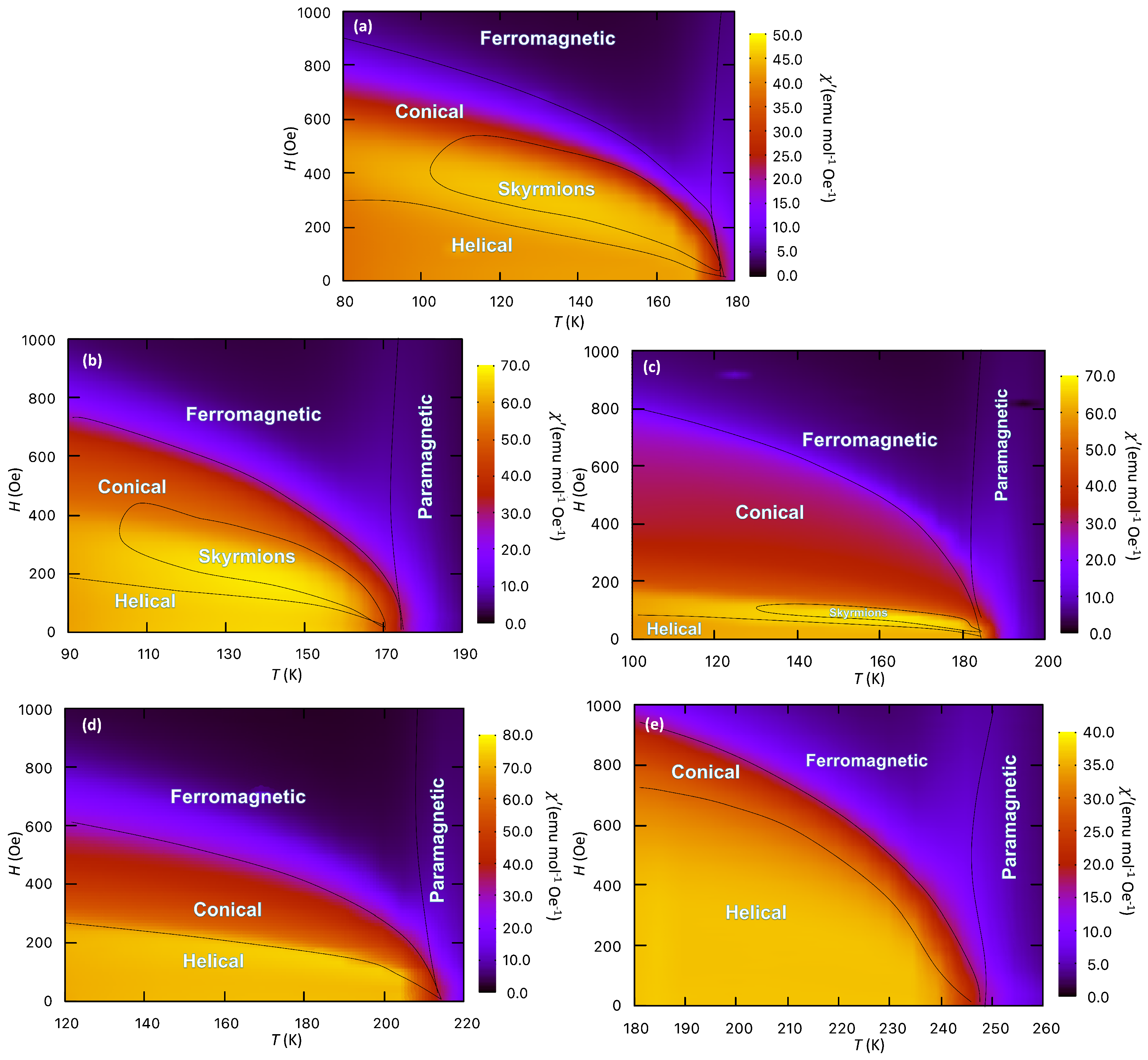
3.3.2. Magnetic Phase Diagram
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bocarsly, J.D.; Heikes, C.; Brown, C.M.; Wilson, S.D.; Seshadri, R. Deciphering structural and magnetic disorder in the chiral skyrmion host materials CoxZnyMnz (x + y + z = 20). Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019, 3, 014402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukleev, V.; Karube, K.; Derlet, P.M.; Wang, C.N.; Luetkens, H.; Morikawa, D.; Kikkawa, A.; Mangin-Thro, L.; Wildes, A.R.; Yamasaki, Y.; et al. Frustration-driven magnetic fluctuations as the origin of the low-temperature skyrmion phase in Co7Zn7Mn6. npj Quant. Mater. 2021, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, Y.; Yu, X.Z.; White, J.S.; Ronnow, H.M.; Morikawa, D.; Taguchi, Y.; Tokura, Y. A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Shiraish, H.; Ishii, Y. Magnetic properties of -MnCoZn alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 1820–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, D.; Yu, X.; Karube, K.; Tokunaga, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; Arima, T.; Tokura, Y. Deformation of Topologically-Protected Supercooled Skyrmions in a Thin Plate of Chiral Magnet Co8Zn8Mn4. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Thimmaiah, S.; Lamsal, J.; Liu, J.; Heitmann, T.W.; Quirinale, D.; Goldman, A.I.; Pecharsky, V.; Miller, G.J. β-Mn-Type Co8+xZn12−x as a Defect Cubic Laves Phase: Site Preferences, Magnetism, and Electronic Structure. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 9399–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, S.W.; Mostovoy, M. Multiferroics: A magnetic twist for ferroelectricity. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, R.B.; Vergara, I.; Schäfer, S.D.; Bischoff, D.; Aqeel, A.; Palstra, T.T.M.; Grüninger, M.; Van Loosdrecht, P.H.M. Optically probed symmetry breaking in the chiral magnet Cu2OSeO3. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 094409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimuth, F.; Bamler, R.; Mokrousov, Y.; Rosch, A. Phase-space Berry phases in chiral magnets: Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction and the charge of skyrmions. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 214409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanh, N.D.; Nakajima, T.; Yu, X.; Gao, S.; Shibata, K.; Hirschberger, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Sagayama, H.; Nakao, H.; Peng, L.; et al. Nanometric square skyrmion lattice in a centrosymmetric tetragonal magnet. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milde, P.; Kohler, D.; Seidel, J.; Eng, L.M.; Bauer, A.; Chacon, A.; Kindervater, J.; Muhlbauer, S.; Pfleiderer, C.; Buhrandt, S.; et al. Unwinding of a Skyrmion Lattice by Magnetic Monopoles. Science 2013, 340, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vir, P.; Kumar, N.; Borrmann, H.; Jamijansuren, B.; Kreiner, G.; Shekhar, C.; Felser, C. Tetragonal Superstructure of the Antiskyrmion Hosting Heusler Compound Mn1.4PtSn. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5876–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazawa, N.; Seki, S.; Tokura, Y. Noncentrosymmetric Magnets Hosting Magnetic Skyrmions. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Z.; Koshibae, W.; Tokunaga, Y.; Shibata, K.; Taguchi, Y.; Nagaosa, N.; Tokura, Y. Transformation between meron and skyrmion topological spin textures in a chiral magnet. Nature 2018, 564, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Karube, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yonemura, M.; Reynolds, N.; White, J.S.; Rønnow, H.M.; Kikkawa, A.; Tokunaga, Y.; Taguchi, Y.; et al. Correlation between site occupancies and spin-glass transition in skyrmion host . Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 064407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachenko, K. Understanding spin glass transition as a dynamic phenomenon. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 366003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mydosh, J.A. Spin glasses: Redux: An updated experimental/materials survey. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 052501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, S.; Torrens-Serra, J.; Salje, E.K.H.; Beshers, D.N. Re-entrant spin glass transitions: New insights from acoustic absorption by domain walls. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, K.; White, J.S.; Morikawa, D.; Dewhurst, C.D.; Cubitt, R.; Kikkawa, A.; Yu, X.; Tokunaga, Y.; Arima, T.; Rønnow, H.M.; et al. Disordered skyrmion phase stabilized by magnetic frustration in a chiral magnet. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, D.; Baabe, D.; Litterst, F.; Steinki, N.; Dietze, K.; Sach, M.; Rubrecht, B.; Sullow, S.; Hoser, A. Local structure determination in helimagnetic Co8Zn8Mn4−xFex. J. Phys. Comun. 2019, 3, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karube, K.; White, J.S.; Ukleev, V.; Dewhurst, C.D.; Cubitt, R.; Kikkawa, A.; Tokunaga, Y.; Rønnow, H.M.; Tokura, Y.; Taguchi, Y. Metastable skyrmion lattices governed by magnetic disorder and anisotropy in beta-Mn-type chiral magnets. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 064408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebelin, N.; Kleeberg, R. Profex: A graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrott, A.; Noakes, J.E. Approximate Equation of State For Nickel Near its Critical Temperature. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 19, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrott, A. Criterion for Ferromagnetism from Observations of Magnetic Isotherms. Phys. Rev. 1957, 108, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, I.; Roshko, R.M.; Williams, G. Arrott-plot criterion for ferromagnetism in disordered systems. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 34, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, S. Static critical phenomena in ferromagnets with quenched disorder. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1985, 53, 5–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guillou, J.C.; Zinn-Justin, J. Critical exponents from field theory. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 21, 3976–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvel, J.S.; Fisher, M.E. Detailed Magnetic Behavior of Nickel Near its Curie Point. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, A1626–A1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benka, G.; Bauer, A.; Schmakat, P.; Säubert, S.; Seifert, M.; Jorba, P.; Pfleiderer, C. Interplay of itinerant magnetism and spin-glass behavior in FexCr1−x. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2022, 6, 044407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlawska, M. Spin-glass freezing in single-crystalline Pr2NiSi3. Intermetallics 2019, 115, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, D. A spin glass perspective on ferroic glasses. Phys. Status Solidi B 2014, 251, 1967–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, P.; Somesh, K.; Nath, R. A study of cluster spin-glass behaviour at the critical composition Mn0.73Fe0.27NiGe. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 165977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.; Sharma, M.K.; Singh, S.; Mukherjee, K. Exotic magnetic behaviour and evidence of cluster glass and Griffiths like phase in Heusler alloys Fe2−xMnxCrAl. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rault, J. Origin of the Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann law in glass-forming materials: The alpha-beta bifurcation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 271, 177–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtrikman, S.; Wohlfarth, E. The theory of the Vogel-Fulcher law of spin glasses. Phys. Lett. A 1981, 85, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholence, J. On the frequency dependence of the transition temperature in spin glasses. Solid State Commun. 1980, 35, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souletie, J.; Tholence, J.L. Critical slowing down in spin glasses and other glasses: Fulcher versus power law. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Dey, T.; Mahajan, A.V.; Bttgen, N. LiZn2V3O8: A new geometrically frustrated cluster spin-glass. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, P.R.T.; Ramírez, J.M.M.; Vidyasagar, R.; Machado, F.L.A.; Rezende, S.M.; Dahlberg, E.D. GMI in the reentrant spin-glass Fe90Zr10 alloy: Investigation of the spin dynamics in the MHz frequency regime. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.; Pal, A.; Singh, P.; Alam, M.M.; Joshi, A.G.; Mohan, A.; Chatterjee, S. Emergence of Griffiths phase, re-entrant cluster glass, metamagnetic transition and field induced unusual spin dynamics in Tb2CoMnO6. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13734. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, R.; Singh, K.; Arora, S.K.; Shvets, I.V.; Kumar, R. Evidence for spin glass state of NdCo1−xNixO3 (x = 0.3–0.5). J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 073903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiel, S. Evidence for a re-entrant character of magnetism of alfa-phase Fe–Mo alloys: Non-linear susceptibilities. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 408, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bałanda, M.; Dubiel, S. An AC magnetic susceptibility study of a sigma-phase Fe65.9V34.1 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 663, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bitla, Y.; Kaul, S.N.; Fernández Barquín, L. Nonlinear susceptibilities as a probe to unambiguously distinguish between canonical and cluster spin glasses. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 094405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Kelley, C. Gnuplot 5.2: An Interactive Plotting Program. 2019. Available online: http://gnuplot.sourceforge.net/ (accessed on 10 June 2024).
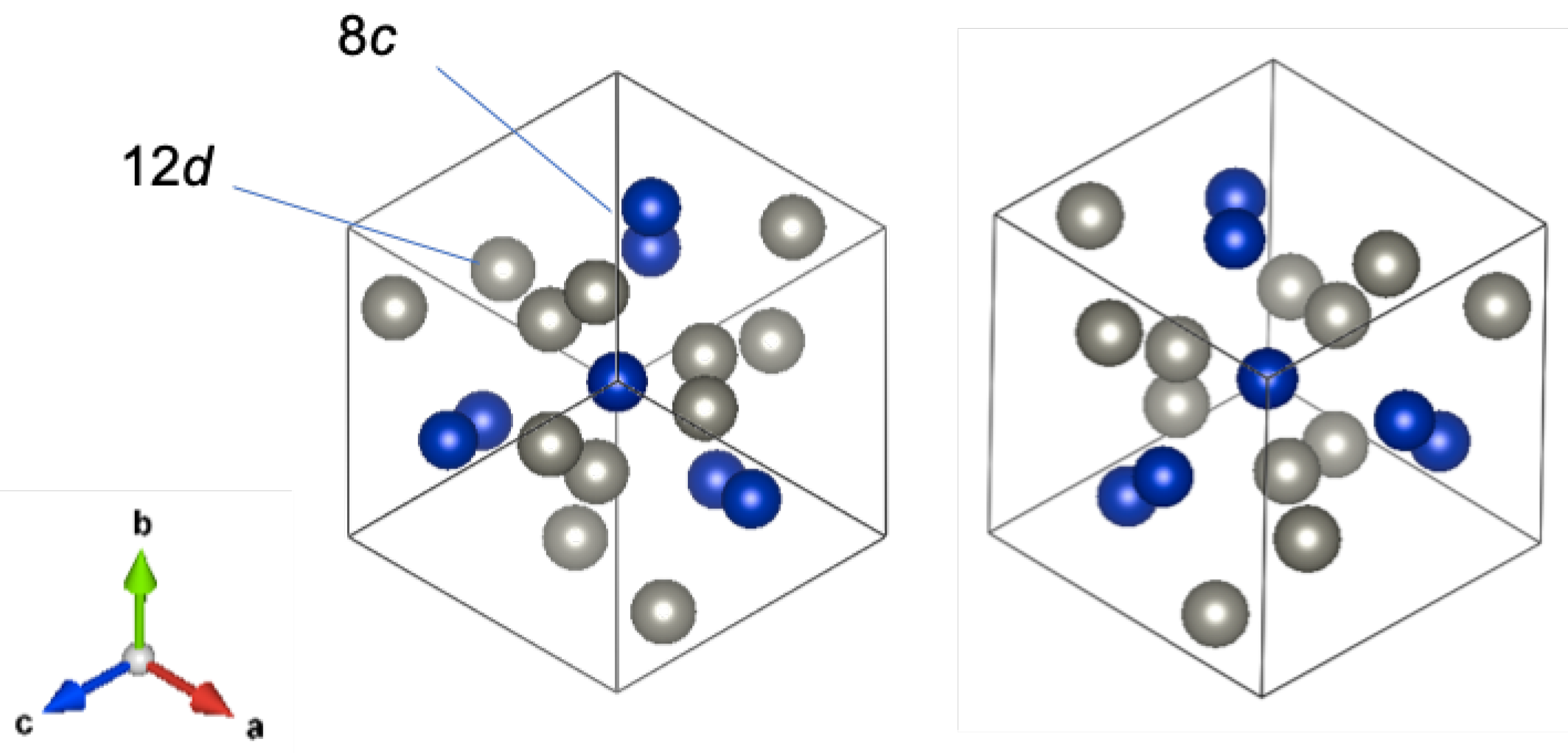
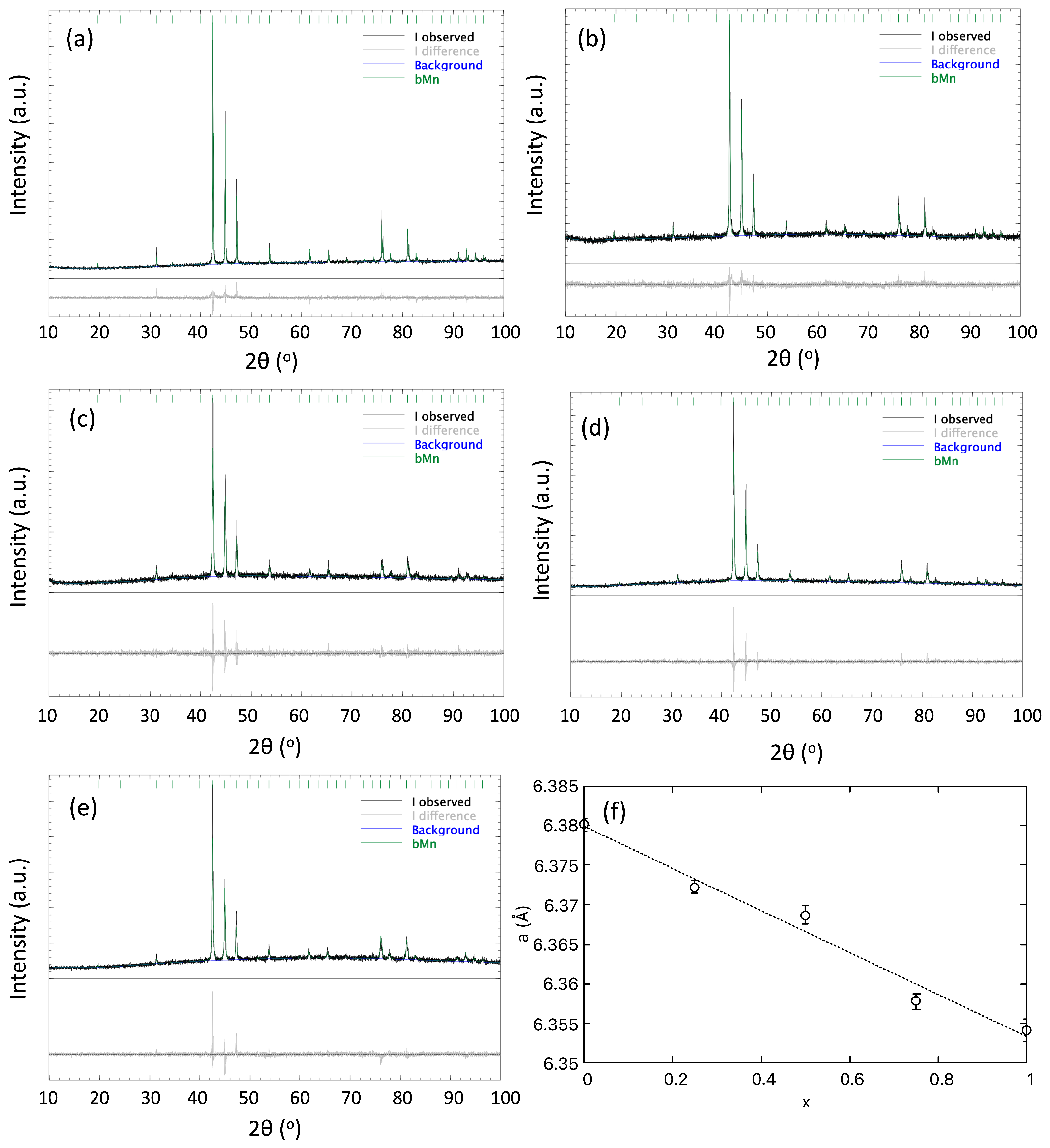
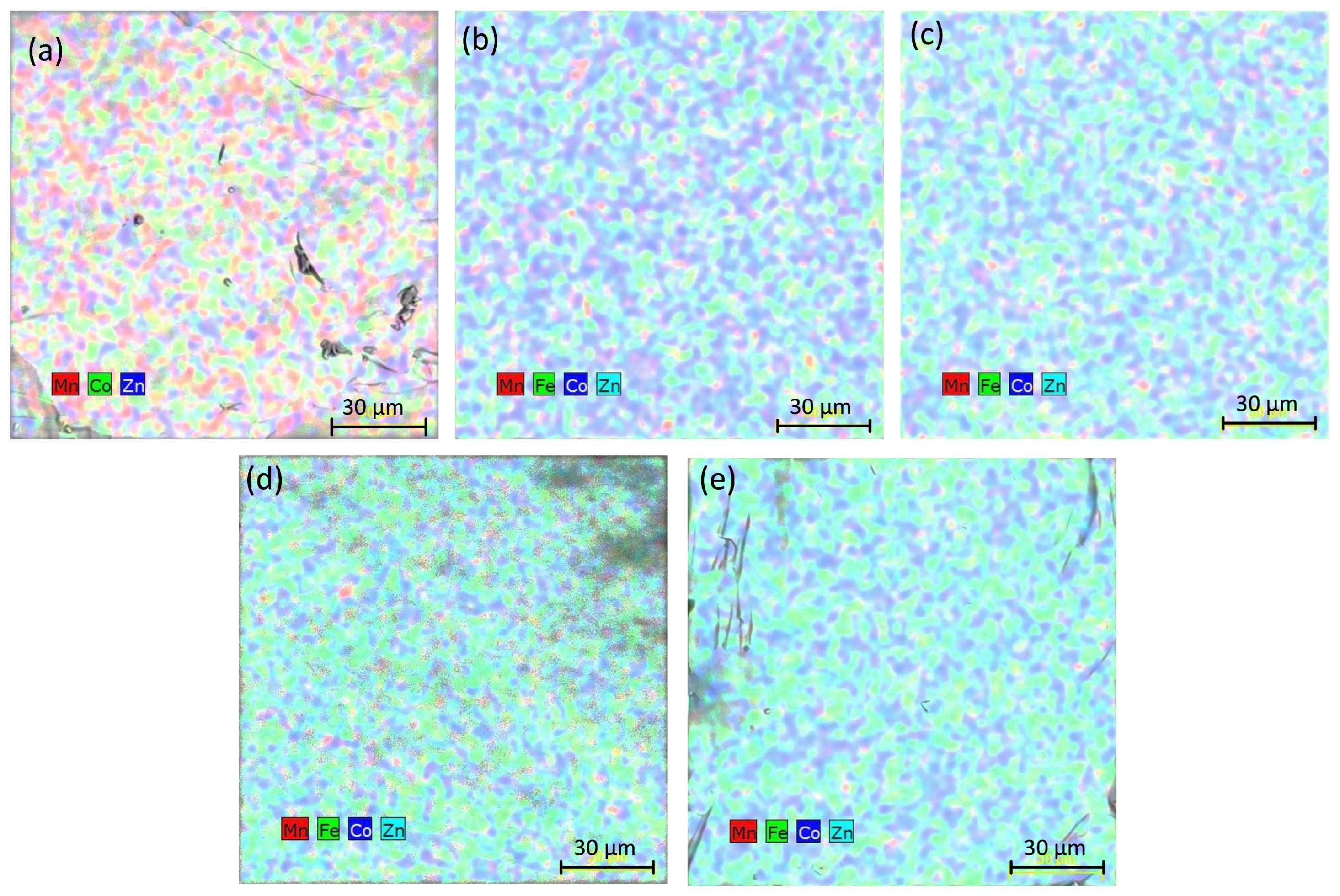

| Alloy | a (Å) | GOF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co7 Zn7Mn6 | 6.3801 (4) | 8.19% | 6.00% | 1.88 | 1.37 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 6.3781 (4) | 8.29% | 7.36% | 1.27 | 1.13 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 6.3741 (6) | 9.54% | 7.43% | 1.65 | 1.28 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 6.3725 (5) | 7.62% | 6.34% | 1.44 | 1.20 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 6.3705 (7) | 7.76% | 5.58% | 1.93 | 1.39 |
| Alloy | Co | Zn | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co7Zn7Mn6 | 7.07 ± 0.26 | 7.10 ± 0.27 | 5.83 ± 0.18 | - |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 7.12 ± 0.26 | 6.99 ± 0.24 | 5.57 ± 0.19 | 0.32 ± 0.02 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 6.97 ± 0.25 | 7.15 ± 0.25 | 5.36 ± 0.18 | 0.52 ± 0.03 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 7.08 ± 0.26 | 7.06 ± 0.27 | 5.18 ± 0.17 | 0.68 ± 0.03 |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 7.18 ± 0.25 | 7.06 ± 0.31 | 4.83 ± 0.15 | 0.93 ± 0.04 |
| Alloy | (Oe) | (/f.u.) | M (90 kOe) (/f.u.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Co7Zn7Mn6 | 1312 (3) | 3.410 (1) | 7.786 (3) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 1130 (2) | 3.435 (1) | 8.515 (4) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 895 (1) | 3.456 (1) | 9.163 (4) |
| Co7 Zn7 Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 682 (1) | 3.855 (2) | 9.866 (5) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 645 (1) | 3.890 (2) | 11.610 (6) |
| Alloy | (K) |
|---|---|
| Co7Zn7Mn6 | 173.8 (2) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 179.6 (1) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 188.1 (2) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 218.1 (2) |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 243.6 (3) |
| Alloy | (K) | (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co7Zn7Mn6 | 24.7 (2) | 6.67 (1) | 0.056 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 23.1 (2) | 5.25 (1) | 0.081 | |
| Co7 Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 22.6 (2) | 5.88 (1) | 0.079 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 20.2 (3) | 5.29 (2) | 0.054 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 14.7 (3) | 6.02 (8) | 0.067 |
| Alloy | (K) | (s) | (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co7Zn7Mn6 | 24.4 (1) | 22.1 (5) | 0.106 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.75Fe0.25 | 22.6 (1) | 24.9 (6) | 0.150 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.5Fe0.5 | 21.2 (1) | 21.4 (5) | 0.187 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5.25Fe0.75 | 19.6 (2) | 20.9 (3) | 0.139 | |
| Co7Zn7Mn5Fe | 13.7 (1) | 18.1 (3) | 0.189 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malta, J.F.; Henriques, M.S.C.; Paixão, J.A.; Gonçalves, A.P. Reentrant Spin Glass and Magnetic Skyrmions in the Co7Zn7Mn6−xFex β-Mn-Type Alloys. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080061
Malta JF, Henriques MSC, Paixão JA, Gonçalves AP. Reentrant Spin Glass and Magnetic Skyrmions in the Co7Zn7Mn6−xFex β-Mn-Type Alloys. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(8):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080061
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalta, José F., Marta S. C. Henriques, José A. Paixão, and António P. Gonçalves. 2024. "Reentrant Spin Glass and Magnetic Skyrmions in the Co7Zn7Mn6−xFex β-Mn-Type Alloys" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 8: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080061
APA StyleMalta, J. F., Henriques, M. S. C., Paixão, J. A., & Gonçalves, A. P. (2024). Reentrant Spin Glass and Magnetic Skyrmions in the Co7Zn7Mn6−xFex β-Mn-Type Alloys. Magnetochemistry, 10(8), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080061







