Exploring the Utilization of Magnetic Composite Materials for High-Risk Contaminant Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption and Catalytic Processes—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Magnetic Composite Materials as Adsorbents and Catalysts
2.1. Functionalized Magnetic LDH-Based Composites as Adsorbents for High-Risk Contaminants Removal from Wastewaters
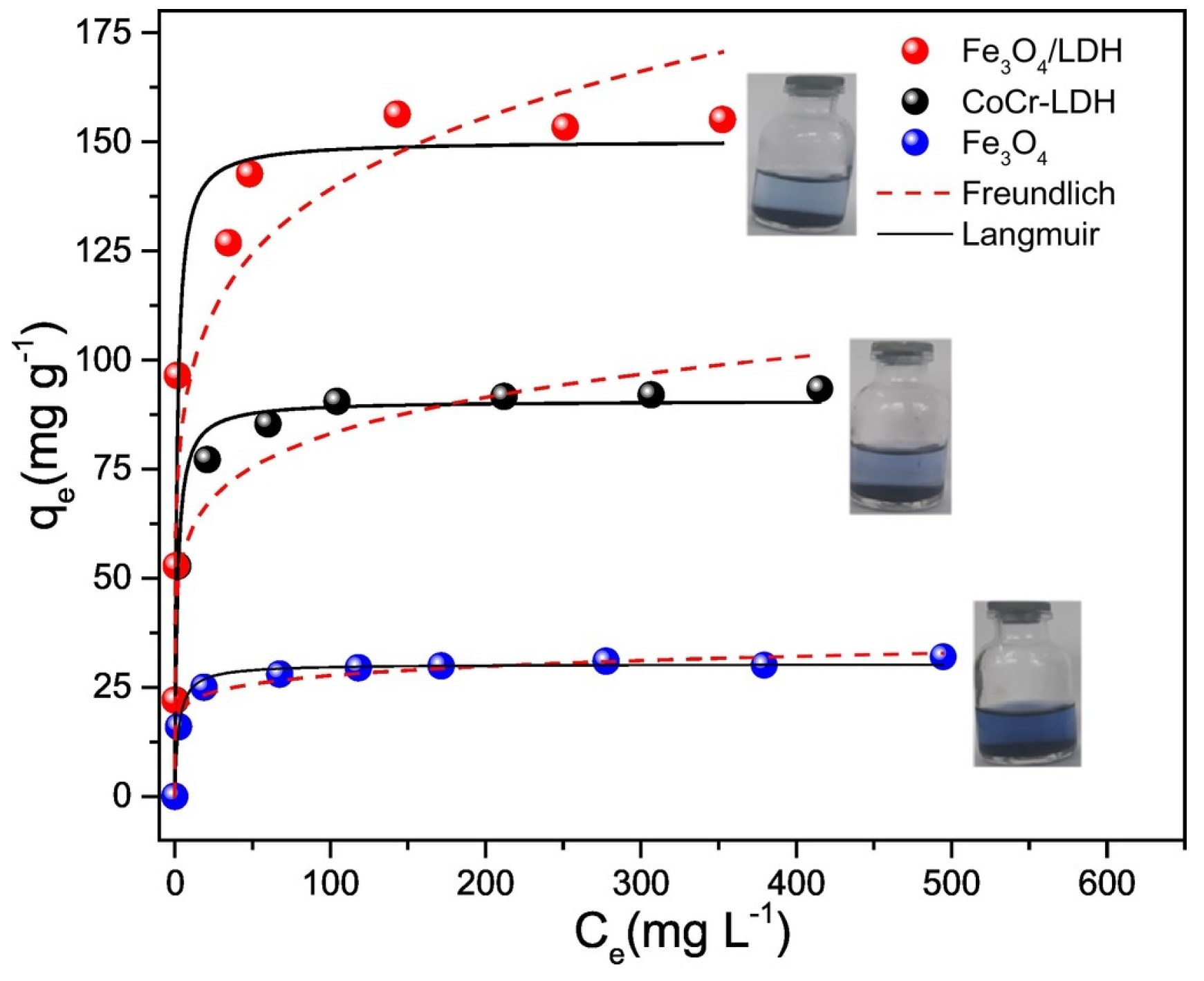
2.1.1. Heavy Metals Removal
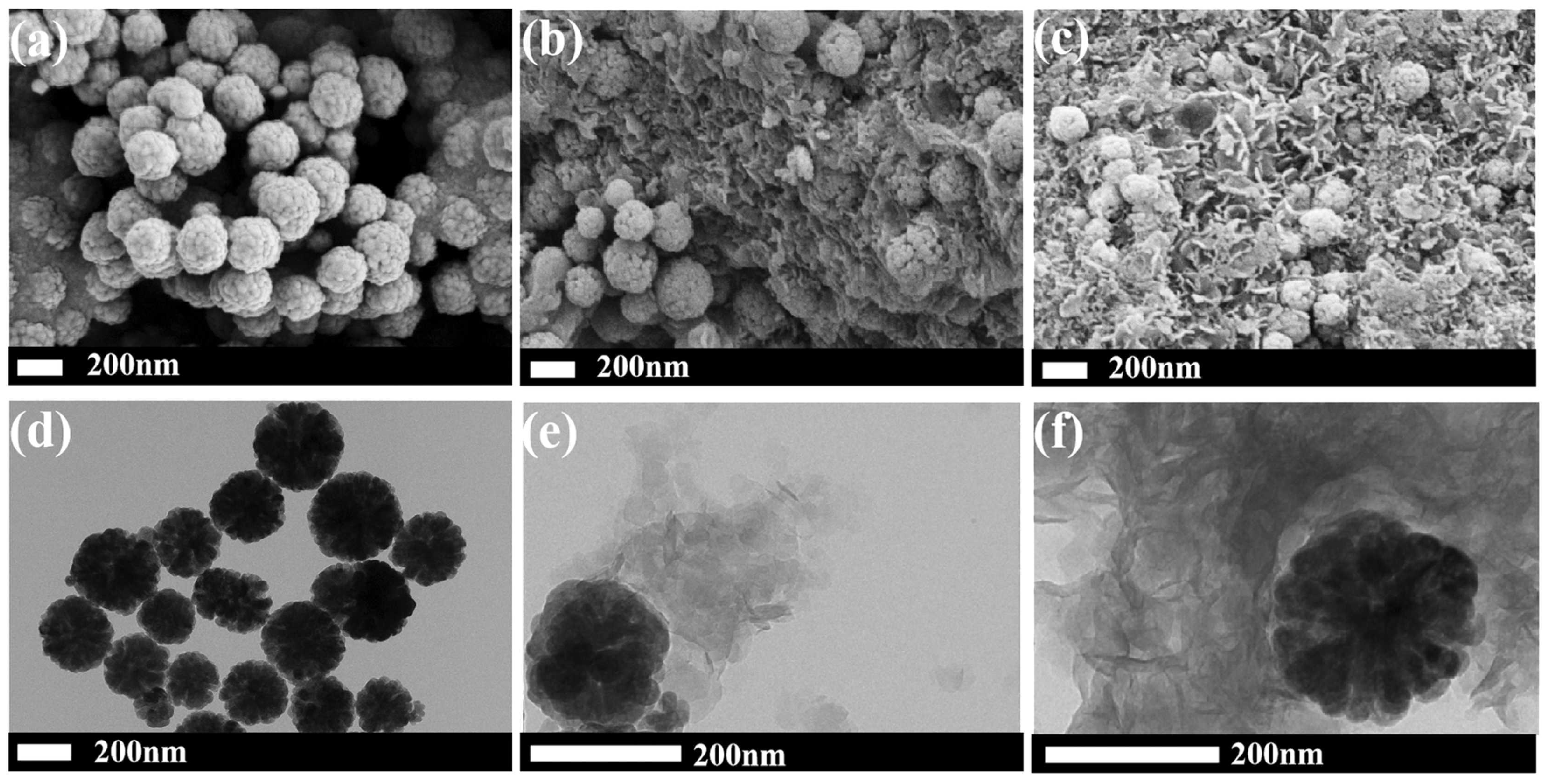
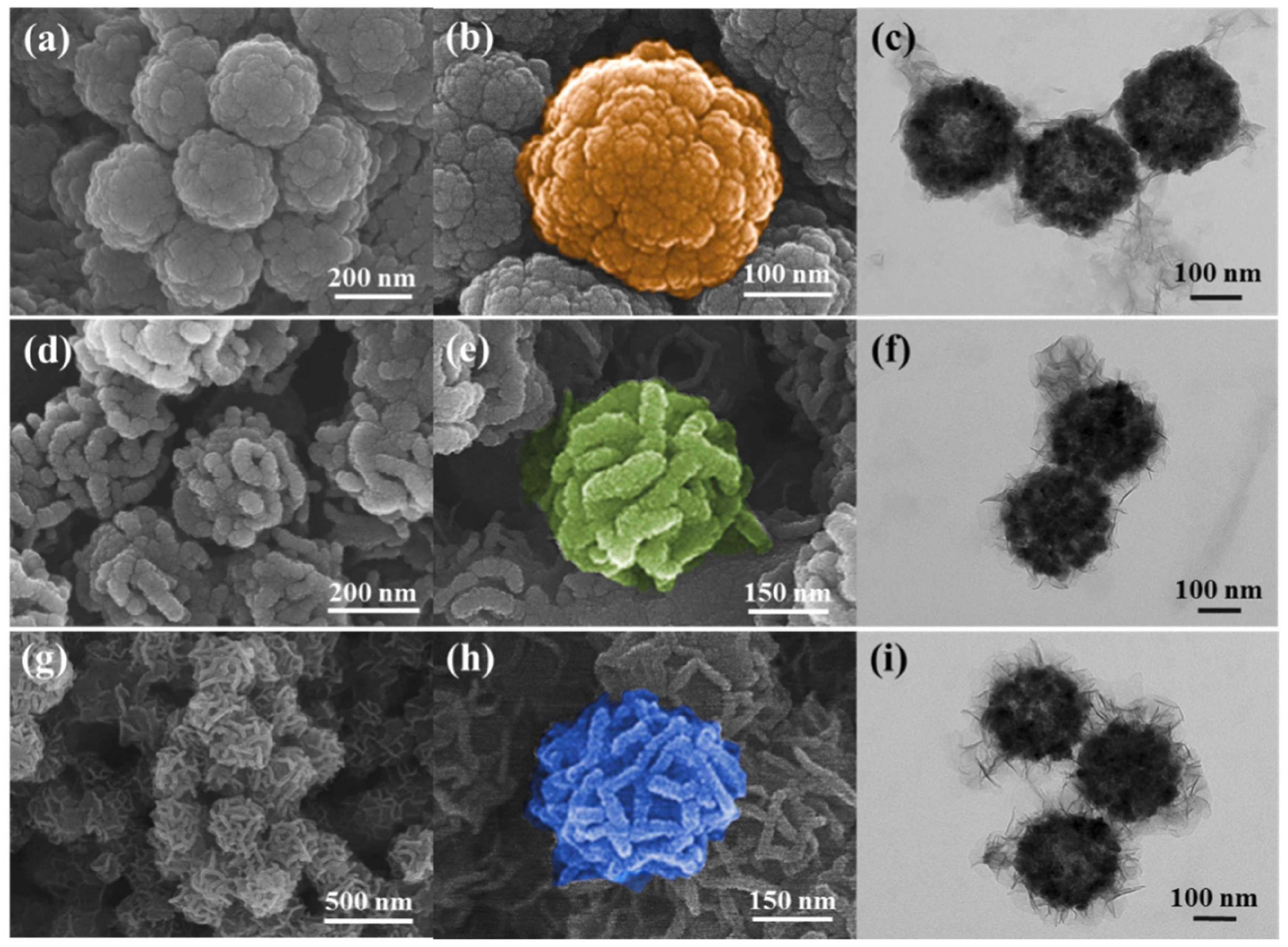
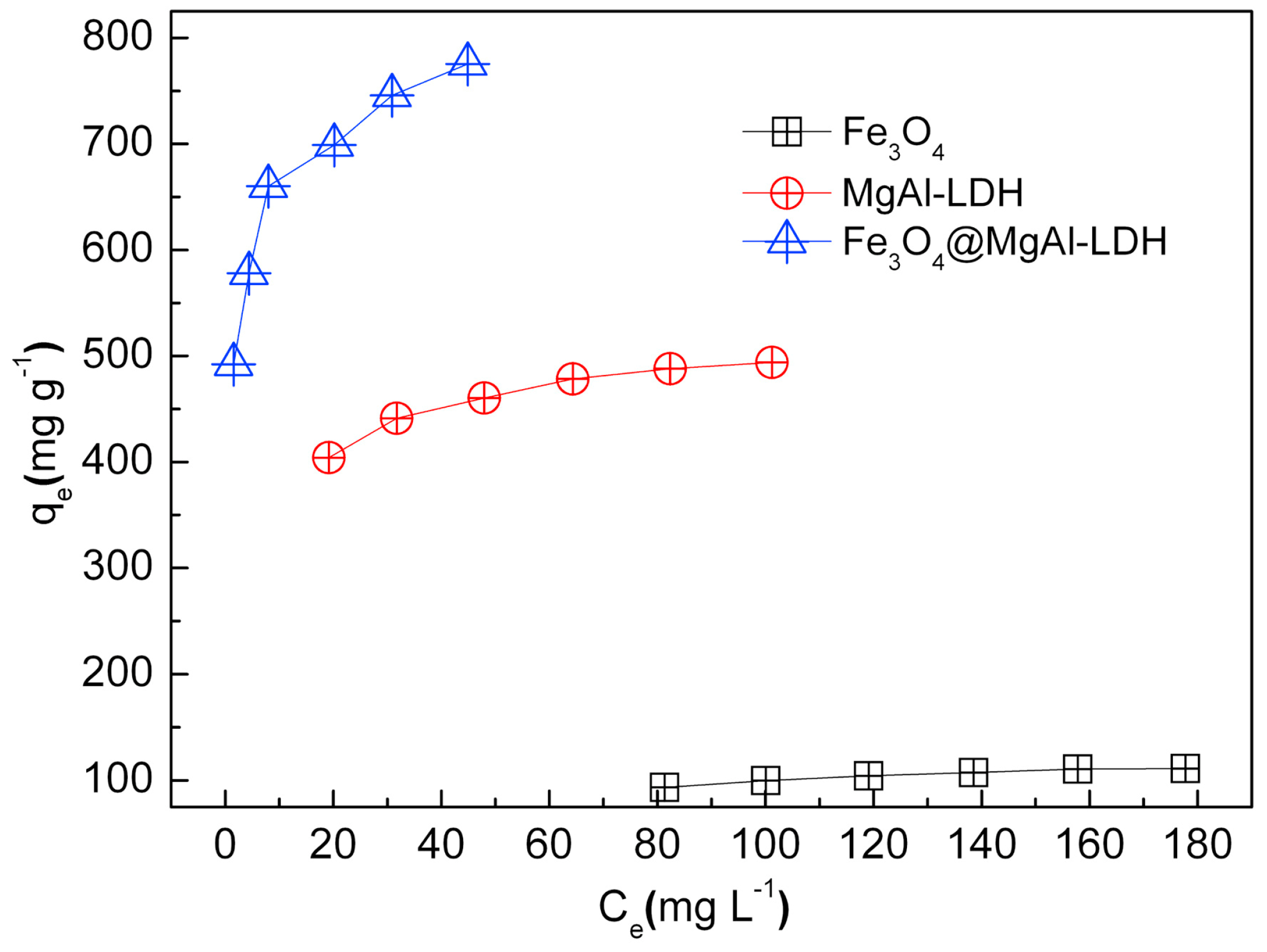
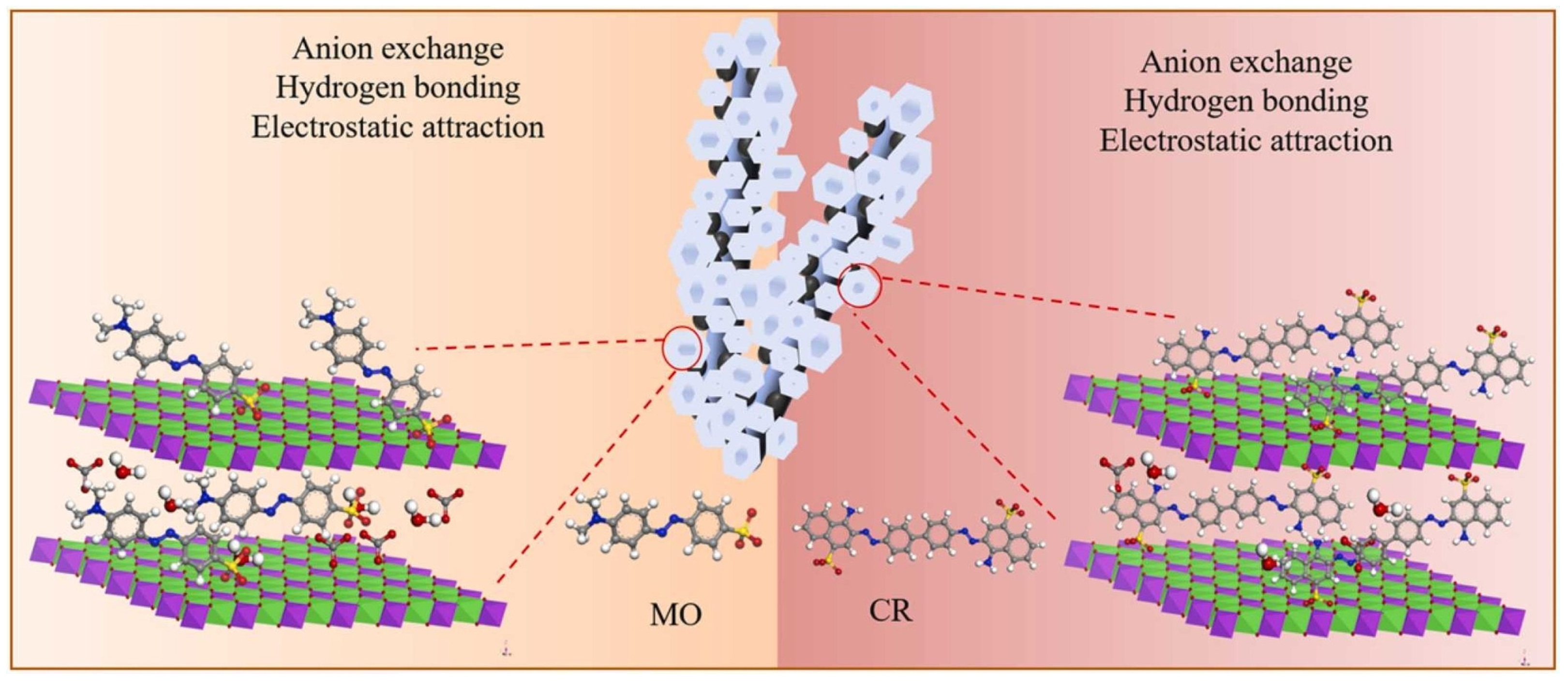
2.1.2. Dye Removal
- The kinetic study was carried out using Fe3O4/ZnCr-LDH composite at room temperature, 0.25 g/L adsorbent dosage, and 100 mg/L MO dye concentration. The contact time was between 5 min and 24 h. For comparison, the performance of ZnCr-LDH, Fe3O4, and an adsorbent obtained by physical mixture between Fe3O4 and ZnCr-LDH (abbreviated as Fe3O4+ ZnCr-LDH), was studied as well.
- Fe3O4/ZnCr-LDH and Fe3O4+ZnCr-LDH materials were used for the adsorption isotherm study. The adsorbent dosage was set at 0.25 g/L. The initial MO concentration varied from 50 mg/L to 500 mg/L.
- Mag-MgAl/SDS material is recommended as adsorbent for MB dye removal.
- Mag-MgAl adsorbent is recommended as adsorbent for PR dye removal.
- The simultaneous removal of both dyes have demonstrated that Mag-MgAl/SDS has the ability to remove a higher quantity of MB dye; in contrast, the Mag-MgAl adsorbent has the ability to better remove PR dye.
2.1.3. Removal of Other Categories of Pollutants
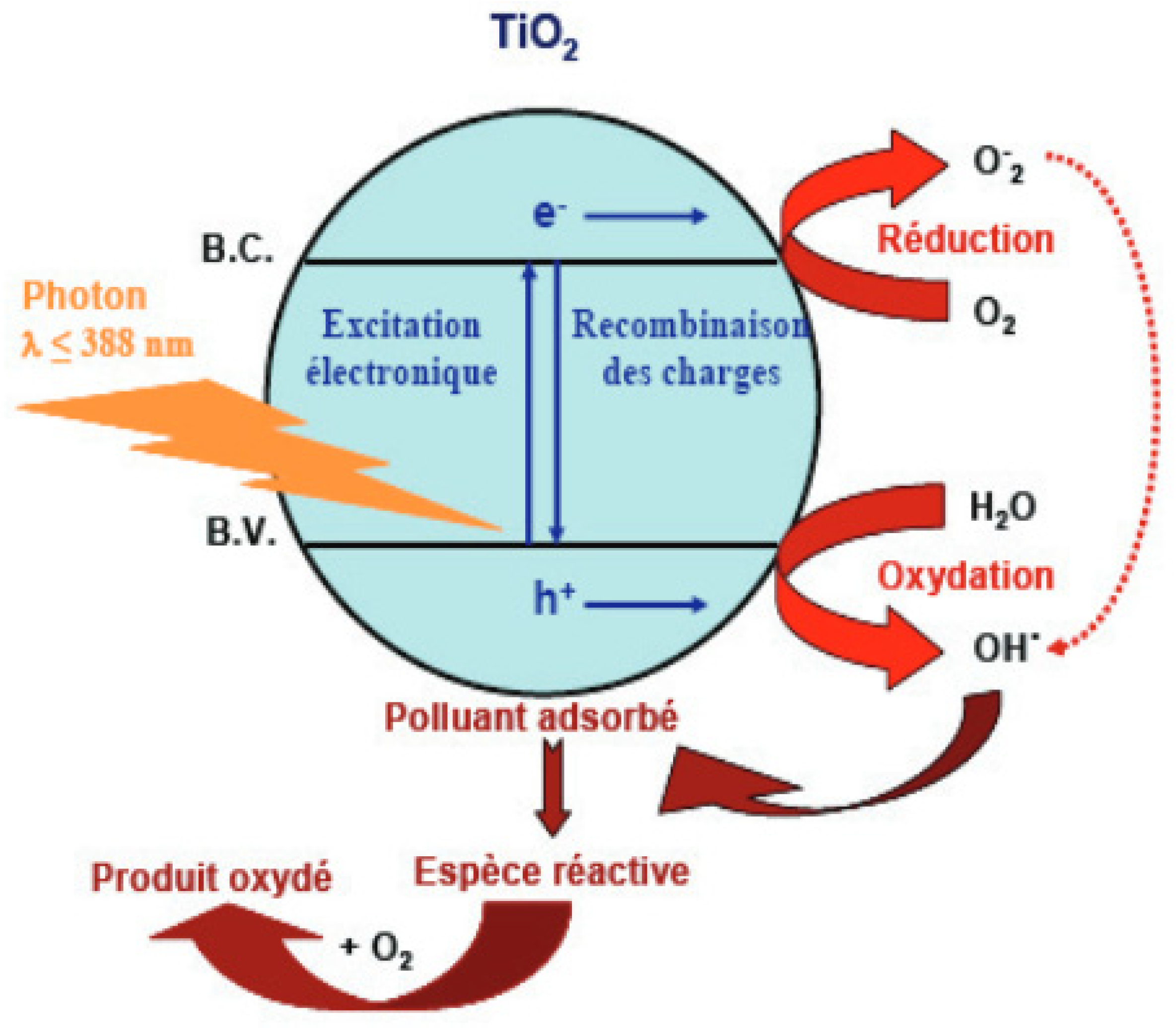
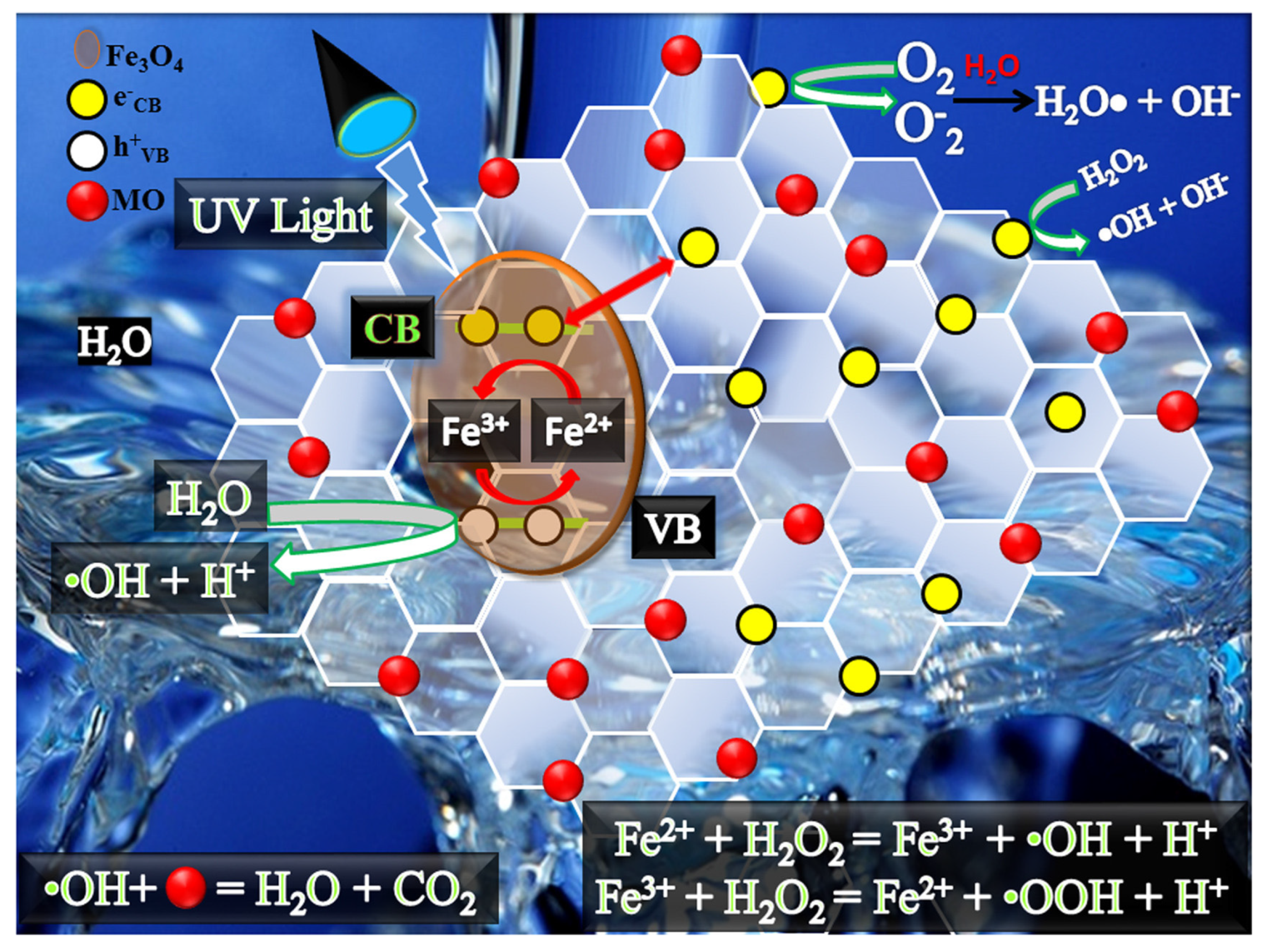
2.2. Magnetic Compounds as Catalysts for Water Treatment
2.2.1. Dye Removal
2.2.2. Phenolic Compounds Removal
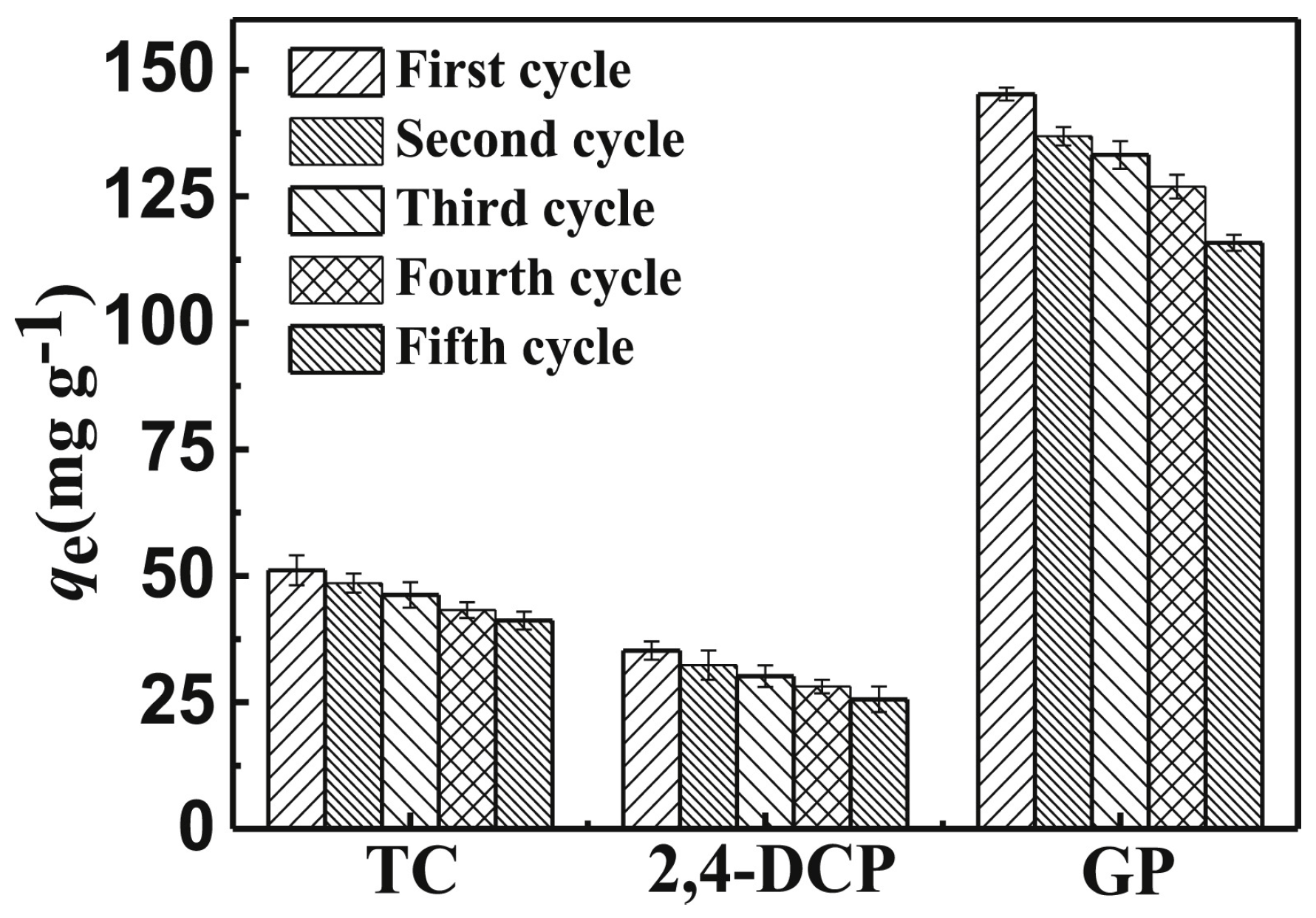
2.2.3. Simultaneous Removal of High-Risk Contaminants
3. Conclusions
- The critical water pollutants, specifically heavy metals, dyes, pharmaceutical products, phenolic compounds, phytohormone, and fungicides can be successfully removed by using both the adsorption and/or catalytic processes.
- Based on the reviewed papers, where results have been presented for real waters and, mostly, for synthetically prepared wastewaters, it can be concluded that the magnetic composite materials based on LDH and Fe3O4 may be considered as efficient adsorbents, especially for heavy metals and dye removal.
- Although the wastewaters contaminated with phenolic compounds are frequently treated by using the catalytic processes, the studies have demonstrated that the adsorption method is a good alternative.
- The ability of composite magnetic materials for the elimination of other categories of pollutants, specifically for the removal of some antibiotics and fungicides, was also reviewed. The results demonstrated that these types of composite magnetic materials can be successfully applied in water depollution.
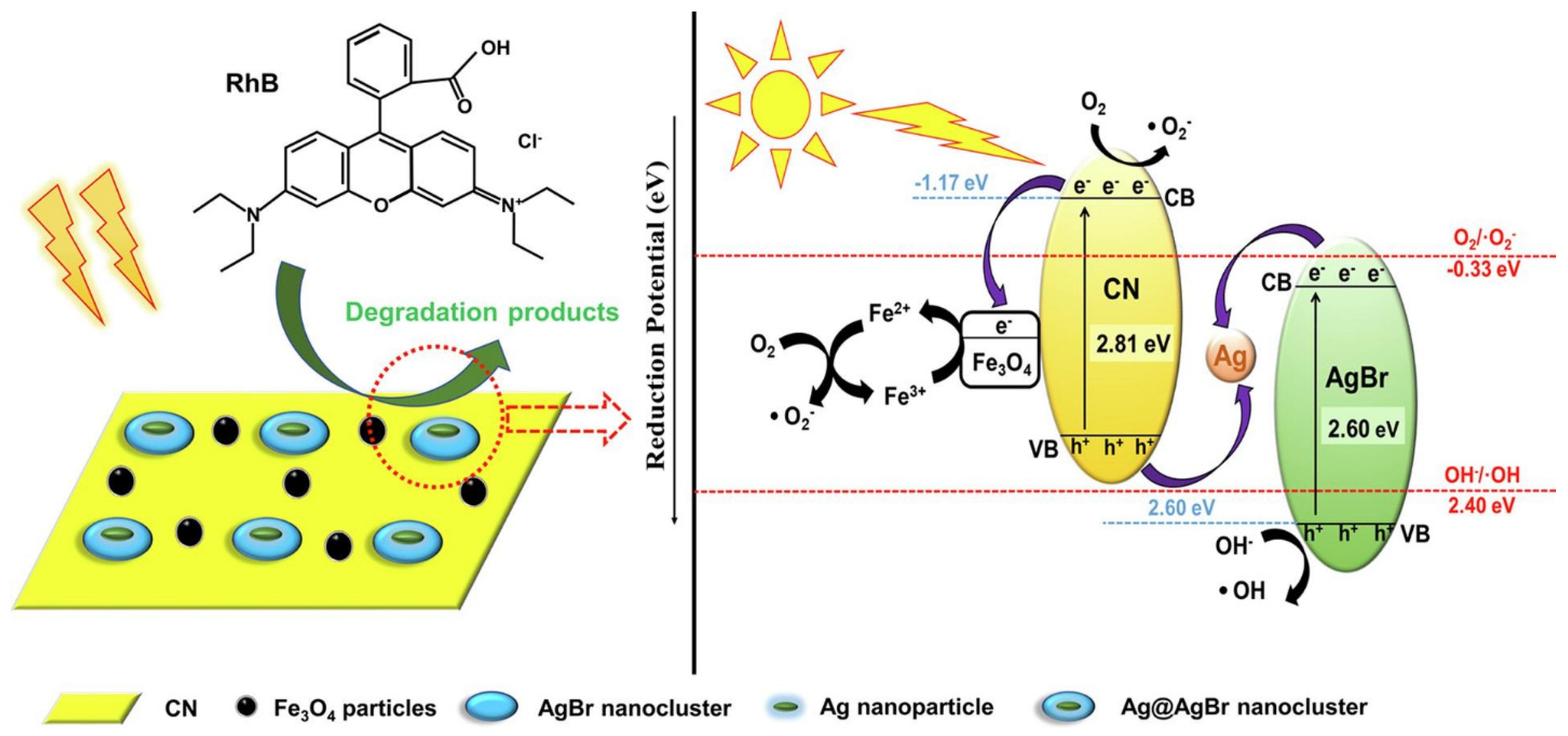
- The removal of dyes from polluted waters, using catalytic degradation, can be achieved with high efficiency (higher than 98%) using composite magnetic materials based on magnetite TiO2, SiO2, CeO2, MoS2 as catalysts but also using hybrid materials containing an organic compound as well as magnetite (such as PGO-TiO2/Fe3O4, Ag@AgBr/CN/Fe3O4, rCu2O-rGO/Fe3O4@SiO2, Fe3O4/MMT).
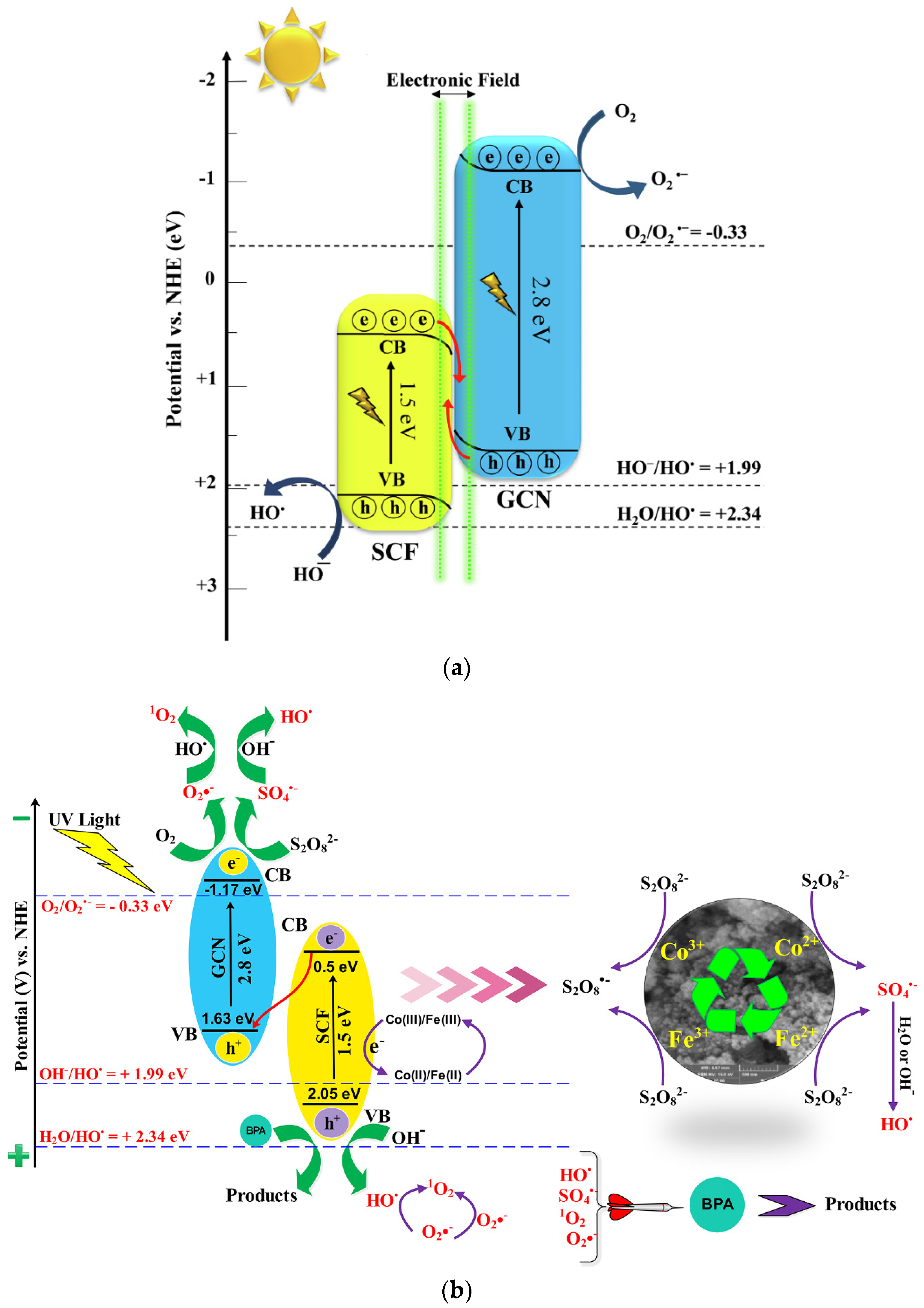
- The catalytic degradation of phenols from wastewaters can achieve 100% efficiency by using Fe3O4-BC heterogeneous catalysts. The increase in the catalytic efficiency from 54.77% (when Fe3O4 is used as catalyst) to 100% (when Fe3O4 –BC is used as catalyst) is due to the synergistic effect between the Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the biochar.
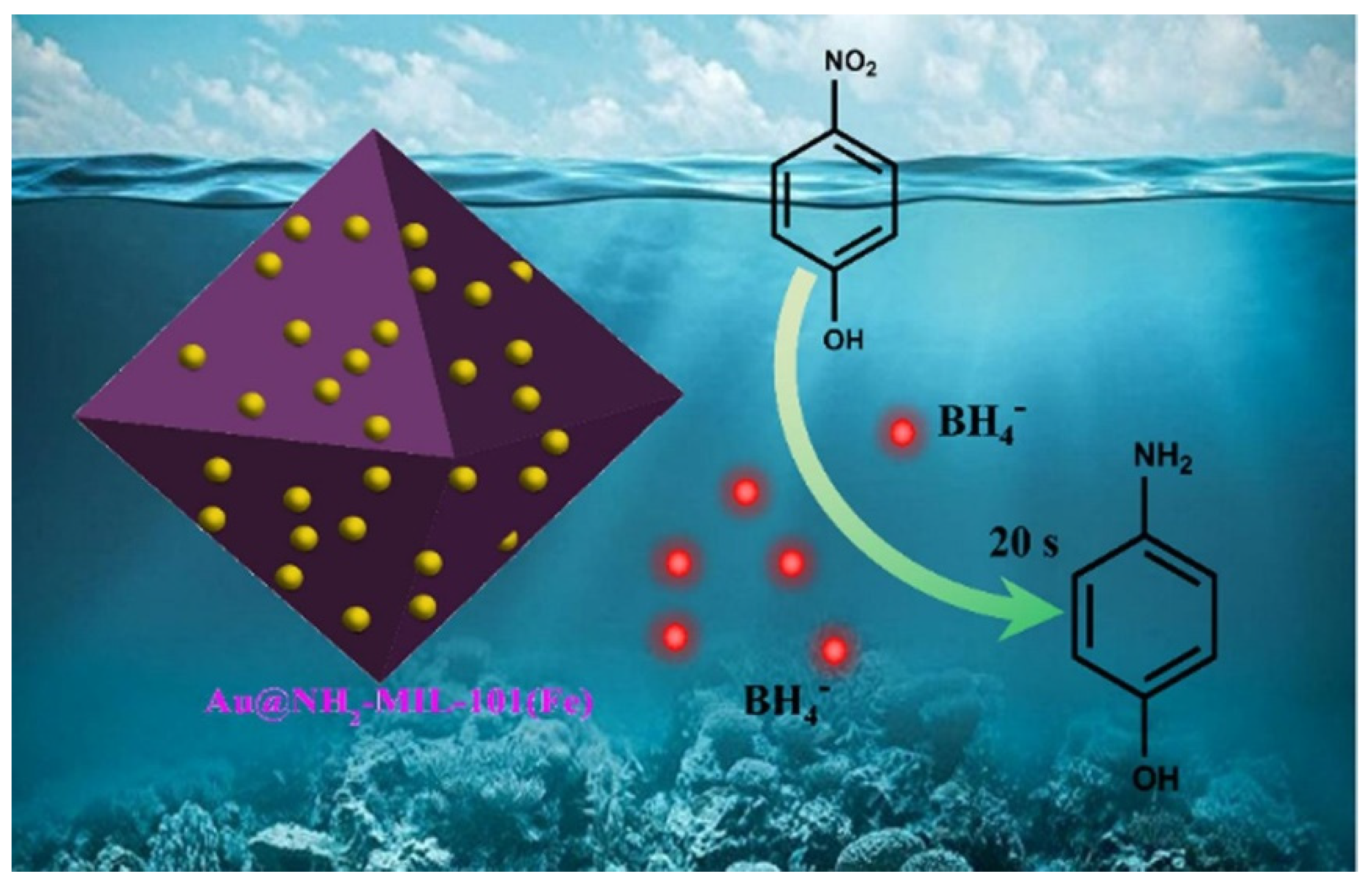
- The second approach used for the treatment of wastewaters polluted with phenols (more precisely nitrophenols), is the catalytic reduction of the nitro group in the amino group. The magnetic nanocomposite materials can be successfully used as catalysts for performing the chemical reduction in presence of NaBH4.
- Pharmaceutical products can also be eliminated from polluted waters by catalytic degradation, the reaction being able to reach an efficiency as high as 89.1%.
- Several authors have shown that catalytic degradation is efficient also for purifying waters polluted with multiple pollutants. Thus, multifunctional materials have been developed in order to efficiently clean waters polluted with dyes and phenols, heavy metals, or dyes and nitrophenols.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abin-Bazaine, A.; Campos Trujillo, A.; Olmos-Marquez, M. Adsorption Isotherms: Enlightenment of the Phenomenon of Adsorption. In Wastewater Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Kajjumba, G.; Emik, S.; Öngen, A.; Kurtulus Özcan, H.; Aydın, S. Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Shuaib, D.T.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Etsuyankpa, M.B.; Sumaila, A.; Mohammed, U.M.; Nasirudeen, M.B. Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for the removal of Pb(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions using Albizia lebbeck pods. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Akbar, J.; Iqbal, S.; Noreen, S.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Study of Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Parameters for Adsorption of Cadmium: An Overview of Linear and Nonlinear Approach and Error Analysis. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3463724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, M.; Singh, A.; Suryawanshi, B.; Yash Jaiswal, Y. Synthesis and characterization of MgAl- layered double hydroxide with graphene oxide intercalation: Application in lead removal from spent batteries effluent. Mater. Today Proc. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.L.; Lester, E.; Williams, O.; Gomes, R.L. Understanding Layered Double Hydroxide properties as sorbent materials for removing organic pollutants from environmental waters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Liang, C.; Lin, W.; Zeng, J.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y. Preparation and characterization of phase change material microcapsules with carbon nanotubes loaded with MgAl layered double hydroxides for controlling temperature in the building. J. Energy Storage 2024, 80, 110357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, K.; Zhang, F.; Johnson, Q.; Jitianu, M.; Tan, W.K.; Kawamura, G.; Matsuda, A.; Jitianu, A. Control of Micro- and Nanostructures of Layered Double Hydroxides by Hydrothermal Treatment. Cryst. Growth Des. 2023, 23, 2128–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanashi, I.; Kameda, T.; Kumagai, S.; Saito, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Kawamura, D.; Yoshioka, T. Synthesis of layered double oxide with high specific surface area by innovative sol-gel method through its application to arsenate anion adsorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomeyrani, S.F.N.; Ghalami-Choobar, B.; Azqhandi, M.H.A.; Foroughi, M. An enhanced removal of para-nitrophenol (PNP) from water media using CaAl-layered double hydroxide-loaded magnetic g-CN nanocomposite. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knorpp, A.J.; Zawisza, A.; Huangfu, S.; Borzì, A.; Clark, A.H.; Kata, D.; Graule, T.; Stuer, M. Hydrothermal synthesis of multi-cationic high-entropy layered double hydroxides. RCS Adv. 2022, 12, 26362–26371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.Q.; Van, D.C.; Thang, D.X.; An, N.T.K.; Trang, T.T.; Nhi, B.D.; Thao, N.P.; Son, L.; Huy, N.N.; Dung, N.T. Hydrothermal synthesis of CuCoFe layered double hydroxide and its performance in the degradation of antibiotics: Influencing factors, degradation pathways, and reaction mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhtiyarova, M.V. A review on effect of synthesis conditions on the formation of layered double hydroxide. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 269, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Long, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Bai, Z.; Liu, X. A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by layered double hydroxide and its composites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, L.A.; Barrera, D.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Sapag, K. Influence of the synthesis method of layered double hydroxides on the textural properties and nitrate removal. Catal. Today 2023, 422, 114222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichit, D.; Layrac, G.; Alvarez, M.G.; Marcu, I.C. Formation pathways of MII/MIII layered double hydroxides: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 248, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillot, D.; Bennici, S.; Brendlé, J. Layered double hydroxides and LDH-derived materials in chosen environmental applications: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24375–24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, M.J. Magnetic two-dimensional Ca-Al layered double hydroxide/Fe3O4@dextran nanocomposites as drug delivery systems. J. Cryst. Growth 2023, 611, 127186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wu, H.; Han, Z.; Chen, L.; Tang, B.; Cui, P.; Liu, H.; Chao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Z. Boron nitride modified CuZn-calcinated layered double hydroxides as efficient adsorbents for tetracycline removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 340, 126648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudchenko, N.; Pawar, S.; Perelshtein, I.; Fixler, D. Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Optics and Nanophotonics. Materials 2022, 15, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiola, A.R.; Bessa, R.A.; Oliveira, C.P.; Freitas, A.D.L.; Soares, S.A.; Bohn, F.; Pergher, S.B.C. Magnetic zeolite composites: Classification, synthesis routes, and technological applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 560, 169651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Han, M.; Su, Q.; Xia, L.; Hui, Z. Adsorption Properties of Magnetic Magnetite Nanoparticle for Coexistent Cr(VI) and Cu(II) in Mixed Solution. Water 2020, 12, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudcová, B.; Veselská, V.; Filip, J.; Číhalová, S.; Komárek, M. Highly effective Zn(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solutions using Mg-Fe layered double hydroxides: Comprehensive adsorption modeling coupled with solid state analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lin, C.C.; Woo, S.H.; Huang-Ping Chao, H.P. Efficient removal of copper and lead by Mg/Al layered double hydroxides intercalated with organic acid anions: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 154, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Nora, F.B.; Lima, V.V.C.; Oliveira, M.L.S.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Lima Burgo, T.A.; Meili, L.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorptive potential of Zn–Al and Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides for the removal of 2–nitrophenol from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awes, H.; Zaki, Z.; Abbas, S.; Dessoukii, H.; Zaher, A.; Abd-El Moaty, S.A.; Shehata, N.; Farghali, A.; Mahmoud, R.K. Removal of Cu2+ metal ions from water using Mg-Fe layered double hydroxide and Mg-Fe LDH/5-(3-nitrophenyllazo)-6-aminouracil nanocomposite for enhancing adsorption properties. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47651–47667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hady, E.E.; Mohamed, H.F.M.; Hafez, S.H.M.; Fahmy, A.M.M.; Magdy, A.; Mohamed, A.S.; Ali, E.O.; Abdelhamed, H.R.; Mahmoud, O.M. Textural properties and adsorption behavior of Zn-Mg-Al layered double hydroxide upon crystal violet dye removal as a low cost, effective, and recyclable adsorbent. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, A.G.; Ahmad, J.; Alasmari, Z.; Ibrahim, H.M. Removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated soil and water by Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide and its composite with biochar. Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iconaru, S.L.; Guégan, R.; Popa, C.L.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Ciobanu, C.S.; Daniela Predoi, D. Magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles as adsorbents for As and Cu removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, C.; Tang, H.; Liu, W. Magnetic Fe3O4 based layered double hydroxides (LDHs) nanocomposites (Fe3O4/LDHs): Recent review of progress in synthesis, properties and applications. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.Q.; Yan, L.G.; Du, B.; Pei, Z.G. Removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions by magnetic alginate microsphere based on Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Yan, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Shan, L.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption performance and mechanistic study of heavy metals by facile synthesized magnetic layered double oxide/carbon composite from spent adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, E.S.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, M. Fe3O4-FeMoS4: Promise magnetite LDH-based adsorbent for simultaneous removal of Pb (II), Cd (II), and Cu (II) heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherca, D.; Borhan, A.I.; Mihai, M.M.; Herea, D.D.; Stoian, G.; Roman, T.; Chiriac, H.; Lupu, N.; Buema, G. Magnetite-induced topological transformation of 3D hierarchical MgAl layered double hydroxides to highly dispersed 2D magnetic hetero-nanosheets for effective removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 284, 126047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, H.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Mao, X.M.; Li, H. Synthesis of novel magnetic rhamnolipid-activated layered double hydroxides nanocomposite for simultaneous adsorption of Cu(II) and m-cresol from aqueous solution. Powder Technol. 2021, 386, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, S.; Sedghi-Asl, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Mohammadi-Asl, Z.; Rahmanian, M. Magnetic layered double hydroxide composite as new adsorbent for efficient Cu (II) and Ni (II) ions removal from aqueous samples: Adsorption mechanism investigation and parameters optimization. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.Y.; Yuan, X.Z.; Wu, Z.B.; Zeng, G.M.; Jiang, L.B.; Peng, X.; Li, H. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide with Fe3O4-carbon spheres on the removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, F.; Liu, D.L.; Shi, P. Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater via adsorption with novel magnetic Fe3O4@C@MgAl-layered double-hydroxide. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Hao, B.; Xu, F.; Liu, K. Self-assembled morphology-controlled hierarchical Fe3O4@LDH for Cr(VI) removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Ding, C.; Shi, M.; Ding, Z.; Du, P.; Xia, M.; Wang, F. Easy separation dual-function Cu2O@LDH@Fe3O4 adsorbent for the removal of Cr(VI) under dark conditions: Experimental and mechanistic study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.F.; Wu, M.; Jing, R.S.; Liu, X.J.; Shao, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, F.Z.; Liu, A.J.; Meng, Z.L. One-pot formation of magnetic layered double hydroxide based on electrostatic self-assembly to remove Cr(VI) from wastewater. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 182, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinari, M.; Shirani, M.A.; Maleki, M.H.; Tabatabaeian, R. Green cross-linked bionanocomposite of magnetic layered double hydroxide/guar gum polymer as an efficient adsorbent of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylinska, N.; Puzyrnaya, L.; Pshinko, G. Magnetic nanocomposites based on Zn,Al-LDH intercalated with citric and EDTA groups for the removal of U(vi) from environmental and wastewater: Synergistic effect and adsorption mechanism study. RCS Adv. 2022, 12, 32156–32172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, J.X.; Jiang, C.F.; Wang, F.; Qiu, M.Q.; Xu, Q.G. Fabrication of Fe3O4/MgAl-layered double hydroxide magnetic composites for the effective decontamination of Co(II) from synthetic wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 207, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, J.; Ng, D.H.L.; Yang, P.; Song, P.; Zuo, M. Synthesis of novel hierarchically porous Fe3O4@MgAl–LDH magnetic microspheres and its superb adsorption properties of dye from water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 46, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.G.; Li, B.; Wen, X.G. Synthesis and adsorption properties of hierarchical Fe3O4@MgAl-LDH magnetic microspheres. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengqian, F.; Yimin, D.; Ling, C.; Zhiheng, W.; Qi, L.; Yaqi, L.; Ling, C.; Bo, L.; Yue-Fei, Z.; Yan, L.; et al. One-step coprecipitation synthesis of Cl− intercalated Fe3O4@SiO2 @MgAl LDH nanocomposites with excellent adsorption performance toward three dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengqian, F.; Wanbing, L.; Yimin, D.; Zhiheng, W.; Yaqi, L.; Ling, C.; Bo, L.; Siwen, Y.; Junlong, W.; Xianglong, D.; et al. Synthesis of a novel hierarchical pillared Sep@Fe3O4/ZnAl-LDH composite for effective anionic dyes removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663, 130921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Hatami, M. An effective, low-cost and recyclable bio-adsorbent having amino acid intercalated LDH@Fe3O4/PVA magnetic nanocomposites for removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 174, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Anitha, V.; Gajula, G.P.; Thiagarajan, V. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Superadsorbent Fe3O4-PEG-Mg-Al-LDH Nanocomposites for Ultrahigh Removal of Organic Dyes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Guo, Y.; Hong Liu, H. Magnetic Fe3O4/ZnCr-layered double hydroxide composite with enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, H.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Mao, X.M.; Li, H. A magnetic core-shell dodecyl sulfate intercalated layered double hydroxide nanocomposite for the adsorption of cationic and anionic organic dyes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooni, M.A.K.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Davardoostmanesh, M. Magnetic graphene oxide/Mg-Al layered double hydroxide nanocomposite as an efficient adsorbent for removal of methylene blue: A study of equilibrium isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamic and reusability. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 300, 117123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaeian, R.; Dinari, M.; Aliabadi, H.M. Cross-linked bionanocomposites of hydrolyzed guar gum/magnetic layered double hydroxide as an effective sorbent for methylene blue removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Y. Facile synthesis of magnetic ZnAl layered double hydroxides and efficient adsorption of malachite green and Congo red. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.; Wen, X. A novel Fe3O4/MgAl-LDH hollow microspheres for effective removal of dyes from wastewater. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 959, 170528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.H.M.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Thalij, K.M.; Althomali, R.H.; Abdullaev, S.; Abdulameer, S.F.; Alawadi, A.H.; Alsaalamy, A.; Dawood, F.A.; Ahmed, N.M. An efficient magnetic nanoadsorbent based on functionalized graphene oxide with gellan gum hydrogel embedded with MnFe layered double hydroxide for adsorption of Indigo carmine from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagtash, M.; Zolgharnein, J. Carbon-Magnetic Layered Double Hydroxide as a New Nanosorbent for Efficient Removal of Tartrazine and Indigo Carmine Dyes from Water Solutions; Multivariate Optimization and Adsorption Characterization. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2022, 44, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Babamoradi, M.; Ali Maleki, A. A magnetic and antibacterial nanocomposite based on graphene oxide nanosheets embedded with Zn-Fe layered double hydroxide as a novel and highly effective adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue dye. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 111010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, A.; Negarestani, M.; Kazemi, S.; Shayesteh, H.; Javanshir, S.; Ghiasinejad, H. Adsorption behavior of rhamnolipid modified magnetic Co/Al layered double hydroxide for the removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, A.C.R.; Zago, J.V.G.; Tremarin, B.G.; Mezalira, D.Z.; Cursino, A.C.T.; Bail, A.; Basso, R.L.D.; Giona, R.M. Enhancing adsorption capacity of magnetic magnesium-aluminum layered double hydroxide by surface modification with sodium dodecyl sulfate for efficient removal of organic contaminants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagtash, M.; Zolgharnein, J. Response surface optimization for simultaneous removal of Alizarin Red S and Alizarin Yellow dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic Zn-Al-Zr layered double hydroxide. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlnasab, L.; Ezoddin, M.; Karimi, M.A.; Hatamikia, N. MCM-41@Cu-Fe-LDH magnetic nanoparticles modified with cationic surfactant for removal of Alizarin Yellow from water samples and its determination with HPLC. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 3249–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.G.L.; Lopes, P.A.; Resende, J.A.; Pinto, F.G.; Tronto, J.; Guerreiro, M.C.; de Oliveira, L.C.A.; Nunes, W.D.; Neto, J.L. Performance of magnetite/layered double hydroxide composite for dye removal via adsorption, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 179, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhu, M.Y.; Yu, J.G.; Meng, H.W.; Jiao, F.P. Effective removal of brilliant green from aqueous solution with magnetic Fe3O4@SDBS@LDHs composites. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mao, L.; Shuai, H.; Rong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of magnetic layer CaAl hydrotalcite composite for removal of fuchsin acid in simulated solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, A.; Ghiasinejad, H.; Javanshir, S.; Khadir, A.; Jamshidi, E. Efficient removal of Ibuprofen via novel core—shell magnetic bio-surfactant rhamnolipid—layered double hydroxide nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smata, A.; Yoshimura, C. One-step synthesis of magnetic–layered double hydroxide and its application for oxytetracycline removal from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azqhandi, M.H.A.; Foroughi, M.; Gholami, Z. Efficient removal of levofloxacin by a magnetic NiFe-LDH/N-MWCNTs nanocomposite: Characterization, response surface methodology, and mechanism. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 113967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, A.; Negarestani, M.; Kazemi, S.; Shayesteh, H.; Javanshir, S.; Ghiasinejad, H.; Jamshidi, E. Design and preparation magnetic bio-surfactant rhamnolipid-layered double hydroxide nanocomposite as an efficient and recyclable adsorbent for the removal of Rifampin from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, X.F.; Zhou, H.; Pan, Z.Q.; Wang, D.S. Preparation of magnetic polyimide@ Mg-Fe layered double hydroxides core-shell composite for effective removal of various organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Cremosphere 2019, 219, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.B.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, L.X.; Li, N.; Luan, L.Y.; Yan, Z.X.; Lin, J.M.; Zhao, R.S. Magnetic ternary layered double hydroxides for efficient removal of 1-naphthalene acetic acid from waters: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.X.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.H.; Xie, M.; Li, N.; Zhao, R.S. Effectively removing indole-3-butyric acid from aqueous solution with magnetic layered double hydroxide-based adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.H.; Senosy, I.A.; Zhou, D.D.; Yang, Z.H.; Guo, H.M.; Liu, X. Synthesis and adsorption properties investigation of Fe3O4@ZnAl-LDH@MIL-53(Al) for azole fungicides removal from environmental water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmina, M.; Mourad, K.; Mohammed, S.H.; Khaoula, C. Treatment heterogeneous photocatalysis. Factors influencing the photocatalytic degradation by TiO2. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Gafer, A.K.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Tawfeek, A.M.; Ezzat, A.O. Hybrid Ionic Silver and Magnetite Microgels Nanocomposites for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue. Molecules 2019, 24, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Fermah, A.; Rajput, J.K.; Singh, H.; Badhan, J. Efficient solar light-driven degradation of Congo red with novel Cu-loaded Fe3O4@TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19546–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Kong, X.; Yang, C.; Ren, B.; Tang, Q. Fabrication and characterization of the magnetic separation photocatalyst C-TiO2@Fe3O4/AC with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Bakr, S.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M. Magnetic hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4@ZIF-67/CuNiMn-LDH catalyst with enhanced redox cycle for Fenton-like degradation of Congo red: Optimization and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75332–75348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Lu, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, L. Synergistic photocatalysis-fenton reaction of flower-shaped CeO2/Fe3O4 magnetic catalyst for decolorization of high concentration congo red dye. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Salam, A.; Khan, H.; Qureshi, A.; Saeed, A. Green synthesis of magnetic chitosan composite hydrogel (Fe3O4@CS photocatalyst) for the solar light driven catalytic degradation of organic contaminants. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2024, 14, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdallat, Y.; Jum’h, I.; Al Bsoul, A.; Jumah, R.; Telfah, A.; Telfah, A. Photocatalytic Degradation Dynamics of Methyl Orange Using Coprecipitation Synthesized Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Ahmad, I.; Israr, M. Graphene/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Interplay between photo-Fenton type reaction, and carbon purity for the removal of methyl orange. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2643–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhai, J.; Cui, W. Adsorption and catalytic removal of methyl orange from water by PIL-GO/TiO2/Fe3O4 composites. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 154, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, B.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, B.; Yu, P.; Sun, Y.; Mei, D. Efficiently enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity by in situ deposition of Ag@AgBr on g-C3N4/Fe3O4 magnetic heterogeneous materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Huang, G.; Zhu, D.; Hu, K. Facile synthesis of MoS2/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with excellent Photo-Fenton-like catalytic performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, H. Sodium citrate functionalized reusable Fe3O4@TiO2 photocatalyst for water purification. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 686, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-H.; Lu, J.-S.; Yang, S.-W. Highly visible-light-responsive Cu2O/rGO decorated with Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles as a magnetically recyclable photocatalyst. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 305606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, H.; Khaled, A.; Halladja, S.; Boudraa, I.; Rehimi, Z.; Chehimi, M.M. Fe3O4/MMT Fenton-like heterogeneous catalyst for the methylene blue degradation. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 260, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Song, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhu, A.; Yang, H.; Yang, S. An effective and magnetic Fe2O3-ZrO2 catalyst for phenol degradation under neutral pH in the heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 201, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, D.; Huang, J.; Zhu, K.; Lei, L.; He, H.; Ai, Y. One-step synthesis of novel Fe/Fe3O4 embedded in N-doped graphite-like carbon nanosheets with the entangled CNTs to activate peroxymonosulfate for bisphenol a degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, S.-S.; Geng, Y.; Zhen, J.; Zhan, J.; Cao, C.; Ni, S.-Q. Synergistic catalysis by Fe3O4-biochar/peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of bisphenol a. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Yang, W.; Gao, K.; Tang, J. Concave gold nano-arrows (AuCNAs) for efficient catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, J.; Bhunia, T.; Gorai, S.; De, D.; Karmakar, P.; Gachhui, R. Efficient degradation of 4-nitrophenol and colorimetric detection of Fe (III) by biogenic silver nanoparticles of Papiliotrema laurentii. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 296, 116647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Qiang, Z.; Ren, J. Au-Fe3O4 decorated polydopamine hollow nanoparticles as high performance catalysts with magnetic responsive properties. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 215606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, X.; Subhan, S.; Gong, W.; Li, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Ji, H.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Construction of novel Cu-based bimetal polycrystal@carbon catalyst prepared from bimetal HKUST-1 type MOFs (MOF-199s) for ultrafast reduction of 4-nitrophenol via interfacial synergistic catalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhen, S.; Zhan, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Y. Rapid and facile synthesis of Au nanoparticle-decorated porous MOFs for the efficient reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiano, V.; Sacco, O.; Sannino, D.; Stoller, M.; Ciambelli, P.; Chianese, A. Photocatalytic removal of phenol by ferromagnetic N-TiO2/SiO2/Fe3O4 nanoparticles in presence of visible light irradiation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 47, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgaonkar, I.Z.; Pandit, A.B. Sonophotochemical destruction of aqueous solution of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. Ultrason. Sonochem. 1998, 5, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, U.I.; Abdullah, A.H.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z. Photocatalytic removal of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol from water exploiting commercial ZnO powder. Desalination 2010, 263, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-J.; Fang, G.-C.; Wang, C.-C. A nanometer-ZnO catalyst to enhance the ozonation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 260, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, S.; Vinu, A.; Mori, T.; Gokulakrishnan, N.; Srinivasu, P.; Murugesan, V.; Ariga, K. Photocatalytic degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol using lanthanum doped ZnO in aqueous suspension. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Díaz, G.; Celis-García, M.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Heterogeneous catalytic 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degradation at hemin–acrylic copolymer. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 96, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Xu, J.; Yu, J.; Cong, S.; Yan, X. Experimental and quantum chemical investigation on the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by Ag/TiO2 nanotube electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 921, 116662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Cui, J.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, X. Improved photodegradation and detoxification of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by lanthanum doped magnetic TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, Q.; Lv, B.; Zheng, M.; Zhan, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, R.; Zeng, H.; Mao, B. Surface modified silver/magnetite nanocomposite activating hydrogen peroxide for efficient degradation of chlorophenols. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 617, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.-H.; Min, J.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, B.J.; Jung, J.-S. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tri-chlorophenol by Fe3O4@TiO2@Au photocatalyst under visible-light. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9477–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Ahmadi, M.; Gohari, F. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate via nanocomposite CeO2-Fe3O4 for organic pollutants removal: The effect of UV and US irradiation and application for real wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, J. Degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol using magnetic nanoscaled Fe3O4/CeO2 composite as a heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Pan, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y. Fe3O4@CNT as a high-effective and steady chainmail catalyst for tetracycline degradation with peroxydisulfate activation: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 273, 118705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, F.; Feng, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zuo, S.; Cui, A.; Yao, C. Magnetically Separable Mesoporous Fe3O4@g-C3N4 as a Multifunctional Material for Metallic Ion Adsorption, Oil Removal from the Aqueous Phase, Photocatalysis, and Efficient Synergistic Photoactivated Fenton Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 8895–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Kakavandi, B.; Bahadoran, A.; Giannakis, S.; Dehghanifard, E. Intensification of persulfate-mediated elimination of bisphenol A by a spinel cobalt ferrite-anchored g-C3N4S-scheme photocatalyst: Catalytic synergies and mechanistic interpretation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi, J.; Khaleghian, M.; Mirtamizdoust, B.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. Fabrication of Copper (II)-Coated Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticles Fe3O4@SiO2: An Effective and Recoverable Catalyst for Reduction/Degradation of Environmental Pollutants. Crystals 2022, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Dong, Y.; Rahman, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ren, C.; Chen, X. In situ preparation of core-satellites nanostructural magnetic-Au NPs composite for catalytic degradation of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, J.; Twinkle; Tisha; Nisha; Baig, A.; Sonal Dubey, P.; Sonkar, S.K. Photoactive Fe3O4@Fe2O3 Synthesized from Industrial Iron Oxide Dust for Fenton-Free Degradation of Multiple Organic Dye. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 10487–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wei, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; Li, Z. In situ doping lignin-derived carbon quantum dots on magnetic hydrotalcite for enhanced degradation of Congo Red over a wide pH range and simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dragos-Pinzaru, O.-G.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H.; Buema, G. Exploring the Utilization of Magnetic Composite Materials for High-Risk Contaminant Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption and Catalytic Processes—A Review. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080057
Dragos-Pinzaru O-G, Lupu N, Chiriac H, Buema G. Exploring the Utilization of Magnetic Composite Materials for High-Risk Contaminant Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption and Catalytic Processes—A Review. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(8):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080057
Chicago/Turabian StyleDragos-Pinzaru, Oana-Georgiana, Nicoleta Lupu, Horia Chiriac, and Gabriela Buema. 2024. "Exploring the Utilization of Magnetic Composite Materials for High-Risk Contaminant Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption and Catalytic Processes—A Review" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 8: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080057
APA StyleDragos-Pinzaru, O.-G., Lupu, N., Chiriac, H., & Buema, G. (2024). Exploring the Utilization of Magnetic Composite Materials for High-Risk Contaminant Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption and Catalytic Processes—A Review. Magnetochemistry, 10(8), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10080057








