The Influence of Current Magnitudes and Profiles on the Sedimentation of Magnetorheological Fluids: An Experimental Work
Abstract
1. Introduction
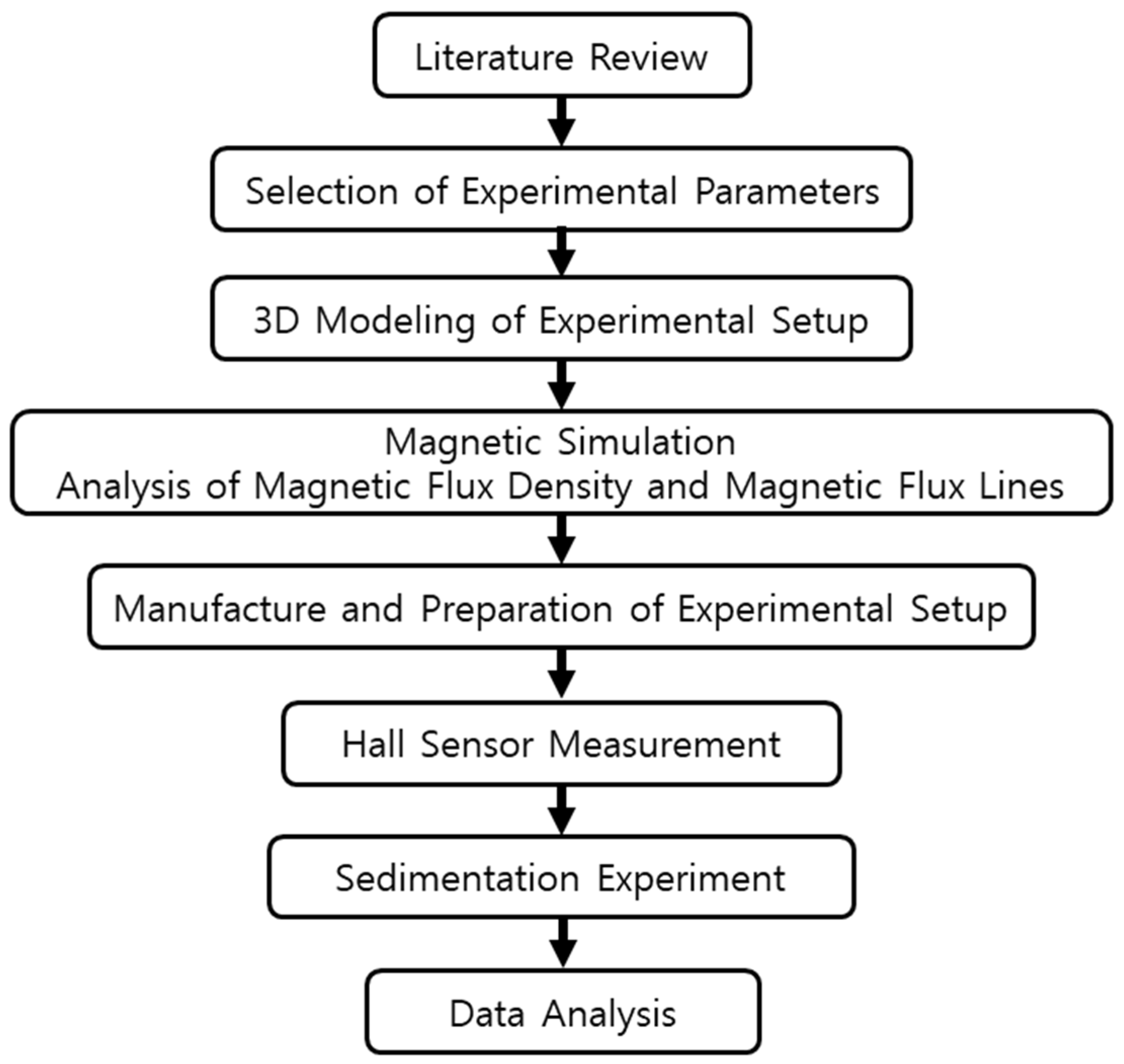
2. Materials and Methods
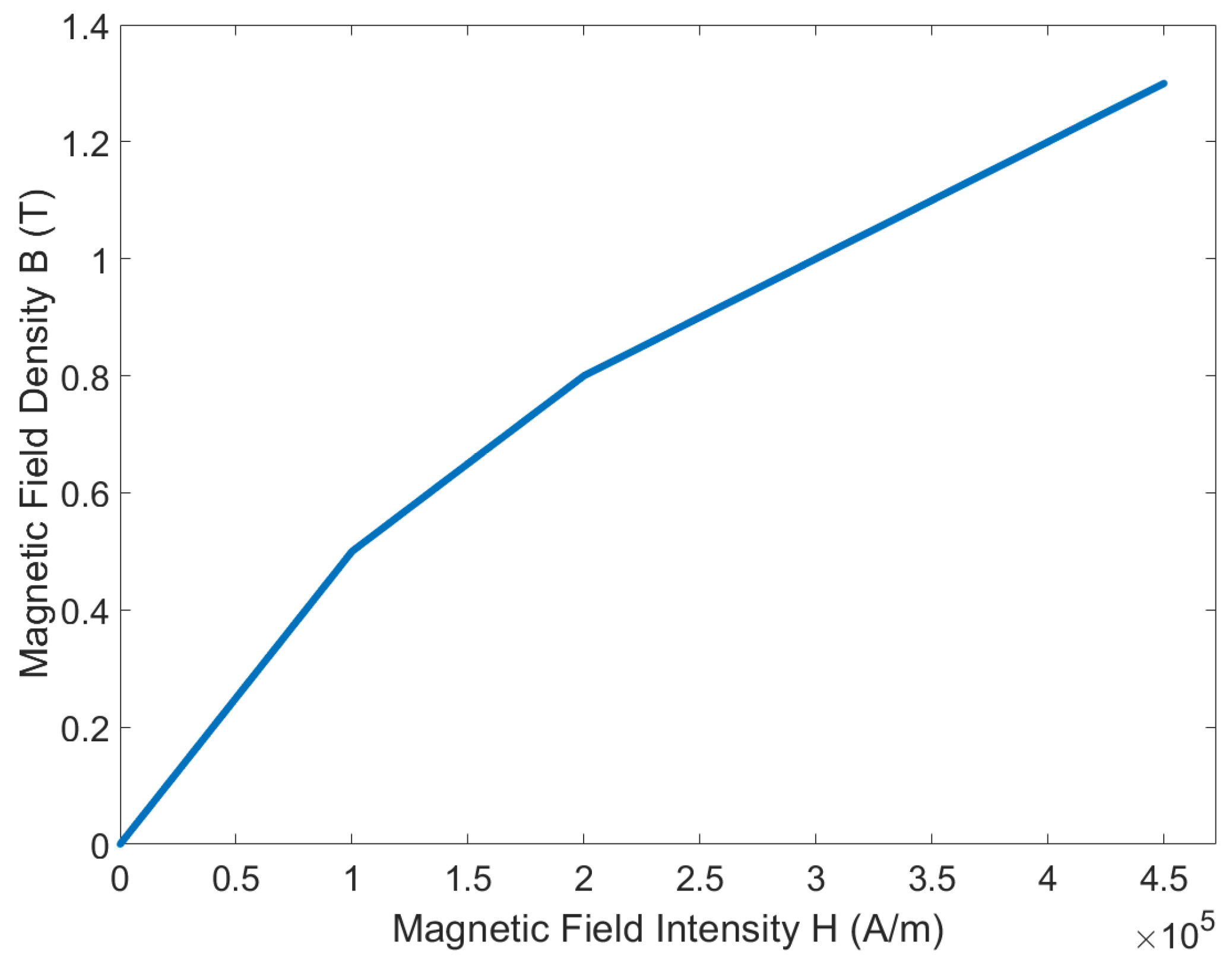
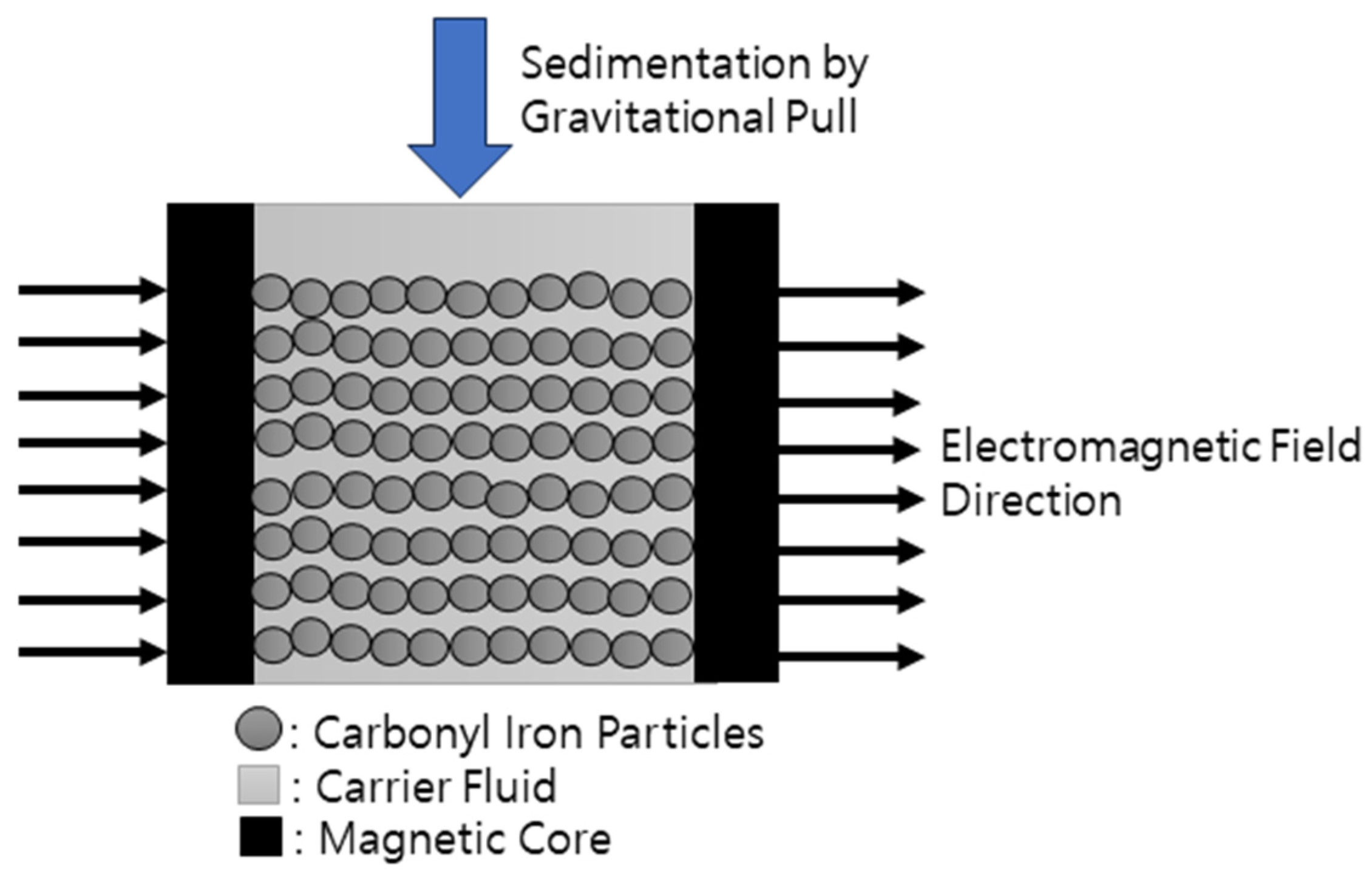
2.1. Magnetic Analysis
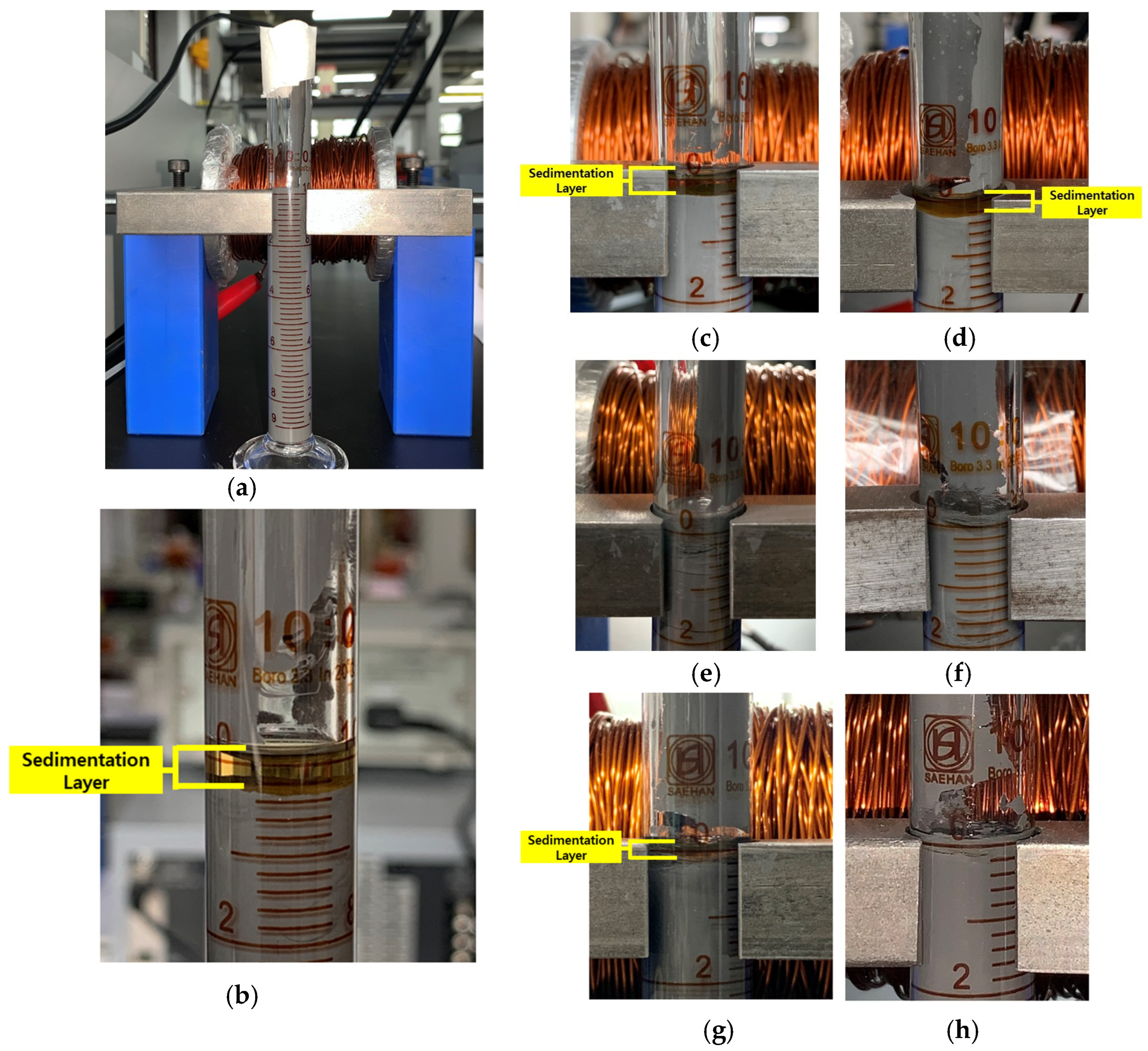
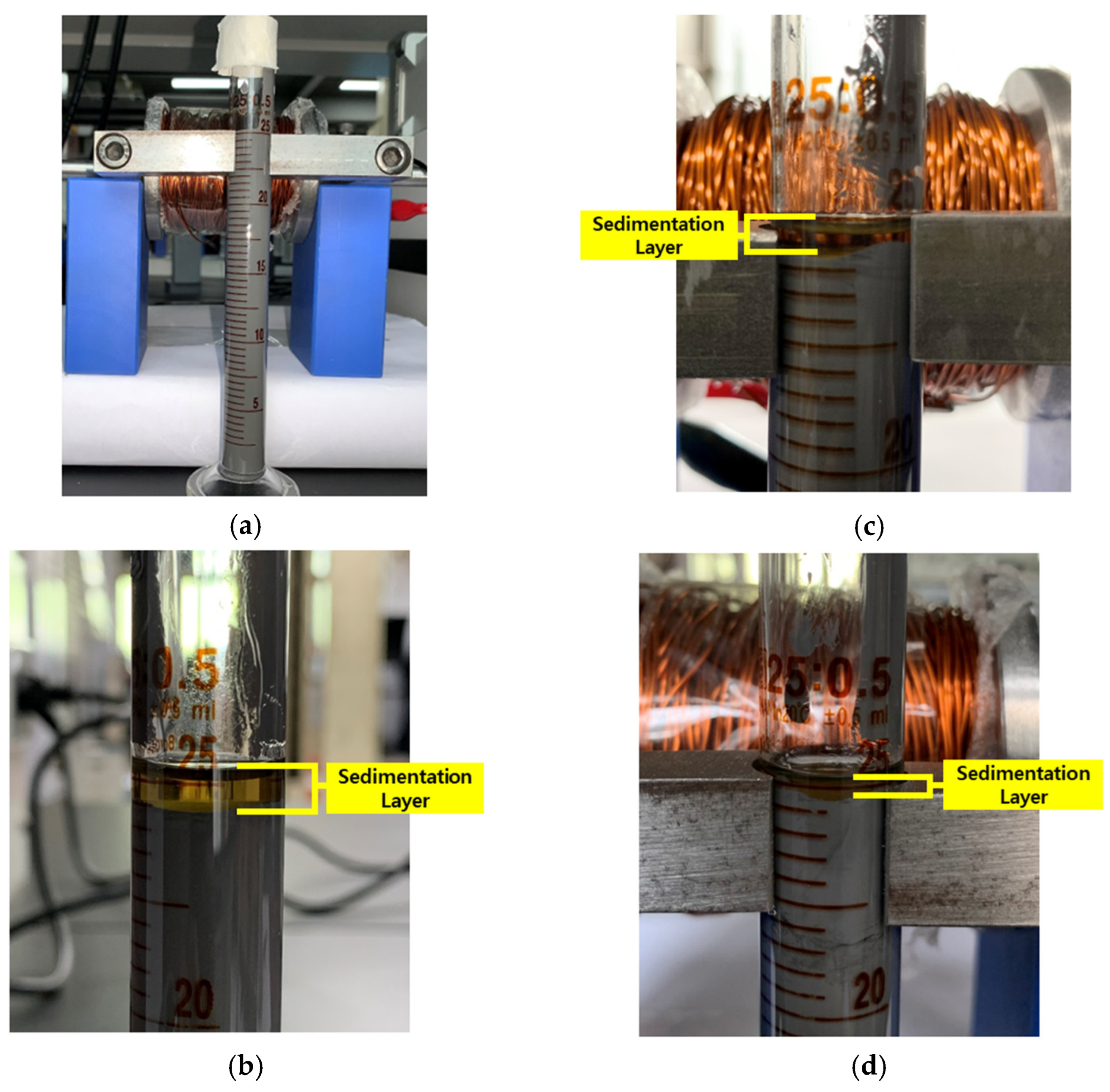
2.2. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
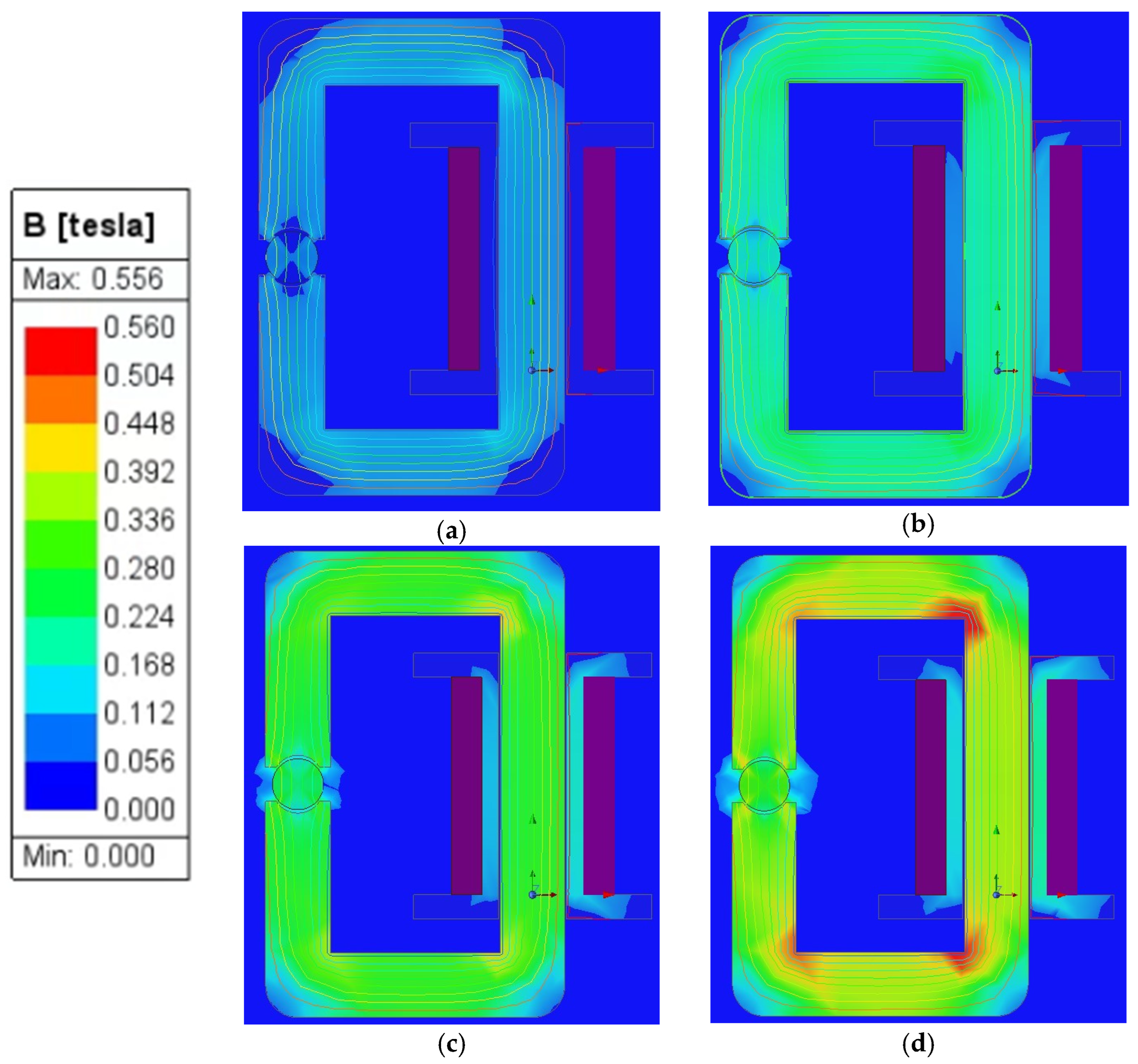
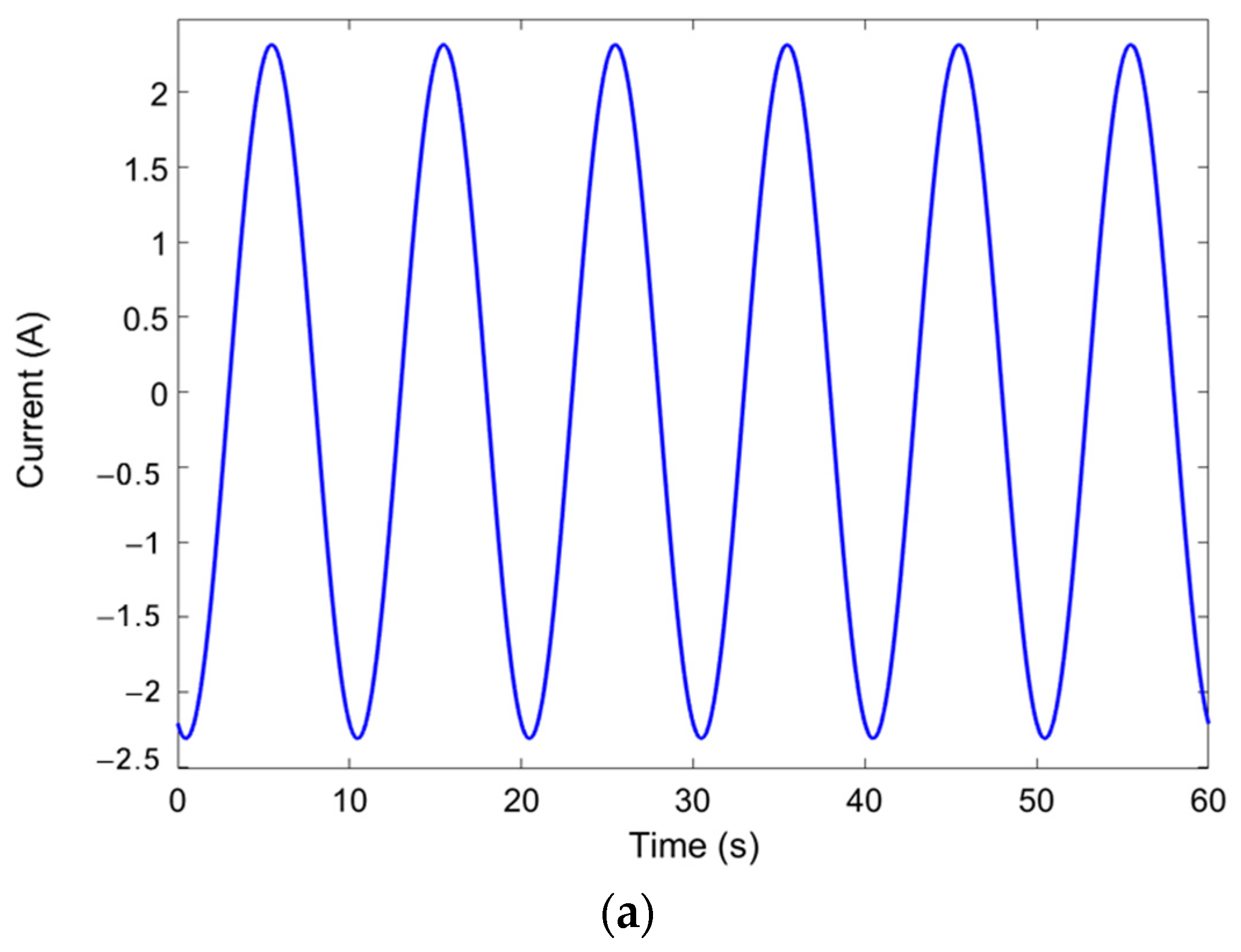
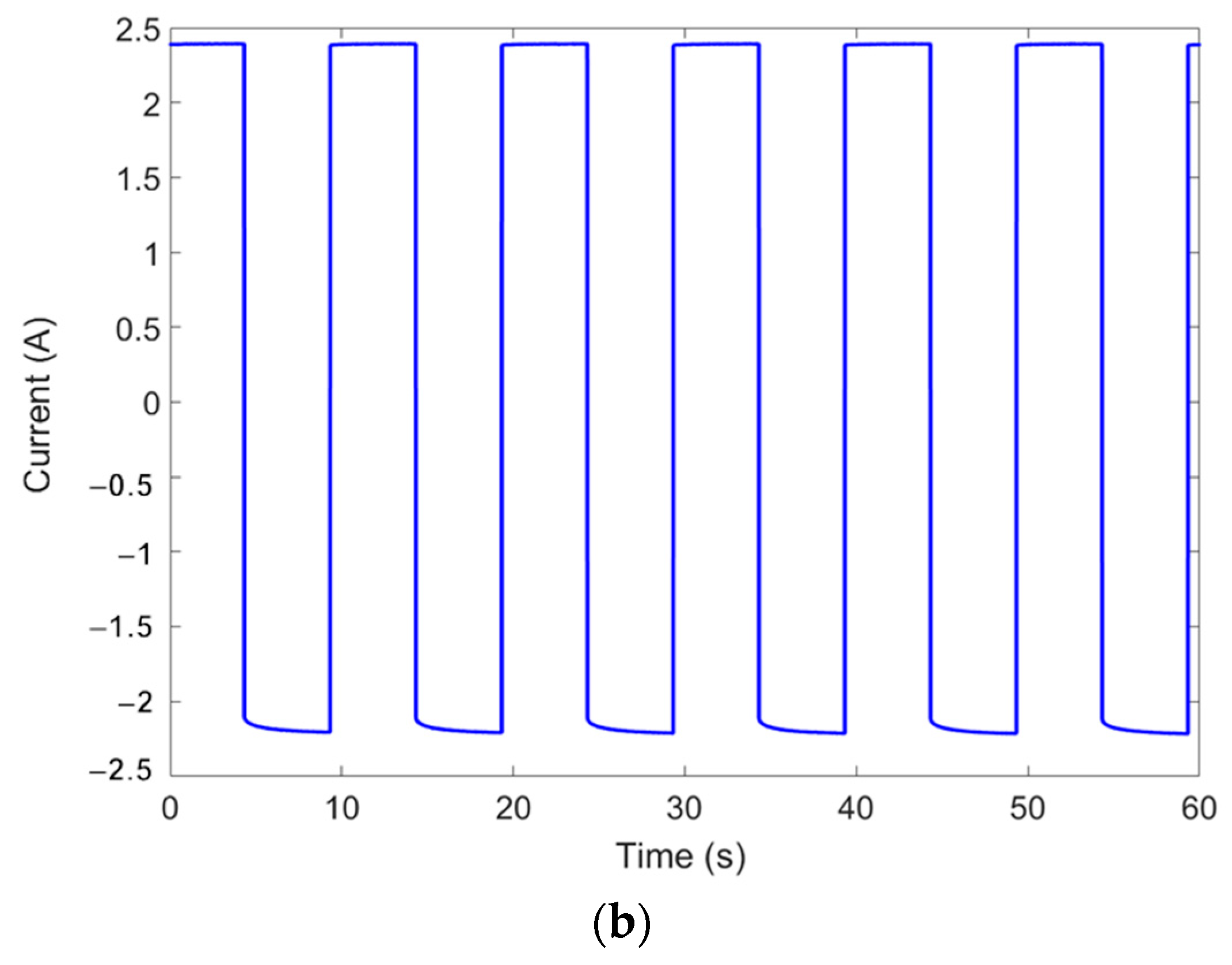
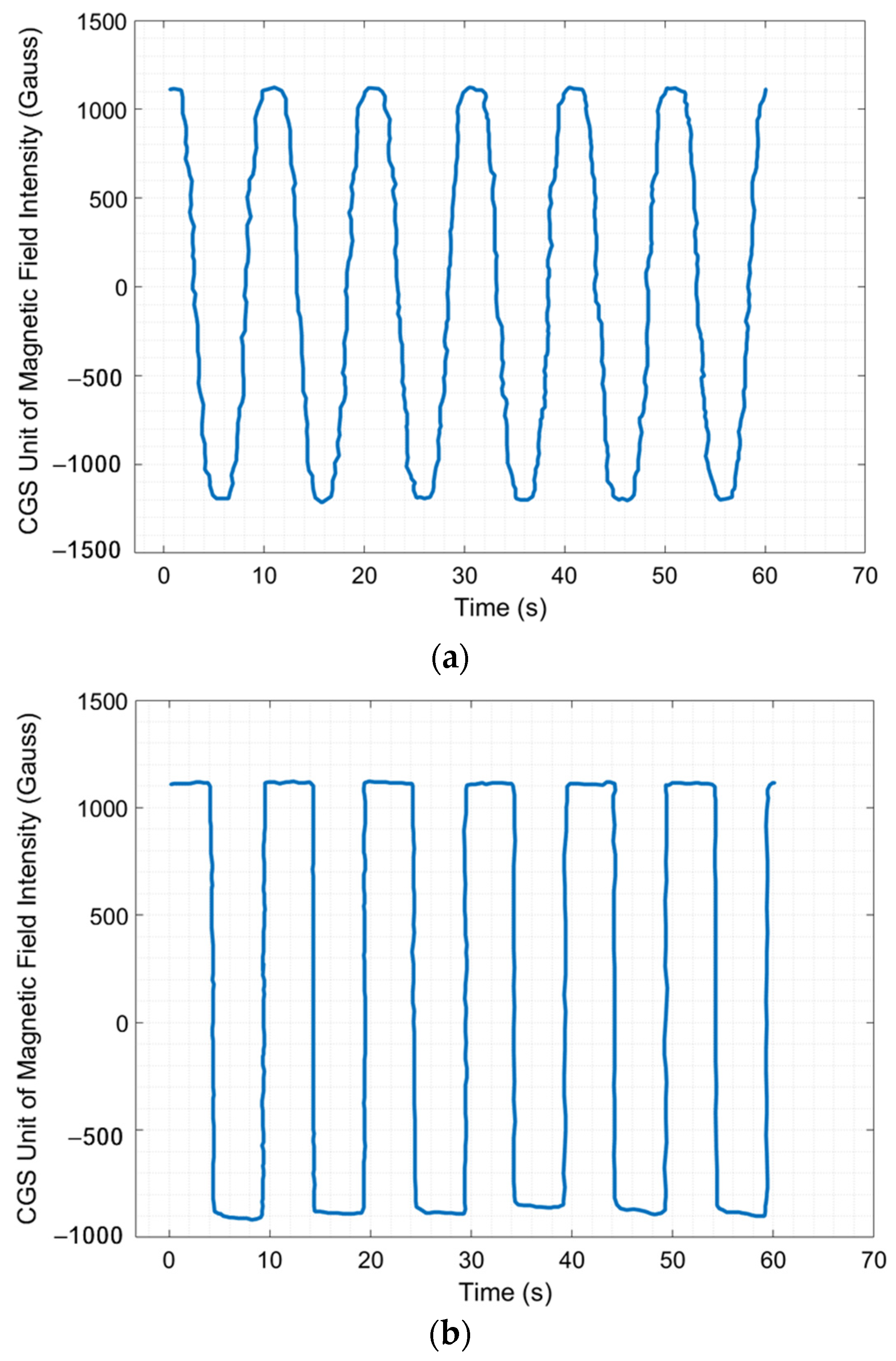
3.1. Hall Sensor Measurement
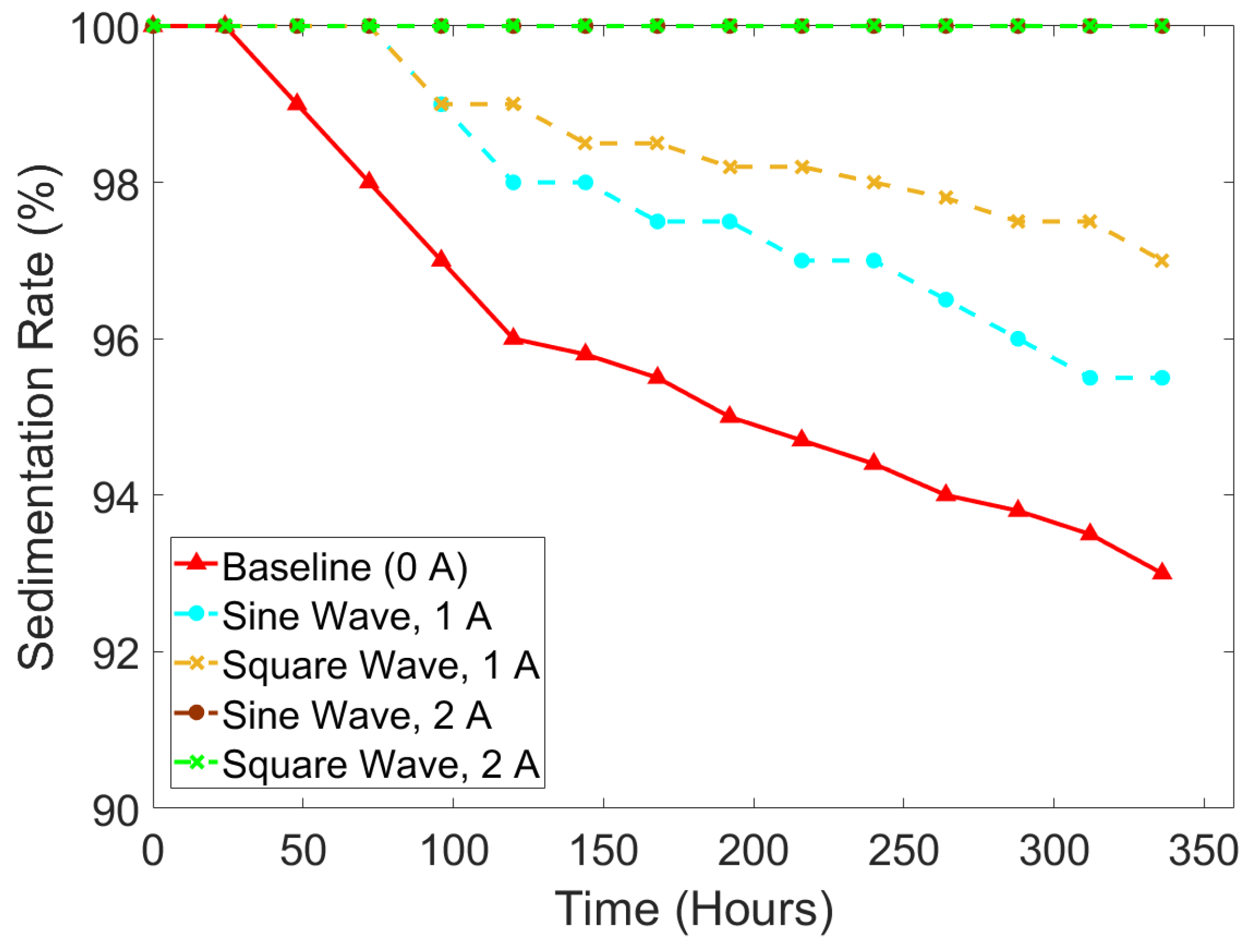
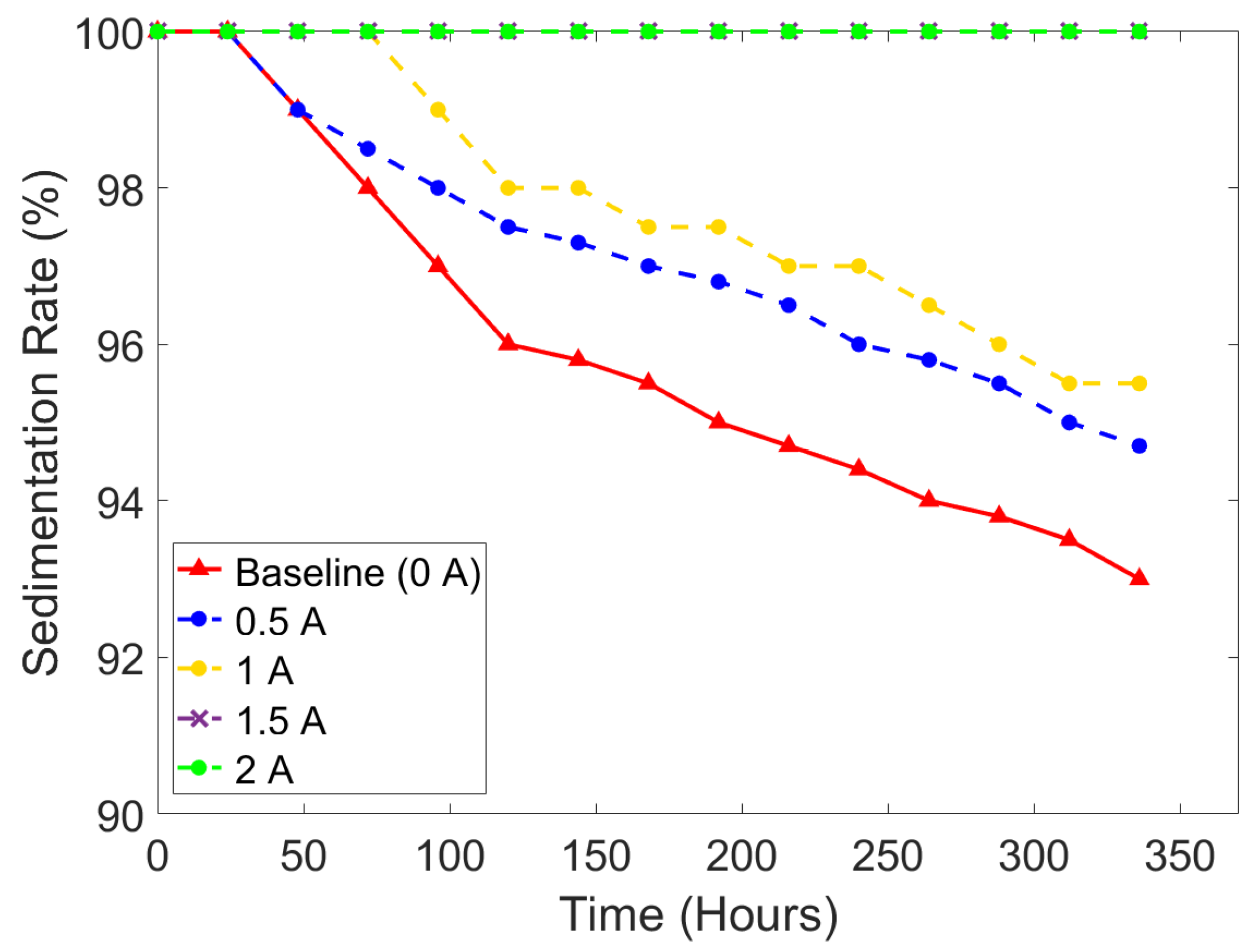
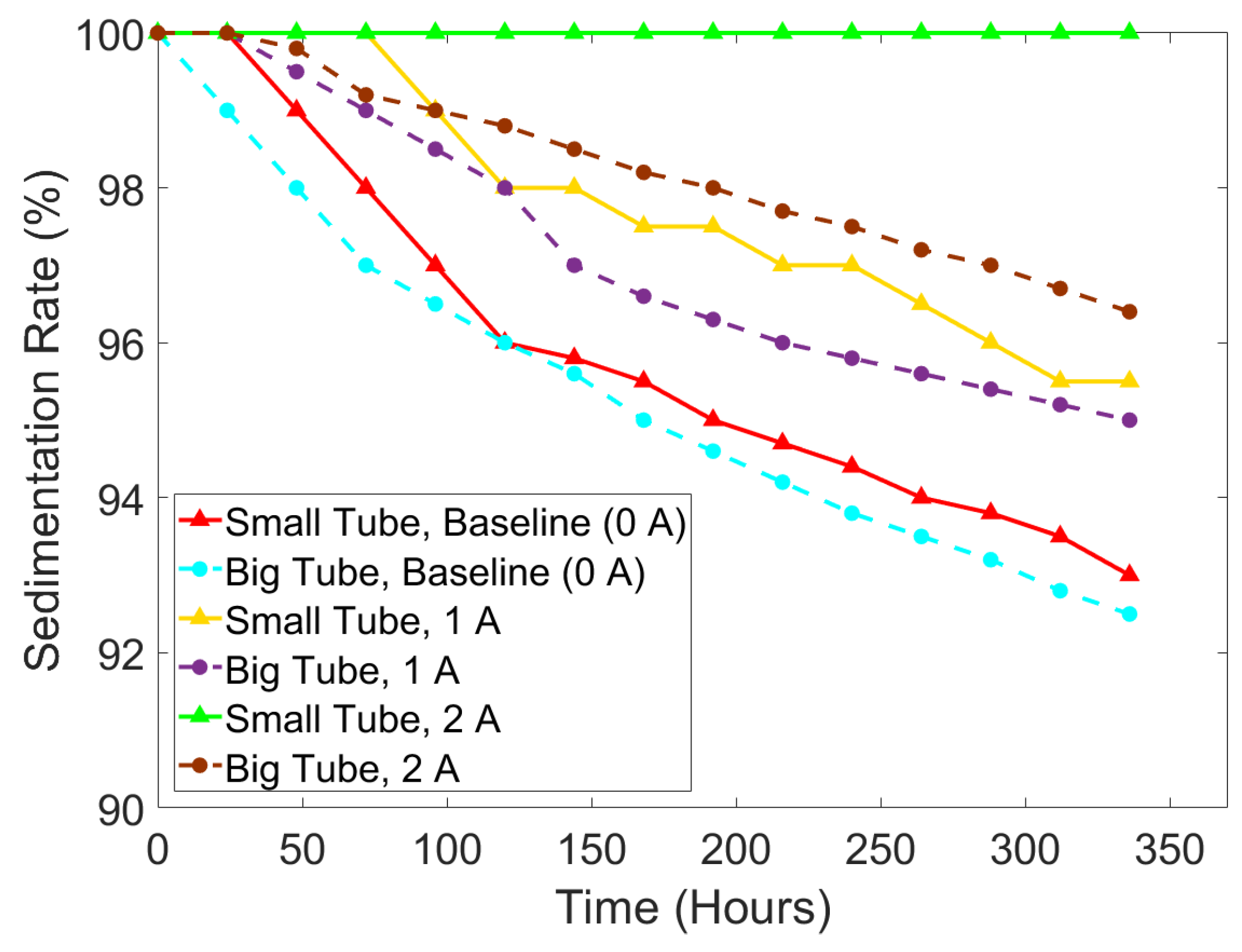
3.2. Sedimentation Rate
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The square current wave shows slower sedimentation compared to the sine wave. When the intensity of 1 A current input was applied, the average sedimentation rate under the square wave was observed at 98.61%, while the average sedimentation rate under the square wave was 97.83%.
- (2)
- The higher intensity of the applied current input resulted in a stronger electromagnetic field, which could slow down the sedimentation of MR fluids caused by the strongly formed chain-like structure. The minimum current input for preventing sedimentation was identified as 1.5 A, which generated magnetic flux density around 0.073 T.
- (3)
- The walls on the smaller tube diameter could hinder the movement of the particles resulting in slowing down the sedimentation rate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashtiani, M.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Ghaffari, A. A review on the magnetorheological fluid preparation and stabilization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar Thakur, M.; Sarkar, C. Design and development of a wedge shaped magnetorheological clutch. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2020, 234, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayatullah, F.H.; Ubaidillah, U.; Purnomo, E.D.; Tjahjana, D.D.D.P.; Wiranto, I.B. Design and simulation of a combined serpentine T-shape magnetorheological brake. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 13, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.S.; Shin, Y.J.; Koo, H.W.; Kim, H.C.; Park, J.H.; Choi, S.B. Vibration control of a semi-active railway vehicle suspension with magneto-rheological dampers. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Southern, B.M. Isolation properties of low-profile magnetorheological fluid mounts. Fluids 2021, 6, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordonski, W.I.; Shorey, A.B.; Tricard, M. Magnetorheological Jet (MR JetTM) Finishing Technology. J. Fluids Eng. 2006, 128, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-B.; Nam, E.-S.; Min, B.-K.; Choi, D.-S.; Je, T.-J.; Jeon, E.-C. Material removal of glass by magnetorheological fluid jet. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Choi, S.B. A new tactile transfer cell using magnetorheological materials for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Sensors 2021, 21, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy Srinivasan, R.; Shanmugan, S.; Palani, S. Application of magnetorheological fluid in machining process. Int. J. Control Theory Appl. 2016, 9, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Hua, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Hnydiuk-Stefan, A. The Roles of Magnetorheological Fluid in Modern Precision Machining Field: A Review. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 678882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girinath, B.; Mathew, A.; Babu, J.; Thanikachalam, J.; Bose, S.S. Improvement of Surface Finish and Reduction of Tool Wear during Hard Turning of AISI D3 using Magnetorheological Damper. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2018, 77, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mutalib, N.A.; Ismail, I.; Soffie, S.M.; Aqida, S.N. Magnetorheological finishing on metal surface: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 469, 012092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodkin, S.R.; Kordonski, W.I.; Medvedeva, E.V.; Novikova, Z.A.; Shorey, A.B. A method and device for measurement of a sedimentation constant of magnetorheological fluids. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 2476–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Kariganaur, A.; Kumar, H.; Arun, M. Effect of temperature on sedimentation stability and flow characteristics of magnetorheological fluids with damper as the performance analyser. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 555, 169342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B. Sedimentation Stability of Magnetorheological Fluids: The State of the Art and Challenging Issues. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Phu, D.X.; Seong, M.S.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Choi, S.B. A low sedimentation magnetorheological fluid based on plate-like iron particles, and verification using a damper test. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 027001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhibin, S.; Yiping, L.; Ying, W.; Jiao, L.; Dongsheng, J. Study on sedimentation stability of magnetorheological fluids based on different lubricant formulations. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 085702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Wereley, N.M. Improving sedimentation stability of magnetorheological fluids using an organic molecular particle coating. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 075030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas, J.R.; de Vicente, J. Magnetorheology: A review. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 9614–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh Gill, H.; Sehgal, S.S. Synthesis and Sedimentation Analysis of Magneto Rheological Fluids. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, S.; Koh, A.S. Performance and Stability of Magnetorheological Fluids—A Detailed Review of the State of the Art. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.P.; Song, K.H.; Cho, M.W.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Magnetorheological properties and polishing characteristics of silica-coated carbonyl iron magnetorheological fluid. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijesh, K.P.; Muzakkir, S.M.; Hirani, H. Rheological measurement of redispersibility and settling to analyze the effect of surfactants on MR particles. Tribol.–Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2016, 10, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, M.T.; de Vicente, J.; Bossis, G.; González-Caballero, F.; Durán, J.D.G. Preparation of stable magnetorheological fluids based on extremely bimodal iron–magnetite suspensions. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roupec, J.; Berka, P.; Mazůrek, I.; Strecker, Z.; Kubík, M.; Macháček, O.; Taheri Andani, M. A novel method for measurement of MR fluid sedimentation and its experimental verification. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitkam, S.; Yoshitake, Y.; Toquet, F.; Langevin, D.; Salonen, A. Speeding up of sedimentation under confinement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 178302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, P.J.; Budiana, E.P.; Ubaidillah, U.; Imaduddin, F. Magnetically-induced pressure generation in magnetorheological fluids under the influence of magnetic fields. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubík, M.; Goldasz, J. Multiphysics Model of an MR Damper including Magnetic Hysteresis. Shock Vib. 2019, 2019, 3246915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharani, E.T.; Ubaidillah, U.; Imaduddin, F.; Wibowo, W.; Utami, D.; Mazlan, S.A. A mathematical modelling and experimental study of annular-radial type magnetorheological damper. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2021, 66, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Yao, G.Z.; Chen, G.; Yeo, S.H.; Yap, F.F. Testing and steady state modeling of a linear MR damper under sinusoidal loading. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.A.N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Samin, P.M.; Idris, A.; Ubaidillah, U. Performance of bidisperse magnetorheological fluids utilizing superparamagnetic maghemite nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1710, 030050. [Google Scholar]
- Aruna, M.N.; Rsahman, M.R.; Joladarashi, S.; Kumar, H.; Devadas Bhat, P. Influence of different fumed silica as thixotropic additive on carbonyl particles magnetorheological fluids for sedimentation effects. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 529, 167910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, M.N.; Rahman, M.R.; Joladarashi, S.; Kumar, H. Investigation of sedimentation, rheological, and damping force characteristics of carbonyl iron magnetorheological fluid with/without additives. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Qi, M. Iron nanoparticles-based magnetorheological fluids: A balance between MR effect and sedimentation stability. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 491, 165556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, J.C. Basic AC Circuit, 2nd ed.; Butterworth–Heinemann: Woburn, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 29–63. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Choi, Y.-T.; Liao, C.-R.; Wereley, N.M. Long term stability of magnetorheological fluids using high viscosity linear polysiloxane carrier fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 075006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

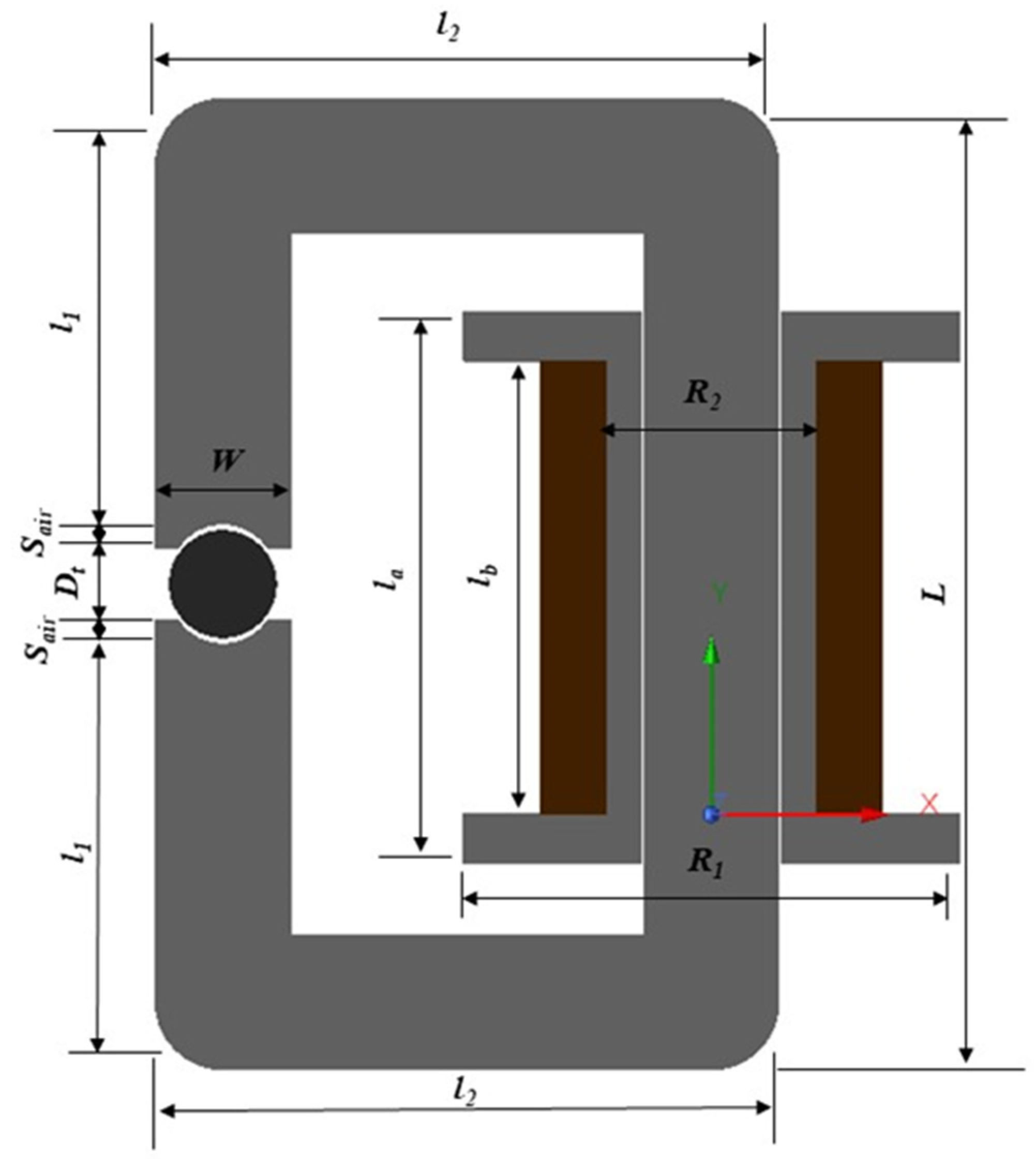
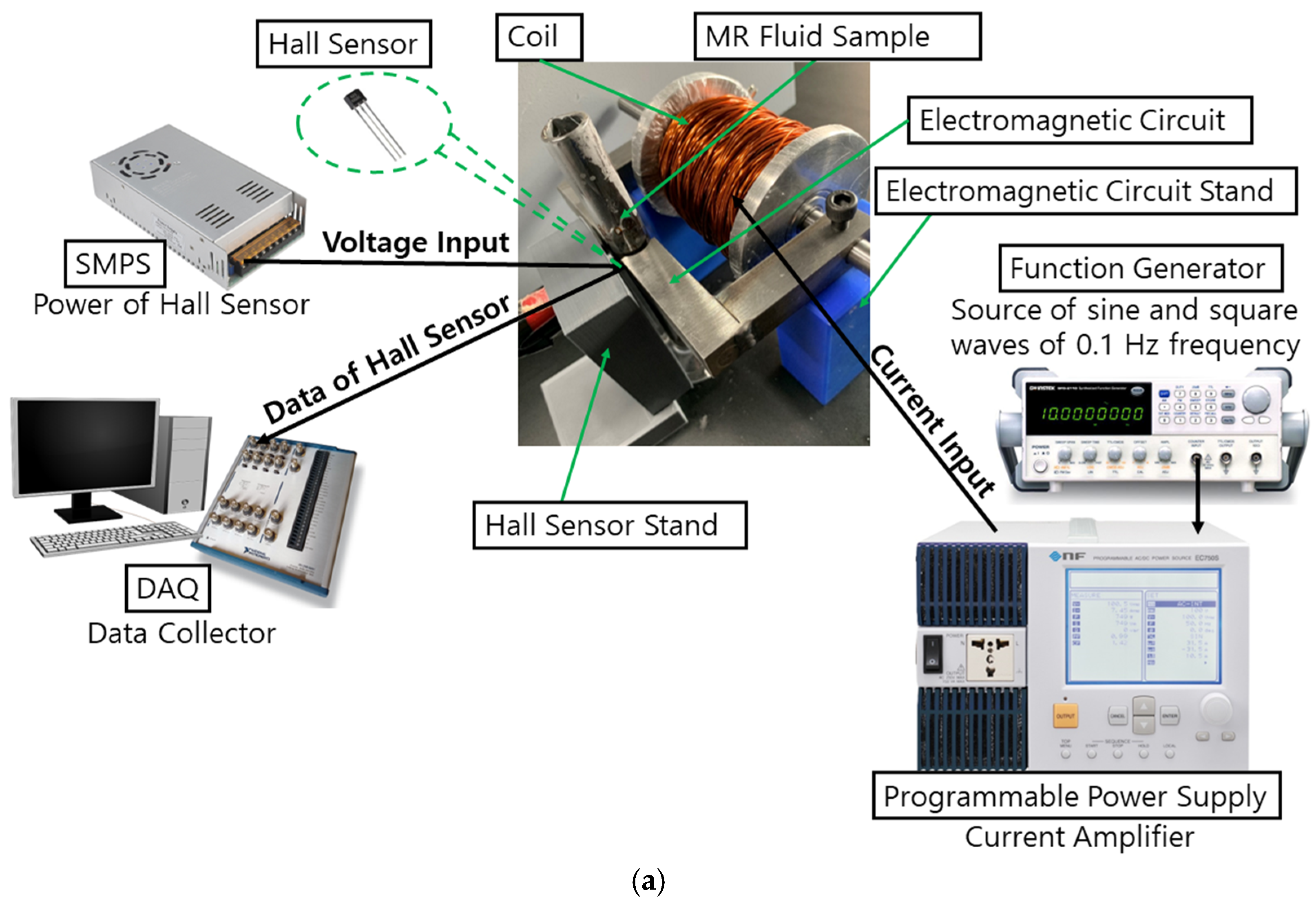
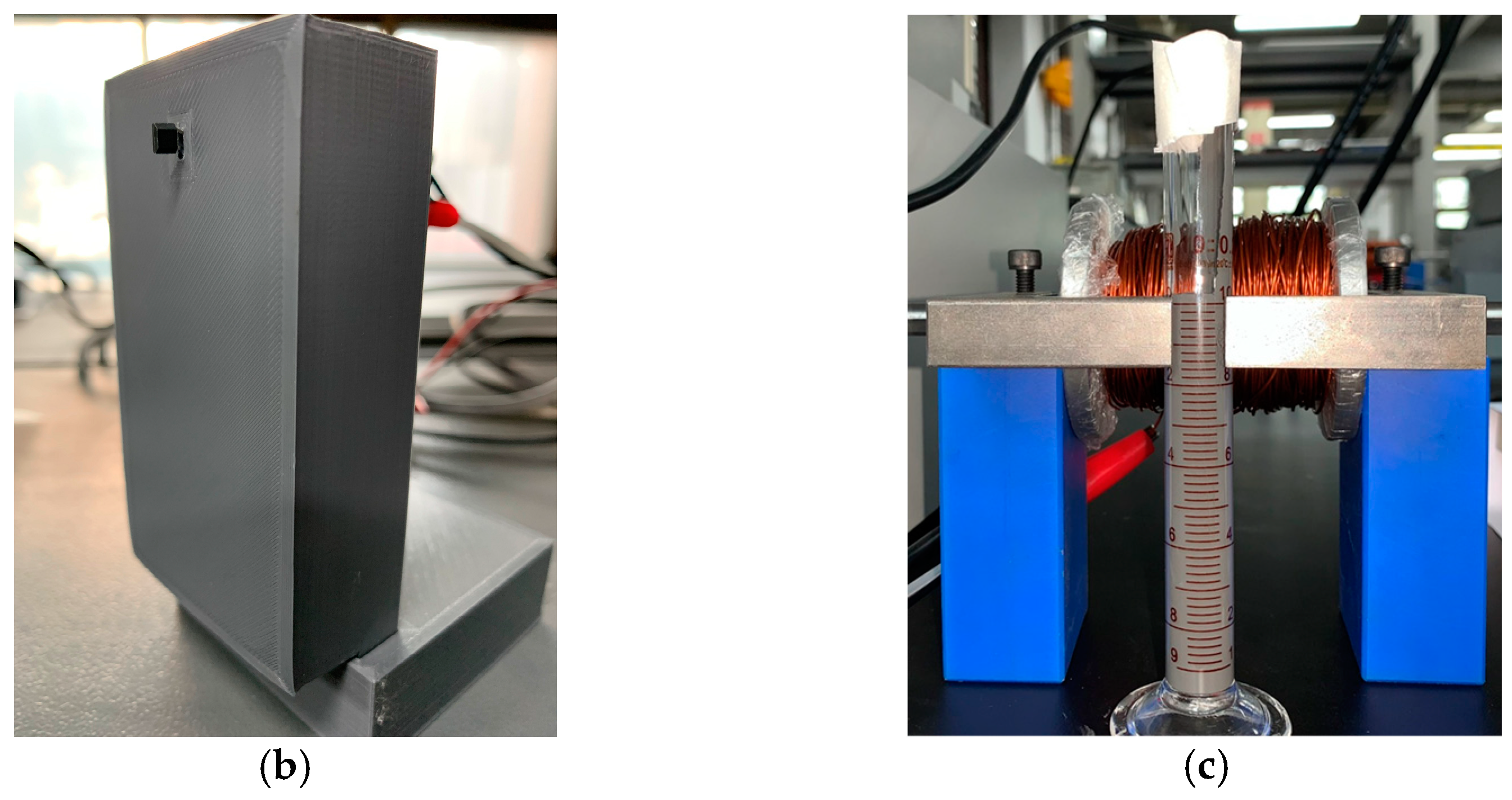
| Parameters | Description | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| W | Magnetic Core Width | 19 | mm |
| L | Magnetic Core Length | 118 | mm |
| l1 | Magnetic Core Length 1 | 50.5 | mm |
| l2 | Magnetic Core Length 2 | 88 | mm |
| R1 | Bobbin Outer Radius 1 | 35 | mm |
| R2 | Bobbin Inner Radius 2 | 10 | mm |
| la | Bobbin Total Length | 78 | mm |
| lb | Bobbin Length | 64 | mm |
| r | Coil Radius | 0.5 | mm |
| N | Coil Winding | 500 | turns |
| Sair | Air Gap Length | 2 | mm |
| Dt | MR Fluids Diameter | 15 | mm |
| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | 0.112 | Pa·s |
| Density | 2.95–3.15 | g/cm3 |
| Solid Content by Weight | 80.90 | W% |
| Flash Point | >150 | °C |
| Temperature | −40 to +130 | °C |
| Wave Type | Current Input | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | - | - |
| Sine Wave | 0.5 A | 0.1 Hz |
| Sine Wave | 1 A | 0.1 Hz |
| Sine Wave | 1.5 A | 0.1 Hz |
| Sine Wave | 2 A | 0.1 Hz |
| Square Wave | 1 | 0.1 Hz |
| Square Wave | 2A | 0.1 Hz |
| Wave Type | Current Input | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | - | - |
| Sine Wave | 1 A | 0.1 Hz |
| Sine Wave | 2 A | 0.1 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maharani, E.T.; Seo, M.-W.; Sohn, J.W.; Oh, J.-S.; Choi, S.-B. The Influence of Current Magnitudes and Profiles on the Sedimentation of Magnetorheological Fluids: An Experimental Work. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10030018
Maharani ET, Seo M-W, Sohn JW, Oh J-S, Choi S-B. The Influence of Current Magnitudes and Profiles on the Sedimentation of Magnetorheological Fluids: An Experimental Work. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(3):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaharani, Elliza Tri, Myeong-Won Seo, Jung Woo Sohn, Jong-Seok Oh, and Seung-Bok Choi. 2024. "The Influence of Current Magnitudes and Profiles on the Sedimentation of Magnetorheological Fluids: An Experimental Work" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 3: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10030018
APA StyleMaharani, E. T., Seo, M.-W., Sohn, J. W., Oh, J.-S., & Choi, S.-B. (2024). The Influence of Current Magnitudes and Profiles on the Sedimentation of Magnetorheological Fluids: An Experimental Work. Magnetochemistry, 10(3), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10030018









